CM02 - Tissues and Epithelium
1/56
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What is actin (microfilaments)?
Form the core of microvilli
Cause locomotion of cell through extension of cell processes (lamellipodia)
Have a polar structure
Grow and shrink on both + and - ends
What are microtubules?
Form the core of cilia
Movement of cilia and flagella
Organize chromosomes during mitosis and intracellular vesicular transport
Polar structure → grow and shrink only at + ends
What are intermediate filaments?
Ropelike fibers to withstand mechanical stress
Important for tensile strength
Non-polar (no growing or shrinking)
Keratins (cytokeratins), vimentin, desmin, neurofilaments, lamins
What is the role of intermediate filaments in epithelium?
Form the cytoskeleton
Provide mechanical strength by connecting cells (via desmosomes) and attaching to connective tissue/basement membrane (via hemidesmosomes).
What are the main characteristics of epithelium?
Polarized cells (apical, basal, lateral domains)
Tightly packed with little ECM
Covers body surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands
Rests on basement membrane
Avascular but innervated
Non-specific line of defense
How is epithelium classified?
By cell number: simple (1 layer), (>1 layer), pseudostratified
By shape: squamous, cuboidal, columnar
What is the function of stratified epithelium?
Protection (friction, abrasion, infection), waterproofing, first defense.
Special types: transitional (urinary tract), pseudostratified (respiratory tract).
What is the function of simple epithelium?
Regulatory barrier: controls transport into the tissue (membrane proteins, endocytosis, tight junctions).
Special types: endothelium (lines blood vessels), endocardium, mesothelium.
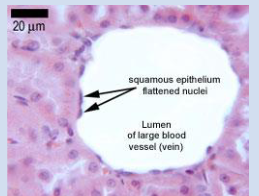
What is the function of simple squamous epithelium?
Filtration, diffusion, secretion, exchange
Located in the kidneys, lungs, and blood vessels
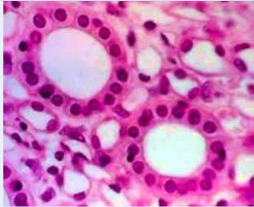
What is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium?
Absorption and secretion
Located in the kidneys, lining of ducts, and thyroid gland
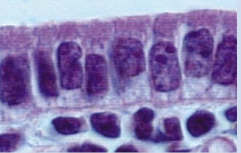
What is the function of simple columnar epithelium?
Absorption and secretion
Located in the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine
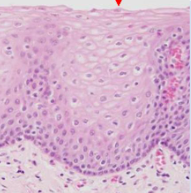
What is the function of stratified squamous epithelium?
Protection against abrasion and dessication and environmental factors, non-specific line of defence
Located in the oral cavity, eye, esophagus, epidermis of skin, and vagina
Can be orthokeratinized, perakeratinized, or non-keratinized
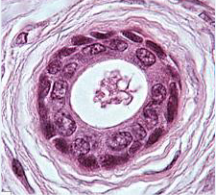
What is the function of stratified cuboidal epithelium?
Protection, strengthens the walls of ducts
Located in the eccrine sweat glands, lining of ducts, and mammary glands
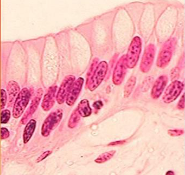
What is the function of stratified columnar epithelium?
Protection and secretion
Large ducts of some glands, male urethra
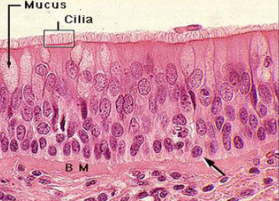
What is the function of pseudostratified epithelium?
Conditions the air that is breathed in, traps mucus and debris
Contains cilia
Located in the respiratory tract
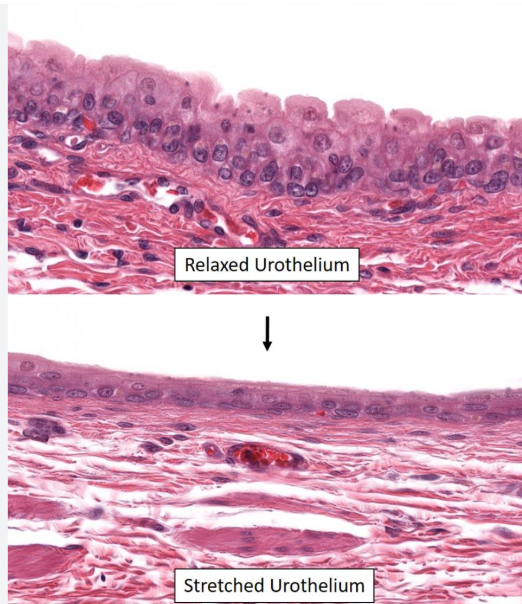
What is the function of transitional epithelium?
Allows cells to change shape/accommodates changes in size
Located in the urinary bladder
Can have a relaxed vs stretched state
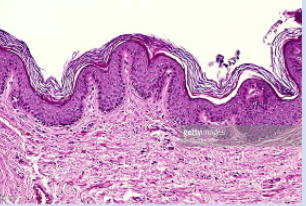
What are orthokeratinized cells?
Stratified squamous epithelium where the layers closest to the environment lack nuclei and are basically bags of keratin (intermediate fibers)
Located in the hard palate, gingiva, and epidermis of skin
Fully keratinized with morphology changes
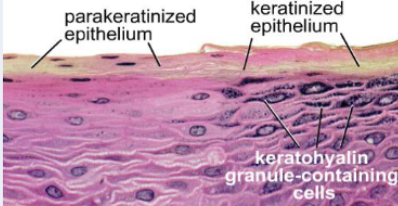
What are perakeratinized cells?
Stratified squamous epithelium in which some cells closest to the environment have nuclei and some don’t
Located in the oral cavity
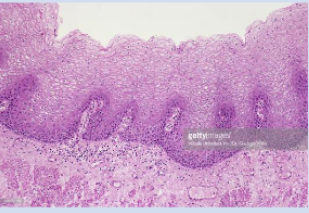
What are non-keratinized cells?
Stratified squamous epithelium in which all cell layers have nuclei and maintain cell morphology
Located in the esophagus, areas of the oral cavity, and vagina
What is keratinization (cellular differentiation)?
Cytoplasmic events in keratinocytes as they differentiate from mitotic cells to keratin-filled cells, mainly in stratified squamous epithelium.
Cells closest to connective tissue (basement) are non-differentiated. They contain keratin, are mitotic, and move up through cell layers
Cells closest to the environment are terminally differentiated. They are no longer mitotic, just bags of keratin (IF)
Which cells contain intermediate filaments as part of the cytoskeleton?
ALL OF THEM
What are the different epidermal layers?
Basal: melanocytes reside here, cell proliferation happens, deposit pigment
Spinous: desmosomes are visible (prickle layer), differentiation begins
Granular: granules appear that cross-link keratin, cell dehydrates, nuclei and organelles disintegrate
Corneal: dead cells, lipid envelope barrier is formed. Pigment ends up here.
Desquamation: shedding of outermost corneal layer (2-week cycle)
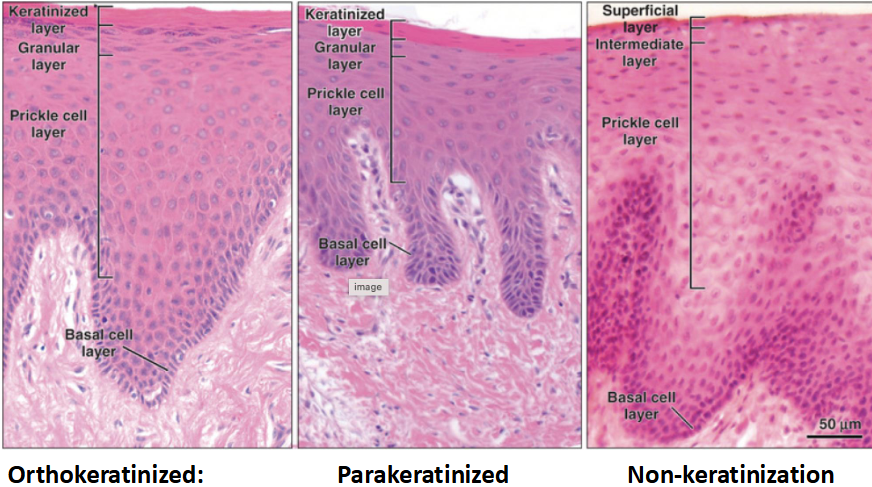
What are the types of keratinization?
Orthokeratinized: nuclei lost (gingiva)
Parakeratinized: pyknotic nuclei remain (gingiva)
Non-keratinized: nuclei visible in upper layers, no clear strata (buccal mucosa)
What is the apical domain?
Free surface of the epithelial sheet facing the lumen/external environment.
What is the lateral domain?
Surfaces for cell-cell contact, contain cell junctions
What is the basal domain?
Surface contacting the basement membrane, a specialized form of connective tissue
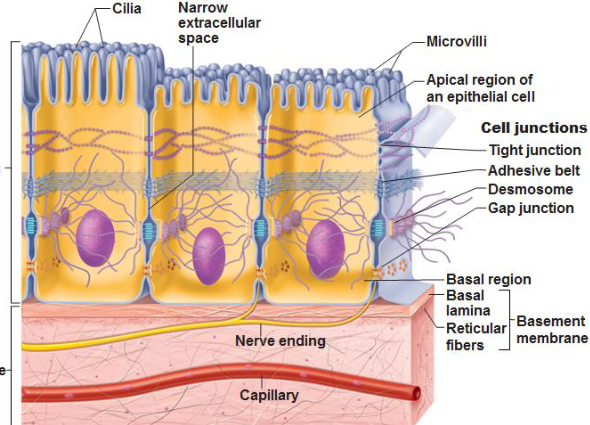
What are microvilli?
Non-motile apical membrane projections that have an actin core and are covered with plasma membrane
Increase surface area
Anchored in the cytoplasm by proteins that make up the terminal web.
Contain tight junctions on the apical side
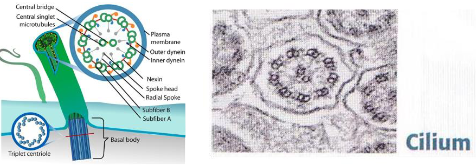
What are cilia?
Projections of the apical membrane covered by plasma membrane
Motile extensions of the cell
Each cilium contains an axoneme that has a 9+2 microtubule structure (9 pairs on the outside, one pair of 2 on the inside)
Move substances across surface
Anchored in the cytoplasm by a basal body made of microtubules

What are stereocilia?
Long, actin-based projections (not true cilia)
Found in the inner ear (hearing) and male reproductive tract (absorption).
What are cell junctions?
Protein complexes that function in cell to cell adhesion.
Provide stability to an epithelial sheet
Keep the apical domain separate from the basolateral domain
Control the movement of solutes, ions, and water across an epithelial sheet
What is a zonula?
Describes an adhesion structure that surrounds the entire perimeter of the cell (ex: zonula occludens, zonula adherens)
What is a macula?
A spot-like adhesion structure that is restricted to one small region of the lateral domain of two cells (ex: macula adherens)
What are tight junctions (zonula occludens)?
Occluding junctions at the top of the lateral domain near the apical domain
Prevents diffusion of membrane lipids and proteins between the apical and basolateral domains; regulates the paracellular pathway
What are adherens junctions (zonula adherens)?
Belt-like adhesions beneath tight junctions
Functions in the adhesion of two epithelial cells
Part of the junctional complex consisting of one tight junction, one zonula adherens, and one desmosome
What is the junctional complex?
The junctional complex is in the simple columnar epithelium of the small intestine consisting of one tight junction, one zonula adherens, and one desmosome
What are desmosomes (macula adherens)?
Anchoring junctions located beneath the zonula adherens that function in the adhesion of two epithelial cells
Holds stratified squamous epithelium as an intact sheet
Proteins in the intercellular space are indirectly attached to keratin intermediate filaments by plaque proteins
What are gap junctions?
Communicating junctions that cause ionic coupling
Located between two epithelial cells and in cardiac myocytes
Connexons form channels in the plasma membrane between two cells
Many connexons form one gap junction
Cells can share metabolites
What are hemidesmosomes?
Cell-matrix anchoring junctions connecting epithelial cells to basement membrane via keratin filaments.
What is the basement membrane?
Specialized ECM between epithelium & connective tissue, contains mainly type IV collagen.
What are functions of basement membrane?
Supporting connective tissue
Transition barrier between epithelium and CT
Kidney filtration and urine formation
Embryonic migration guide
Scaffold for tissue regeneration
Establishes polarity
Signals for cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival
What epithelium covers the cornea?
Anterior: stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium; Posterior: simple squamous/cuboidal epithelium.
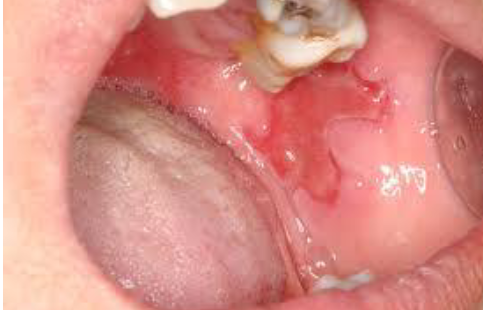
What autoimmune disease targets desmosomes?
Pemphigus, caused by antibodies against desmoglein 1 & 3.
What epithelium lines blood vessels?
Endothelium (simple squamous).
What epithelium lines the heart chambers?
Endocardium.
What epithelium lines serous cavities?
Mesothelium.
What is transitional epithelium?
Specialized stratified epithelium found in the urinary tract; accommodates stretching.
What is pseudostratified epithelium?
Appears stratified but all cells touch the basement membrane; common in the respiratory tract.
What does “fascia” describe?
An adhesion junction covering more surface area than a macula but not continuous like a zonula (e.g., fascia adherens).
What are the three tunics of the eye?
Fibrous tunic: cornea, limbus, sclera
Vascular tunic: iris, ciliary body, uvea
Retinal tunic: retina & nonsensory extension
What is the role of suspensory ligaments in the eye?
Hold the lens in place, transmit tension from the ciliary body to adjust lens convexity.
What do ciliary processes produce?
Aqueous humor.
What epithelium covers the anterior corneal surface?
Stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium.
What epithelium covers the posterior corneal surface?
Simple squamous-to-cuboidal epithelium.
What are Bowman’s and Descemet’s membranes?
Thin acellular layers in the cornea; Bowman’s lies under anterior epithelium, Descemet’s under posterior epithelium.
What makes the corneal stroma transparent?
Regular arrangement of collagen fibers and fibroblasts.
What is the terminal web?
Cytoplasmic network of actin-binding proteins that anchor microvilli.
What structures anchor cilia?
Basal bodies (derived from centrioles, microtubule-based).