Cognitive Theories of Learning (done)
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover the key concepts from the Cognitive Theories of Learning lecture, focusing on information processing, memory models, strategies for learning, and the implications of cognitive theories.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What does the information processing model describe?
The processing, storage, and retrieval of knowledge in the mind.
How does the information processing model differ from the behavioral model?
The information processing model describes internal cognitive processes
the behavioral model treats the mind as a black box and focuses on observable behavior.
What are the basic components of the mind according to the information-processing model?
Sensory Register, Working Memory, Long-term Memory.
What is schema theory?
It is the theory that information is stored in networks of connected facts and concepts that help make sense of new information.
What factors affect memory?
Interference, automaticity, practice, and the effects of primacy and recency.
What is dual code theory?
The theory that information represented both visually and verbally is recalled better than information coded in only one format.
How can you enhance working memory capacity?
Utilize strategies like chunking information and using mnemonic devices.
What is meaningful learning according to levels of processing theory?
Learning that is actively interpreted and connected to prior knowledge for better retention.
What strategies can be used to enhance memory?
Use imagery, keyword method, pegword method, and the method of loci.
What is proactive interference?
When previously learned information interferes with the learning of new information.
What is the importance of prior knowledge in learning?
Prior knowledge influences new learning through processes like positive or negative transfer.
What instructional implications arise from cognitive theories of learning?
Provide multiple representations of materials and facilitate connections between new information and prior knowledge.
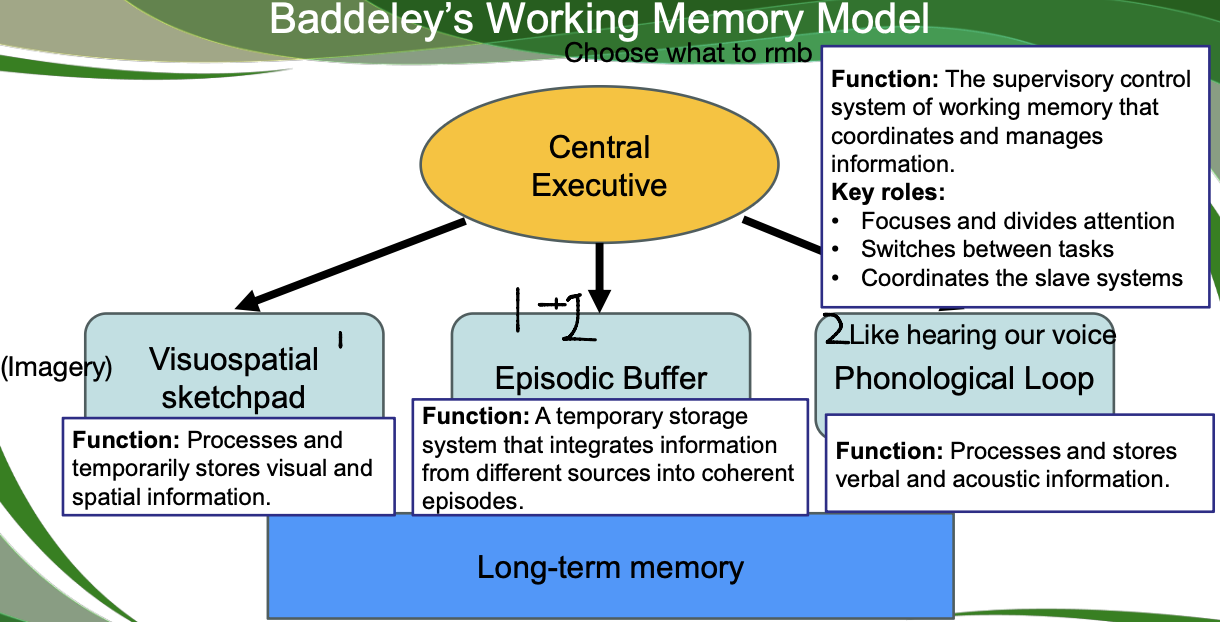
What are the components of Baddeley's Working Memory Model?
Central Executive, Visuospatial Sketchpad, Episodic Buffer, Phonological Loop.
According to cognitive theories, why is revising just one night before an exam ineffective?
Information Processing Theory says there's not enough repetition, and Levels of Processing Theory says there's no time for meaningful correlation, leading to a focus on rote learning.
What are the four key cognitive processes in learning in Information-Processing Model?
Attention, Encoding, Storage, Retrieval.