Sports Psych Complete Midterm
1/196
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
197 Terms
What is sports psyc?
Interdisciplinary scientific and applied field combining sport science with psychology
The areas of sports psychology are:
Cognitive, clinical, counselling, behavioural, social, developmental, and health.
What is The North American Society for the Psychology of Sport and Physical Activity (NASPSPA)?
Focuses on training specialist in motor learning and sports psyc
When was the North American Society for the Psychology of Sport and Physical Activity (NASPSPA) first founded?
1967
What is the Canadian Society of Psychomotor Learning and Sport Psychology?
A society who’s main objective was improving the quality of research and teaching the sports psych, motor development, and learning/control
When was the Canadian Society of Psychomotor Learning and Sport Psychology first founded?
1977
What does sport psychology focus on?
What processes enable groups to thrive? (applied psyc)
Effects of sport and exercise on ppl/groups
The 3 Career Applications of Sport Psyc
Teaching, Research, Consulting
What do the consulting/interventions in SEP focus on?
Emotional: change negative emotions to positive
Cognitive: how do thoughts influence daily lives
Behavioural: how behaviours effect outcomes
1885-1920
Social facilitation study (Norman Triplet)
1921-1938
Griffith era, 1st lab, 25 articles, 2 books (Coleman Griffith)
1938-1965
Academic discipline of exercise, IILSP, International SP development
(Franklin Henry = motor learning)
(Ferrucio Antonelli = journals)
1966-1977
Applied sports psychology, NASPSPA, CSPLSP
1978-Present
AASP, JSEP, etc.
Ontology
The nature of reality, what can be known
Realism
External world exists out of human perception
Relativism
External world exists as mental constructs
Epistemology
Nature of knowledge, what is relation between knower and know?
Objectivist
Empirical evidence, objective observations, right or wrong
Constructivist
Active roles of ppl gaining knowledge through interactions
Subjectivist
Knowledge + truth is relative to cultural, historical, + individual
Methodology
What are ways of finding knowledge?
Quantitative vs. Qualitative
Independent Variable
Manipulated to produce change
Dependent Variable
Expected to change as a result of manipulation
Scale
Measured with pictures and diagrams
Analogue
Example of understandable structure
Theoretical
Composed of # of interrelated constructs
A theory
Specifies relationships across a number of scientific constructs and attempts to explain a phenomena
The 2 types of inquiry
Quantitative
Qualitative
Combining both = mixed method
Quantitative
Quantifies variables, emperical, facts (experiments, tests, surveys)
Qualitative
Associate meaning with data, interpretation, feelings (interviews)
Research Objective
Objectively analyze the relationship between performance + athletes
Research Paradigm
The framework a scientific displacing uses to reason, addresses 3 central questions (2 major)
Positive Psychology
An area of psychology concerned primarily with understanding the processes that enable people and groups to thrive.
Personality
Systematic variation in the way people think, feel, and behave
Trait
Relatively stable characteristic or quality that may represent a portion of one’s personality
States
Momentary feelings and thoughts that change depending on the CURRENT SITUATION
5 Personalities in Sport
Risk-Taking
Competiveness
Passion
Mental-Toughness
Perfectionism
Risk-Taking Personality
Risk-assesment, sensation seeking, alexithymia (inability to identify one’s emotions, describe feelings)
Competitiveness Personality
Goal orientation, win orientation
Harmonious Passion
Engaging in an activity as part of one’s personal identity and for the pleasure of the activity
Obsessive Passion
Rigid and uncontrolled urge to engage in activities because of external control or feelings of guilt (Not as healthy)
Mental-Toughness Personality
Self confidence/motivation, manage stress, maintain focus
Perfectionism Personality
Perfectionistic striving (high motivation to suceed and do well),
Perfectionistic concerns (excessive self-critisim and concerns over mistakes)
Self-Report Questionnaires
Big 5 indicator (OCEAN), Myers-Briggs type indicator
Behaviour Assessments
Methods observing and evaluating behaviours
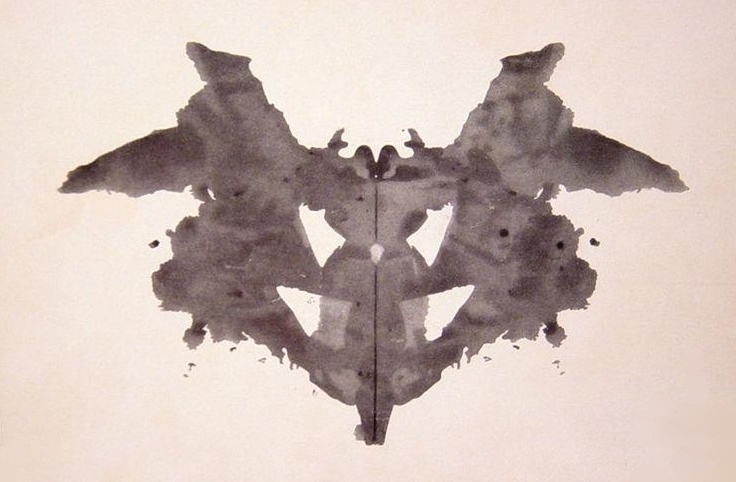
Projective Tests
Rorsarch inkblock test (associating pictures with meaning)
Interviews
Can be structured or unstructured
Biological Measures
Brain or physiological images and assesments
Ex. Measuring HR and Cortisol levels
Online and Digital Data
Explore online usage
Ex. exploring social media posts, online behaviour)
BIG-5 (OCEAN)
Openness
Conscientiousness
Agreeableness
Extraversion
Neuroticism
How does Personality Develop?
Humanistic Psychology
Cognitive-Behavioural
Biological/Evolutionary
Interactionist Approach
Personality Traits
Humanistic Psychology
Focuses on personality, human growth, personal striving, and individual dignity
Self-actualization
Attempts to fulfill one’s potential
Cognitive-Behavioural
Individual’s thoughts, perceptions, and interpretations of experiences
Influenced by rewards and punishment
Social learning
People learn through self-experiences + actions
Biological/Evolutionary
Personality can be moderately heritable, suggesting an evolutionary bias
Interactionst Approach (Best way)
Personal/Situational factors impact behaviour predictively
Personality Traits
Meta-analyses: Summary of all studies done in the area are cross-examined
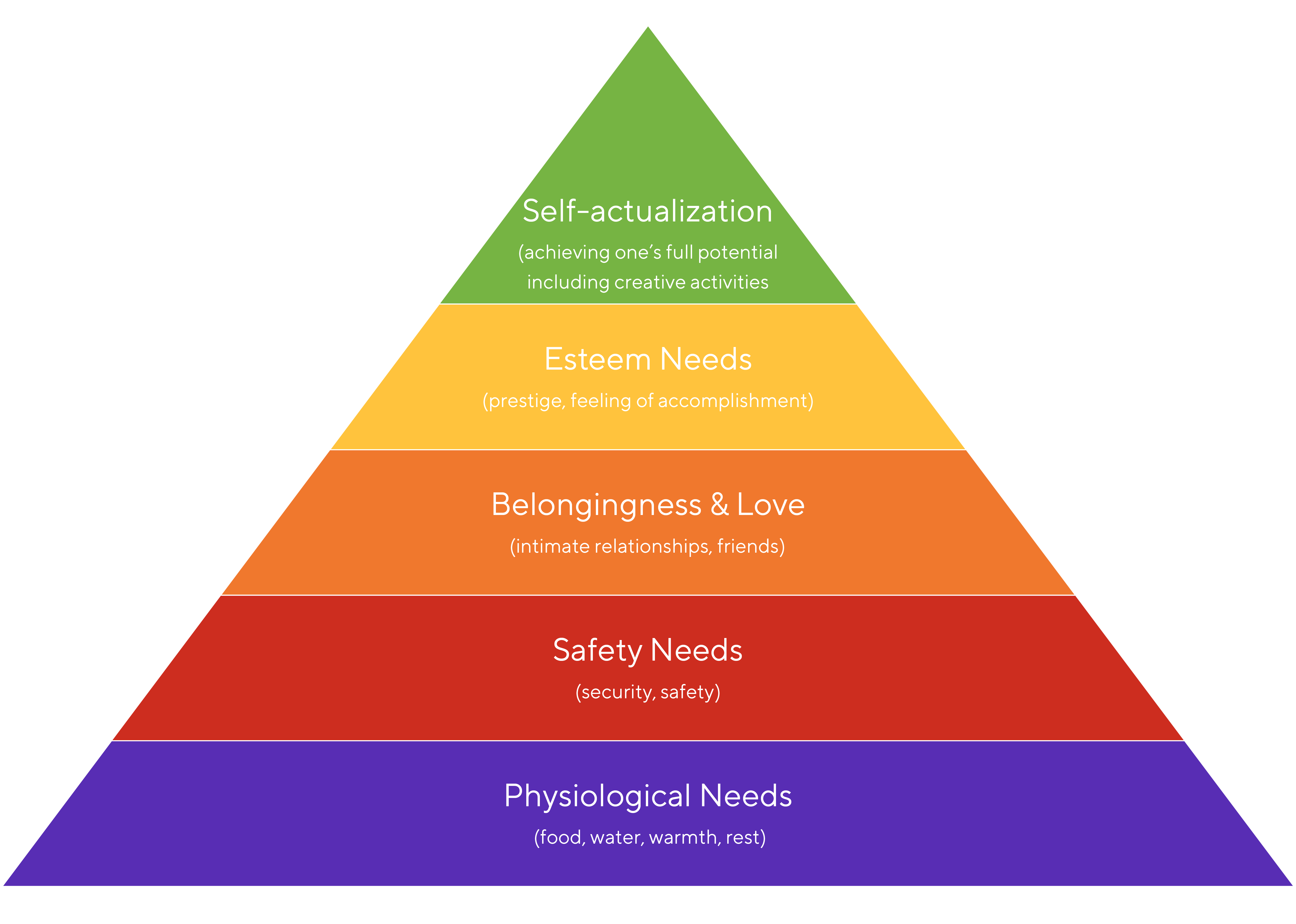
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Once basic needs have benn met, you can move up the pyramid
Carl Rogers
Humanist psychology who contributed massively to the field of personality study. He believed that there is a discrepancy between what is being experienced.
What is motivation?
An internal process, such as thoughts and emotions that give your behaviour energy and direction
It is why you do what you do
The 3 main approaches to help understand motivational change
Behavioural Approach
Cognitive Approach
Cognitive-Behavioural Approaches
Behavioural Approach
Motivation focus on conditioning or learning from the environment
Ex. operant conditioning, vicarious conditioning, operant strategies
Cognitive Approach
Emphasis on role of thought patterns + cognitive habitats as determinants of behaviour. (Directly contradict behavioural approach)
Teaches rational thoughts, logic, and reasoning
Cognitive-Behavioural Approach
Understand motivational behaviours based on cognitive and behavioural influences
What is motivation influenced by?
Perceptions of personal risk, outcome expectations, and ones efficacy to make change
Intention-Behaviour Gap
people do not always do what they intend to do
Action Plans
Designed to foster commitment by specifing when, where, and how to implement intended behaviour
Ex.
“I will go to the gym every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday at 4 PM after class to complete my strength workout.”
Coping Plans
Barrier-focused, self-regulation strategies to help anticipate difficulties that might derail physical activity
Ex.
“If I feel too tired after class and want to skip the gym, I will remind myself of how good I feel after workouts and do a shorter 30-minute session instead.”
Problem-Focused Coping Plan
Changes the situation = task oriented
Emotion-Focused Coping Plan
Change the interpretation = distraction oriented
Avoidance Coping Plan
Remove themselves from the situation = disengagement oriented
Effectiveness
Perceived coping effectiveness, Achievement outcomes, Physical outcomes, Emotional otucomes
Primary Cognitive Appraisal
What is at stake for a person
Secondary Cognitive Appraisal
What can be done in a stiuation
Attributes to cognitive appraisal
Harm → damage is done
Threat → damage is at stake
Challenge → damage can be overcome
Transtheoretical Model
How individuals initiate and maintain regular physical activity
Focuses a lot on intention-behaviour continuum
Transtheoretical Model: Precontemplation
Consider no change at all
First stage
Transtheoretical Model: Contemplation
Starting to consider a change
Second Stage
Transtheoretical Model: Preperation
Taking small steps to make a change
Intend to change
Third Stage
Transtheoretical Model: Action
~6 months of creating active change
4th stage
Transtheoretical Model: Maintenance
Past the 6 months of active change
No struggles to live this lifestyle
5th and final stage
What is the Theory of Planned Behaviour?
A theory that highlights personal and social factors influencing behaviour
The 3 determinants of the theory of planned behaviour
Attitude: how + or - you feel about performing a behaviour
Subjective Norms: social pressures, significant others (family/friends)
Perceived behavioural control: personal and environmental barriers (controlled beliefs)
What is the Social Cognitive Thoery?
A theory that describes the factors that influence behaviours
Believes that individuals engage in their own development
Ways to change Self-Efficacy
Mastery Experience: Building confidence through personal success or past accomplishments
Vicarious Experience: Gaining confidence by observing others succeed (modeling).
Self Persuasion: Boosting confidence through positive self-talk and encouragement.
Physiological and Affective States: Interpreting physical and emotional reactions (like nerves or excitement) as signs of readiness or weakness.
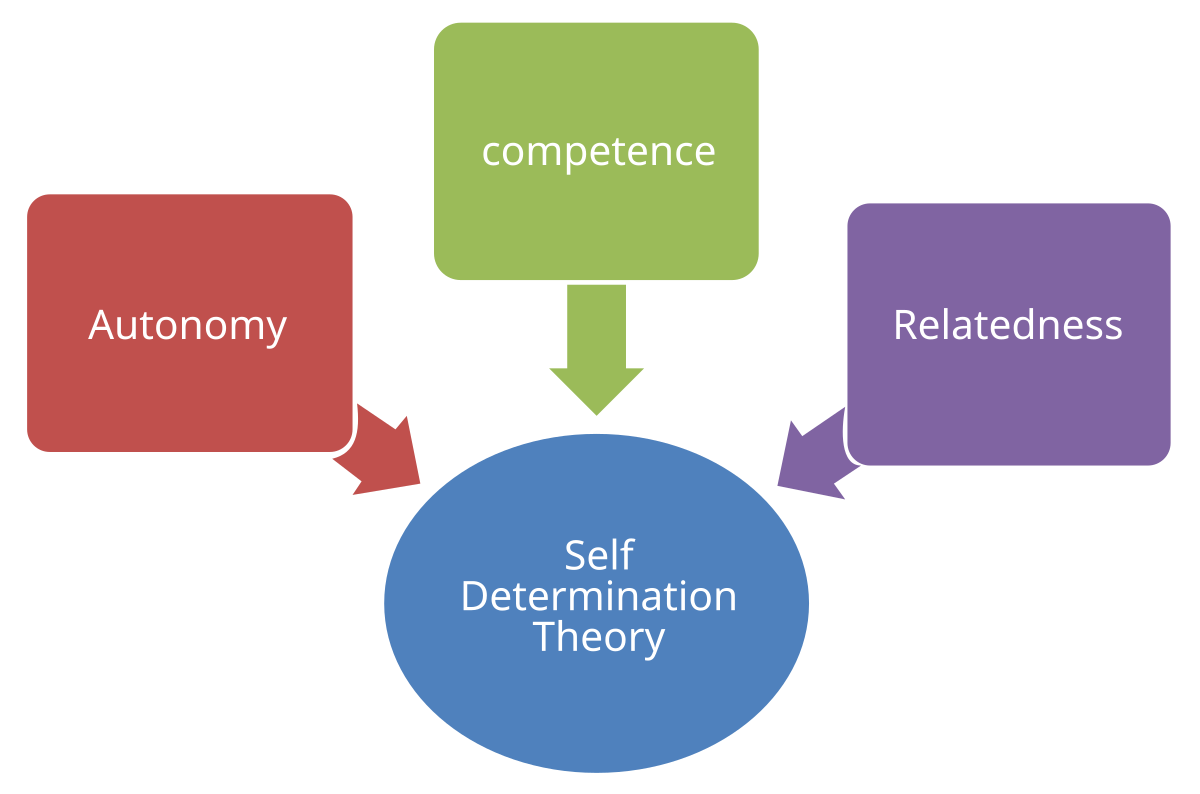
Self-Determination Theory
Global theory of human motivation and development that has evolved from pioneering work
Organismic Integration Theory
Behaviour is motivated by extrinsic behaviours
Casuality Orientation Theory
Personality level constructs
Basic Psychological Needs Theory
Experienced universally, acquired to thrive
Cognitive Explanation Theory
Identifies the importance of competence and autonomy
Intention
Person’s readiness to perform a behaviour
Attitude
Positive or negative evaluations of behaviour
Stress
Caused by external trigger, shorter time
Anxiety
More internalized, longer lasting time periods
Stressors
External events, forces and situations
Acute Stressor
Stressors that occur within a short period of time, with a sudden onset
Chronic Stressors
Stressors that occur over a long period of time
Expected Stressors
Stressors that an athlete plans or prepares for