NRES 250 Exam #2 UWSP
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Disease
Any alteration in the normal condition of an organism
Enzootic
disease occurs at a regular rate in an area
Intestinal flukes
Epizootic
Disease occurs at a time or place that is not expected, or at a higher rate
Hemorrhagic disease
Sublethal effects
The effects of an environmental hazard that are not lethal, but which may impair an organism's behavior, indirect mortality, or reproduction
How do diseases affect reproduction?
Some diseases can cause early abortion
Vectors
any agent which carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism

Reservoirs
the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally lives and reproduces
Types of management actions
Vaccinations
Regulations; ex. Baiting
Interrupt life cycle of pathogen
Viruses
Replicates inside its host, Nonliving, needs vector (Malaria)
Bacteria
Living, one-celled (Brucellosis)
Prions / Midges
Always fatal, Chronic Wasting Disease, irregular shaped proteins
Defer Grazing
Defer grazing until range plants set seed
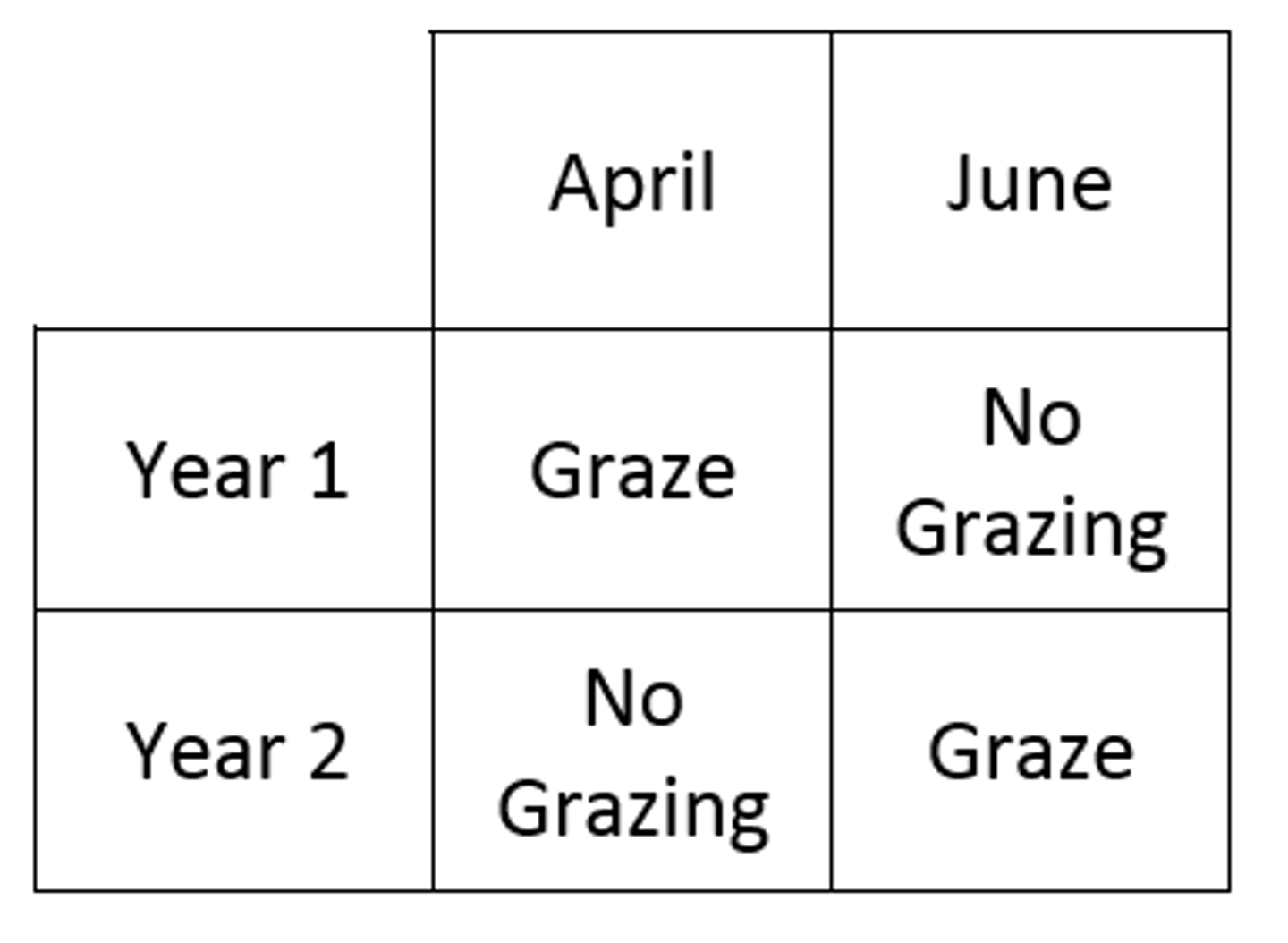
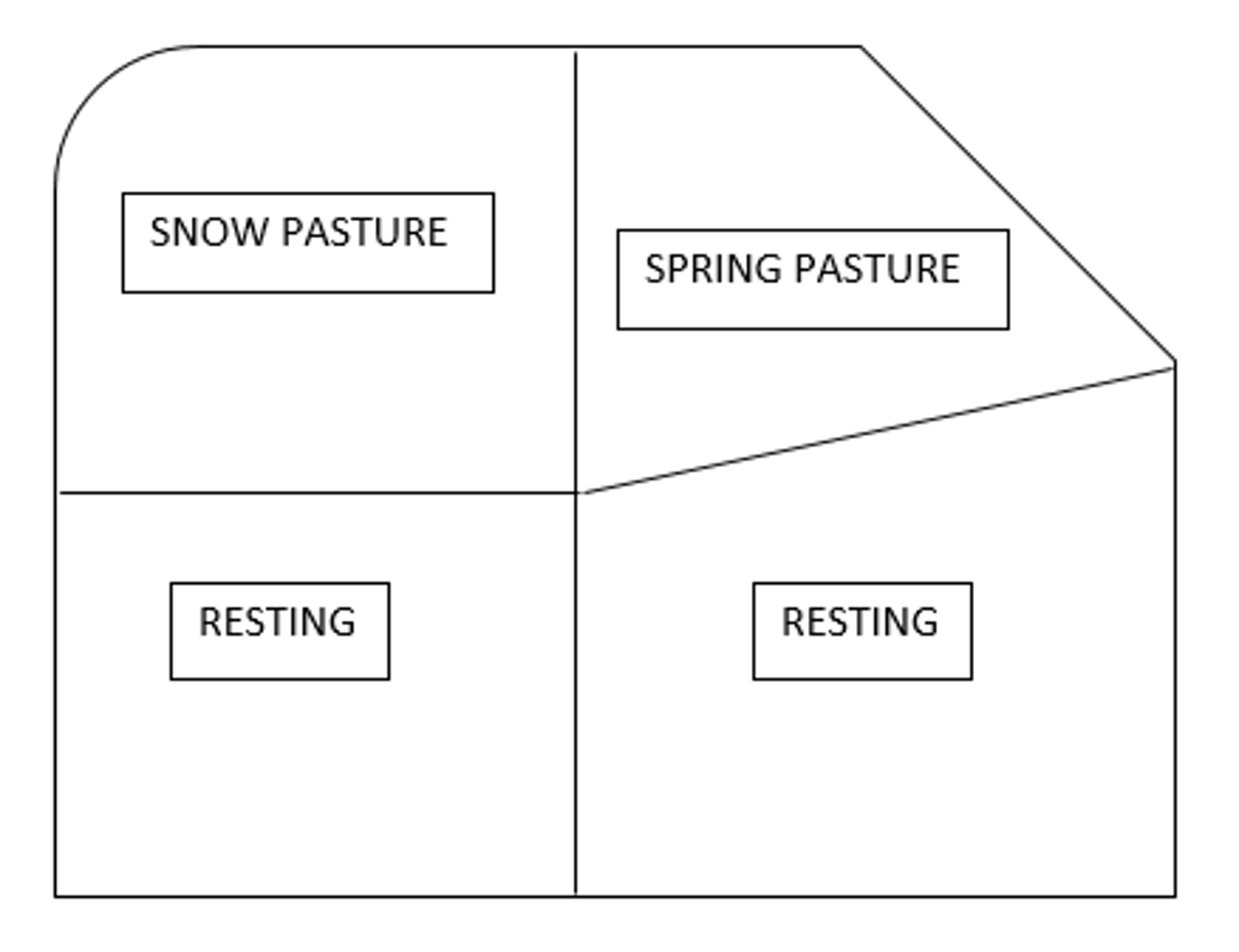
Rest Rotation Grazing
Rest period is a year or more. Mosaic pattern seen
Continuous Grazing
Grazing. All the Time.
How do fences influence wildlife?
Fences can influence an animals ranges.
How can we modify them to be wildlife-friendly?
We can modify them by lifting the wires or moving the wires around so animals can either jump them or go underneath them.
What are Riparian Zones?
Riparian zones are areas of vegetation around a water source, usually rivers

Why are Riparian Zones important
Wildlife Cooridors, Filters,
What is a Rangeland
Plant community dominated by grasses, forbs, and shrubs

What do humans use Rangelands for?
Cattle grazing

Benefits to fire management
Succession, rotation of nutrients, clearing of non-native plants, good for species that enjoy disturbance, some species need it for reproduction
Challenges to fire management
Animal casualties, reset succession
How do we manage wetlands for wildlife?
We control the water levels of the wetlands to a specific species preference
How do target species respond to wetland management
Their populations have increased
Which species are common in wetlands
Cranes, Amphibians, Ducks, Raptors
Why are wetlands important
They are natural filters
Importance of Field Borders
Field Borders allow for wildlife habitat
Decrease erosion
Difficulty with managing on Ag Lands
Permissions, Lacking reliable knowledge, divergent goals, human wildlife conflicts, communication to the public, changes in farm conservation
How has farming changed since 1930's and how has it affected wildlife?
Larger equipment , more fertilizers and pesticides, row crop, less edges.
Wildlife has had less habitat within agricultural areas and has been severely harmed by pesticide use
Describe set-aside programs
Set aside a portion of land that is not productive for wildlife habitat. 10-15 years. Paid by the govt. For hunting.
What does Early Successional Stages Offer Wildlife
•Abundant ground cover
•Open spaces
•Bare ground
•Abundant seeds/insects
What does Brush Stages Offer Wildlife
•Young trees and shrubs
•Nesting, roosting, and loafing cover
•Seeds, fruit, insects, browse
What does a Mature forest Offer Wildlife
•Canopy may be closed
•Mast, foliage, browse, insects= food
•Trees with cavities
•Provide seasonal cover
•Provide year-round cover (conifers)
•In maintained long enough = old growth
What Does Intermediate Stages Offer Wildlife
•Canopy closed
•Sparse understory
•Trees too small for cavities
•Little mast
•Very limited food and cover when compared to other stages
Difference between whooping cranes and sandhill cranes
Whooping are endangered
Sandhill are common
Management concerns for Whooping Cranes
Only One Wild Population
Low Nest Success
Management concerns for Sandhill Cranes
Damage on Ag Lands
Eat COrn Seeds in Spring
Why is the Eastern Migratory Population of Whooping cranes not considered self-sustaining
Because it relies heavily upon human intervention
What is causing the birds to abandon nests
Blackflies
Is the current management strategy of forced re-nesting working
Yes
Are colts surviving like expected?
No
Do cranes renest?
Yes
Are cranes nests successful
After a renesting, yes
The Three Dynamic Rate Functions
Recruitment (Natality)
Growth
Mortality
Recruitment ( Natality )
Addition of new organisms to a population
Growth
Addition of biomass to an individual or population
Mortality
Deaths in a population
What data is required to estimate the three dynamic rate functions
Weight
Length
Population Estimate
Density Dependent
relies upon population details
Density Independent
Weather related
Additive Mortality
total mortality increases with increase in harvest mortality
Compensatory Mortality
natural mortality changes in response to harvest mortality such that total mortality stays the same.
Standing crop or stock
number or biomass present at a specific time.
Production
biomass accumulated during a specific time interval (usually 1 year).
"Surplus" production
that portion which can be removed without adverse effects. - Theoretically anyway!
Yield
biomass or numbers harvested.
What structures are used to estimate fish age?
Calcified Structures
Calcified Structures
Scales
Spines
Otoliths
Cleithra
What structures are used to estimate wildlife age?
Cementum annuli
Anatomical measurements
Gonad development
Morphology
Coloration
Feathers
Cementum annuli
Annual deposits in teeth
Seasonal growth causes "annuli" formation
Section teeth
When and how do annuli form on calcified structures of fish and wildlife
Deposition of daily rings or circuli
Circadian rhythm (circular, 24 hrs)
Temperate regions - growth slows in winter
Daily rings closer together in winter
Faster growth- daily rings farther apart
Different in marine fish, tropics, and other cases
What are some common ways to determine sex of wildlife?
Coloration
Feel Around
Characteristics
What are some of the applications of genetics in fisheries and wildlife
Management and conservation
Forensics
Management and Conservation App. for Genetics
Population structure
Parentage
Sex determination
Individual identification
Propagation
Tagging
T & E species
Forensics App. for Genetics
Sale of illegal products
What is an allele?
Alternative forms of a gene that occupy specific locus
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
Phenotype
physical characteristics of an organism
Why is genetic diversity important?
Genetic diversity allows for the potential of adaptation
What is phenotypic plasticity?
The ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to the environment.
Two organisms can have the same genotype and look physically different
Stock
Stock is a population or a group of populations WITHIN a species and are adapted to similar environments
Species
Species is a naturally occurring group of organisms that can interbreed and create viable offspring
What are the two modes of speciation?
allopatric and sympatric
Is allopatric or sympatric speciation more common?
allopatric
Evolution
Change in allele frequencies due to differential survival of offspring
Natural Selection
Leads to change in allele frequency due to death of weak individuals
Natural Selection vs. Artificial Selection
Natural Selection happens at a slower rate and occurs naturally
Artificial Selection happens quickly and occurs due to a human influence
Parameter
The actual value for a specified metric
Accuracy Vs. Precision
Accuracy - A measure of distance from true value
Precision - A measure of "repeatability" or variation
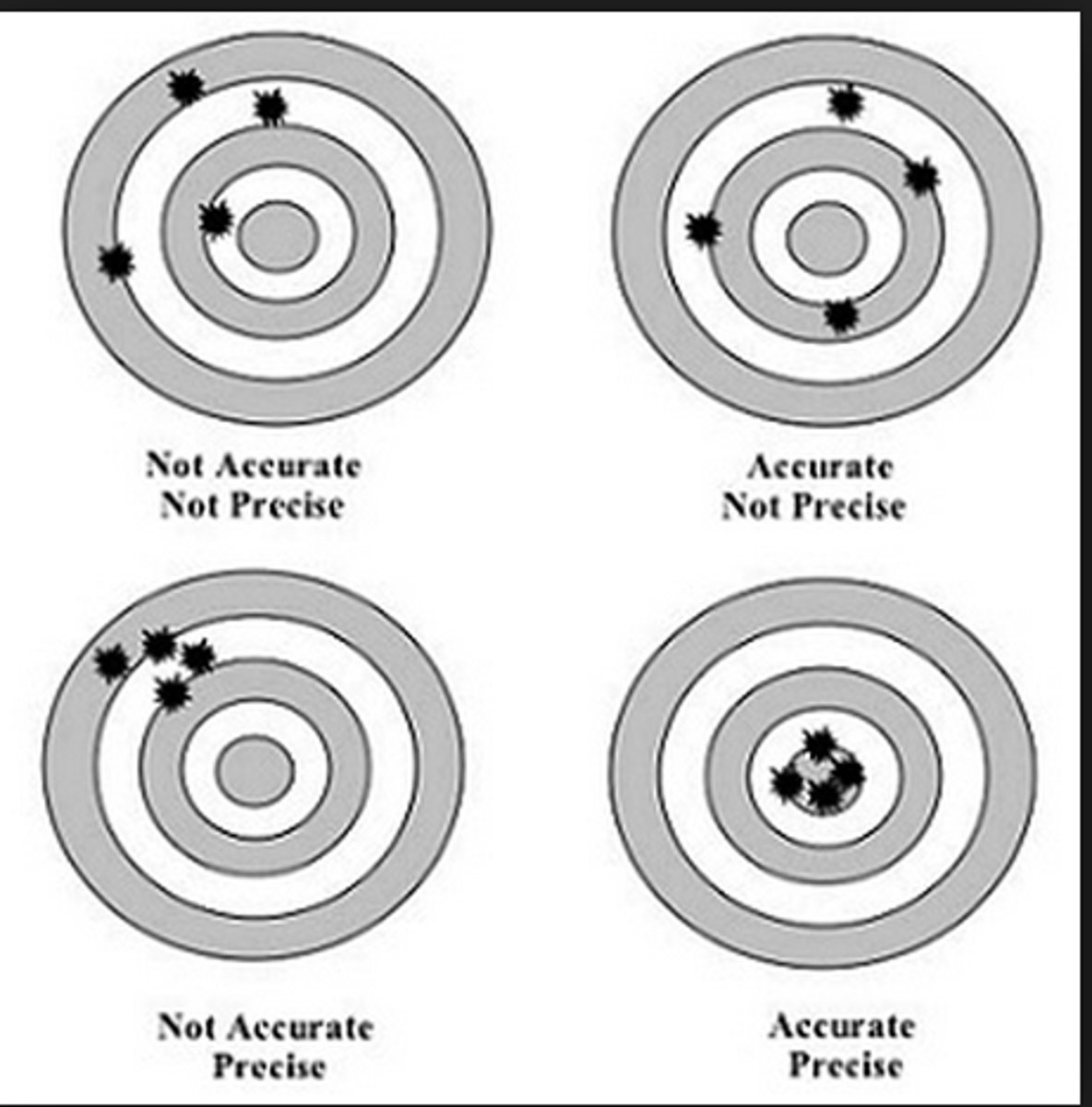
Bias
A description of inaccuracy
Mean
average
Variance
(n.) - a difference between what is expected and what actually occurs
relative abundance
the proportion each species represents of all individuals in the community
Why do we calculate relative abundance?
Assumes changes in catch or counts reflect changes in population size
Track changes in abundance using sampling program
The Ecological Roles of Wetlands
Acts like a filter
Essential Habitat
Links Food Web
Why are wetlands important?
reduce impacts of storm damage, maintain good water quality
Necessary Aspect of other ecosystems
What do fish use wetlands for?
Breeding Grounds, Nursery
What is an ephemeral Wetland
Wet only a portion of the year
How does stratification work?
Amount of oxygen and the temperature of the water at different depths
What are the layers of stratification
Epilimnion
Metalimnion
Hypolimnion
When is the warmest water on the top vs. bottom of a lake?
Epilimnion is coldest during winter and warmest during summer
Hypolimnion is coldest during summer and warmest during winter
Eutrophic vs. Mesotrophic vs. Oligotrophic
Eutrophic - low visibility, higher chlorophyll, higher phosphorus
Mesotrophic - Higher visibility, lower chlorophyll, lower phosphorus
Oligotrophic - Highest visibility, lowest chlorophyll, lowest phosphorus
Littoral vs. Limnetic
Littoral - where light reaches the bottom sediment, plants root
Limnetic - more open water, plants are unable to be rooted
Benthic vs. Pelagic
Benthic - Bottom layer of sediment
Pelagic - Open water zone of Euphotic area
Photic vs. Aphotic
Photic - Light can reach
Aphotic - Light cannot reach
Riverine Zone
High Flow Rate, High Sedimentation
Transitional Zone
Medium Flow Rate, Medium Sedimentation
Lacustrine Zone
Low to No Flow Rate, No Sedimentation, all settled
When are nutrients the highest in a reservoir
During Filling and Right after filling
Think about the concepts of trophic upsurge and trophic depression
Once filling begins, there is an upsurge in available nutrients, but once carrying capacity is severely over shot, things will die off due to the now low levels of said nutrients, leading to trophic depression