Cognitive Theories of Learning (done)
Levels of processing theory
Information processing theory
Schema theory
Information-Processing Model
Definition: A model describing the processing, storage, and retrieval of knowledge in the mind.
Learning process: attention→ encoding, storage, retrieval
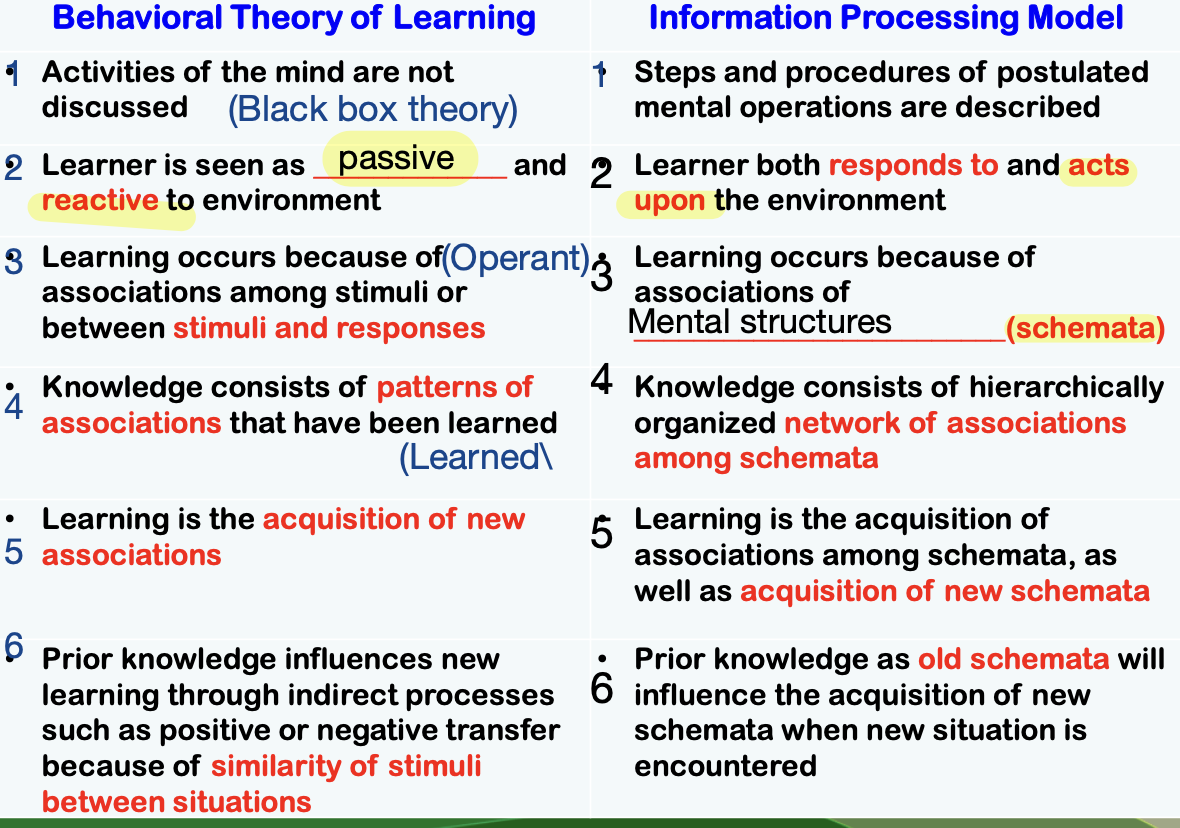
Comparison with Behavioral Model:
The information-processing model emphasizes cognitive operations unlike the behavioral model, which treats the mind as a black box focusing only on observable behavior.

Components of the Information-Processing Model
Sensory Register: Stores sensory information for brief periods.
If unattended, information is lost rapidly.
Through Attention (Affected by single or multiple tasks, similarity between competing tasks, Complexity / difficulty of tasks, Individual ability to control attention, Selective attention)
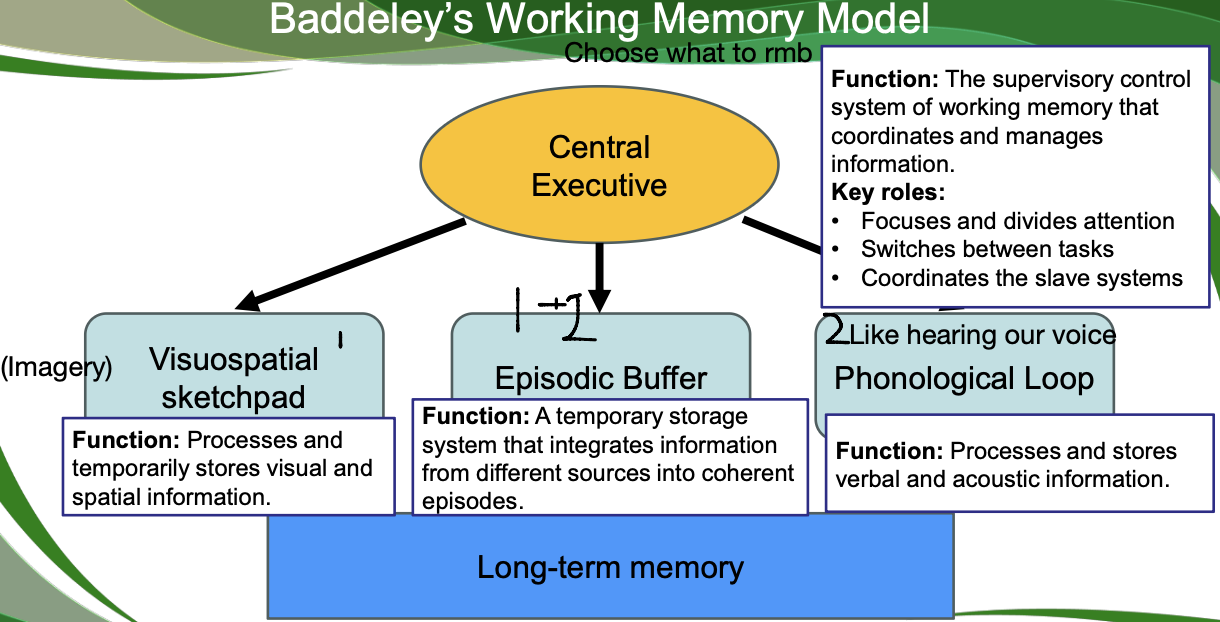
Short-Term Memory/Working memory:
-Organizes information for storage or discarding
- Connects new information to existing information
Capacity: Typically 7±2 items as per Miller's Law.
Through Retrieval and Encoding
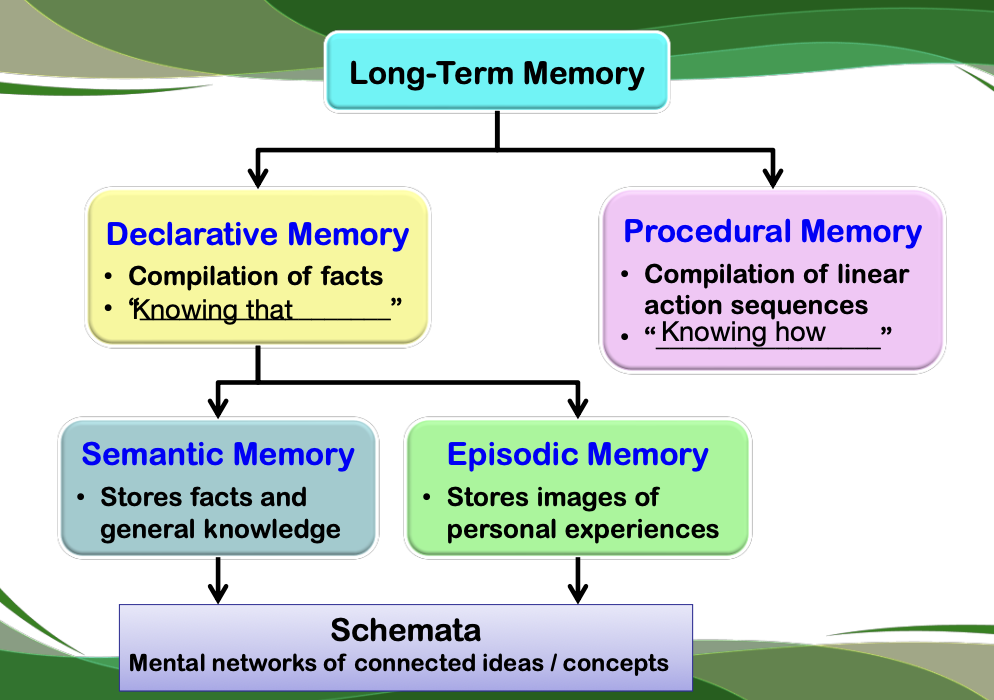
Long-Term Memory
Detailed Long-Term Memory Components
Memory Factors and Learning
Interference/Inhibition
Definitions:
Proactive(future) Interference/inhibition: Past information hinders the ability to learn new information.
Retroactive(past) Interference/inhibition: Newly learned information interferes with the recall of previously learned information
Facilitation:
Proactive Facilitation: Previous knowledge aids in the recall of new information.
Retroactive Facilitation: New learning helps in recalling previously learned information.
Primacy and Recency Effects
Massed vs. Distributed Practice:
Massed practice leads to cramming (revise exam); distributed practice improves retention over timelines.
Enactment (try presenting once is better than looking at the ppt slides)
Generation (create notes)
Automaticity
Memory Enhancement Strategies
Dual Code Theory: Utilizing both visual and verbal representations improves recall better than one mode alone.
Keywords Method: Eg. For "Hippocampus", you could use "hippo" and "campus". Imagine a hippo getting lost on a college campus and trying to remember its way, connecting it to memory.
Pegword Method: Associate words with a sequence (e.g., 1 is a bun, associate breakfast with 1).
Loci Method: associate information with different locations.
Levels-of-Processing Theory
Definition: Information processed at deeper levels is retained longer than that processed superficially.
Rote learning (背誦) vs meaningful learning
Strategies for Making Information Meaningful:
Encourage connections with prior knowledge, daily life examples, and make notes, mindmaps, use of metaphor
Schema Theory
Concept: Information is stored in long-term memory in schema (networks of connected facts and concepts) that provide a structure for making sense of new information
Instructional Implications:
Facilitate connections between new and existing information, add clarity to concepts, minimize interference with learning.
Eg. connect back to prior connect and build on that