Understanding Substance Use Disorders and Treatments
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Substance
Mood, behavior modifying chemical
Intoxication
Reversible symptoms due to the direct effects of a substance ingested or exposed
Tolerance
Using the same amount of a substance no longer has the desired effect
Withdrawal
Specific symptoms (depends on substance used) as a result of ceasing to use or drastically decreasing use of a substance
Substance Use Disorder
A problematic pattern of use (within last 12 mo) causing significant impairment/distress as manifested by 2 or more of the following: Tolerance, Withdrawal, Craving, Use longer and more than you intend, Want to cut down but cannot, Spend a great deal of time getting, using or recovering from use, Use results in failure to fulfill major role obligations
Mild Substance Use Disorder
2-3 symptoms
Moderate Substance Use Disorder
4-5 symptoms
Severe Substance Use Disorder
6 or more symptoms
Depressants
Alcohol, sedative hypnotics, opioids
Stimulants
Amphetamines, cocaine, methamphetamines, nicotine, caffeine
Hallucinogens
LSD, mescaline
Cannabinoids
Marijuana, hashish
Inhalants
Solvents, gas
Inhaling
Time to reach brain: 7-60 seconds
Snorting
Time to reach brain: 4 minutes
Injecting (IV)
Time to reach brain: 20 seconds
Injecting (IM)
Time to reach brain: 4 minutes
Oral consumption
Time to reach brain: 20 minutes
Heavy Alcohol Use (Men)
4 or more standard drinks on any given day constitutes heavy alcohol use
Heavy Alcohol Use (Women)
3 or more standard drinks on any given day constitutes heavy alcohol use
Binge drinking (Men)
5 or more standard drinks on the same occasion (or within 2 hours)
Binge drinking (Women)
4 or more standard drinks on the same occasion (or within 2 hours)
Alcohol
Slows the activity of the CNS and binds to neurons that typically bind to GABA, helping GABA shut down neurons
Alcohol dehydrogenase
Metabolized by liver
Average alcohol metabolism rate
Average: .25 ounces/hour
BAC = 0.06
Relaxation and comfort
BAC = 0.09
Intoxication
BAC > 0.55
Death
Long-term excessive alcohol use
Damage physical health
Cirrhosis
Especially damaged is the liver

Korsakoff's syndrome
Nutritional problems due to long-term excessive alcohol use
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
Women who drink alcohol during pregnancy place their fetuses at risk
Sedative Hypnotics
Impaired judgment, mood swings, risk of aggressive/sexual behavior, relaxed, sleepy, slurred speech, incoordination, unsteady gait, impaired attention and memory, 'eye drifting,' stupor, coma
Risk of addiction for Sedative Hypnotics
Moderately high risk
Withdrawal symptoms from alcohol or sedative/hypnotics
Sweating, increased heart rate, anxiety, insomnia, vomiting, hallucinations, tremor, agitation, seizures, delirium, possibly death (rare instances)
DTs
Occurs in 5-10% of chronic alcohol abusers and carries up to 5% mortality with treatment and up to 35% mortality without treatment
Opioids
Natural or synthetic substances like Morphine, Heroin, Methadone
Biggest risk of Opioids
Overdose can close down respiratory center in the brain
Heroin withdrawal symptoms
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle ache, fever, insomnia, pupil dilation, runny nose and/or eyes, yawning, dysphoric mood
Stimulants
Substances that increase the activity of the central nervous system (CNS)
Common stimulants
Cocaine, Amphetamines, Caffeine

Stimulant intoxication symptoms
Increased/decreased heart rate, euphoria, pupil dilation, elevate/lower blood pressure, sweating/chills, nausea/vomiting, weight loss, psychomotor agitation/retardation, cardiac arrhythmia/chest pain, confusion, seizure, coma
Stimulant withdrawal symptoms
Dysphoric mood, fatigue, unpleasant dreams, increased appetite, psychomotor, sleep disturbance
Dangers of cocaine/stimulants
Overdose can depress the brain's respiratory function, causing the person to stop breathing
Methamphetamine
Synthetic drug with high risk of tolerance
Amphetamine psychosis
A condition that may occur in individuals using amphetamines, characterized by symptoms similar to schizophrenia.
Stimulant withdrawal
A syndrome that occurs when a person stops using stimulants like cocaine or amphetamines, leading to symptoms such as fatigue and depression.
Hallucinogens
Substances like LSD, peyote, and mushrooms that alter perceptual experiences and may cause sweating, heart palpitations, and blurred vision.
Neurotransmitter: Serotonin
A chemical in the brain that is affected by hallucinogens, influencing mood and perception.
Cannabis
A drug containing THC, which acts as a depressant, stimulant, and/or hallucinogen, leading to various effects including euphoria and impaired coordination.
Anandamide
A neurotransmitter in the brain that is decreased with heavy cannabis use.
Cannabis Withdrawal
A condition that occurs after stopping heavy cannabis use, characterized by symptoms like irritability, anxiety, and sleep difficulties.
Cannabis: Excessive Use
Heavy use of cannabis that may lead to panic reactions, accidents, poor concentration, and links to psychosis.
Opioids
A class of drugs that can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as dilated pupils and chills.
Polysubstance Use
The concurrent use of multiple drugs, which can enhance or negate the effects of each other and lead to dangerous levels in the body.
Gambling Disorder: Criteria
A set of symptoms including the need to gamble with increasing amounts of money and preoccupation with gambling, leading to significant distress.
Gambling Disorder: Mild
Characterized by meeting 4-5 criteria for gambling disorder.
Gambling Disorder: Moderate
Characterized by meeting 6-7 criteria for gambling disorder.
Gambling Disorder: Severe
Characterized by meeting 8-9 criteria for gambling disorder.
Gambling Disorder: Men vs. Women
Women experience later onset and faster progression to problematic gambling compared to men.
Etiology of SUD/GD: Causes
A variety of factors including sociocultural, psychodynamic, cognitive behavioral, and biological influences contribute to substance use disorders and gambling disorders.
Genetic link in Gambling Disorder
Evidence suggests a genetic predisposition to gambling disorder, particularly among non-white groups.
Dopamine and Gambling Disorder
Some individuals may experience onset of gambling disorder when taking medications that increase dopamine levels.
Sociocultural views
Those most likely to develop these disorders: Live in stressful socioeconomic conditions, Have families that value or tolerate drug use.
Psychodynamic views
Those most likely to develop these disorders: Have powerful childhood dependency needs, Display a "substance abuse personality."
Cognitive-behavioral views
Those most likely to develop these disorders: Are "conditioned" by tension-reduction, rewarding effects of drugs (self-medication), About 20% have a SUD and another disorder, Have rewards-produced expectancy that substances will be rewarding, May be influenced by classical conditioning when cues or objects are present during drug use.
Biological views - Genetic predisposition
Similarity of alcohol preferences among alcohol-preferring animals and their offspring, Alcoholism concordance rate in identical twins, Biological parent-adoptee child alcohol abuse rate, Abnormal form of dopamine-2 (D-2) receptor gene in people with substance use disorders.
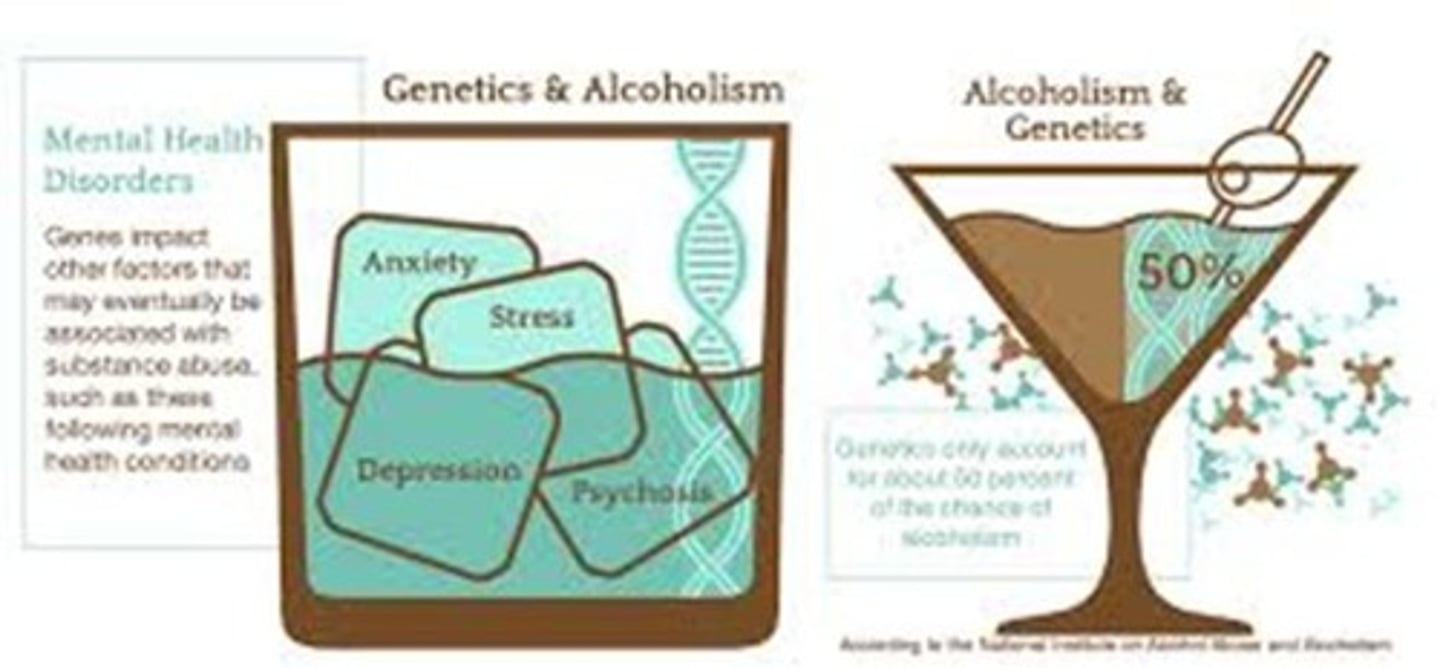
Biological views - Neurotransmitters
Drug tolerance and withdrawal symptoms are caused by cutbacks in the brain's production of particular neurotransmitters during excessive and chronic drug use: Lower GABA production: Alcohol or sedative hypnotics, Lower endorphin production: Heroin, Lower dopamine production: Cocaine or amphetamines, Reduced anandamide production: Cannabis.
Biological views - Brain circuits
Dopamine is the key NT for most, Drugs stimulate structures directly and indirectly.
Incentive-sensitization theory
When substances repeatedly stimulate the reward center, it develops a hypersensitivity to substances.
Reward-deficiency syndrome
The reward center is not readily activated by "normal" life events so the person turns to drugs to stimulate this pleasure pathway, particularly in times of stress.
Developmental psychopathology view
Genetically inherited predisposition, Externalizing or internalizing temperament, Numerous stressors throughout childhood, Inadequate parenting, Rewarding substance use experiences, Relationships with peers who use drugs.
CAGE Assessment
1. Have you ever felt you needed to Cut down on your drinking? 2. Have people Annoyed you by criticizing your drinking? 3. Have you ever felt Guilty about drinking? 4. Have you ever felt you needed a drink first thing in the morning (Eye-opener) to steady your nerves or to get rid of a hangover?
Benefits of Treatment
Increase in physical and emotional wellbeing, Decrease in criminal activity (40-50% decreases), Increased productivity, Decrease in use of tax payers' $, One study estimated that rehab costs were paid back to society 12 fold when an addicted person was in treatment.
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment
Relapse Prevention is Part of CBT.
Cognitive Behavioral Treatment Goals
Identify maladaptive thoughts and modify them, Learn ways to cope with negative feelings and cravings that might result in drug use, Identify triggers for drug use, Prepare for high risk situations.
Relapse Prevention (CBT)
A cognitive-behavioral therapy approach that includes two important concepts: Abstinence violation effect (AVE) and Seemingly irrelevant decisions (SID).
Abstinence violation effect (AVE)
One slip results in a binge.
Seemingly irrelevant decisions (SID)
A person starts with one small, seemingly innocent decision which leads to other small decisions on the wrong path and eventually leads to using drugs and/or alcohol.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
A type of cognitive-behavioral therapy that encourages acceptance of thoughts and cravings rather than trying to suppress them, using the metaphor of the mind as the sky and thoughts and cravings as clouds.
Motivational Interviewing (MI)
A technique and treatment that helps people clarify their feelings and motivation surrounding drug/alcohol use, with supportive and empathic therapists.
Behavior Therapy
Includes aversion therapy and contingency management; aversion therapy uses repeated pairings of an averse stimulus and drug.
Aversion therapy
Used sparingly, it involves repeated pairings of an averse stimulus and drug, such as shock and alcohol or alcohol use while on a drug that makes you vomit.
Contingency Management
Provides reinforcers for drug-free urines and is typically not used in isolation.
Biological Treatments
Include detoxification, antagonist medications, and agonist medications.
Detoxification
Medically supervised withdrawal, typically ineffective when done alone.
Antagonist medications
Medications that block or change the effects of the drug of choice.
Agonist medications
Mimic the effects of the drug of choice and are used as a safer substitute.
Common Medications
Include Antabuse for alcohol use disorder, Naltrexone for opioids and alcohol, Campral for alcohol, Narcan for opioid overdose, Methadone as a full opioid agonist, and Buprenorphine as a partial opioid agonist.
Antabuse
A medication that treats alcohol use disorder.
Naltrexone
Used for treating opioid and alcohol dependence.
Campral
Normalizes GABA and decreases craving for alcohol.
Narcan
Administered during an opioid overdose to block the effects.
Methadone
A full opioid agonist used as a substitute for opioids.
Buprenorphine
A partial opioid agonist that is also available with Narcan.
Common Approach: Harm Reduction
A strategy to reduce the negative effects of drug use while helping people get ready to engage in treatment.
Harm Reduction examples
May include free condoms, needle exchange programs, Narcan distribution programs, and 'wet shelters'.
Attitude of providers
Shown to be most helpful in getting people to start treatment.
Example of Portugal
Utilization of Motivational Interviewing (MI) in drug treatment.