VF: Week 4 Sympathetic Nervous System
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
What are the neurotransmitters released at the autonomic ganglion and the adrenergic nerve terminal?
Norepinephrine
Acetylcholine
Epinephrine
Where is norepinephrine synthesized?
Adrenergic nerve terminal
Where is Acetylcholine synthesized?
Located in the Autonomic Ganglion
Where is epinephrine synthesized?
The Adrenal Gland
What pre-synaptic adrenergic receptor (AR) is linked to inhibition of norepinephrine release?
Alpha-2 AR
What is the Motor Structure Function?
The ANS and the SNS are almost entirely separated in the periphery.
How are the SNS and the ANS related to the CNS?
They are closely connected in the CNS.
What is the Function of the SNS?
Voluntary Controls the function of the skeletal muscle
What is the Function of the ANS?
Mainly regulated function of the internal organs and adapts them to the needs of the moment.
What is the Reciprocal Effect?
The effect that the parasympathetic and the sympathetic in which they counteract each other.
Are parasympathetic and sympathetic antagonist of each other?
No they are not they are complementary.
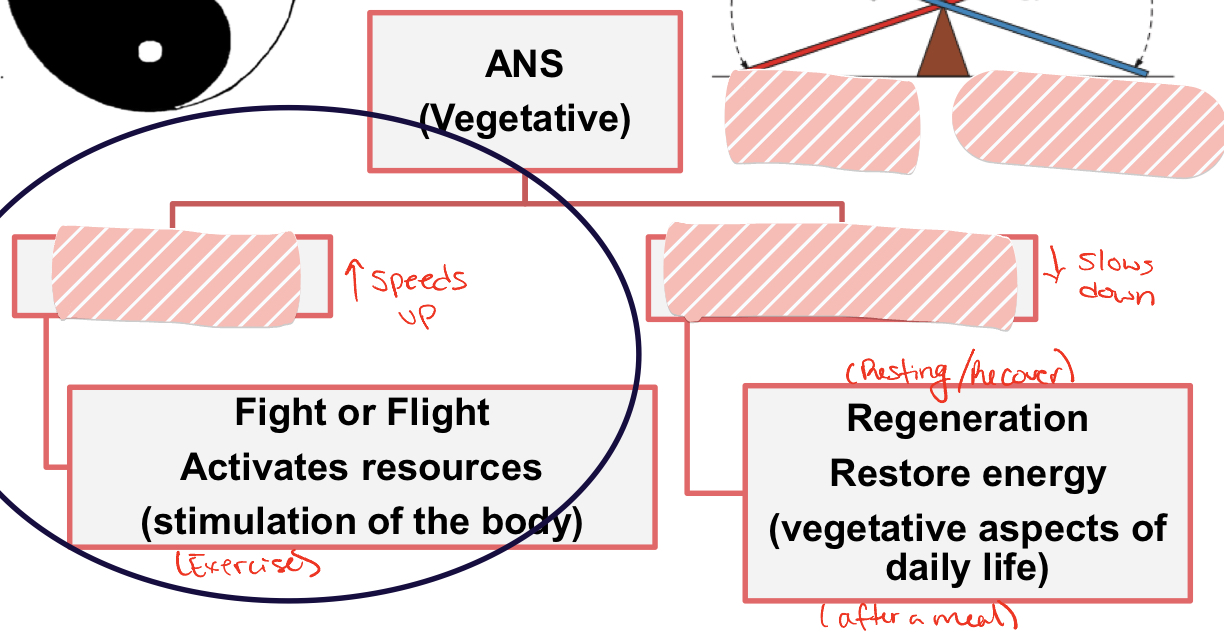
Fight or flight": Sympathetic
Regeneration: Parasympathetic
What is the origin of preganglionic neurons?
Throacolumbar region
Where are the preganglionic neurons found in the spinal cord?
Intermediolateral gray matter
What does most ganglia of the sympathetic system belong to?
The network of sympathetic chain ganglia that runs alongside the vertebral column
What is the ratio of preganglionic fiber to postganglionic fiber?
1:20
What is a ganglion?
A cluster of nerve cell bodies located outside the central nervous system. In the ANS, ganglia serve as relay points for transmitting signals between the central nervous system and target organs
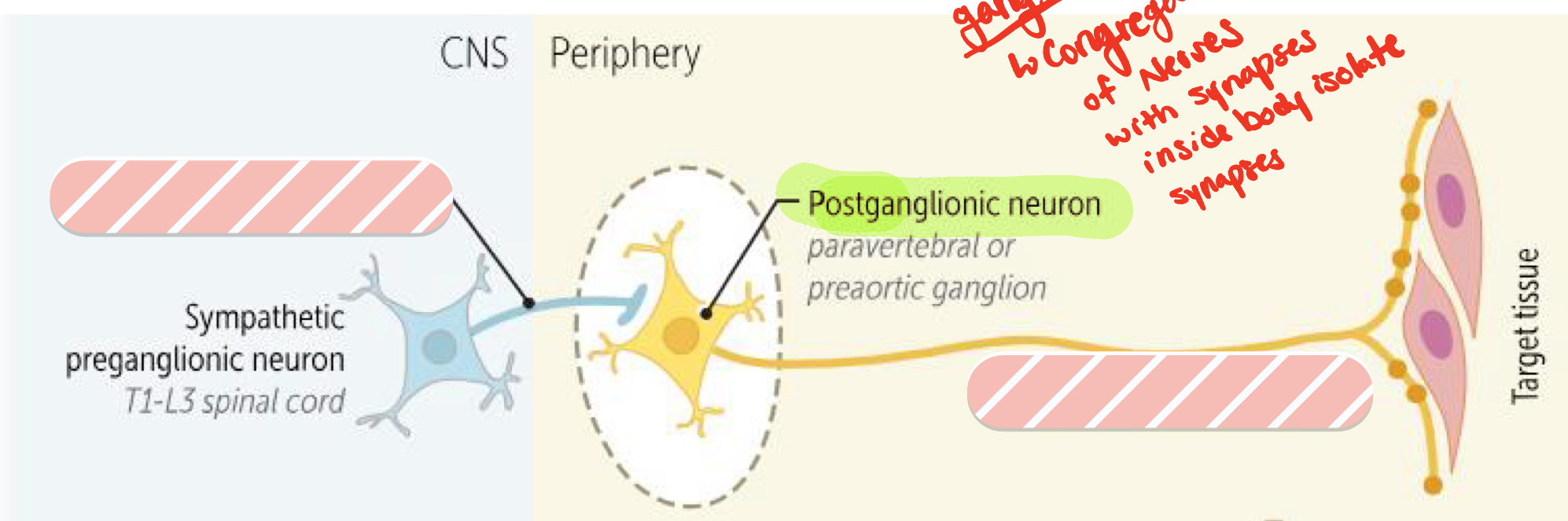
Presynaptic ganglia: short
Postsynaptic ganglia: long
What does it mean when all preganglionic neurons are cholingeric?
They synthesize and release acetylcholine as their primary neurotransmitter.
Autonomic ganglia is always mediated by what neurotransmitter?
Acetylcholine
What is the receptor for the cholinergic?
Nicotinic
What cells in the adrenal medulla release epinephrine in the bloodstream?
Chromaffin Cells
What does it mean when a postganglionic neuron is adrenergic?
It means that they synthesize and release norepinephrine or noradrenaline as their primary neurotransmitter.
What are the receptors called that bind to the adrenergic receptors?
Alpha and beta
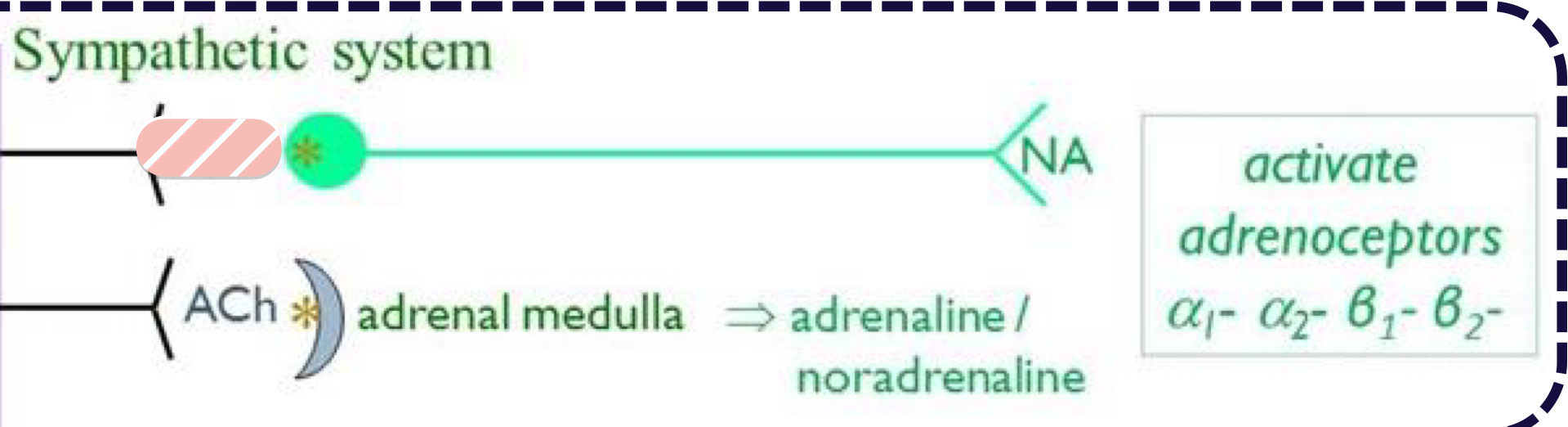
What is hidden?
ACH
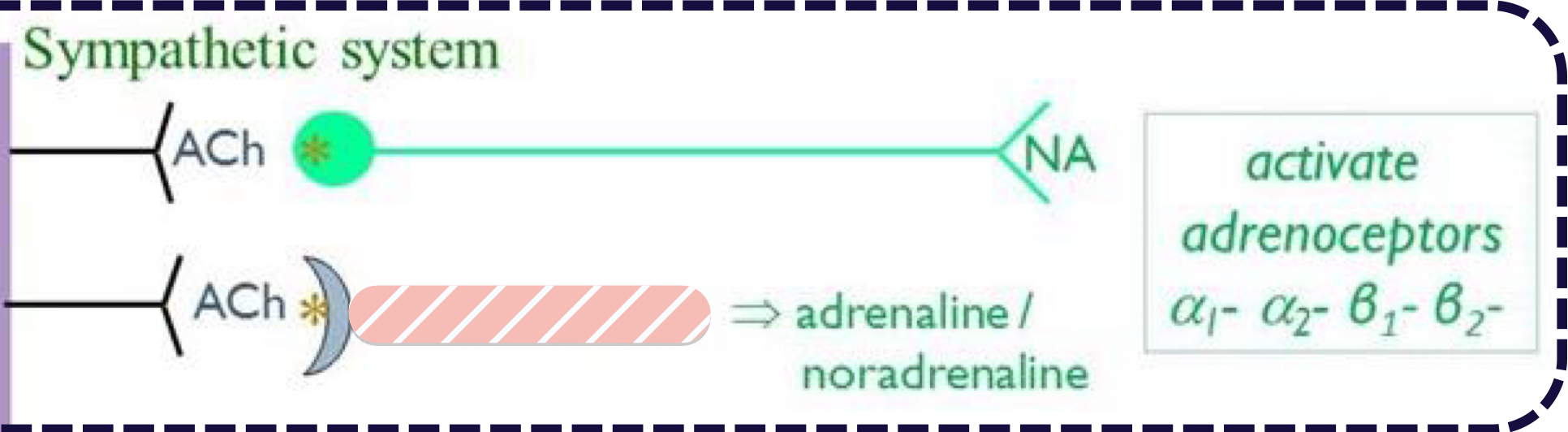
What is hidden?
Adrenal Medulla
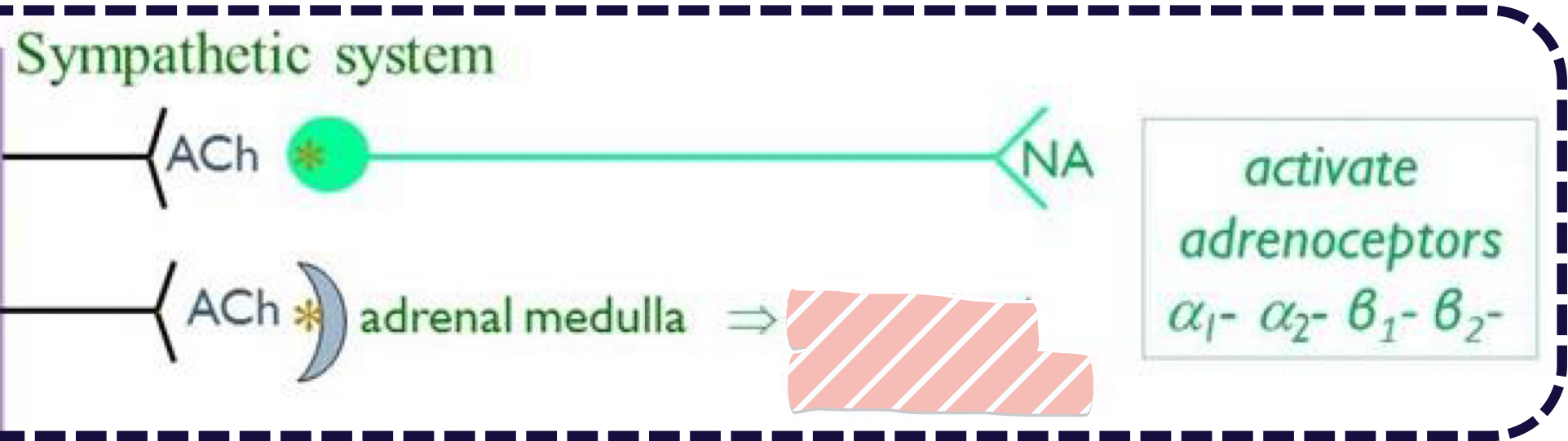
What is Hidden?
Adrenaline/Noradrenaline
What are the active adrenoceptors?
Alpha 1
Alpha 2
Beta 1
Beta 2
How does the sympathetic neurons and adrenal medulla effect the eyes?
Dilation of pupils (A1-AR)
How does the sympathetic neurons and adrenal medulla effect the Gastrointestinal activity?
Inhibits it with several receptors
How does the sympathetic neurons and adrenal medulla effect the Lungs?
Brochodilation (B2-AR)
How does the sympathetic neurons and adrenal medulla effect the Heart?
Increased heart rate:
Cardiac output (B2-AR)
Vasoconstriction (increase in BP) (A1-AR)
How does the sympathetic neurons and adrenal medulla effect the BG?
Increases the BG concentration (A2-AR)
How does the sympathetic neurons and adrenal medulla effect insulin?
Inhibits insulin release (B2-AR) by stimulating glugagon release
How does the sympathetic neurons and adrenal medulla effect the Blood supply?
Increases the blood supply to the skeletal muscles
What G-protein coupled membrane receptor (GPCR) stimulation leads to Bronchodiluation?
B2-AR
What type of receptor is Phenylephrine an agonist?
a1-adrenergic receptor
What doe a sympathomimetic mean?
mimics sympathetic dilution
What are the uses of Phenylephrine?
dilutes pupils
Vascoconstriction
What are the side effects of phenylephrine?
High blood pressure
What kind of adrenergic receptor is Phenylpropanolamine an agonist?
A1-adrenergic receptor
What are the uses of Phenylpropanolamine?
Constriction of the inner sphincter of the urinary bladder for incontinance or urinary dribbling
What are the side effects of Phenylpropanolamine?
Tachycardia and High blood pressure
What adrenergic receptor is Brimonidine Tartrate an agonist?
A2-adrenergic receptor
What are the effects of Brimonidine Tartrate?
Reduces intraocular pressure
How does Brimonidine Tartrate reduce intraocular pressure?
Decreases Aqueous humor production
Increasing aqueous humor outflow
What is the Therapeutic use of Brinonidine Tartrate?
Glaucoma
What is Glaucoma?
Increase of the intraocular pressure
How is Glaucoma harmful?
Fluid cannot drain from the eye causing increase in IOP. Prolonged high IOP can damage optic nerve and result in blindness
What type of adrenergic receptor is Xylazine an agonist?
A2-adrenregic receptor
What is the Mechanism of action for Xylazine?
Activation of presynaptic A2-adrenergic in the brainstem and spinal cord, leading to decreased sensorial or descending motor sympathetic outflow.
What are the effects of Xylazine?
Produces sedation, muscle relaxation, and analgesia
What animals are mostly effected by Xylazine?
Horses
cattle
large animals
Deer
What is the therapeutic use of Xylazine?
Anesthetic premedication
Sedation
Total IV anesthesia
Vomiting in cats
What are the adverse effects of Xylazine?
Brachycardia
Heart Conduction disturbances
What is the adrenergic receptor for Detomidine and Romifidine?
A2-adrenergic receptor
What is the mechanism of action for Detomidine and Romifidine?
Activation of presynaptic A2-adrenergic receptors in brainstem and spinal cord, leading to decreasing sensorial or descending motor sympathetic outflow
What are the effects and uses of Detomidine and Romifidine?
Sedation and anesthetic premedication, IV anesthesia in horses
What are the adverse effects of Detomidine and Romifidine?
Bradycardia
Heart Conduction Disturbances
What is the adrenergic receptor for Medetomidine?
A2-adrenergic receptor
What is the adrenergic receptor for Dexmedetomidine?
A2-adrenergic receptor
What is the effects and uses of Medetomidine?
Sedative with analgesic action in small animals and horses
What are the effects and uses of Decmedetomidine?
emetic in cats
Treat emergence delirium following anesthesia
What drug could be used for treating hyptension associated with anesthesia?
Phenylephrine
What is the Adrenergic receptor for Isoproterenol?
B adrenergic receptor
What are the effects of Isoproterenol?
Increases the force of contraction
The rate
Conductivity of the heart impulses
Vasodilation
Urine Relaxation
What does a non-selective adrenergic receptor mean?
Doesn’t respect receptor types such as B1 and B2
What does tocolytic effect mean?
Urine relaxation
What are the therapeutic uses of Isoproterenol?
Brachycardia
heart block
What are the adverse effects of Isoproternol?
Tachycardia
Arrhythmias
What type of adrenergic receptor is Dobutamine an agonist?
B1 adrenergic receptor
What are the effects of Dobutamine?
Increase the myocardium force of contraction
Heart rhythm is stable but depends on the dos and species
What is the Therapeutic uses of Dobutamine?
Congestive heart failure
Hypotension during surgery by increasing CO
What are the adverse effects of Dobutamine?
Increases AV conduction
Tolerance (tachyohylaxis)
What type of adrenergic receptor is Terbutaline an agonist?
B2 adrenergic receptor
What is the mechanism of action and effects of Terbutaline?
Produces relaxation of smooth muscle found principally in bronchial, vascular and uterine tissues.
What are the therapeutic uses of Terbutaline?
Brochodilater: treats asthma
Particularly used in cats
What is the adverse effects of Terbutaline?
Tachycardia
What is the adrenergic receptor for Clenbuterol agonist?
B2 adrenergic receptor
What is the mechanism and the effect of Clenbuterol?
Bronchodilator
Banned in food-producing animals due to anabolic/performance enhancer in human consumers.
What sympathomimetic drug can be used as part of the treatment of acute congestive heart failure in dogs?
Dobutamine
What are the three types of a-adrenergic receptor antagonists?
Non-selective
Selective A1
Selective A2
What is a non-selective alpha-adrenergic receptor?
Works on any alpha receptor
What are examples of Non-selective a-adrenergic antagonists?
Phenoxybenzamine
ACP
What is an example of a Selective A1 adrenergic anatgonist?
Prazosin
What is an example of Selective A2 adrenergic antagonsit?
Yohimnine
Atipamezole
What are the two type of B adrenergic antagonists?
Non selective
Selective B1
What are examples of non-selective B-adrenergic anatagonist?
Propanolol
Timolol
Satalol
What is an example of a selective B1 antangonist?
Atenolol
What type of receptor is for the Phenoxybenzamine antagonist?
A-adrenergic receptor
What does Phenoxybenzamine do to the receptor?
Irreversible inhibition of the a-adrenergic receptor
What are the pharmacological actions fo Phenoxybenzamine?
Prevents vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels
What is the theraputic use of Phenoxynenzamine?
Tumor of the adrenal gland medulla (pheochromocytoma)
Reduces urinary sphincter tone and allow easier urination
What type of receptor is used for Acepromazine (ACP) antagonist?
A-adrengenic
What is the mechanism and use of ACP?
Phenothiazone tranquilizer that blocks dopamine receptors in CNS and depresses reticular-activity resulting in sedation
What is does ACP block?
Dopamine
A-adrenergic receptor
Is ACP and analgesic?
No, but potentiates the effects of analgesic drugs
What are the effects of ACP?
Sedation without significant respiratory depression
Systemic BP can be reduced due to vasodiluation.
Vagally-induced Bradycardia
Antiemetic
Antihistaminic
Antisympathetic
Antiarrhythmic
Antishock
What receptor is used for Prazosin antagonist?
A1 adrenergic
What are the effects of Prazosin?
decreased peripheral resistant and lowers BP
Reflex tachycardia is less significant caused by beta receptors