ch 17 Carbohydrates: Functions, Structures, and Reactions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Monosaccharide
Simple carbohydrate most commonly consisting of three to six carbon atoms
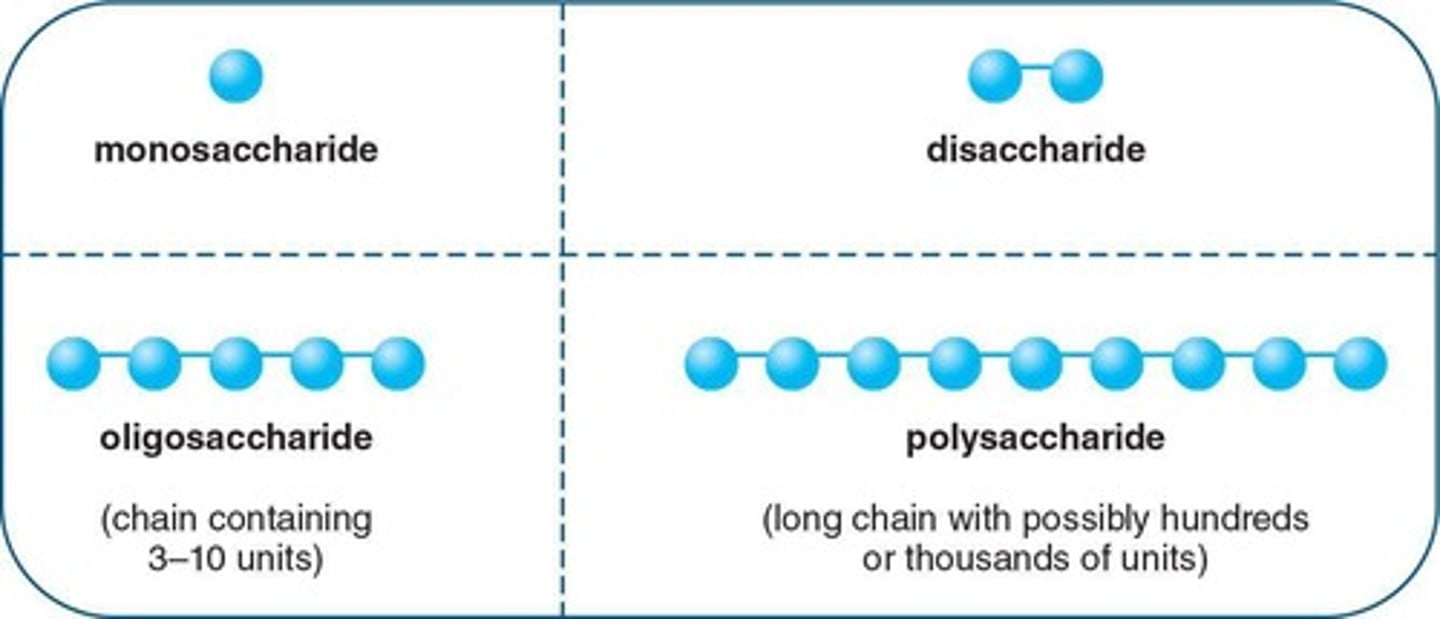
Disaccharide
Carbohydrate formed by the combination of two monosaccharide units
Polysaccharide
Carbohydrate formed by the combination of many monosaccharide units
Isomers
Molecules that have the same chemical formula but differ in either how the atoms are connected or how the connected atoms are arranged in space
Structural Isomers
Isomers that differ only in their connectivity
Stereoisomers
Isomers that differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms
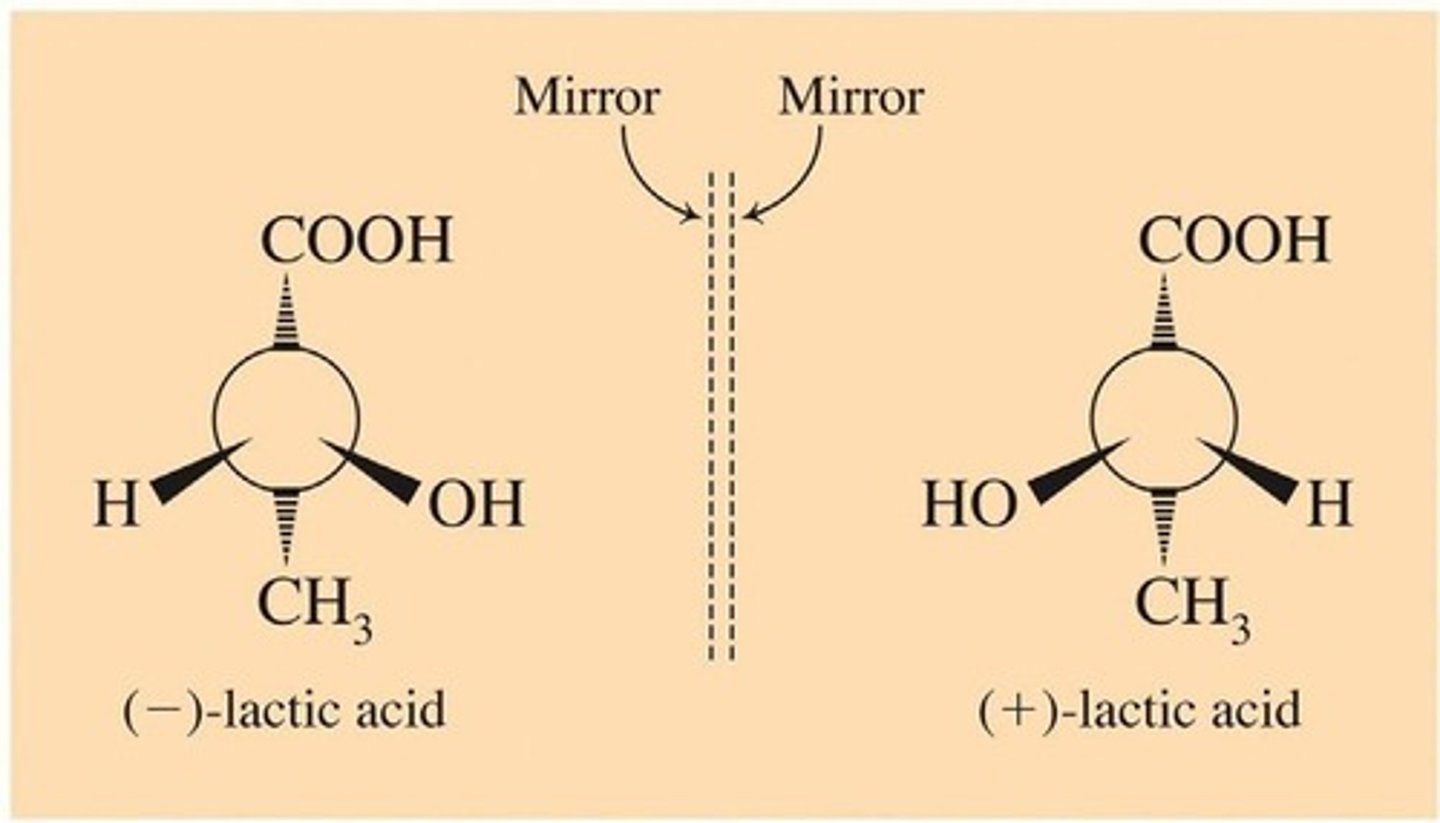
Optical isomers
Compounds that have the ability to rotate the plane of plane-polarized light
Oxidation Reaction of Monosaccharides
Chemical reactions involving the loss of electrons from monosaccharides
Glycoside Formation
The process of forming glycosides from monosaccharides
Hydrolysis of Disaccharides
Chemical reaction that breaks down disaccharides into monosaccharides
Enantiomers
Stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images
Maximum number of stereoisomers
2n, where n is the number of chiral carbon atoms
Fischer Projections
Depict three-dimensional shapes for chiral molecules, with the chiral carbon represented by the intersection of two lines
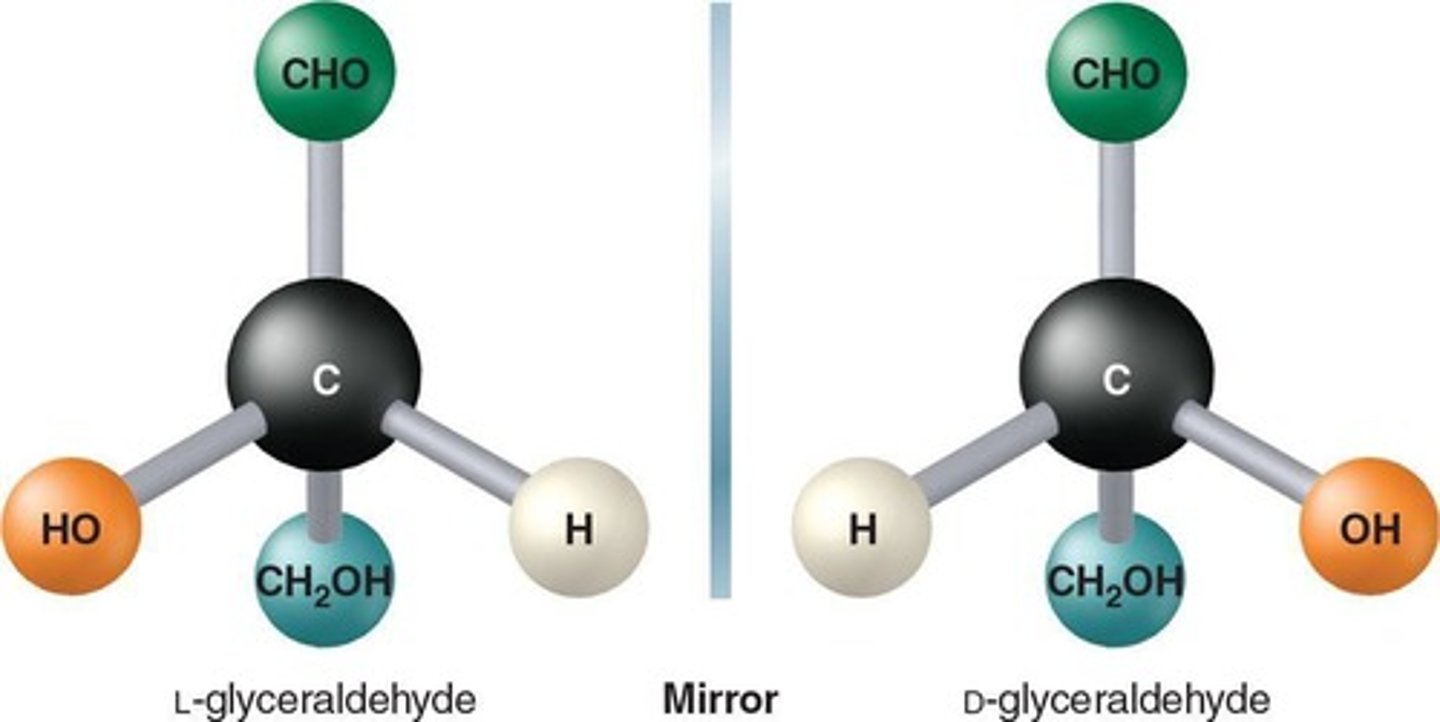
D-isomers of monosaccharides
Humans can only metabolize the D-isomers
L-isomers of amino acids
Most animals are able to utilize only the L-isomers to synthesize proteins
(+) enantiomer
Rotates light clockwise +2.6°
(-) enantiomer
Rotates light counterclockwise -2.6°
Classification of Monosaccharides
Questions to ask when classifying a monosaccharide include whether it is an aldehyde (aldose) or a ketone (ketose) and how many carbon atoms are present.
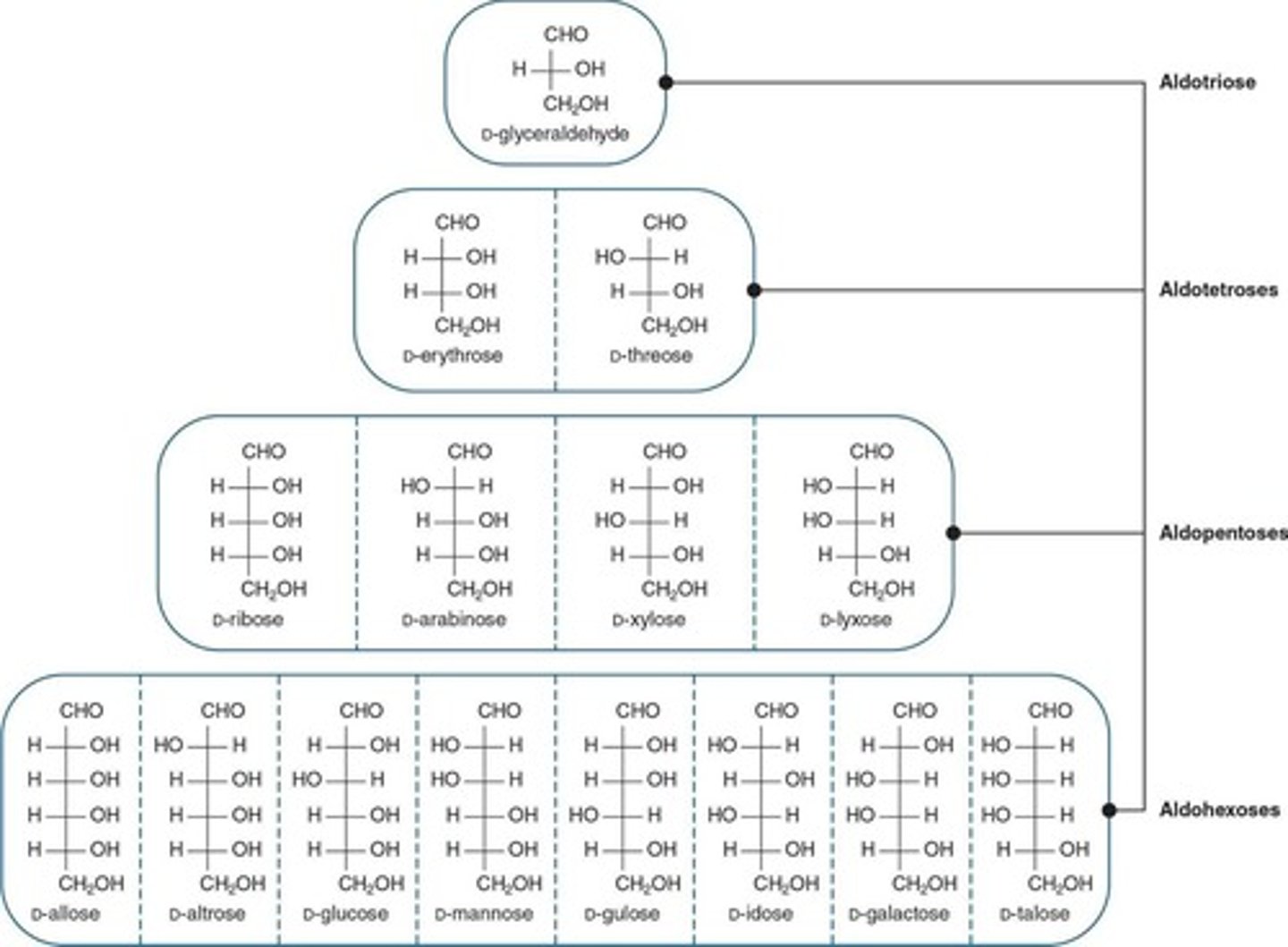
D series
Almost all natural monosaccharides belong to this series.
Cyclic hemiacetals and hemiketals
Formed by monosaccharides with at least five carbon atoms.
Haworth structure
Method of depicting three-dimensional carbohydrate structures.
Anomeric carbon
Former carbonyl carbon atom that is now chiral.
α anomer
Anomer with —OH on the anomeric carbon pointing down.
β anomer
Anomer with —OH on the anomeric carbon pointing up.
Anomers
Stereoisomers that differ in the 3-D arrangement of groups at the anomeric carbon.
Glycoside
General name for a carbohydrate containing an acetal or ketal group.
Glycosidic linkage
New carbon-oxygen-carbon linkage that joins the components of the glycoside to the ring.
Galactose
Hexose component of lactose and similar to glucose.
Fructose
Most important ketohexose, sweetest monosaccharide.
Maltose
Disaccharide containing two glucose units joined by α(1→4) glycosidic linkage.
Lactose
Disaccharide composed of galactose and glucose units joined by β(1→4) glycosidic linkage.
Sucrose
Disaccharide composed of fructose and glucose units joined by α1→β2 glycosidic linkage.
Polysaccharides
Condensation polymers containing thousands of units.