Biopsychology Exam 1
1/294
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
295 Terms
disembodied mind
cultural / religious perspective
- body = biological machine, robot to the spirit
- spirit = seat of personality memory, choice, mood, emotion
- brain = interface between body and spirit that exchanges info (contains no memory and not responsible for choice)
embodied mind
mind 'arises' from the brain, more scientifically accurate
- for every brain state, there is a corresponding mental state at that moment
biopsychology
physical processes fully cause and underlie all behaviors
- everything we do, think, feel, perceive, sense, etc. is the SOLE result of brain / body processes (embodied)
is a conscious mind necessary for adaptive behavior?
no
- ex: blindsight - cortical blindness; will state that they cannot see a dot on a screen (even though eyes work fine), but can accurately say which direction the dot moved
- schizophrenia
- alcohol disinhibits dopamine release, which is involved in desire, reinforcement, pleasure, etc.
parts of a neuron
dendrites, cell body (soma), nucleus, axon hillock, axon, axon terminal, synaptic cleft
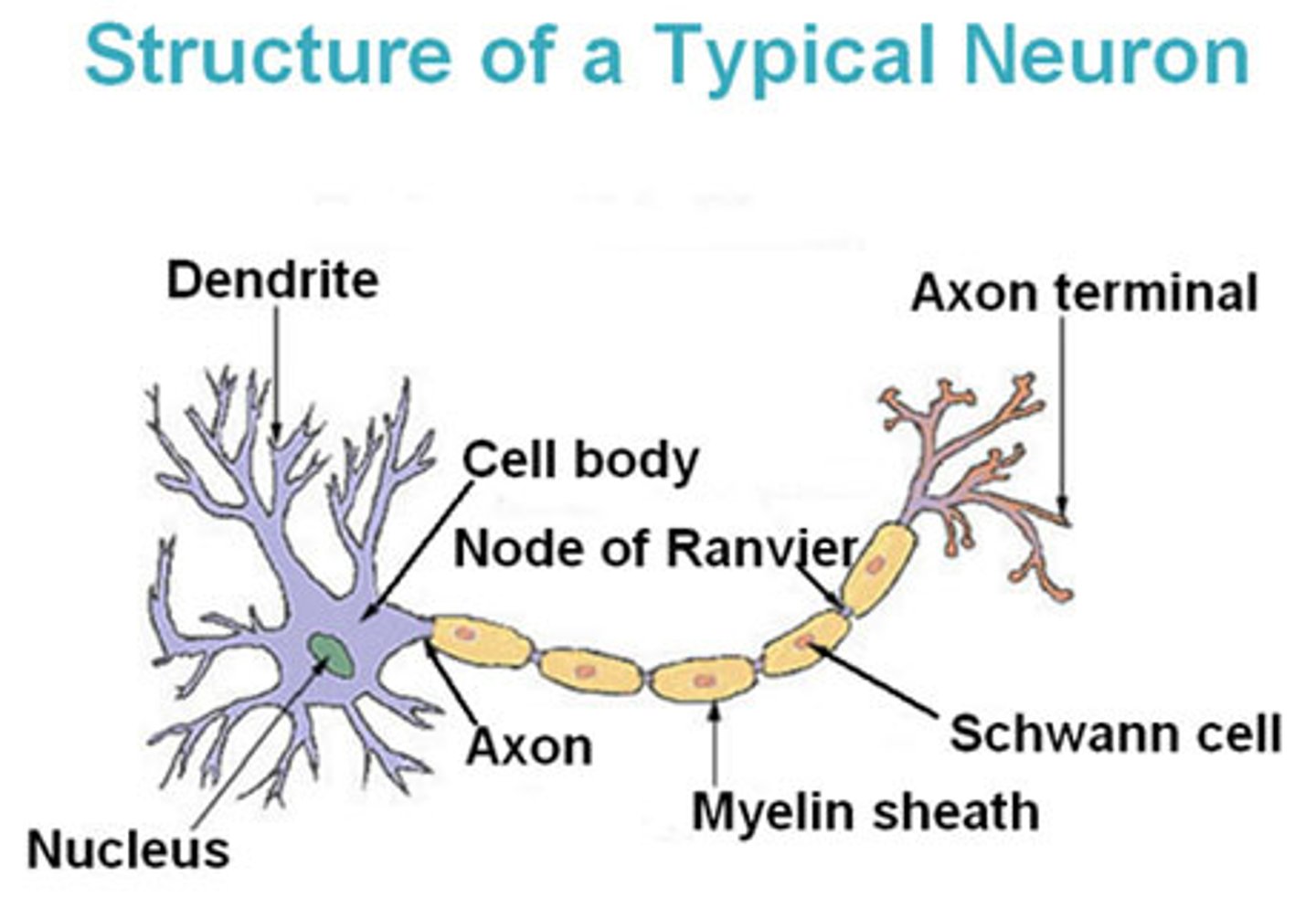
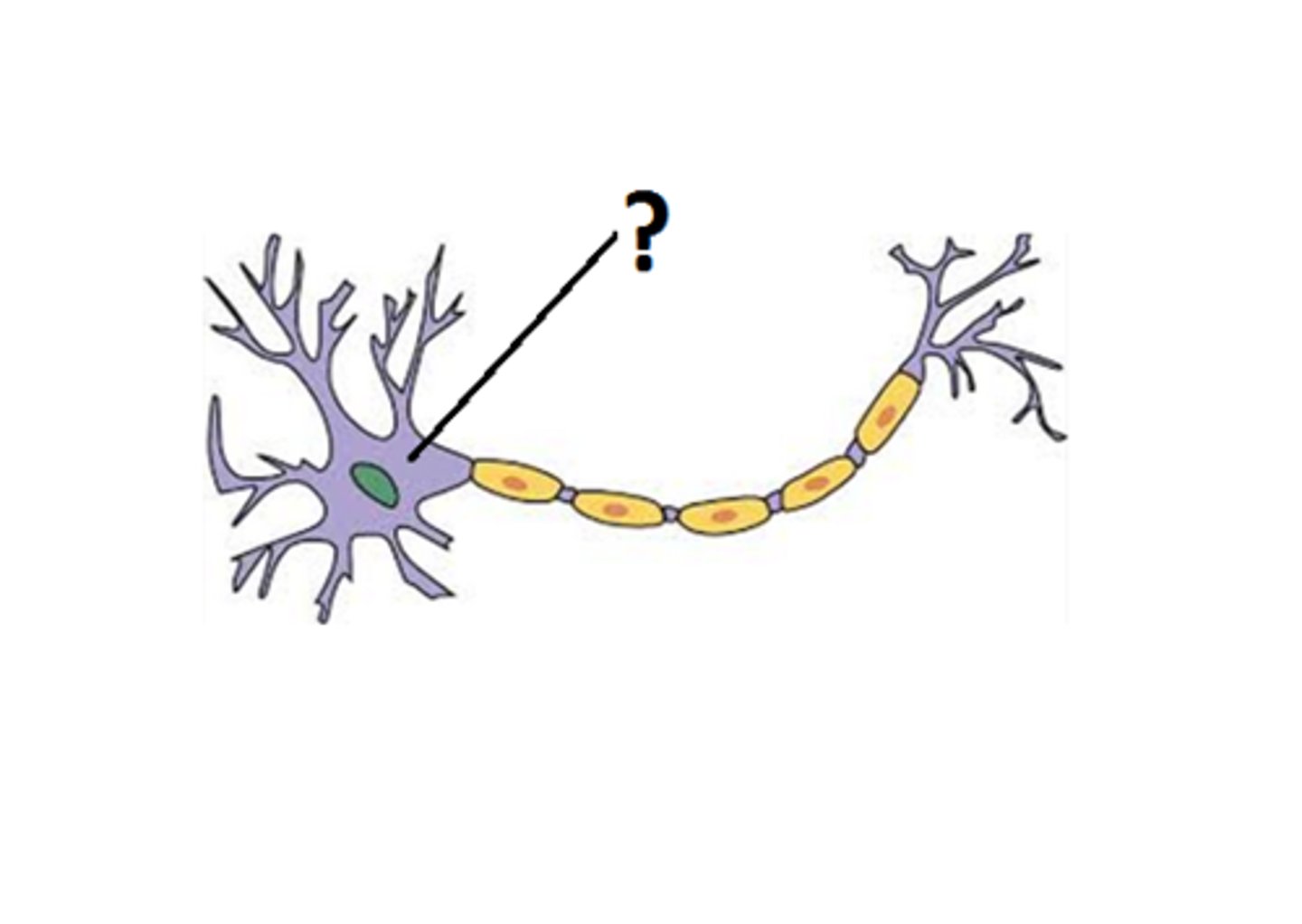
cell body (soma)
contains the nucleus and other parts of the cell needed to sustain its life
- info filters into here
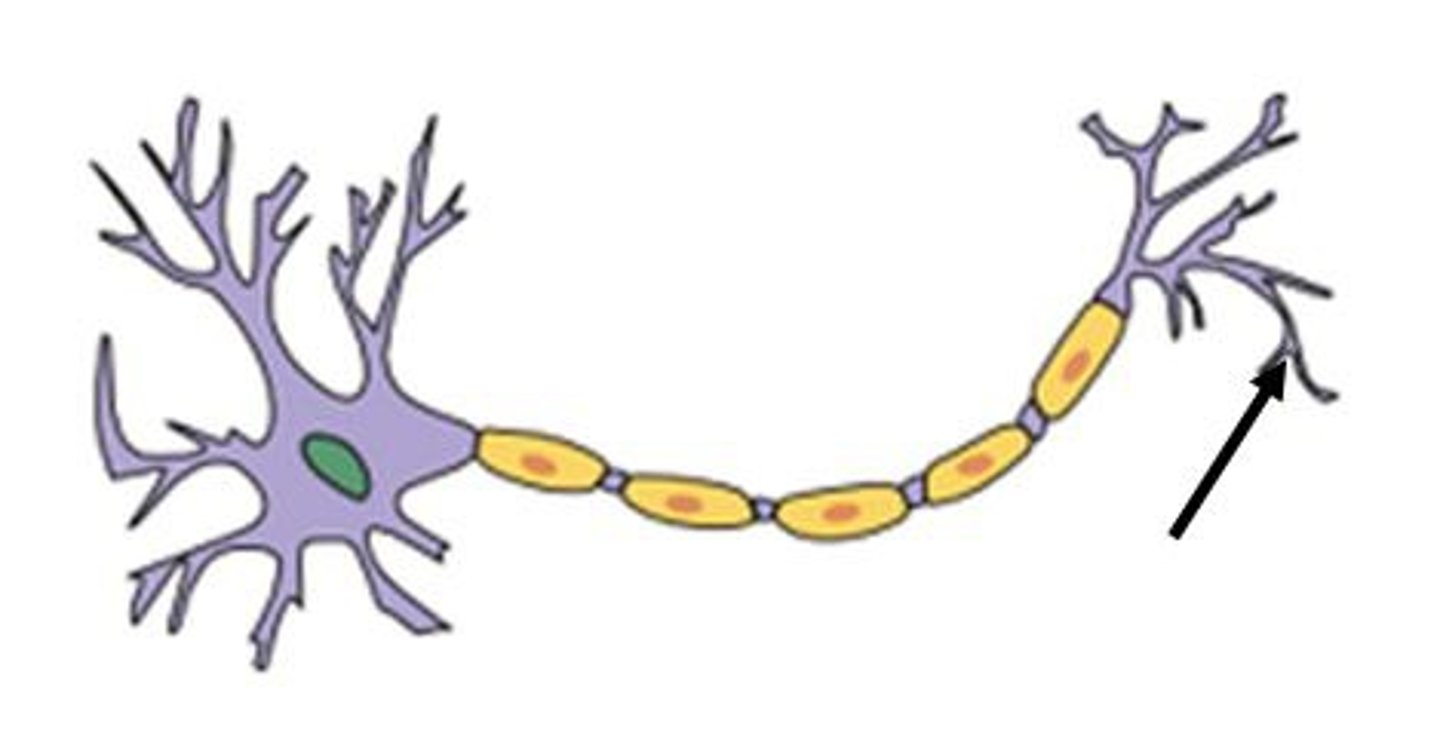
axon terminal
the endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
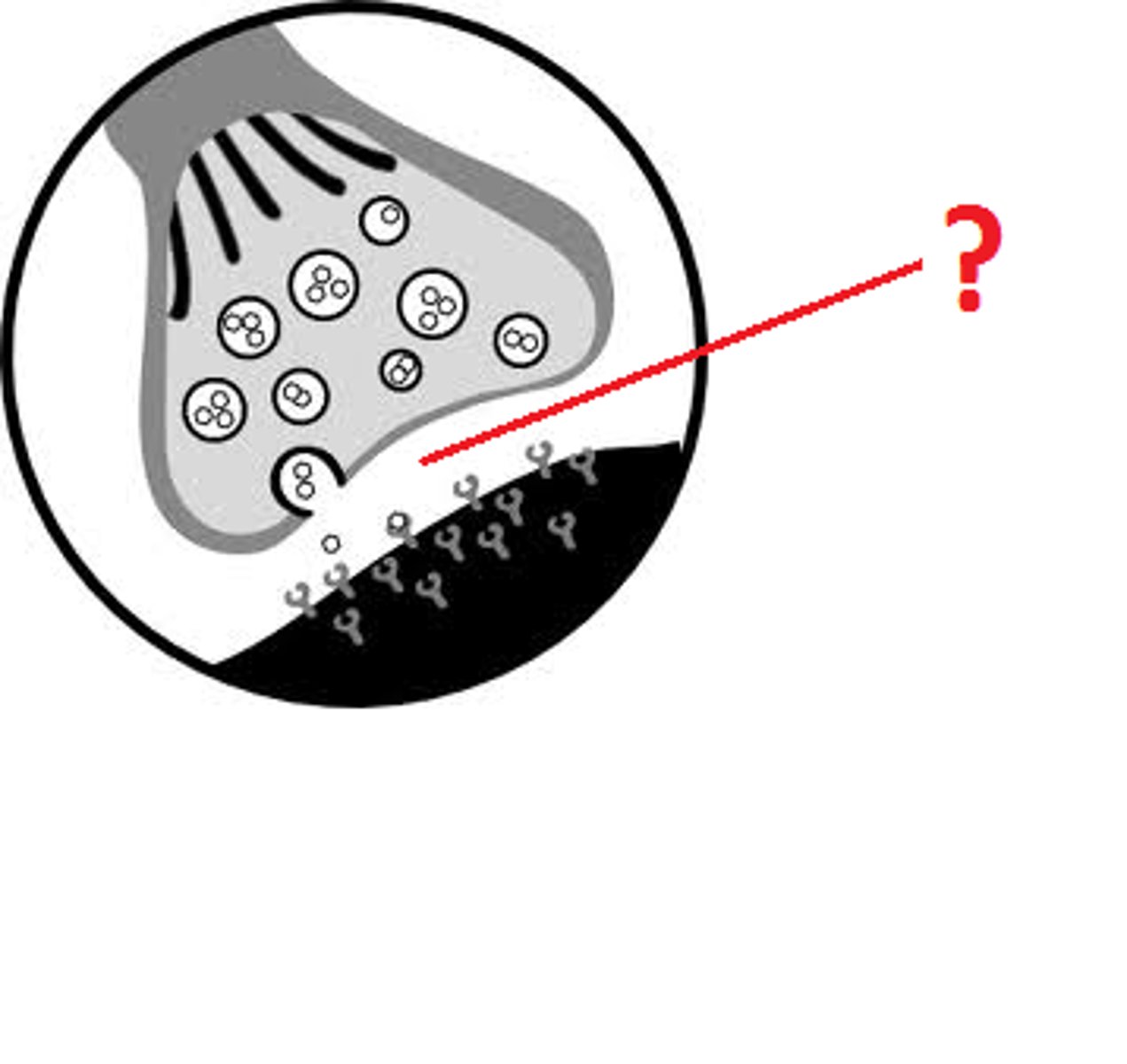
synaptic cleft
a gap into which neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal
- physical distance that separates neurons
oligodendrocytes
type of glial cell that wraps axons in a myelin sheath (CNS)
radial glia
structural support
microglia
cell repair
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (brain+spinal cord) to the rest of the body
3 important cranial nerves
olfactory nerve, optic nerve (or chiasm), and vagus nerve
olfactory bulb
first site of input for odor information from nose
- NOT a nerve
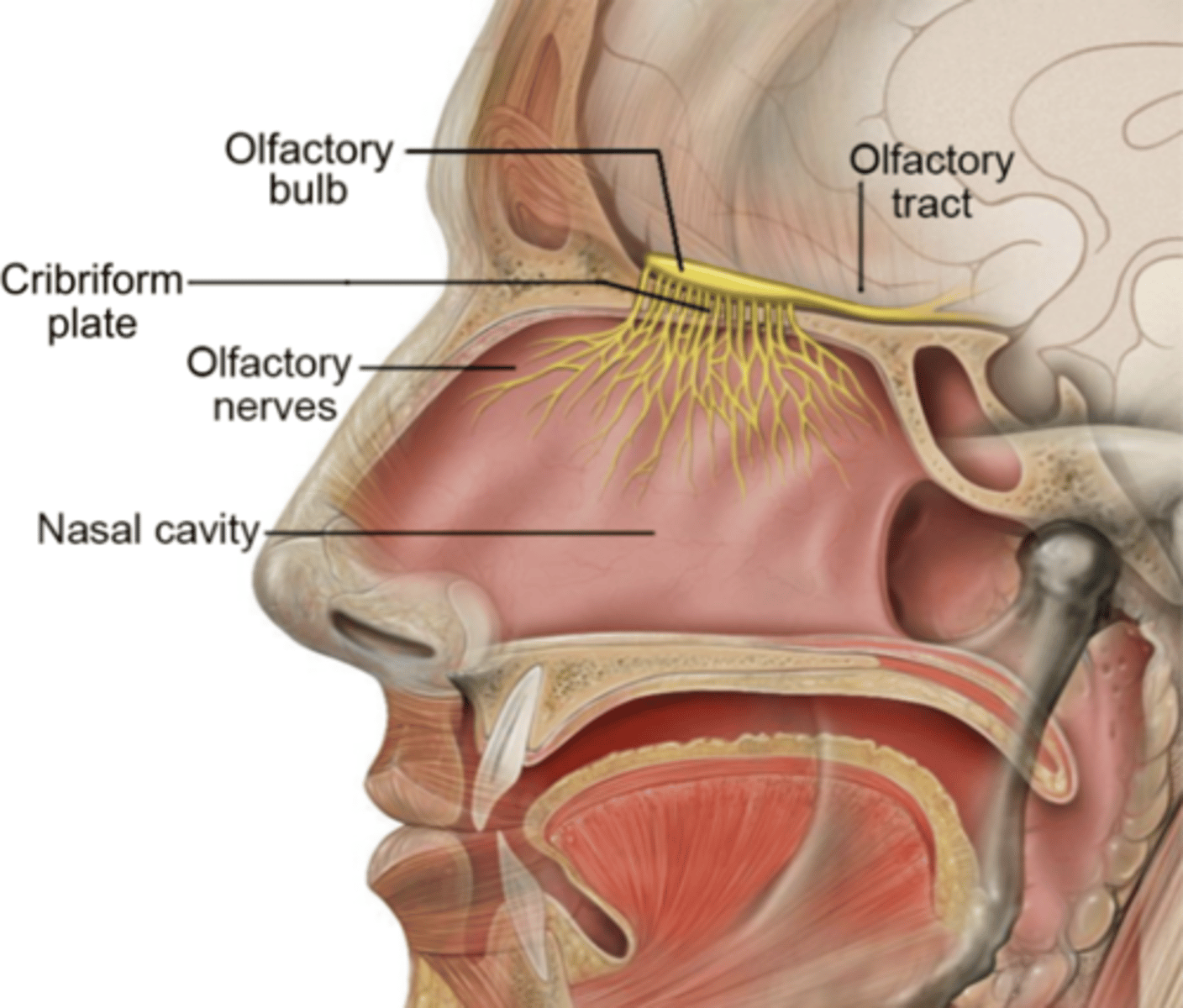
optic nerve / chiasm
carries visual information from the retina to the thalamus; allows left visual field to cross over to right hemisphere

autonomic nervous system
- the part of the PNS that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart)
ventral side of brain
bottom (aka inferior)
caudal side of brain
back (aka posterior)
horizontal plane
ipsilateral
on the same hemisphere of the brain / side of body
afferent
sensory, where a projection comes from
vertebra of spinal column
spinal cord runs through dorsally to ventrally, anatomically organized
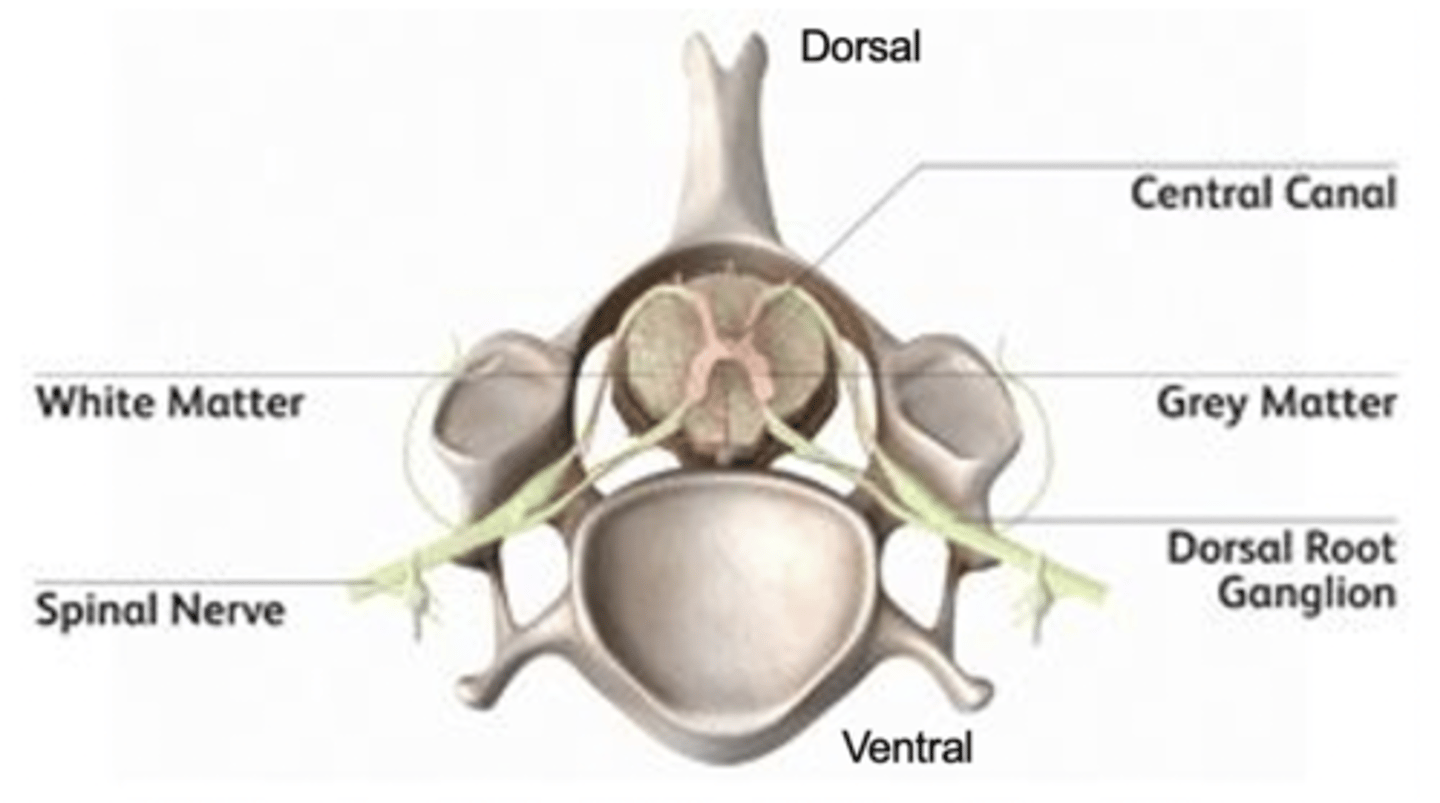
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing info from the CNS to the muscles and glands
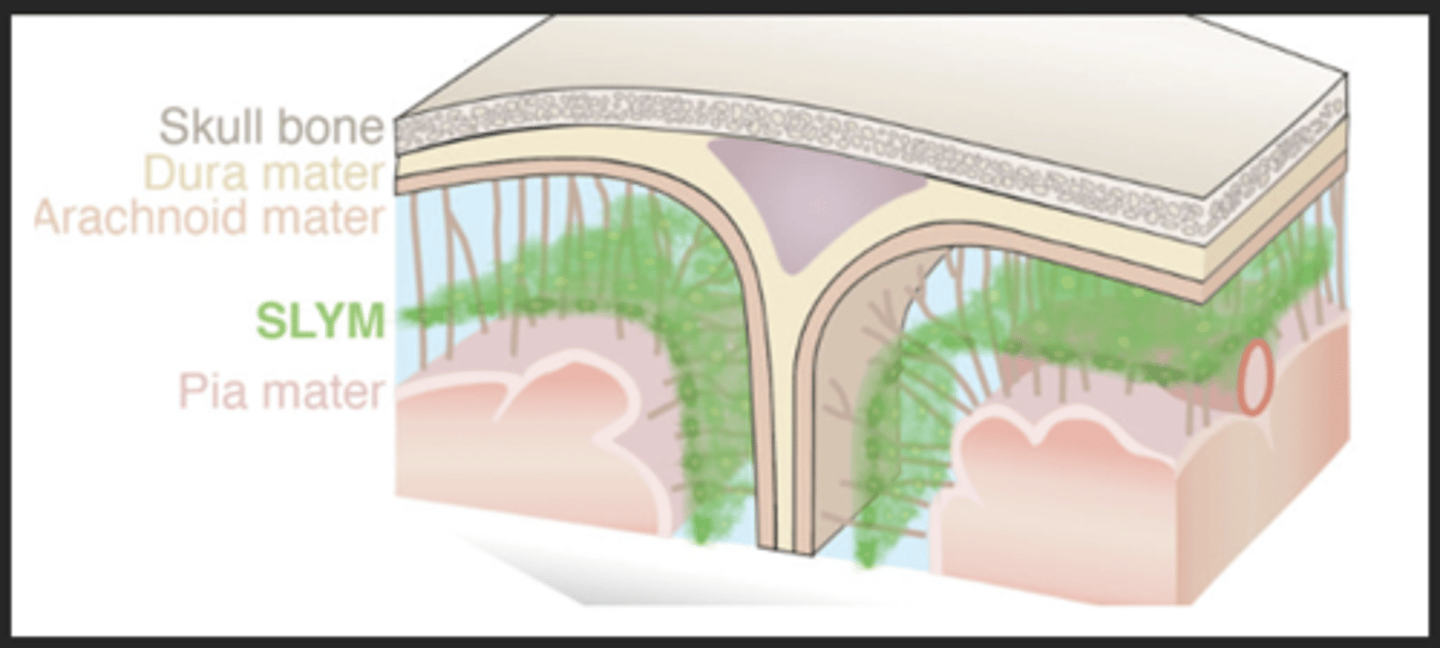
meninges of the brain
tightly-regulated membranous sacs that protect and minimize brain damage
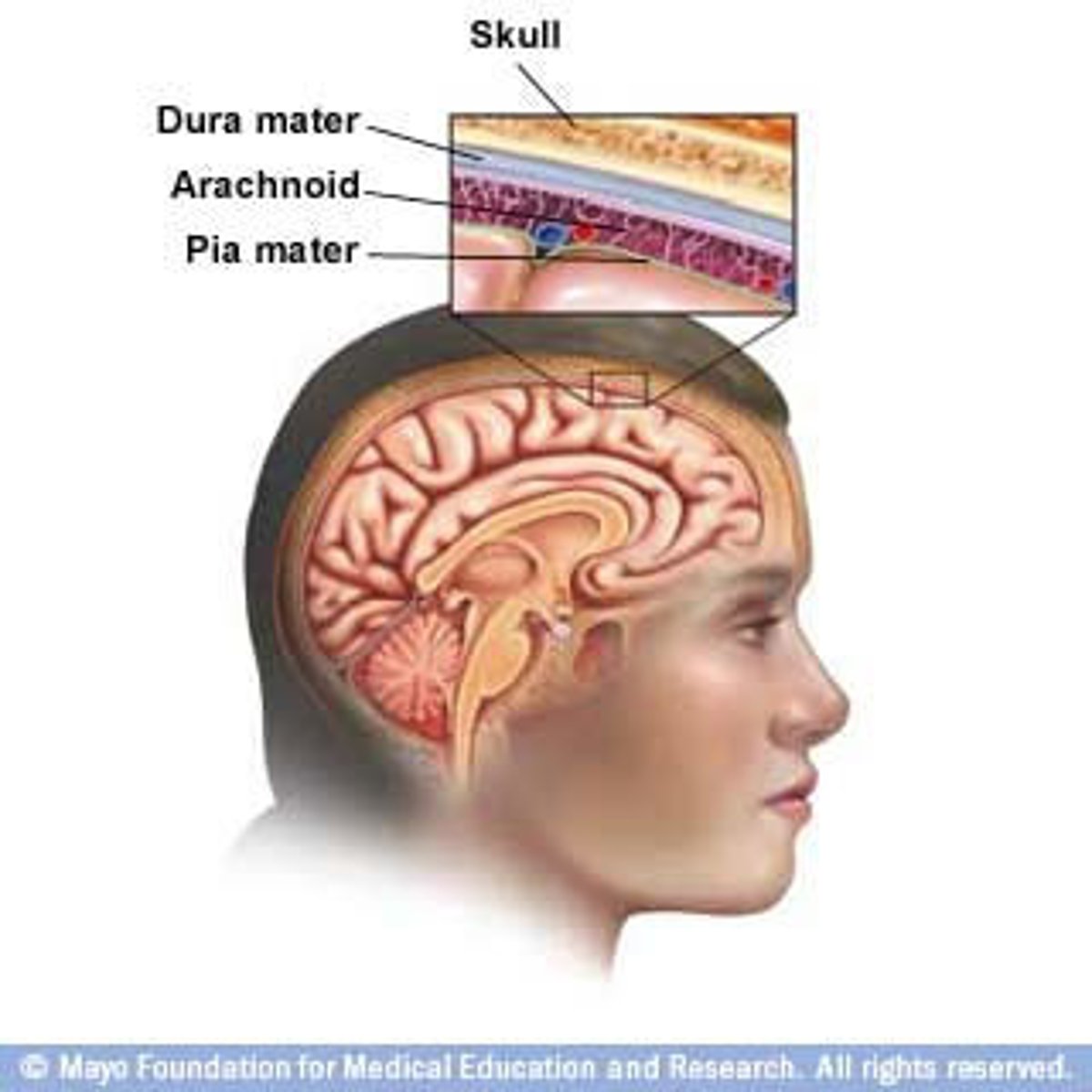
sub-arachnoid lymphatic-like membrane
new, glymphatic system
sub-arachnoid space
contains cerebrospinal fluid
pia mater (meninge)
thin membrane next to brain; contains nerves and blood vessels to nourish cells of brain and spinal cord beneath
spinal cord meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater (same ones as brain)
central canal
filled with cerebrospinal fluid (made by the choroid plexus in the ventricles), which is released to immerse the brain, and is then absorbed by the bloodstream
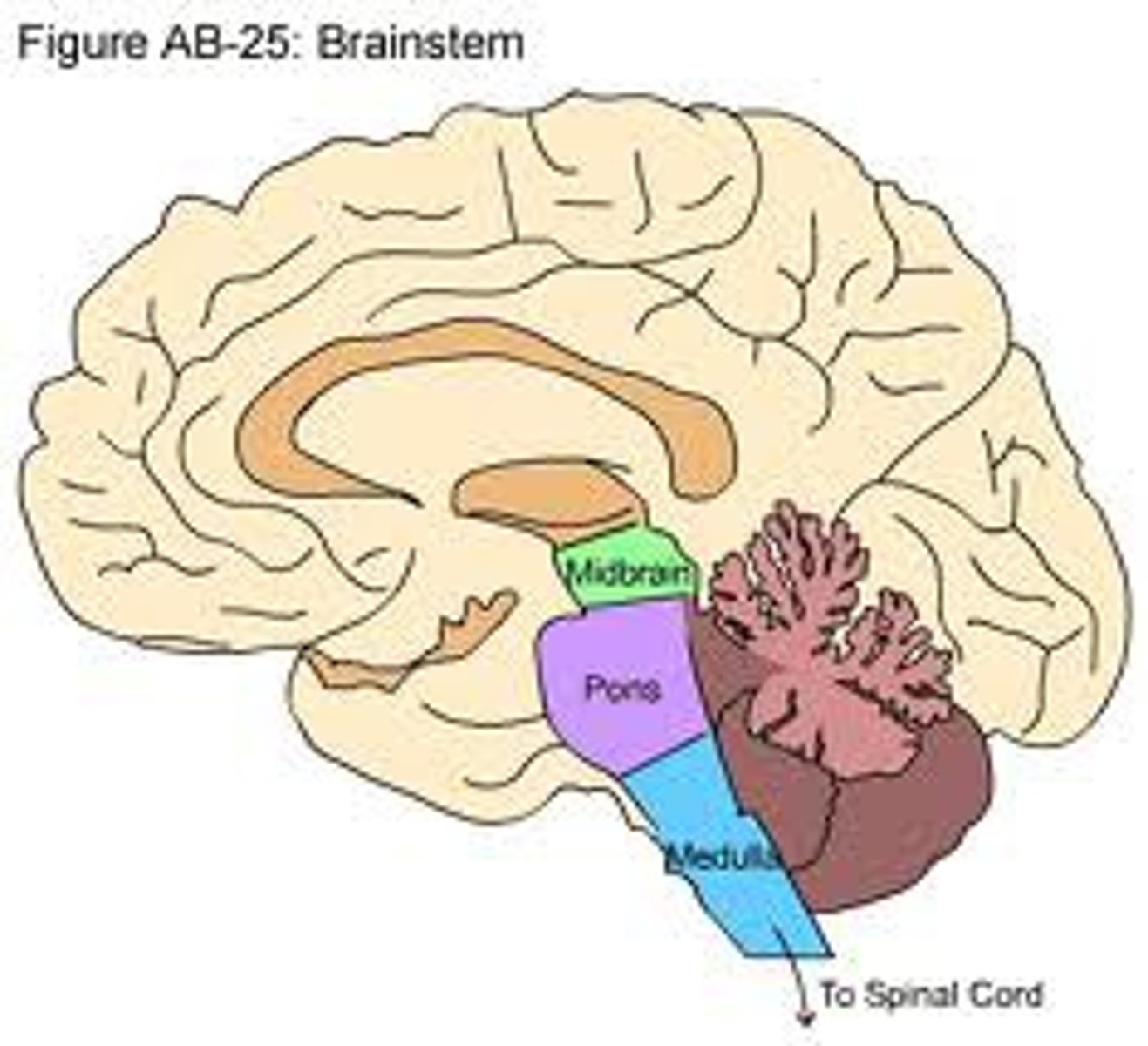
medulla
spinal thalamic fibers of passage; respiration, salivation, etc.

midbrain
on top of pons, broken into subsets of tissues: tectum and tegmentum
inferior colliculus
auditory localization (pitch, etc)

cerebral cortex
aka cerebrum; higher processing, includes all the lobes
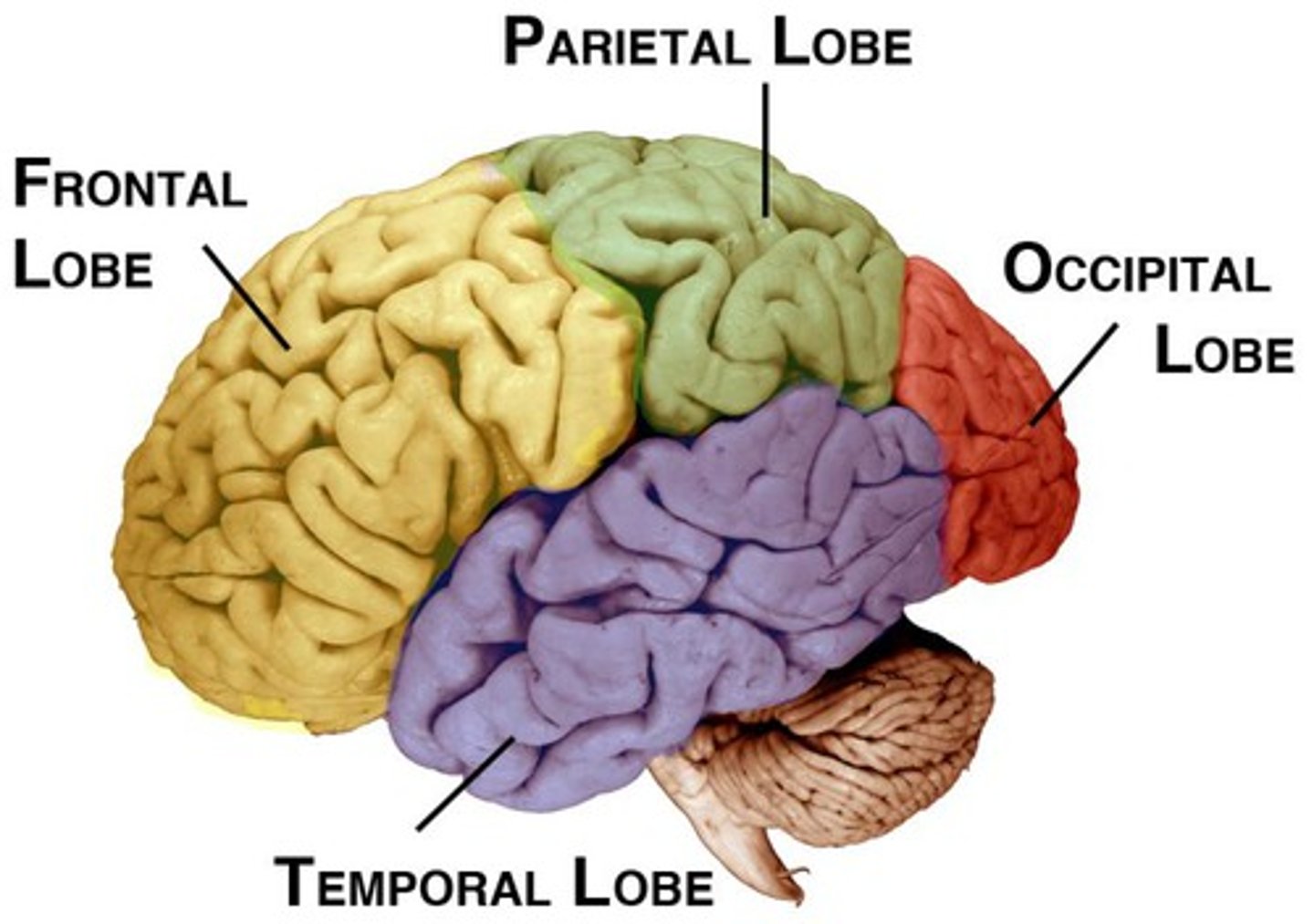
4 cortical lobes of the brain
frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital
sulcus (sulci)
depression or groove in the surface of the cerebral cortex; fissure
lateral fissure separates what lobes?
frontal and temporal
central sulcus separates what lobes?
frontal and parietal
longitudinal fissure separates what?
left and right hemispheres
occipital lobe
visual processing
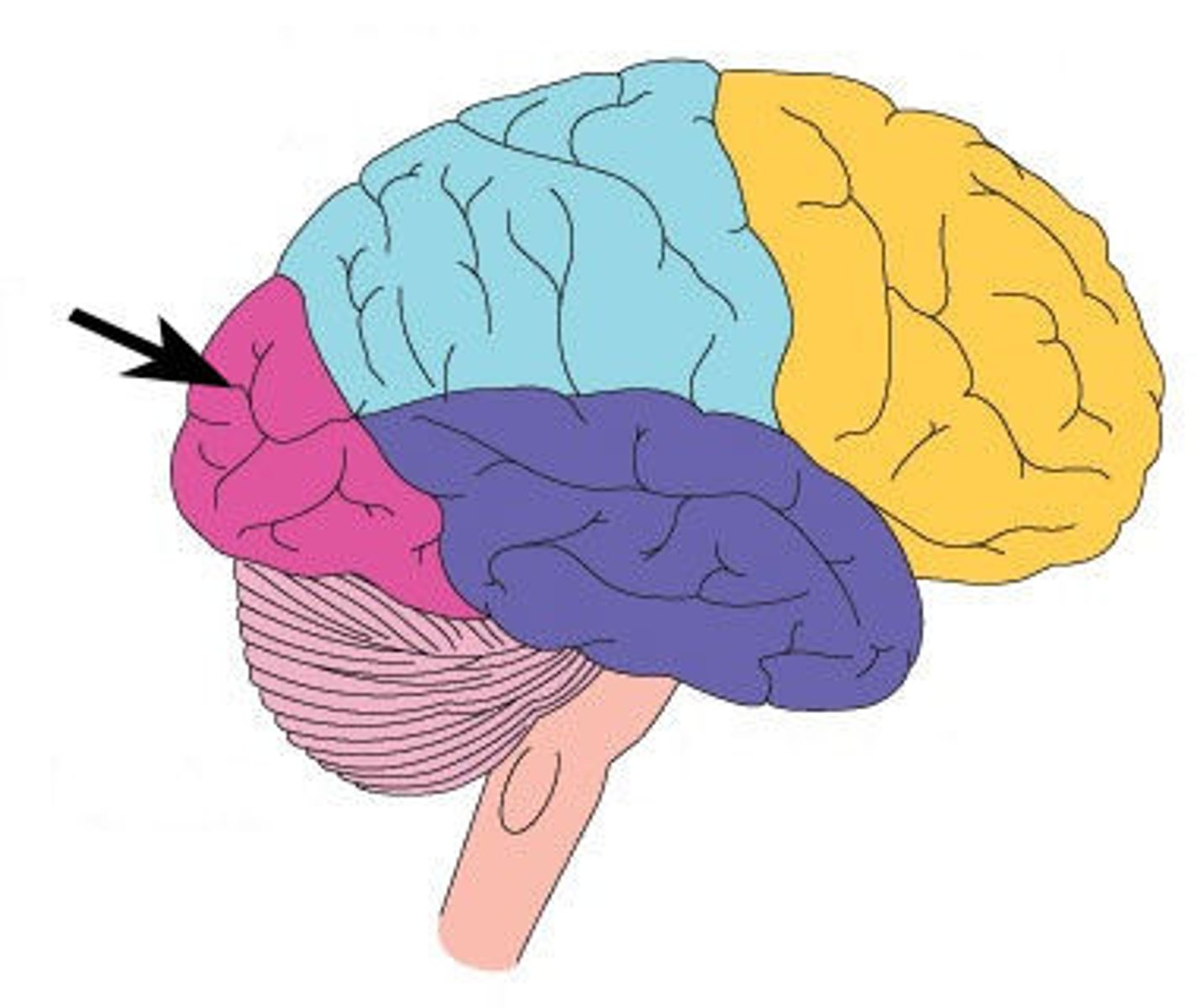
parietal lobe
somatosensory processing (touch, body position), attention, body space awareness
Phineas Gage
railroad worker, pole went through his head, became an ill-tempered man (was originally good / friendly)
- personality change due to lesion in frontal lobe
what parts does the brainstem consist of?
medulla, pons, midbrain, thalamus, and hypothalamus
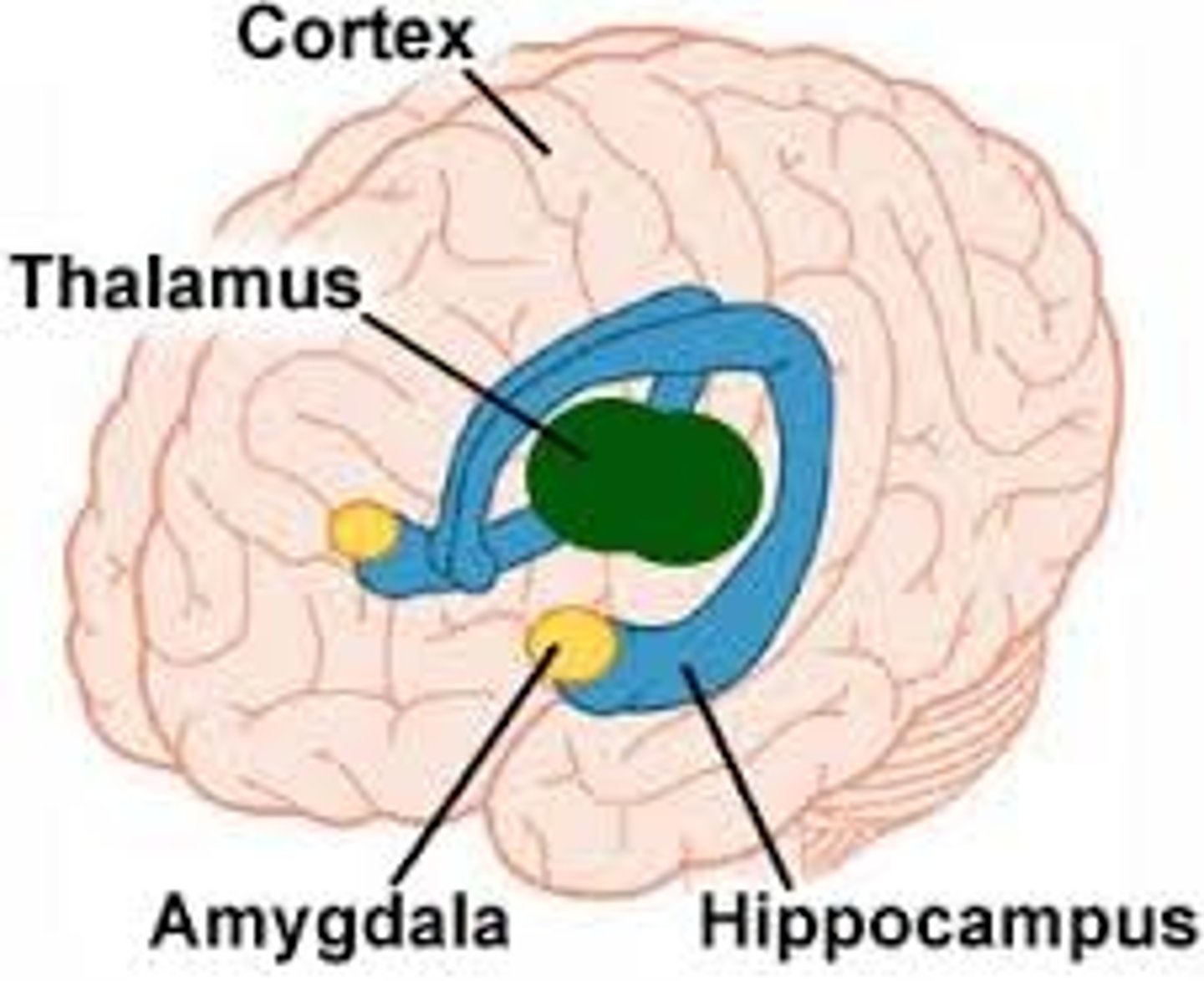
limbic system
neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions, motivations / drives, and memory
what does the basal ganglia consist of?
Striatum (composed of caudate and putamen) and Globus Pallidus
the brain is not just cell bodies, but dendrite and axon connecting areas called...
coronal radiations and association fibers
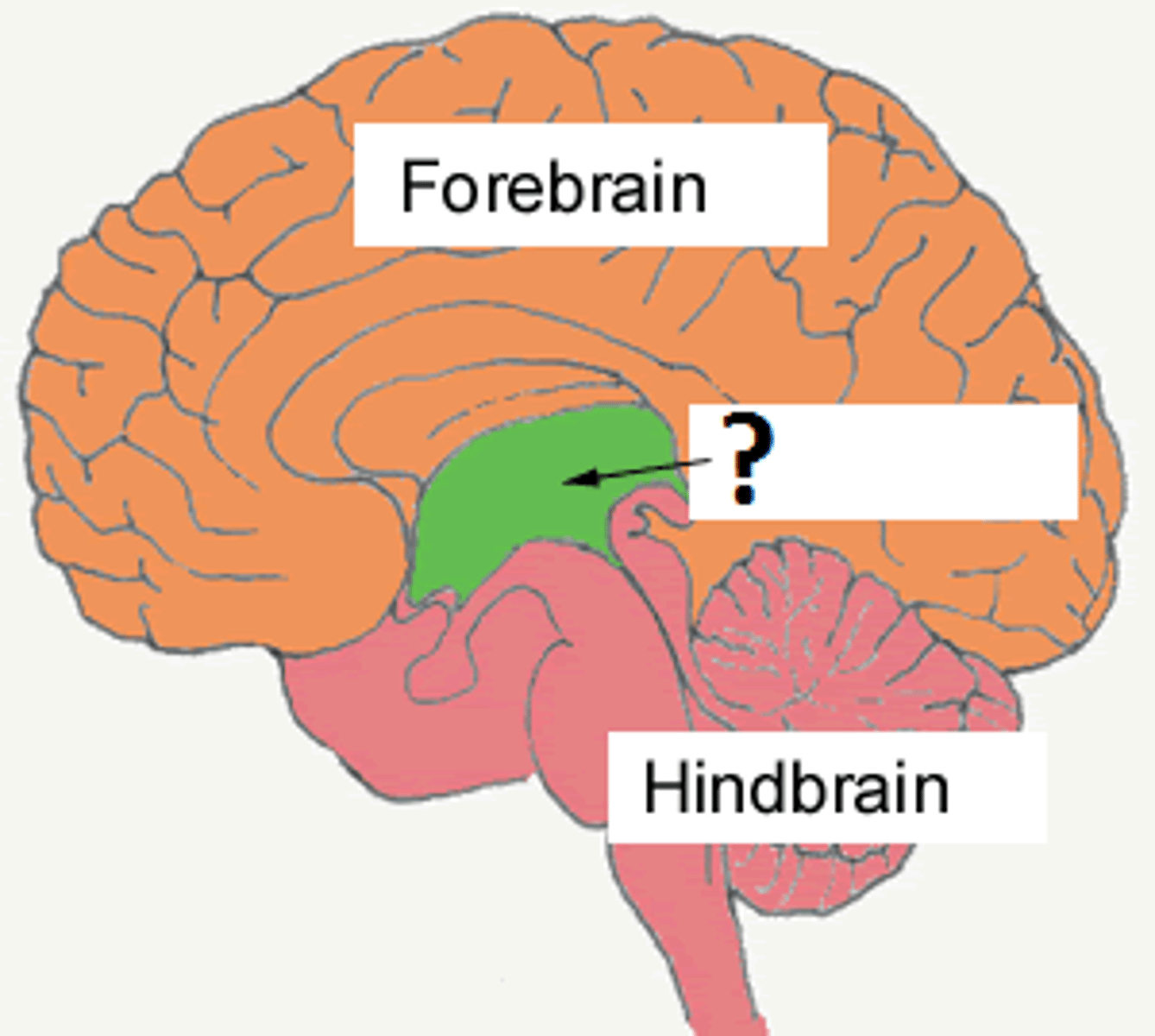
embryonic divisions
forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
hindbrain divisons
myelencephalon and metencephalon
metencephalon
pons, cerebellum, and 4th ventricle
midbrain divisions
mesencephalon
hypothalamus
motivated behavior (4 F's):
fighting, fleeing, feeding, and fornication (sex)
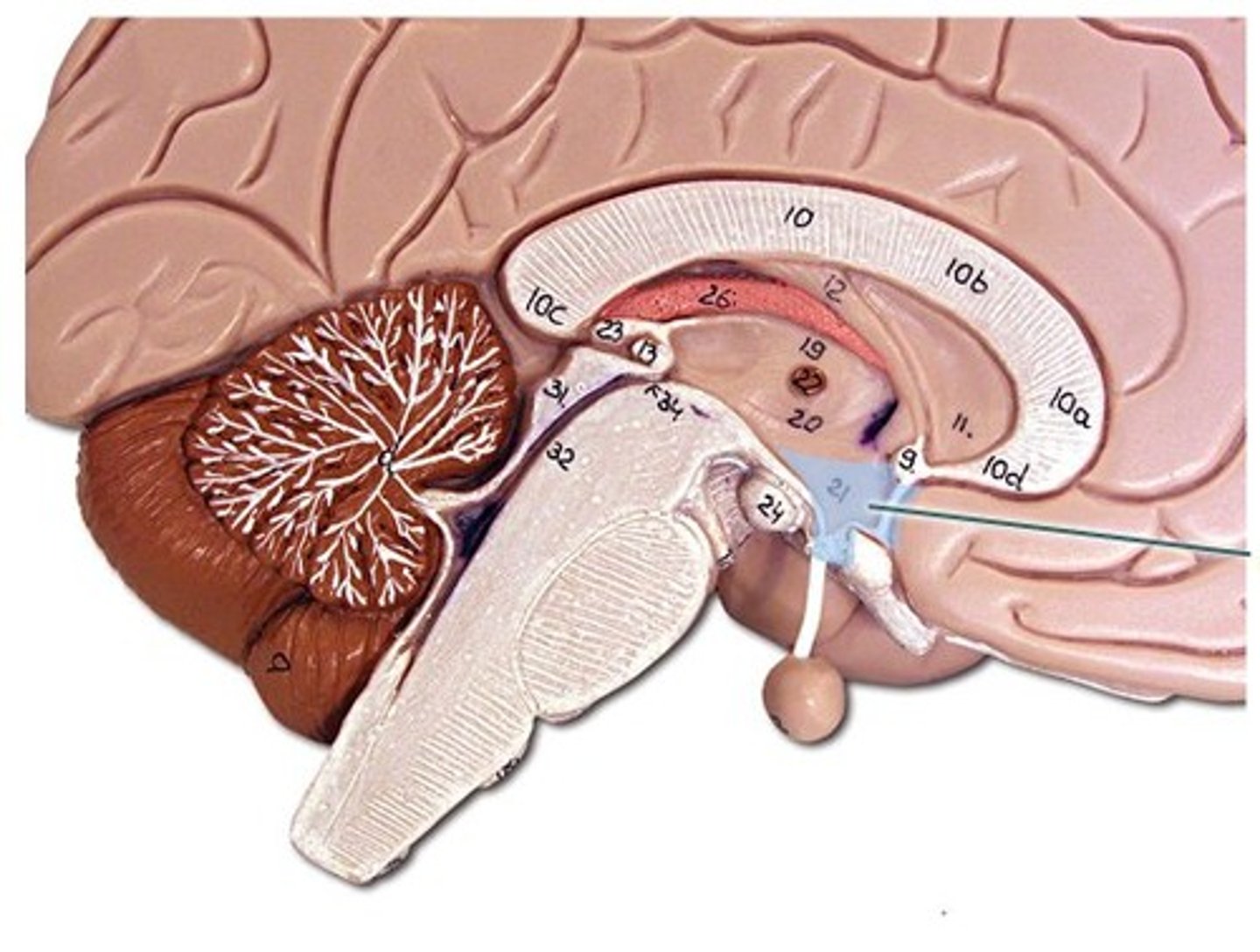
Nissl-Stained rat brain
stains cell bodies, saw different shades (layers) in the cortex
lamina
cell layers (usually of the cortex)
projection neuron
primary axons leave structure or layer
nucleus
1. collection of cell bodies in the CNS
2. part of neuron holding DNA
pituitary gland
"master" gland - in endocrine system, releases hormones that influence other glands

pineal gland
sleep wake cycle, not repeated in both hemispheres (just 1)
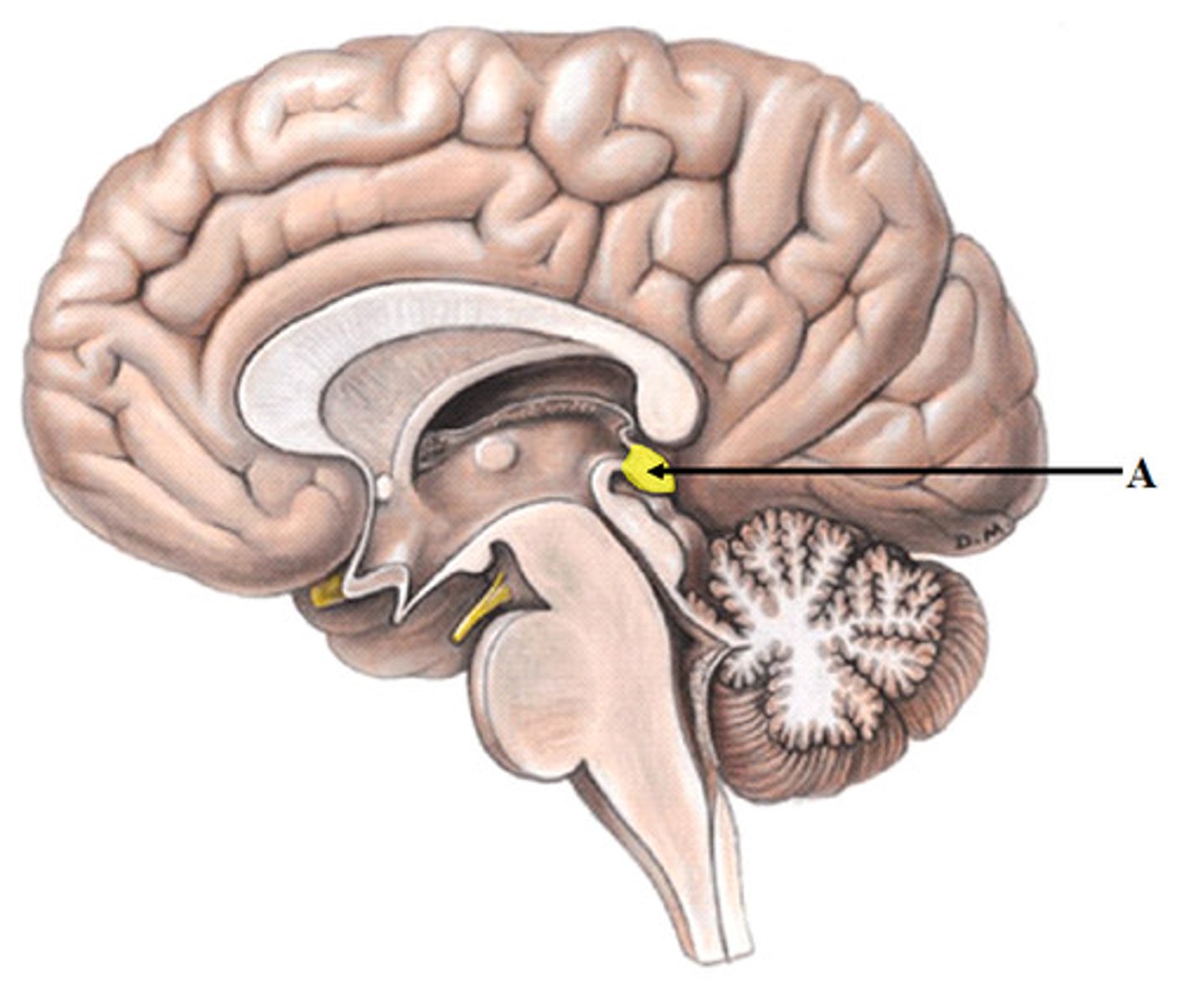
what would a stroke in the left hemisphere parietal lobe impair?
speech, motor, and memory
presynpatic neuron
neuron that sends the signal
what does an action potential represent?
information being carried / transported
basic flow of information in a neuron: step 5/10
electric potential summates in space / time, producing 'graded' potential
basic flow of information in a neuron: step 6/10
if voltage that reaches axon hillock is sufficient, neuron initiates an action potential to transmit a message to other neurons
basic flow of information in a neuron: step 9/10
when AP reaches axon terminal, it causes neurotransmitter to be released to the next neuron
ion channels
protein "tunnels" in the cell membrane that are typically selective for a particular ion (ex: Na+)
leak channels
open all the time, permeable to potassium (K+)
if we measure ion flow when the neuron is "at rest", we will find that...
- Na+ ions continuously ENTER the cell through leak channels
- K+ ions continuously LEAVE the cell through leak channels
why do ions flow in the direction they do?
they have different concentration gradients
- the inside and outside of the neuron contain billions of ions
- the internal and external concentrations of each ion differ, providing a gradient which the ions move DOWN
potassium (K+) ion concentration is greater....
INSIDE the cell (than outside)
what is the result of the electrical potential in the cell?
negatively drawing K+ back into the cell
- the 'reversal'
- 2 forces of moving ions in/out of the cell until the concentration force pushing out is exactly balanced by the electrical force pulling in
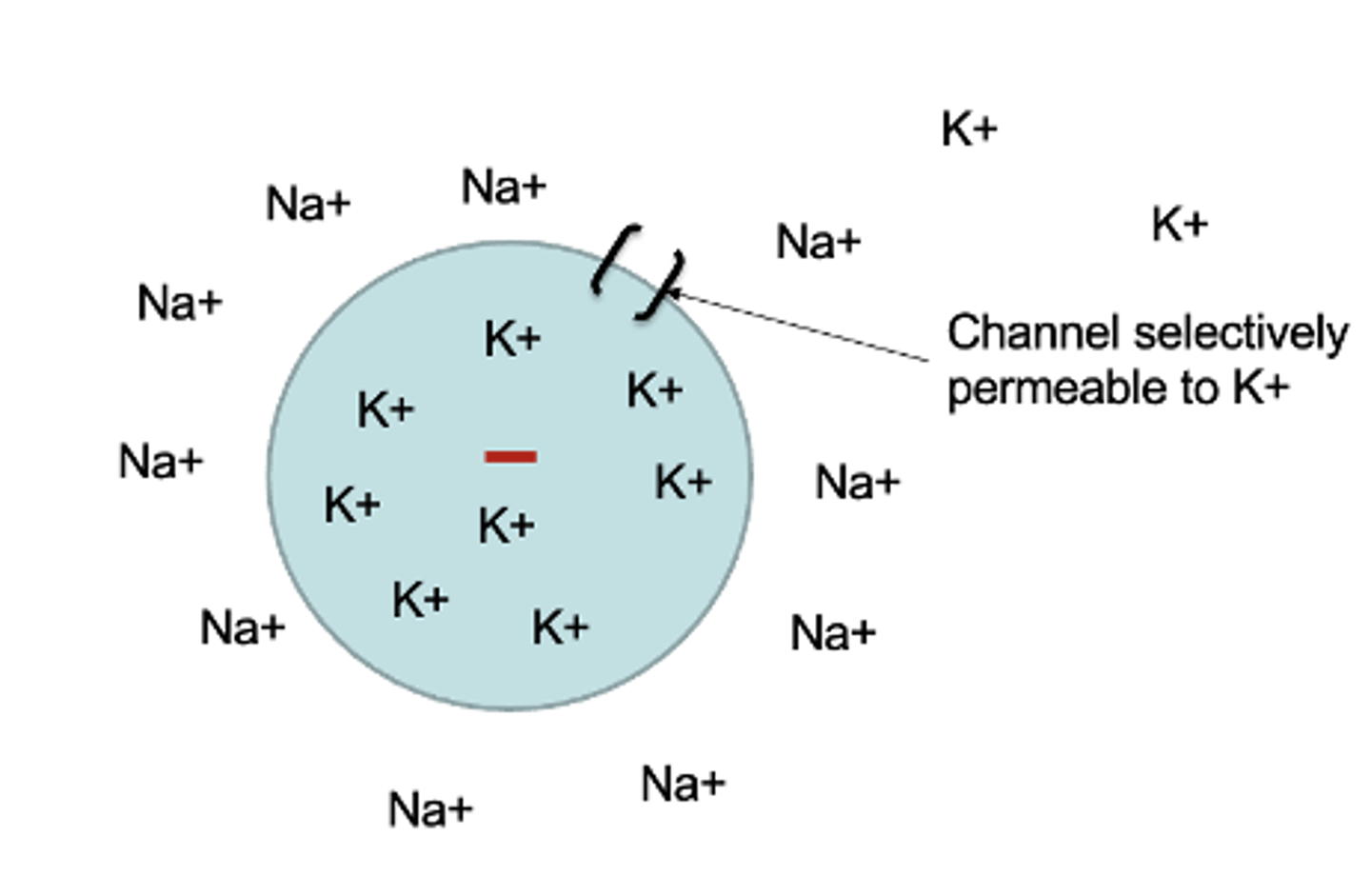
equilibrium potential (aka reversal potential)
the voltage at which an ion stops flowing down its concentration gradient
what is the typical voltage for K+ concentrations in neurons?
-80 mV
in normal conditions, do cells ever get more negative than -80 mV?
no, so K+ always flows out (>-80) or net flow will be equivalent (at -80mV)
do action potentials affect the concentration gradient of a cell?
BARELY
- approx 2,000,000 K+ ions leave during an action potential, but there are 47,000,000,000 K+ ions inside the cell
- so, each action potential decreases K+ concentration by .004%,
- thus, the concentration gradient remains effectively unchanged
what is the equilibrium potential voltage for sodium?
+55 mV
describe natural flow of Na+ down its concentration gradient
- 15x more Na+ outside than inside
- flows INTO neuron until the cell is more positive than +55 mV, thus preventing influx
describe natural flow of chloride (Cl-) down its concentration gradient
- there is ~7x more Cl- outside than in
- will flow INTO the cell until the cell is more negative than -60mV
what is the equilibrium potential voltage for calcium?
+150 mV
describe natural flow of calcium (Ca++) down its concentration gradient
there is >10,000x more outside than in
- it will ALWAYS flow INTO the cell
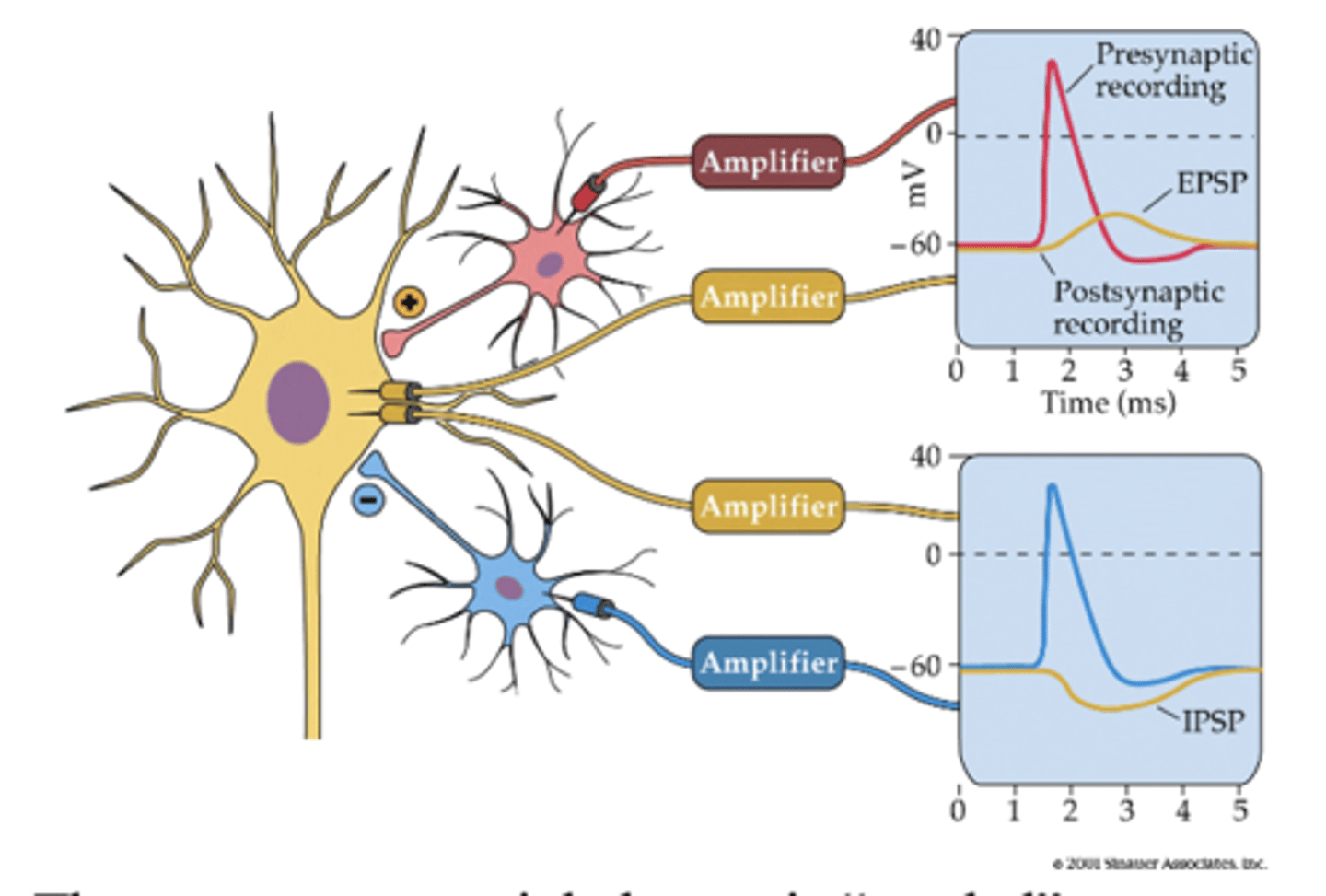
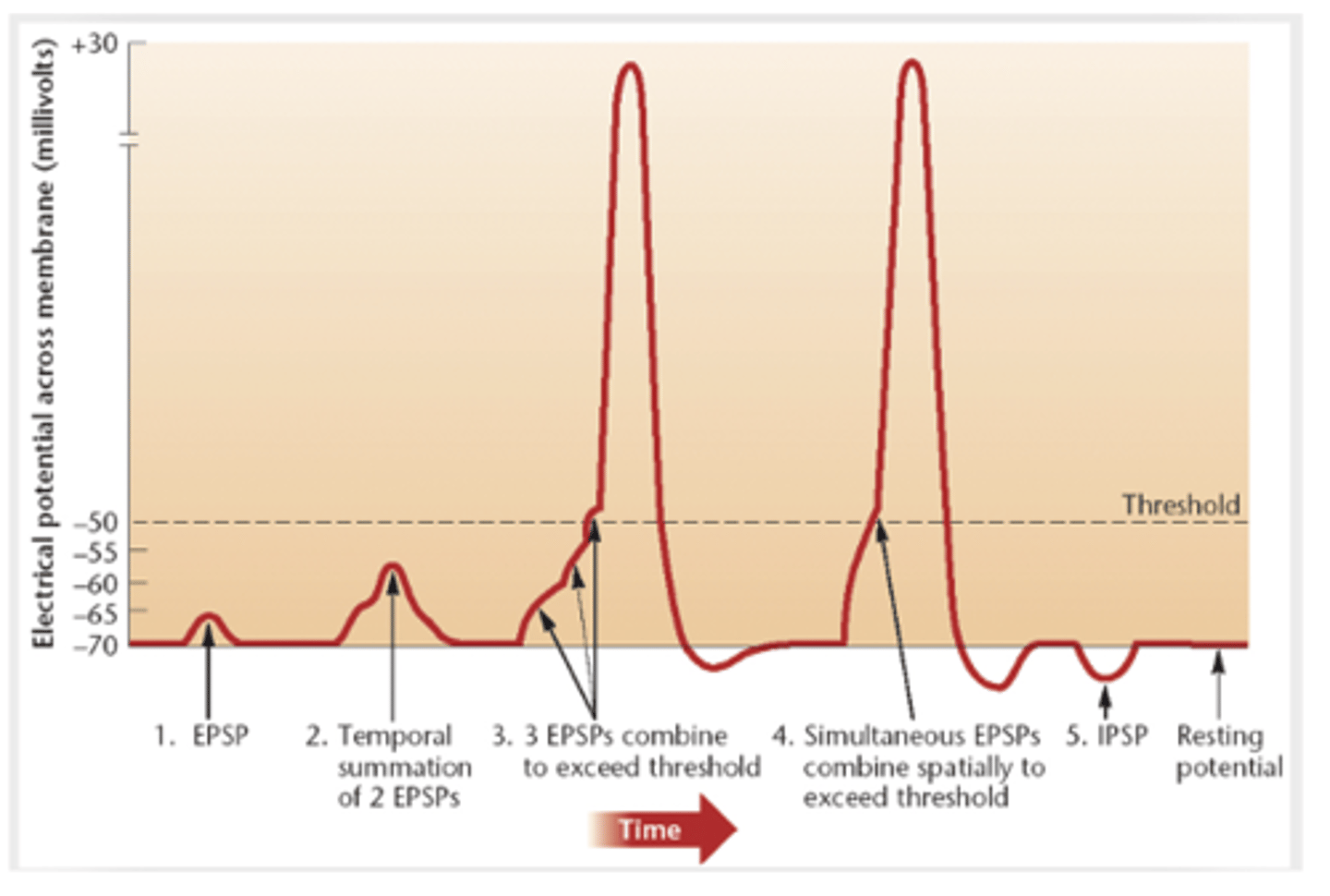
EPSP
excitatory post synaptic potential
what causes a EPSP?
action potential and neurotransmitter release from a excitatory presynaptic neuron
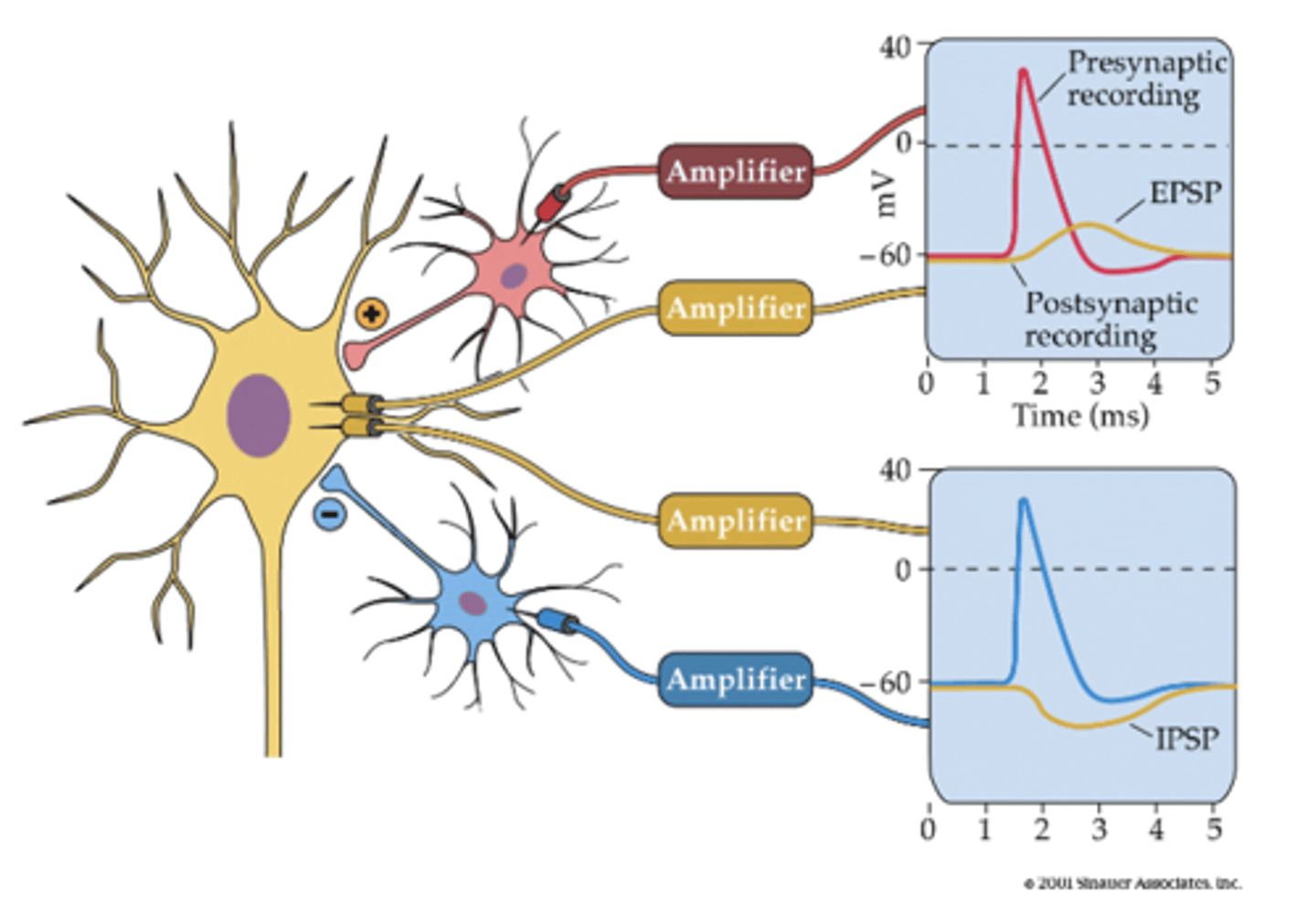
what causes a IPSP?
action potential and neurotransmitter release from an inhibitory neuron
receptor potential: Na+
enters cell, results in EPSP, depolarizing
- results from excitatory neurotransmitter binding (e.g., glutamate)
- also involved in positive phase of action potential
receptor potential: Cl-
enters cell, results in IPSP, hyperpolarizing
- results from inhibitory neurotransmitter (e.g., GABA)
- influx keeps cell from reaching threshold for AP
when do action potentials occur?
when the cell depolarized enough (to threshold level of -50mV at axon hillock)
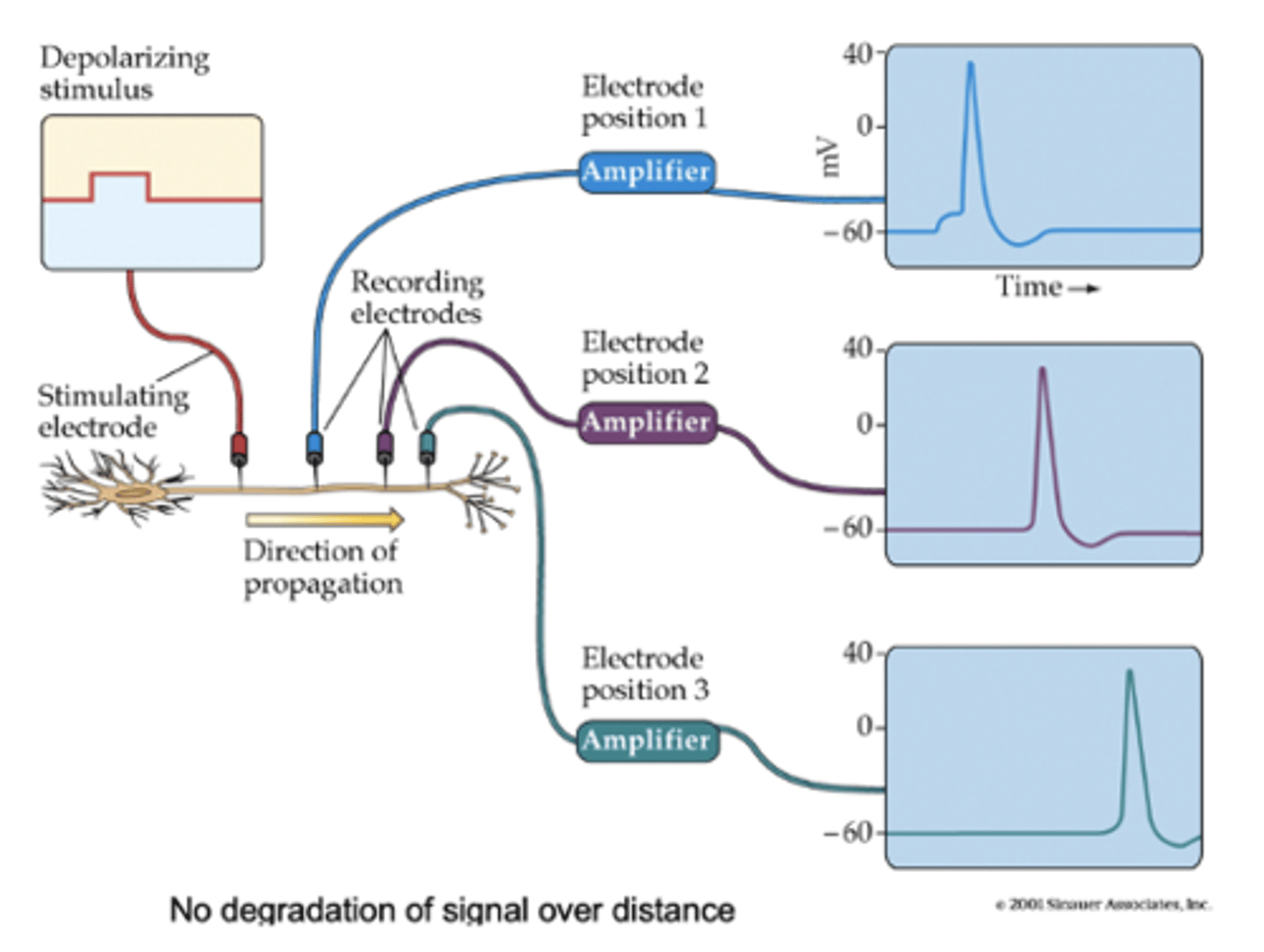
do action potentials diminish?
no, regenerates at each point along the axon
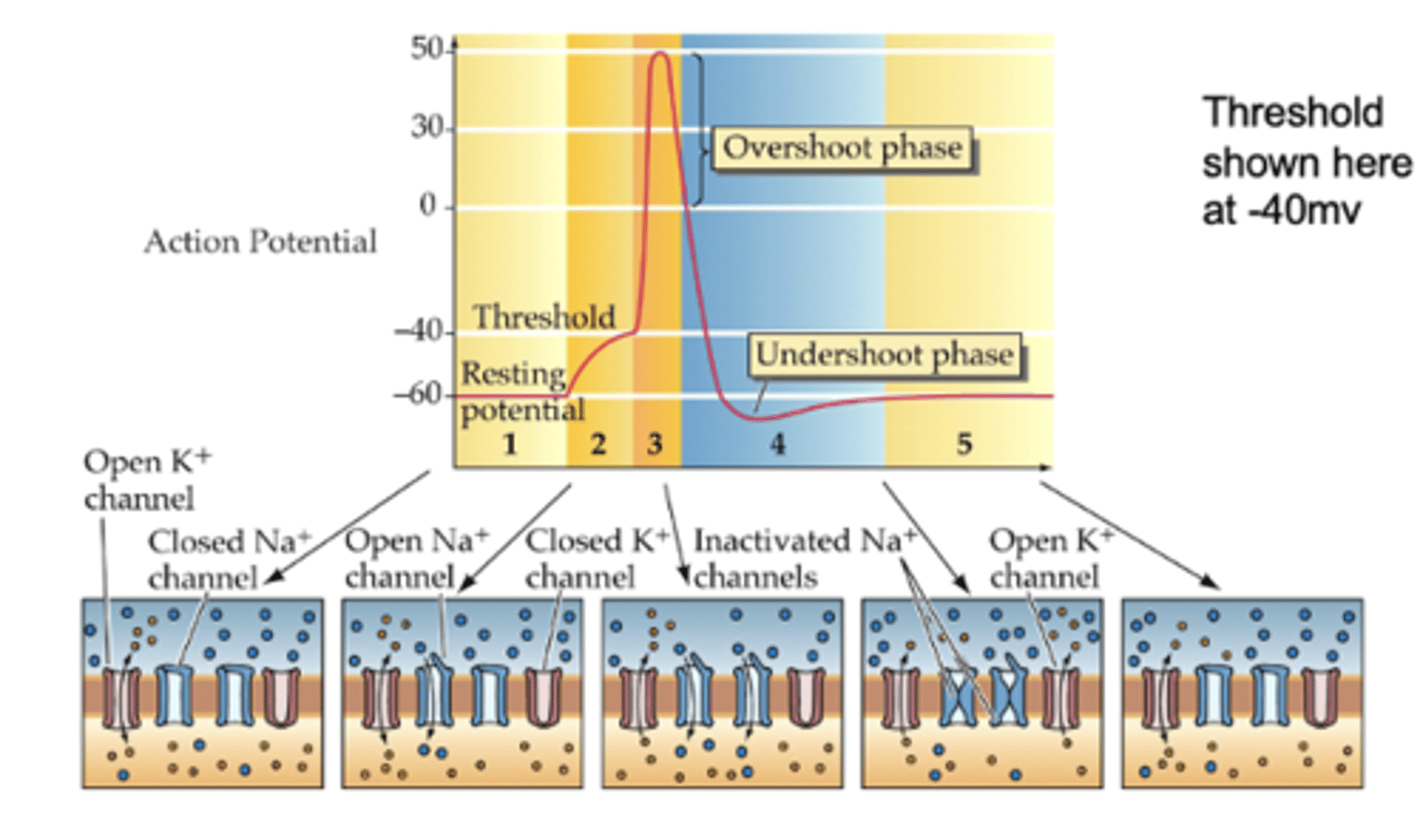
voltage-gated ion channels
channel in axon hillock / axon that open and close based on voltage, NOT neurotransmitter binding
when do voltage-gated ion channels open?
when the membrane potential at the axon hillock reaches approximately -50 mV
- K+ and Na+ channels are activated at the same time and voltage (-50mV)
mechanisms of voltage-gated Na+ ion channels VS voltage-gated K+ ion channels
- Na+: open rapidly and stay open for ~1ms before inactivating; they then de-inactivate after cell is more negative than -50mV
- K+: open more slowly and close more slowly; they do not inactivate, but slowly close when cell is more negative than -50mV
Nodes of Ranvier
the unmyelinated distance between the sets of voltage gated ion channels in myelinated axons
Synaptosomal associated protein
sodium-potassium pump
maintains concentration gradient at resting potential
- slow process and is used for long-term balancing of ions (it is NOT used to bring the potential back to rest after an action potential)
how do K+ and Na+ move in a potassium pump?
- K+ will be pumped IN
- Na+ will be pumped OUT
- used to keep ions’ concentration at appropriate levels, by moving 3 Na+ out for 2 K+ in
steps in neurotransmitter utilization
1. synthesis
2. storage
3. release
4. binding
5. deactivation
step 1: synthesis
neurotransmitter synthesized at axon terminal or in cell body and then transported to terminal
step 3: release
vesicles fuse to axon terminal membrane and contents (~500-1000 NT molecules) diffuse into synaptic cleft (exocytosis)
which of the five steps can drugs disrupt / alter?
all of them!
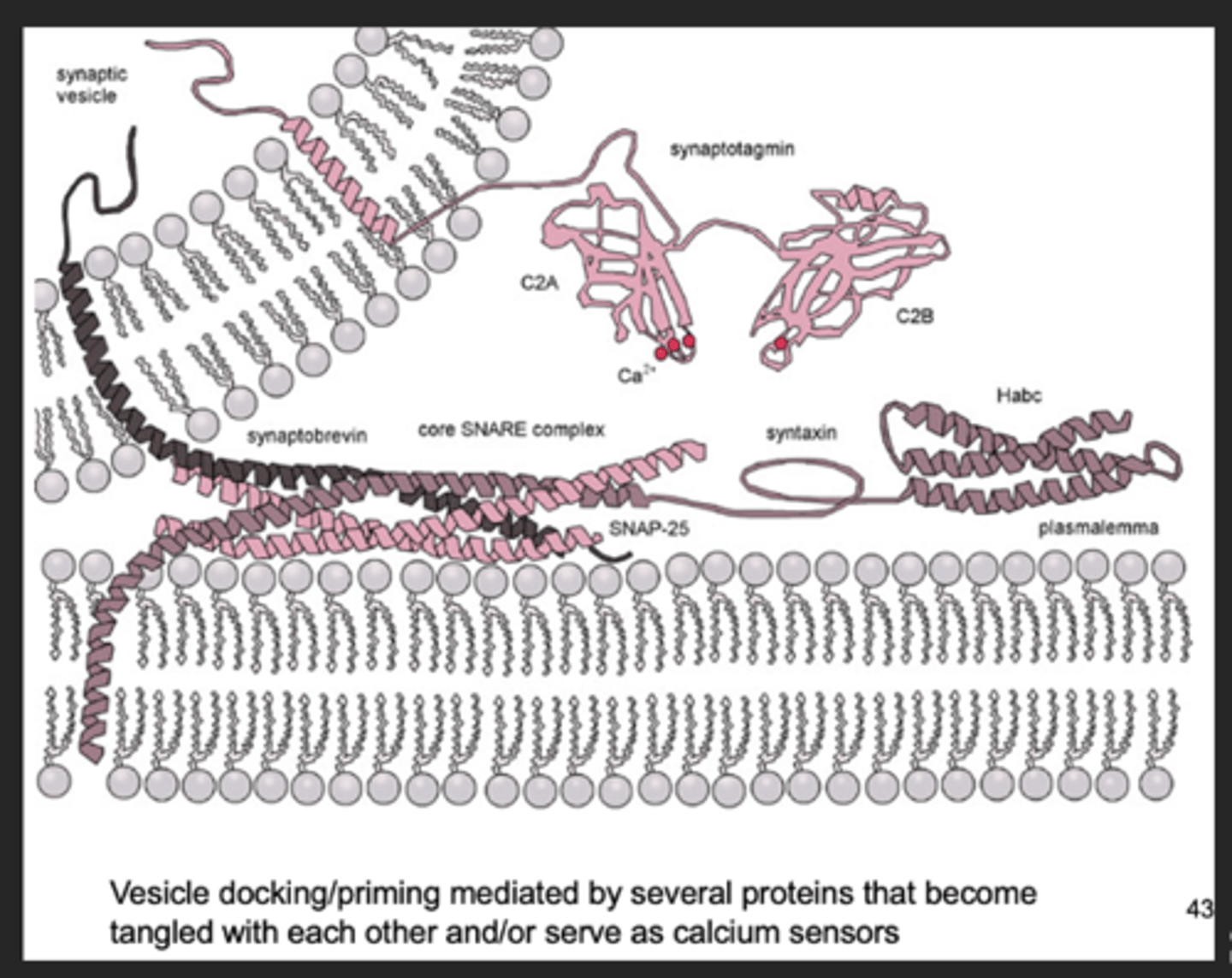
vesicle availability
- ready and releasable pool, recycling pool, reserved pool
- only ready and releasable pool are actually released
- generation of AP doesn’t necessarily mean neurotransmitter will be released
- function: docking and priming
vesicle docking / exocytosis
- 2 vesicle snares (v-snare) and 2 proteins target snares (t-snare)
- t-snares tangle with v-snares, so vesicle can be docked
which is the most prevalent inhibitory neurotransmitter (ionotropic)?
GABA
- opens Cl- channels (IPSP)
g-protein coupled receptors (metabotropic)
induce intracellular cascades that change the state or "tone" of the neuron and/or produce long-term changes in connectivity or functioning
different g-protein coupled receptors & their different effects
- Gαs and Gαi/o excite and inhibit Adenylate Cyclase respectively
- Gαq/11 pathway excite phospholipase C