IMED1004 - Health and Environment (L27)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Contact with the natural environment
- lower crime rates
- improved social relationships
- reductions in reported heath problems (e.g heart disease, cancer, musculoskeletal problems)
- faster recovery from surgery
- reduced levels obesity; hgher rates physical activity
- improved immune functioning;
• higher self-rated mental health;
• improved relaxation;
• reduced behaviour problems in children;
• better cognitive performance (attention restoration);
• reduction of the ill effects of pollution, including noise pollution;
• reduction urban heat island effect:
• higher productivity;
• optimized exposure to sunlight and improved sleep.
WHO reports on urban green spaces and Health (NO LEARNING OUTCOME)
"The results indicate that urban green space is a necessary component for delivering healthy, sustainable and liveable cities. Interventions to increase or improve urban green space can deliver positive health, social and environmental outcomes for all population groups, particularly among lower socioeconomic status groups. There are very few, if any, other public health interventions that can achieve all of this, and especially the impact on active lifestyles, mental well-being and social interaction is frequently highlighted as a key benefit" (P 5).
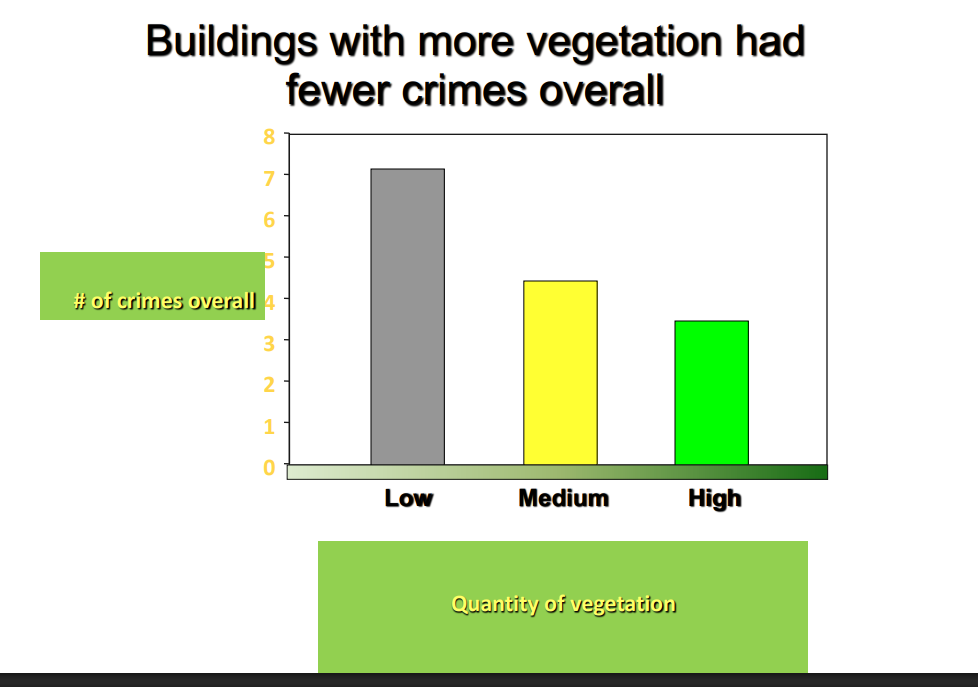
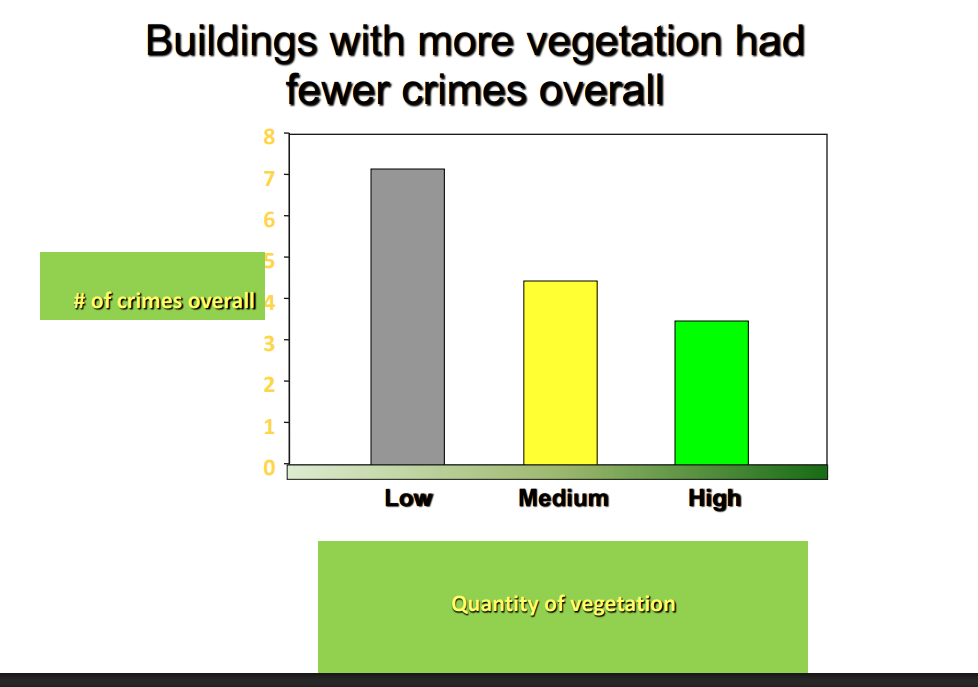
Buildings with more vegetation had fewer crimes overall
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 6
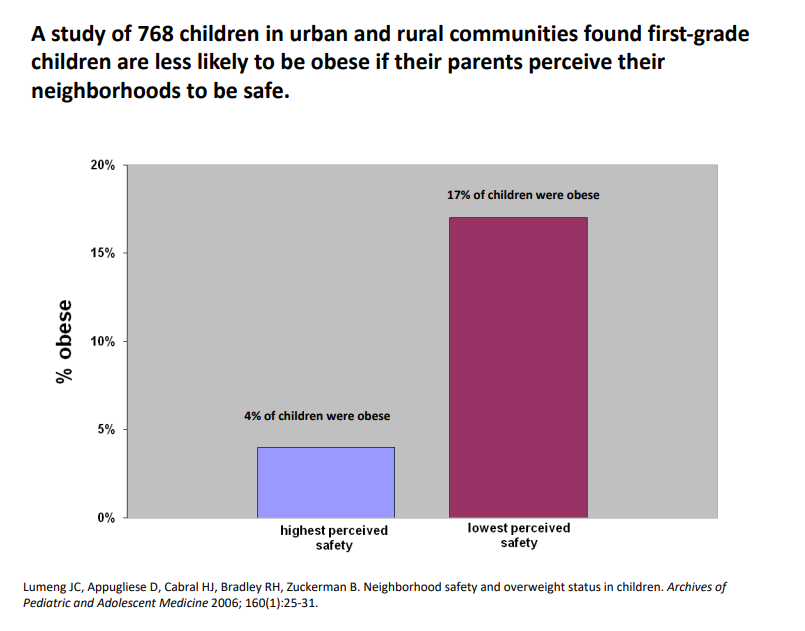
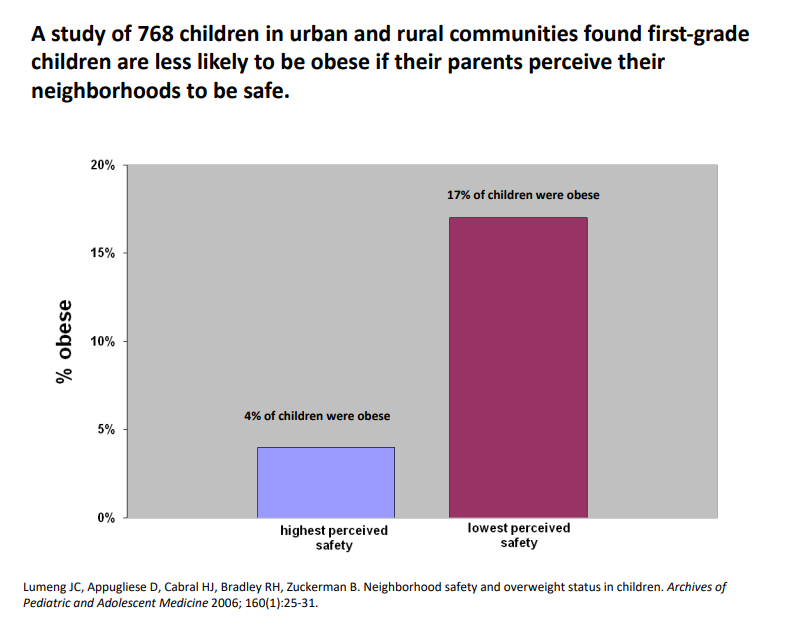
A study of 768 children in urban and rural communities found in first-grade children are less likely to be obese if their parents perceieve their neighbourhood to be safe
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 7
Health Effects
Exposure to and use of green spaces:
• Reductions in health problems (e.g. heart disease, cancer, respiratory, gut & musculoskeletal problems);
• Reduced levels obesity, higher rates physical activity (note - greater benefits from 'green' exercise);
• Improved cognitive function;
• Higher self-rated mental health, well-being;
Intervention: spending time in the natural environment
Spending time in natural settings appears to activate involuntary attention, giving the brain's directed attention time to rest
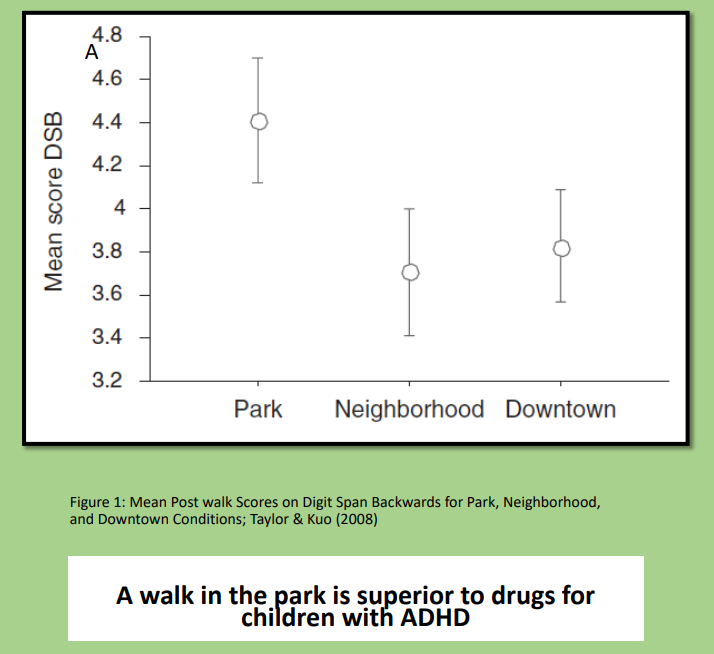
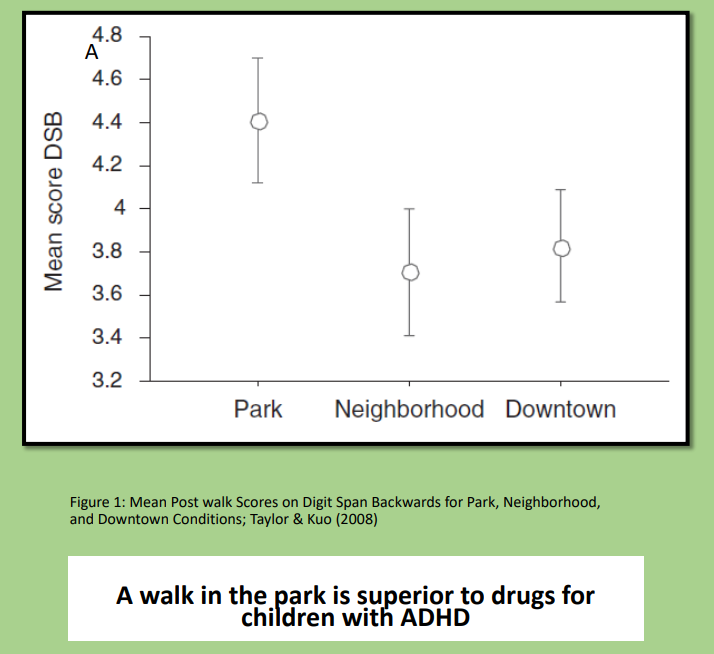
A walk in the park is superior to drugs for children with ADHD
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 10

Where to put your best foot forward: psycho-physiological repsonses to walking in natural and urban environemnts
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 11

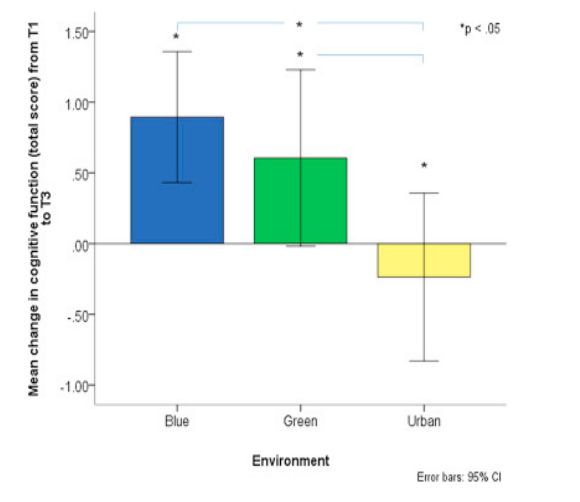
Attention restoration theory:
- increase in involuntary attention restores directed attention
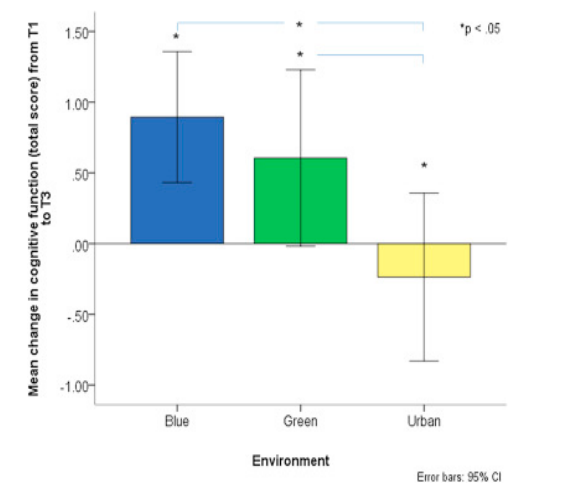
- mean change in cognitive function (backwards digit span task) from baseline to 60min post exposrue follow up by environenbt

Gardening
- improves mood, self-esteem, physiological indices; for parents with dementia reduces agitation, aggression and other symptoms

Physiological Effects of Contact with Nature
LOWER STRESS INDICIATORS:
- salivary cortisol, blood pressure, heart rate, skin conductanve, muscle tension (forsest vs urban walk)
- Japanese studies of "forest bathing" - decreased blood glucose levels in diabetic patients; more than exercise alone
- Decreased heart rate, improved performance on attention orienting task following exposure to natural vs urban landscape vidoes
- imrpoved brain health
Workplace design: Effects on productivity
STUDY OR OFFICE BUILDING:
- 30% of offices overlooked trees, manicured landsacpe
- 31% overlooked a treet, building and parking lot
- 39% of the offices - no outside view at all
- occupants prefrred the vegetated views, some view over no view
.
RESULTS:
Employees with the views of trees and landscape took less sick leave: averaged 57 hours per year, compared with 68 hours for employees with no view; those with urban view ranked between the two. Quality of a person's view found to be the primary predictor of absenteeism.
Cox et al (2017) found that in five different types of neighbourhood the amount of vegetation cover and afternoon bird abundance were
positively associated with a lower prevalence of depression, anxiety, and stress.

Conversely, environmental degredation produces ill efects
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 17


Health effects of air pollution
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 18

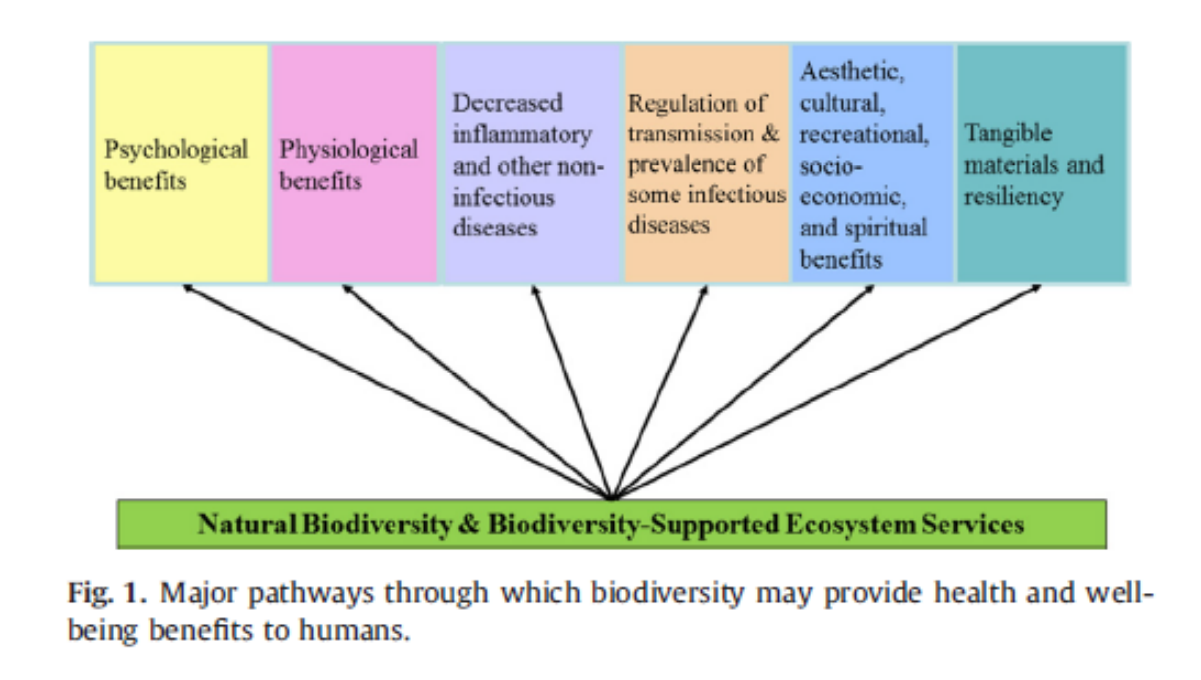
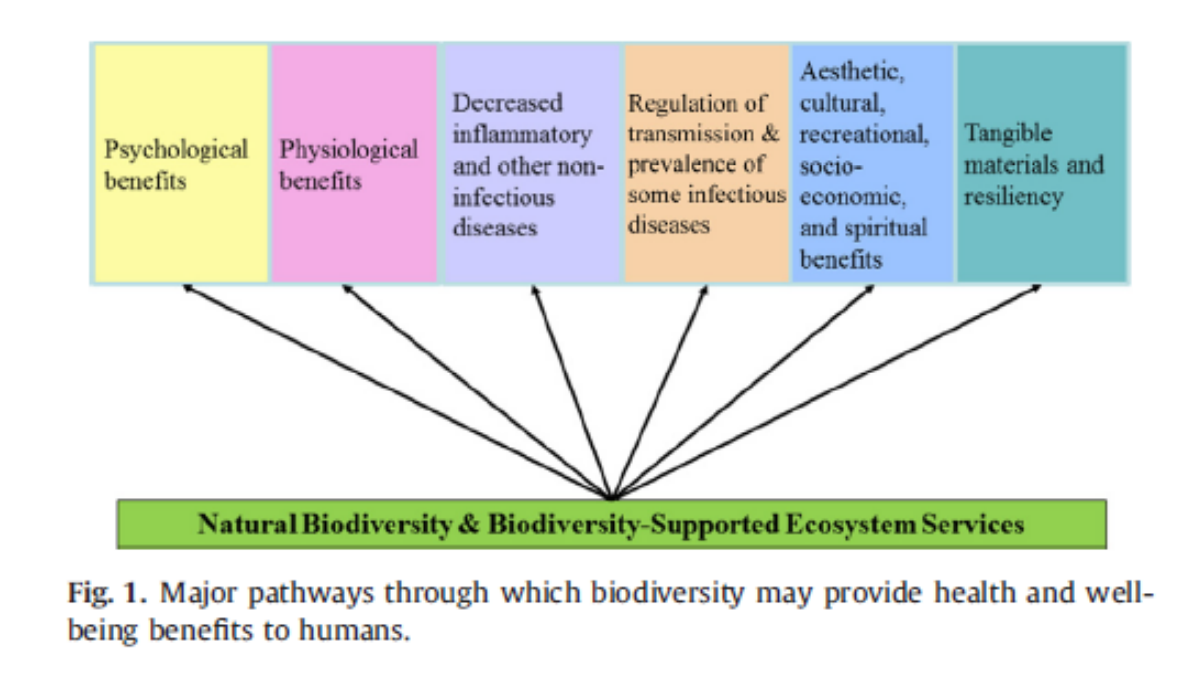
Natural Biodiversity and Biodiveristy supported ecosystem services
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 19