Simple harmonic motion.
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is simple harmonic motion?
A specific type of oscillation where:
There is repetitive movement back and forth through an equilibrium, so the max vertical or horizontal displacemnt on one side is equal to the max vertical or horizontal displacement on the other side.
The time interval of each complete vibration is the same (periodic)
The force responsible for the motion (restoring force) is always directed vertically or horizontally towards the equilibrium position and is directly proportional to the distance from it.
What are some examples of SHM?
pendulum on a clock
child on a swing
guitar strings vibrating
mass on a string
An oscillation is defined to be SHM when:
The acceleration is proportional to the horizontal or vertical displacement
The acceleration is opposite to the direction of displacement.
In SHM how is acceleration and horizontal displacement related?
a ∝ -x
What are the two models of SHM you will be required to explain and perform calculations on?
A simple pendulum, a mass-spring system.
Is a person jumping on a trampoline an example of SHM?
No, the restoring force is not proportional to the displacement from equilibrium.
What is the equation for object oscillating in simple harmonic motion?
a= -ω²x
ω= angular frequency (rad s-¹)
x= displacement
What does the SHM acceleration equation show?
acceleration reaches a maximum value when the displacement is at a maximum, acceleration and displacement are always opposite to each other.
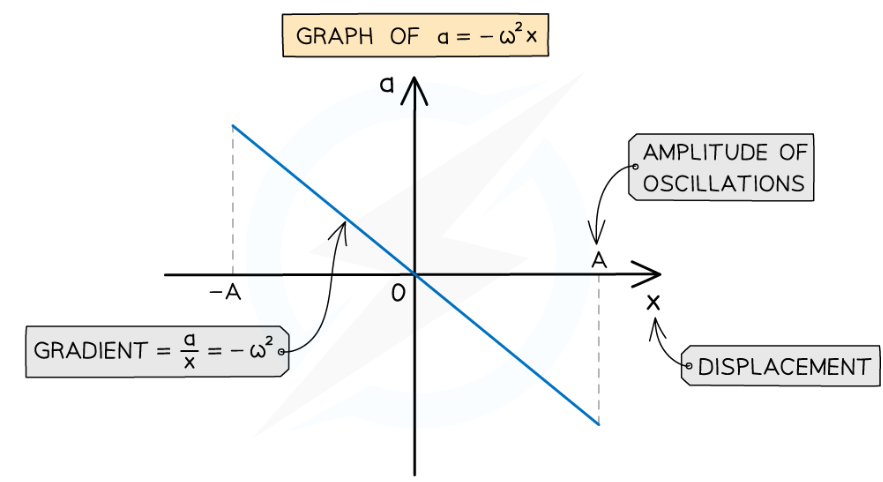
What is the graph that represents a= -ω²x?
gradient is equal to -ω², the max and min displacements are the amplitudes -A and +A.
What is the SHM displacement equation?
Acos(ωt)
A= amplitude
this is because graph of x=cos(t) starts from amplitude A when t=0, the displacement is at its max when cos(ωt) = 1 or -1, when x=A
If an object is oscillating from its equilibrium position what will the displacement equation be?
x= Asin(ωt)
In SHM what is the equation for where speed is the magnitude of its velocity?
v= ±ω√(A²-x²)
For oscillations that start from the equilibrium position what are the SHM graphs?
The displacement-time graph is a sine curve
The velocity-time graph is a cos graph
The acceleration-time graph isa negative sine graph
For oscillations that start at amplitude position what are the SHM graphs?
The displacement-time graph is a cos graph
The velocity-time graph is a negative sine graph
the acceleration-time graph is a negative cos graph.
What are the key feature of a displacement-time graph?
The velocity of an oscillator can be determined from gradient.
What is the equation for max speed of a oscillator?
Vmax=ωA
A= amplitude ω=angular frequency
What is the equation for max acceleration of an oscillator?
a max= ω²A
In a mass-spring system, what is the equation for restoring force?
F= -kx
In a mass-spring system what is the time period equation?
T=2π√m/k
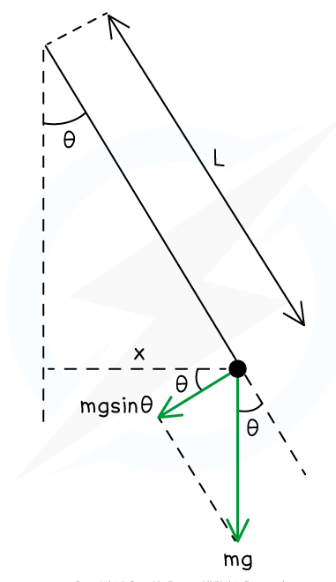
In a simple pendulum what is the equation for time period?
T=2π√L/g
L=string length
g=gravitational field strength (N kg-¹)
This formula is limited to small angles and therefore small amplitudes, the restoring force of the pendulum is the weight component acting along the arc of the circle towards equilibrium position,
What does the energies of a horizontal mass-spring system look like?
Mx elastic potential energy when spring is stretched beyond equilibrium, when mass is released kinetic energy increases, at equilibrium position kinetic energy is at maximum and elastic potential is at minimum, once past equilibrium position kinetic energy decreases and elastic potential increases.
What does the energies of a simple pendulum look like?
At amplitude at top of swing, the pendulum has maximum gravitational potential, when pendulum is releases kinetic energy increases and gravitational potential decreases. Once mass has passed equilibrium position kinetic energy decreases and gravitational potential energy increases.
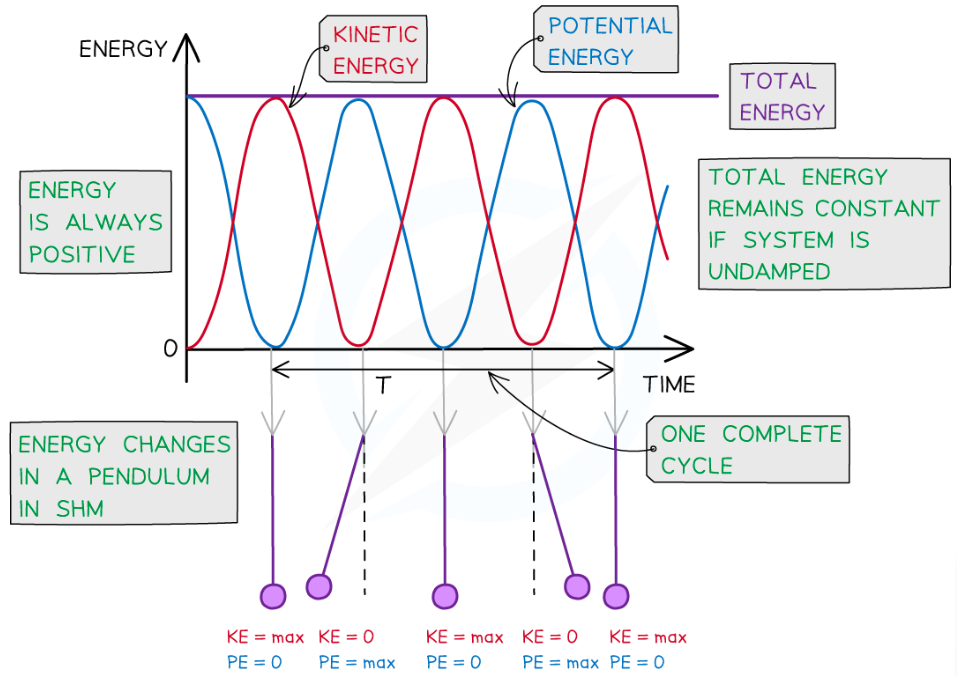
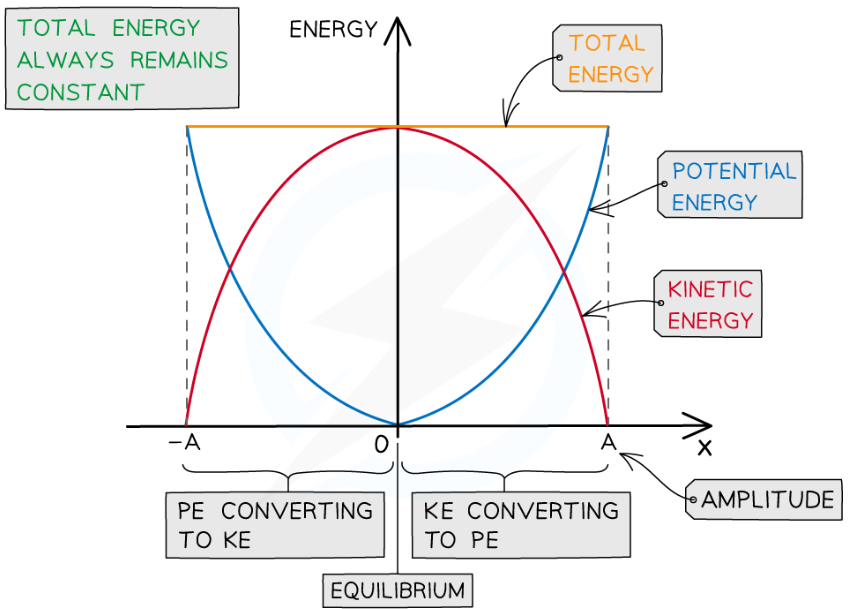
Explain the total energy in a SHM system?
total energy remains constant but amount of energy in one form goes up while amount in the other form goes down.
What is the graph showing the total potential and kinetic energy transfers in half a SHM oscillation?
What is the energy time graph for a simple pendulum?