ch 2: the chemistry of life PT 2
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
four essential macromolecules
-carbs
-lipids
-proteins
-nucleic acids
monosaccharides
-simple carbohydrate
-three important monomers → glucose, galactose & fructose
disaccharides (carb)
-sugars made of two covalently bonded monosaccharides
-three important disaccharides → sucrose, lactose & maltose
polysaccharides (carb)
long chains of multiple monosaccharides
three important polysaccharides → glycogen, starch & cellulose
HDL (high-density lipoprotein) = “good cholesterol”
• Lower ratio of lipid to protein
• May help to prevent cardiovascular disease
50% protein to 50% fat
LDL (low-density lipoprotein) = “bad cholesterol”
• High ratio of lipid to protein
• Contributes to cardiovascular disease
25% protein to 75% fat
amino acids have a central carbon with three attachments
- Amino group
-Carboxyl group
- R (radical) group️
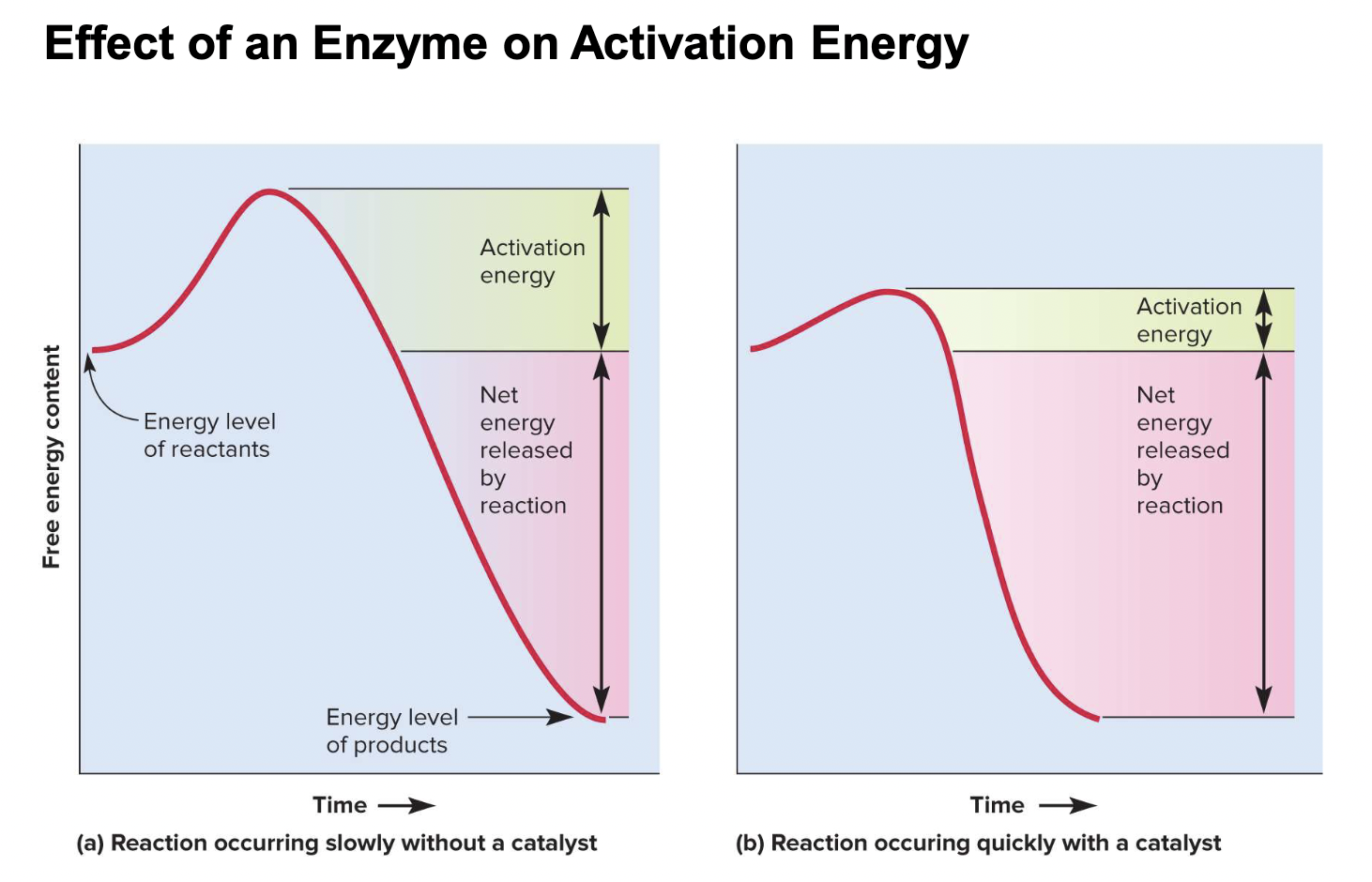
enzymes (3 characteristics)
-speed up chemical reaction by lowering the activation
energy
-highly specific for substrates
-used again and again in reactions
Nucleotides components
- Nitrogenous base (single or double carbon–nitrogen ring)
-Sugar (monosaccharide)
-One or more phosphate groups
DNA
-contains millions of nucleotides
-constitutes genes, the instructions for synthesizing proteins
*more stable
RNA
-carries out genetic instruction for synthesizing proteins
-assembles amino acids in right order to produce proteins
*more reactive & flexible
primary protein structure
-amino acid sequence joined by peptide bonds
secondary protein structure
-local coils fold
-alpha helix / beta sheet formed by hydrogen bonding
tertiary protein structure
overall 3D shape
-polypeptide chain folded & coiled by interactions in the R groups
quaternary protein structure
-most complex
-multiple chains joining & cluster of several tertiary units
ex→ HEMOGLOBIN