Chemical Safety Systems: OSHA, NFPA, and SDS Overview
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
OSHA
Occupational Safety & Health Administration, a federal agency under the U.S. Department of Labor responsible for the enforcement of safety and health legislation in all work/school environments.
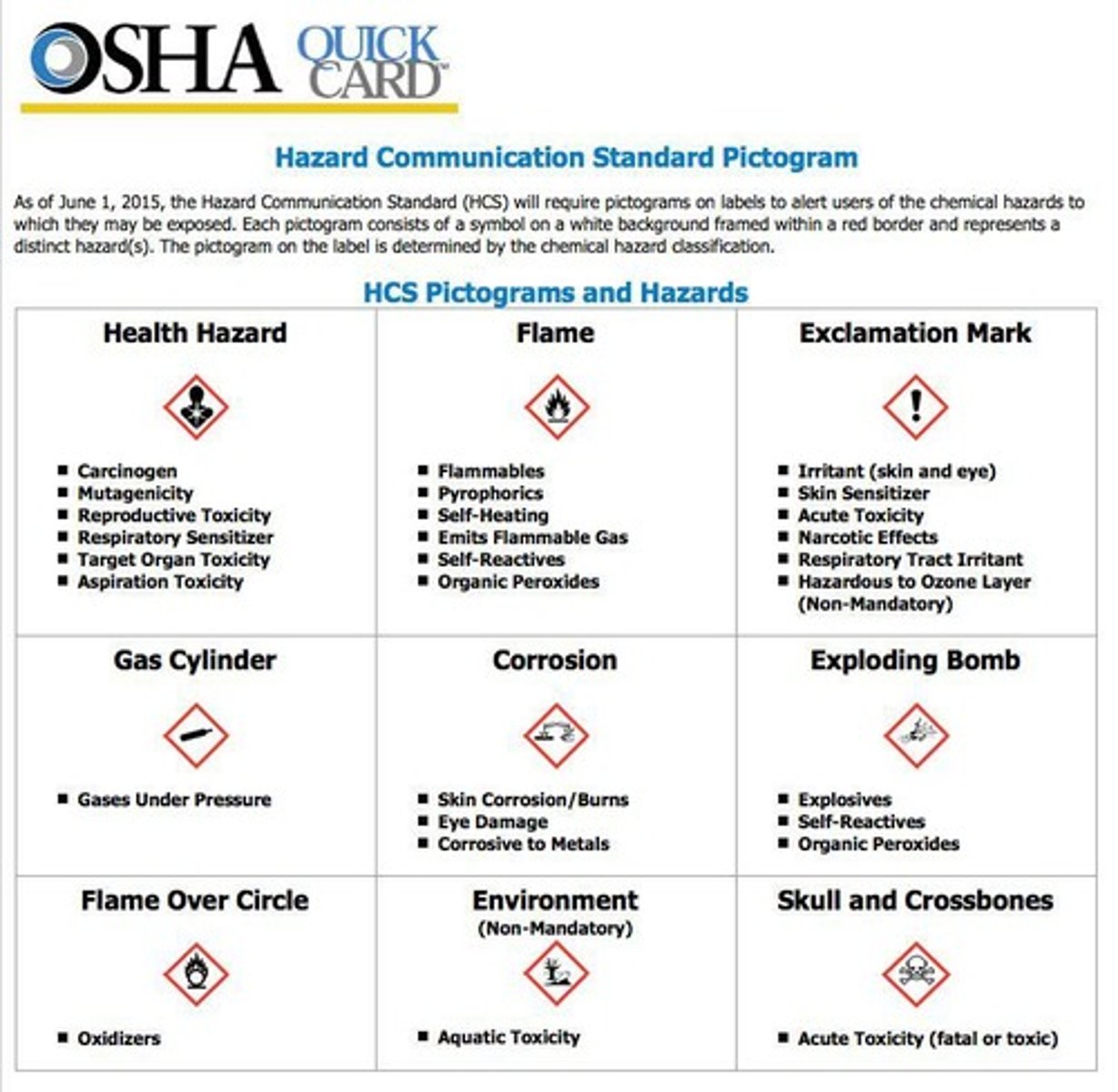
NFPA
National Fire Protection Association, responsible for a visual label system which easily identifies chemical hazards.
SDS
Safety Data Sheets, a text document which lists the hazards for each chemical as well as other important chemical information.
NFPA Labeling system
Designed for emergency response to protect the health and safety of individuals who use these chemicals and/or respond to emergencies in facilities or storage locations.

NFPA Color Codes
Color codes for safety concern categories: Blue for Health (toxicity), Red for Flammability, Yellow for Reactivity (instability/explosiveness), White for other specific hazards.
NFPA Numerical Scale
Each chemical is rated on a scale from 0 to 4 in three safety categories (not including the white category): 0 = minimal hazard, 1 = slight hazard, 2 = moderate hazard, 3 = serious hazard, 4 = severe hazard.
SDS Sheets Requirement
OSHA enforces that any work or school properties carry SDS sheets for each and every chemical present within the building.
SDS Information
An SDS provides all the info on an NFPA label, including physical data & descriptions, first aid, storage, disposal, protective equipment needed when handling, spill clean-up, exposure limits, and much more.
SDS Format Variability
SDS sheets are made by the company that manufactures the chemical, thus formats can vary from source to source.
NFPA Label Creation
To create your own NFPA label, choose an SDS sheet and include chemical name & formula, NFPA label with appropriate colors and ratings, elaborate on the hazard with the highest rating, one additional interesting fact about your substance, draw any pictogram hazards associated with the chemical, and include students names & class mods.
Chemical Hazard Examples
Examples of specific hazards include acid, alkali, radioactive, corrosive, oxidizer, reactive with water.
Emergency Response
The NFPA labeling system is designed for emergency response to ensure safety during incidents like fires or chemical spills.
Health Hazard
In the NFPA labeling system, the blue color
Flammability Hazard
In the NFPA labeling system, the red color.
Reactivity Hazard
In the NFPA labeling system, the yellow color
Special Hazards
In the NFPA labeling system, the white color .
Minimal Hazard
In the NFPA numerical scale, a rating of 0 indicates minimal hazard.
Chemical Handling Procedures
SDS sheets describe procedures for handling or working with substances in a safe manner.
Health Hazard Symbol

Flame symbol

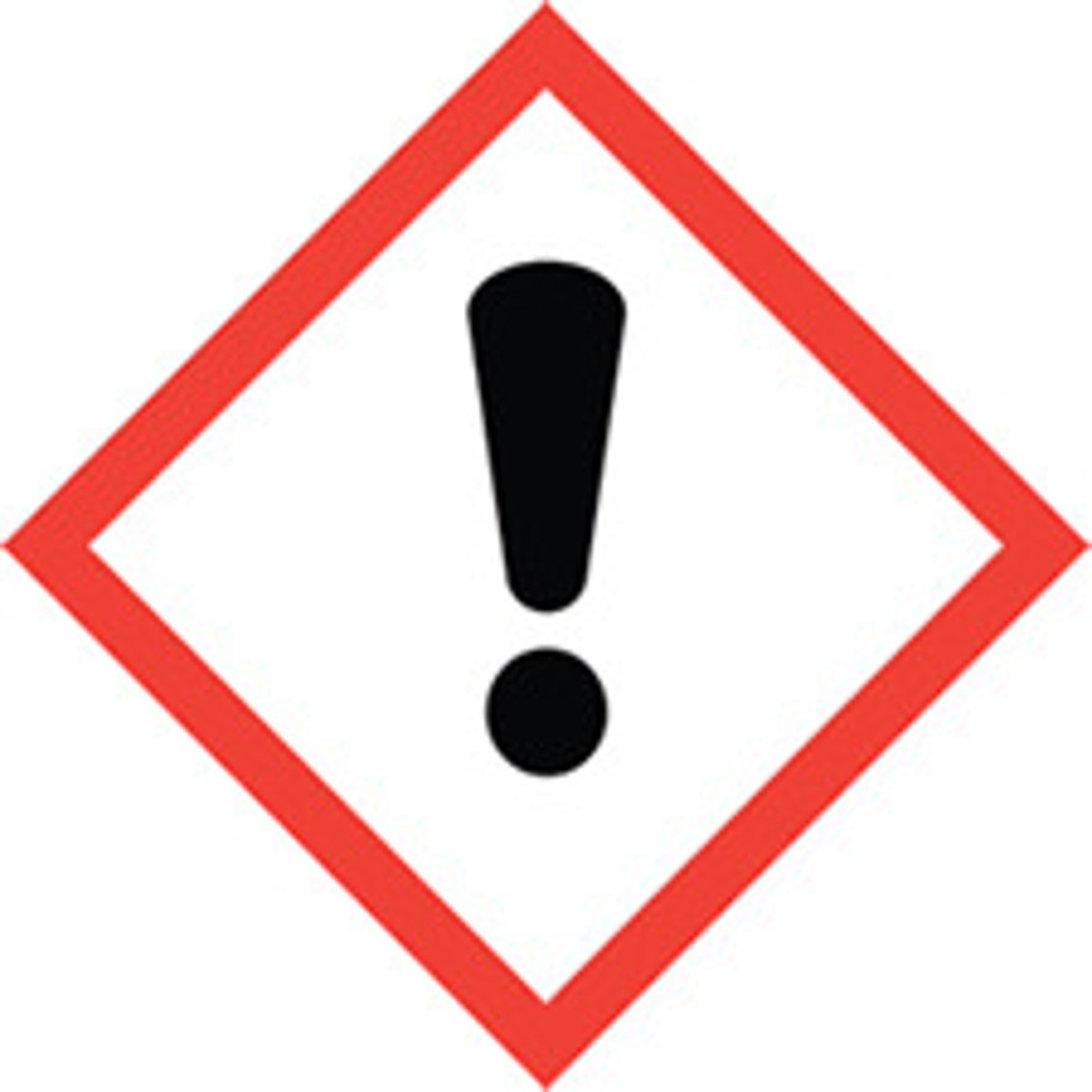
irritant, skin sensitizer, acute toxicity, narcotic effects, respiratory tract irritant, hazardous to ozone layer symbol

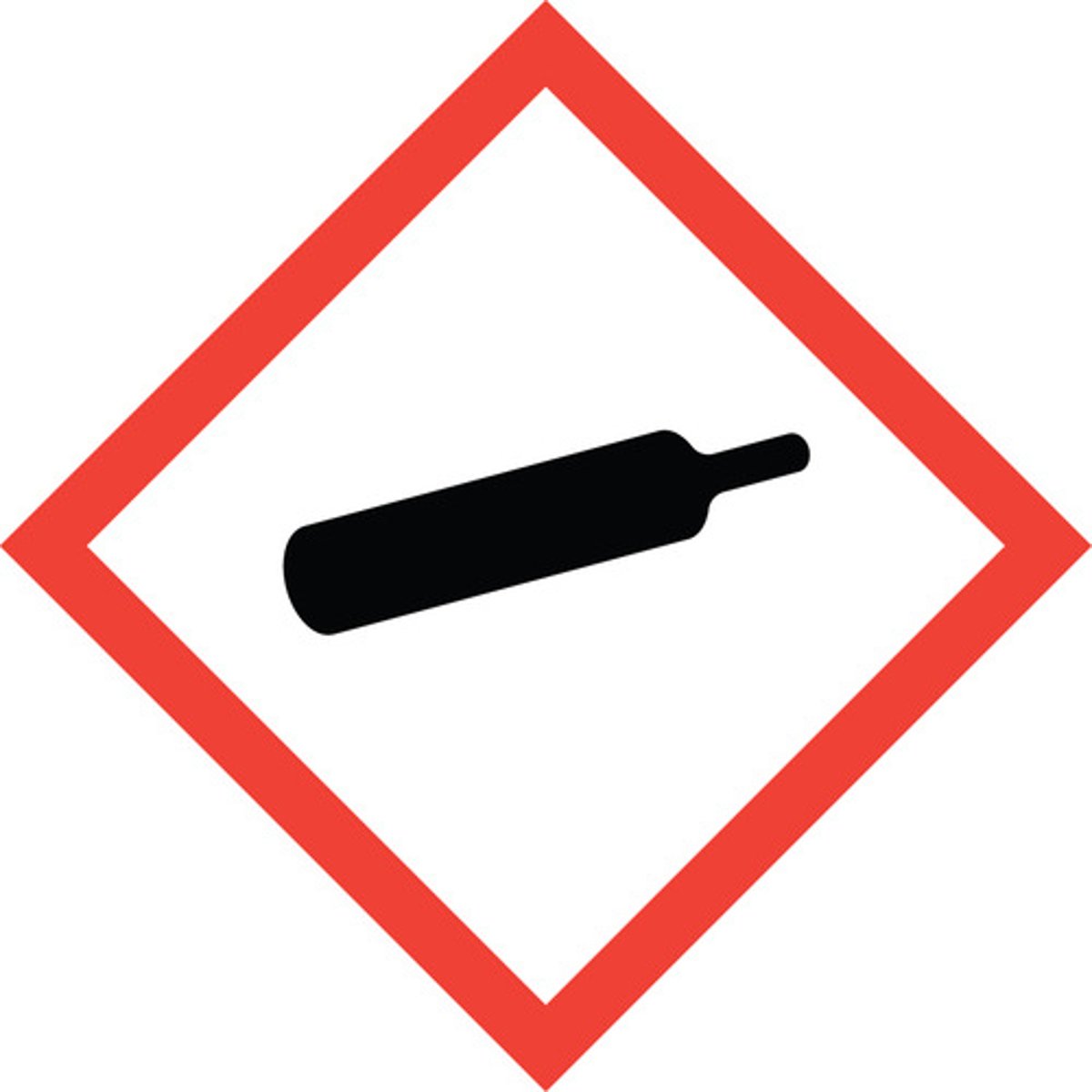
Gas Cylinder Symbol (Gases under pressure)

Corrision symbol
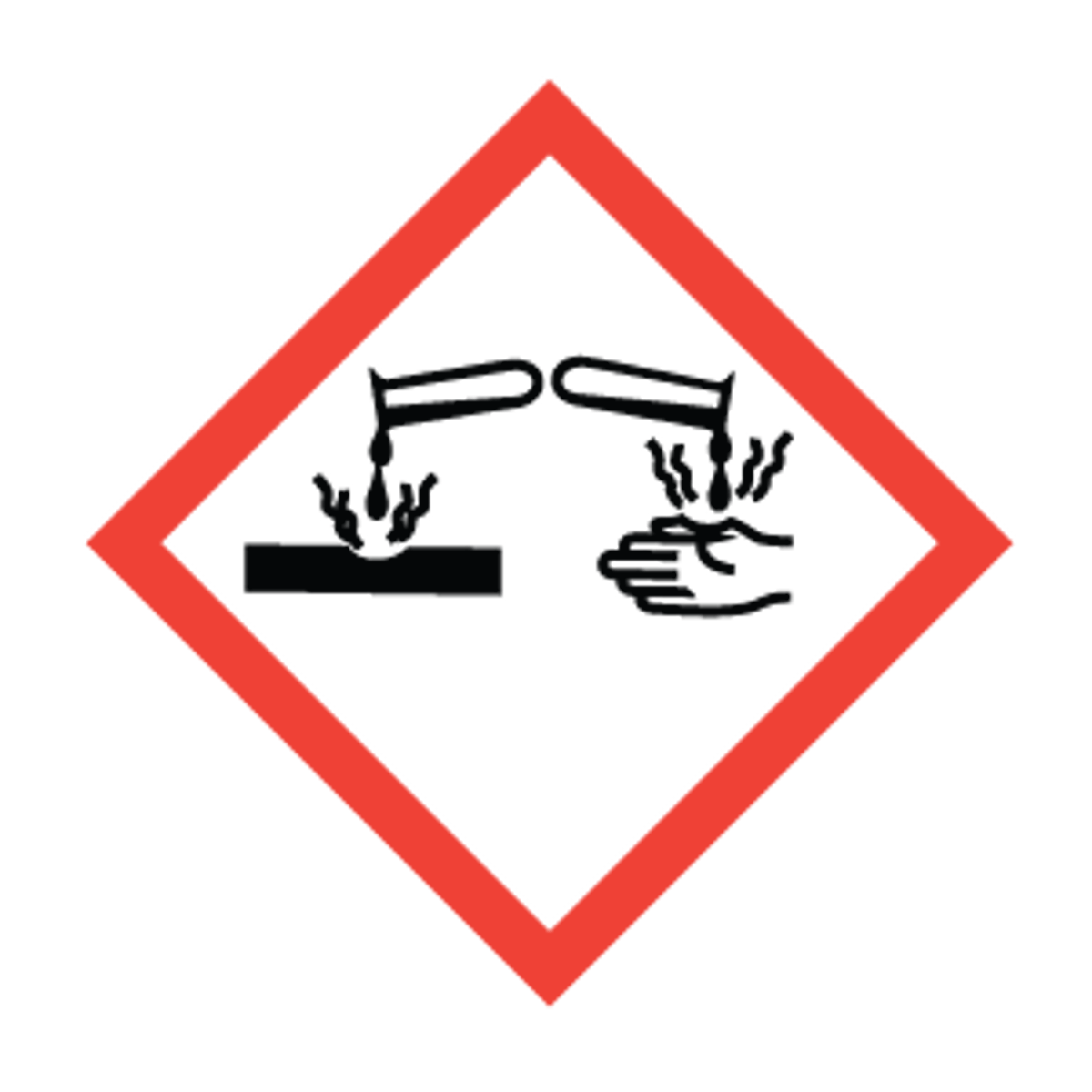
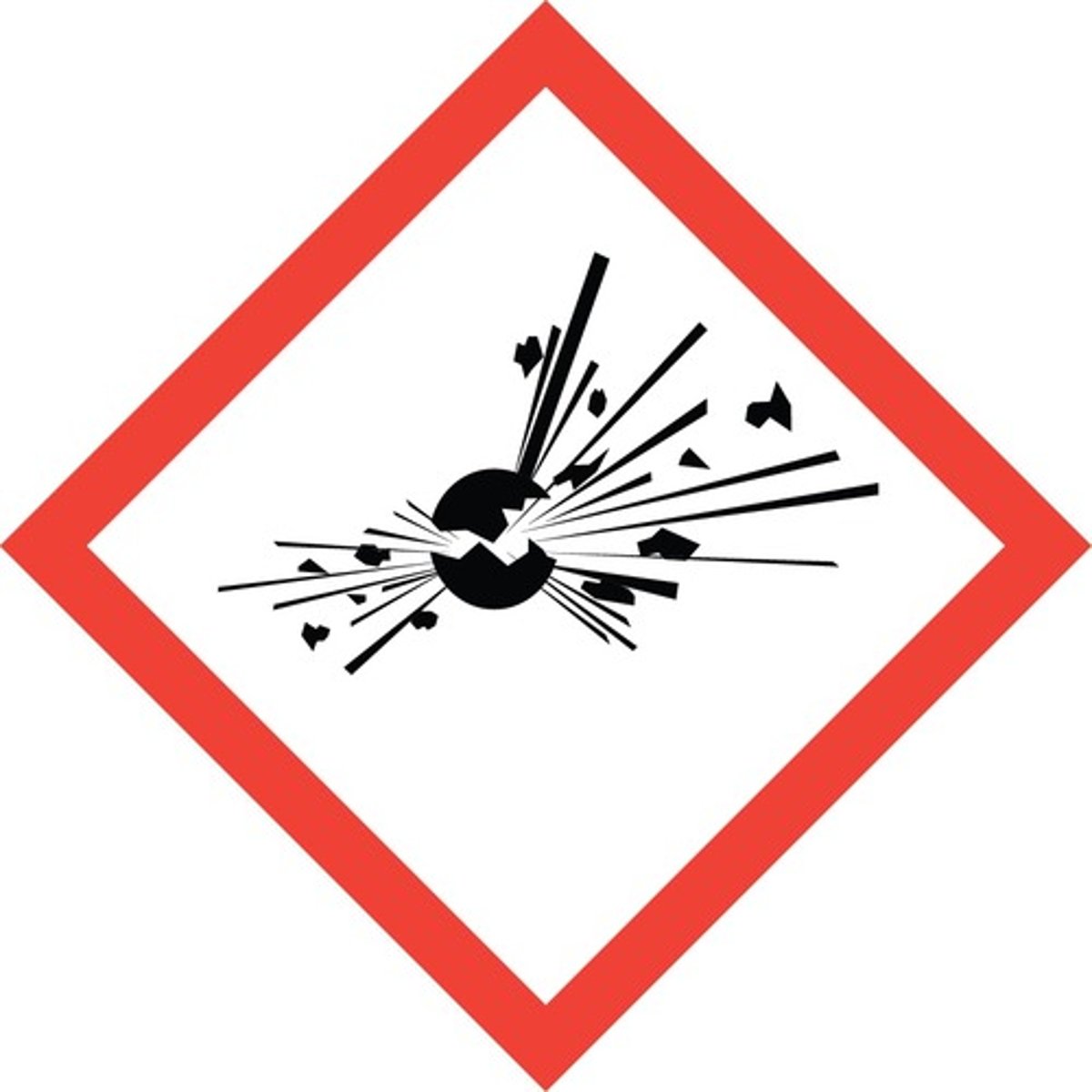
Exploding bomb symbol

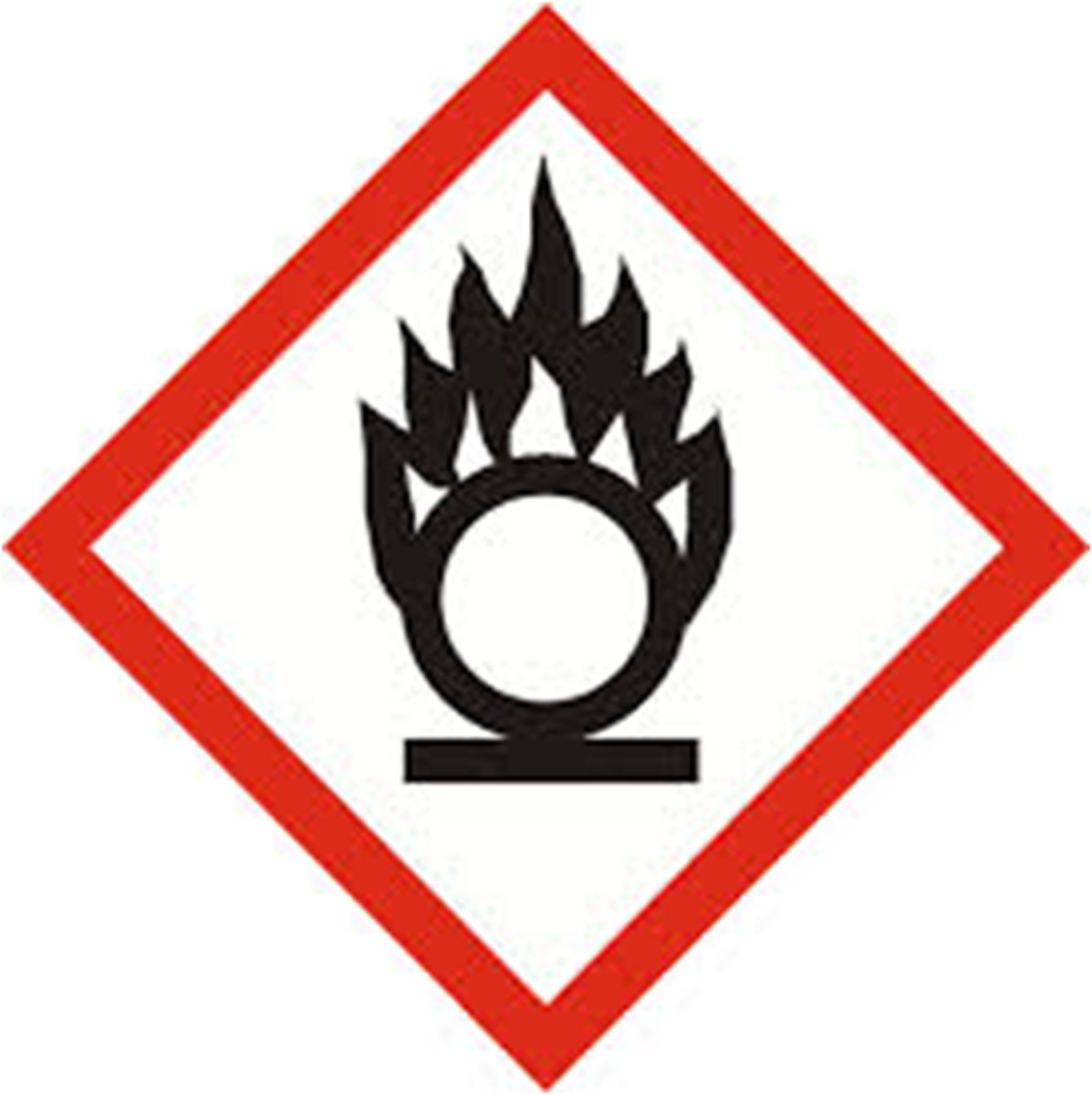
Flame over circle symbol (oxidizers)

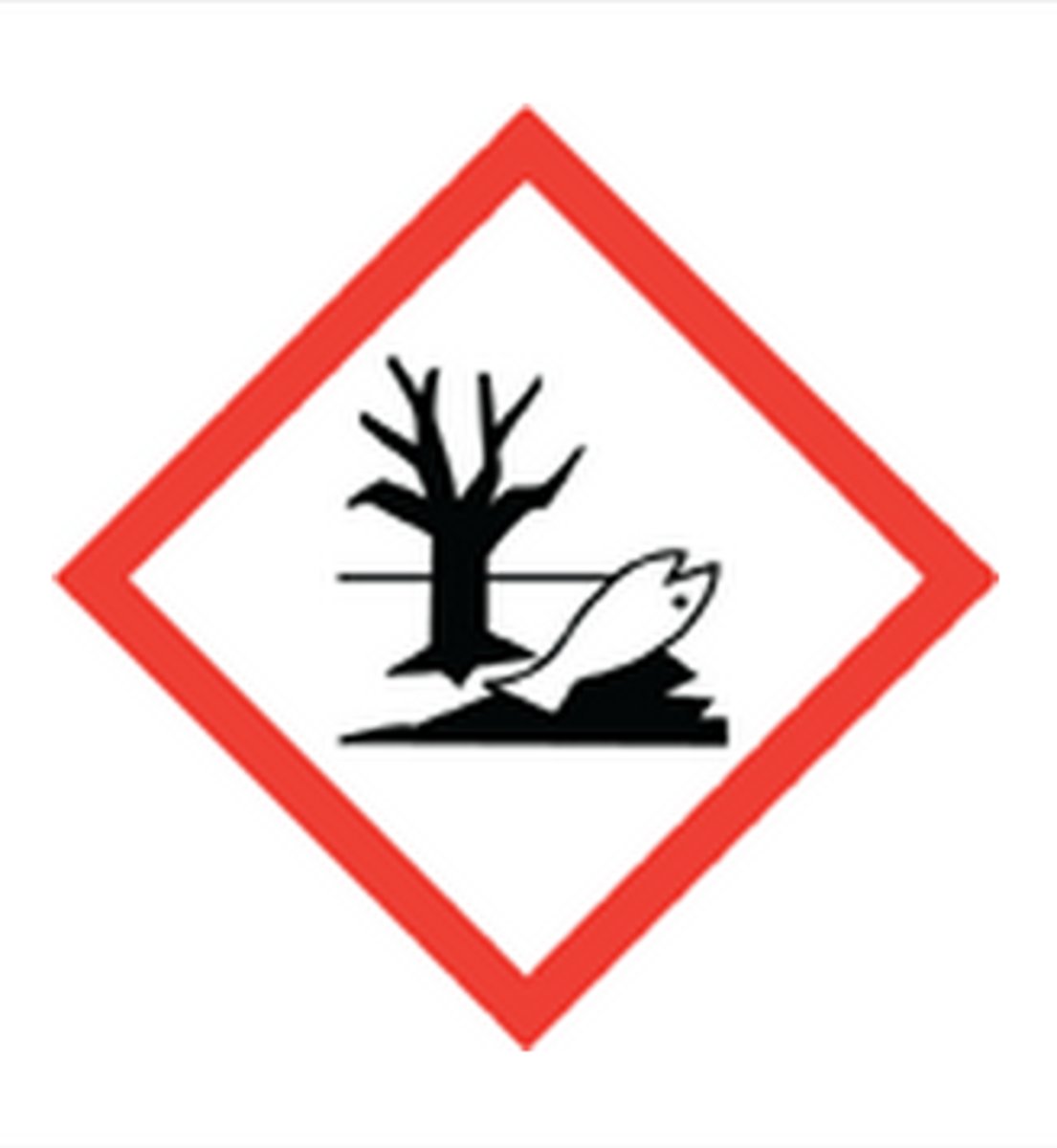
Enviorment hazard symbol

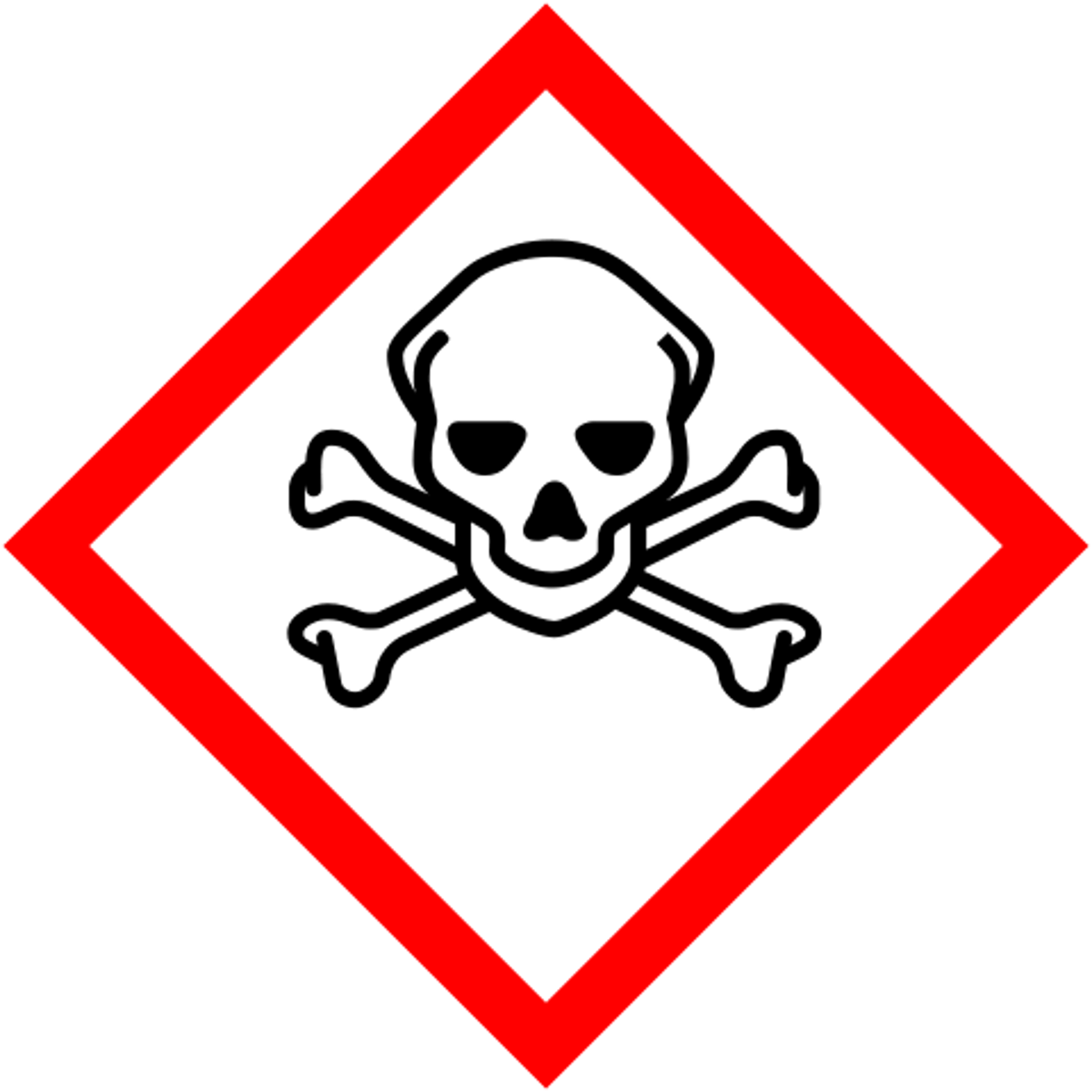
Acute toxicity symbol (fatal)

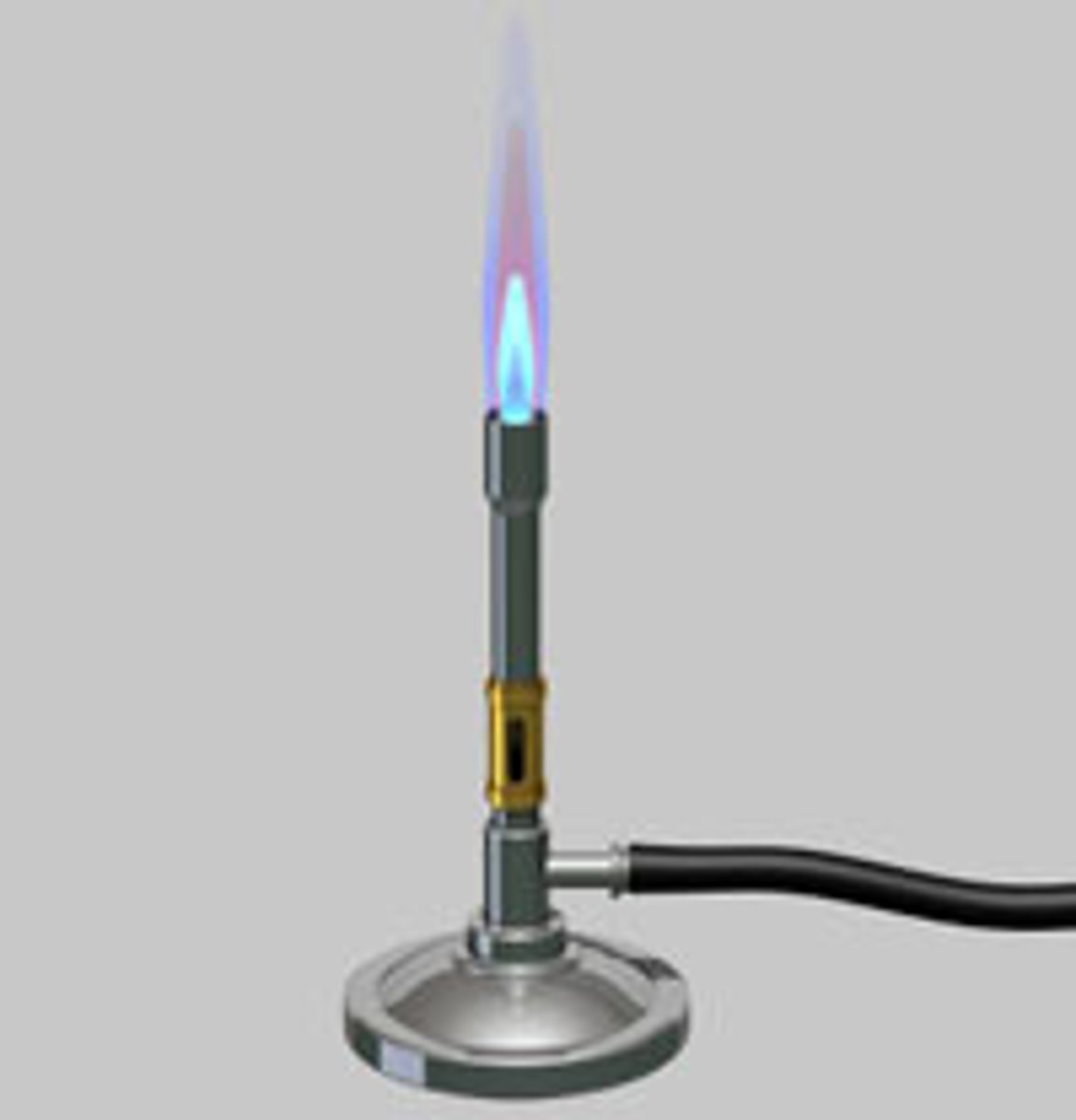
Bunsen Burner
ambient air gas burner used as laboratory equipment

Ring Stand
act as a versatile and stable support for holding glassware and other apparatuses during experiments

Evaporating Dish
facilitate the removal of a solvent (like water) from a solution through evaporation, leaving behind a more concentrated solution or a solid precipitate

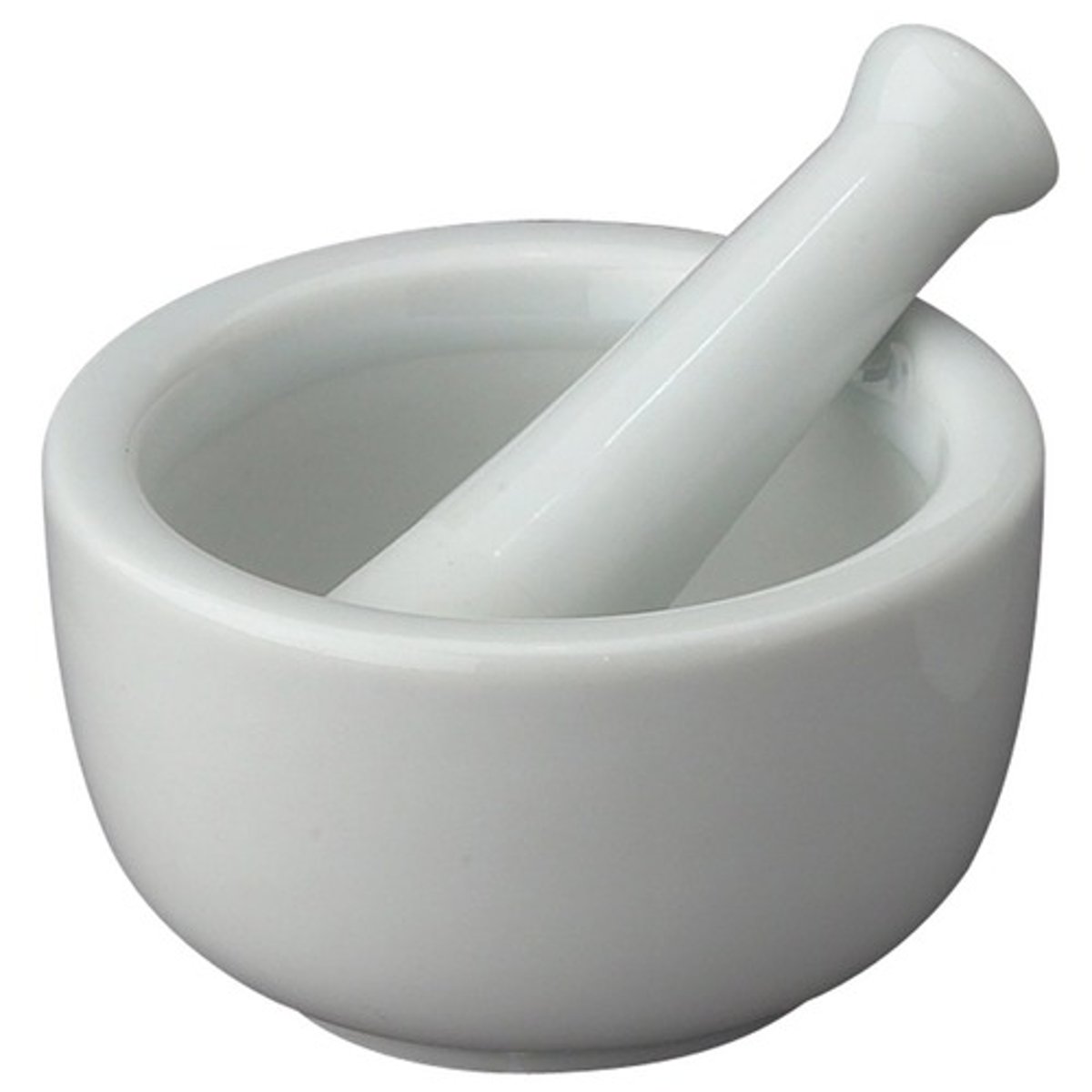
Mortar and Pestle
to crush, grind, and mix ingredients or substances into a fine paste or powder

Wire Gauze
support and evenly distribute heat to glassware, protecting it from direct flame contact and preventing breakage due to heat shock

Buret
a tool that precisely measures and delivers variable volumes of liquid

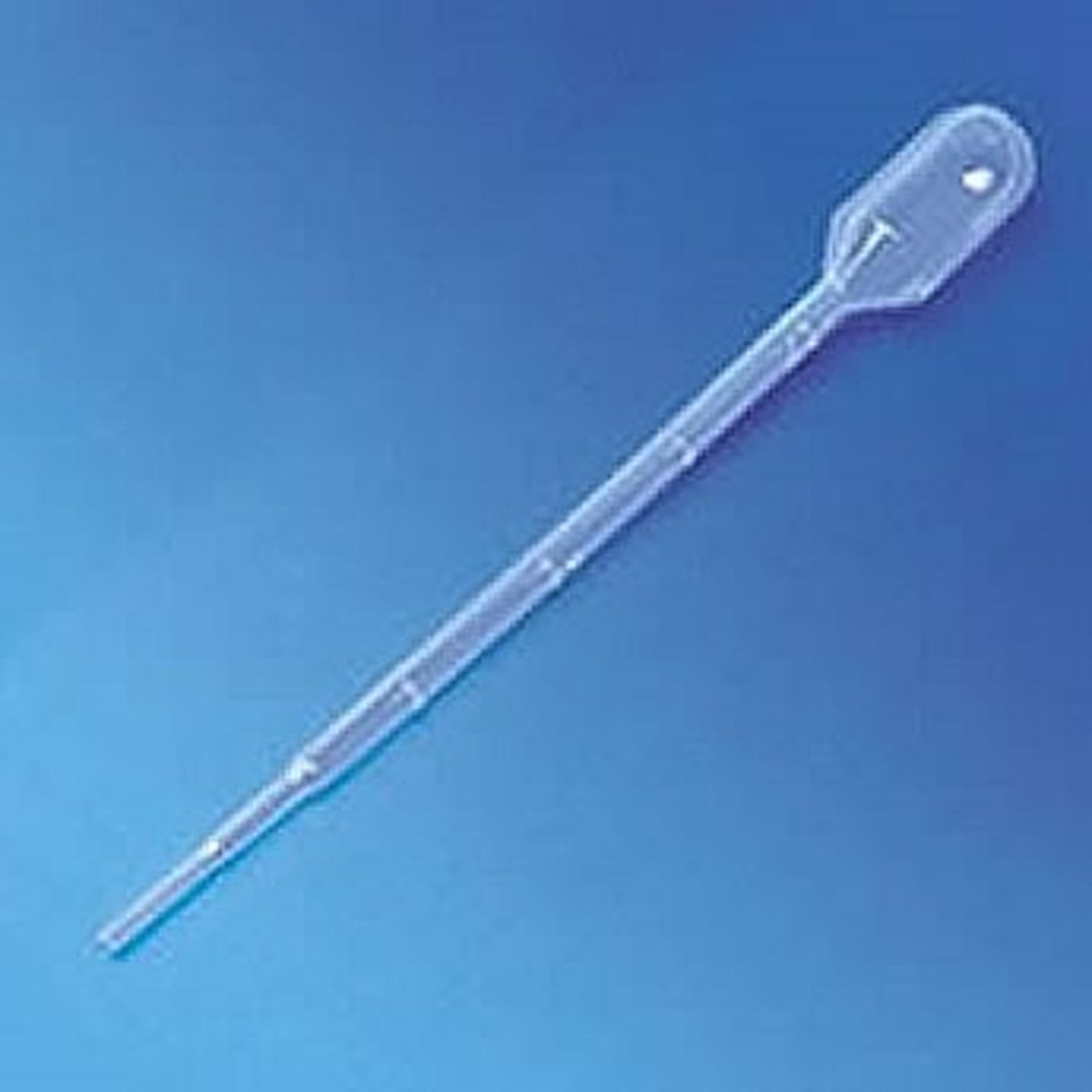
Pipette
transfer small quantities of liquids
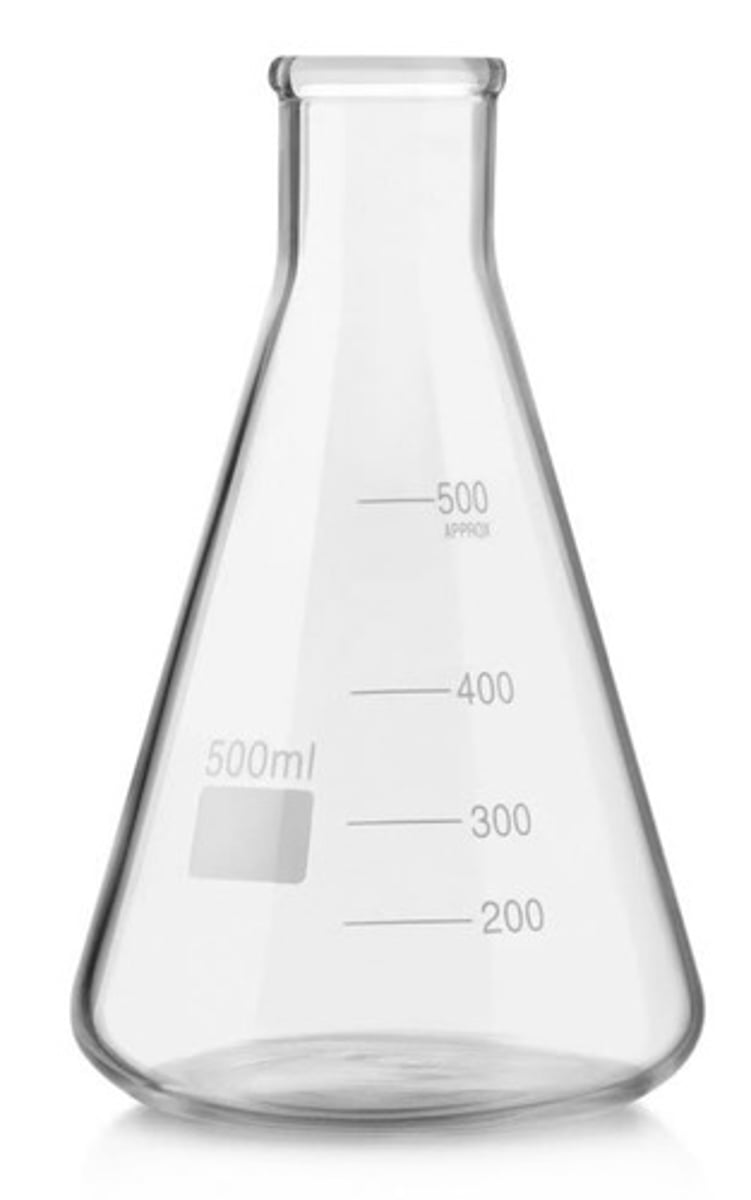
Erlenmeyer Flask
a flat bottom, a conical body, and a cylindrical neck. Its function is to hold, mix, and heat liquids

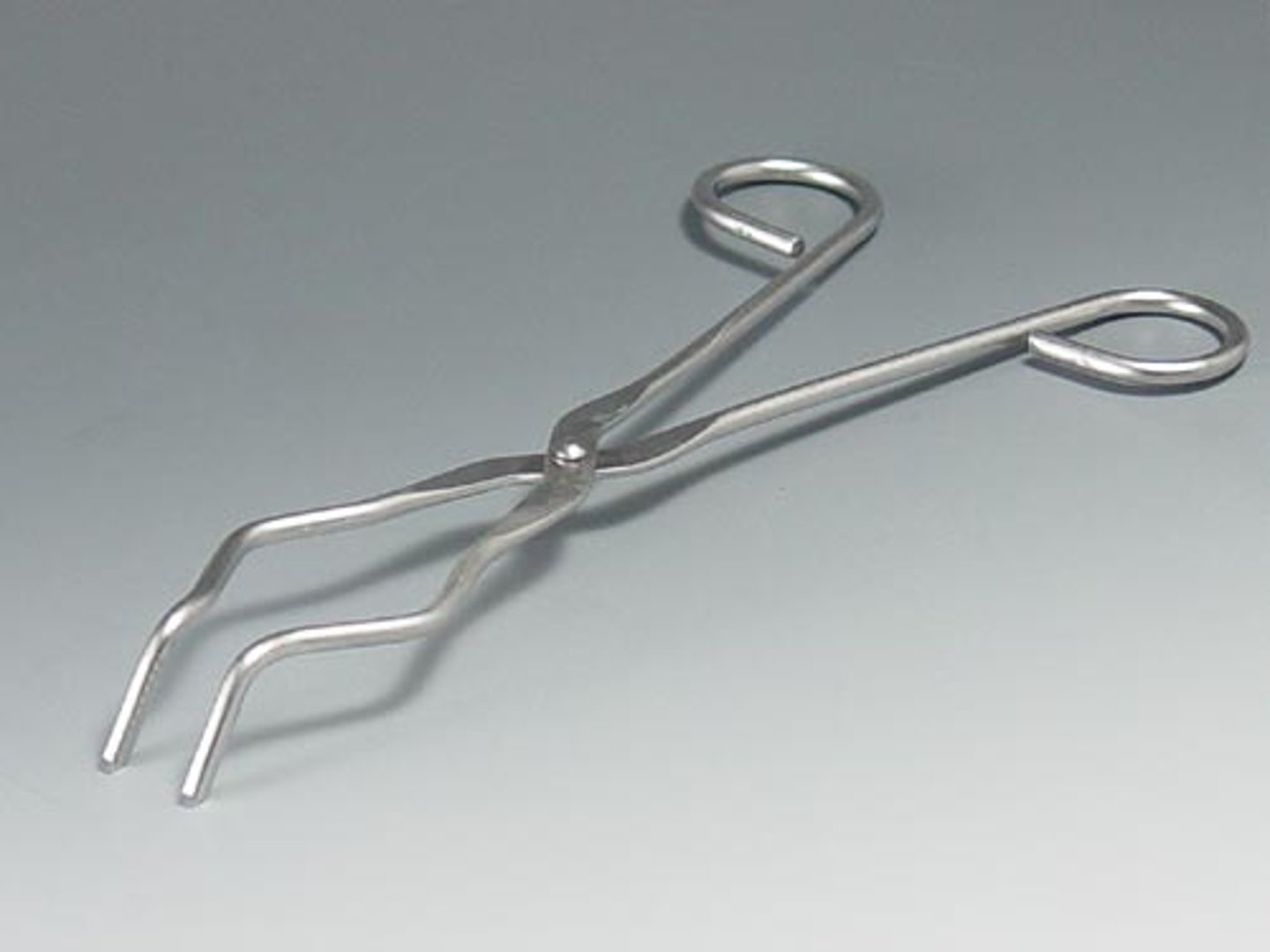
Tongs
a tool to securely grip, lift, and manipulate objects

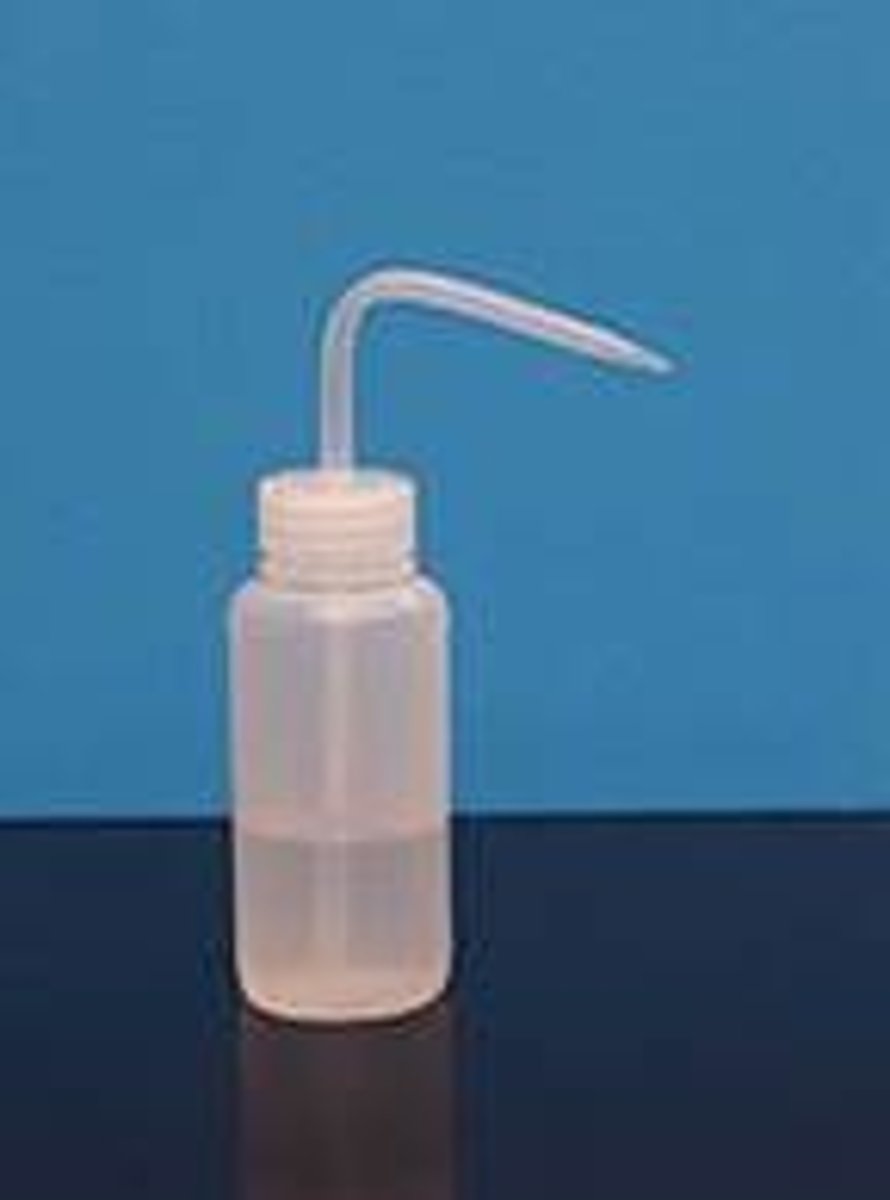
Wash bottle
to deliver a small, controlled stream of liquid, usually water or a solvent, for rinsing, cleaning

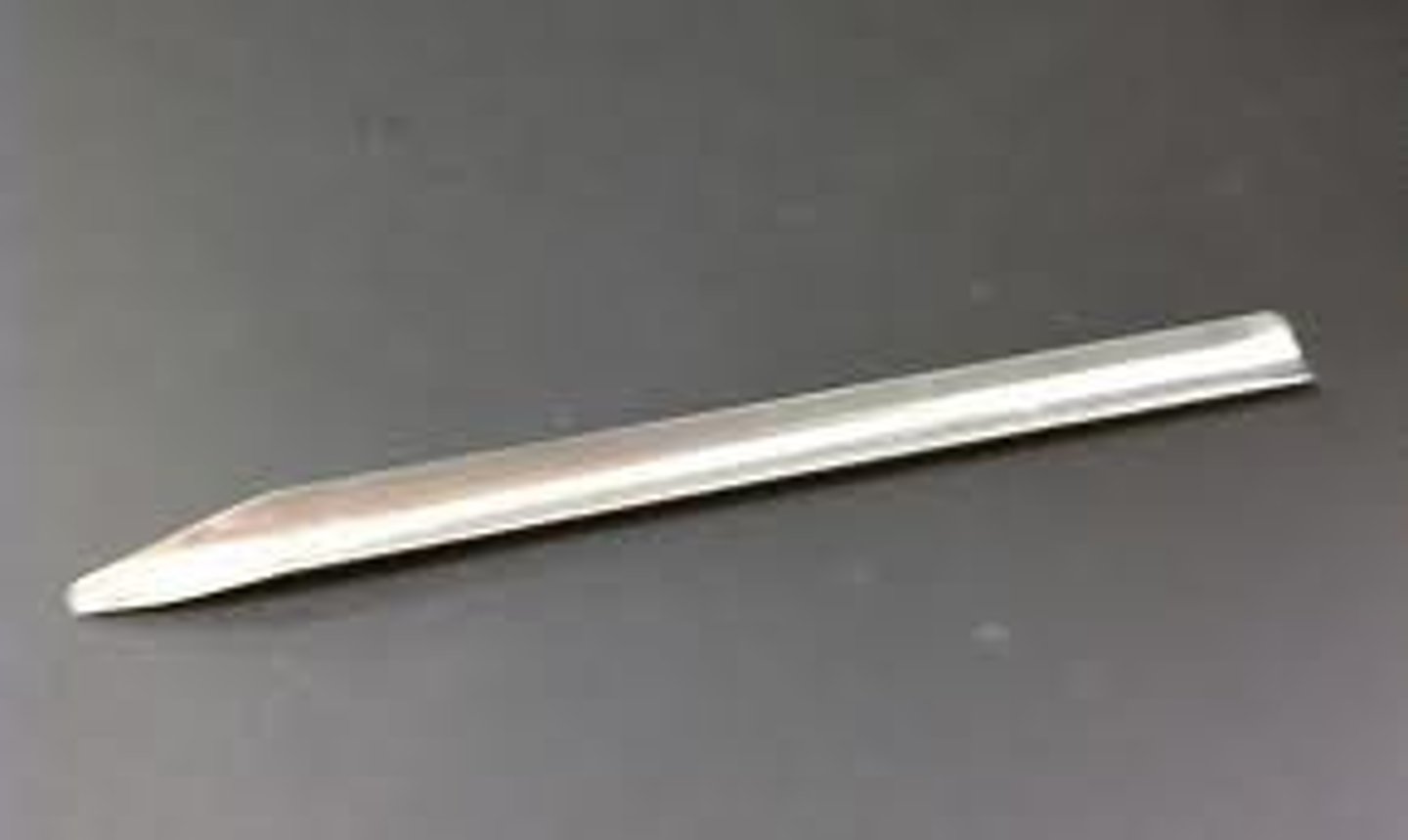
Scoopula
to safely and precisely transfer small quantities of solid chemicals, like powders or crystals

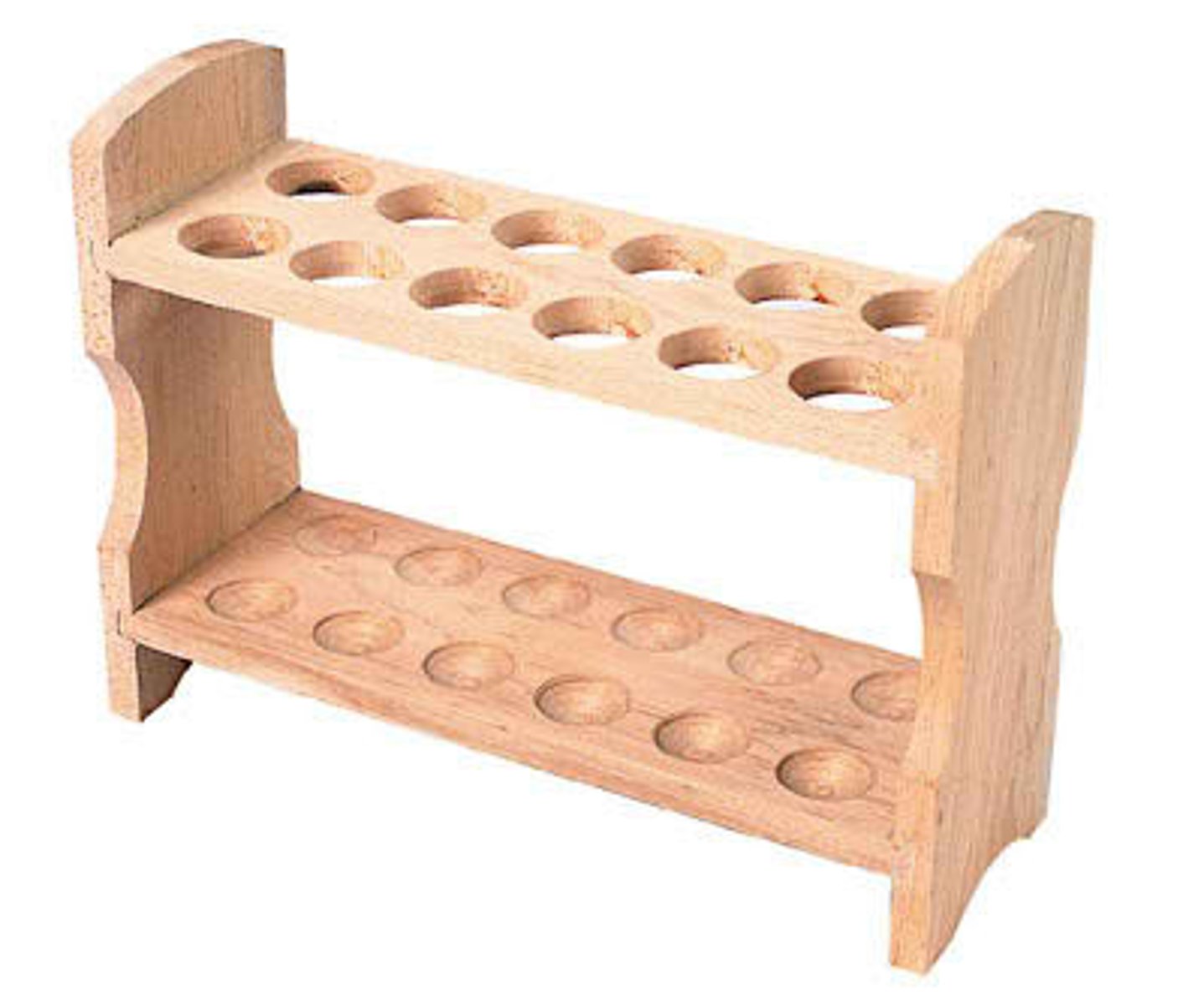
Test Tube

Test tube holder/clamp
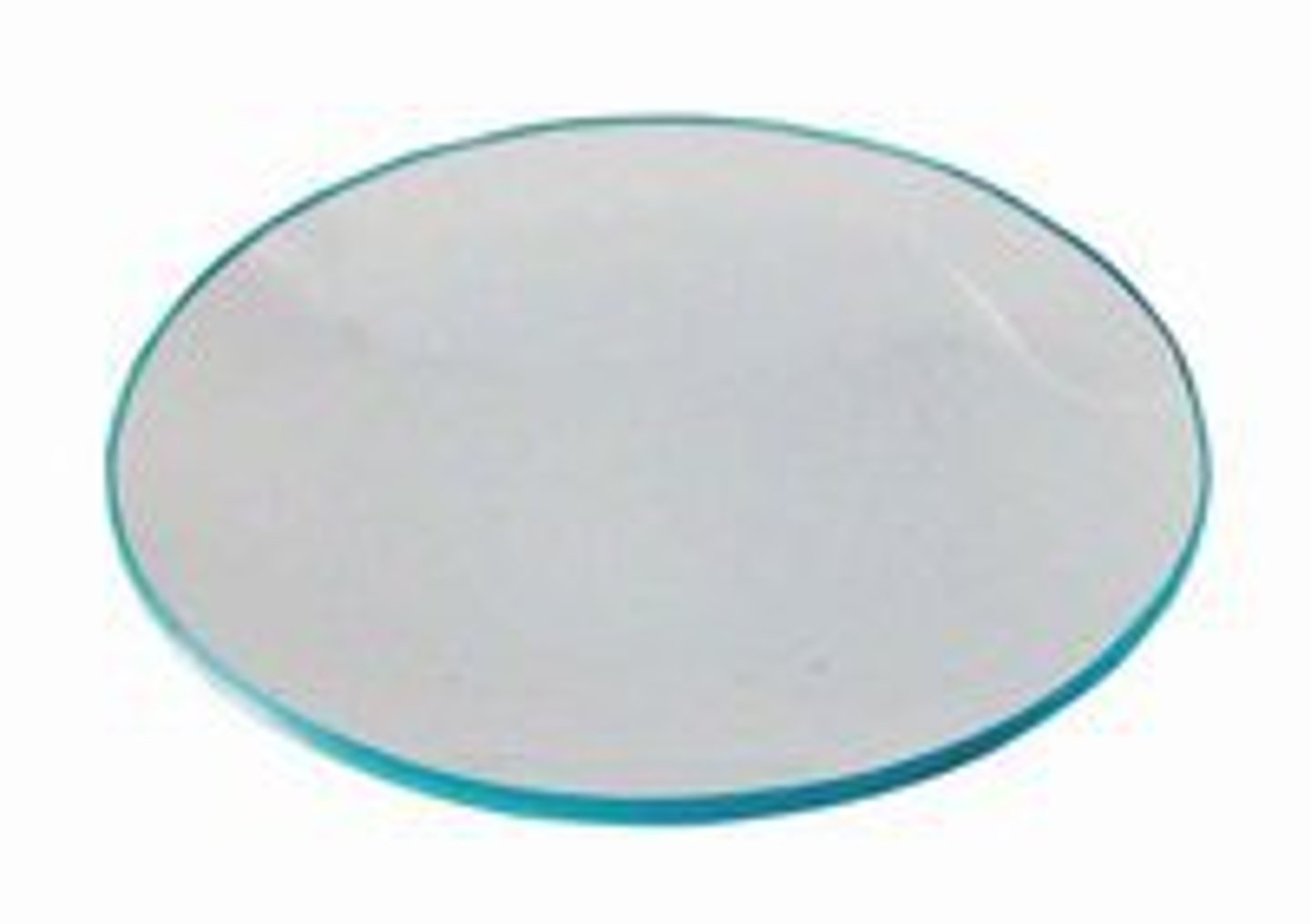
Watch Glass
evaporating small amounts of liquid, weighing solids, heating substances, and covering beakers or flasks to prevent contamination

Beaker
hold, mix, heat, and pour liquids during scientific experiments

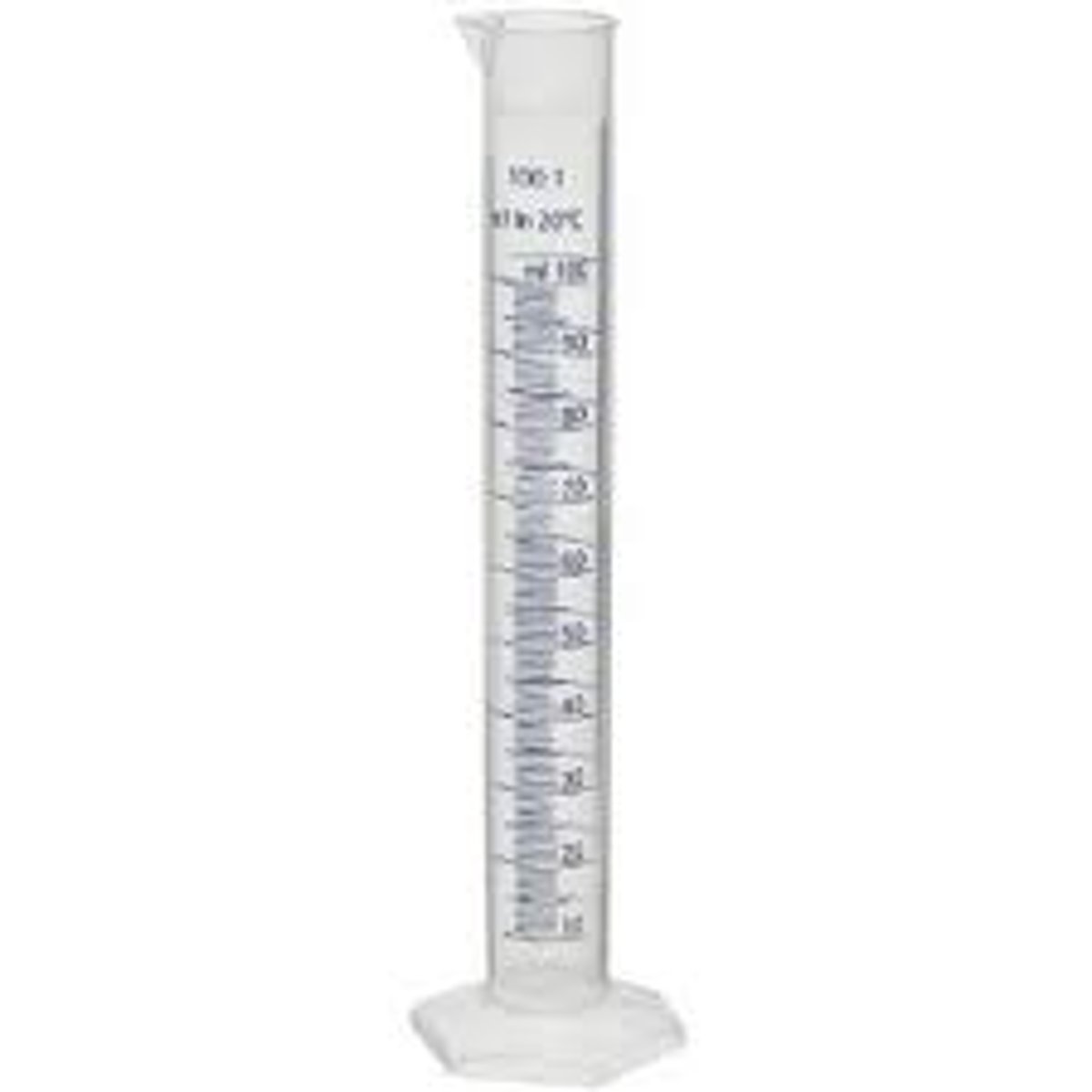
Graduated Cylinder
hold, mix, heat, and pour liquids during scientific experiments

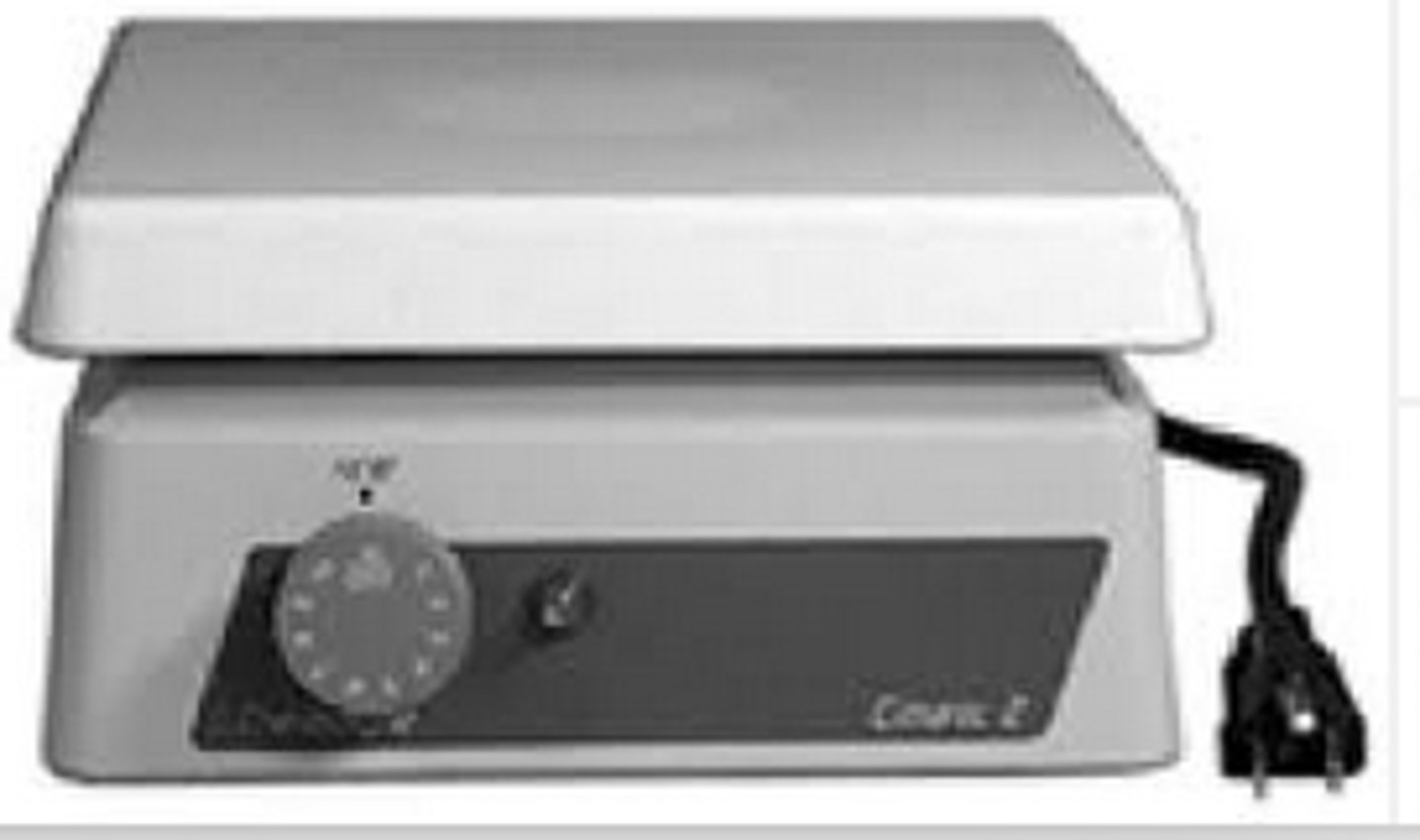
Hot plate
provide controlled, consistent heating for laboratory or cooking applications, using an electric heating element under a flat surface

Test tube rack

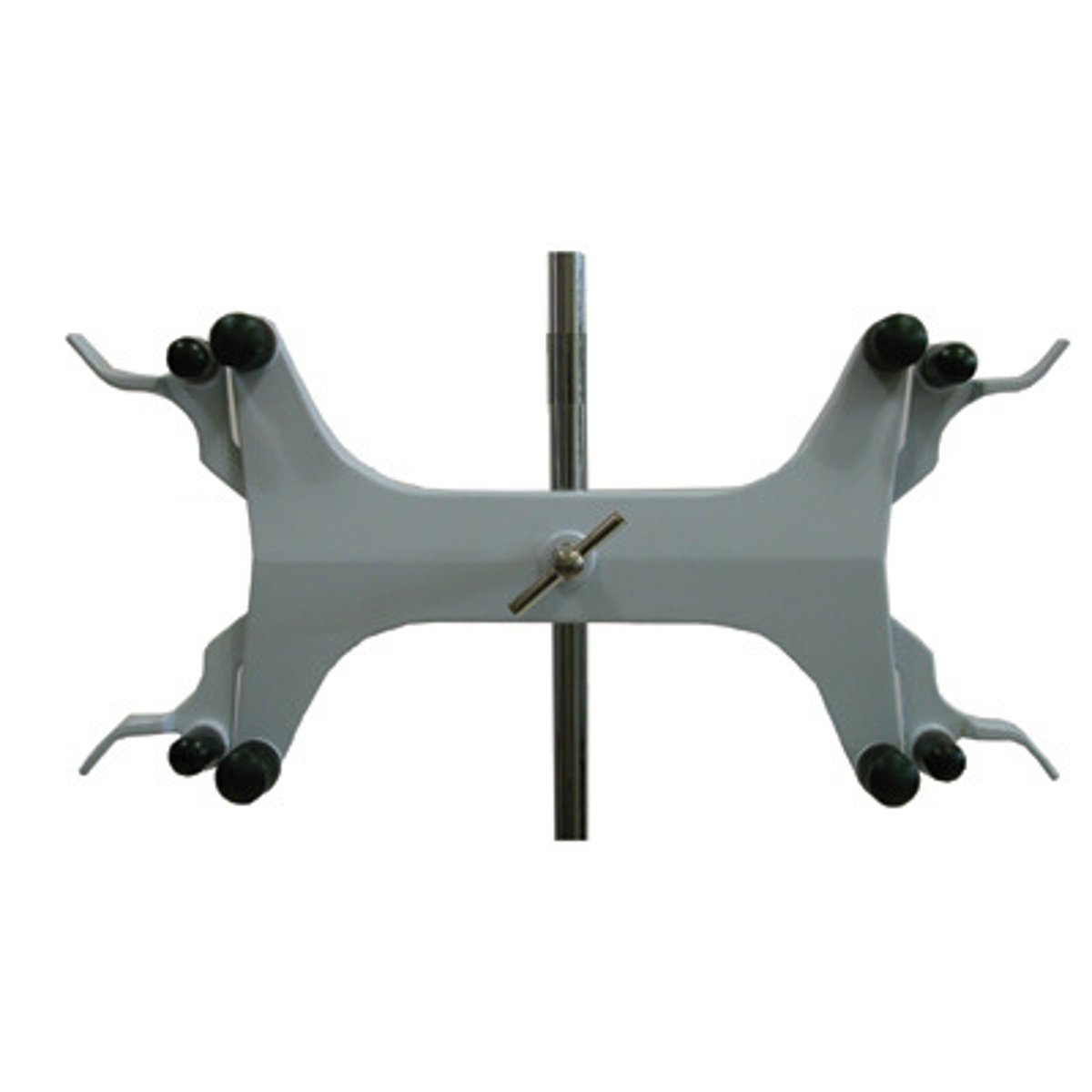
Buret clamp
securely holds a burette to a ring stand or support rod during laboratory experiments

Weighing boat
facilitate precise measurements by allowing easy and complete transfer of samples, preventing loss and cross-contamination, and providing a stable surface to avoid spills
