Special Pops Lecture 8: General Dermatology
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
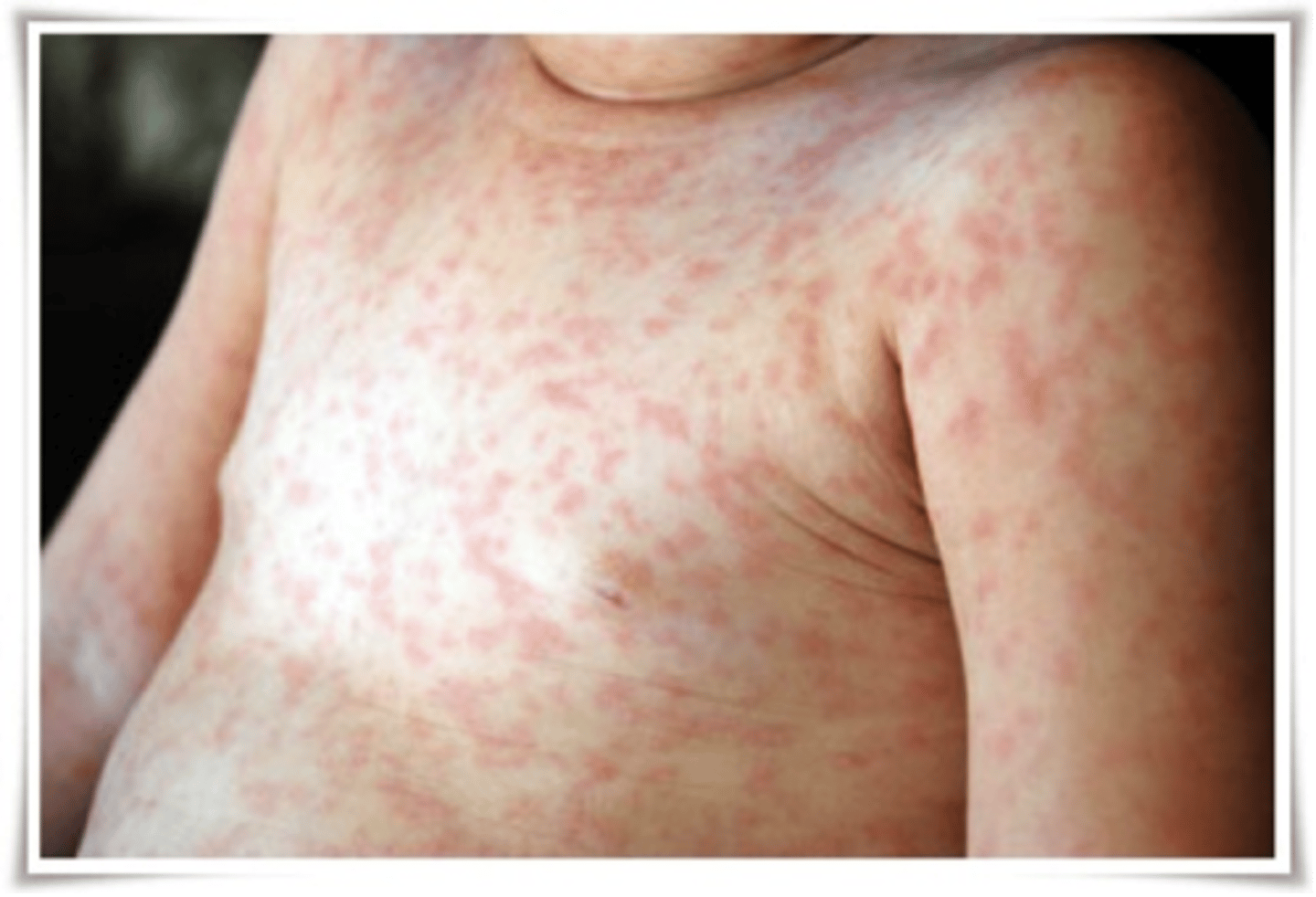
Macules
flat, reddened lesions that can be differentiated by color
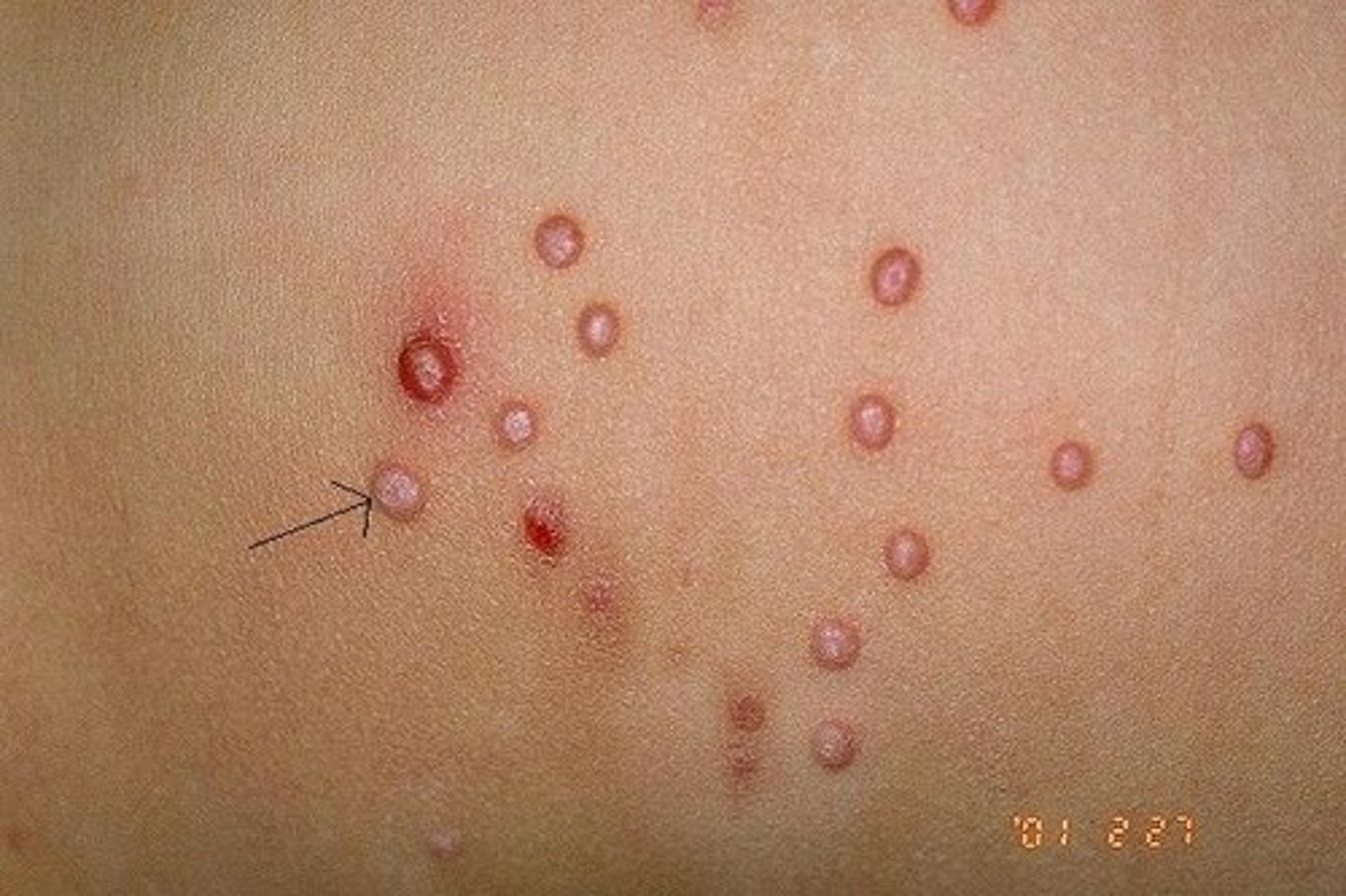
Papules
solid, elevated lesions that are small (<1 cm in diameter)
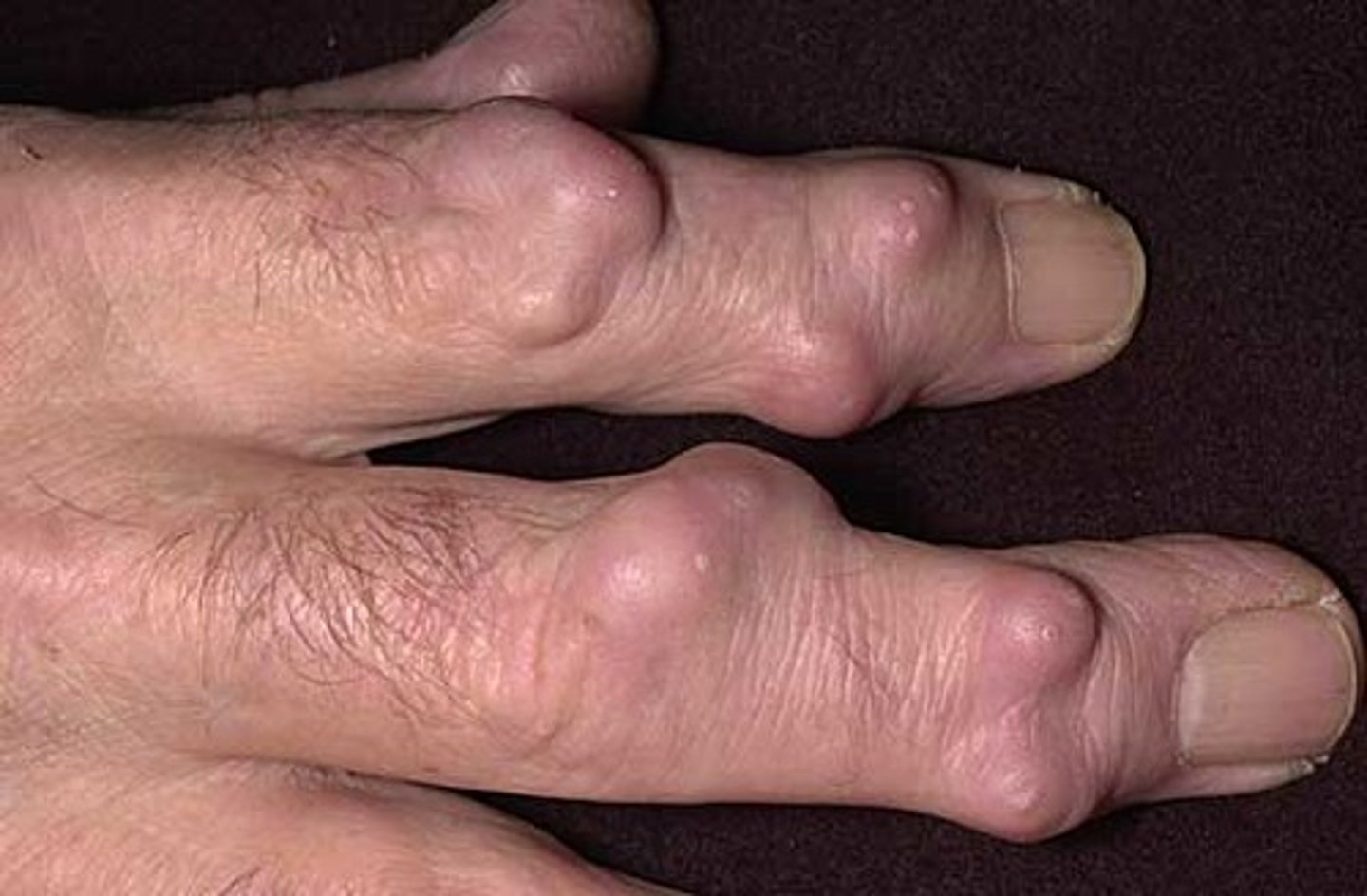
Nodules
solid, round, ellipsodial lesions that can extend into the dermis
How can we differentiate a papule from a nodule?
depth of skin - nodules can get into the dermis
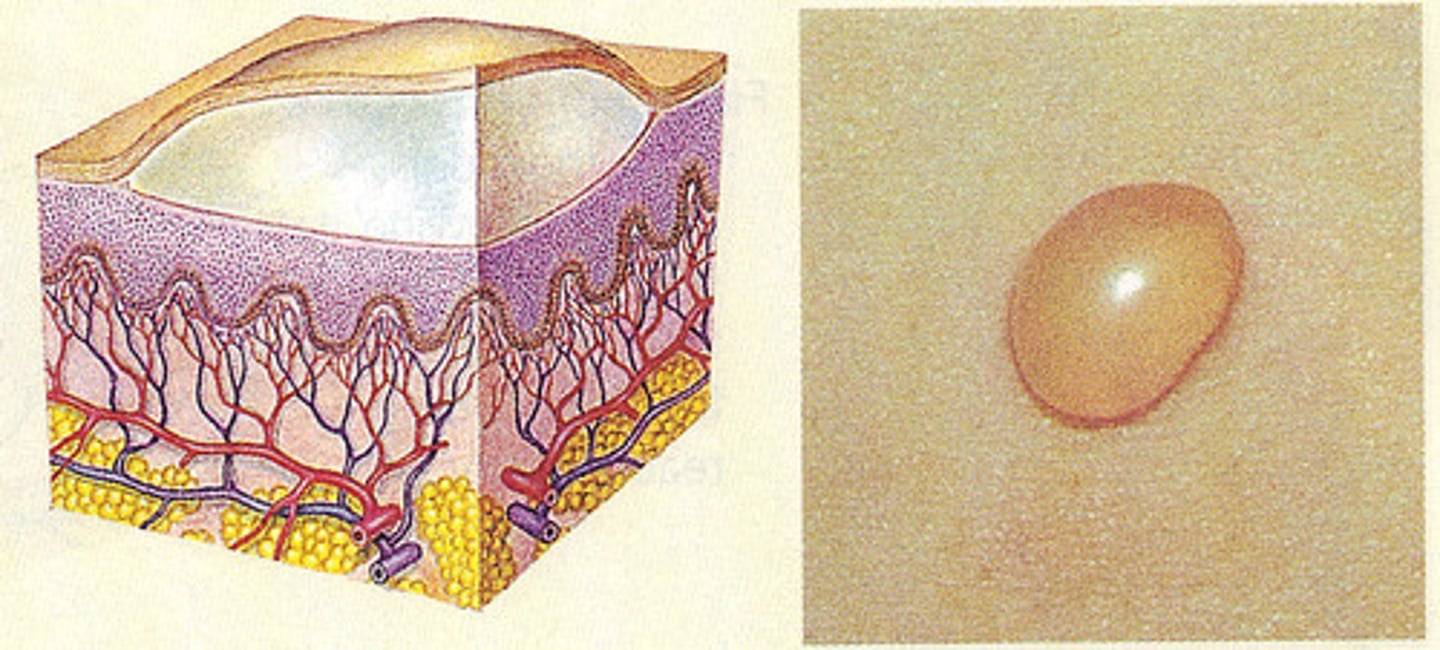
Blister
vesicles and bullae
Vesicle
lesion that contains clear fluids
Bullae
vesicles larger than 0.5 cm in diameter
Plaque
Large, slightly elevated lesion with flat surface, often topped by scale
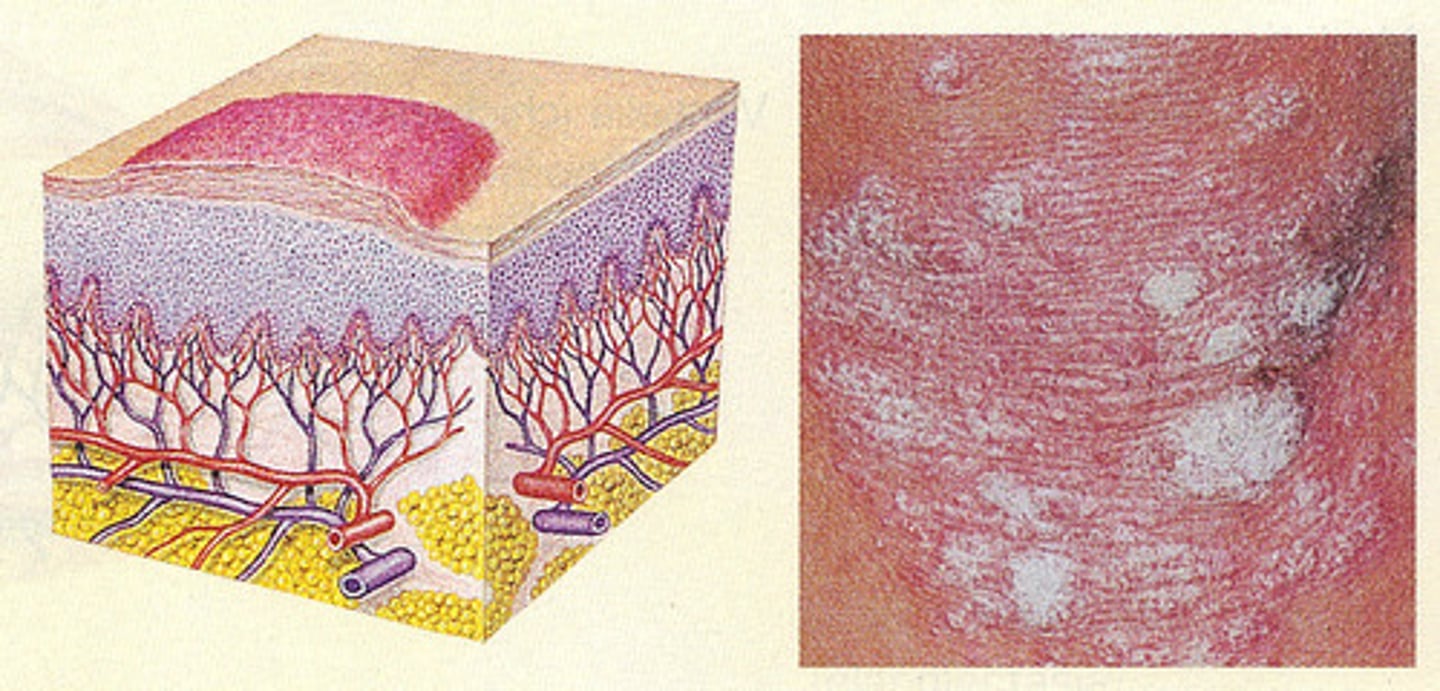
Wheal
rounded or flat topped elevation that is red and itchy
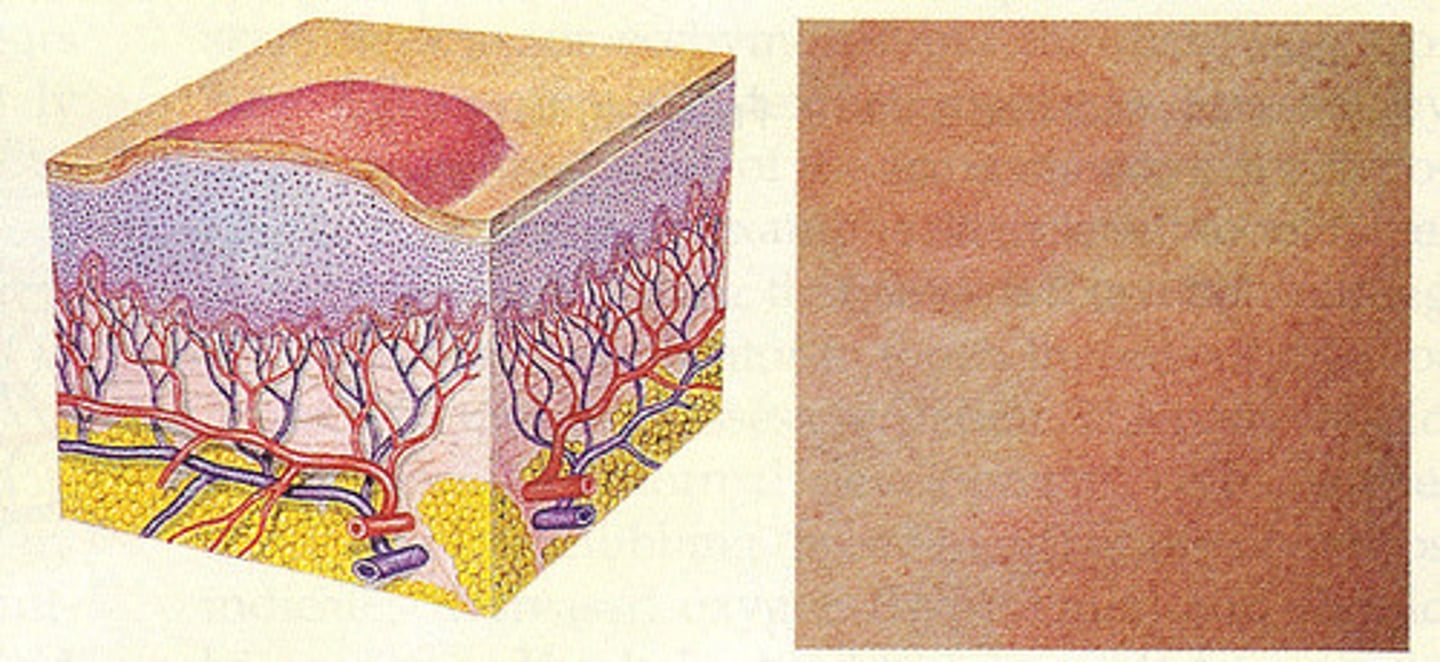
What are the risk factors for developing skin reactions?
Prior drug reactions
On multiple drugs
Repeated use of the same drug
Current viral illness
Higher levels of drug in serum
Topical ROA
Genetics
Comorbidities
What are the two types of drug induced skin reactions?
Allergic
Irritant
Allergic skin reaction
delayed systemic reaction that has an immune response from the host
Irritant skin reaction
fast onset and localized skin reaction
What systemic drugs typically cause ADRs?
Allopurinol
Sulfonamides
Anticonvulsants
Dapsone
Penicillins
Maculopapular skin reaction
afebrile patient with erythematous macules and papules that may itch across the whole body
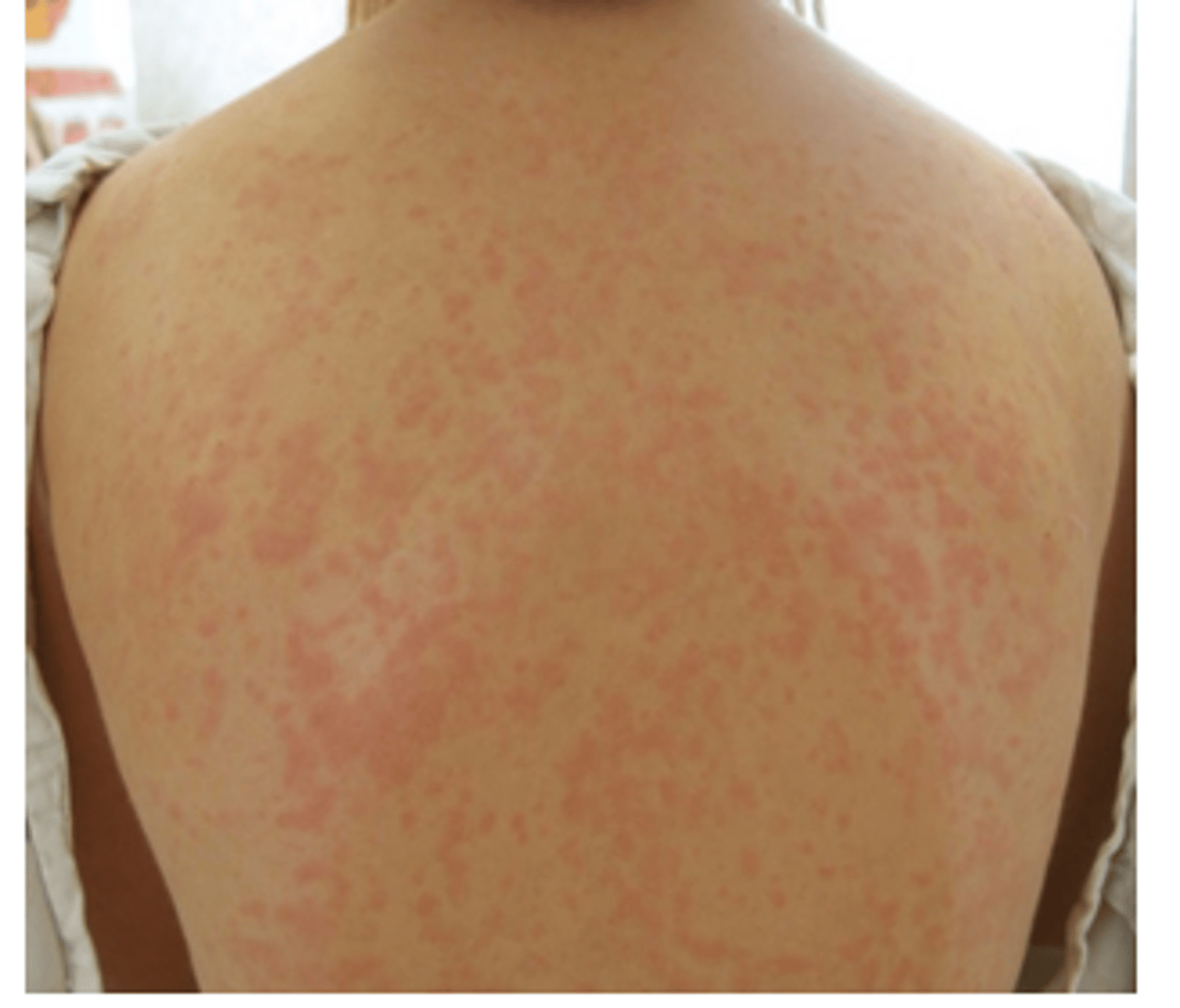
How long does it take for a maculopapular rash to develop?
7-10 days
What is the most commonly encountered skin reaction?
Maculopapular skin reactions
How long does it take for maculopapular rashes to resolve?
7-14 days after D/C
What drugs commonly cause a maculopapular skin reaction?
Penicillins
Cephalosporins
Sulfonamides
Angioedema
edema of the SQ or submucosal tissues that are typically in the face but can spread to the GI tract
What drugs commonly cause angioedema?
ACEi/ARBs
Penicillin
NSAIDs
MAbs
Contrast media
Urticaria
IgE mediated allergic reaction that appears as itchy wheals with central blanching
- may be a precursor to anaphylaxis
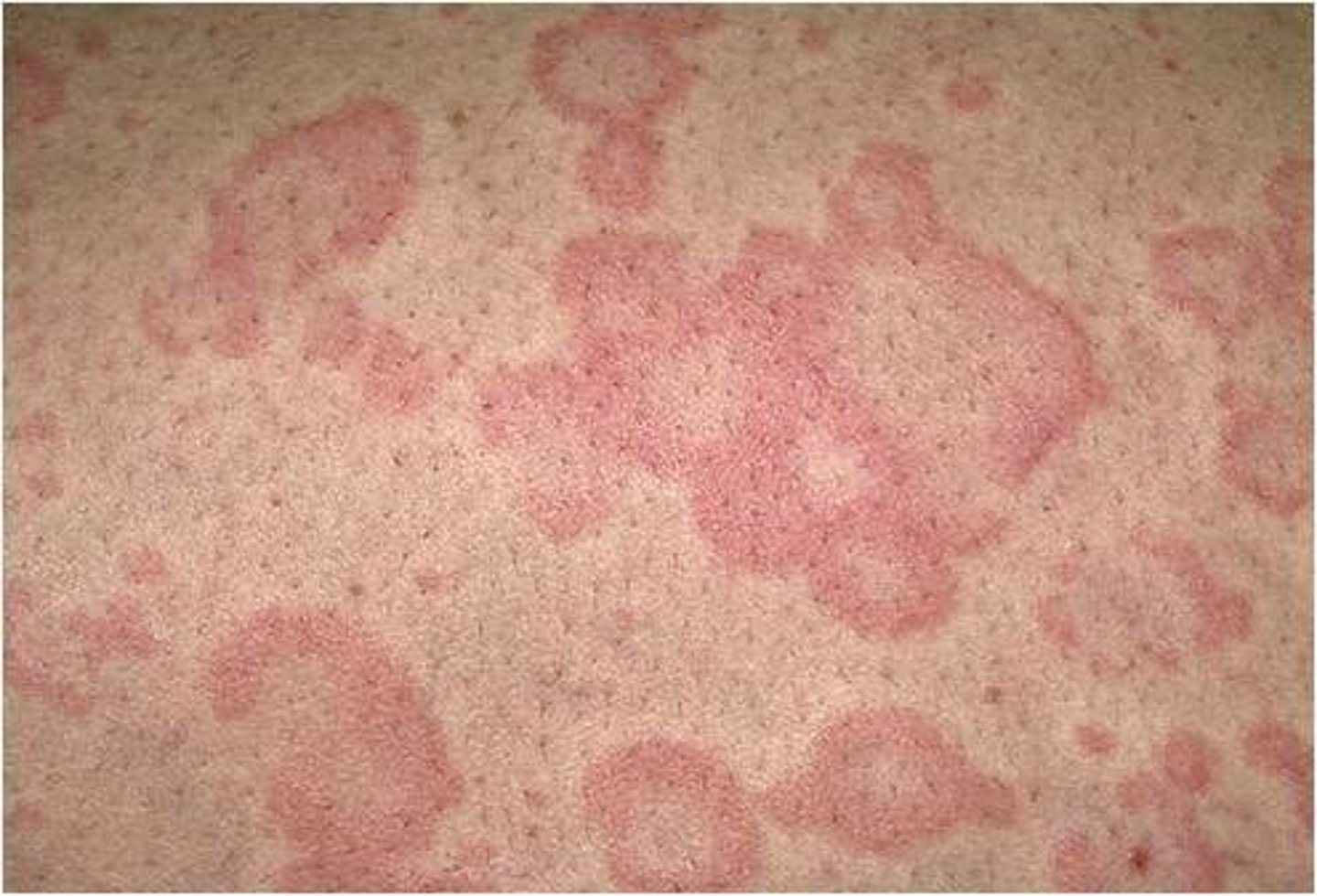
How long does urticaria last?
Starts within minutes and resolves within 24 hours
What drugs commonly cause urticaria?
Penicillins
Aspirin
Sulfonamide
Contrast media
Opiates
Latex
MAbs
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilis and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
exanthematous eruption AND eosinophilia, fever, lymphadenopathy, and multiorgan involvement
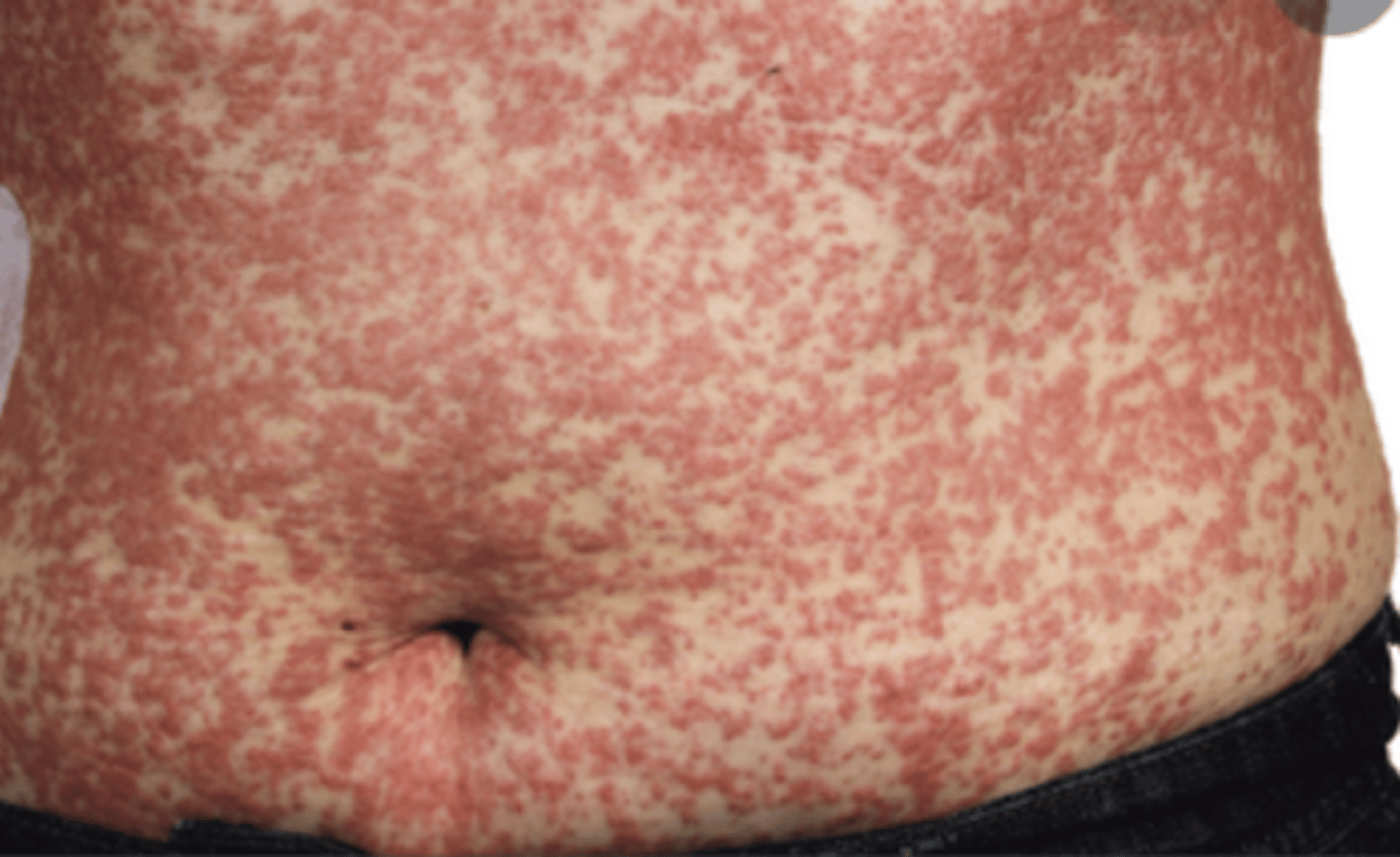
How long does DRESS last?
develops in 1-4 weeks and can take weeks/months to resolve
What drugs commonly cause DRESS?
Allopurinol
Sulfonamides
Dapsone
Serum Sickness-Like Reaction
urticarial eruptions PLUS fever, rash, and arthralgias with NO IMMUNE INVOLVEMENT
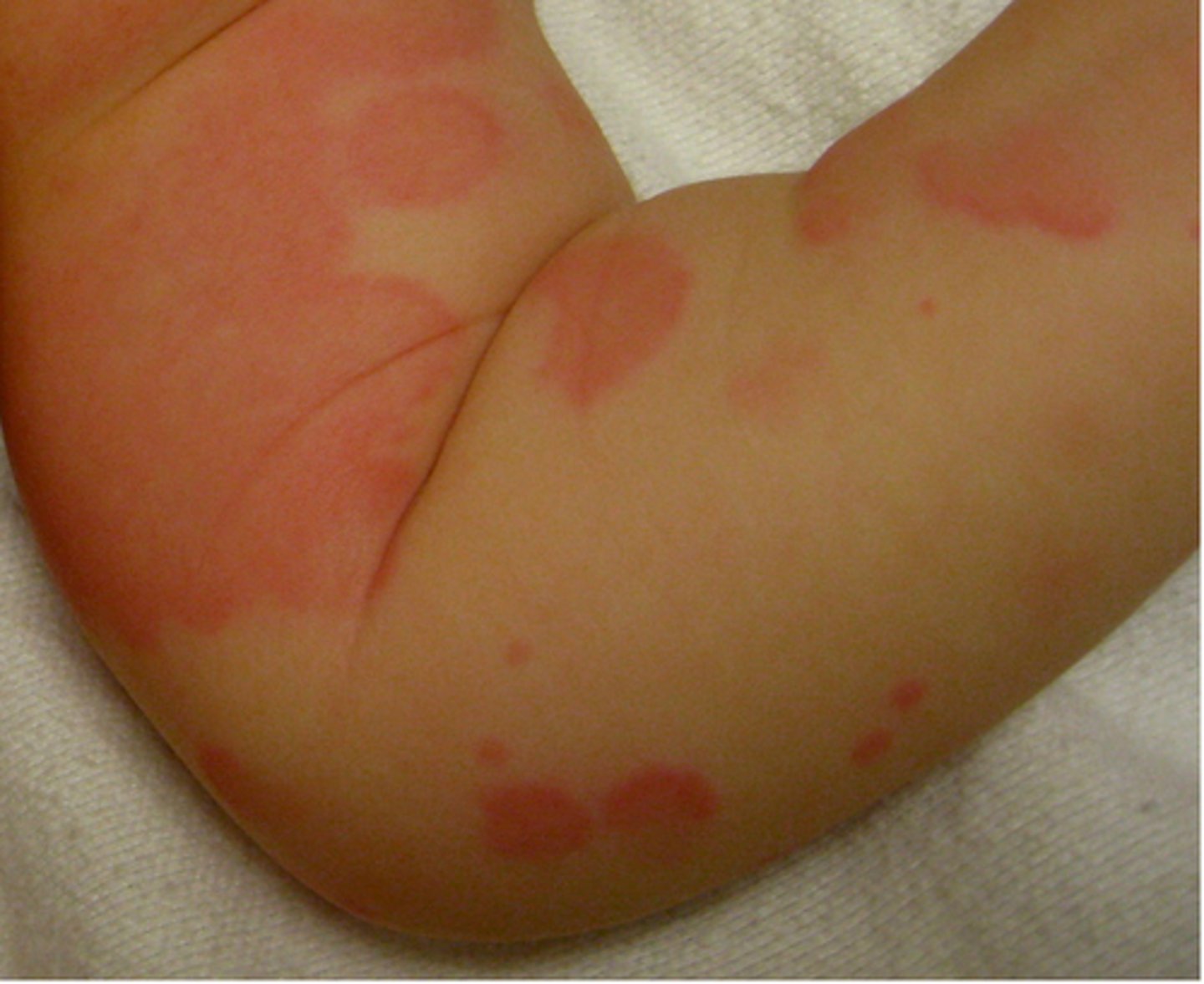
What is the onset time of serum-sickness like reactions?
1-3 weeks
What drugs commonly cause serum-sickness like reactions?
Antibiotics
Fixed drug eruptions
pruritis, red, raised lesion that may blister and evolve into a plaque at the same location where the drug is given
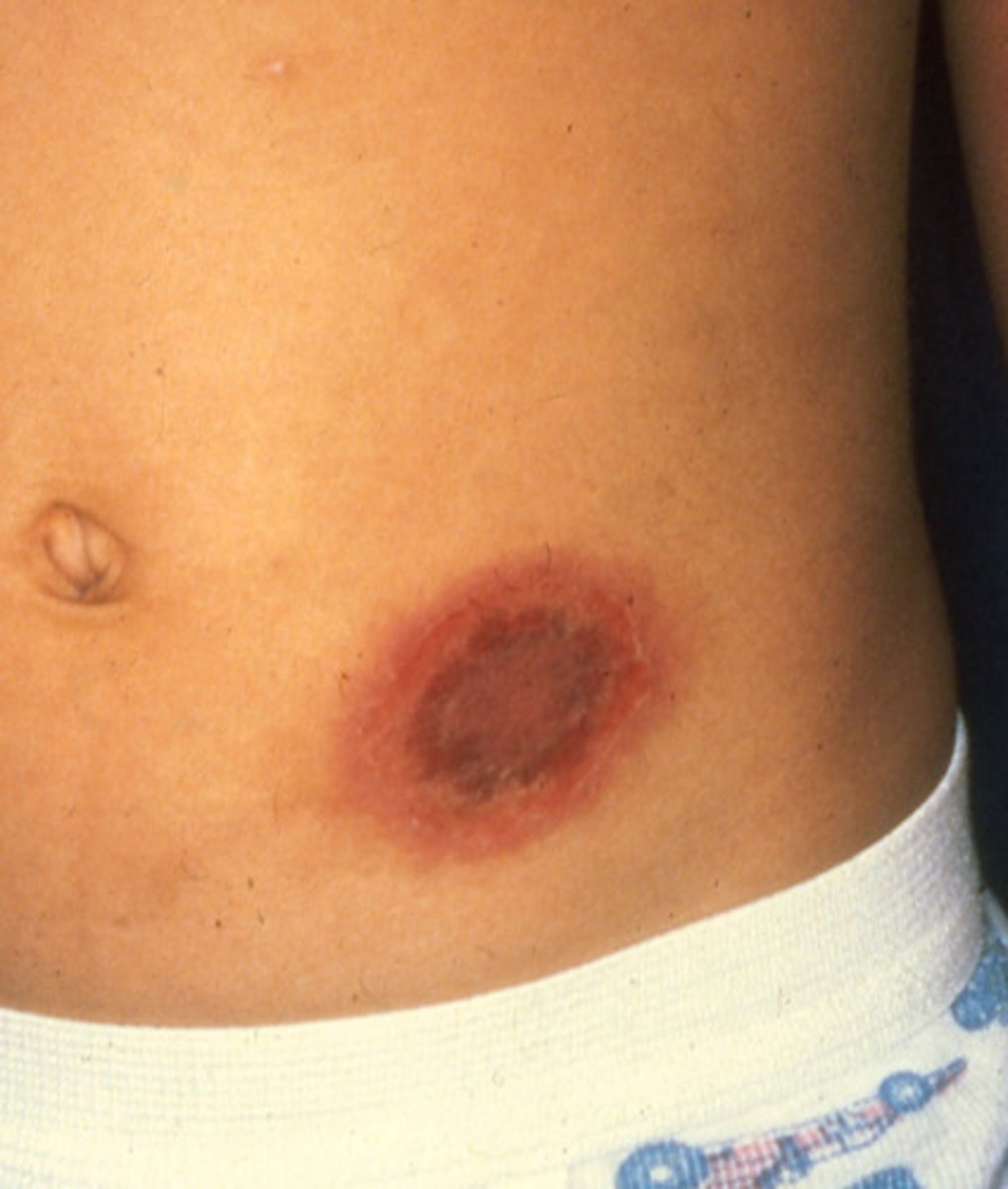
How long does a fixed drug eruption last?
appears in minutes to days and resolves within days BUT leaves behind hyperpigmented skin for months
What drugs typically cause fixed drug eruptions?
Tetracyclines
Barbiturates
Sulfonamides
Codeine
Acetaminophen
NSAIDs
Metronidazole
Stevens-Johnson's Syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
allergic blistering eruption (SJS) that can eventually slough off (TEN) and be life threatening
What is the difference between SJS and TEN?
Body surface area: TEN > SJS
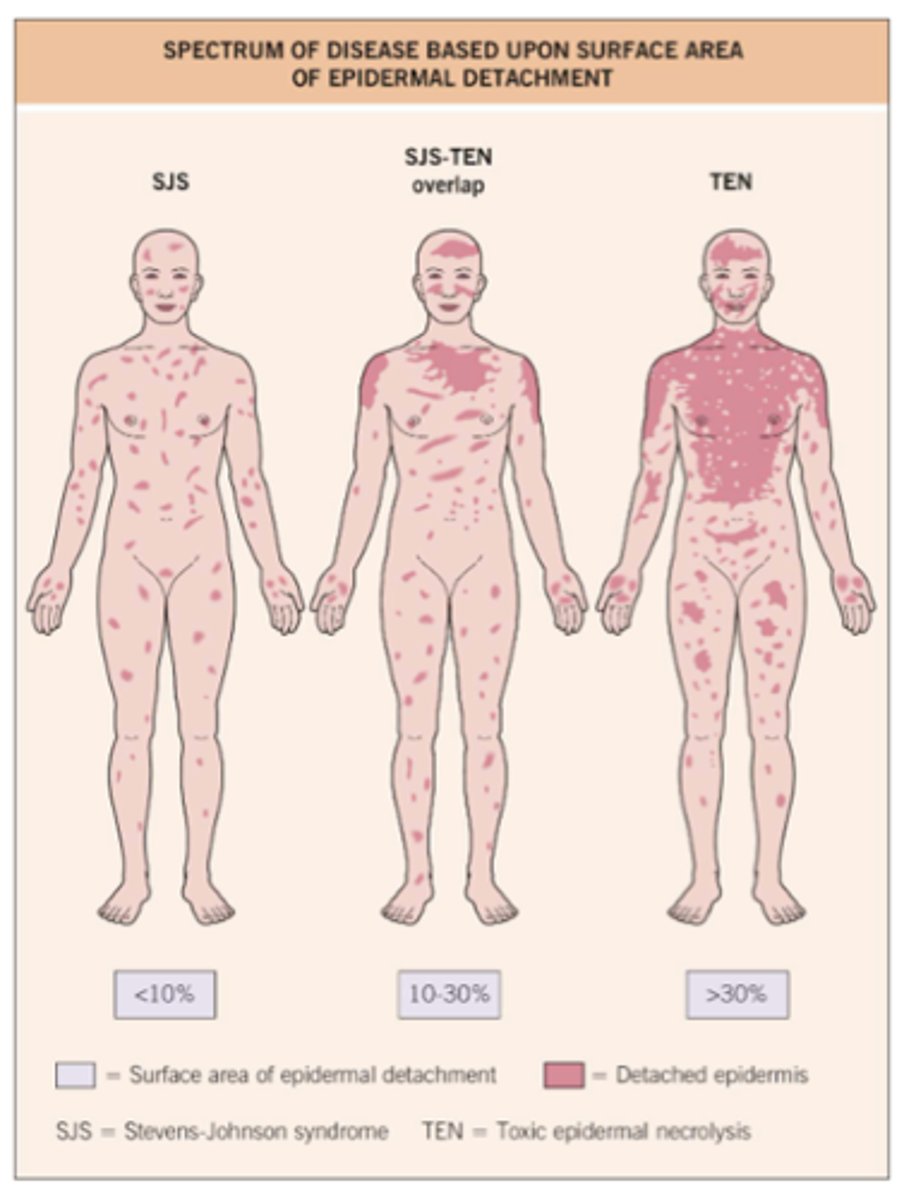
What are the complications of SJS/TEN?
Fluid loss
Kidney failure
Corneal ulcerations
Infections
Erosive vulvovaginitis
What drugs commonly cause SJS/TEN?
Sulfonamides
Penicillins
NSAIDs
Allopurinol
How long does SJS/TEN take to arise?
7-14 days
Acneiform reactions
pustular eruptions that appear in 1-3 weeks
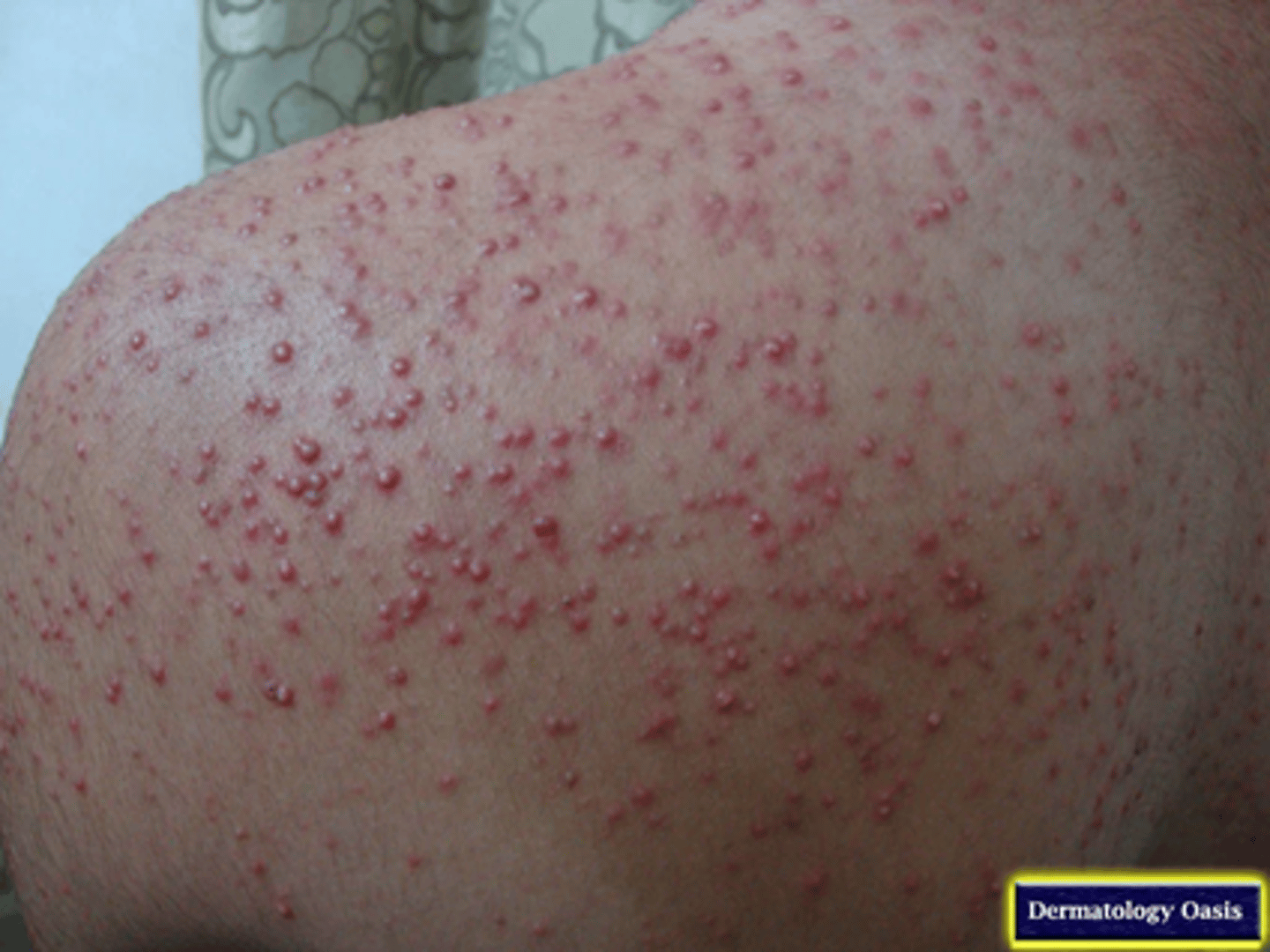
What drugs commonly cause acneiform drug reactions?
Corticosteroids
Androgenic hormones
Isoniazid
Lithium
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP)
acute pustular eruption PLUS fever and diffuse erythema that can appear within days
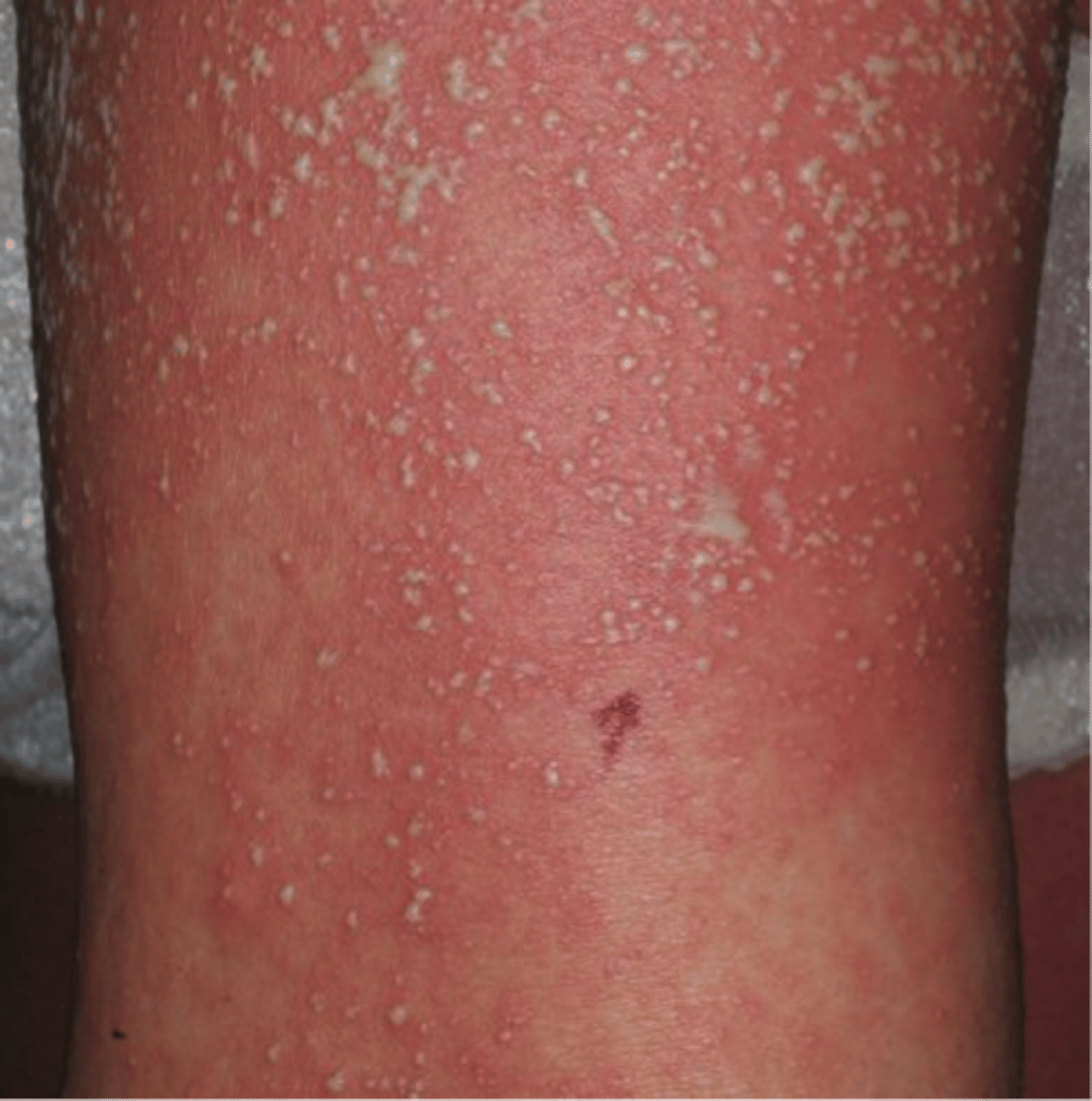
What drugs commonly cause AGEP?
Beta lactams
Macrolides
Calcium channel blockers
Phototoxic Photosensitivity Rection
rapid onset of a burning sensation that is similar to a severe sunburn - ONLY on sun-exposed skin
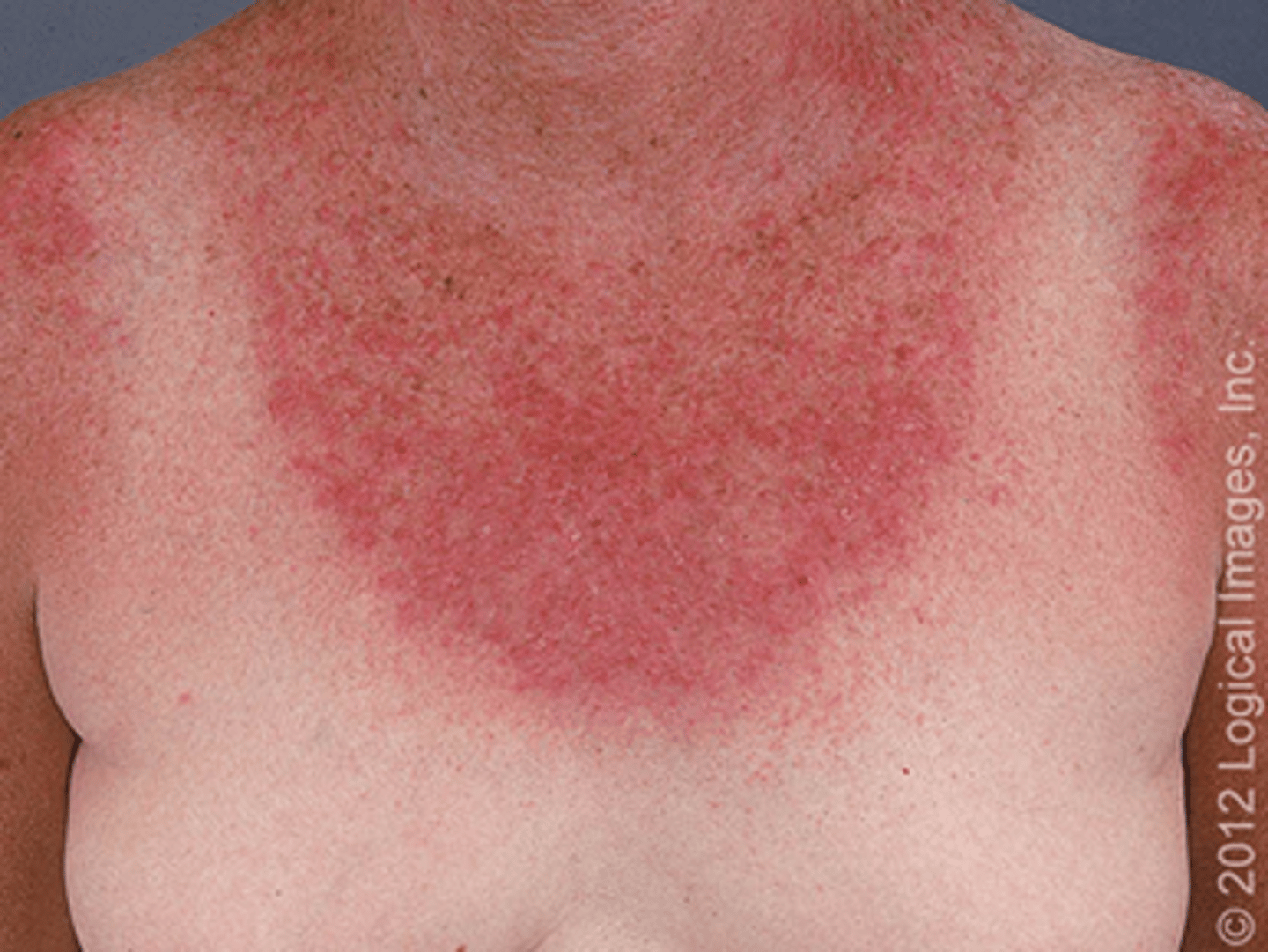
What drugs commonly cause phototoxic reactions?
Amiodarone
Tetracyclines
Sulfonamides
Photoallergic photosensitivity reaction
rash that transforms UVA light into allergens and includes non-sun exposed skin 24-72 hours after exposure
What drugs commonly cause photoallergic reactions?
Sulfonamides
Sulfonylureas
Thiazides
NSAIDs
Chloroquine
Carbamazepine
What is the management for skin ADRs?
Stopping the offending agent
Supportive/symptomatic treatment
Cystic acne
a cyst of connective tissue that forms due to infection of sebaceous glands that requires aggressive treatment
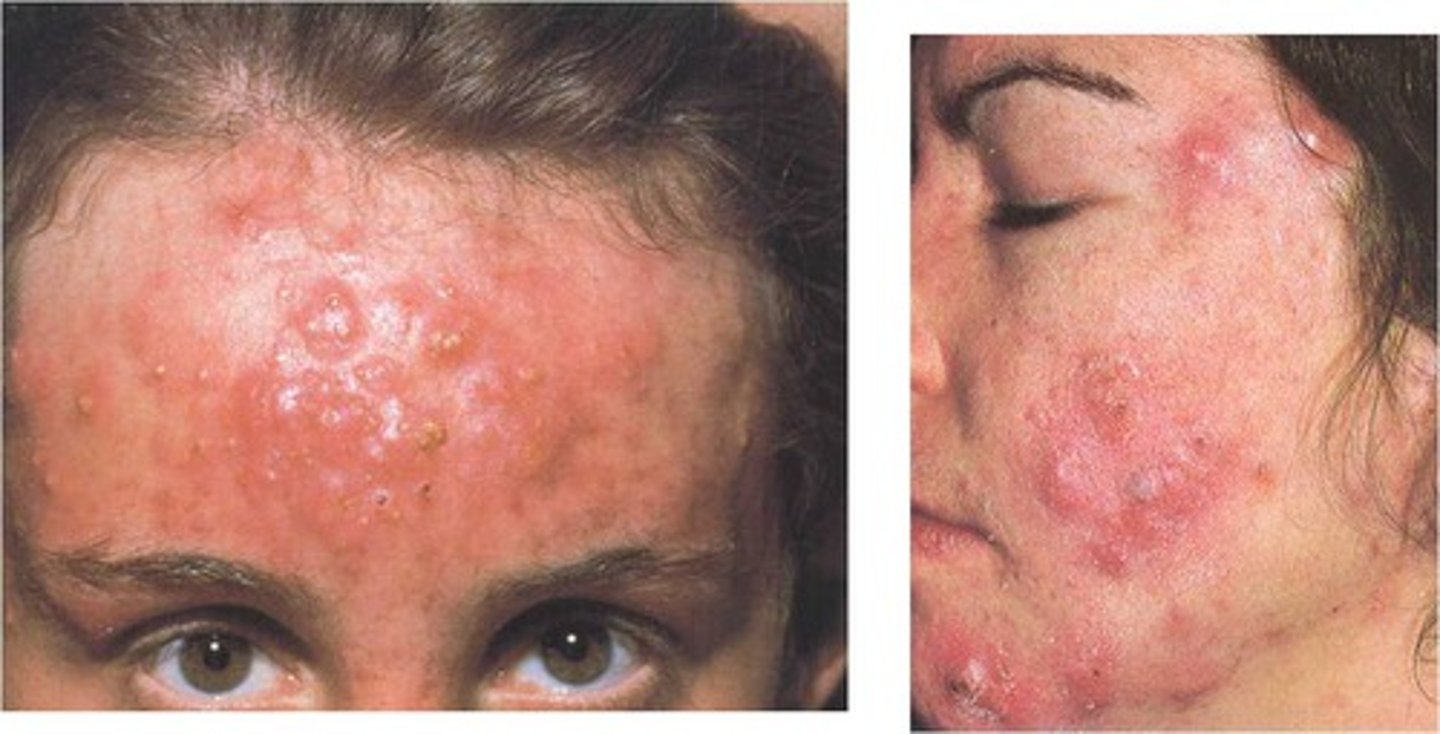
What are the types of cystic acne?
Acne conglobata
Ance fulminans
Pyoderma faciale
Acne conglobata
a chronic, highly inflammatory form of cystic acne in which involved areas contain a mixture of double comedones, two blackheads that communicate under the skin, papules, pustules, communicating cysts, abscesses, and draining sinus tracts
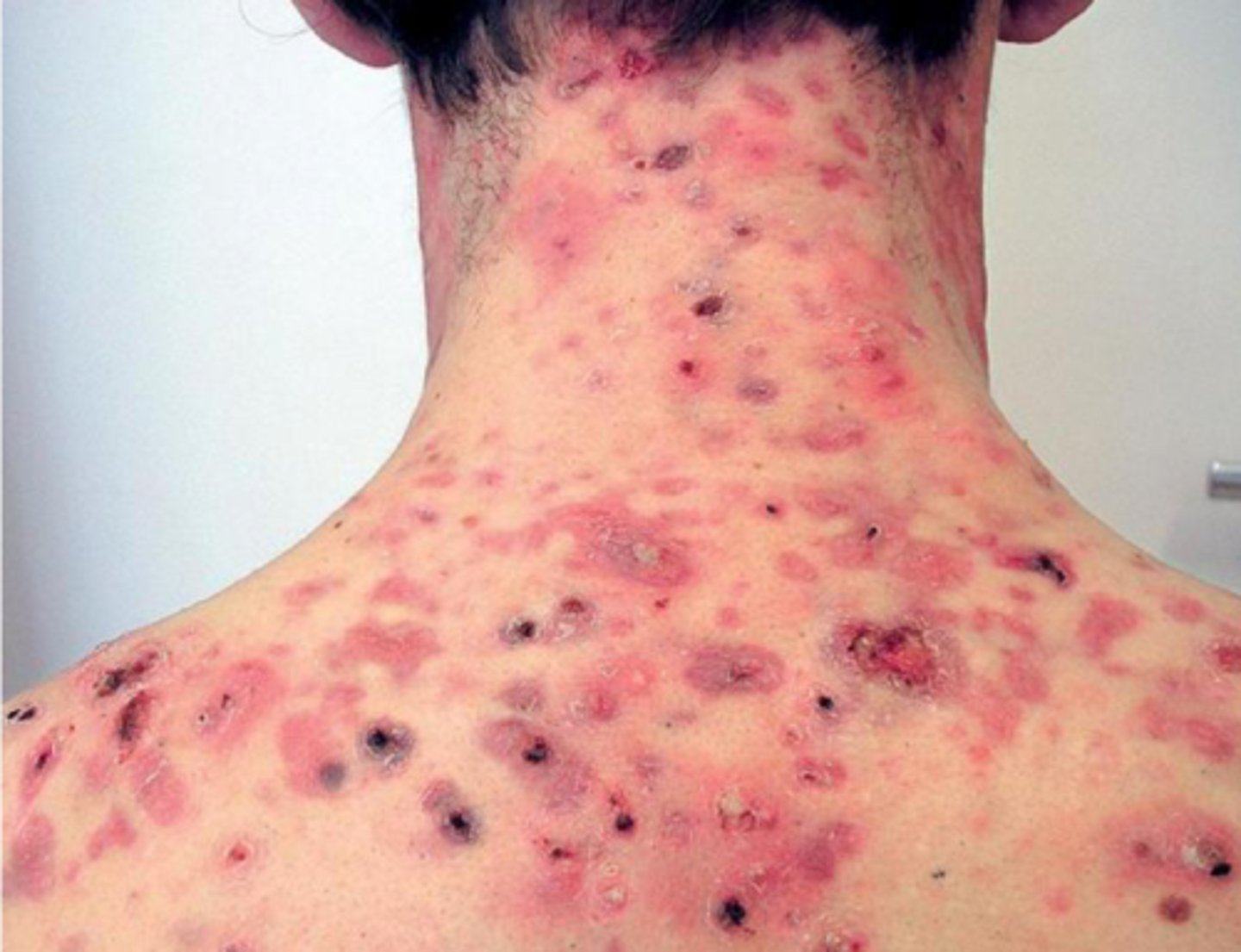
Acne Fulminans
rare, ulcerative form of necrotic acne
Pyoderma faciale
cystic acne that remains confined to the face fo adult women
What are the treatment options for cystic acne?
Oral and topical antibiotics
Kenalog injections into cysts
Isotretinoin
Psoriasis
A noncontagious inflammatory skin disease characterized by recurring reddish patches covered with silvery scales caused by uncontrolled T cell replication
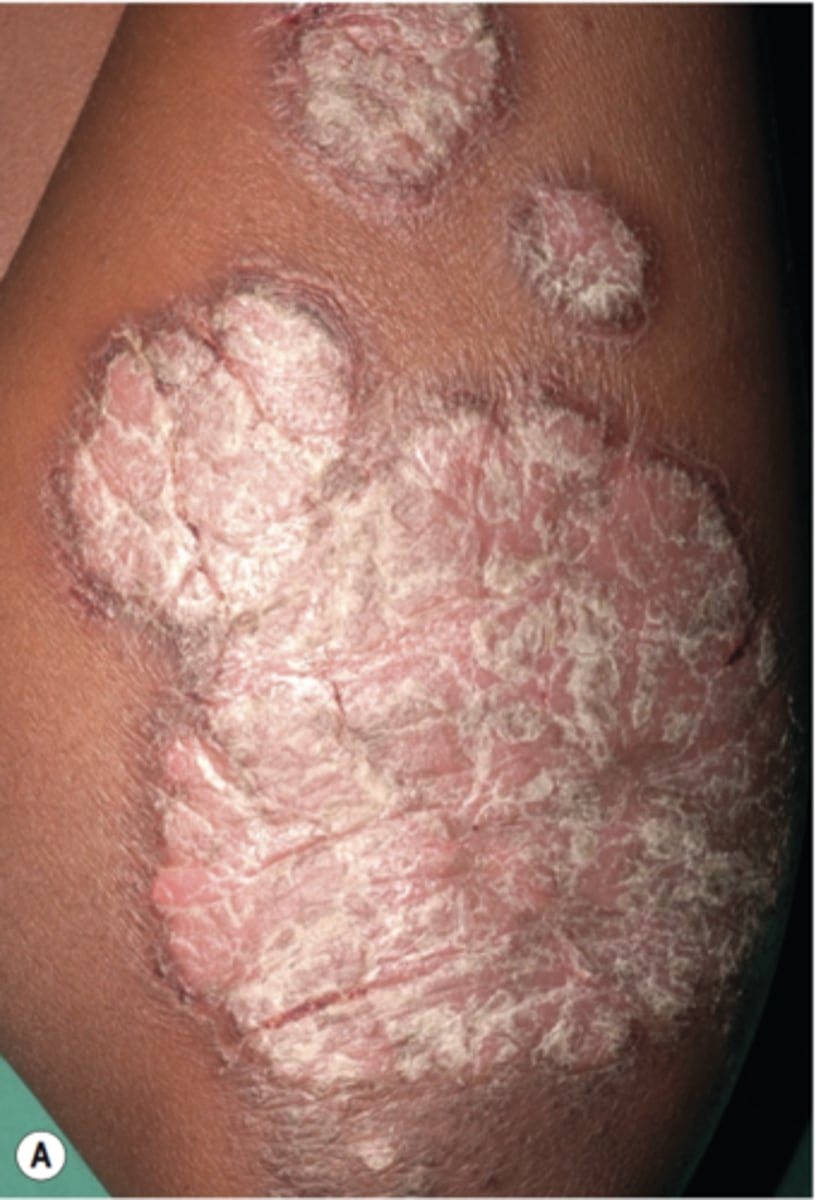
What are the topical treatment options for psoriasis?
Calcipotriol
Calcitriol
Calcipotriene
Steroids
Anthralin
Tazarotene
What are the systemic treatment options for psoriasis?
Acitretin
Cyclosporine
Methotrexate
Alefacept
Efalizumab
Eczema
noninfectious, inflammatory skin disease characterized by redness, blisters, scabs, and itching
What are the treatment options for eczema?
Hydration
Topical steroids
Phototherapy
Antihistamines
Pimecrolimus cream
Tacrolimus cream
MOA of topical steroids
anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, immunosuppressive