MK323 Midterm
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
221 Terms
value cocreation
consumers act as collaborators with a manufacturer or retailer to create the product
customer relationship management (CRM)
focuses on identifying and building loyalty among the firm's most valued customers
upstream strategic decisions
- where is the market opportunity
- who are the target customers?
a producer focused selling concept makes profits through _________ ____________
sales volume
marketing plan
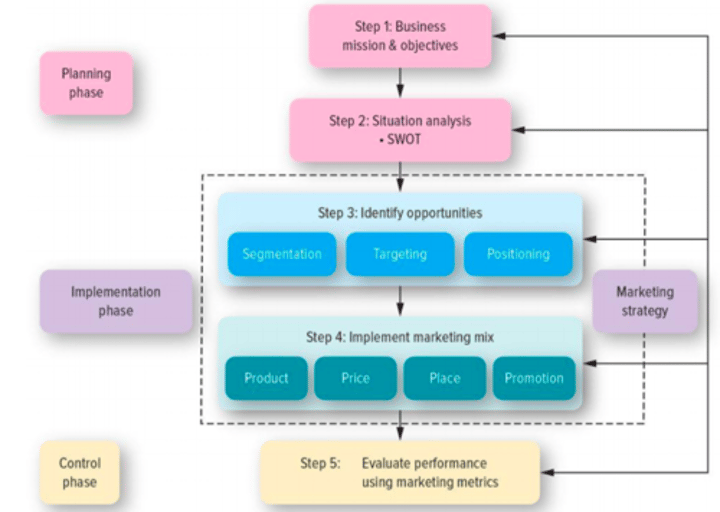
what are the 3 phases and 5 steps in the marketing plan?
planning phase
1. define business mission + objectives
2. conduct situation analysis (SWOT)
implementation phase
3. identify + evaluate opportunities
4. implement marketing mix + allocate resources
control phase
5. evaluate performance using marketing metrics
business mission (objectives)
sets growth goal in specific, measurable business terms
strategy
specifies means to achieve objective, characterized by a specific target market and marketing mix (4 Ps)
tactics
details day-to-day operational decisions essential to overall success of marketing strategies
metrics
assess success by measuring key results in terms of changes (yearly, monthly)
bcg growth-share matrix

describe stars from the bcg growth-share matrix
- require heavy resource investment
- as growth slows, will move to heavy generators of resources and become cash cows
describe cash cows from the bcg growth-share matrix
- already received heavy investments
- excess resources can be spun off to products that need it
marketing
activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, capturing, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large
marketing mix (4 Ps)
1. Product
2. Price
3. Promotion
4. Place
B2B marketing
selling products from business to business
B2C marketing
selling products from business to consumer
downstream strategic decisions
- what are the benefits customers want?
- how should the product be priced
true or false: marketing has shifted focus from consumer to producer
false
- producer to consumer
a consumer focused marketing concept makes profits through ______________ ______________
customer satisfaction
describe question marks from the bcg growth-share matrix
- require significant resources
- must decide to infuse with resources generated by cash cows so they become stars or withdraw resources to phase out
describe dogs from the bcg growth-share matrix
- not destined for stardom
- should be phased out unless needed to complement or boost sales of another product or for competitive purposes
strategic growth matrix
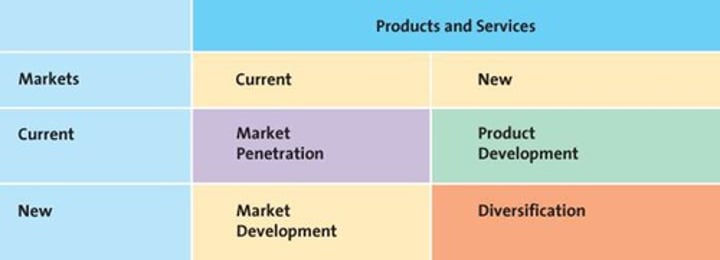
describe market penetration from the strategic growth matrix
increasing consumption frequency often a key to growth
- ex. Arm + Hammer putting reminders on packaging to replace baking soda
describe product development from the strategic growth matrix
firms develop products to leverage brand, add revenue within current target market
- ex. Old Spice launched line of men's grooming products
describe market development from the strategic growth matrix
explore demand in new markets for growth
- ex. Dunkin' expanded internationally
describe diversification from the strategic growth matrix
new products in new markets means more complexity
- ex. 3M releases new product innovators
marketing strategy
identifies target markets, related marketing mix, and bases to build sustainable competitive advantage
sustainable competitive advantage
advantage over the competition that is not easily copied and can be maintained over a long period of time
4 strategies to develop sustainable competitive advantage
1. customer excellence
2. operational excellence
3. product excellence
4. locational excellence
STP
segmentation, targeting, positioning
market segmentation
dividing market into groups of customers with different needs, wants, or characteristics
target marketing
evaluates each segment's attractiveness and decides which to pursue
market positioning
defining marketing mix to give customers a clear, distinctive, desirable understanding of what the product does in comparison to competing products
integrated marketing communications (IMC)
encompasses a variety of communication disciplines to provide clarity, consistency, and maximum communicative impact
5 steps of marketing research process
1. defining objectives + research needs
2. designing research
3. data collection process
4. analyzing data + developing insights
5. action plan + implementation
primary data
gives insight about local, specific context
secondary data
collected prior to start of focal research project, gives broader context
data collected from the US census would be an example of _____________ data
secondary
data collected from an interview on the OneClub would be an example of _________________ data
primary
qualitative data
aim for explanation, context, surprises, new ideas, insight
- ex. focus groups, reviews, interviews, social media
quantitative data
aim for prediction, generalizability, quantifying
- ex. surveys, A/B tests, sales data
syndicated data
secondary data available for a fee from commercial research firms
observation
examining purchase and consumption behaviors by video or tracking customer's movements electronically
survey
systematic means of collecting information from people using a questionnaire
questionnaire
document with a set of questions designed to gather information from respondents and accomplish objectives
unstructured v. structured questions
open ended to answer with own words v. closed ended for evaluation
experimental research
systemically manipulates one or more variables to determine which variables have a causal effect on other variables
what are the advantages and disadvantages of primary research?
advantages- specific to needs, offers behavioral insights
disadvantages- costly, time-consuming, requires training
what are the advantages and disadvantages of secondary research?
advantages- time-saving, free/inexpensive
disadvantages- not precise/timely/original, may be biased
big data
data sets too large and complex to analyze with conventional data management software
data warehouse
large computer files that store big data
data mining
statistical tools to analyze variables in big data databases
5 Vs of big data
1. volume
2. variety
3. velocity
4. veracity
5. value
marketing analytics
analyzes data for marketer to improve decision making, optimize returns, and make appropriate customer-related decisions
descriptive analytics tools
help firms organize, tabulate, and depict available data into easy-to-understand visuals
- ex. excel
predictive analytics tools
rely on historically available data to forecast the future
prescriptive analytics tools
analyses that use simulations, which ask a series of what if questions and optimization techniques to find the best result
active analytics tools
AI algorithms used to analyze input gathered by the Internet of Things
- ex. amazon alexa
neuromarketing
examining consumers' brain patterns to determine responses
convenience sampling
no guarantee each member of the population will have the same chance of being included
- ex. you survey everyone in one Core class
probability sampling
every member of the population has a known, non-zero probability of being selected
- ex. you survey BU students randomly selected by BUID
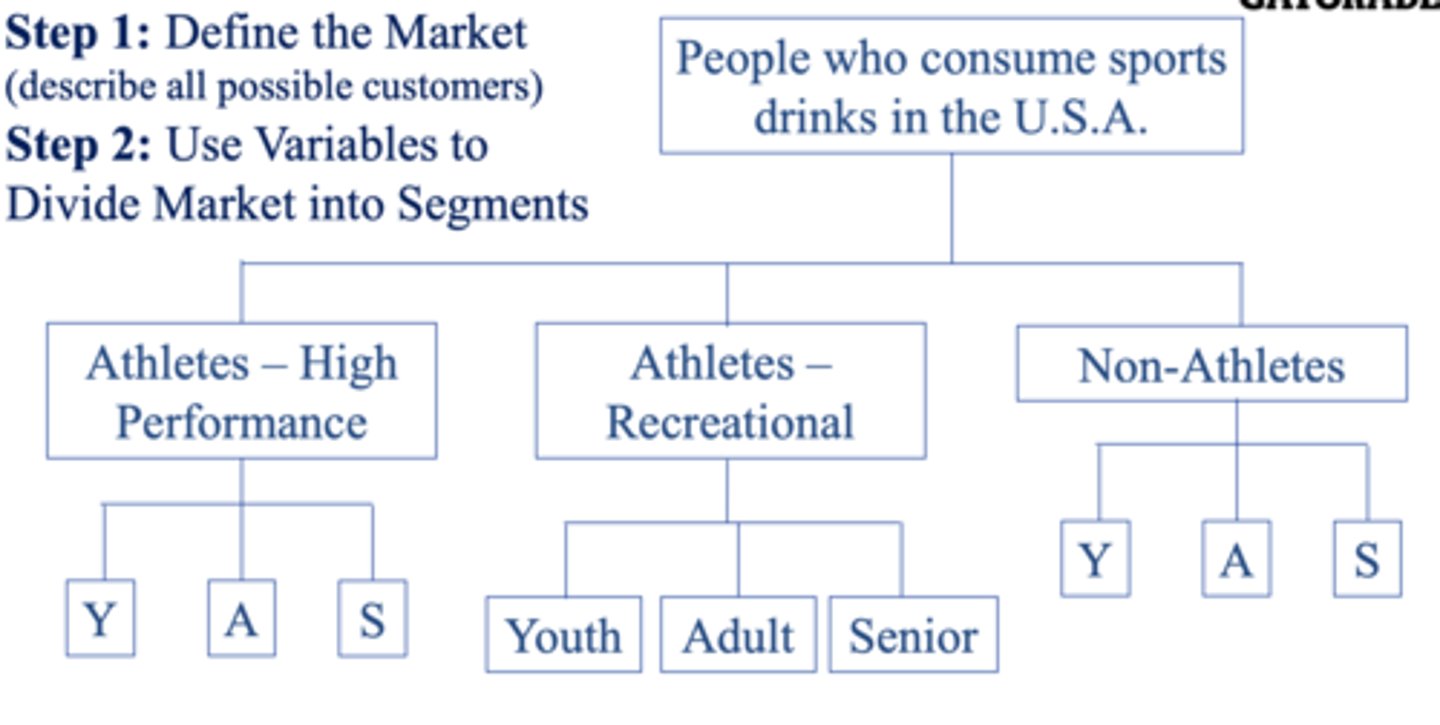
STP process
segmentation
1. set objective or strategy
- SWOT
2. select key segmentation variables
3. create segmentation tree + grid
- estimate size, reachability
targeting
4. evaluate segment attractiveness
5. select target market
positioning
6. identify + develop positioning
- establish value proposition
geographic segmentation
where customers live
- ex. country, region, state
demographic segmentation
easily measured, objective characteristics
- age, gender, income
_______________ segmentation is the most common way to define segments because they are easy to identify and reach
demographic
psychographic segmentation
how customers describe themselves
- ex. eco-friendly, dairy-free, health-conscious
3 components of psychographics
1. self-values
- goals for life
2. self-concept
- image of oneself
3. lifestyles
- way one lives
benefit segmentation
benefits consumers derives from products
- ex. nutrition, texture, taste
behavioral segmentation
how consumers use a product
- ex. heavy/light user
occasion segmentation
type of behavior segmentation based on when a product is purchased/consumed
loyalty segmentation
type of behavioral segmentation that invests in loyalty initiatives to retain most profitable customers
market basket analysis
mathematical modeling techniques that determines association between a group of items usually purchased
geodemographic segmentation
combines geographic, demographic, and lifestyle characteristics to classify consumers
what 5 descriptive criteria do marketers look at when determining if a segment is worth pursuing?
is the segment identifiable, substantial, reachable, responsive, and profitable
undifferentiated targeting strategy (mass marketing)
no need to develop separate strategies for different groups
differentiated targeting strategy
target several market segments with a different offering for each
concentrated targeting strategy
single, primary target market to focus all energy on
value proposition
communicates benefits to be received and provides reasons to purchase
main value proposition components
1. target market
2. offering name or brand
3. category or concept
4. unique point of difference/benefit
perceptual map
displays the position of products or brands in the consumer's mind
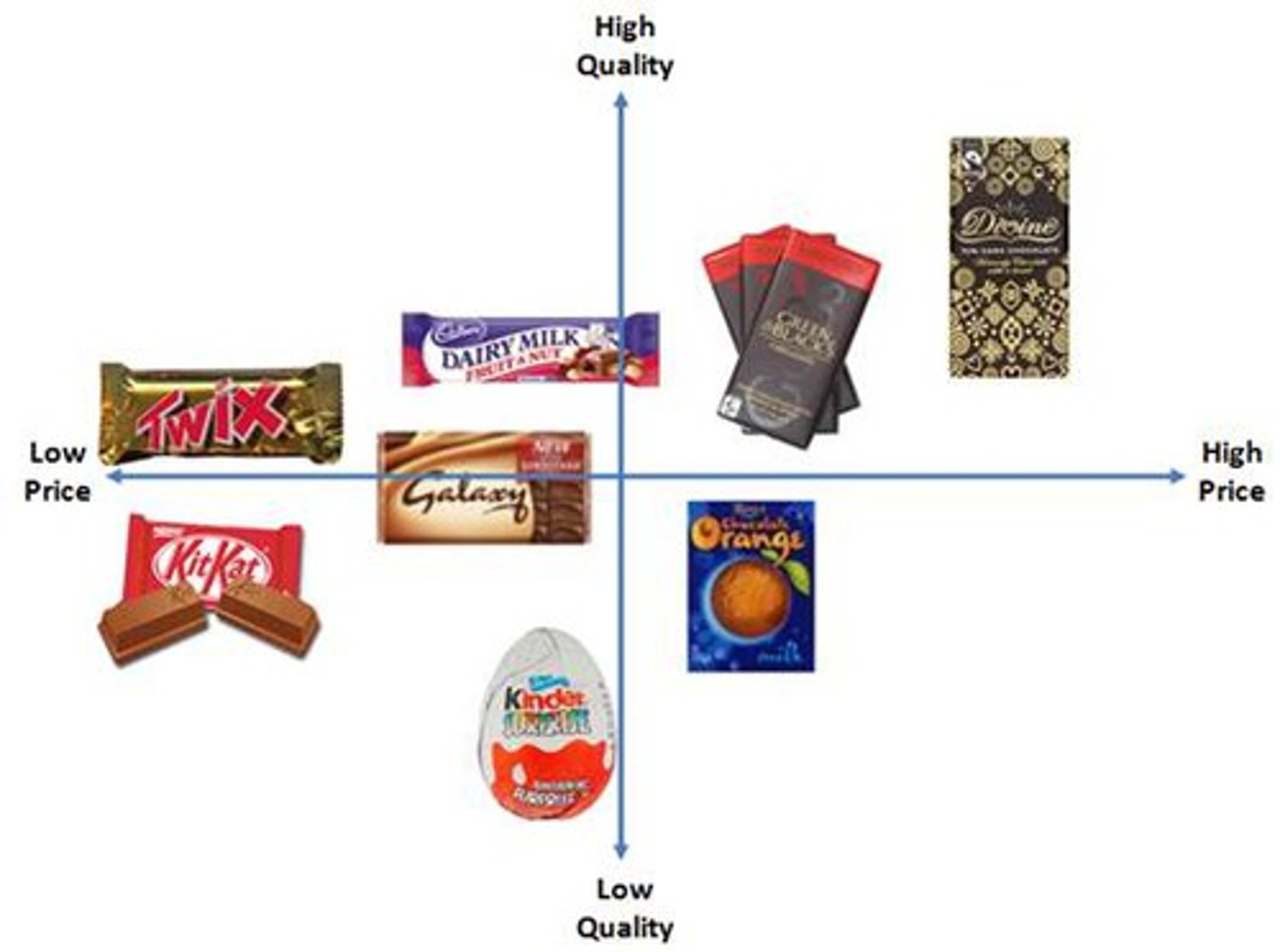
6 positioning steps
1. determine perceptions and evaluations in relation to competition
2. identify market's ideal points and size
3. identify competitors' positions
4. determine consumer preferences
5. select position
6. monitor positioning strategy
segmentation tree
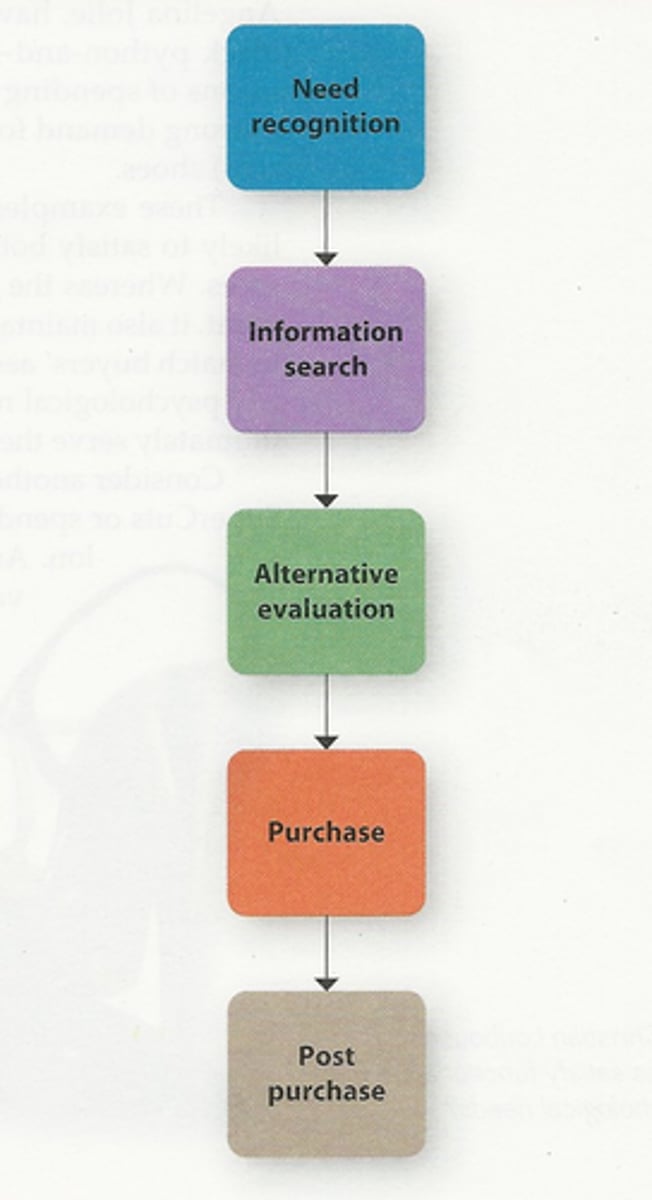
5 steps of consumer decision-making process
1. need recognition
2. information search
3. alternative evaluation
4. purchase
5. post-purchase
the greater the discrepancy between a _________ state and ___________ state, the greater the need recognition
needy; desired
functional needs
pertain to performance of product/service
psychological needs
pertain to personal gratification consumers associate with product/service
internal information search
buyer examines their own memory and knowledge through past experiences
external information search
buyer seeks information outside their personal knowledge base
internal locus of control
believe they have some control over outcomes of their actions, thus engage in more search activities
external locus of control
believe that fate or other external factors control all outcomes
5 types of risk
1. performance
2. financial
3. social
4. physiological/safety
5. psychological
universal set
all possible choices for a product category
retrieval set
brands or stores readily remembered
evoked set
alternative brands or stores a consumer would consider when making a purchase decision
true or false: a company wants to be a part of the universal set
false:
- evoked set
evaluative criteria
consists of salient (important) attributes about a particular product
determinant attributes
important features that competing brands or stores are perceived to differ
consumer decision rules
criteria that consumers use to consciously or subconsciously select from several alternatives
compensatory decision rule
consumer trades off one characteristic against another such that good compensates for bad