Genetics Exam I
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Mitosis
Cell division that generates two genetically identical cells
Cell Cycle
G1 (Gap I): Phase of growth and metabolism
S phase: DNA synthesis (doubling of homologous chromosome pairs)
G2 (Gap II): Growth, DNA Checkpoint, and repair
M phase: Cell Division (mitosis)
Prophase (Mitosis)
Chromosomes condense and centrioles divide
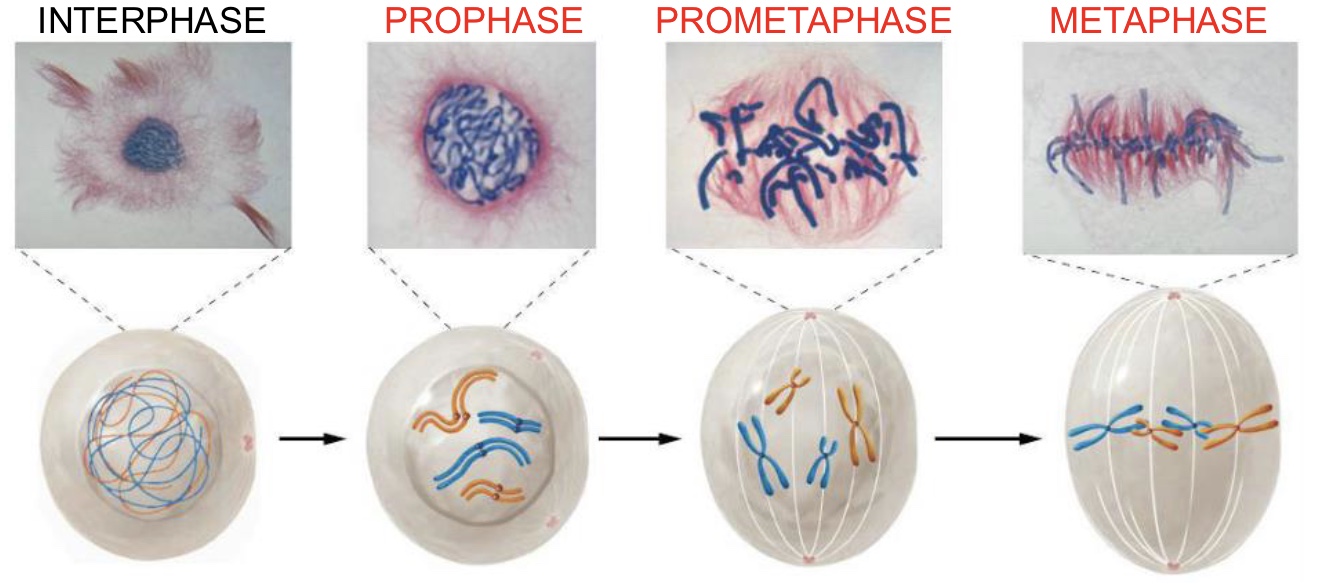
Prometaphase (Mitosis)
Fully condensesd chromosomes move toward the cell equator, centrioles reach opposite poles, and spindle fibers form
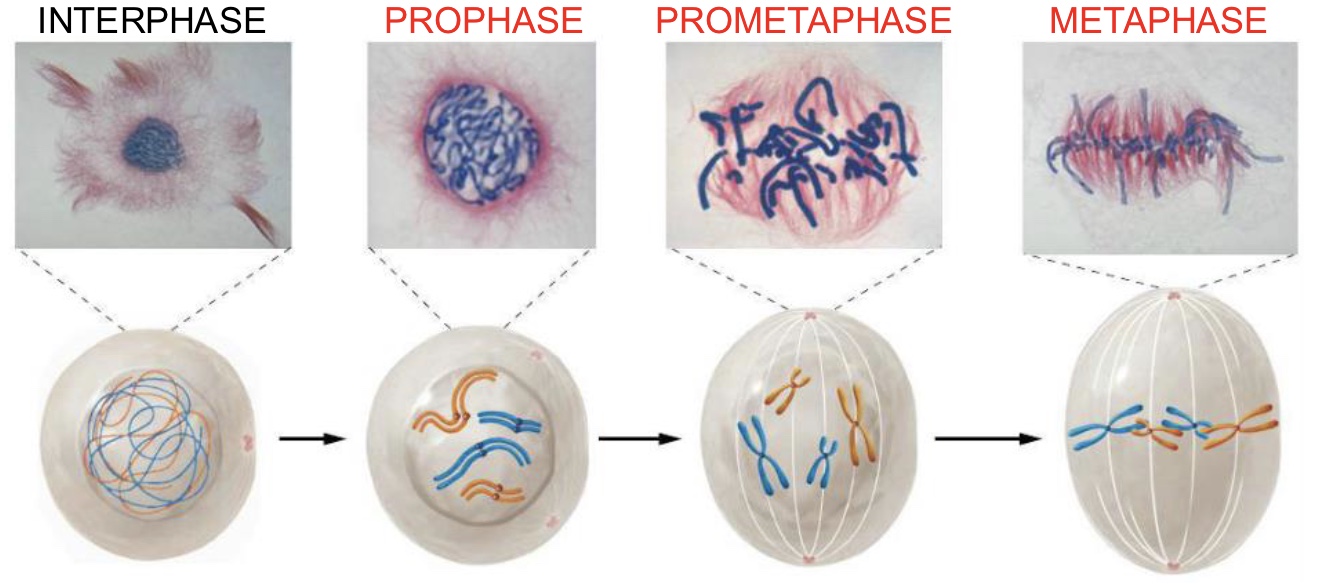
Anaphase (Mitosis)
Centromeres split and sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles
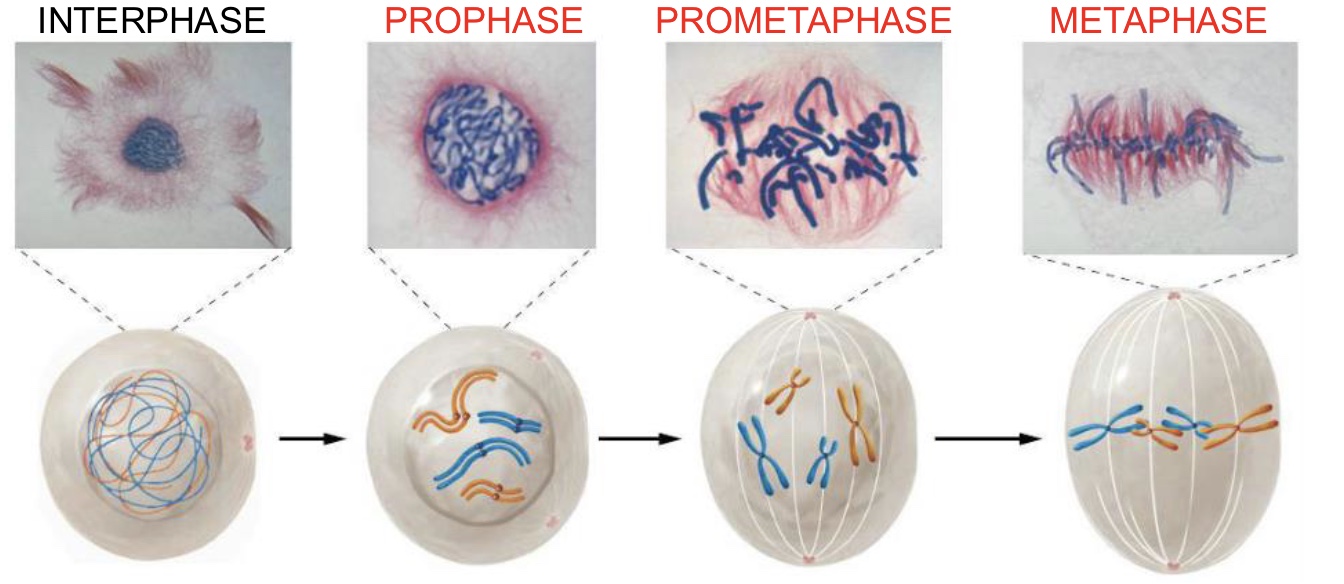
Telophase (Mitosis)
Chromosomes are at the poles and cytokinesis occurs
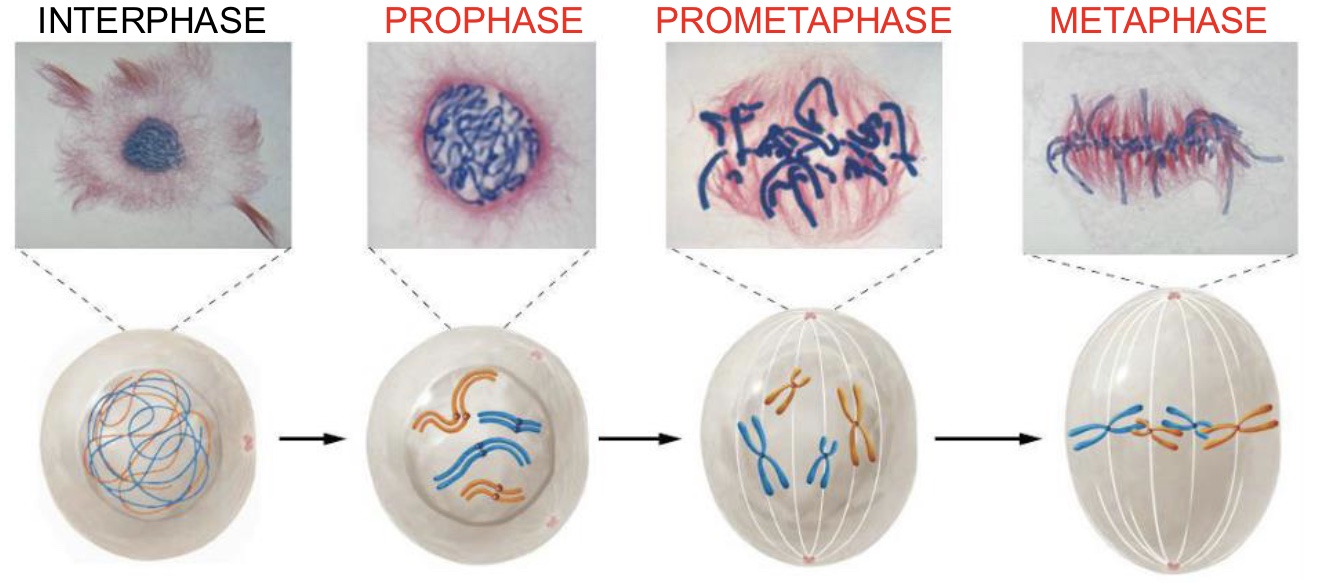
Cytokinesis (Mitosis)
Division of the cytoplasm
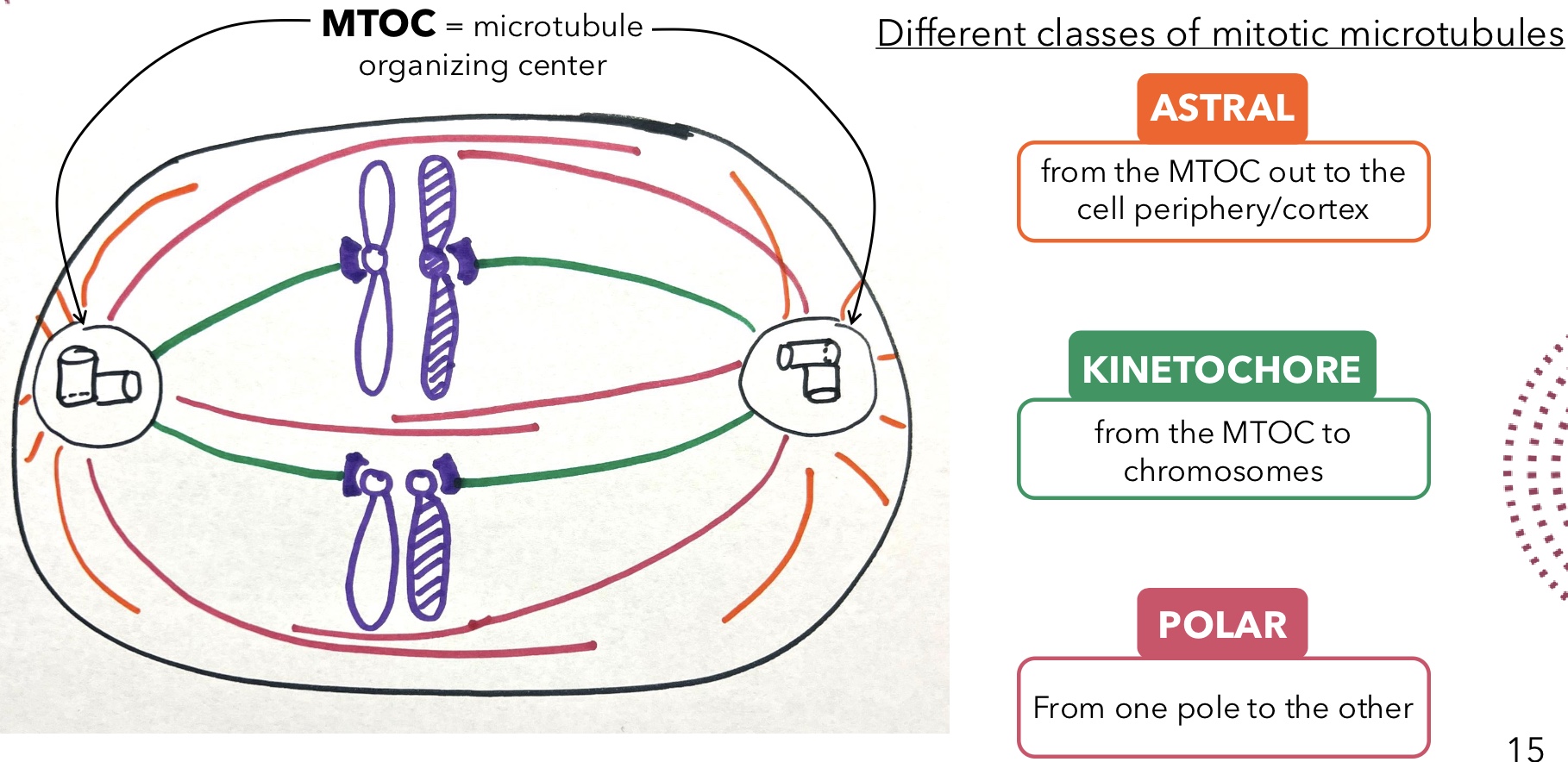
Astral Microtubules
Mitotic microtubules that extend from the MTOC out to the cell periphery/cortex
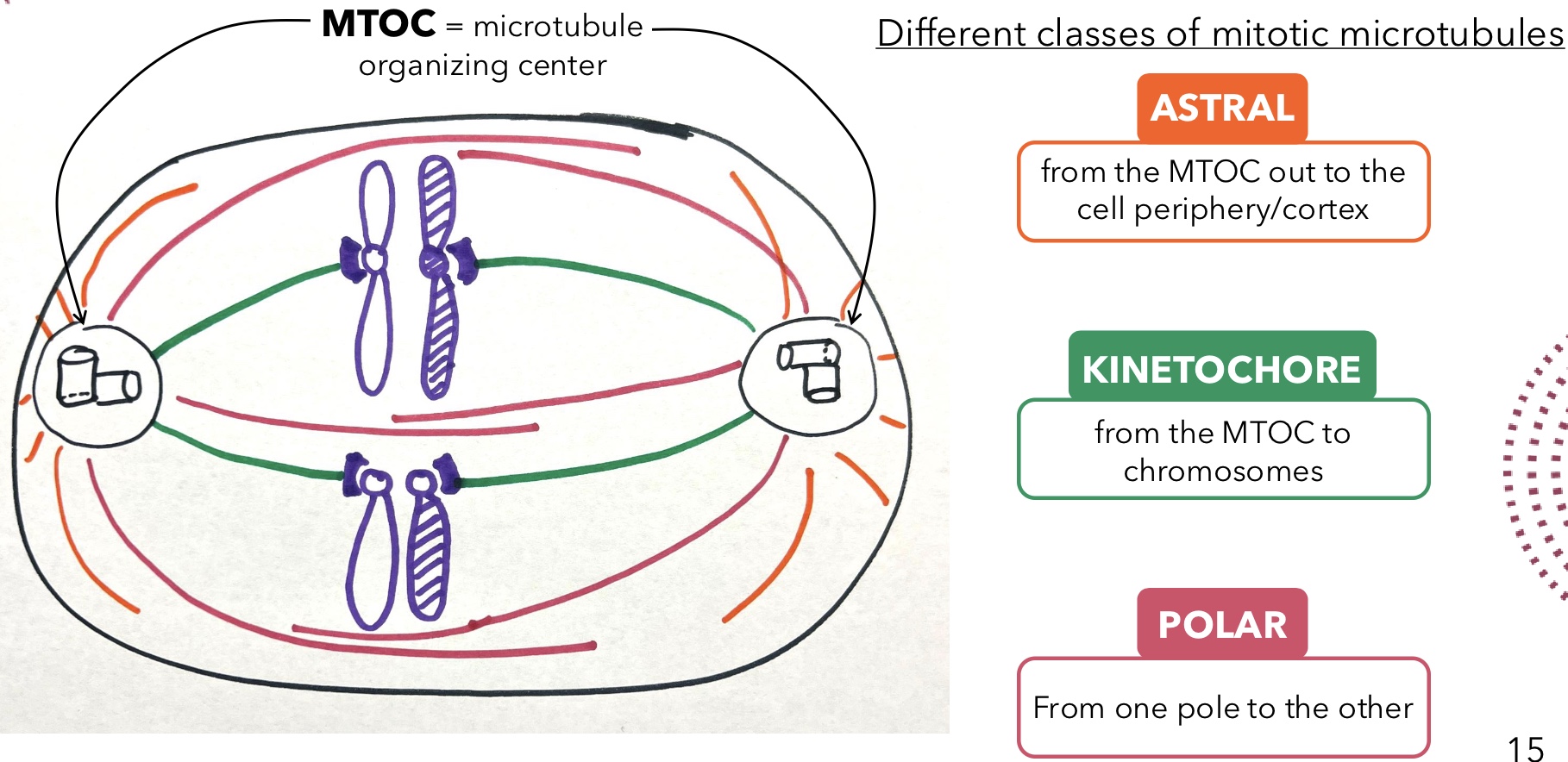
Kinetochore Microtubules
Mitotic microtubules that extend from the MTOC to chromosomes
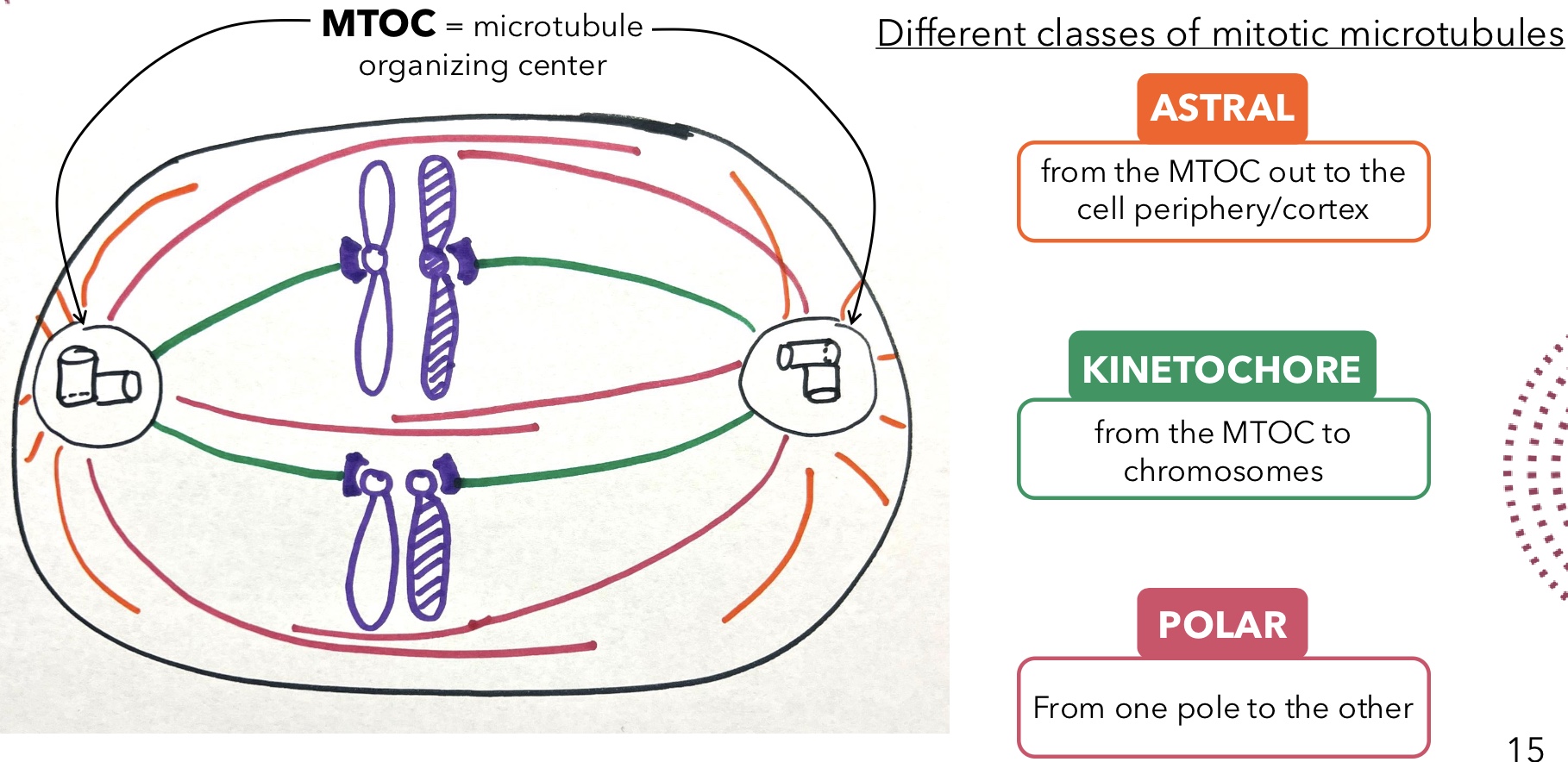
Polar Microtubules
Mitotic microtubules that extend from one pole to the other
Meiosis
Cell division that generates four, haploid cells
Meiosis I
First division in meiosis where homologous chromosomes are separated
Meiosis II
Second division in meiosis during which sister chromatids are separated
Gametes
Haploid cells produced by meiosis (sperm & ovum)
Polar Boidies
Produced along with one haploid ovum/egg during meiosis
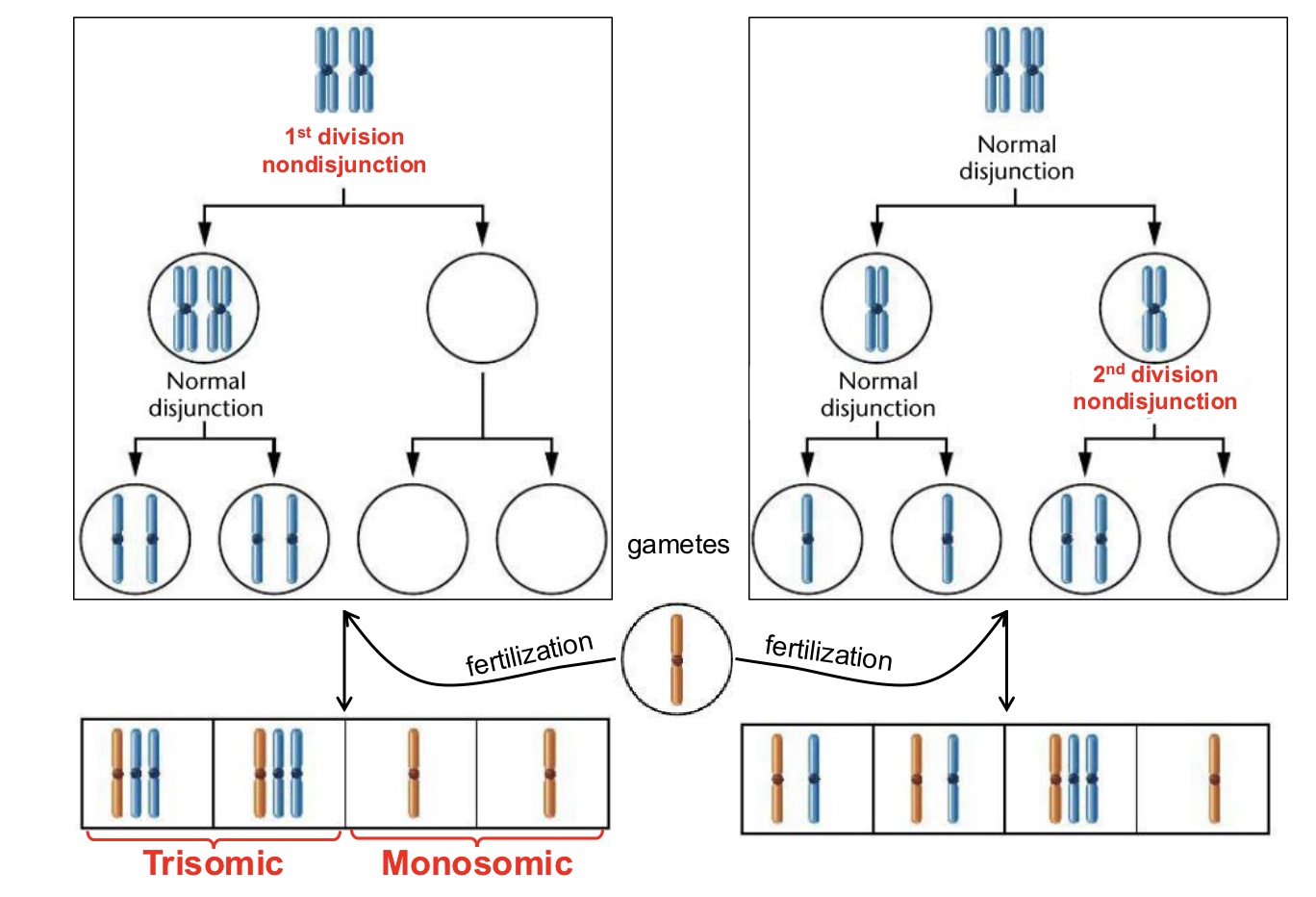
Aneuploidy
Gain or loss of one or more individual chromosomes (primarily results from nondisjunction during meiosis)
Euploidy
Addition of complete haploid sets of chromosomes
Nondisjunction
Process that primarily leads to aneuploidies during meiosis
Trisomy
Condition involving the addition of a single chromosome
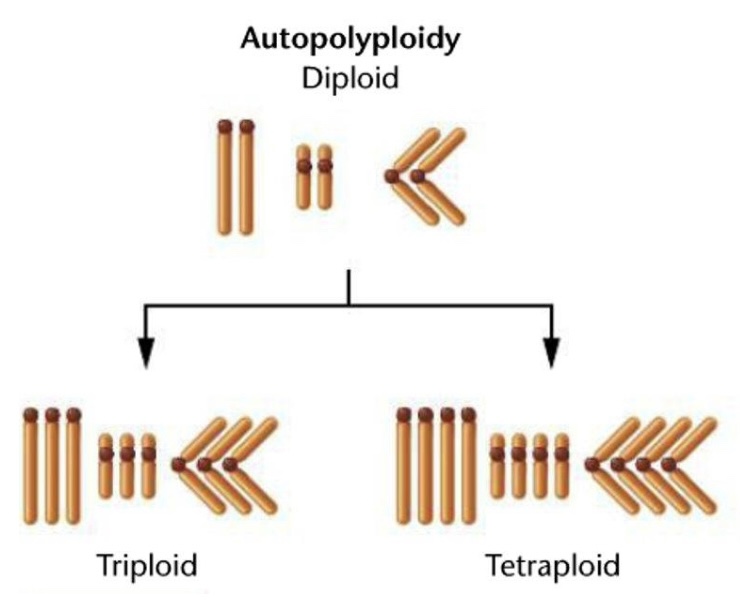
Polyploidy
More than two haploid sets of chromosomes
Autopolyploidy
Additional of one or more chromosome sets that are identical to the haploid complement of the same species
Allopolyploidy
Combination of chromosome sets from different species
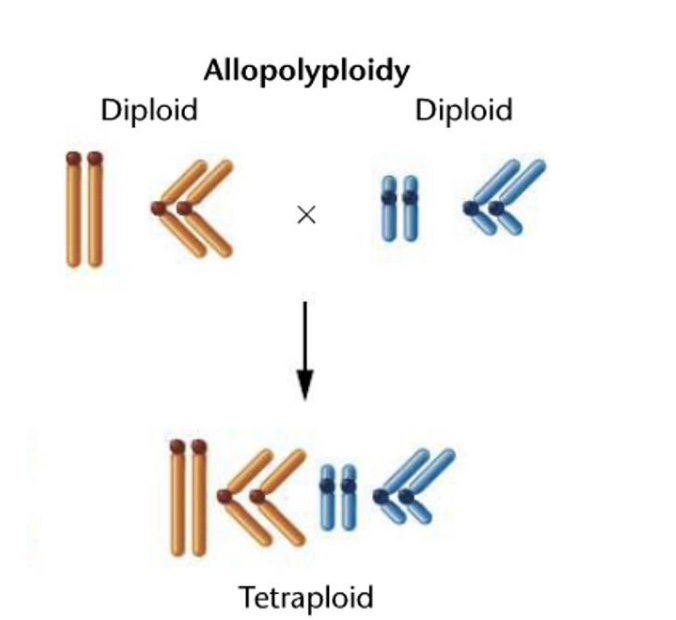
Amphidiploids
Organisms resulting from allopolyploid
Impacts commercialization of plants
Metaphase I (Meiosis I)
Homologous chromosome pairs align at metaphase plate
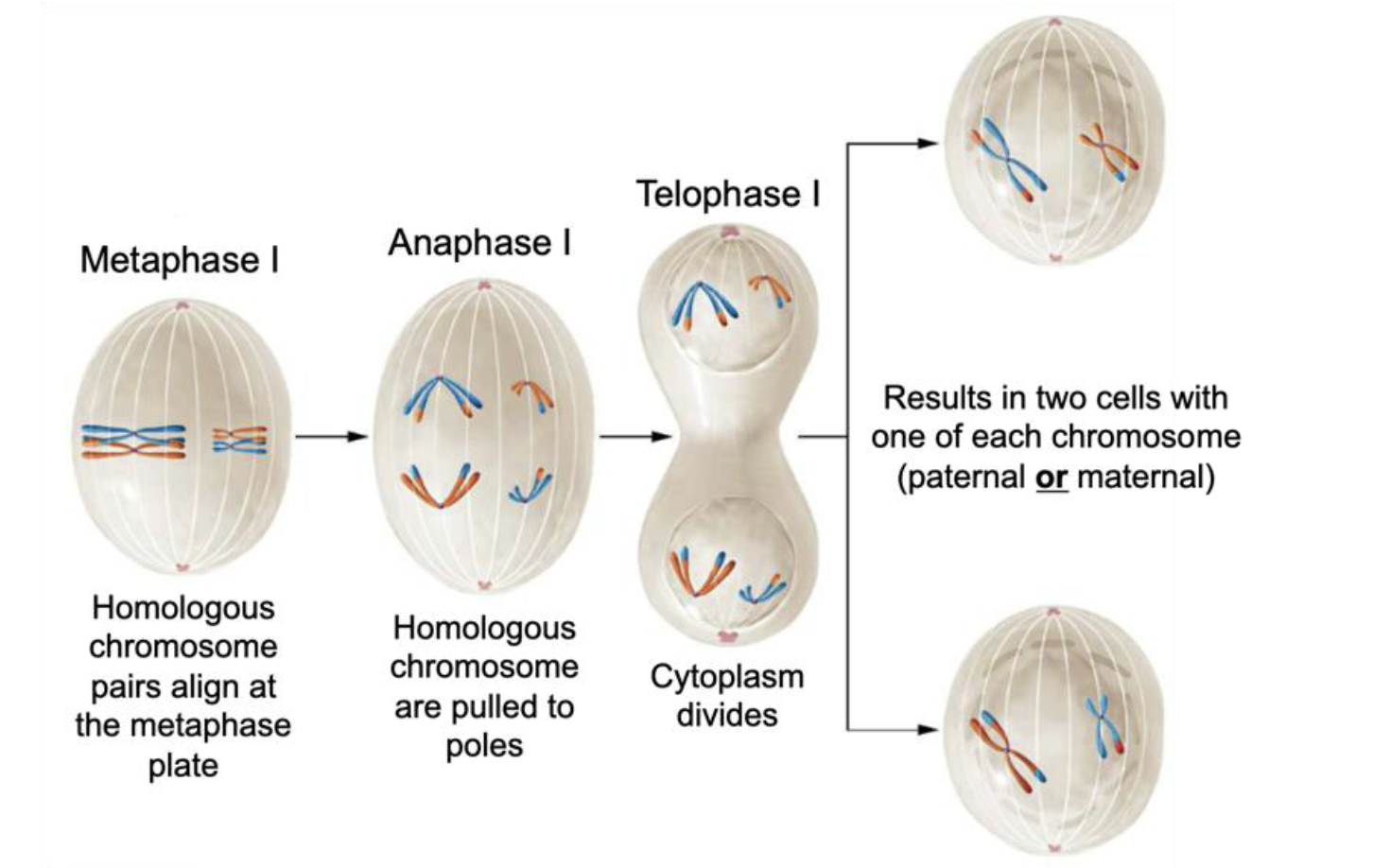
Anaphase I (Meiosis I)
Homologous chromosomes are pulled to poles
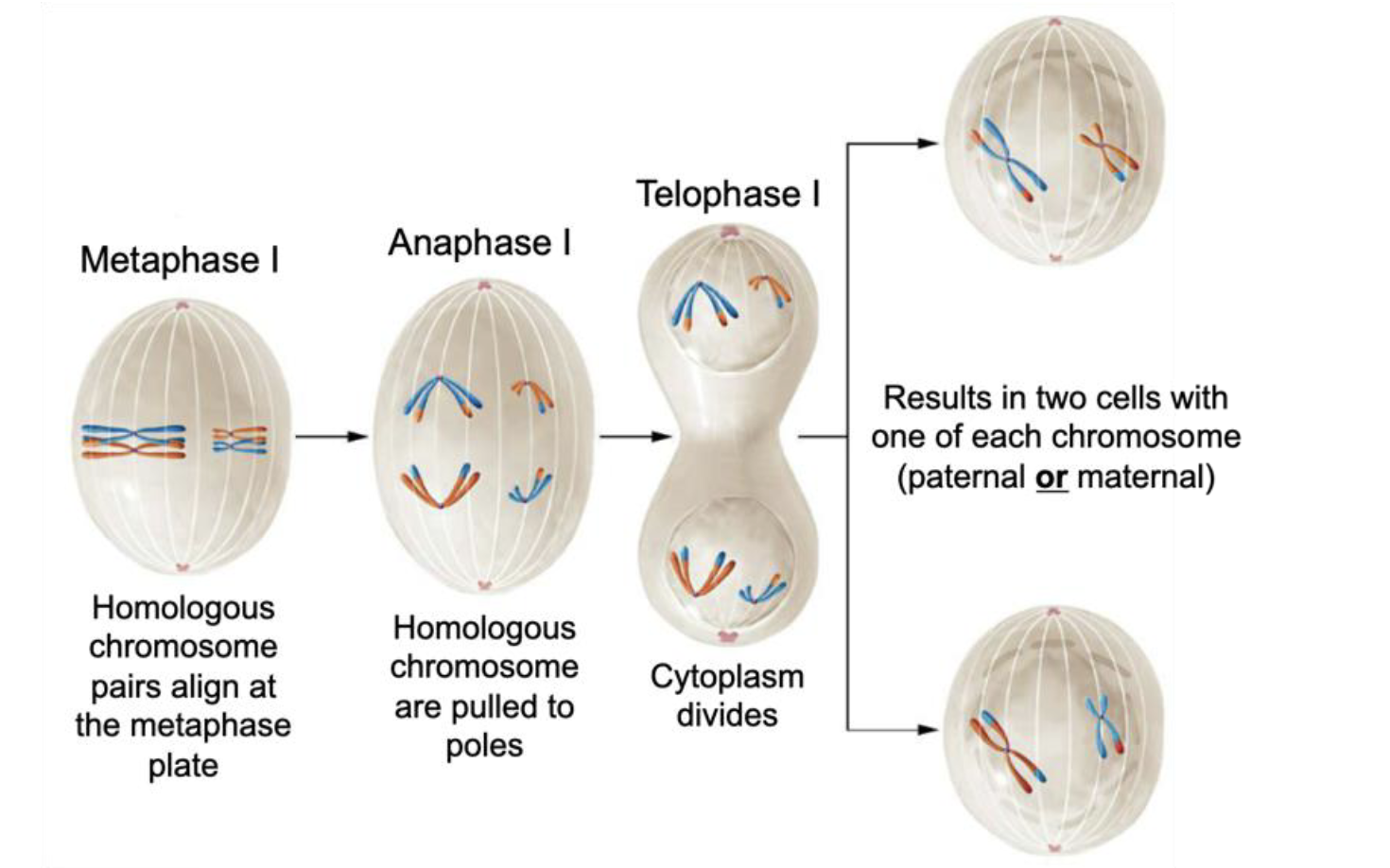
Telophase I
Cytoplasm divides (→ two cells with one of each chromosome [paternal or maternal])
![<p>Cytoplasm divides (→ two cells with one of each chromosome [paternal <strong>or</strong> maternal])</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2ce8a09a-9fcb-4588-8f70-3e57873af2f3.png)
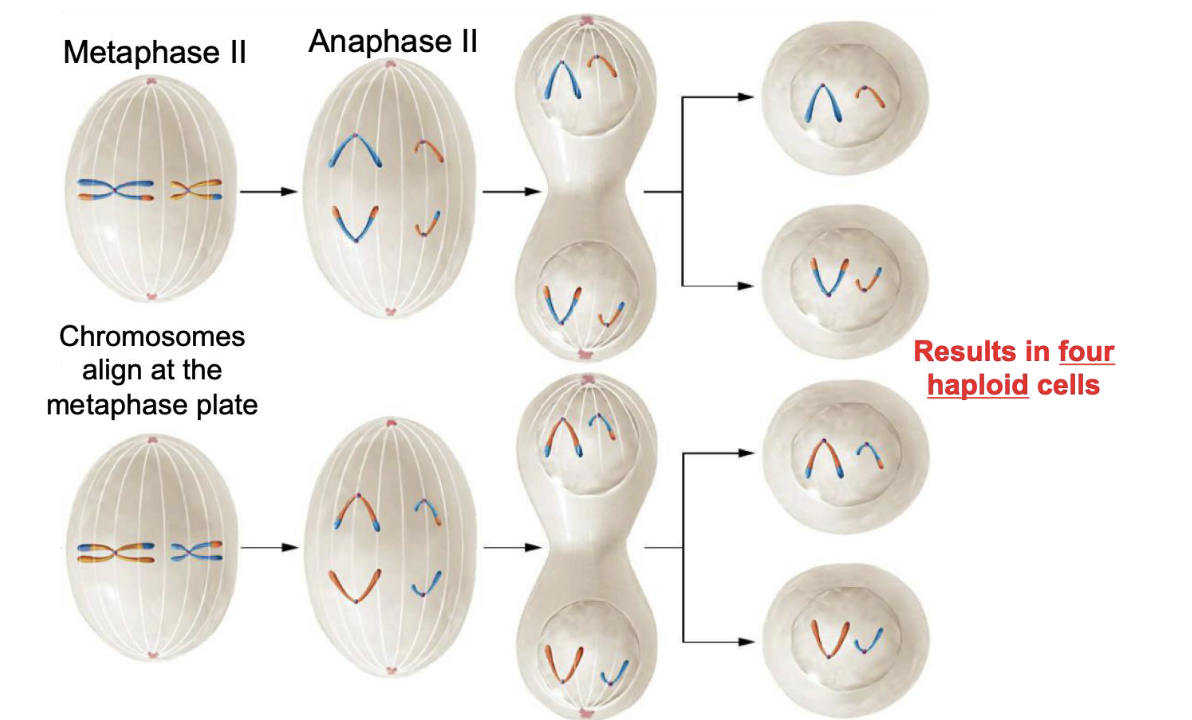
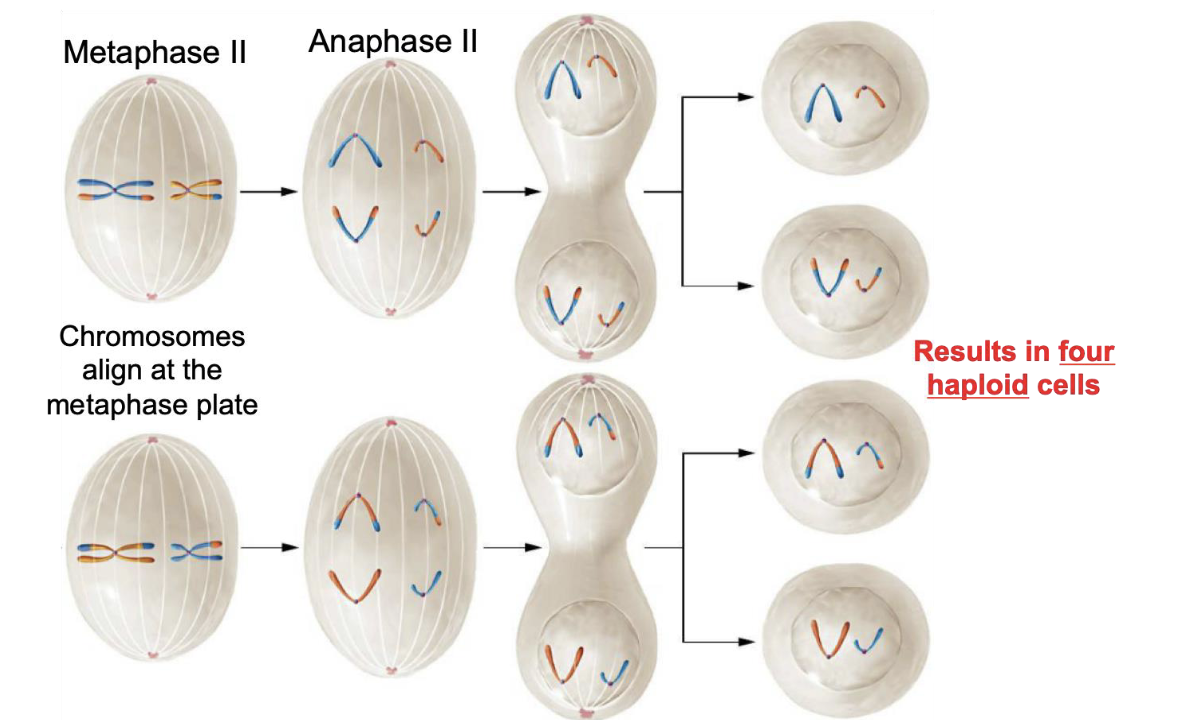
Metaphase II (Meiosis II)
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate
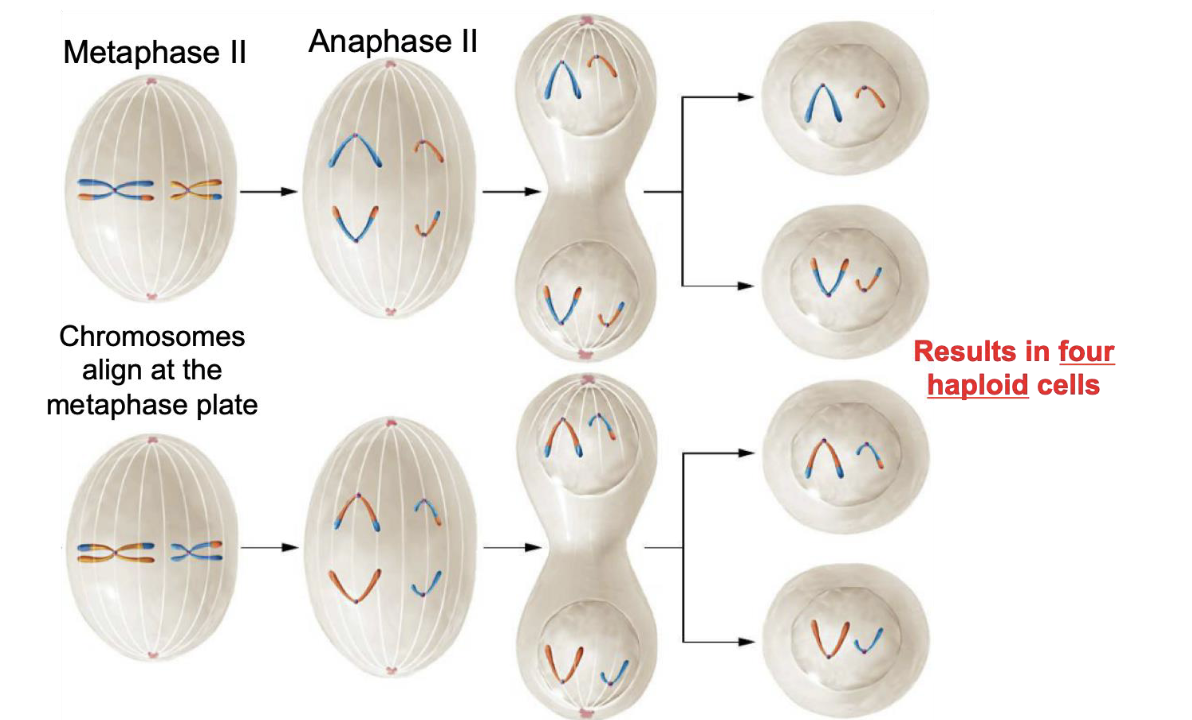
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by spindle fibers
Sister Chromatids
Two identical halves of a chromosome
Telophase II (Meiosis II)
Chromosomes gather at the two poles of the cell and the cell divides (cytokinesis) forming four unique haploid daughter cells
Theory of epigenisis
Adults arise from the growth of a fertilized egg undergoing successive developmental events to form an adult organism
Theory of Preformation
Adults arise from the growth of fully formed organisms already present in the sperm or egg
Nucleotides
Building blocks of DNA (Nitrogenous Base + Pentose + Phosphate Group)
Purine (Nitrogenous Base)
9-member double ring (Adenine, Guanine)
Pyrimadine (Nitrogenous Base)
6-member single ring (Cytosine, Uracil, Thymine)
Phosphodiester Bond
Links two sugars in a polynucleotide backbone
5’ End
End of a polynucleotide where the phosphate group attaches at #5-C
3’ End
End of a polynucleotide where the hydroxyl group is located at the #3-C
Spectrophotometer
Instrument that measures the spectral components of a substance, used to measure nucleic acid concentration by their absorption of UV light at 260nm
A260 Reading (Optical Densitiy)
Measure of light absorption at 260nm
Directly proportional to DNA concentration (A260 of 1 = 50 μg/ml dsDNA)
Hyperchromic Shift
An increase in UV absorption that occurs with DNA denaturation (separation of DNA strands)
Molecular Hybridization
Method to locate specific DNA sequences by created an identifiable complementary RNA probe unique to the sequence of interest, which is mixed with denatured single strands of DNA and allowed to anneal during slow cooling
FISH (Florescence in situ Hybridization)
Method used to analyze DNA using a flourescently labeled complementary RNA probe, unique to a sequence of interest, to locate specific DNA sequences
Gel Electropheresis
Method used to separate DNA molecules based on their charge and size (typically using a porous agarose matrix where DNA fragments move toward the positive anode and are visualized with a DNA dye)
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Method used to amplify specific DNA sequences (used as an analytical method)
DNA Sequencing
Method used to determine the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule (used as an analytical method)
Initiation (DNA Replication)
Helicase unwinds double helix and single strand binding proteins keep unwound strands open
Elongation (DNA Replication)
DNA polymerase adds precursor dNTPS (deoxynucleotide triphosphates) to the 3’ OH end, building new strands in the 5’ to 3’ direction
Termination (DNA replication)
RNA primers are replaced with DNA sequences and ligases covalently links Okazaki fragments
Chromosomal Recombination
Exchange of material between homologous chromosomes
Endonuclease Nicking (Homologous Recombination Step I)
Endonuclease cuts DNA strands
Stand Displacement (Homologous Recombination Step II)
One DNA strand moves out of its original position
Ligation (Homologous Recombination Step III)
DNA strands joined together
Branch Migration (Homologous Recombination Step IV)
Strands have exchanged then move along the DNA molecule
Duplex Separation (Homologous Recomination Step V)
Separation of DNA duplexes
Rotation/Holliday Structure (Homologous Recombination Step VI)
DNA duplexes undergo rotation, forming cross-shaped intermediate (Holliday Structure)
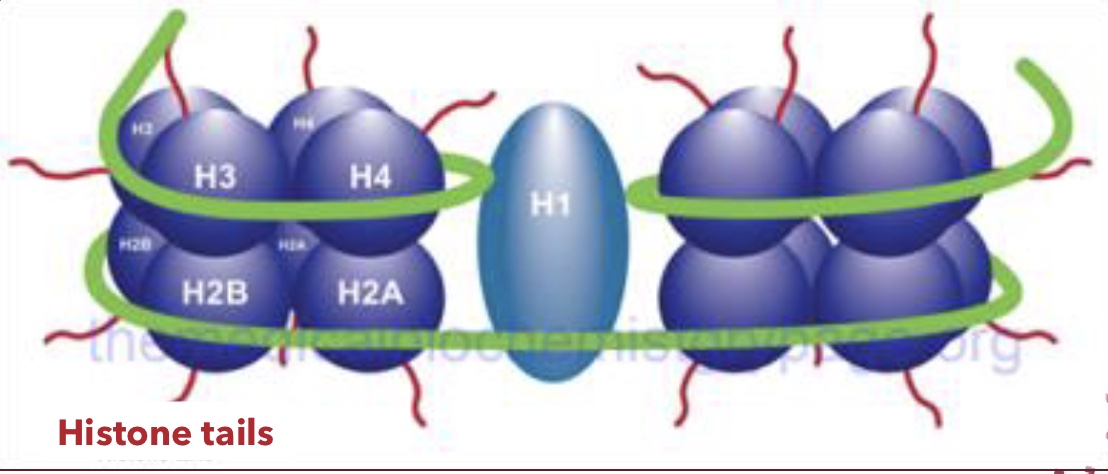
Histones
Positively charged proteins around which negatively charged DNA wraps, forming nucleosomes; amino acids in their tails are positively charged
Solenoids
Higher order structure formed when nucleosomes coil and stack onto each other
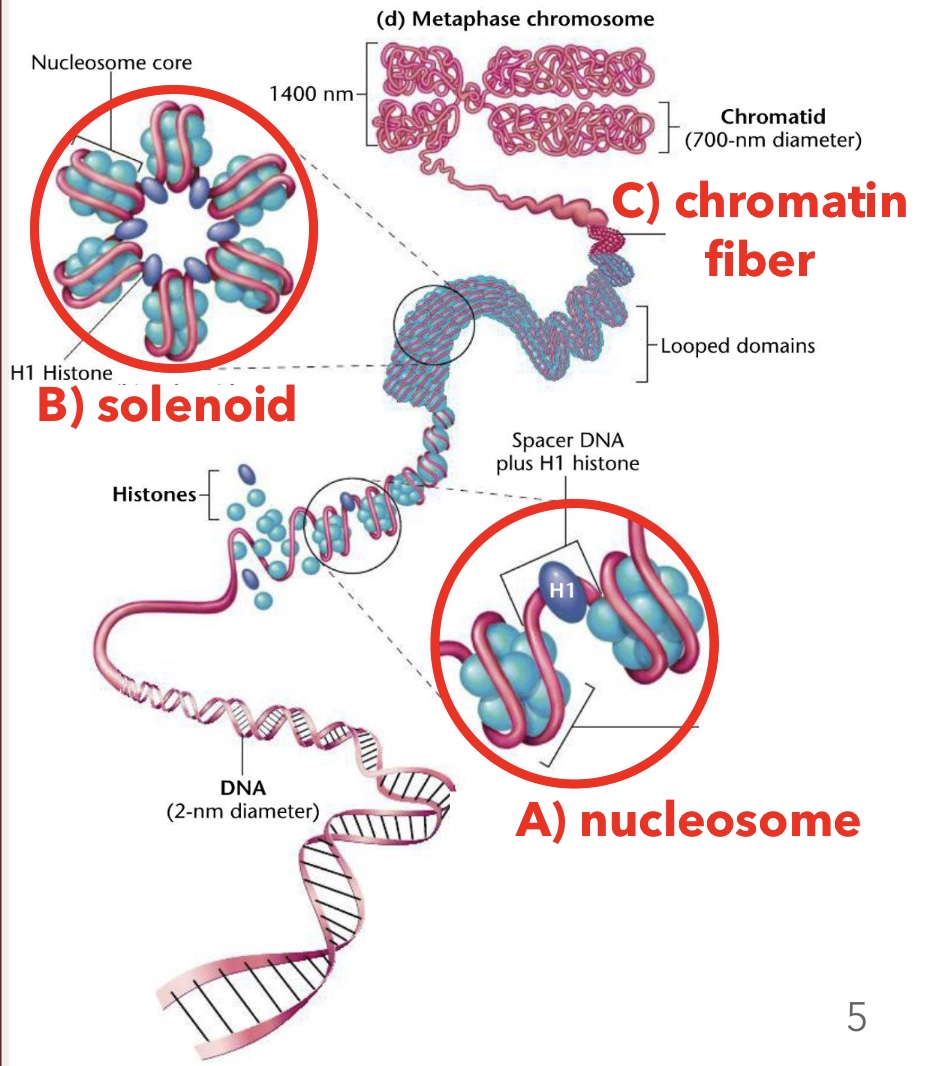
Chromatin Fiber
Looped domains formed by the coiling and stacking of solenoid fibers
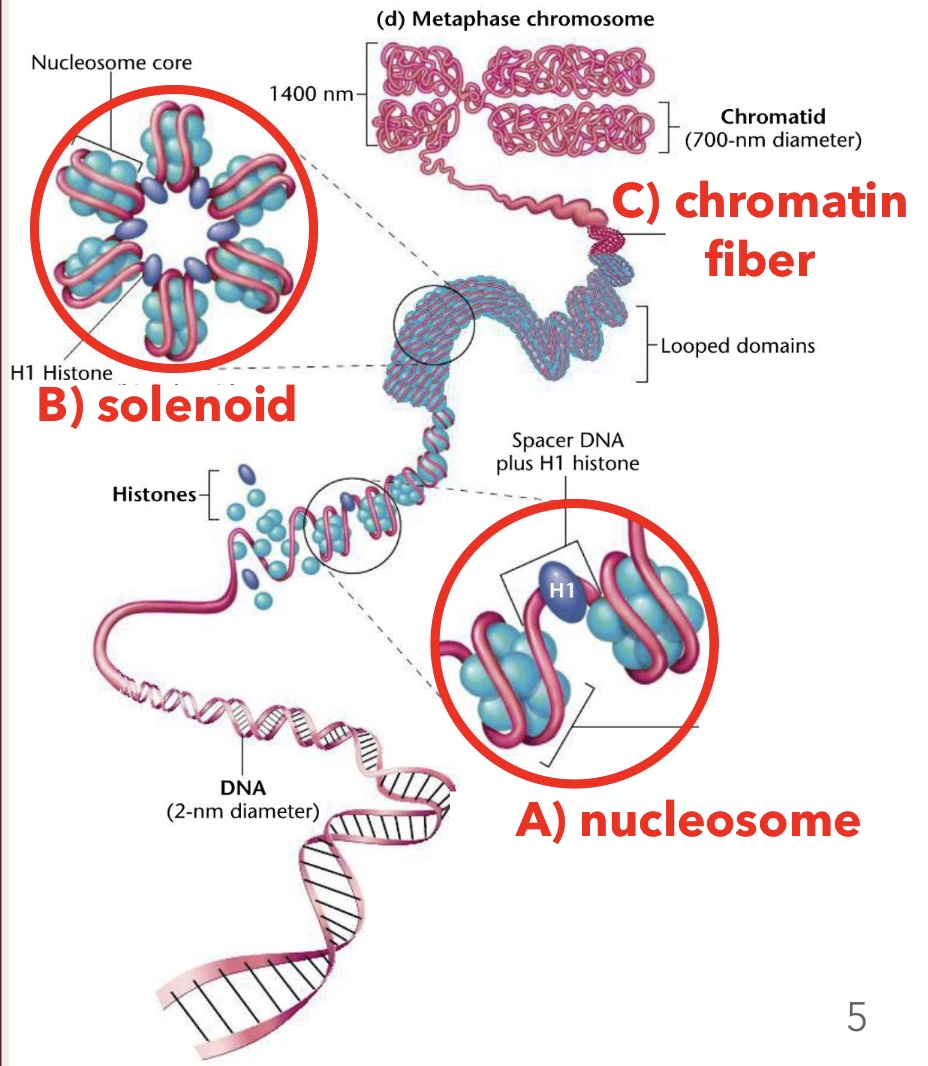
Nucleosome Core Particles
Composed of eight histone proteins (two of each H2A, H2B, H3, H4)
Euchromatin
Open chromatin conformation
Gene activation and active transcription
Heterochromatin
Closed chromatin conformation
Gene repression
Interchromatin Compartment
Regions within the nucleus containing transcription factories and RNA processing machinery
Elongation (Transcription)
RNA nucleotides are added complementary to the template DNA strand (Uracil replaces Thymine)
Termination (Transcription)
Terminator sequences within DNA signal transcription to stop, recruiting proteins that cleave the transcript and causes RNA polymerase to dissociate from DNA
RNA Processing
Modifications that RNA undergoes before being translated into protein (addition of 5’ cap, splicing of introns, and addition of Poly-A tail)
5’ Cap
Modification added to the 5’ end of mRNA for protection and ribosome attachment
Poly-A Tail
Am modification, consisting of a long chain of adenine nucleotides, added to the 3’ end of mRNA for stability and nuclear export
tRNAs
RNA molecules responsible for reading the mRNA message and bringing the corresponding amino acids to the ribosome during translation
A site (Ribosome)
Amino acid or acceptor site on ribosome where charged tRNA binds
P site (ribosome)
Peptides site on the ribosome where peptide bond is formed between amino acids
E site (Ribosome)
Exit site on ribosome where uncharged tRNAs leave
Primary Structure (protein)
Linear sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chain
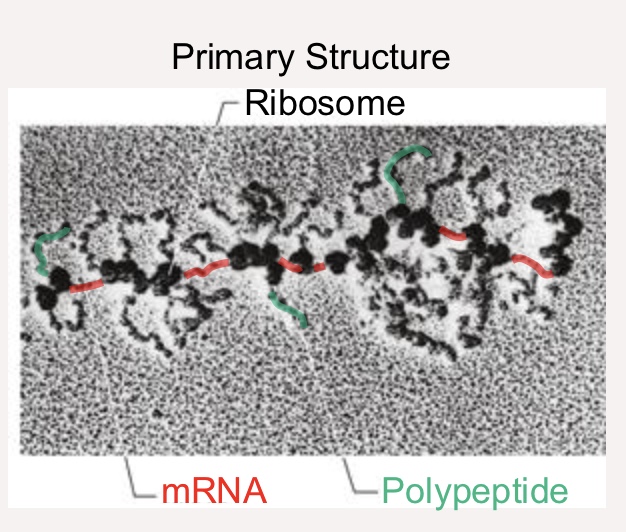
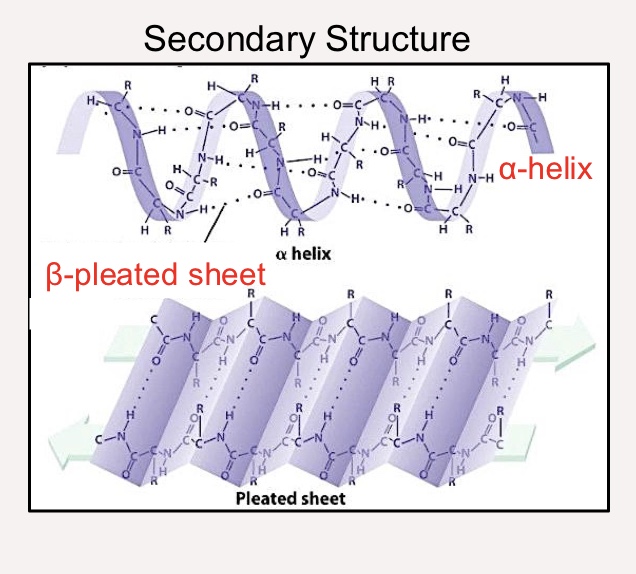
Secondary Structure (protein)
Local folded structures within a polypeptide (such as α-helices and β-pleated sheets)
Tertiary Structure (protein)
The overall three-dimensional shape of a single polypeptide chain
Quanterany Sequence (protein)
The arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains (subunits) in a protein complex
Cis-acting Sites
Specific DNA sequences located in or around genes that are recognized and bound by regulatory proteins to influences gene expression (TATA-box, enhancers, silencers)
General Transcription Factors
Proteins that bind to cis-acting sites to initiate basal levels of transcription; they assemble in a specific order to form a pre-initiation complex (PIC) and some recruit RNA polymerase II (RNAPII)
Histone Tail Modification
Chemical changes to the tails of histone proteins (acetylation, methylation, etc.) that alter their interaction with DNA, affecting chromatin conformation and gene accessibility
Histone acteyltransferases (HATs)
Enzymes that add acetyl groups to histones, reducing their positive charge and typically promoting gene activation
Histone decatylases (HDACs)
Enzymes that remove acetyl groups from histones, increasing their positive charge and typically promoting gene expression
Histone methyltransferatses (HMTs)
Enzymes that add methyl groups to histones, which can be repressive or activating depending on the specific modification
Chromatin Remoldeling Complexes
Promoting complexes that reposition or remove nucleosomes, altering chromatin conformation to control DNA accessibility
DNA Methylation
The addition of a methyl groups to cytosine base, primarily in CpG island by DNMTs (DNA methyltransferases). It inhibits transcription factories binding and recruits repressive chromatin remodelers, leading to repressed gene expression
DNA methyltransferase (DNMTs)
Enzymes responsible for adding methyl groups to DNA
RNA Degredation Pathways
Mechanisms by which mRNA molecules are broken down
Decapping (removal of 5’ cap)
Deadenylation (shortening of poly-A-tail)
Internal cleavage by nucleases
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
Longer, double-stranded RNA molecules involved in RNA-induced gene silencing (from viral infection, transposing, synthetic sources)
MicroRNAs (miRNAs)
Single-stranded RNA molecules with a double-stranded stem-loop structure, involved in RNA-induced gene silencing (from cell’s own genome)
DICER Complex
Protein complex that processes longer double-stranded RNAs into shorter siRNA or miRNA molecules during RNA-induced gene silencing
RISC (RNA-induced silencing complex)
Protein complex that denatures processed short RNAs and degrades the sense strand, mediating mRNA degradation or translation inhibition
RITS (RNA-induced transcriptional silencing complex)
Protein complex that recruits chromatin remodeling enzymes to mediate chromatin modification and transcription repression
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs)
Class of ncRNAs that regulate gene expression by forming RNA-protein complexes with chromatin regulators, recognizing specific genomic locations, participating in chromatin remodeling, and interacting with transcription factors
Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs)
RNA molecules transcribed from the genome that are not translated into protein, but instead play regulatory roles
Histone Code
The sum of patterns and interactions of histone modifications on nucleosomes that influence gene expression