unit 2 - osteology - mcb 245
1/346
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
347 Terms
osteocytes
mature bone cell that maintains the bone matrix
osteoprogenitor cells
stem cells that mature to become osteoblasts
osteoblasts
immature bone cells that secretes osteoid
osteoclasts
multinucleate cells that secrete acids and enzymes to dissolve bone matrix
ossification
formation and development of bone
Osteons
basic functional units of mature compact bone
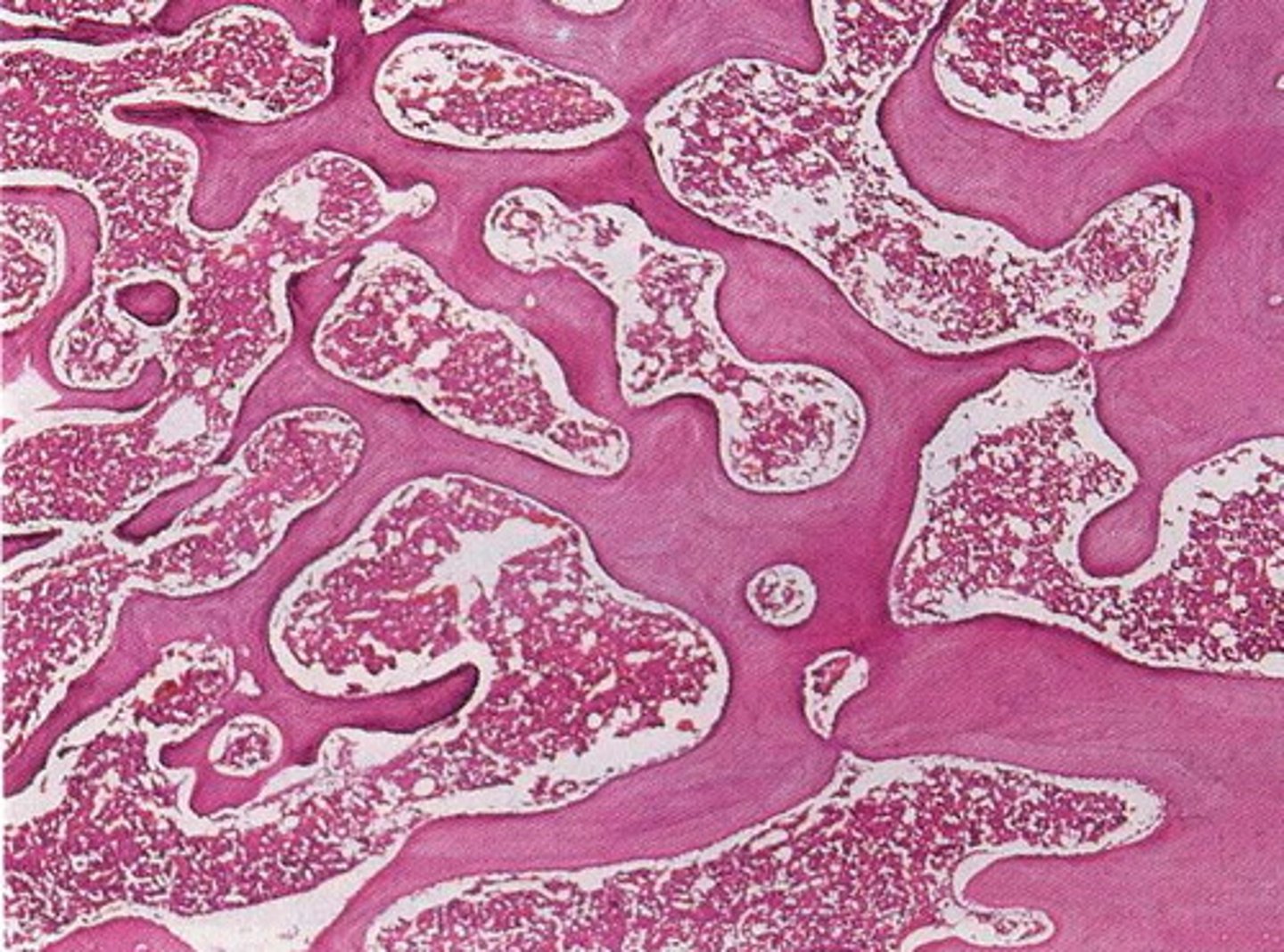
trabeculae
highly porous form of bone tissue that is organized into a network of interconnected rods and plates which surround pores that are filled with bone marrow
condyle
articulating surface: large, smooth, rounded, oval structure
facet
articulating surface: small, flat, shallow surface
head
articulating surface: prominent, rounded epiphysis
trochlea
articulating surface: smooth, grooved, pulleylike process
alveolus
depression: deep pit or socket in the maxillae or mandible
fossa
depression: flattened or shallow depression
sulcus
depression: narrow groove
crest
projection: narrow, prominent, ridgelike projection
epicondyle
projection: projection adjacent to a condyle
line
projection: low ridge
process
projection: any marked bony prominence
ramus
projection: angular extension of a bone relative to the rest of the structure
spine
projection: pointed, slender process
trochanter
projection: massive, rough projection found only on the femur
tubercle
projection: small, round projection
tuberosity
projection: large, rough projection
canal
openings/spaces: passageway through a bone
fissure
openings/spaces: narrow, slit-like opening through a bone
foramen
openings/spaces: rounded passageway through a bone
meatus
openings/spaces: passageway through a bone
sinus
openings/spaces: cavity or hollow space in a bone
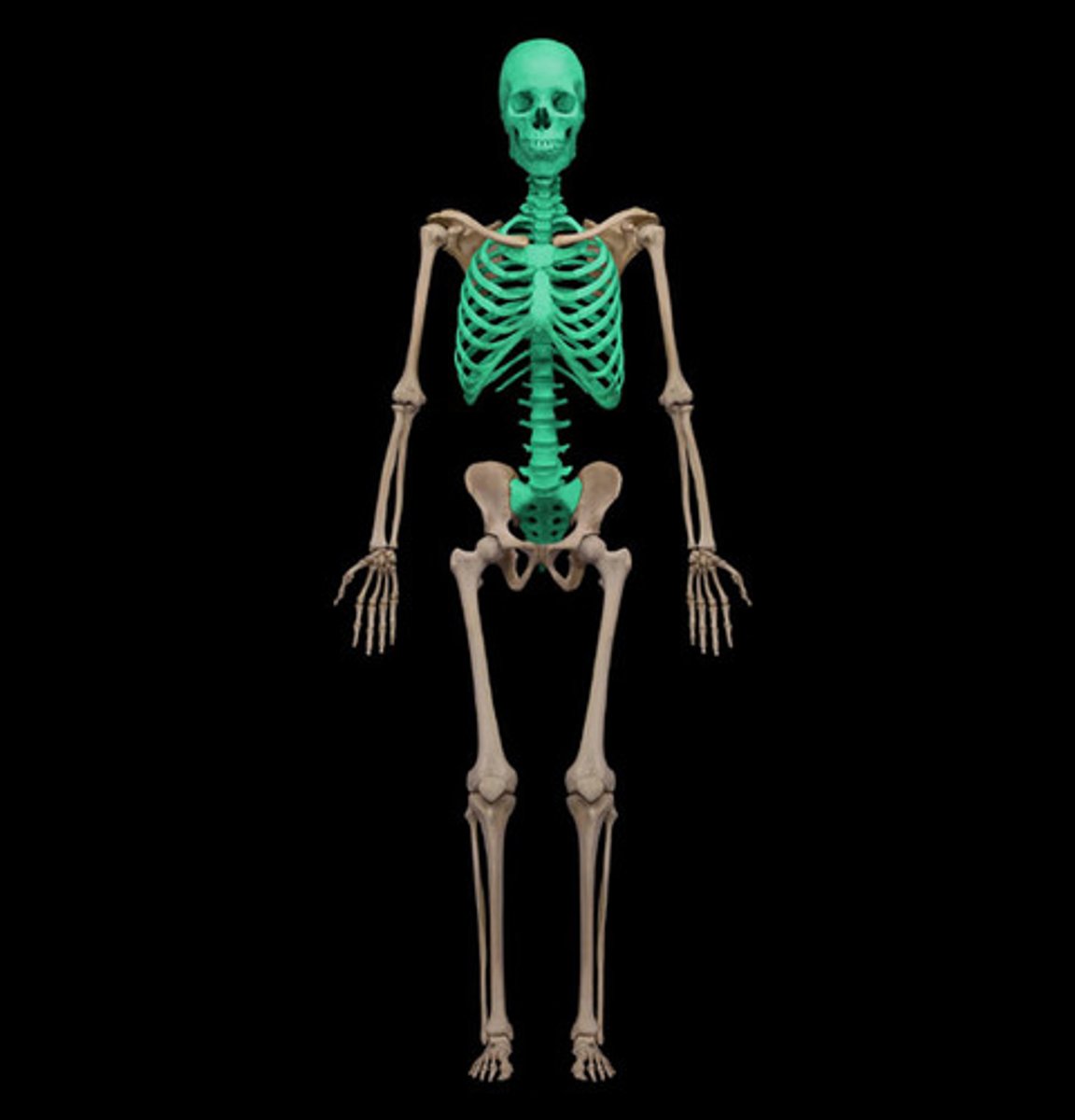
axial skeleton
composed of bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body from the skull to the end of the vertebral column
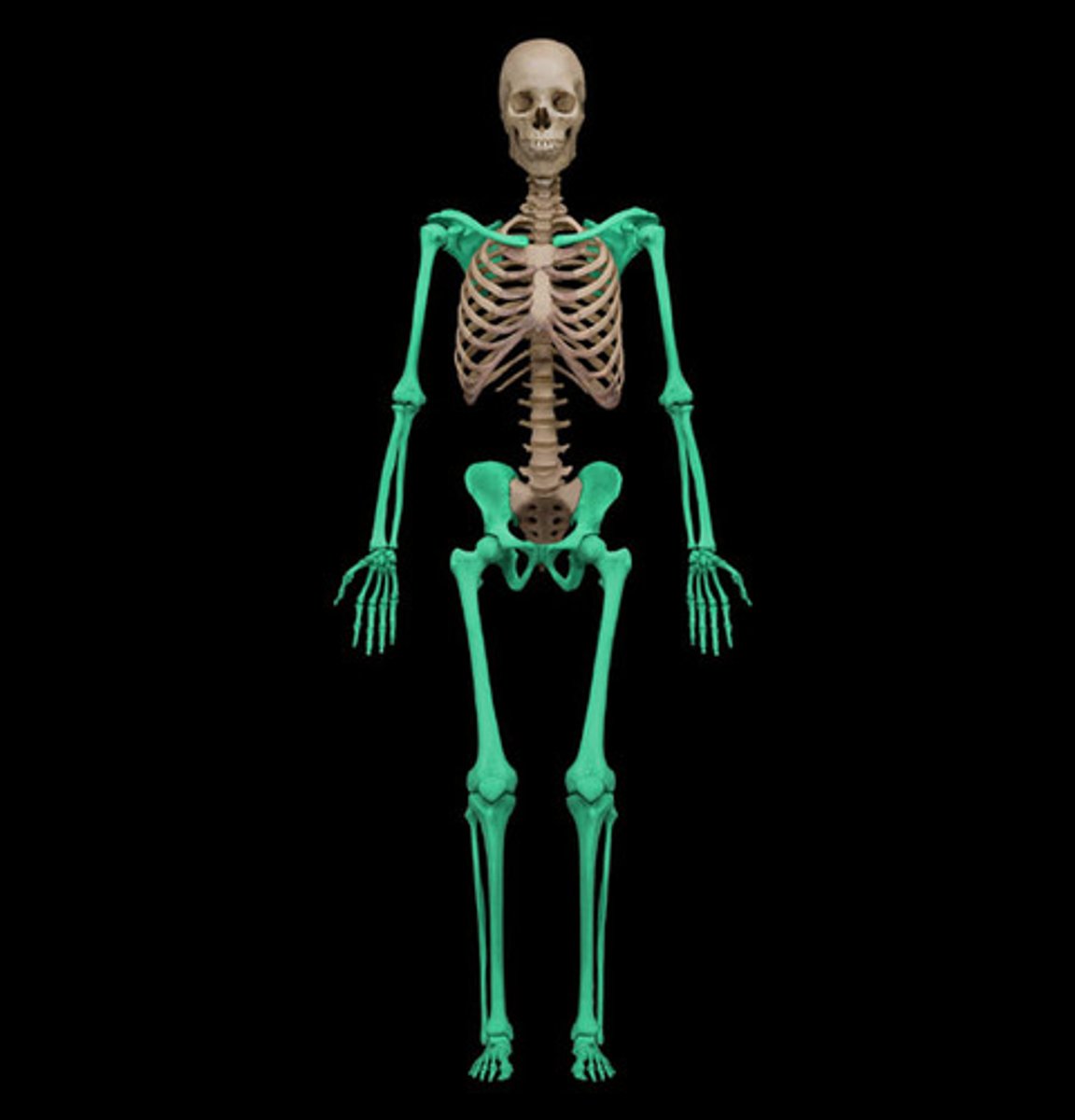
appendicular skeleton
composed of bones that make up the limbs and girdles which attach limbs to the axial skeleton
bone markings
bumps, holes, and ridges on bones where muscles, tendons, and ligaments are attached and where blood vessels and verves pass through
articulation
a joint; where 2 bones meet
fontanels
spaces between bones in an infant skull
canaliculi
tiny canals that radiate outward from the Haversian canal to lacunae to supply the bone cells with nutrients
diaphysis
shaft of a long bone; composed of compact bone
epiphysis
end of a long bone; composed mostly of spongey bone
epiphyseal line
marking left on the bone from growth at the epiphyseal plate
remodeling
process of breaking down and reforming bone that occurs throughout life to maintain proportion and strength as well as healthy calcium levels
fracture
broken bone
rickets
soft bones caused by lack of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphorus
vertebral body
thick anterior weight-bearing structure (part of vertebrae)
vertebral arch
posterior to body (part of vertebrae)
vertebral foramen
opening enclosed by body with vertebral arch
vertebral canal
formed by stacked vertebral foramina, contains the spinal cord
pedicles
originate from posterolateral margins of body (part of vertebrae)
laminae
extend posteromedially from posterior edge of pedicle
spinous process
projects posteriorly from laminae junction
transverse process
lateral projections on both sides of vertebral arch
superior and inferior articular processes
originate at junction between pedicles and laminae, have smooth surface articular facet-articulate with vertebra either above or below
intervertebral discs
pads of fibrocartilage separating vertebral bodies, shock absorbers, allows vertebral column to bend
true ribs
ribs 1-7, connect individually to the sternum by costal cartilages
false ribs
ribs 8-12, costal cartilages not attached directly to the sternum
pectoral
refers to the shoulder region
pelvic
refers to the hip region
clavicle
is an elongated, S-shaped bone which extends between the manubrium of the sternum and the acromion of the scapula
scapula
shoulder blade
humerus
longest and largest upper limb bone
ulna
longer, medially placed bone of the forearm
carpals
wrist bones; allow multiple movements at wrist; arranged in 2 rows of 4 bones each
ilium
largest of 3 coxal bones; forms superior region of the os coxae
femur
longest, heaviest, strongest bone in body
patella
kneecap, large, triangular sesamoid bone
fibula
long, lateral, non-weight-bearing bone of the leg
axial skeleton
appendicular skeleton
ossification
the formation and development of bone connective tissue
endochondral ossification
- process that begins with a hyaline cartilage model
- produces most bones of the skeleton
intramembranous ossification
- bone growth within a membrane (sheet of mesenchymal connective tissue)
- produces flat bones of the skull, some facial bones, the mandible, and the central part of the clavicle
- most ossification occurs during embryological development
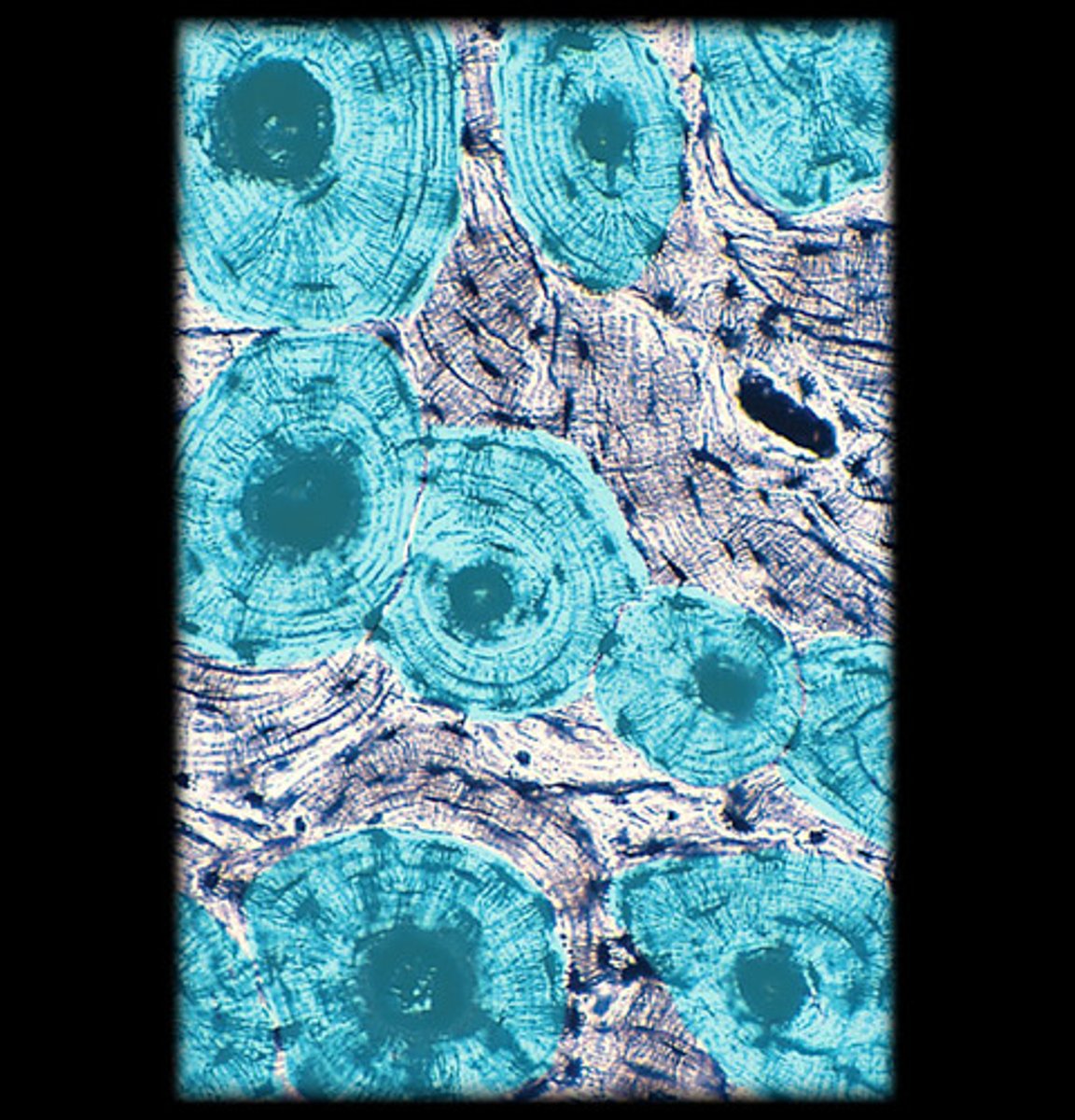
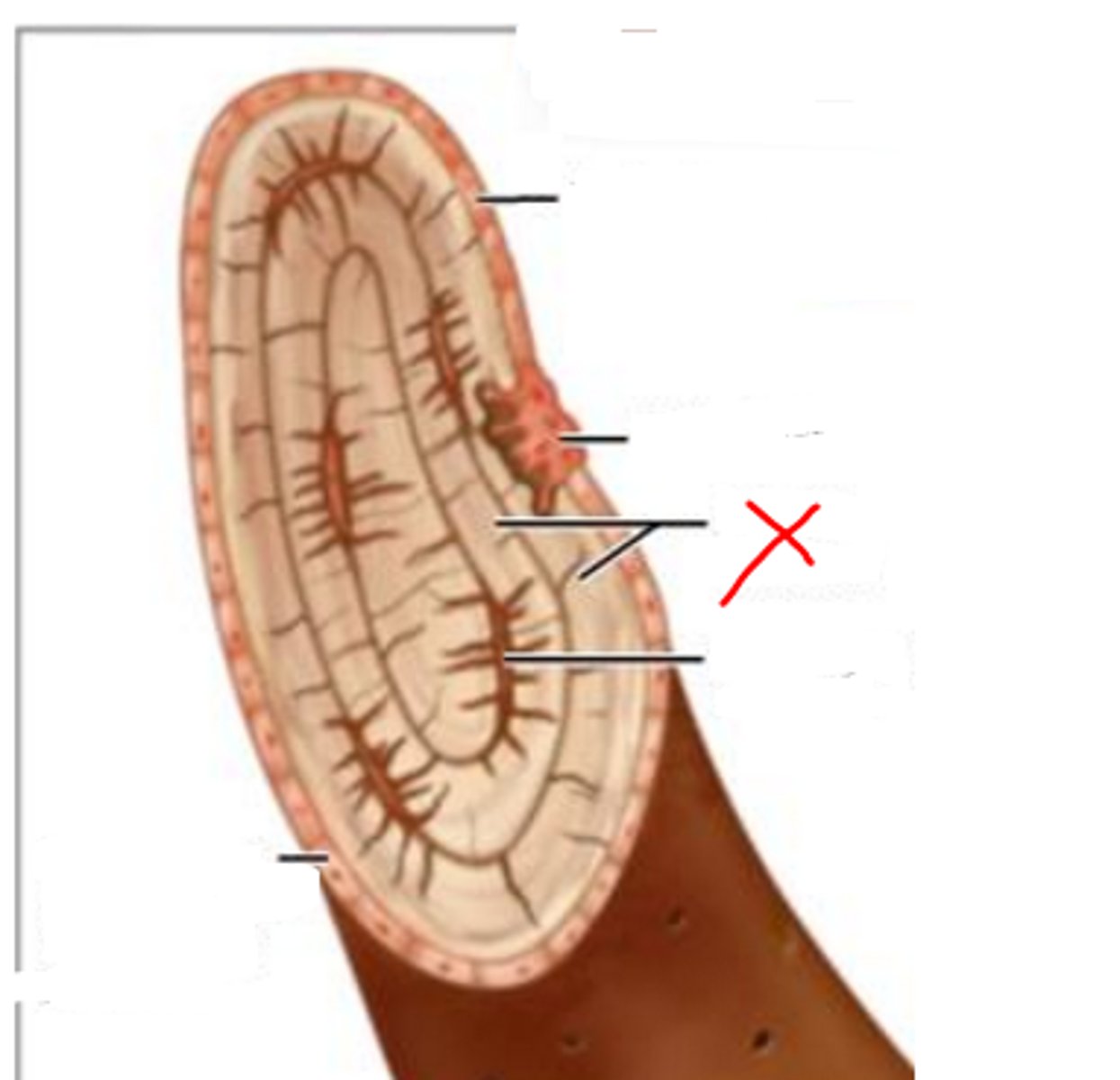
osteon
basic functional and structural unit of mature compact bone
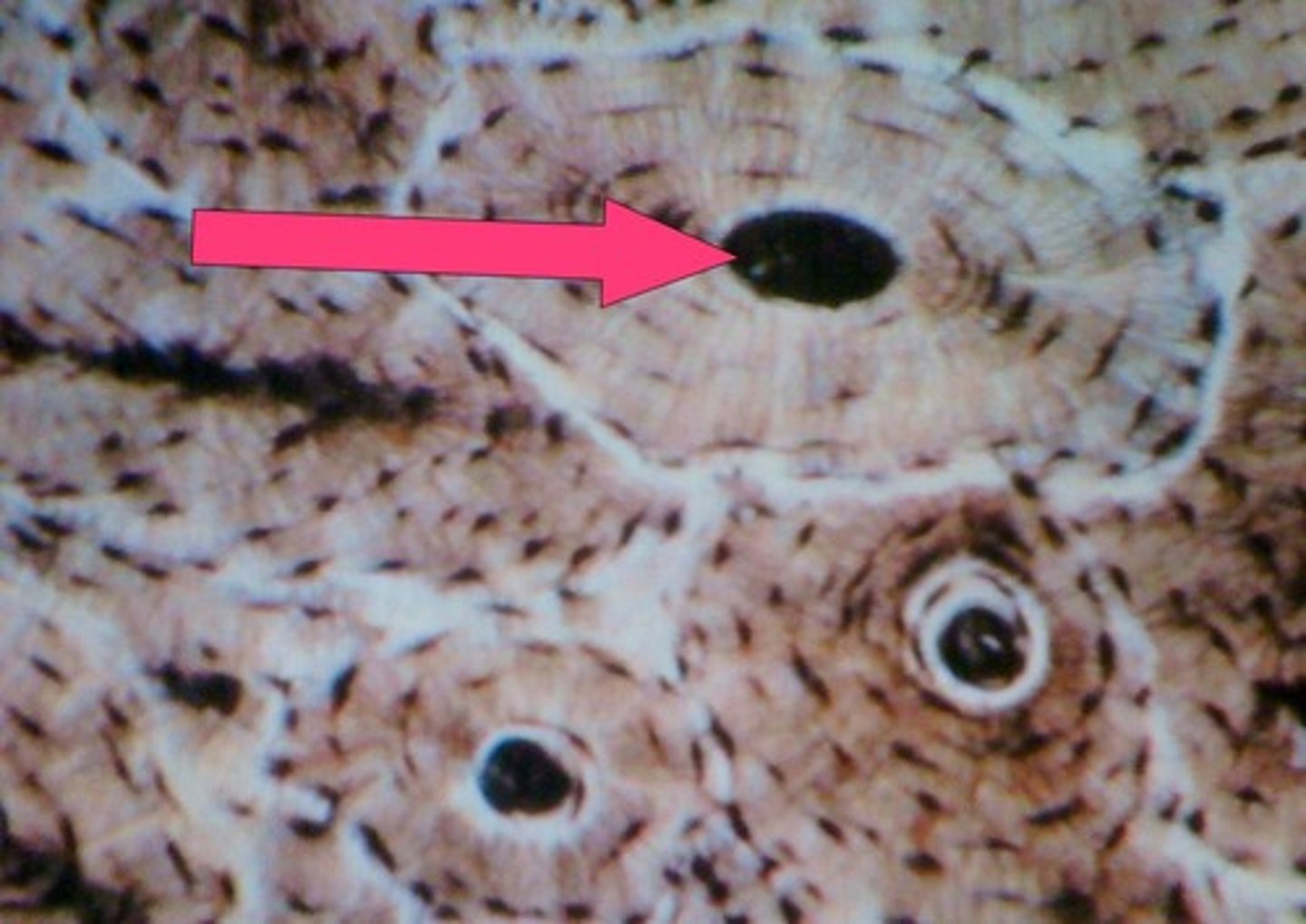
central canal
channel at center of osteon that contains blood vessels and nerves
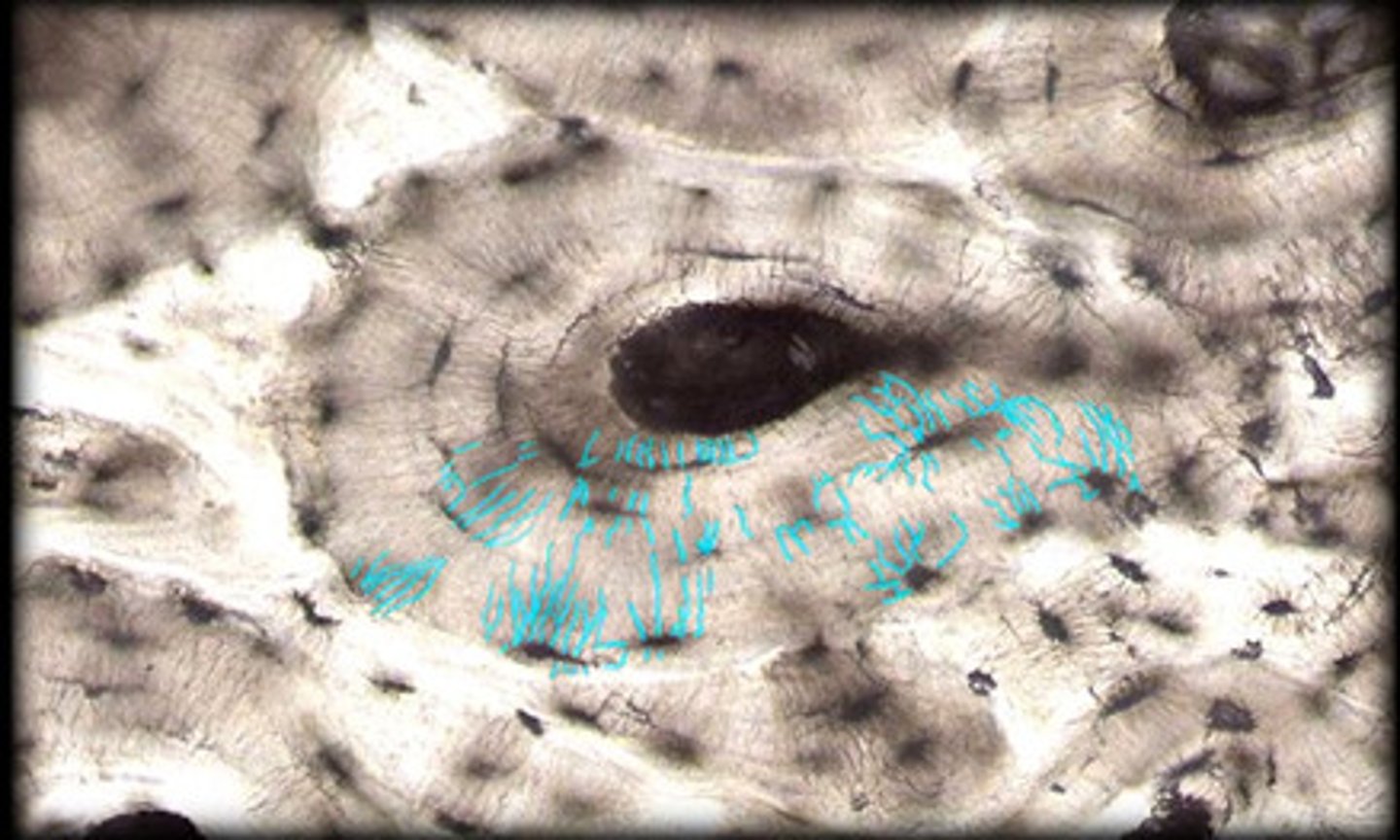
concentric lamellae
bone connective tissue made up of collagen fibers; concentric circles around central canal
osteocytes
mature bone cells found between lacuna to maintain bone matrix
lacuna (with osteocyte)
A
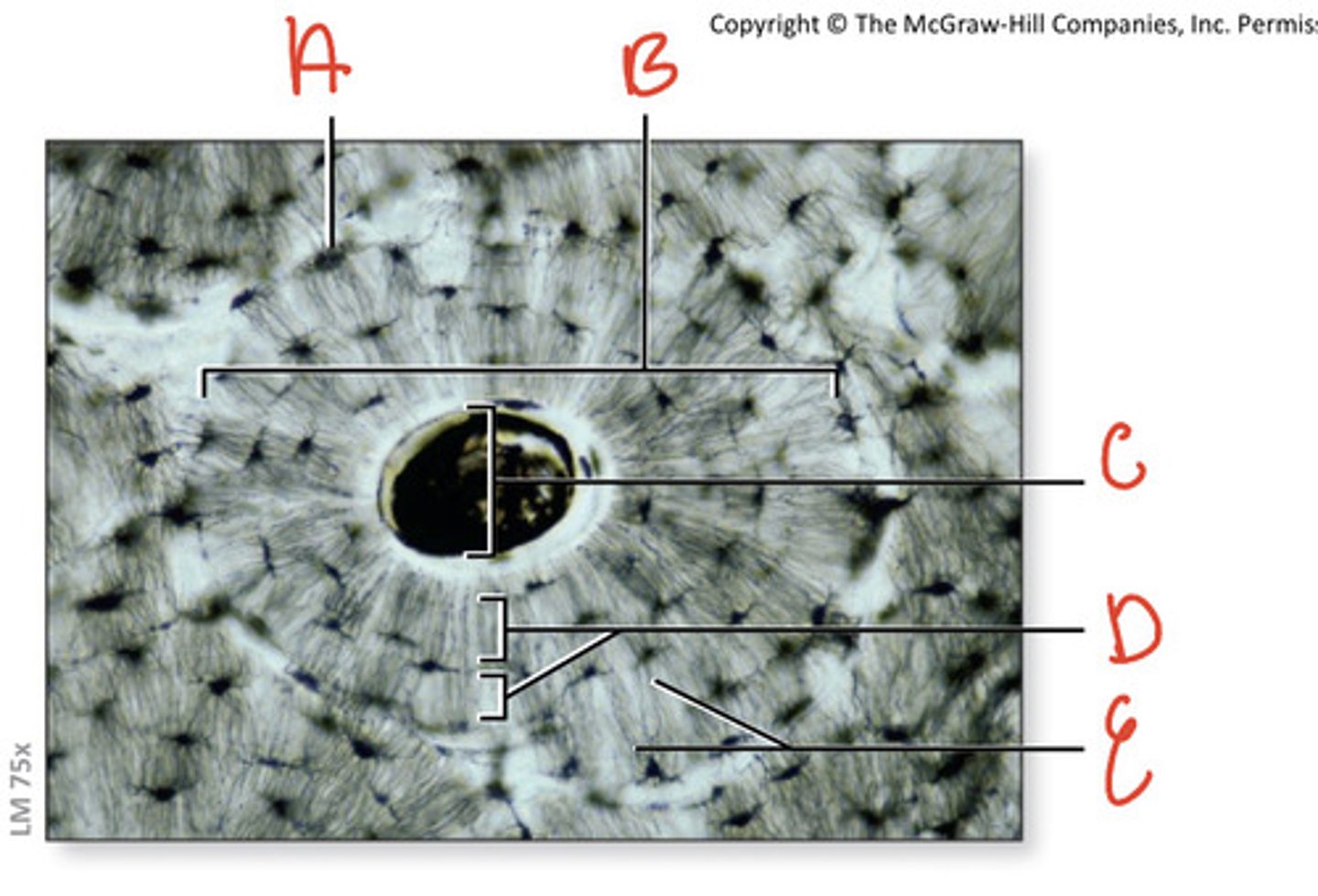
osteon
central canal
concentric lamellae
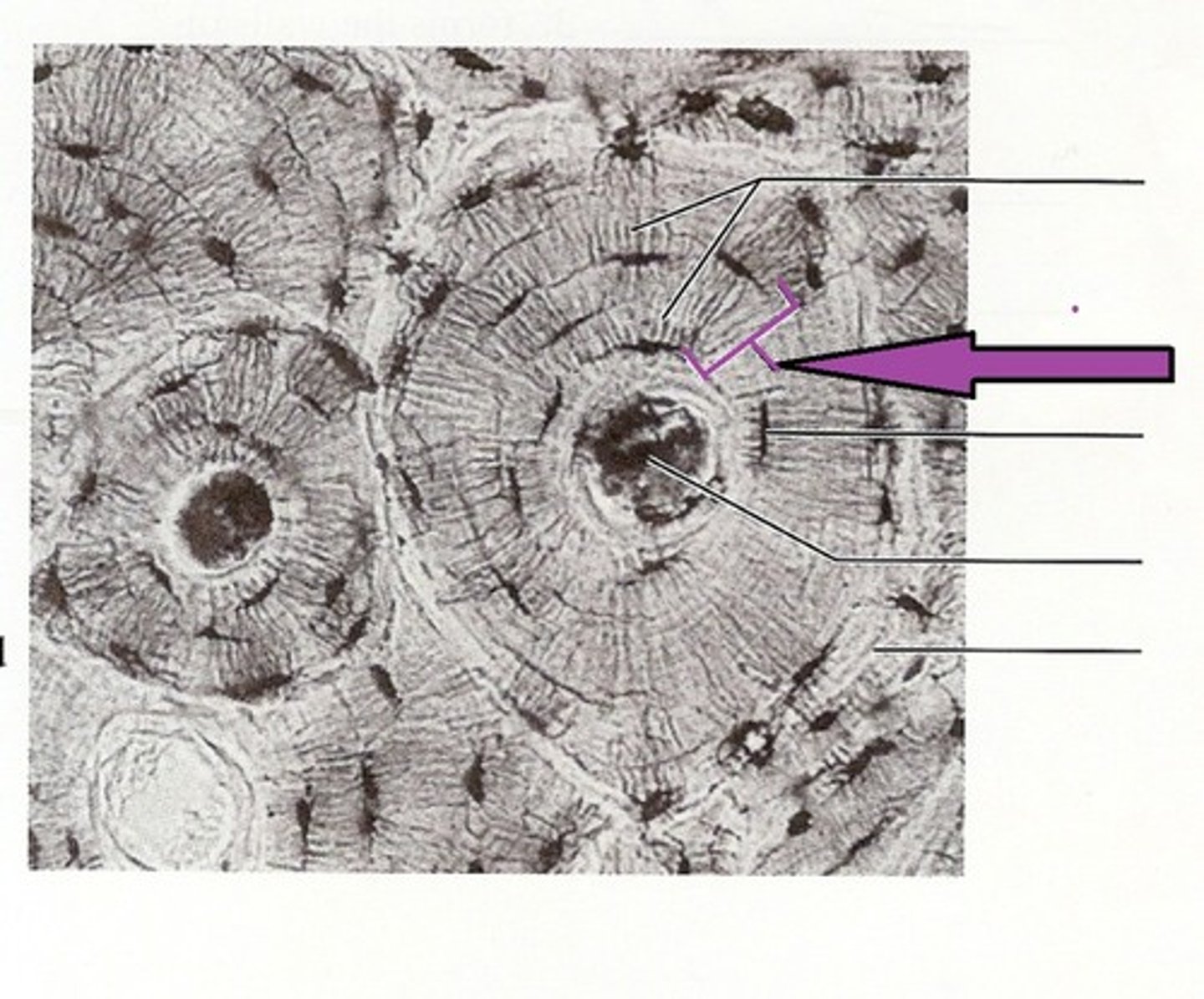
canaliculi
compact bone
spongy bone
trabeculae
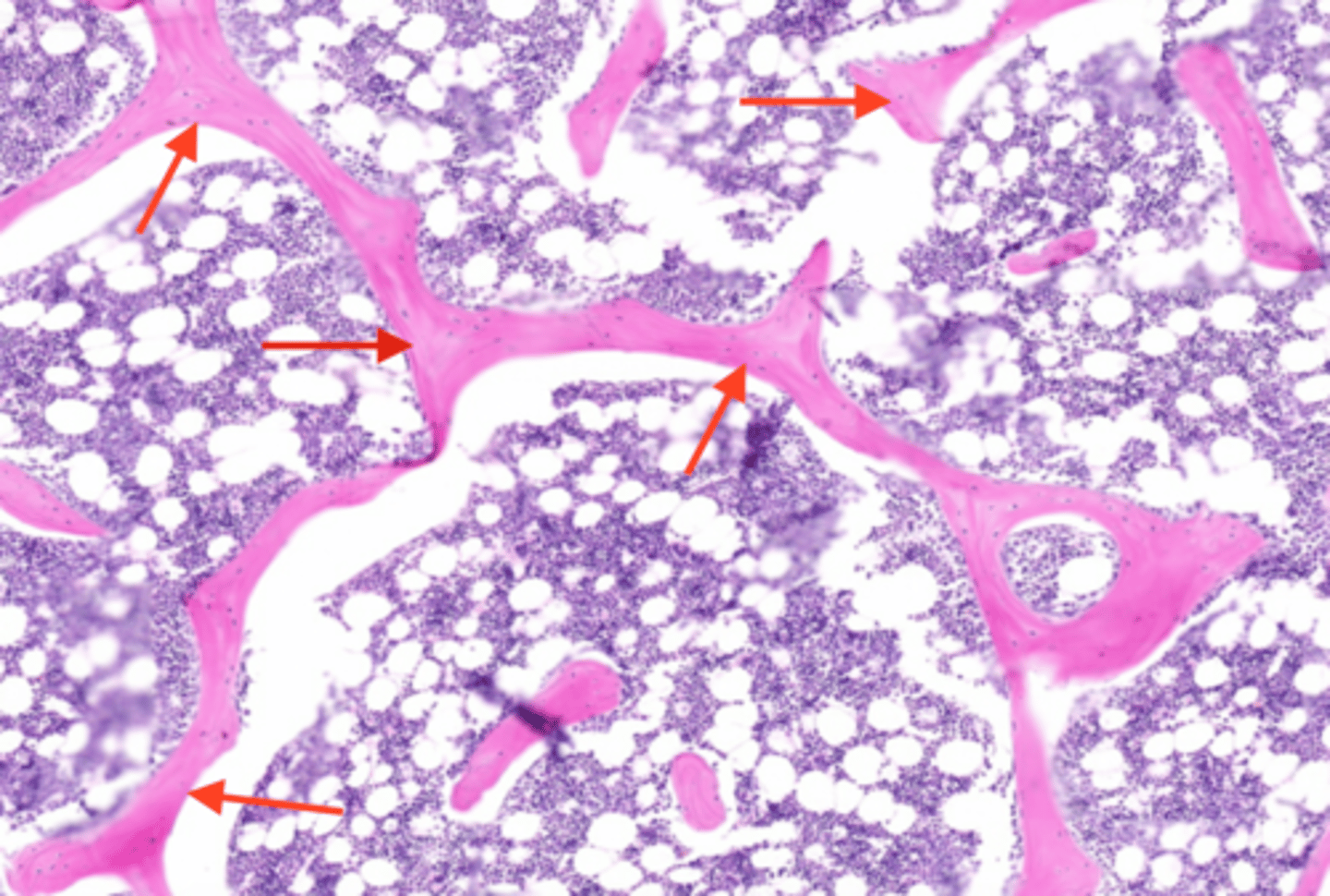
parallel lamellae
Occipital bone
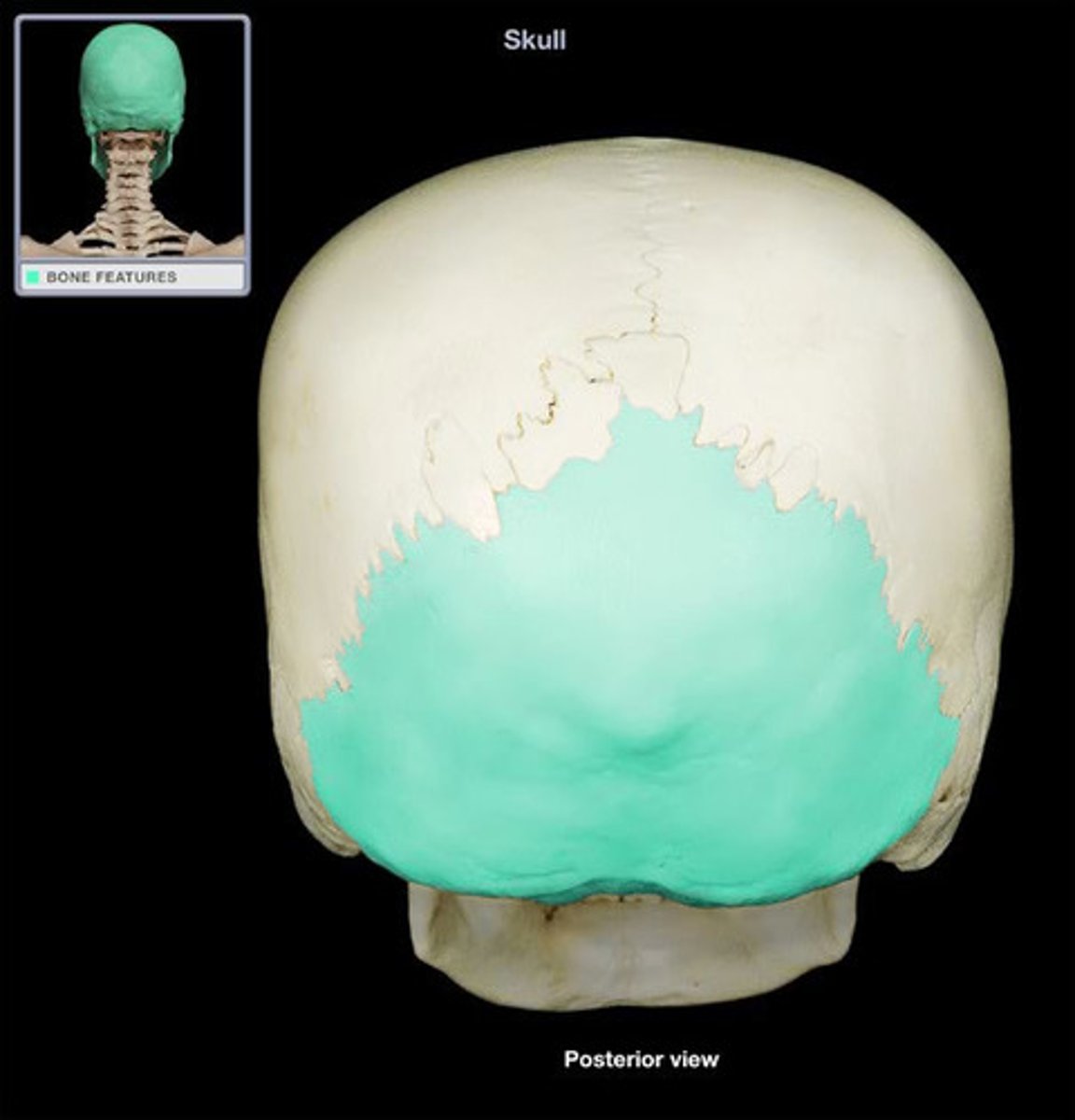
occipital bone
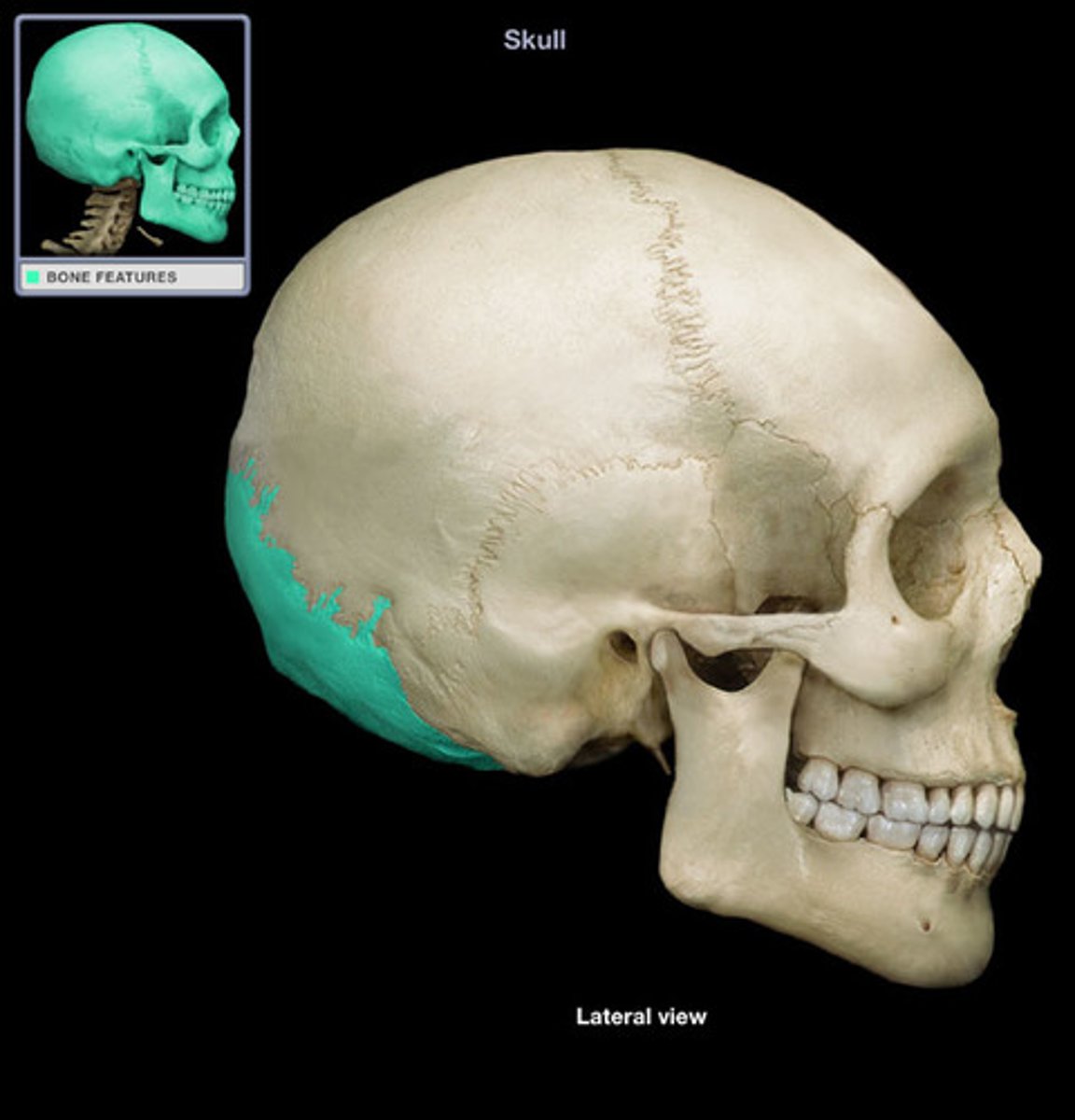
parietal bone
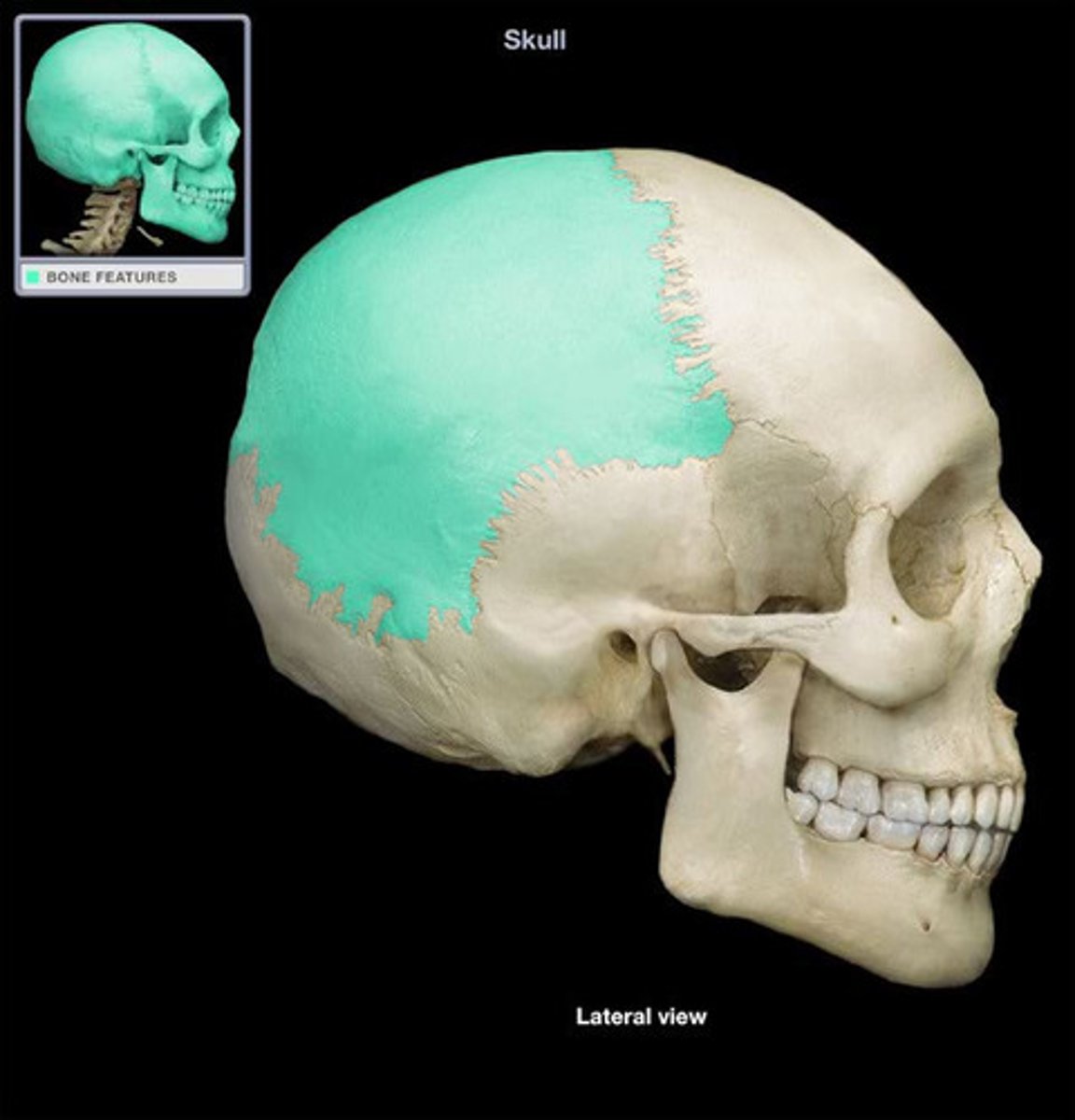
parietal bones
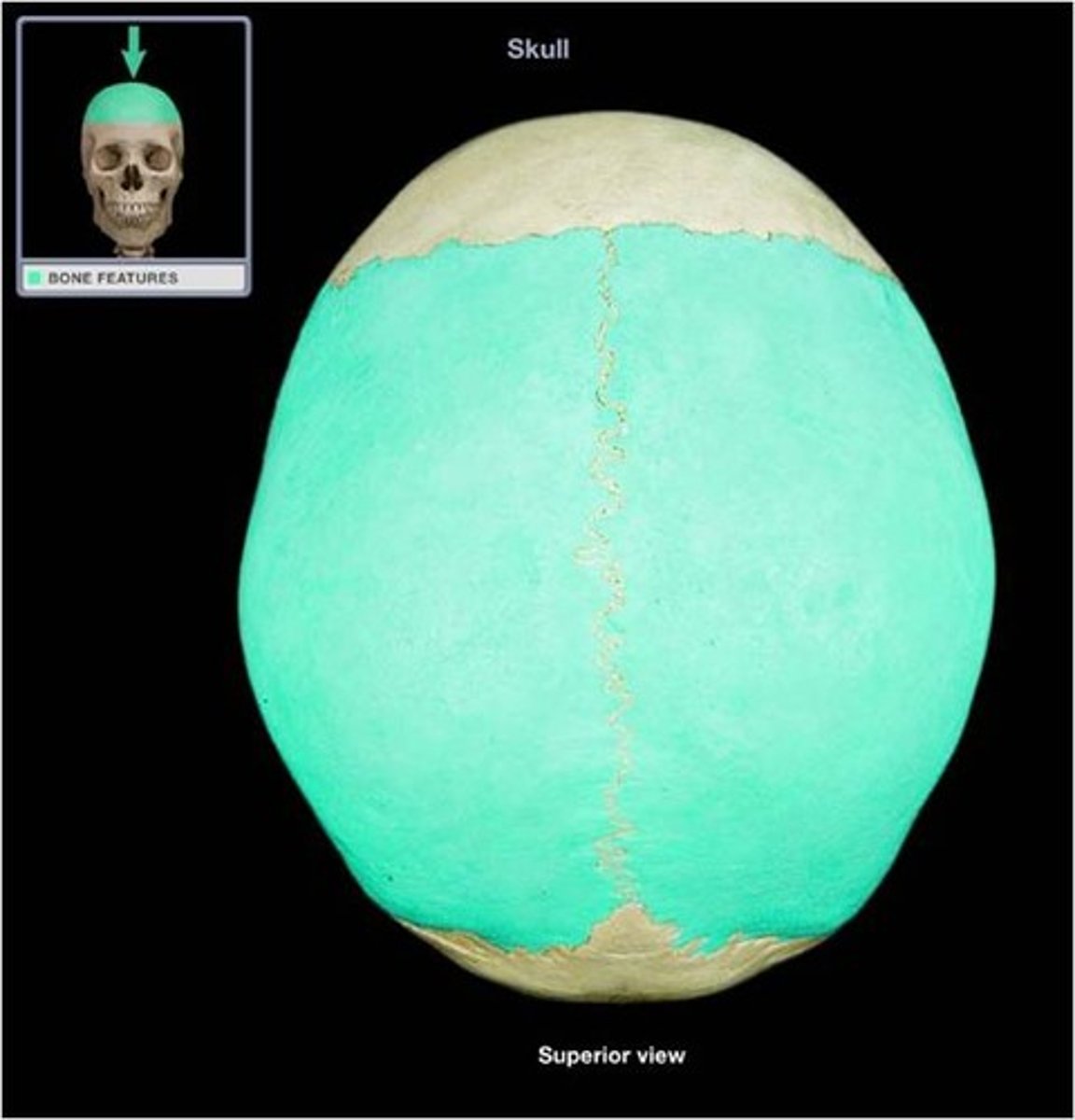
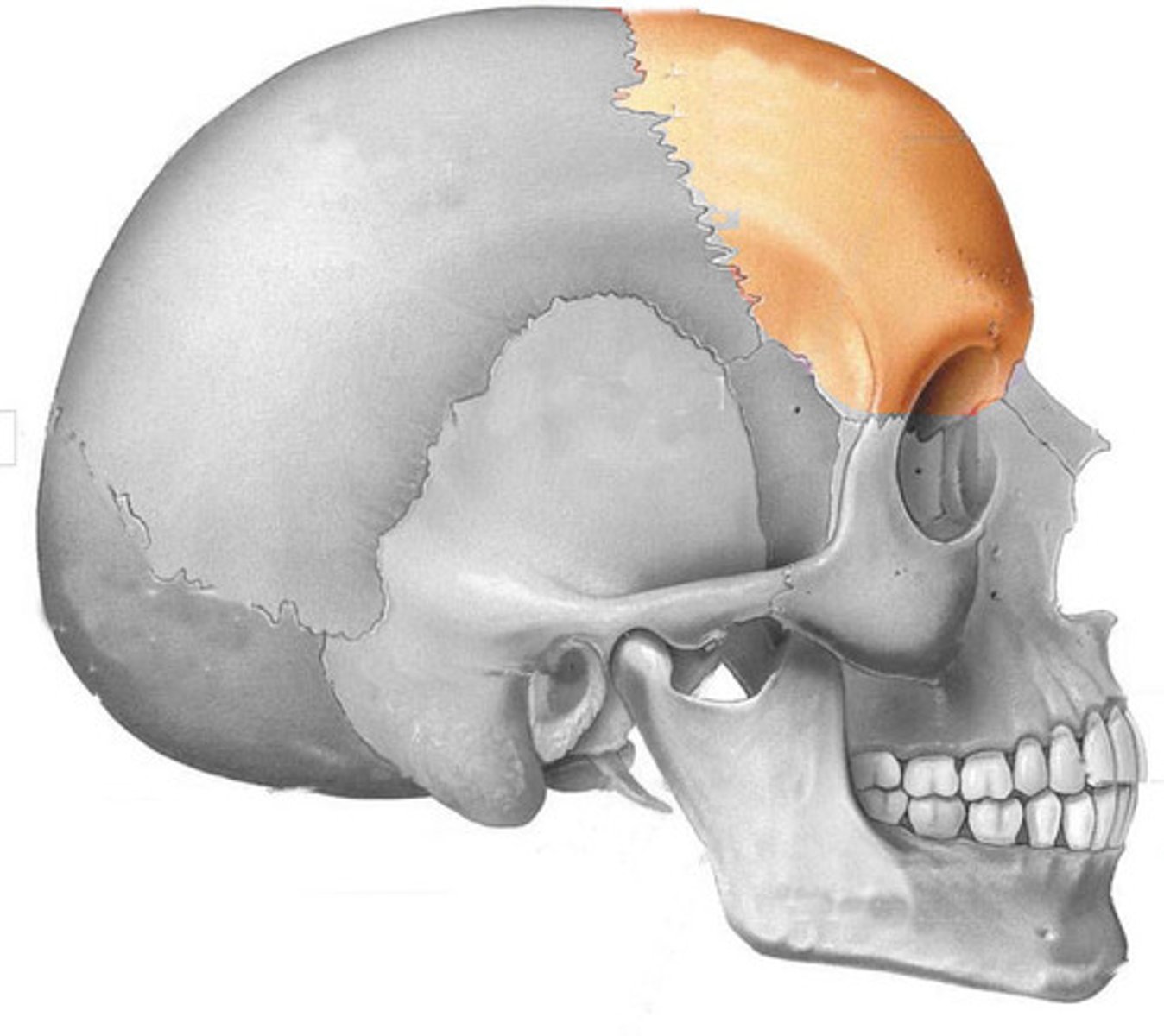
frontal bone
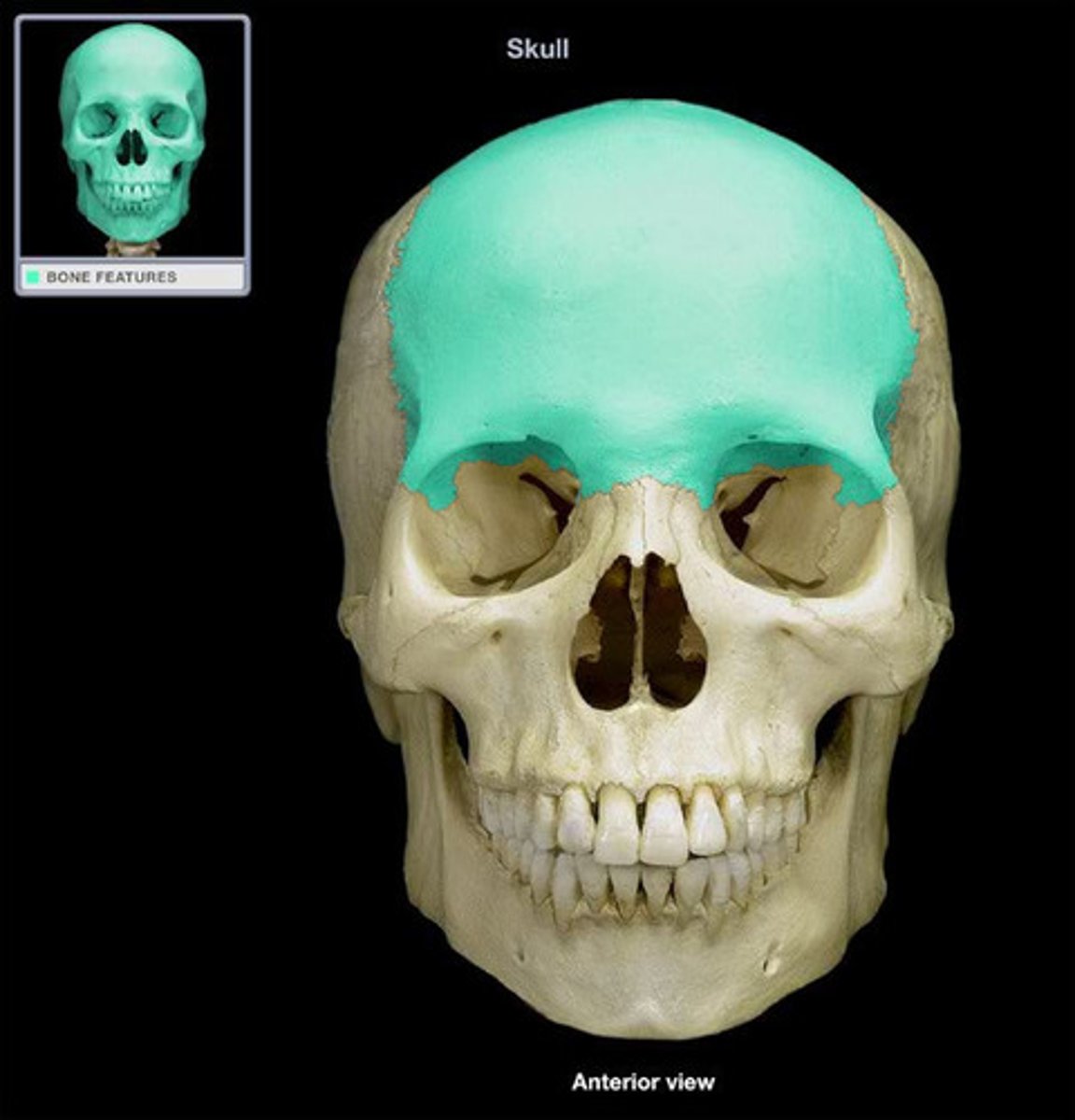
frontal bone
temporal bone
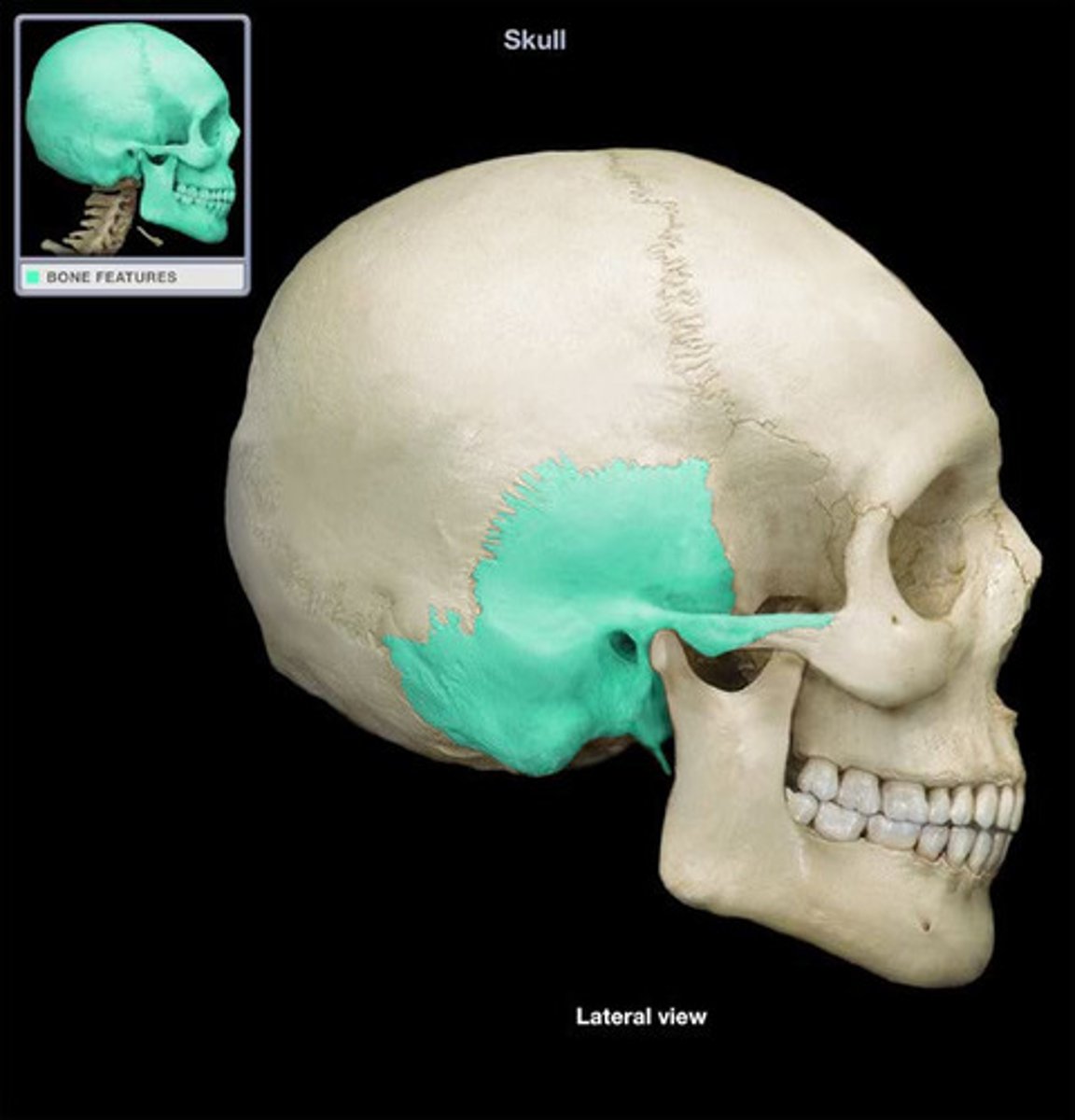
Temporal bone
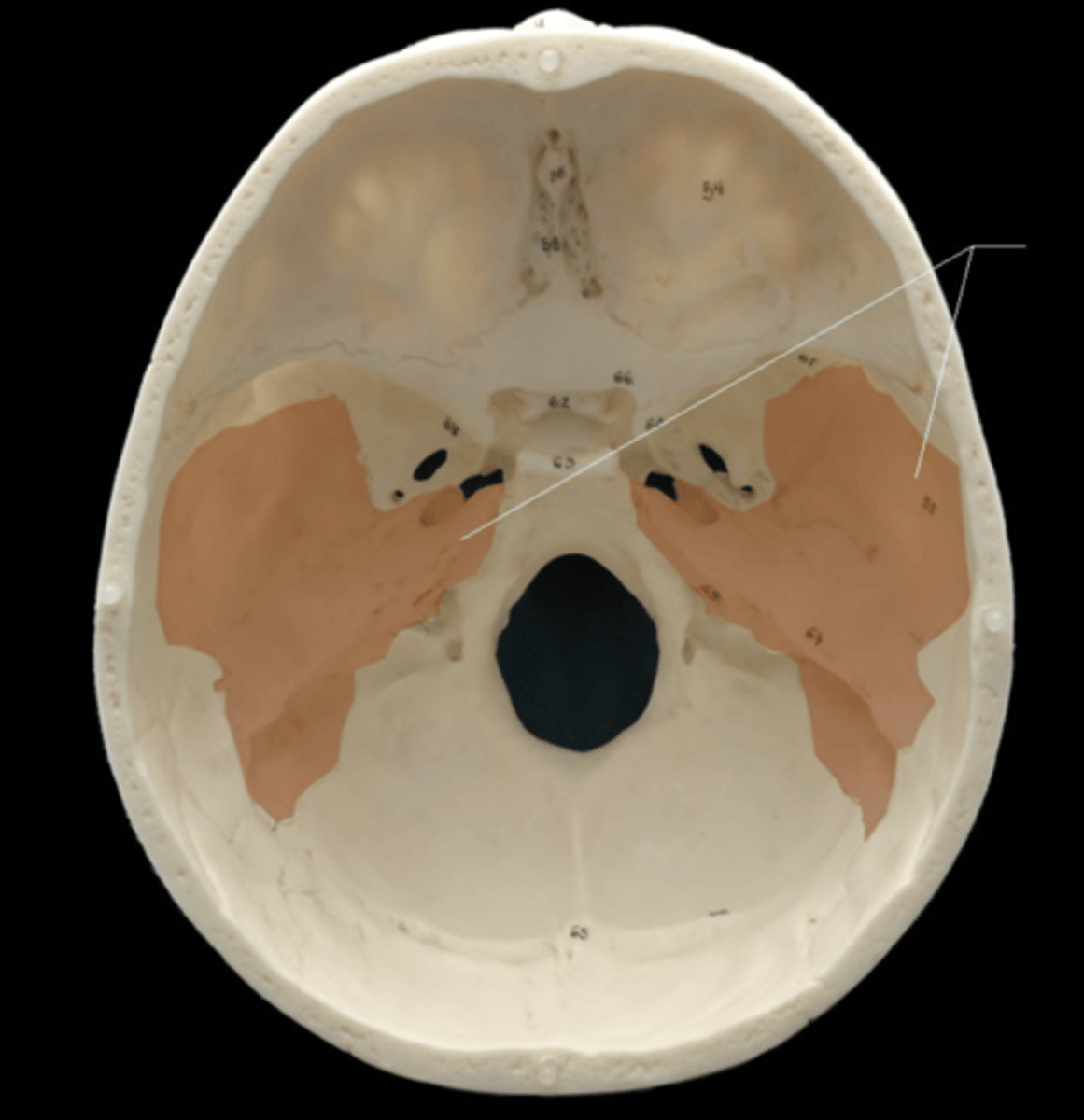
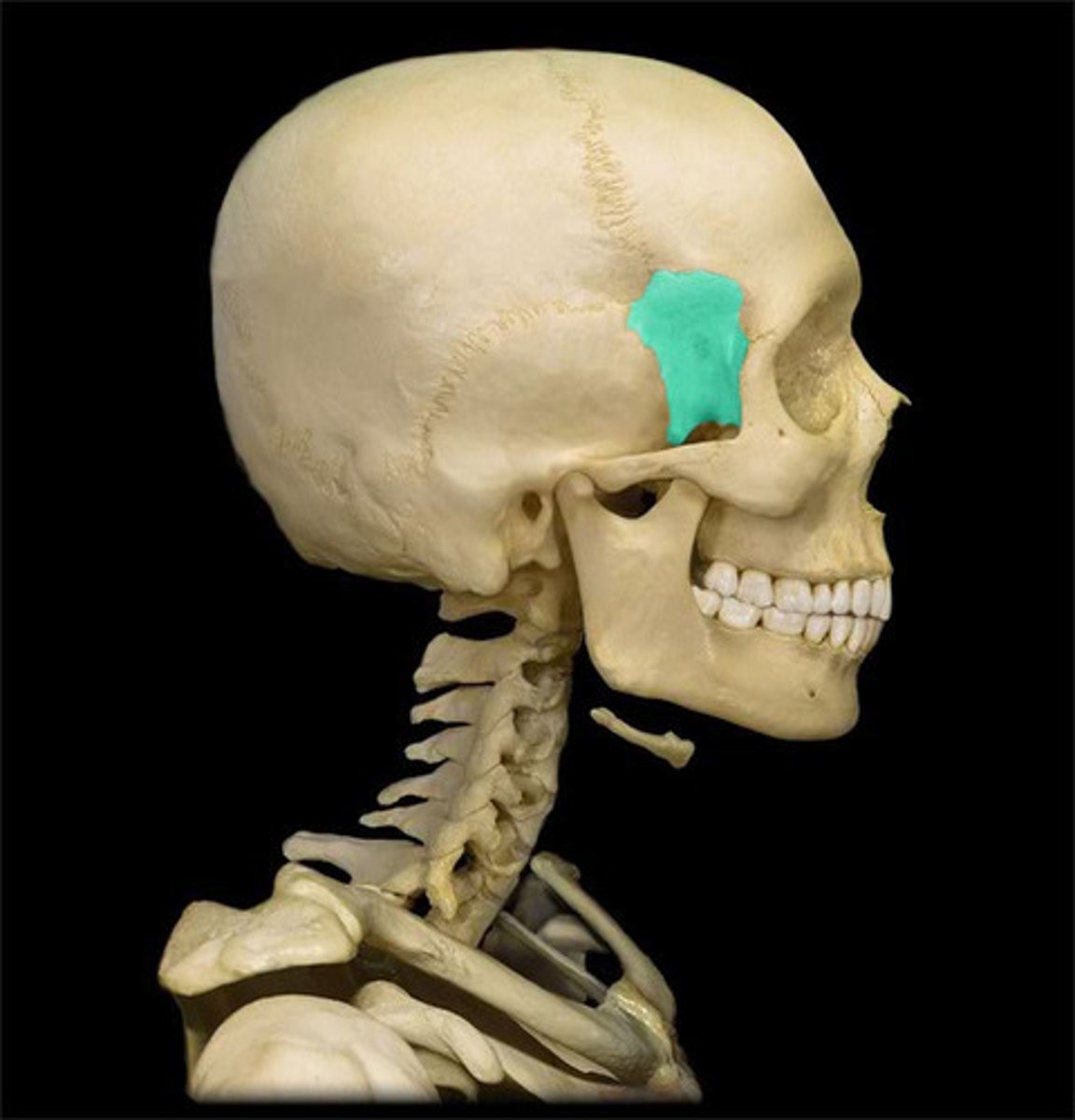
sphenoid
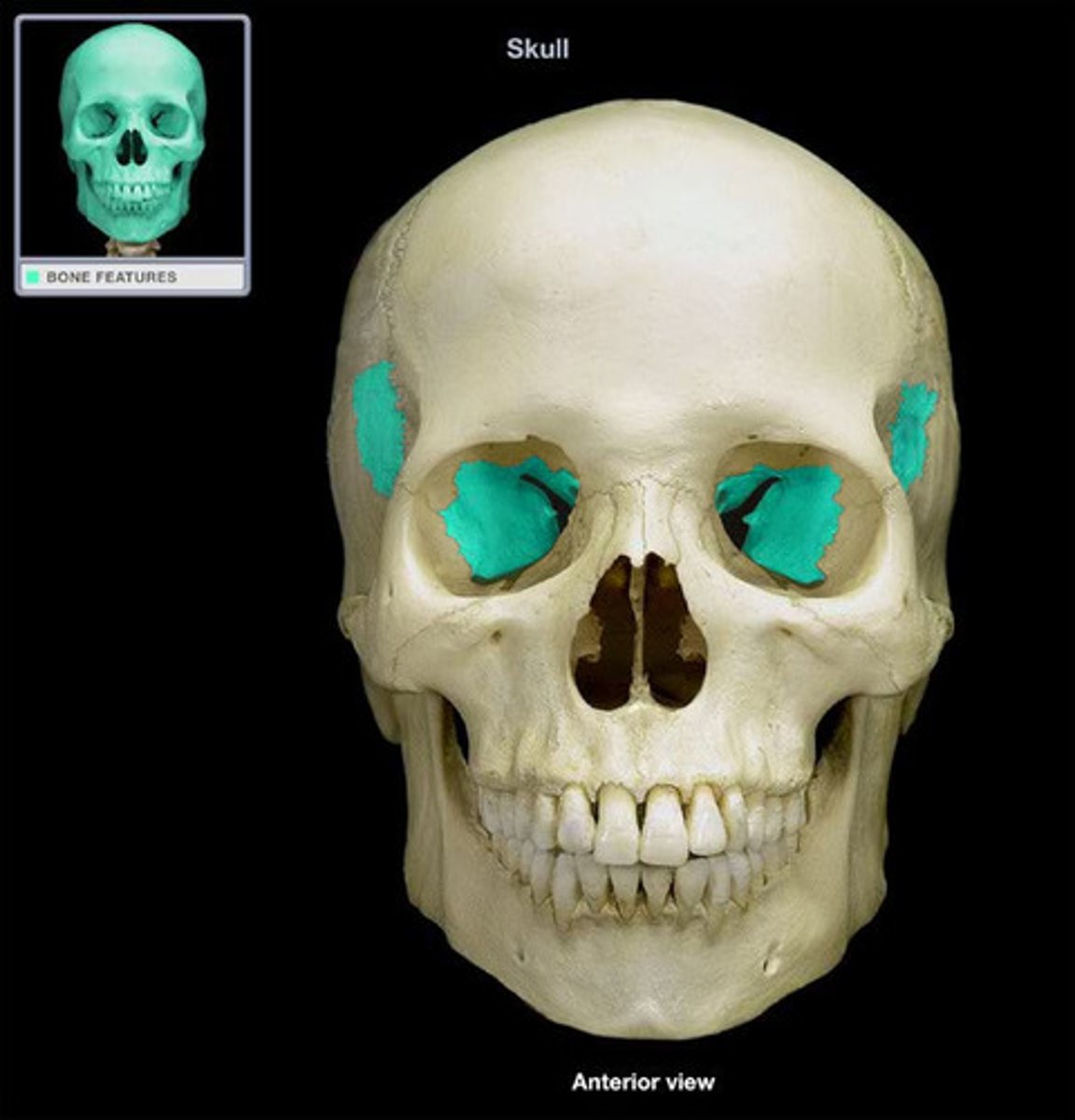
sphenoid
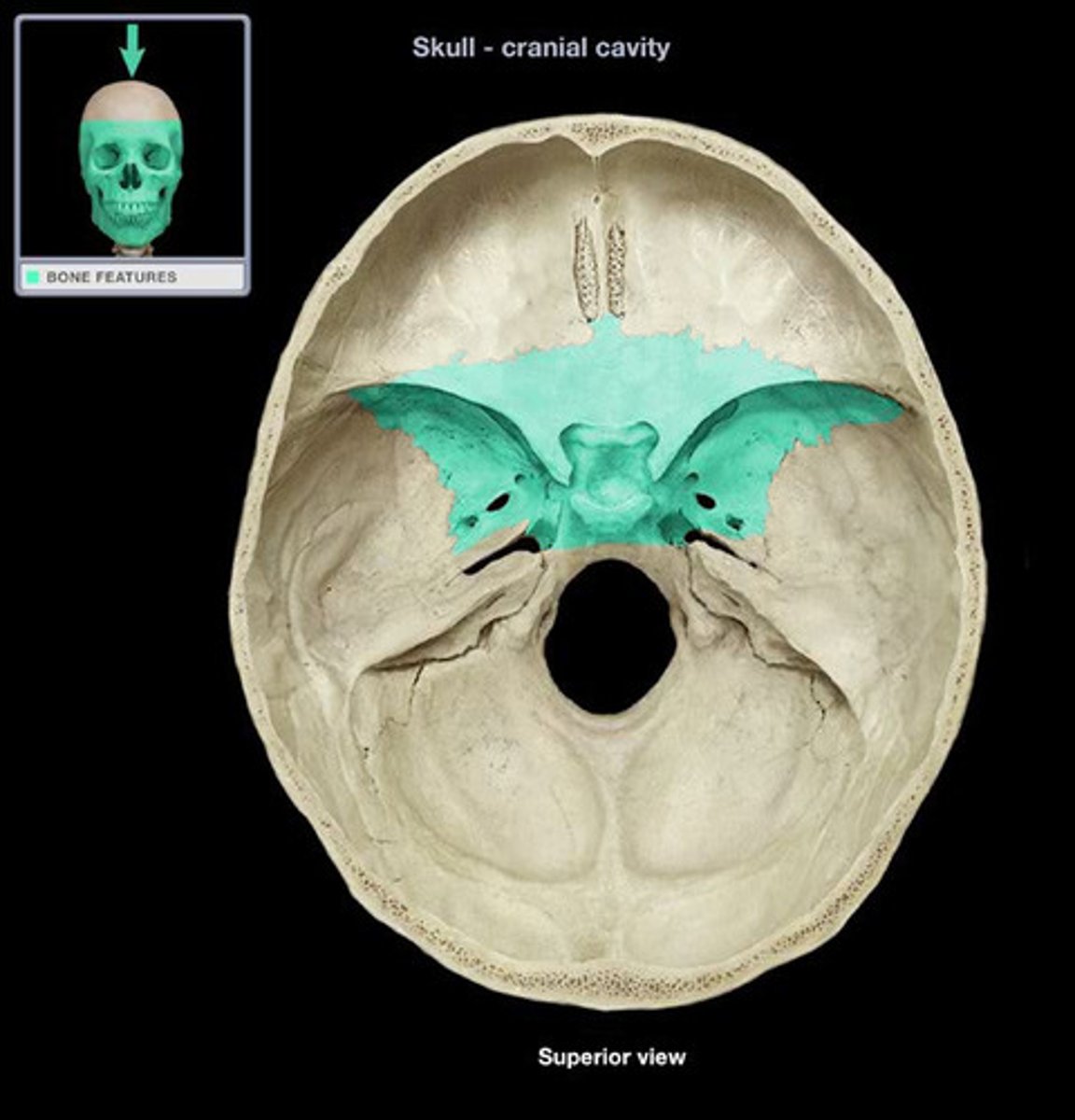
sphenoid
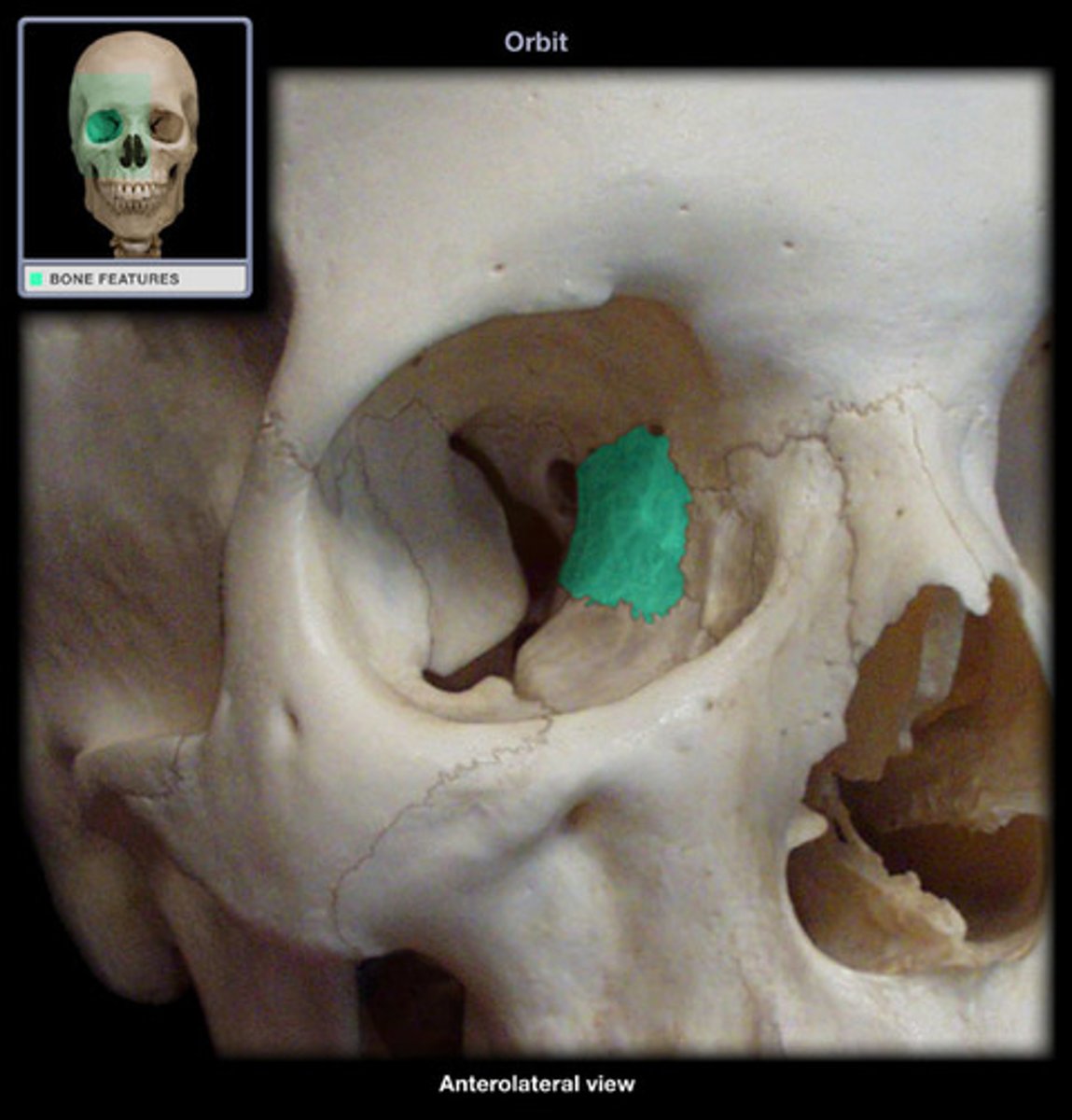
ethmoid
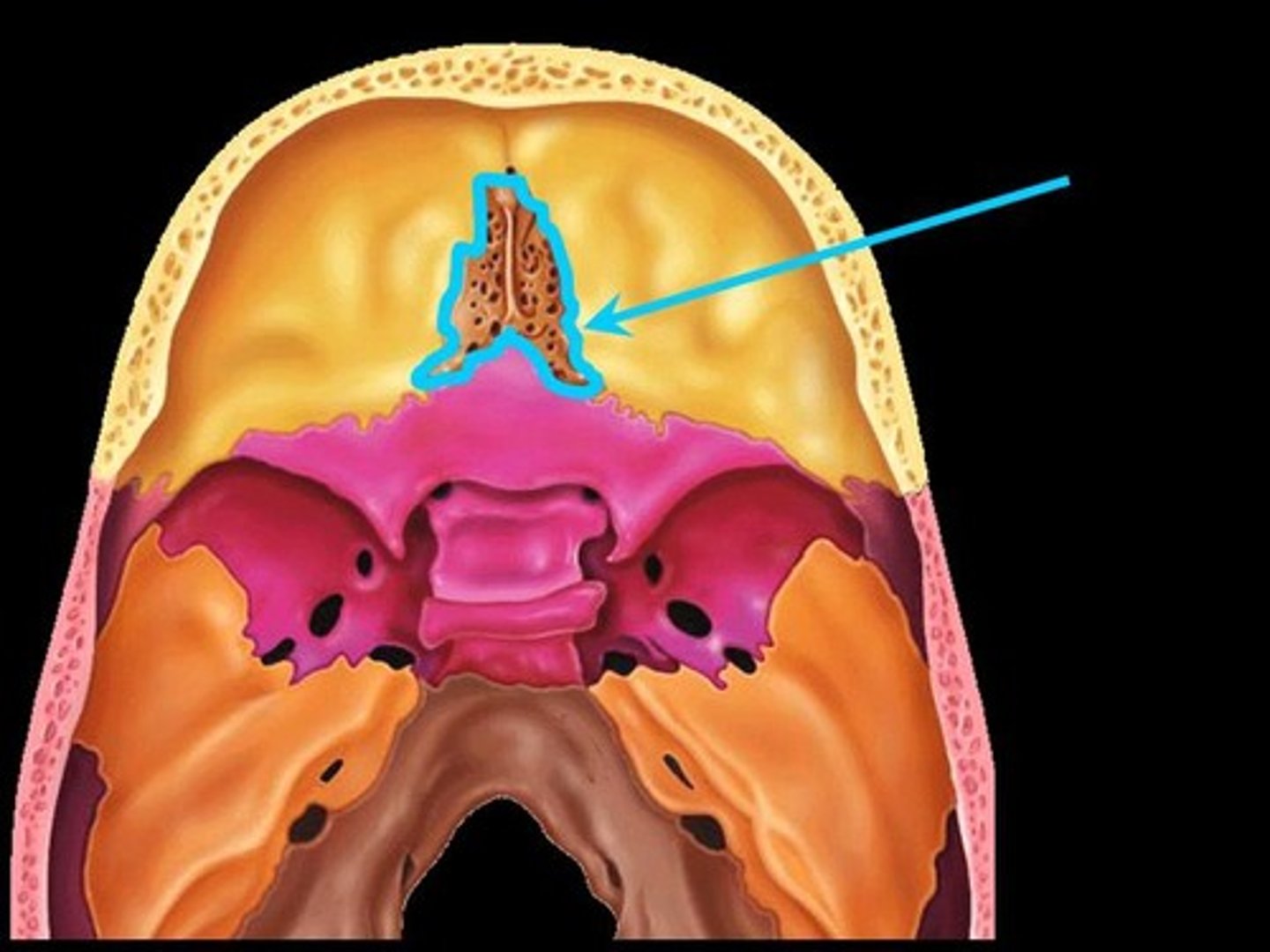
ethmoid
ethmoid
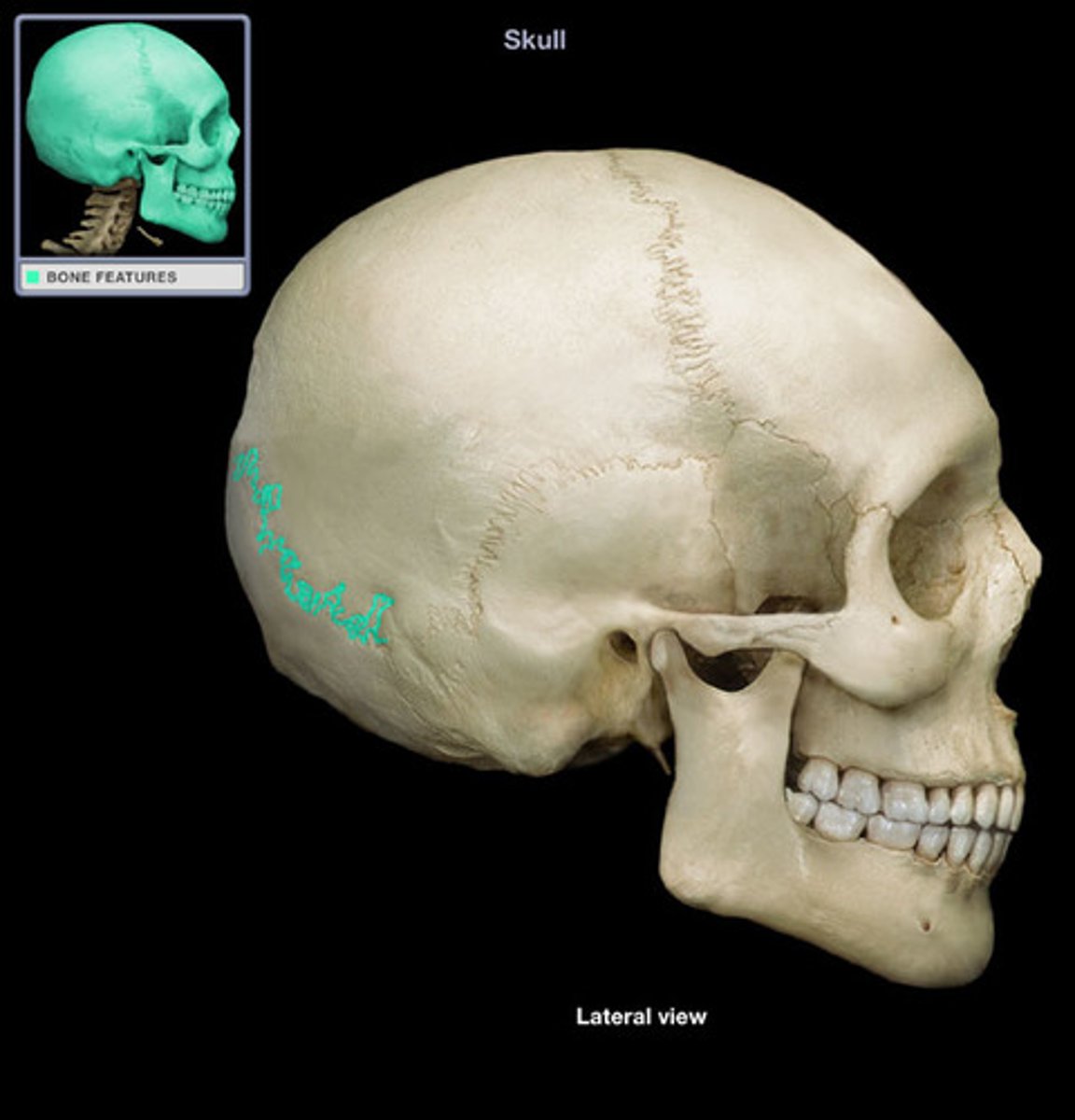
coronal suture
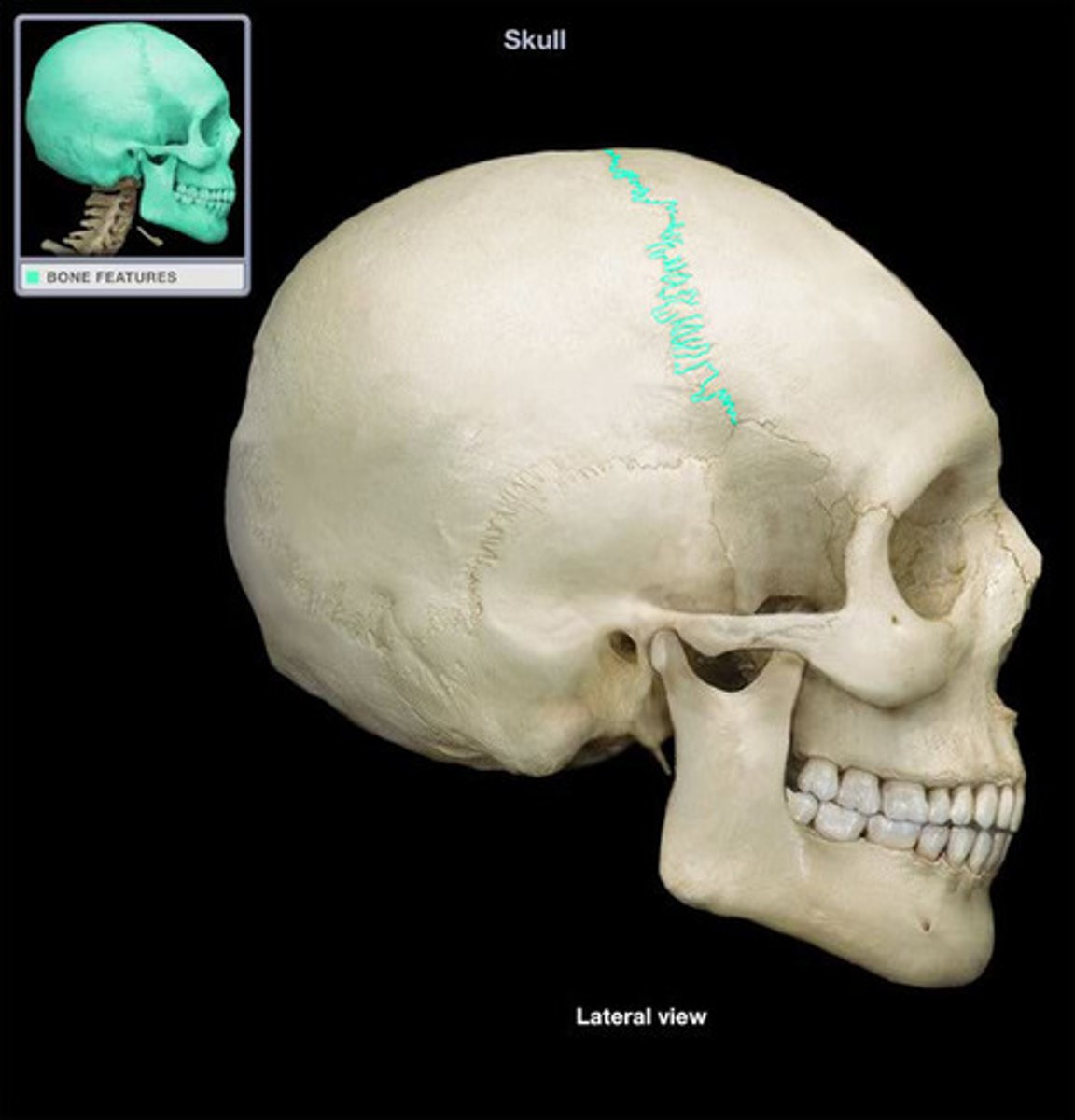
coronal suture
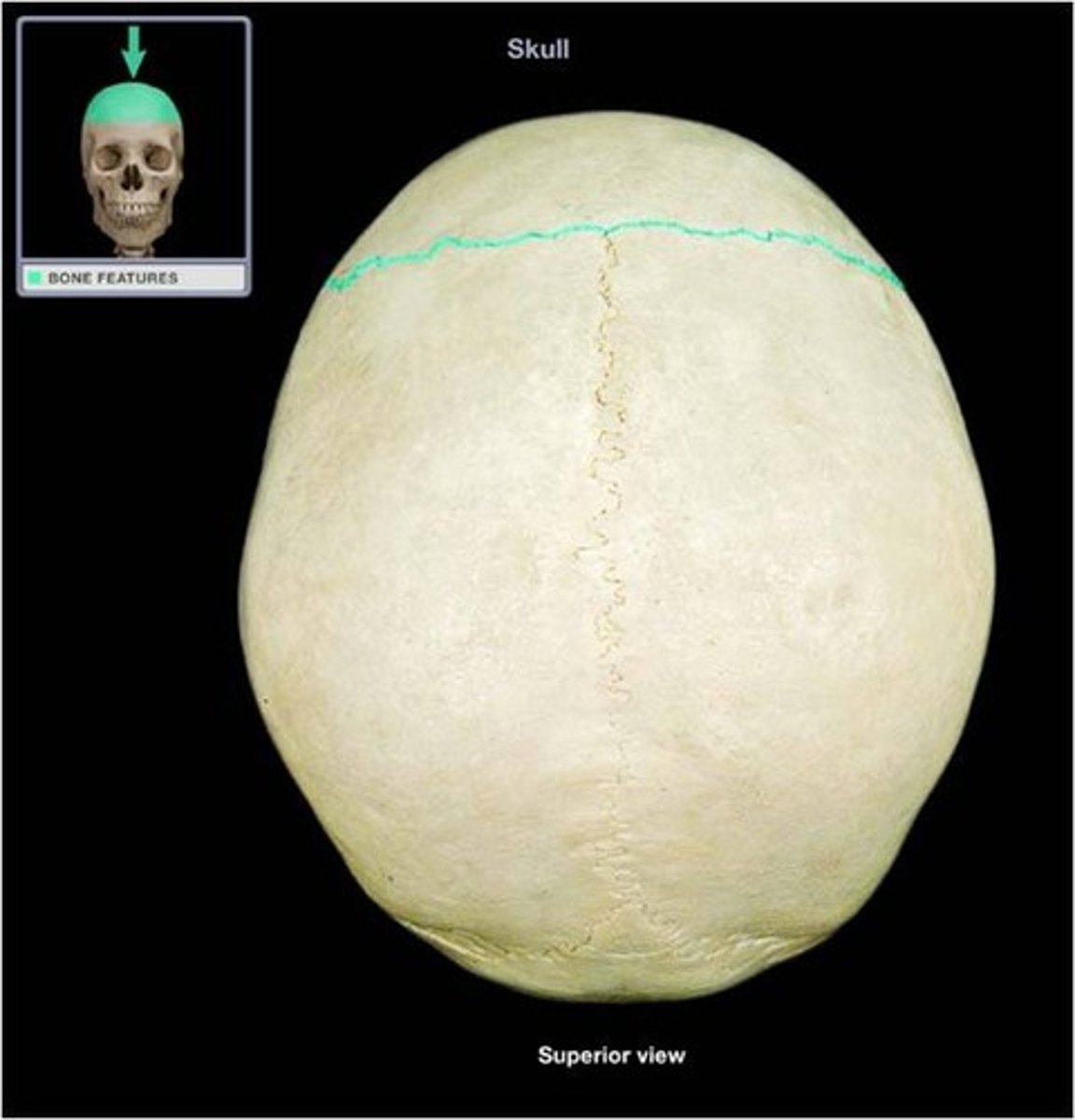
sagittal suture
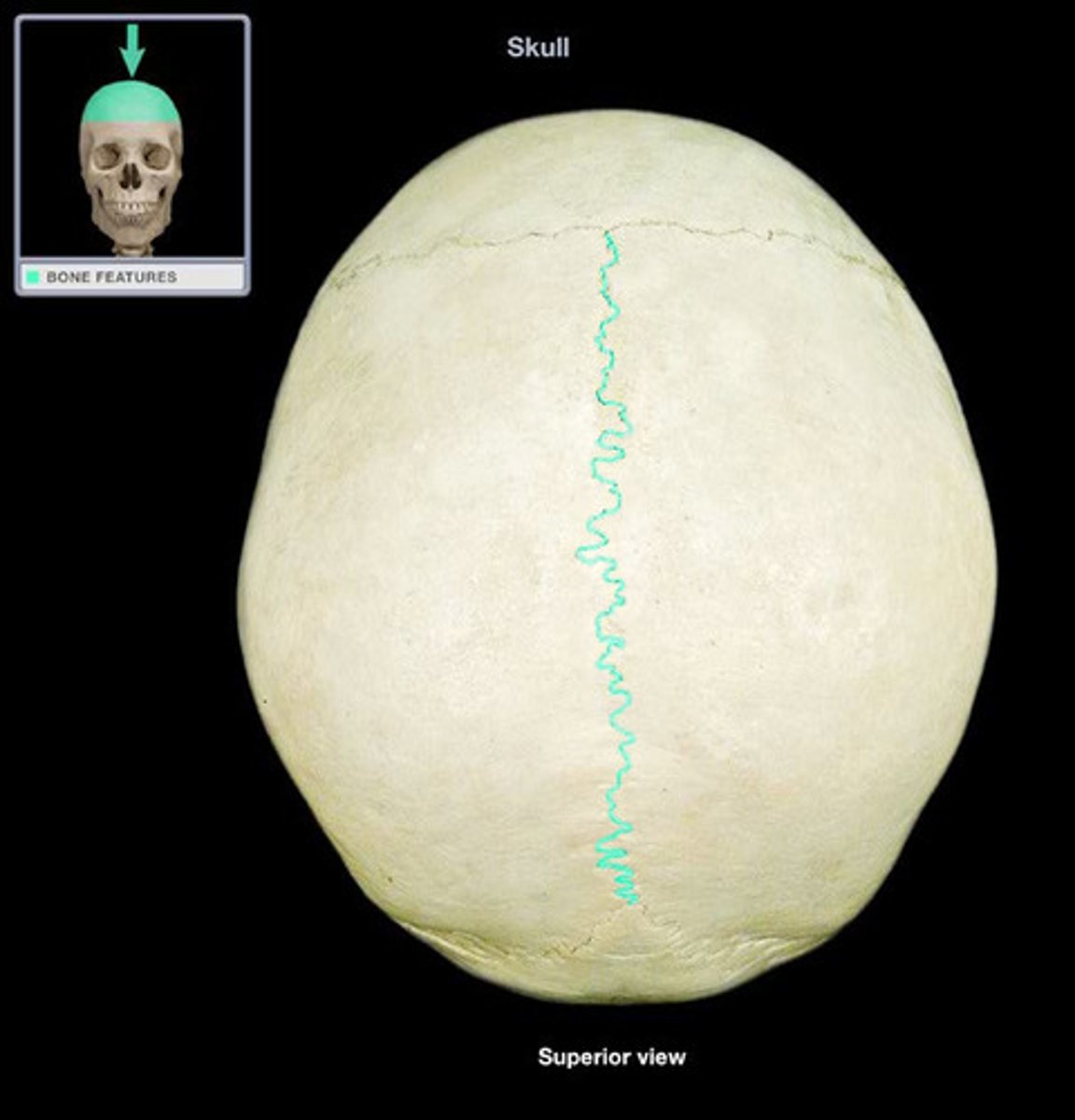
lambdoid suture
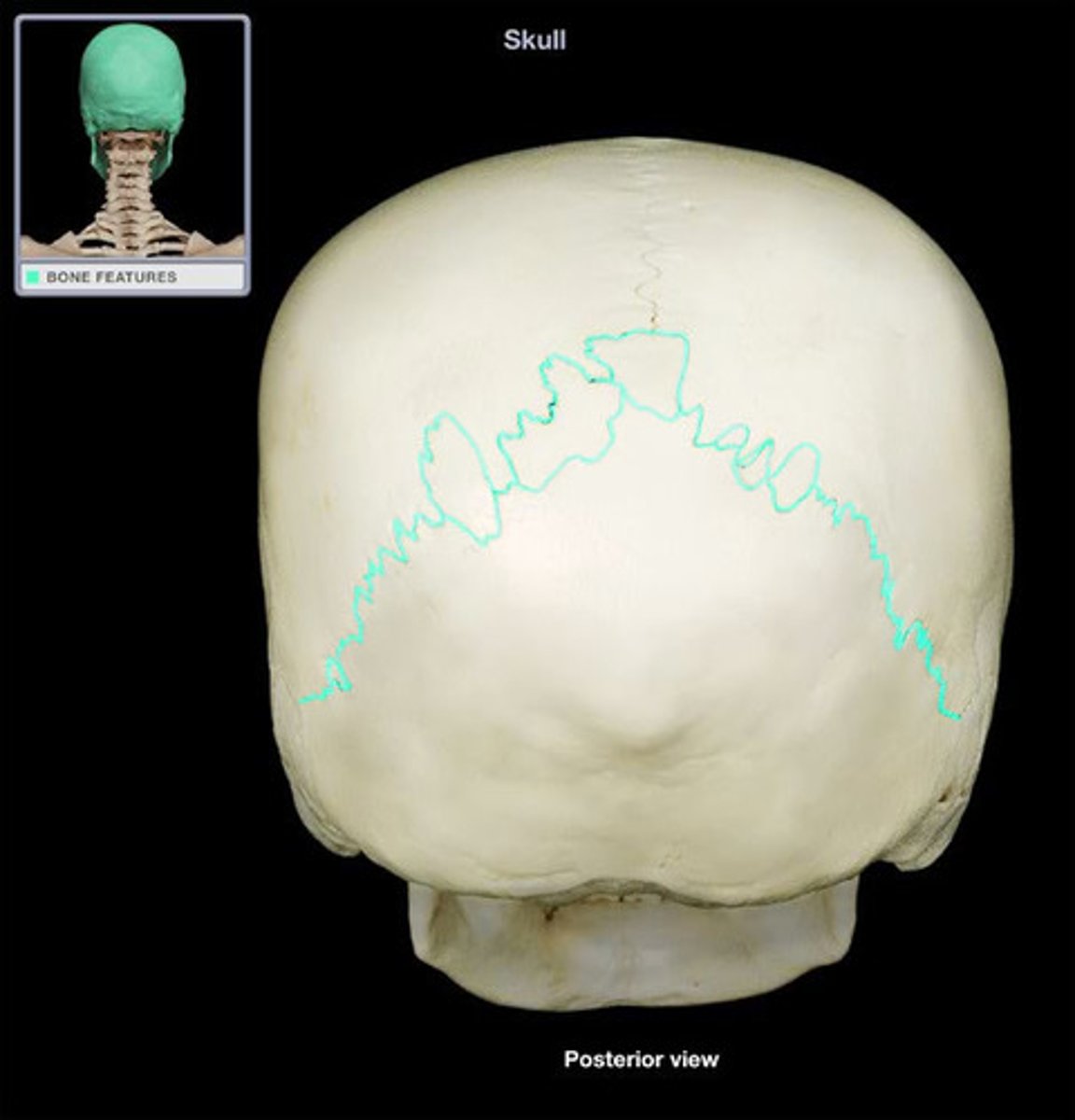
lambdoid suture