BIO 102 Lab Final Exam
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What’s my power?
power of magnification = power of ocular lens x power of the objective
Calculating Magnification
Eye Piece Objective Lens
10x 100x
10x 50x
5x 40x
Magnification
Enlarge objects
Resolution
Distinguish between objects
Contrast
Differences in intensity
What does the oil immersion lens do?
It reduces light scatter, increasing resolution
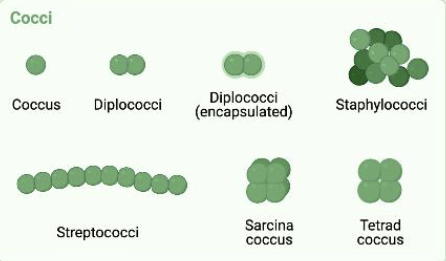
Simple Stain Cocci
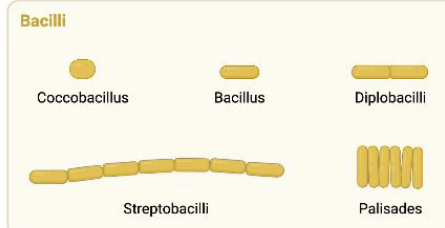
Simple Stain Bacilli
Also referred to as ‘Rod’
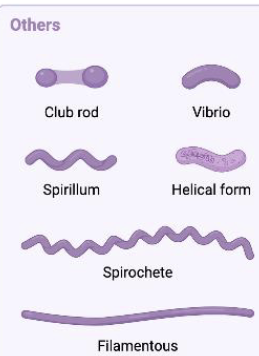
Simple Stain Others
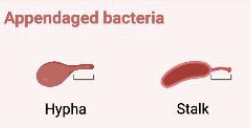
Simple Stain Appendaged Bacteria
How does Gram Positive Bacteria Appear?
Blue
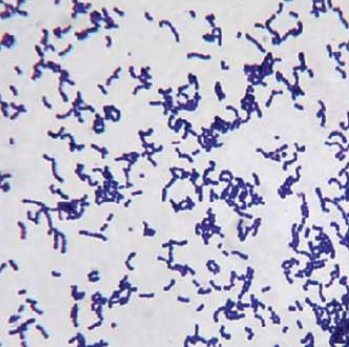
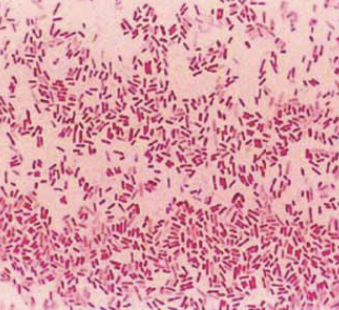
How does Gram Negative Bacteria Appear?
Pink/ Red
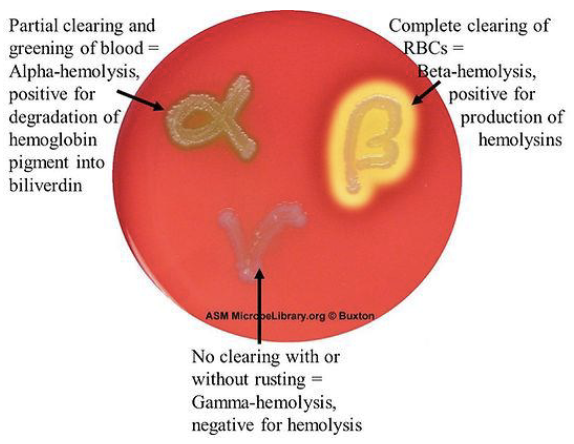
Blood Agar
Hemolysis
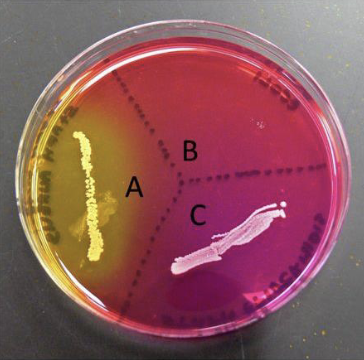
Mannitol Salt Agar
Selective and differential
A) Positive (mannitol fermentation)
B) Inhibit growth
C) Negative
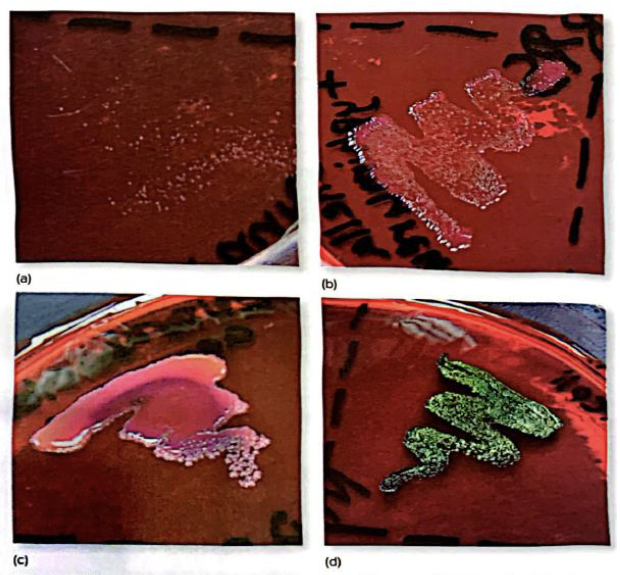
Eosin Methylene Blue
Gram negative
Lactose
Colored colonies
(Picture shows the growth on EMB agar a) gram-positive organism growing poorly due to inhibition by methylene blue in medium b) gram-negative non-lactose fermenter c) coliform lactose fermenter with mucoid pink and purple growth d) E. coli with green sheen caused by rapid lactose fermentation)
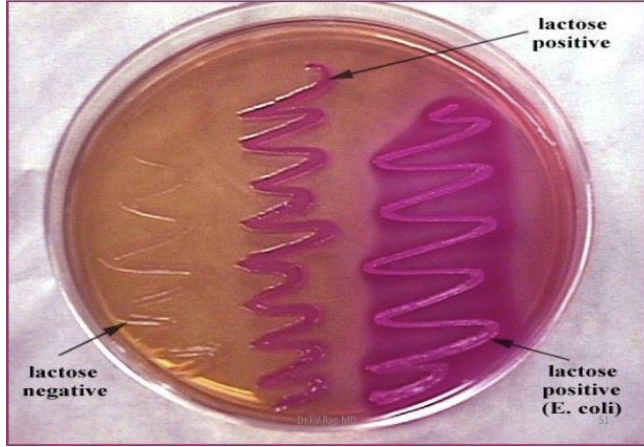
MacConkey
Gram negative
Lactose fermentation
colored colonies
Osmotic Pressure
Absorbance via spectrophotometer
Higher absorbance= higher bacterial number= halophilic
Osmotic Pressure
BHI (brain-heart infusion agar)
Ice bath to limit diffusion of oxygen from atmosphere
Creates gradient from high oxygen near surface to low oxygen at bottom
Catalase
Hydrogen peroxide
Catalase = hydrogen peroxide → O2 = bubbles
2H2O2 --catalase→ 2H2O + O2
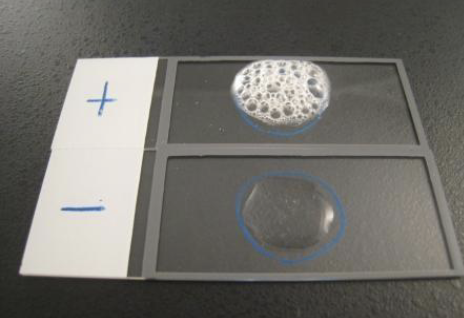
Oxidase
Oxidase reagent
purple=positive
Aerobic gram negative bacteria
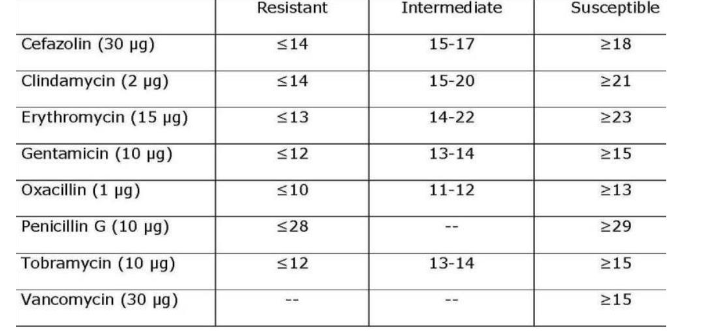
Kirby-Bauer Method
Antibiotic sensitivity
Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA)
Compare measured zone of inhibition to standard table
Sensitive (susceptible), intermediate, resistant
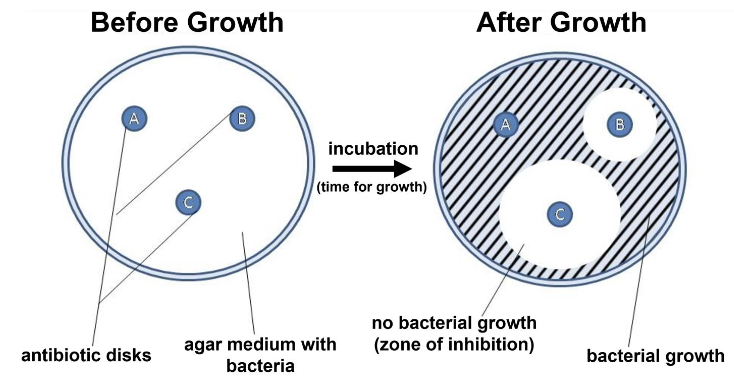
Kirby-Bauer Method
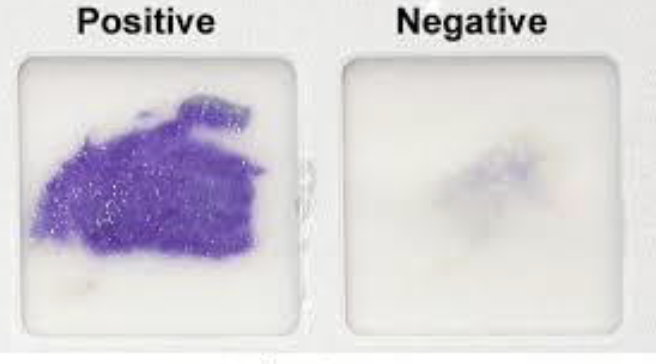
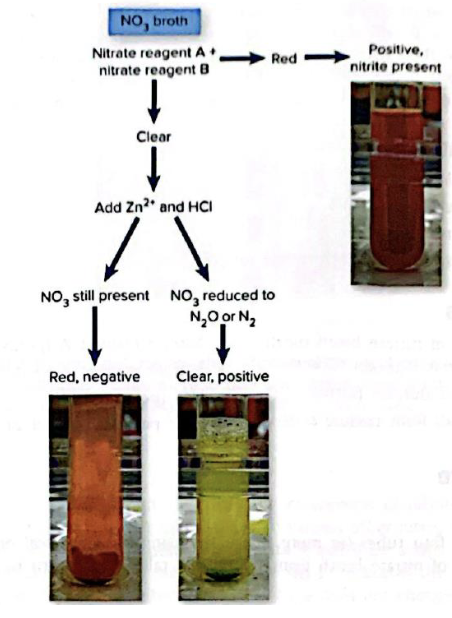
Nitrate Reduction
Nitrate broth
Initial red= positive
Red after Zn^3+ and HCl = negative
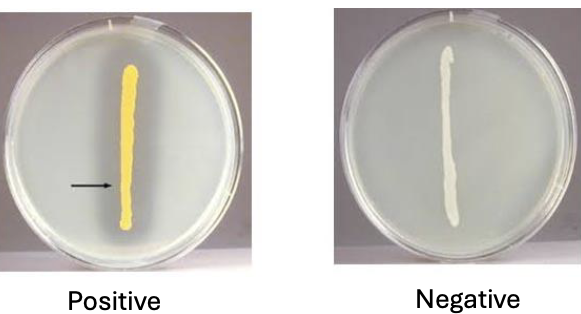
DNase
DNase agar
• Add DNA to nutrient
agar
• Test for presence of DNase
DNase results
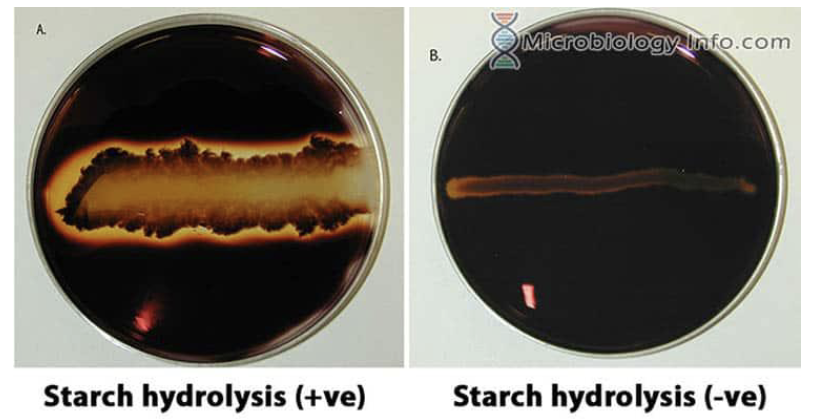
Starch Hydrolysis
• Starch agar plates
• Testing for amylase
• Iodine
Starch Hydrolysis Results
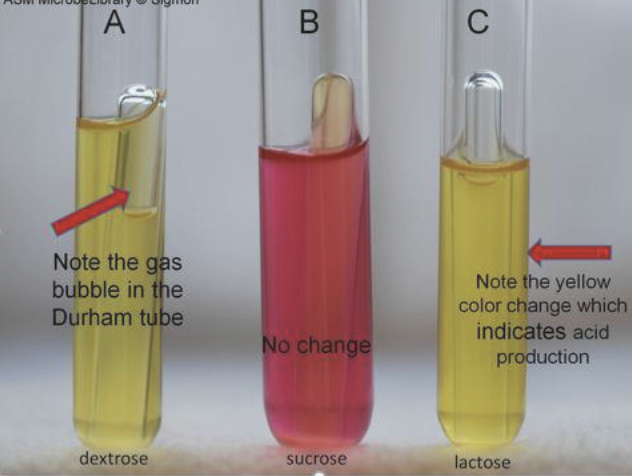
Phenol Red
• pH indicator
• Glucose, lactose, sucrose
• + = yellow
• Acid production
• Substrate utilization
Phenol Red Results

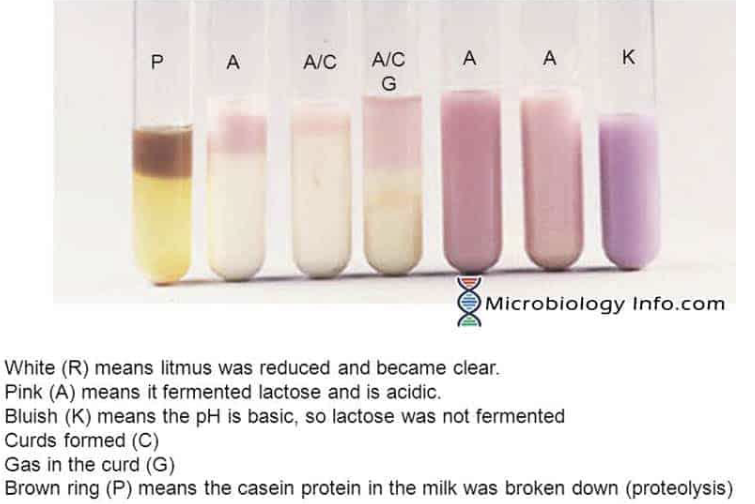
Litmus Milk
• pH
• Pink = acidic (lactose
fermentation)
• Purple/blue = basic
• White = litmus reduction
• Brown = proteolysis/digestion
Litmus Milk results
IMViC
MRVP
• MR = methyl red
• + = red
• VP = Vogues-Proskauer
• VP reagent A +B
• + = red
Methyl Red Test Results

Vogues-Proskauer Test Results

IMViC
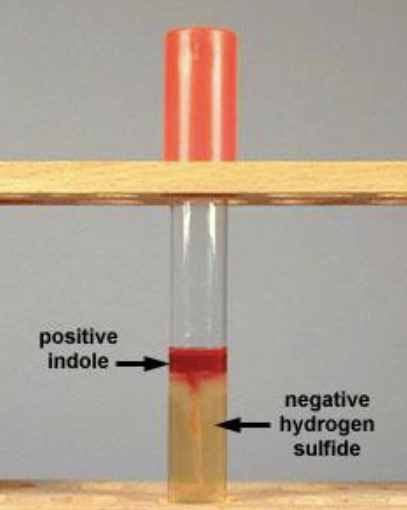
SIM
• Sulfide
• + = black (hydrogen sulfide released when metabolized)
• Indole
• Kovac’s
• + = red
• motility
• Stab semisolid SIM medium
• + = distribution
SIM Results
IMViC
• Citrate utilization
• Simmons citrate
• + = blue
Citrate Utilization Results

Urease
• Urea broth
• Presence of urease
• + = red/pink
Urease Results
