Organic Chemistry Lab 1 UMBC Final
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from lecture notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
When is vacuum filtration used?
Used when the product of interest is the solid.
What is simple distillation used for?
Used to separate a liquid from a solution.
What is liquid-liquid extraction?
Separation of a compound based on its solubility in two different solvents in a container.
If the density of methylene chloride is greater than water, which layer will be on top?
Water
A water layer with dissolved salts will be______ dense than pure water.
More
About how much drying agent should be added initially to an organic solvent?
About 1/10 the volume of the solvent to be dried.
If you break a vacuum adapter, what part do you save?
The ground glass joints.
What is the correct amount of boiling stones necessary in a distillation?
Only a few
At the start of the experiment panacetin will be dissolved in dichloromethane. What component of panacetin is not soluble in dichloromethane and can be removed by filtration?
Sucrose
What are the possible unknown analgesics in panacetin?
Acetanilide, phenacetin
Which way does cooling water run through the condenser and why?
From the bottom to the top so the condenser remains full.
When is gravity filtration used compared to when vacuum filtration is used?
Gravity filtration is for saving the solid; vacuum filtration is for saving the liquid.
After dissolving the panacetin in dichloromethane and filtering it by gravity what compound is present in the filter paper?
Sucrose
What is the gas generated by the reaction of acids with HCO3-?
CO2
At what point in the experiment is the conjugate base of aspirin converted back to its conjugate acid form?
When HCl is added to the sodium bicarbonate extract.
Why is a carboxylic acid a stronger acid than an alcohol?
Resonance structures of the conjugate base of carboxylic acid are more stable than the conjugate base of alcohol.
Why is it necessary to acidify the bicarbonate extract fully to pH 2?
The equilibrium RCOOH ⇀↽RCOO− + H3O+ lies to the left and all acid precipitates.

If panacetin is 40% aspirin as the label states how many millimoles is 1.2 g of aspirin?
6.7
What is the identity of the gas that is evolved in the extraction of aspirin by NaHCO3?
CO2
How many millimoles of NaHCO3 is present in 60 mL of a 5% (0.6 M) solution?
36
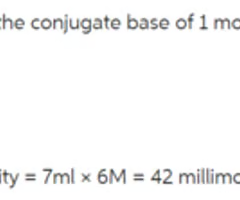
How many millimoles of HCl is in the 7 mL of 6 M HCl that is used to neutralize the conjugate base of aspirin to its neutral form?
42
To what pH is the bicarbonate solution of aspirin conjugate base adjusted to ensure maximum precipitation of aspirin?
2
Which vessel is preferred for recrystallization?
An Erlenmeyer flask because the restricted opening reduces evaporation of the hot solvent while the solid is dissolving.
What are the two effects of an impurity on the melting point of an organic compound?
The impurity lowers the melting point of the compound and broadens its range.
Why is an Erlenmeyer flask better than a beaker for recrystallization?
The narrow opening of the Erlenmeyer flask slows evaporation so the minimum volume of solvent is used.
What is the minimum volume of boiling water necessary to dissolve 0.90 g phenacetin? (solubility at 100◦C is 1.22 g/100 mL)
74 mL
An unknown sugar at a concentration of 0.020 g/mL was found to have an observed rotation of 2.0◦ in a 1.0 dm cell. What is the specific rotation of this unknown sugar?
100 degrees
How many chiral carbons are in the cocaine molecule?
4
An organic compound has a solubility of 1.5 grams/100 mL at 0 ◦C and 6 grams/100 mL at the boiling point of cyclohexane. Four grams of the compound is recrystallized at the boiling of cylcohexane and then cooled in an ice bath. What is the maximum recovery of the solid compound?
3 g
What is meant by the term ``mixed melting point'' as a way to identify an unknown?
Measuring the melting point of the unknown mixed with the compound it's suspected to be.
What is the effect of an impurity on the melting point of an organic compound?
Lowers the melting point and increases the range of temperatures over which the compound is observed to melt.
What is the function of the filter paper that is present in the developing chamber during the chromatography
Saturate the space of the developing chamber with solvent vapor
The term applied to the liquid that carries analytes over the TLC plate in a thin-layer chromatography experiment is the phase?
mobile
Like most organic compounds all of the analgesics in this experiment are white solids. How will you visualize the compounds on the white surface of the TLC plate in this experiment?
UV light, absorption of iodine vapor
Comparing the Rfs of two compounds, the more polar compound in a certain mobile phase will have the Rf and a more polar mobile phase will the Rf.
lower; increase
With the ethylacetate/acetic acid mobile phase you used the analyte spots fell nicely near the middle of the plate. If a mobile phase of ___ polarity were used the spots would have traveled to a ___ Rf.
lower; lower
Which of the compounds would you expect to have the lowest Rf?
butryic acid
How would the reaction rate be affected if bromoethane were used instead of iodoethane?
The rate would be slower because bromine is a poorer leaving group.
The polar ethanol solvent in the SN1 experiment is optimal for unimolecular reactions because it is _ and _ the carbocation intermediate.
protic; stabilizes
Compared to the rate of reaction of 2-bromobutane you can predict that 2-chlorobutane will be
slower in both SN1 and SN2
What will you observe that signals the completion of the reaction?
change from orange to colorless
How many possible monobromination products of butane are there? Include minor product(s) not just the major product(s). If a product exists as a pair of enantiomers be sure to count both enantiomers as a distinct product.
3
Which of the four arene compounds do you predict will react the fastest with bromine?
isopropylbenzene
What is it important that the this bromination reaction be conducted with adequate illumination?
to initiate the formation of bromine atoms from bromine molecules
What reducing solution is used to treat a bromine spill on the skin and at the end of the experiment to clean bromine residue from the glassware?
sodium thiosulfate, Na2S2O3
Which reactant will be limiting?
bromine
When you look through the eyepiece of the polarimeter and see the right hemisphere is brighter than the left hemisphere is your compound dextrorotatory (right-handed rotating) or levoratotary (left-handed rotating)?
dextrorotatory (right-handed rotating)
Which is the most important consideration in getting good TLC results?
Spots shouldn't be applied below the level of the mobile phase.
How would the reaction rates compare if chlorine had been used for the free-radical experiment instead of bromine?
faster
Sodium saccharin is referred to as an ambident nucleophile because it has ———- resonance structures and ————-.
two; N is a nucleophile in one and O a nucleophile in another.
The optimum solvent for an SN1 reaction with AgNO3 is ————- and the optimum solvent for an SN2 reaction with NaI is ——————.
ethanol; acetone
is classified as a ————- alkyl halide.
1-Bromobutane
If the NaI/acetone solution were prepared as 20% NaI instead of 15% the reaction rate would be —————.
faster
Which alcohol is oxidized fastest by KMnO4?
2-propanol
Why might you have to add cyclohexene at the end of the bromination reaction?
react with excess bromine
The reaction of alkenes with bromine is ———— reaction which results in ———- of the organic compound.
an addition; oxidation
What is a danger of using bromine?
corrosive; harmful vapors; forms a lachrymator with acetone
What color change do you expect to observe when potassium permangante is added to 2-methylpropene?
The purple color of KMnO4 would change to the muddy brown color of MnO2.
What is the maximum gas volume in mL of alkene at STP you can expect to be produced from dehydration of 2.0 mL of 2-methyl-2-propanol (density 0.78 g/mL; molecular weight 74.1 g/mol, molar volume of ideal gas at STP 22.4 L/mol K)?
472 mL
Why does the experimental procedure specify immediately beginning a distillation of product from the reaction mixture instead of heating the reaction for a suitable amount of time in the same vessel?
Removing the alkene as it's formed increases the yield.
The melting point of 2-methyl-2-propanol is room temperature (20° C) so it is expected to be a room temperature.
Above
If the addition of bromine to trans-cinnamic acid proceeds purely by the expected anti addition the product will be
erythro racemic mixture of the 2R,3S/2S,3R enantiomers.
Why does the experimental procedure specify immediately beginning a distillation of product from the reaction mixture instead of heating the reaction for a suitable amount of time in the same vessel?
Removing the alkene as it's formed increases the yield.
a precipitate; an immiscible liquid
The indication of a substitution reaction of NaI with an akyl halide will be formation of ————— and the indication of substitution of Cl for an alcohol with HCl/ZnCl2 will be formation of —————.
How would the reaction rate be affected if saccharin were used instead of the sodium salt of saccharine conjugate base?
The reaction would be slower because saccharin is neutral and saccharine conjugate base is negatively charged and a better nucleophile.
In this reaction you will observe a change in the solution of ____ after _____ orange to colorless; all the bromine has reacted.
after
A certain carbohydrate produced an observed rotation of 1.95 degrees at a concentration of 0.020 g/mL in a 1 dm cell. What is its specific rotation? (Do not include any units.)
97.5
You will sniff the odor of a compound that has one enantiomer that smells like caraway seed and the other enantiomer that smells like spearmint. What is the compound?
carvone
mesocompound
What stereochemical term is applied to a molecule having chiral carbons but also being overall achiral?