Unit 1: upper extremity (Fingers, Hand, wrist, forearm, elbow, humerus)
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
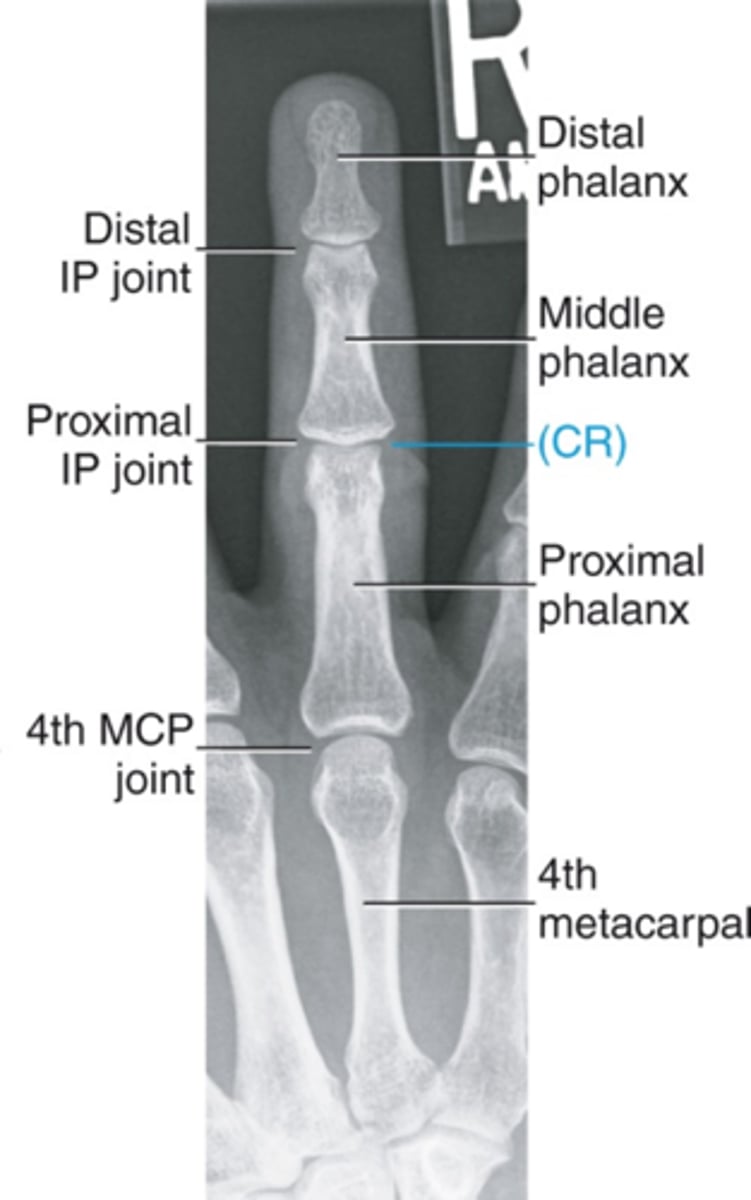
Collimation for PA and PA oblique finger
1 inch on all sides
Central Ray for PA and PA oblique finger
Perpendicular to PIP joint
Evaluation criteria for PA finger
-Equal concavity on both sides
-Open IP and MCP joint spaces
-Entire digit from fingertip to distal portion of adjoining metacarpal
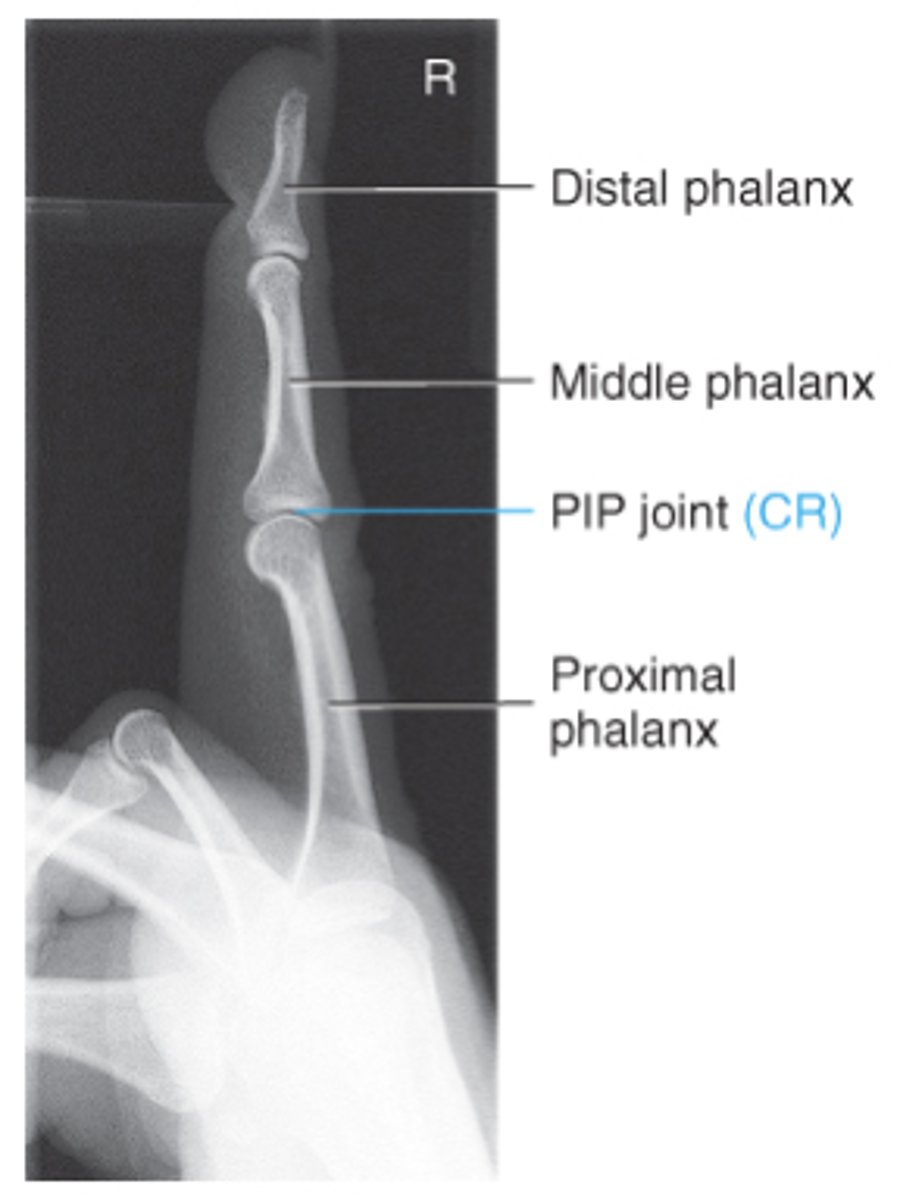
Collimation for lateral finger
1 inch on all sides
Central Ray for lateral finger
Perpendicular to PIP joint
Evaluation criteria for lateral finger
-no rotation
-no superimposition of the proximal phalanx or MCP joint
-open IP joint spaces
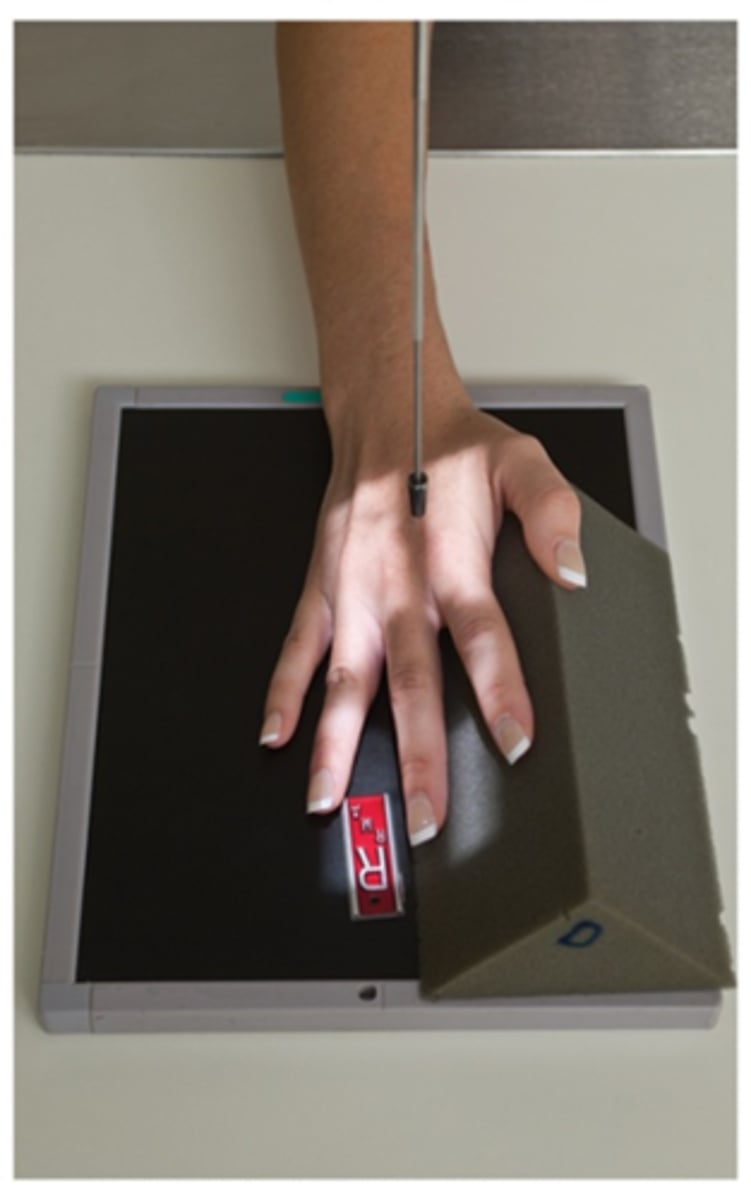
Evaluation criteria for PA oblique finger
-digit rotated at 45 degrees seen by concavity of the elevated side
-no superimposition of the proximal phalanx or MCP joint
-open IP and MCP joint spaces

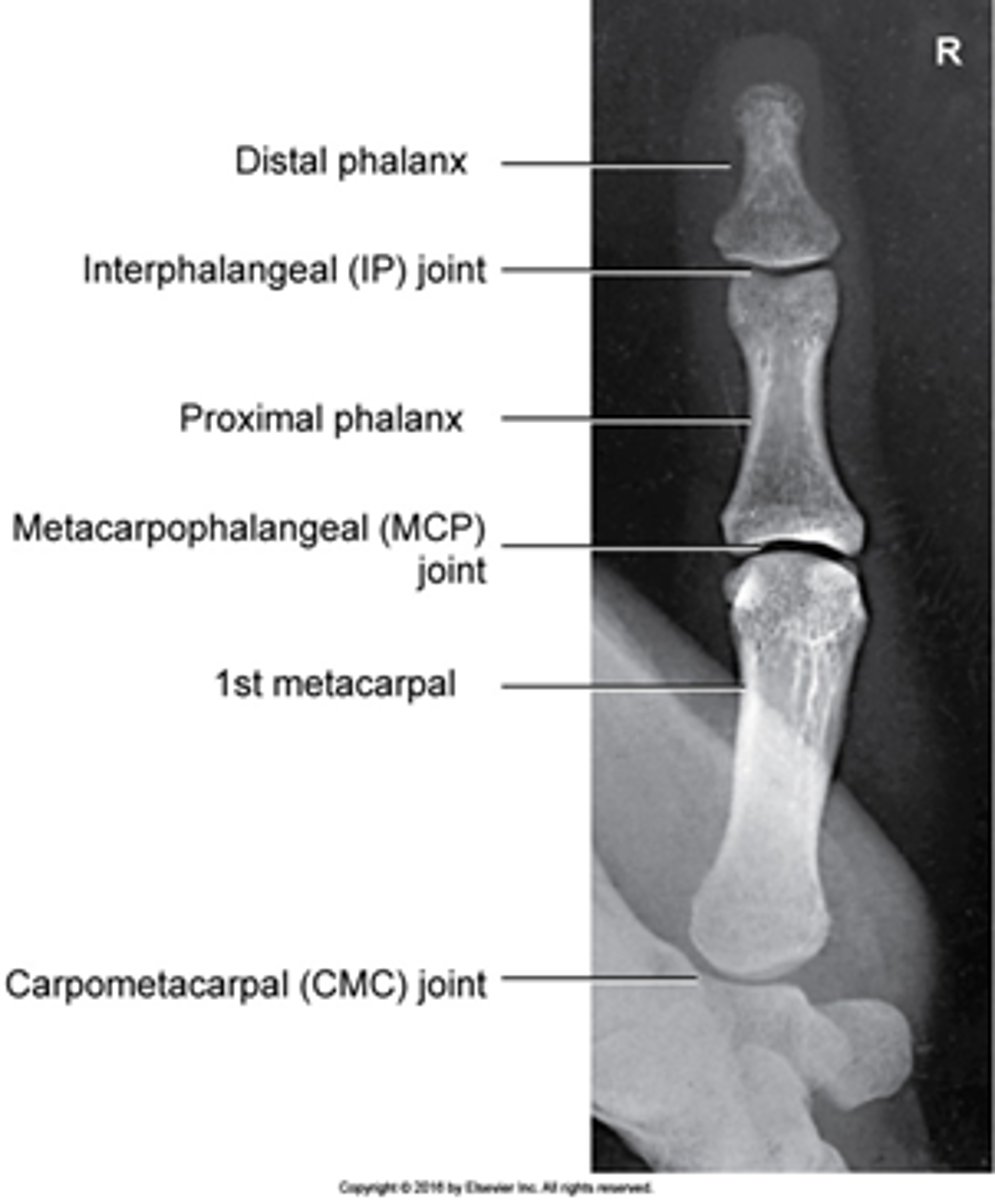
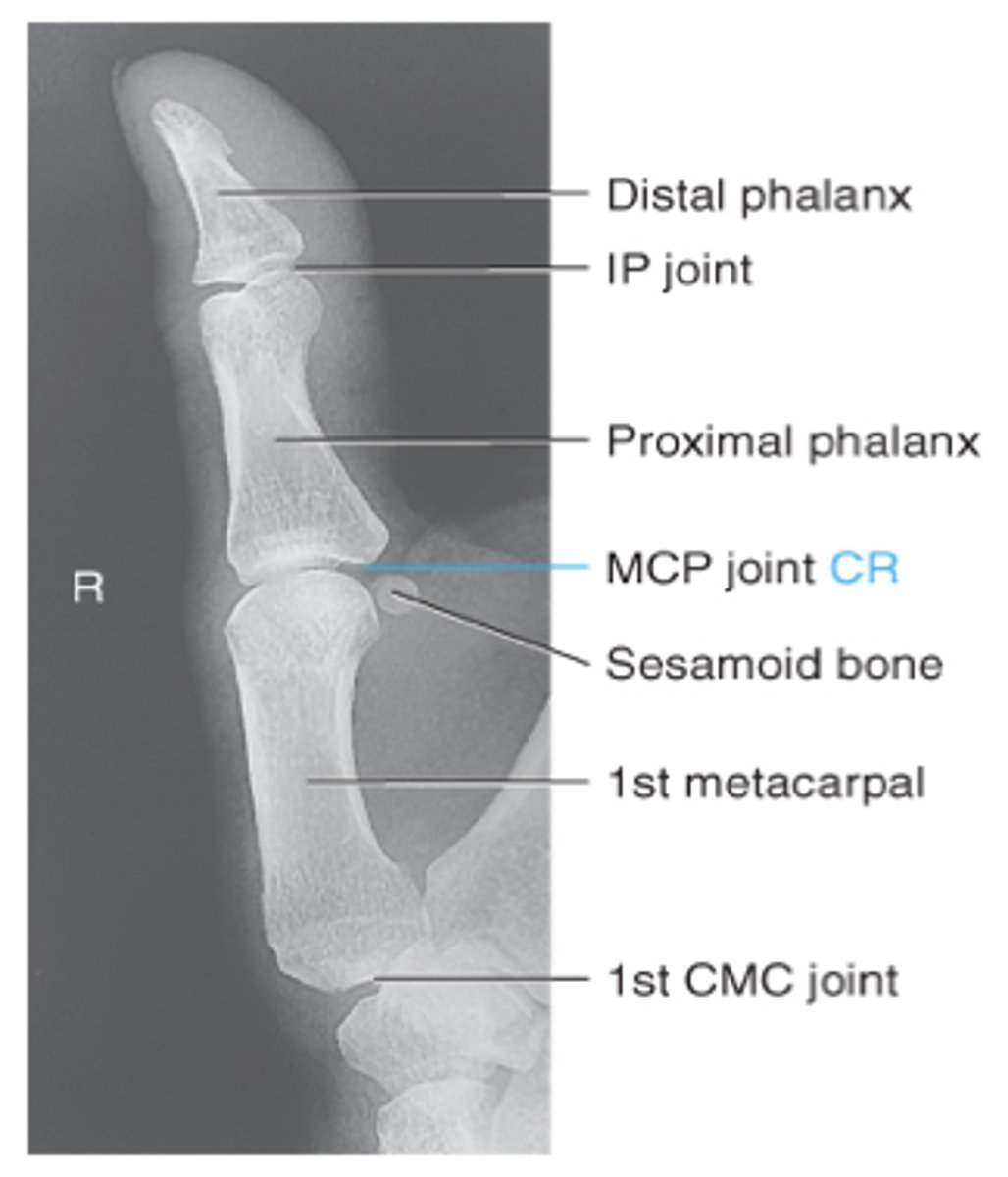
Collimation for AP/oblique/lateral thumb
1 inch on all sides
Central ray for AP/oblique/lateral thumb
Perpendicular to MCP joint spaces
Evaluation criteria for AP thumb
-Entire thumb demonstrated (including first CMC joint)
-CR at first MCP joint
-No rotation
-concavity of phalangeal and metacarpal bodies
-Open IP and MCP joints
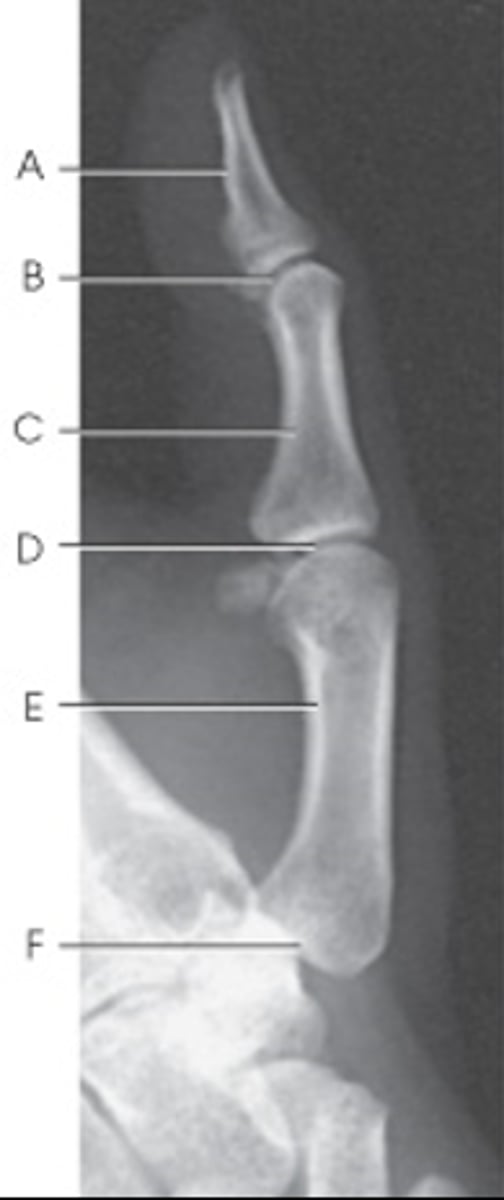
Evaluation criteria for lateral thumb
-entire finger and entire metacarpal from distal thumb to trapezium
-Open IP and MCP joint spaces
-all concavity on anterior side of phalange
Evaluation criteria for oblique thumb
-entire finger and entire metacarpal from distal thumb to trapezium
-Open IP and MCP joint spaces
-concave surface of elevated side of proximal phalanx and metacarpal
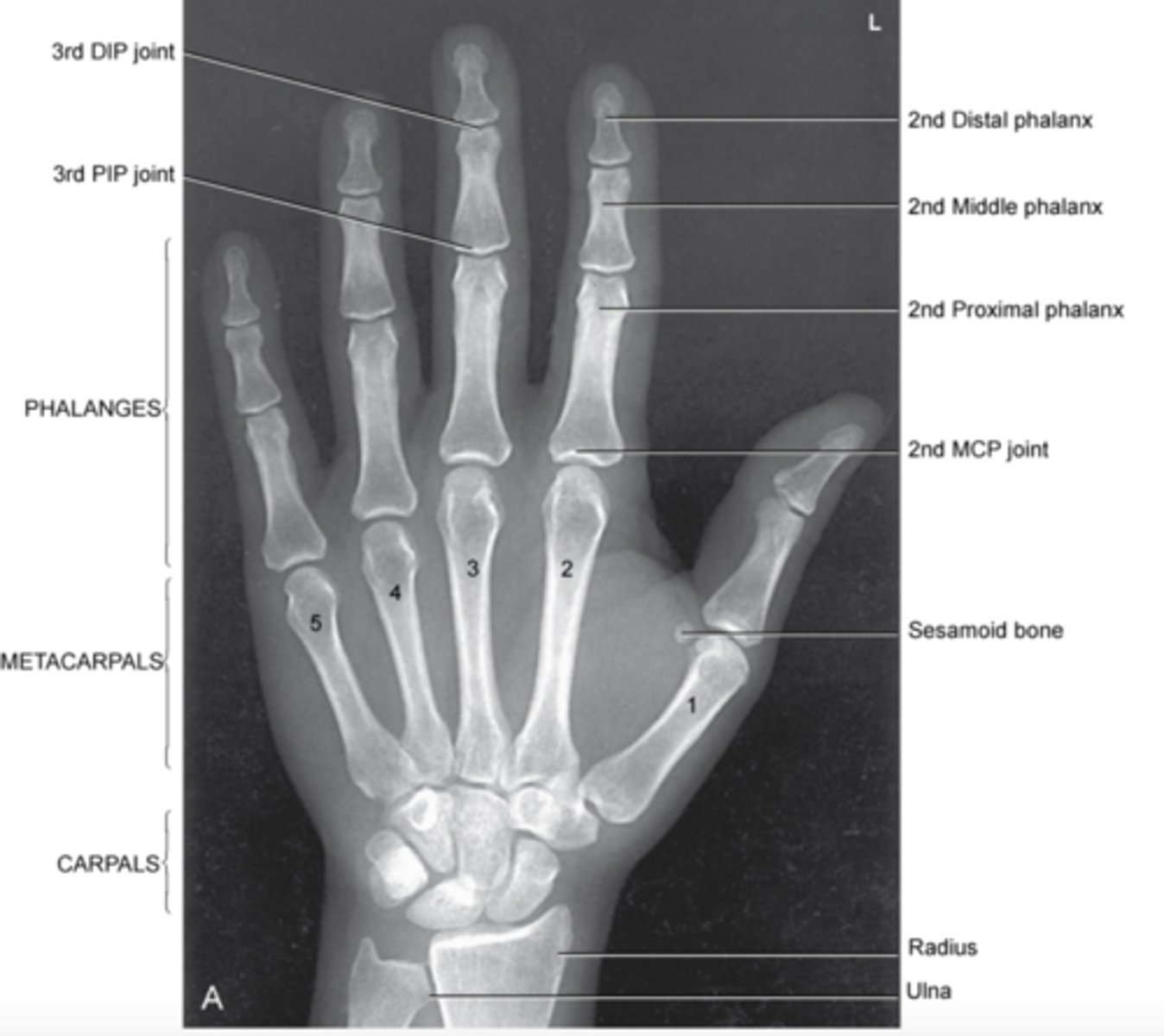
collimation for PA hand, PA oblique
1 inch on all sides of the hand, including 1 inch proximal to the ulnar styloid
Central ray for PA hand and PA oblique
3rd MCP joint
Evaluation criteria for PA hand
-entire hand and wrist are visible
-MCP and IP joint should be open
-slightly separate digits
-equal concavity of metacarpal and phalangeal bodies
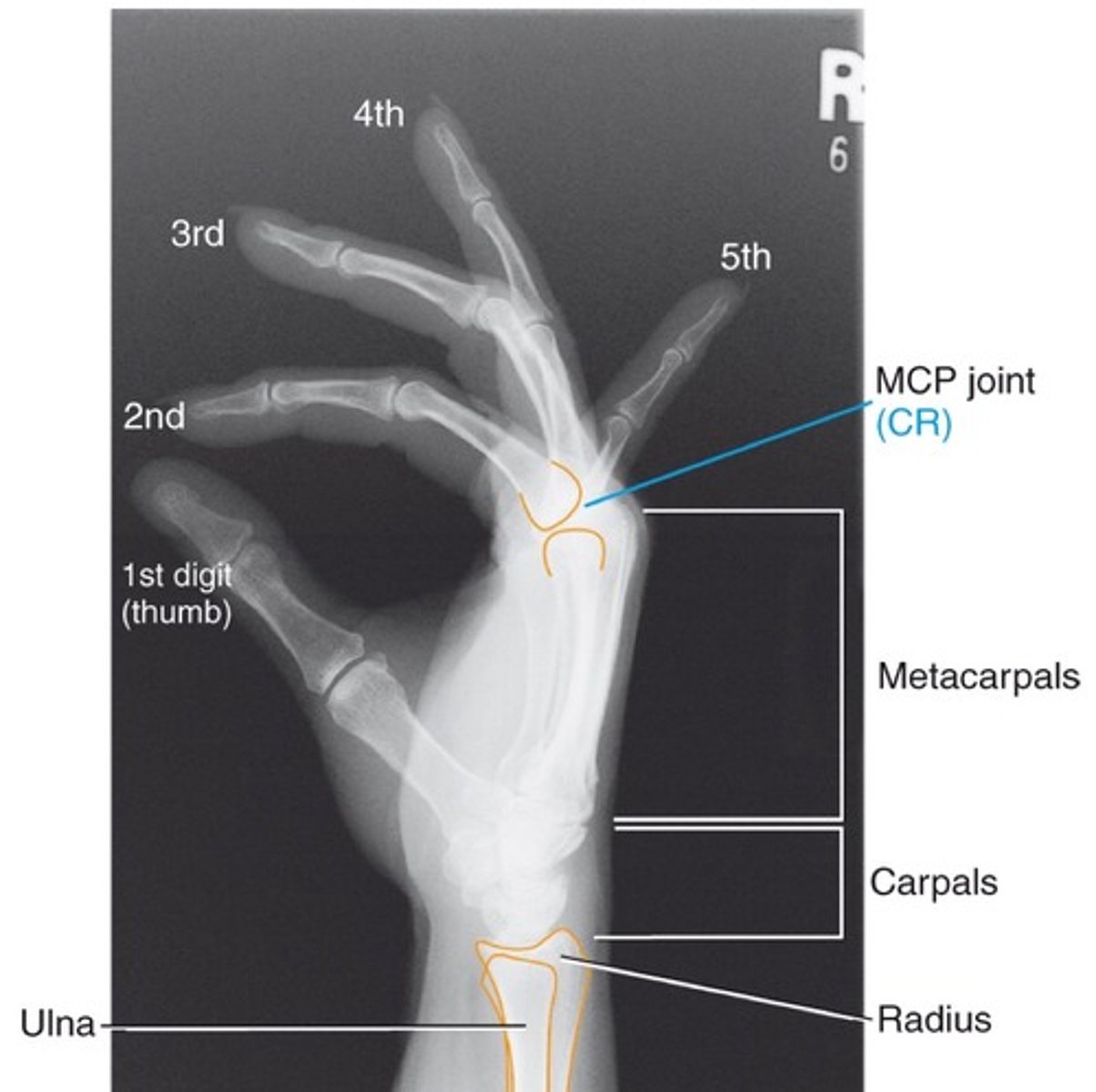
Evaluation criteria for PA oblique hand
-Entire hand, carpals, and 1" of radius/ulna shown
-open MCP and IP joints
-45 degrees of rotation
-partial superimposition of the third fourth and fifth metacarpal bases and heads
Collimation for lateral hand
1 inch in all sides of the shadow of the hand and thumb including 1 inch proximal to ulnar styloid
Central Ray for lateral hand
2nd MCP joint
Evaluation criteria for lateral hand
-extended digits
-Hand in a true lateral position
-superimposed phalanges
-superimposed metacarpals
-superimposed distal radius and ulna
-thumb free of motion and superimposition
Collimation for ALL wrist
2.5 inches proximal and distal to the wrist joint and 1 inch on the sides
Central ray for PA wrist
midcarpal area
Central ray for PA oblique wrist
Perpendicular to midcarpal area, just distal to radius
Central ray for lateral wrist
Perpendicular to the wrist joint
Evaluation criteria for PA wrist
-Distal radius, ulna, and carpals demonstrated
-Center of field at midcarpals
-No rotation
-open radioulnar joint space
-no excessive flexión of digits to overlap
Evaluation criteria for lateral wrist
- distal radius and ulna, carpals, and proximal half of metacarpals
- superimposed distal radius and ulna
- superimposed metacarpals
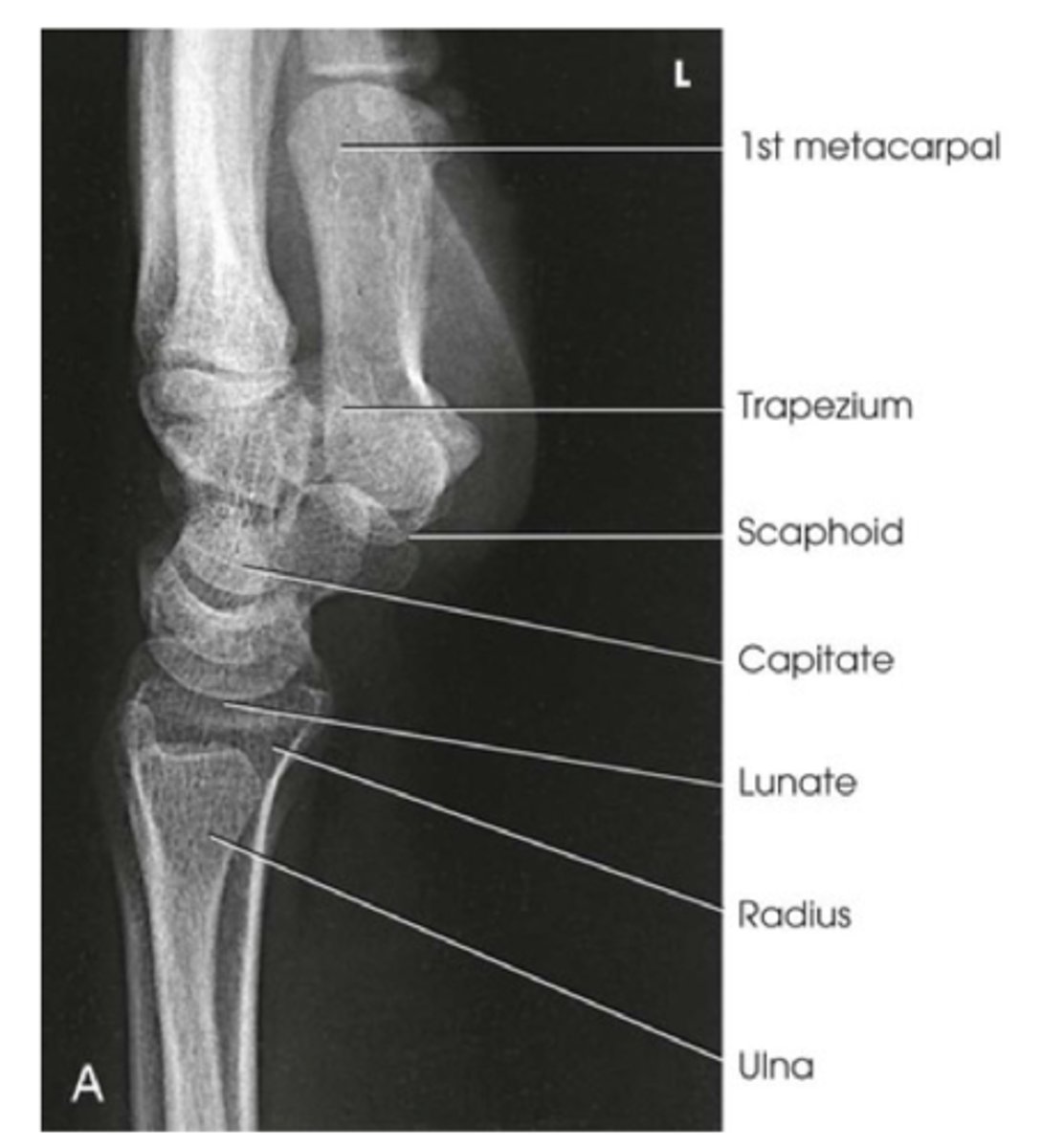
Evaluation criteria for PA oblique wrist
-Distal radius, ulna, and carpals demonstrated
-45 degrees rotation, slight overlap of distal radius and ulna
-Trapezium seen in its entirety and distal half of scaphoid without imposition
-carpals on lateral side of wrist
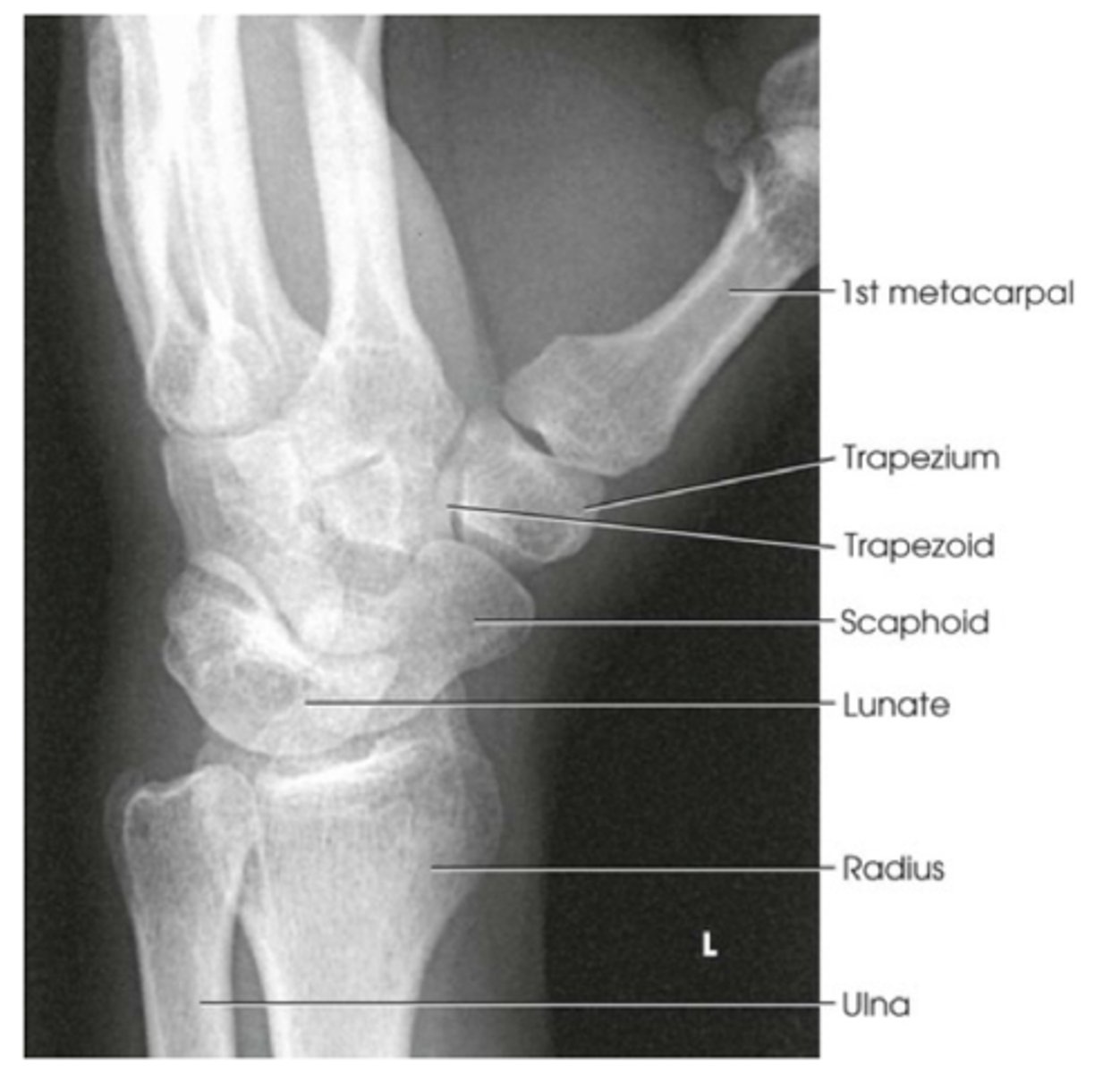
Central Ray for ulnar deviation
Perpendicular to scaphoid
-CR angulation of 10-15 degrees proximally or distally sometimes required
Central ray for PA axial projection (stetcher)
Perpendicular to the table and directed to enter the scaphoid
Evaluation criteria for PA wrist ulnar deviation
Scaphoid w adjacent articulations open
-No rotation of wrist
-maximum ulnar deviation
-distal radius and ulna carpals and proximal half of metacarpals
Evaluation criteria for PA axial wrist
-distal radius and ulna and carpals and proximal half of metacarpals
-scaphoid w adjacent articulations open
-no rotation of wrist
-20 degree angulation
Collimation for for tangential projection (gaynor-hart)
1 inch on all three sides of shadow of wrist
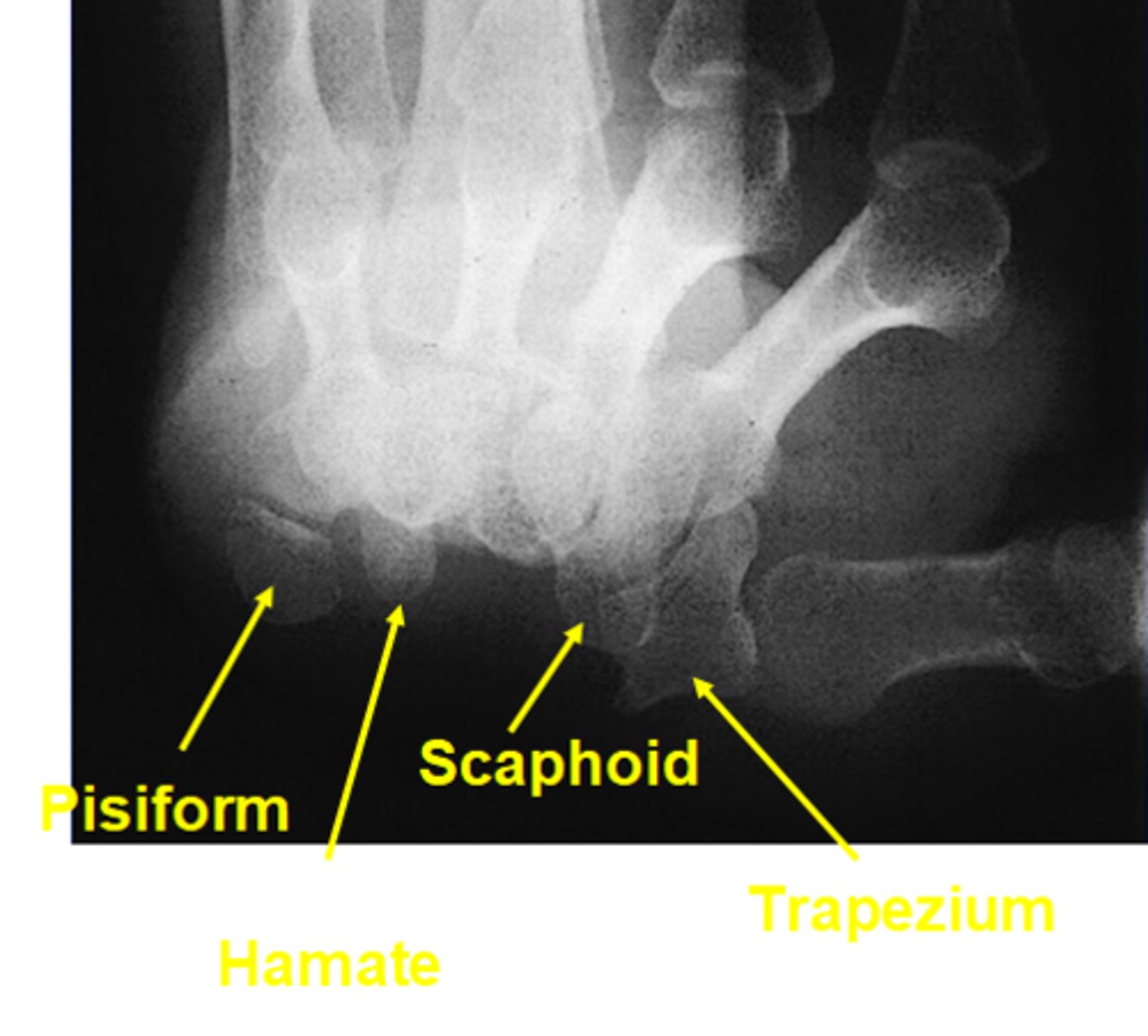
Central ray for tangential projection (gaynor-hart)
-Palm of the hand at 1 inch distal to the base of the third metacarpal at an angle of 25-30 degrees
Evaluation criteria for tangential projection (gaynor-hart)
-carpals in arch arrangement
-pisiform in profile and free of superimposition
-hamulus of hamate
Central ray for AP forearm
Perpendicular to the midpoint of the forearm
Collimation for AP forearm
2 inches distal to the wrist joint and proximal to the elbow joint and 1 inch on the sides
Evaluation criteria for AP forearm
-Entire forearm(include wrist and distal humerus)
-slight superimposition of Radial head/neck/tuberosity over proximal ulna
-No elongation by seeing both epicondyles
-partially open elbow joint (arm on same plane)
-open radioulnar space
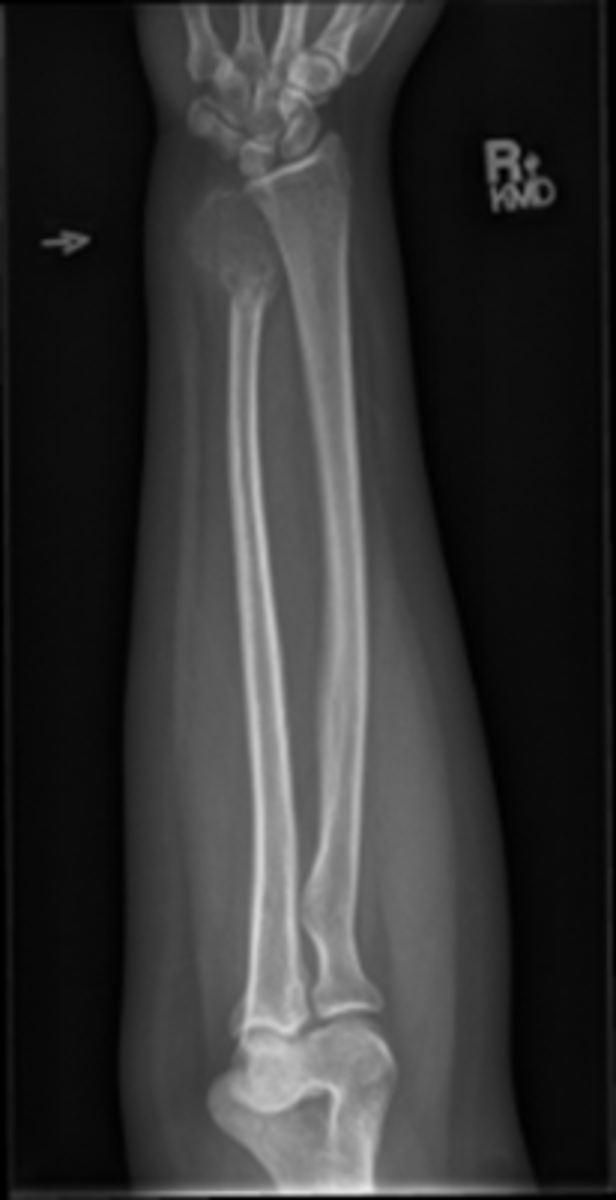
Central Ray for lateral forearm
Perpendicular to the midpoint of the forearm
Collimation for lateral forearm
2 inches distal to the wrist joint and proximal to the elbow joint and 1 inch on the sides
How many bones in the hand
27 bones
How many phalanges are there?
14 per hand
How many metacarpals are there?
5 in each hand
how many carpal bones are there
8 in each hand
How many articulations does the humerus have
three
What type of joint is the IP joint
hinge
What type of joint is the MCP joint
Ellipsoidal (condyloid)
What type of joint is the first digit (CMC)
saddle
what type of joint are digits 2-5 (CMC)
gliding
what type of joint is the intercarpal (CMC)
gliding
What type of joint is the radiocarpal? (CMC)
ellipsoid
What type of joint is proximal radioulnar
pivot
what type of joint is distal radioulnar
pivot
what type of joint is humeroulnar
hinge
what type of joint is humeroradial
hinge
When the elbow is flexed 90 degrees, which fat pads are visible?
anterior and supinator fat pads
What is the SID for all upper extremities
40 SID
What is the collimation for the digits
2"X6"
What is the collimation for the Hand PA
7"X8"
What is the collimation for the Hand oblique
7"X8"
What is the collimation for the Hand Lateral
6"X8"
What is the collimation for the Wrist (PA/ PA Oblique)
4"X8"
What is the collimation for the Wrist Lateral
3"X8"
What is the collimation for the Gaynor Hart
4X4"
What is the collimation for the forearm (AP/Lateral)
5X15"
What is the collimation for the Elbow (AP/Lateral)
5X9"
What is the collimation for the Humerus (AP/Lateral)
7X17"
What is the kVp for the digits
63
What is the kVp for the hand (PA, PA oblique)
66
What is the kVp for the hand (Lateral)
70
What is the kVp for the wrist (PA/ PA oblique)
66
What is the kVp for the wrist (Lateral)
70
What is the kVp for the Gaynor-Hart
70
What is the kVp for the forearm (AP/Lateral)
70
What is the kVp for the Elbow
70
What is the kVp for the Humerus
75
What is the mAs for the digits
0.6 h
What is the mAs for the Hand PA
0.71 h
What is the mAs for the Hand oblique
0.8 h
What is the mAs for the hand lateral
1.25 h
What is the mAs for the wrist (PA/ PA oblique)
0.9 h
What is the mAs for the wrist lateral
1.1 h
What is the mAs for the gaynor-hart
1.25 h
What is the mAs for the forearm (AP/lateral)
1.25 h
What is the mAs for the elbow (AP/lateral)
1.4 h
What is the mAs for the humerus (AP/lateral)
2.8 h
how much do you increase mAs or kVp for a cast (fiberglass)
increase mAs 25% or 4 kVp
how much do you increase mAs or kVp for a cast (plaster medium)
increase mAs 50% or 7 kVp
how much do you increase mAs or kVp for a cast (plaster large)
increase mAs 100% or 10 kVp
bone cyst
Fluid-filled cyst with wall of fibrous tissue
bursitis
inflammation of a bursa
Dislocation
displacement of a bone from its joint
fracture
disruption in the continuity of bone
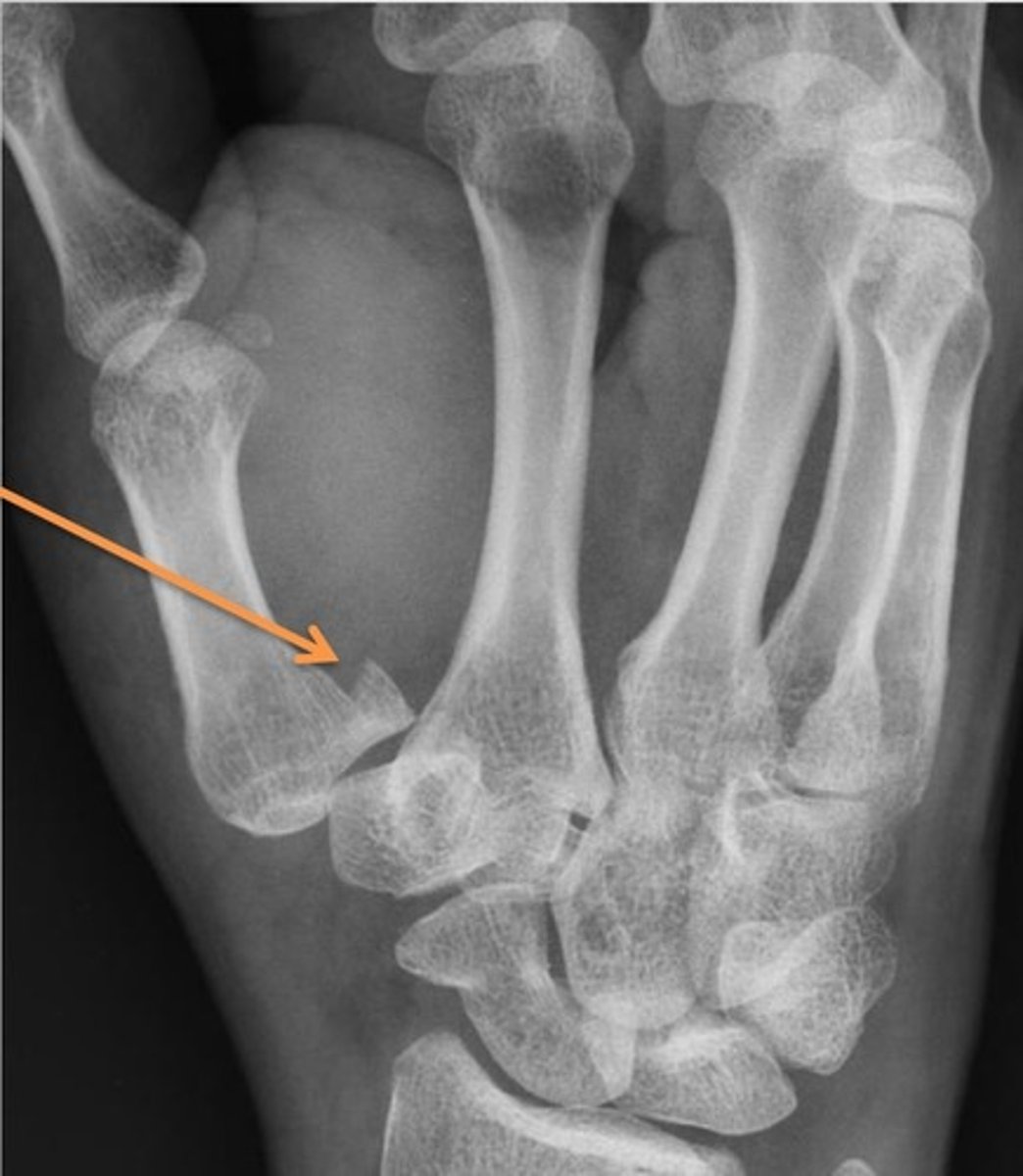
bennett fracture
Fracture at base of first metacarpal
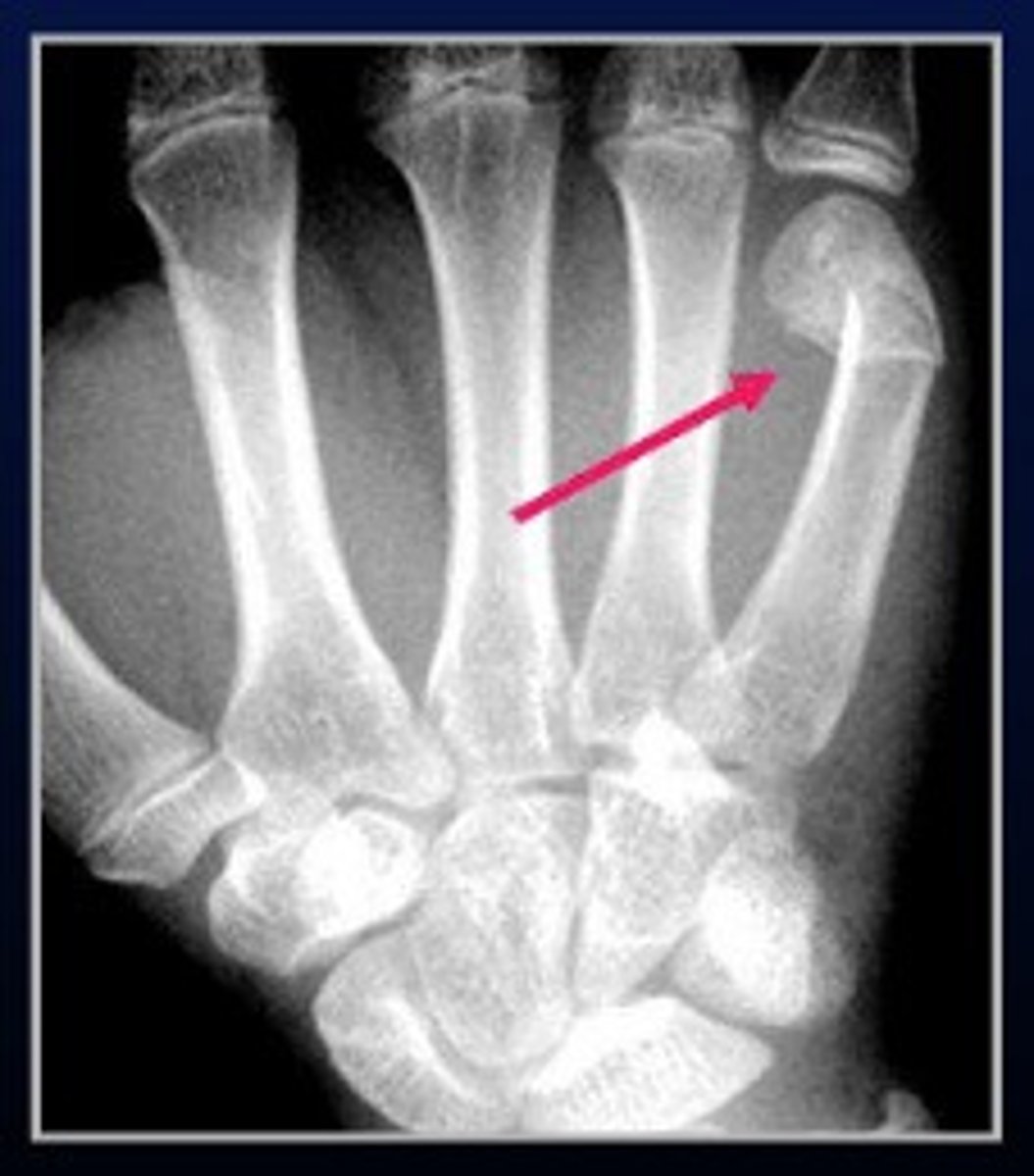
boxer fracture
fracture of metacarpal neck
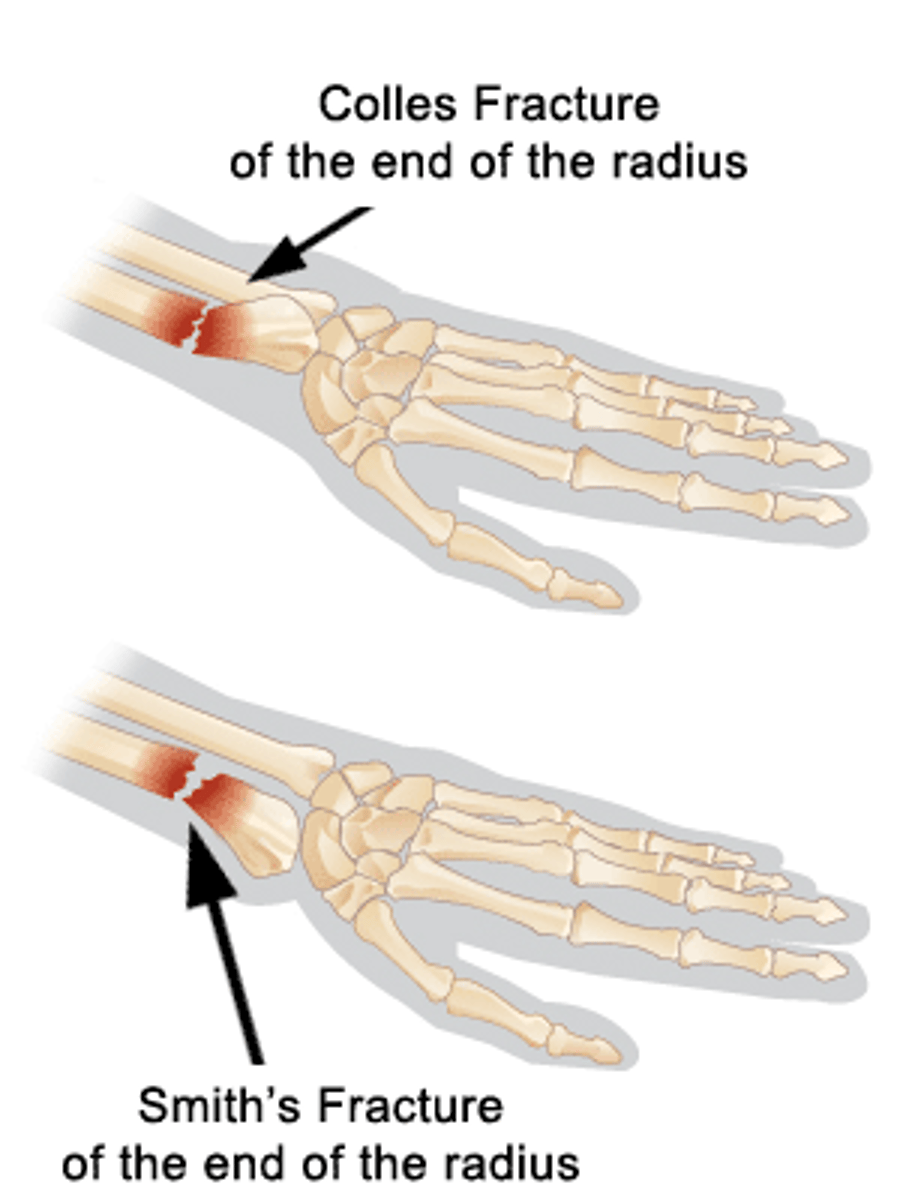
Colles fracture
fracture of the distal radius with posterior displacement
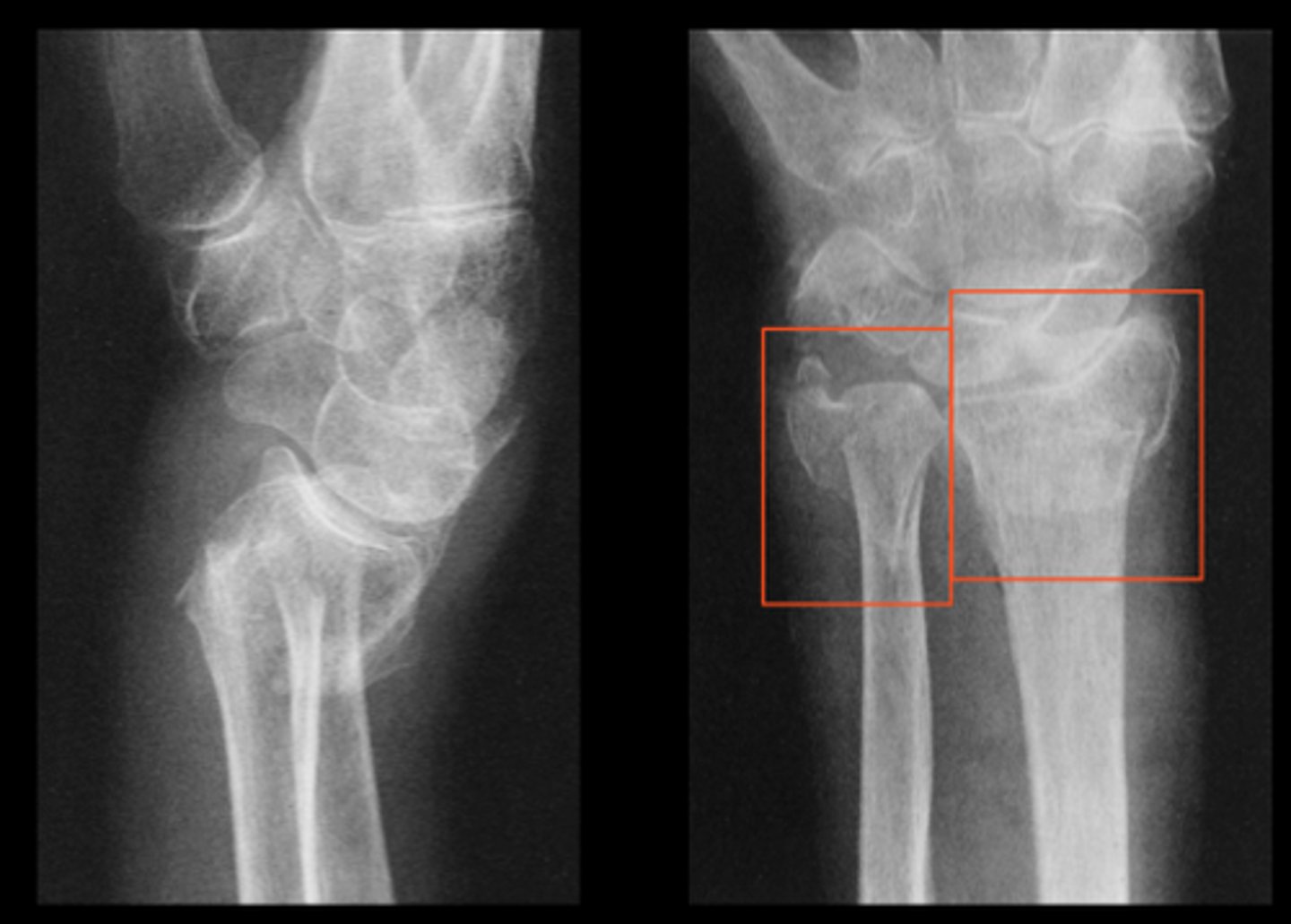
Smith fracture
fracture of distal radius with anterior displacement
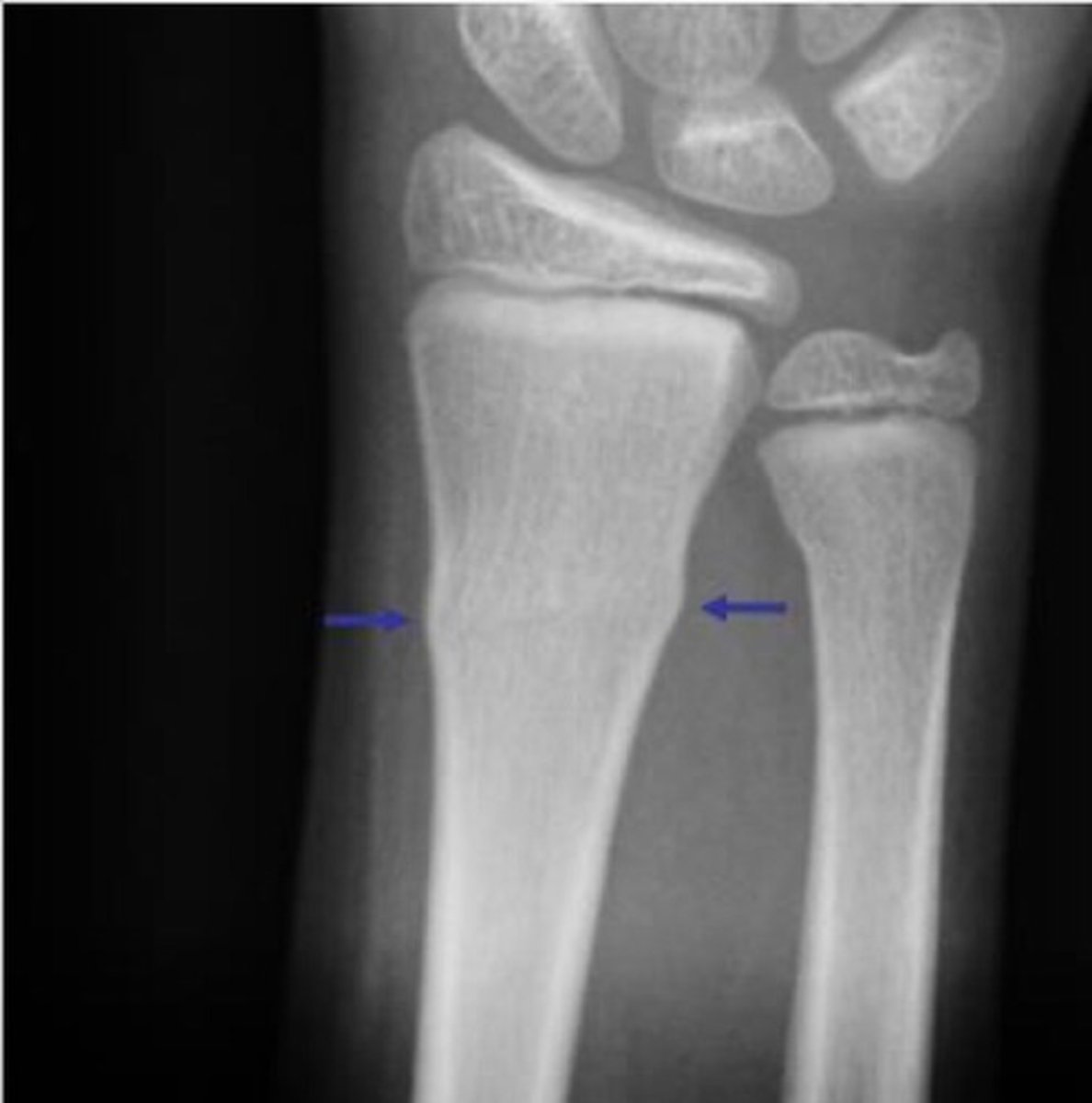
torus/buckle fracture
Impacted fracture with bulging of periosteum
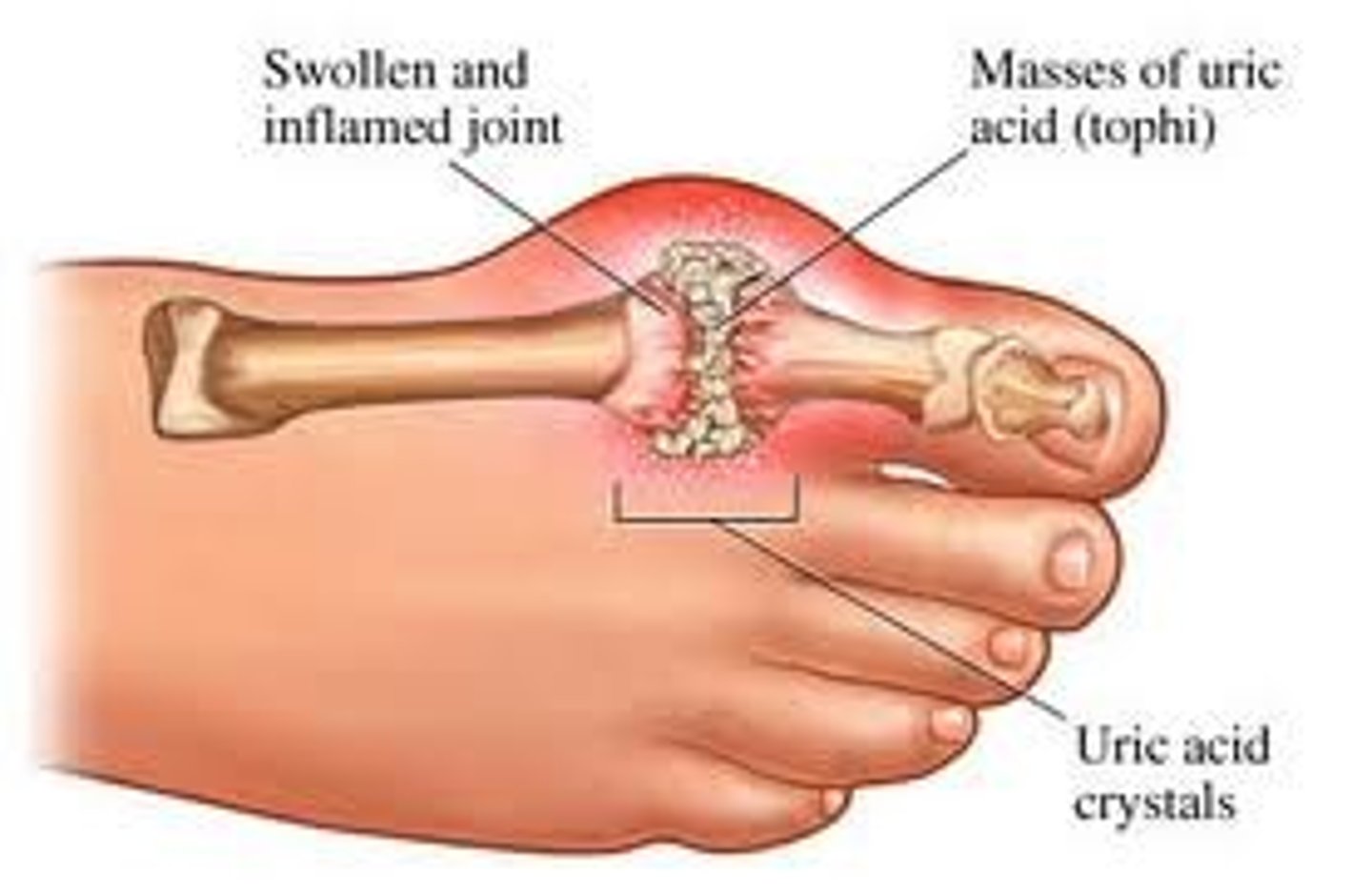
gout
Hereditary form of arthritis in which uric acid is deposited in joints
joint effusion
Accumulation of fluid in joint associated with underlying condition
Metastases
Transfer of a cancerous lesion from one area to another
osteoarthritis
Form of arthritis marked by progressive cartilage deterioration in synovial joints and vertebrae