All Relevant Vocabulary
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Last updated 6:31 PM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
Organelle
Any of several membrane-enclosed structures with specialized functions, suspended in the cytosol of eukaryotic cells
2
New cards
Cell
Life’s fundamental unit of structure and function; the smallest unit of organization that can perform all activities required for life
3
New cards
Tissue
An integrated group of cells with a common structure, function, or both
4
New cards
Organ
A specialized center of body function composed of several different types of tissues
5
New cards
Organ system
A group of organs that work together in performing vital body functions.
6
New cards
Organism
An individual living thing, consisting of one or more cells
7
New cards
Population
A group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area and interbreed, producing fertile offspring
8
New cards
Community
All the organisms that inhabit a particular area; an assemblage of populations of different speciees living close enough together for potential interaction
9
New cards
Ecosystem
All the organisms in a given area as well as the abiotic factors with which they interact; one or more communities and the physical environment around them
10
New cards
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
A nucleic acid molecule
11
New cards
Metabolism
The totality of an organism’s chemical reactions, consisting of catabolic and anabolic pathways, which manage the material and energy resources of the organism
12
New cards
Homeostasis
the steady-state physiological condition of the body
13
New cards
Biodiversity
The variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem
14
New cards
Nucleus
1. an atom’s central core, containing protons and neutrons
2. the organelle of a eukaryotic cell that contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes, made up of chromatin.
3. A cluster of neurons
15
New cards
Kingdom
A taxonomic category, the second broadest after domain
16
New cards
Domain
A taxonomic category above the kingdom level
17
New cards
Covalent bond
Involves sharing of electron (e-) pairs between atoms
18
New cards
Nonpolar covalent bond
Atoms share electrons equally
19
New cards
Polar covalent bond
Atoms don’t share electrons equally
20
New cards
Hydrogen bond
A weak attraction of partial charges
21
New cards
Hydrocarbon
Molecules that consist only of Hydrogen and Carbon. __Nonpolar → very hydrophobic__
22
New cards
Functional group
Bond to hydrocarbons to make them more versatile
23
New cards
Polar
Water soluble
24
New cards
Nonpolar
Water insoluble
25
New cards
Macromolecule
A giant molecule containing a many small subunit molecules
26
New cards
Monomer
A single subunit of any macromolecule, serves as the building block of a polymer
27
New cards
Dimer
Two monomers together
28
New cards
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together by covalent bonds
29
New cards
dehydration synthesis
monomer in, water (H2O) out to form a polymer
30
New cards
Hydrolysis
monomer out, water (H2O) in to break down a polymer. Hydrolytic enzymes needed
31
New cards
enzyme
Speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
32
New cards
Carbohydrate
Sugar molecules
33
New cards
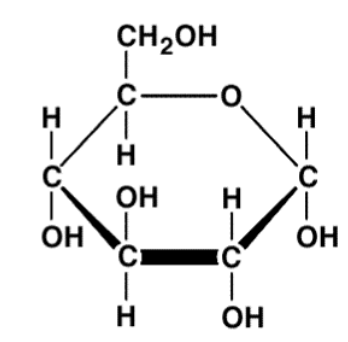
Monosaccharide
Monomer of carbohydrates. Mono= simple, saccharide= sugar
34
New cards
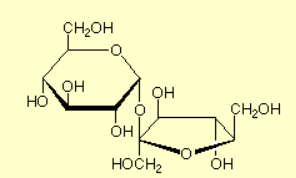
Disaccharide
Broken down for quick energy. Dimer of carbohydrate. Di= two, saccharide= sugar
35
New cards
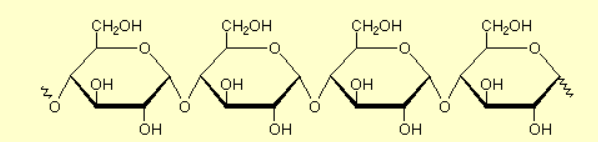
Oligosaccharide
A couple (3-10) monosaccharides
36
New cards
Cellulose
Function: Structural
Found: Plant cell walls
Found: Plant cell walls
37
New cards
Glycogen
Function: Energy storage in __animals__
Where found: stored in liver and muscle cells
Where found: stored in liver and muscle cells
38
New cards
Starch
Function: Energy storage in __plants__
Where found: In plant organs
Where found: In plant organs
39
New cards
Chitin
Function: Structural
Where found: Fungi cell walls
Where found: Fungi cell walls
40
New cards
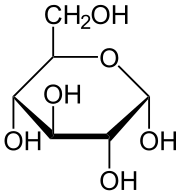
Glucose
For cellular respiration: Fuel to make ATP. 6-sided ring structure
41
New cards
Amino acid
Monomer of proteins
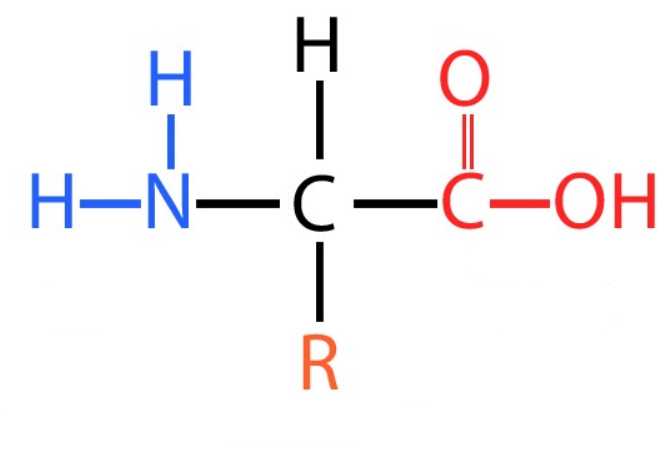
42
New cards
Protein
Tools of the cell. Composed of an amino group, __**R group**__, Hydrogen, and a carboxyl group all attached to a central carbon.
43
New cards
Polypeptide
A polymer of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds
44
New cards
Peptide bond
The covalent bond between the carboxyl group on one amino acid and the amino group on another, formed by a dehydration reaction
45
New cards
Hydrophobic
Water-fearing
46
New cards
Hydrophilic
Water-loving
47
New cards
Reactant
A starting material in a chemical reaction
48
New cards
Product
A material resulting from a chemical reaction
49
New cards
Active site
Location where the substrate binds
50
New cards
Denaturation
What occurs when enzymes are not at their optimal condition. They can no longer function
51
New cards
Conformation
The three-dimensional arrangement of side groups on a molecule which can freely rotate into different positions without breaking any bonds
52
New cards
Lipid
Hydrophobic molecules with many functions:
* Hormones
* Good energy source (lots of covalent bonds)
* Major component of cell membranes
* Hormones
* Good energy source (lots of covalent bonds)
* Major component of cell membranes
53
New cards
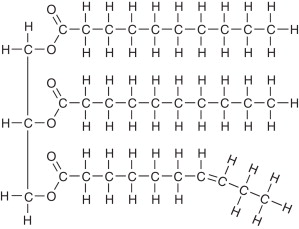
Triglycerides
Fats and oils. Composed of a glycerol (3-carbon) backbone and hydrocarbon tails. Built by 3 dehydration synthesis reactions
54
New cards
Phospholipids
Components of cell membranes. Composed of a __glycerol__ backbone, a hydrophilic __phosphate__ head, and 2 hydrophobic __fatty acid__ tails.
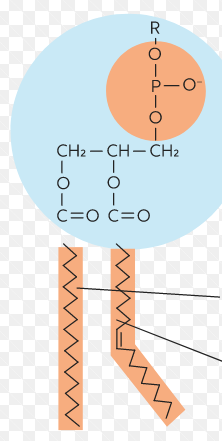
55
New cards
Amphipathic
A molecule that is both hydrophobic and hydrophilic
56
New cards
Micelle
A droplet of phospholipids that form when in water
57
New cards
Lipoprotein
Particles made of lipids and proteins that carry cholesterol through the bloodstream
58
New cards
High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
“good” cholesterol, picks up excess cholesterol from cells → delivers to liver for disposal/recycling
59
New cards
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
“Bad” cholesterol, carries cholesterol from liver to cells. Sticky and buildup causes plaques
60
New cards
Sterol (Steroid)
Four ring structure.
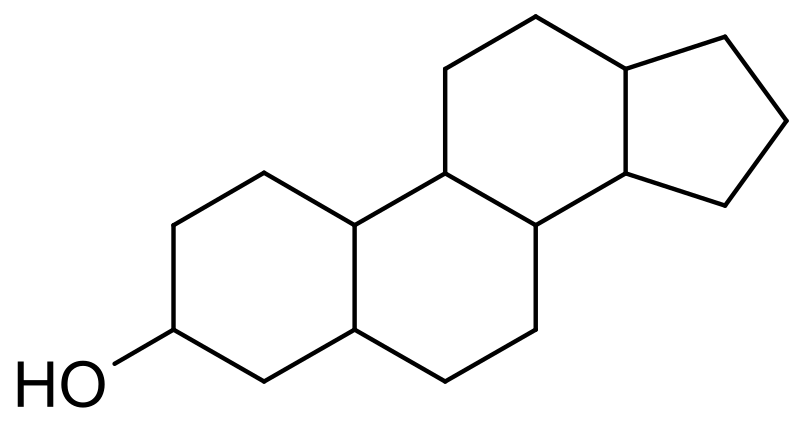
61
New cards
Apoprotein
Proteins in lipoprotein structuers.
62
New cards
Saturated fat
A fatty acid in which there are the maximum number of hydrogens due to there only being a __single bond__.
* Pack tightly, solid at room temp
* Increase levels of HDL and LDL in blood → net negative effect
* Pack tightly, solid at room temp
* Increase levels of HDL and LDL in blood → net negative effect
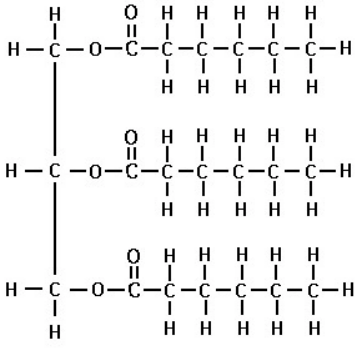
63
New cards
Unsaturated fat
Hydocarbon fatty acid tails are __double bonded__.
* Loosely packed; liquid at room temp.
* Decrease LDL, raise HDL
* Loosely packed; liquid at room temp.
* Decrease LDL, raise HDL
64
New cards
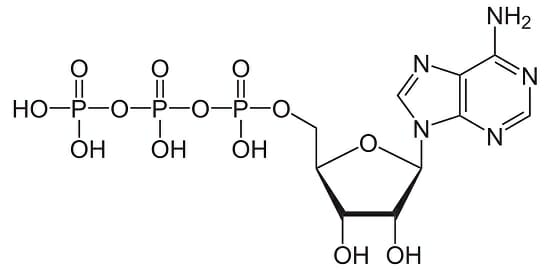
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Broken down to create a source of energy for processes needing energy and a source of energy for storage.
65
New cards
pH
A measure of how acidic/basic (alkaline) the water is. A measure of the relative amount of free H+ and OH- in water.
66
New cards
Acidic
More free H+, a pH less than 7
67
New cards
Basic/Alkaline
More free OH-, pH greater than 7
68
New cards
Transmembrane protein
A type of integral protein that spans the entire membrane. Can receive and transmit signals from the cell outside to the inside and vice versa.
69
New cards
Peripheral membrane protein
Allows cells to coordinate and communicate using networks of proteins and reactions
70
New cards
Glycoprotein
A carbohydrate group attached to a protein (polypeptide chain).
71
New cards
Passive transport
The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane with no expenditure of energy.
72
New cards
Diffusion
The movement of individual molecules of a substance through a semipermeable barrier from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
73
New cards
Concentration gradient
A region along which the density of a chemical substance increases or decreases.
74
New cards
Simple diffusion
A type of passive transport in which no proteins or ATP are needed
75
New cards
Facilitated diffusion
Movement aided (facilitated) by proteins down the concentration gradient
76
New cards
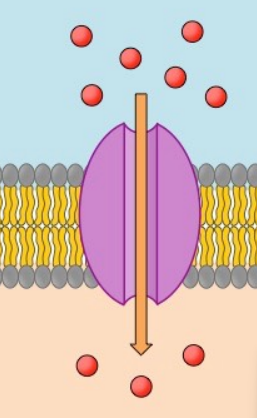
Channel proteins
Pore-forming transmembrane proteins. Make a channel through the membrane. Many channels open and close in response to specific signals.
77
New cards
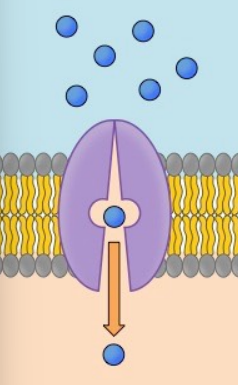
Carrier proteins
Change shape *during* transport
78
New cards
Osmosis
Passive transport of water. From hypotonic → hypertonic. Aquaporins needed for rapid water movement.
79
New cards
Aquaporins
Water channels that facilitate rapid water movement
80
New cards
Active transport
Movement against the concentration gradient. Low → high. Proteins and energy are needed. Example: Sodium/potassium pump.
81
New cards
Vesicular transport
Bulk transport of substances into and out of the cell by vesicles
82
New cards
Vesicle
Membrane-bound sac
83
New cards
Endocytosis
Bulk transport into the cell. Vesicle pinches around the molecule.
84
New cards
Exocytosis
Bulk transport out of the cell. Vesicle fuses w/ the membrane, and everything is spilled out to the outside of the cell.
85
New cards
Phagocytosis
Cell eating. Big “food” or other particle uses specialized cells to create a food vesicle, which is absorbed by the cell.
86
New cards
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking. Brings in whatever happens to be outside of the cell, such as ions and small molecules. NON-SELECTIVE
87
New cards
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Very-selective, only brings in one type of molecule. Receptor-membrane proteins w/ binding cite that is specific for signal to bind.
88
New cards
Hypotonic
Higher concentration of H2O and thus lower concentration of solute
89
New cards
Hypertonic
Lower concentration of water and thus higher concentration of solute
90
New cards
Isotonic
Equal concentration of water and solute
91
New cards
Pump
Transmembrane proteins that actively move ions and/or solutes against a concentration gradient
92
New cards
Receptor
A molecule inside or on the surface of a cell that binds to a specific substance and causes a specific effect in the cell.
93
New cards
Plasma membrane
Boundary mediating interaction between inside and outside
94
New cards
Cytosol
The semifluid portion of the cytoplasm
95
New cards
Ribosome
Site of protein synthesis
96
New cards
Chromosome
DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism
97
New cards
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Nucleic acid molecule that contains instructions (genes)
98
New cards
Nucleoid region
A membrane-less region in a prokaryotic cell where most, if not all, of the DNA in the cell is located
99
New cards
Flagella
An appendage that allows prokaryotes to move
100
New cards
Eubiosis
A healthy and balanced gut marked by high diversity and abundance of microbial populations