Electrochemistry Formulas
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
relation between free energy difference and electric potential difference
∆G= free energy change
n= moles of e⁻
F= Faraday's constant (9.649 X 10⁴ C/mol)
E= Electric potential (volts)
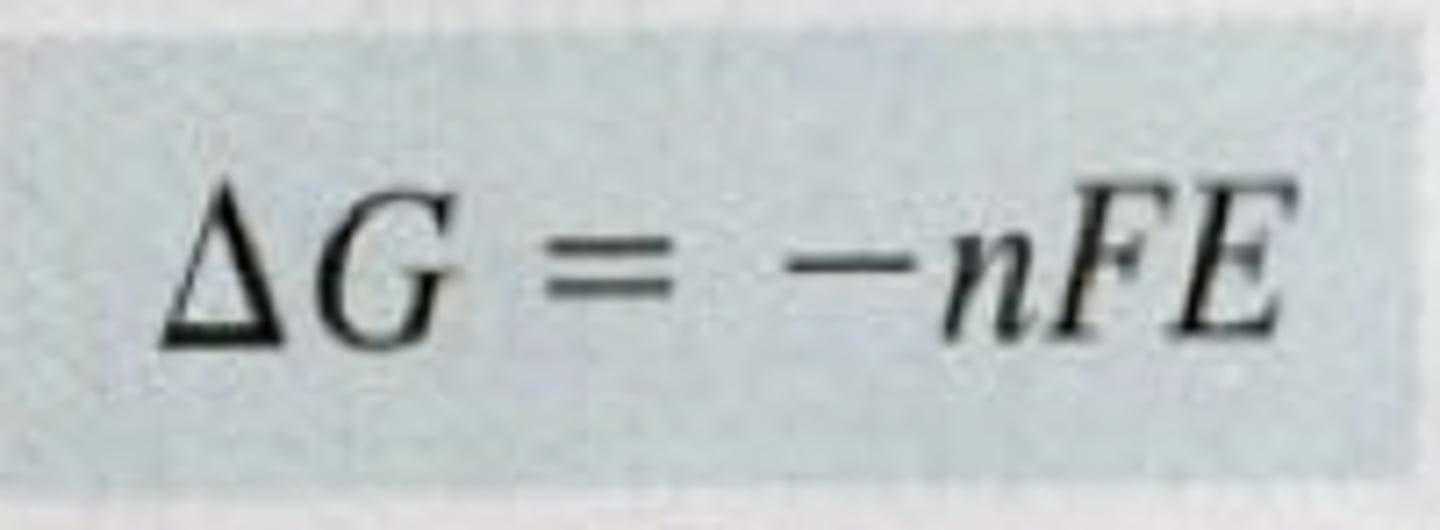
SHE half reaction
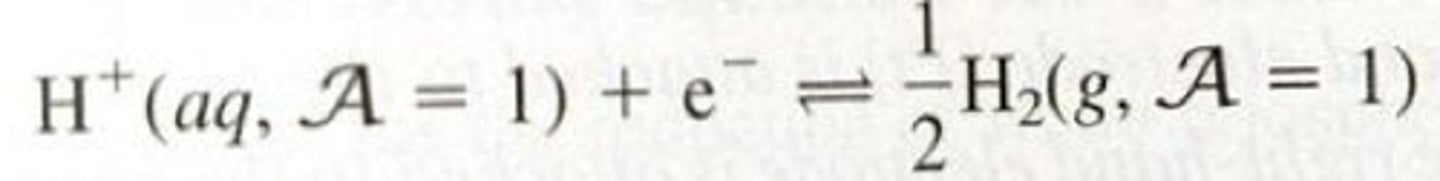
Nerst Equation at standard conditions (25 C)
E= Electric potential (volts)
E°= standard reduction potential (ActA=ActB=1)
R= gas constant(8.314J/(K*mol)= 8.314(V*C)/(K*mol)
T= temperature (K)
n= number of electrons transferred in the half-reaction
Q= reaction quotient

Reaction Quotient
Q= reaction quotient

Nerst Equation at nonstandard conditions
E= Electric potential (volts)
R= 8.314 j/mol/K
Q= reaction quotient, defined as the ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations at any point in a reaction, each raised to the power of their coefficients in the balanced chemical equation.
T= Temperature in Kelvin
F= faradays constant
E°= standard reduction potential (ActA=ActB=1)
n= number of electrons in the half-reaction
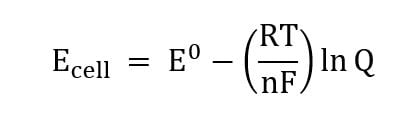
Finding E° from K
E°= standard reduction potential (ActA=ActB=1)
n= number of electrons in the half-reaction
K= equilibrium constant
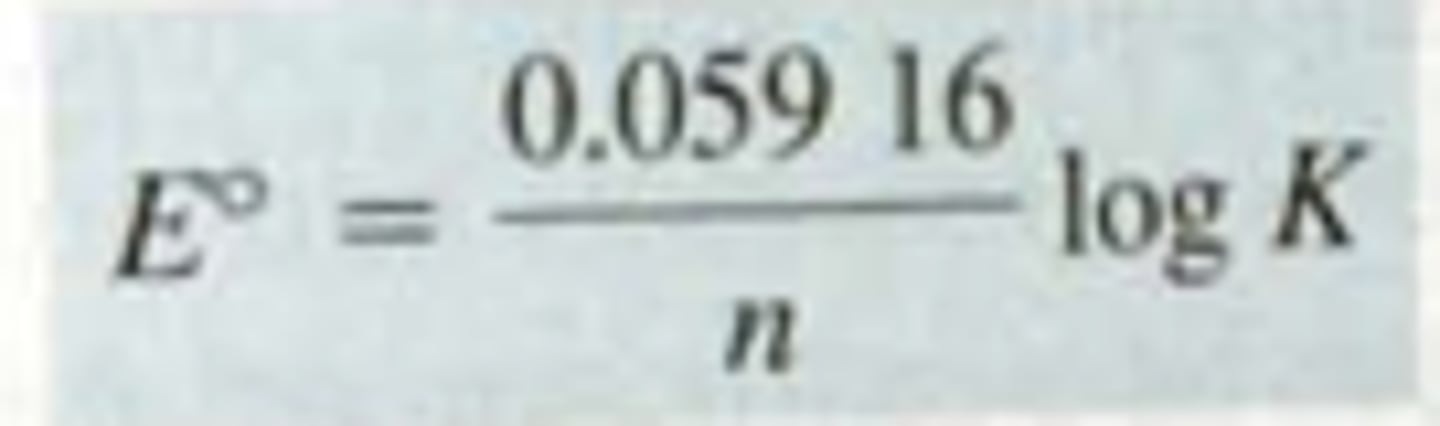
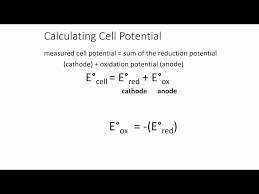
reduction potential formula