Glomerular Disease & Pathology
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Glomerular Anatomy
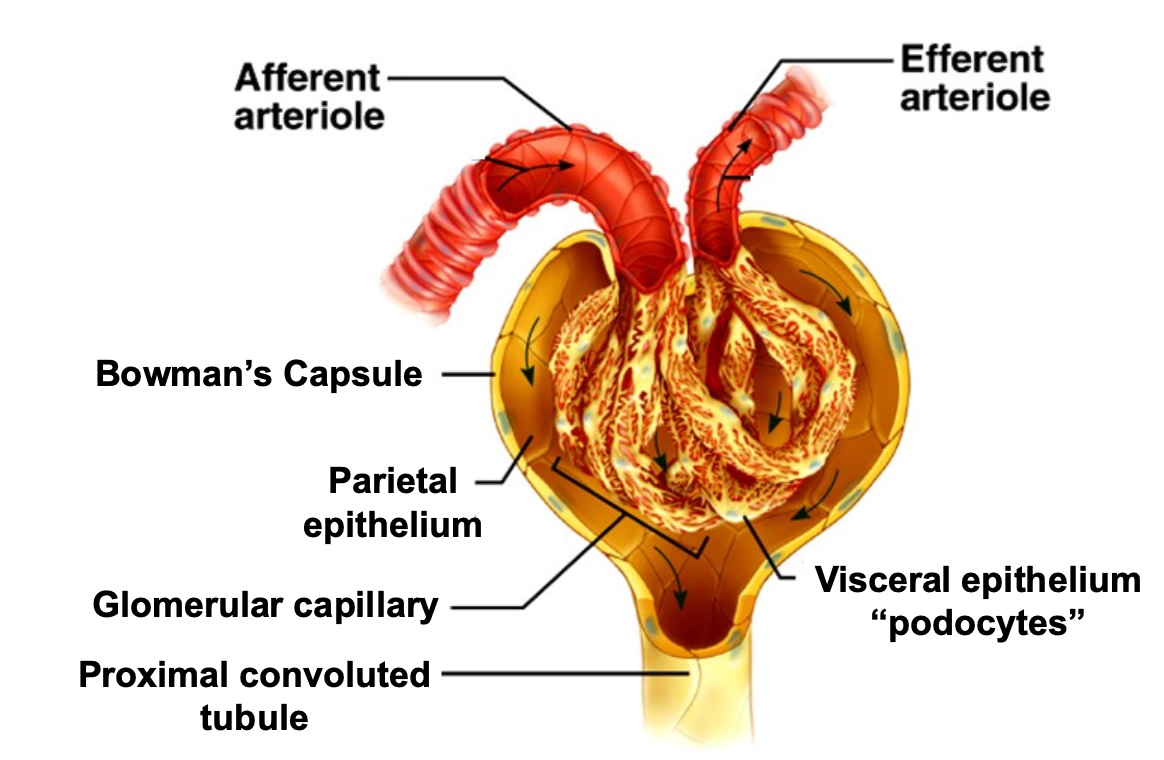
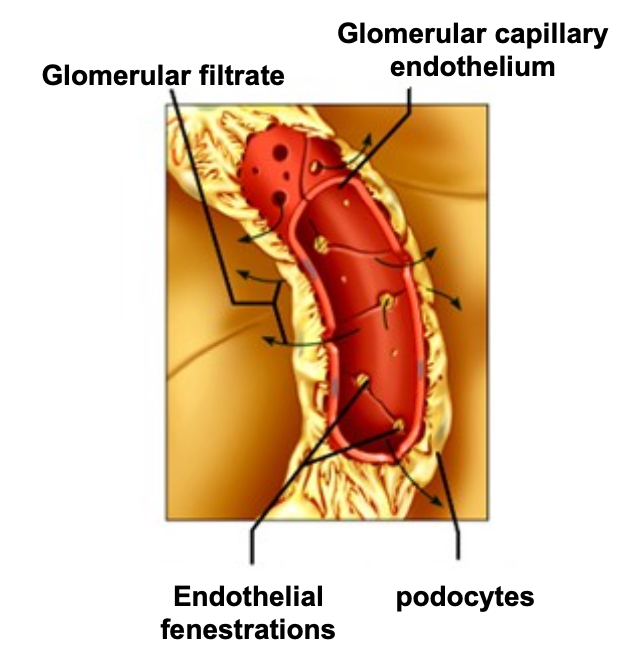
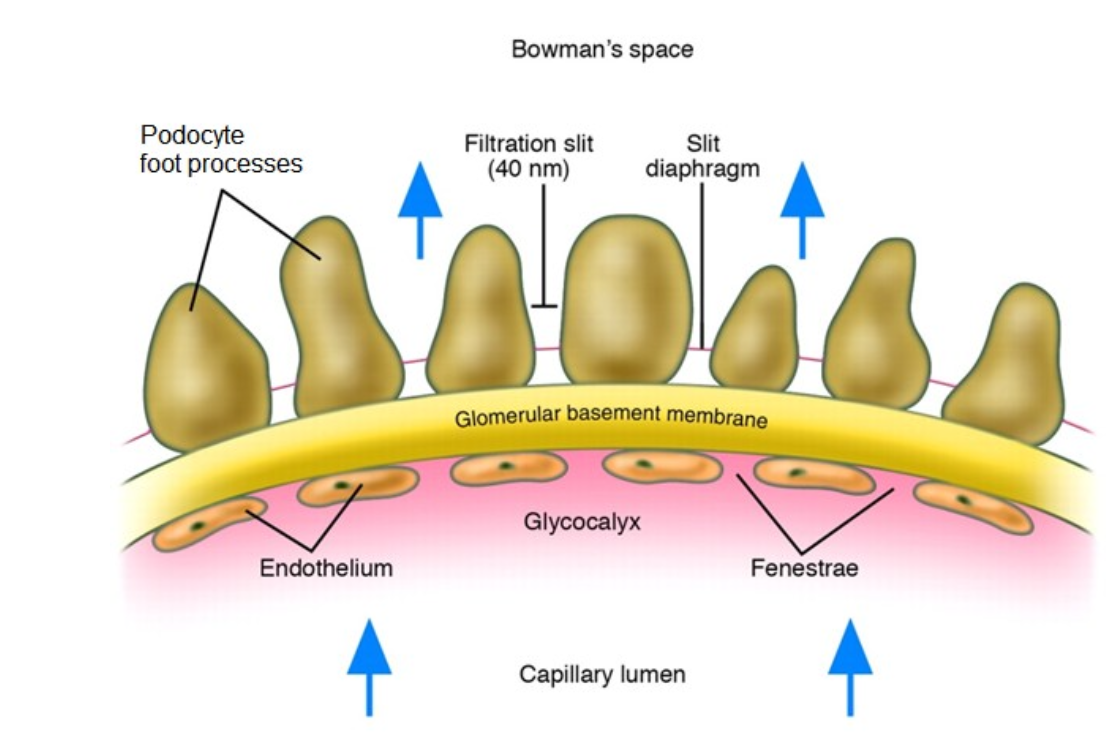
What is the glomerular filtration barrier?
Plasma water is filtered across capillary wall (GFB) into urinary space
Histological image of glomerular filtration barrier
If you see someone with an elevated creatinine and low protein, youd think of
tubulointerstitial or vascular disease
If you see someone with an elevated protein,
It is a major clue to glomerular disease
What are the clinical presentations of glomerular disease
Asymptomatic urinary abnormalities
Nephrotic syndrome
Glomerulonephritis (nephritis)
What conditions do you see in glomerulonephtiris?
Acute Kidney Injury (Acute Nephritis or RPGN)
Chronic Kidney Disease (chronic glomerulonephritis)
Urinalysis abnormalities are common
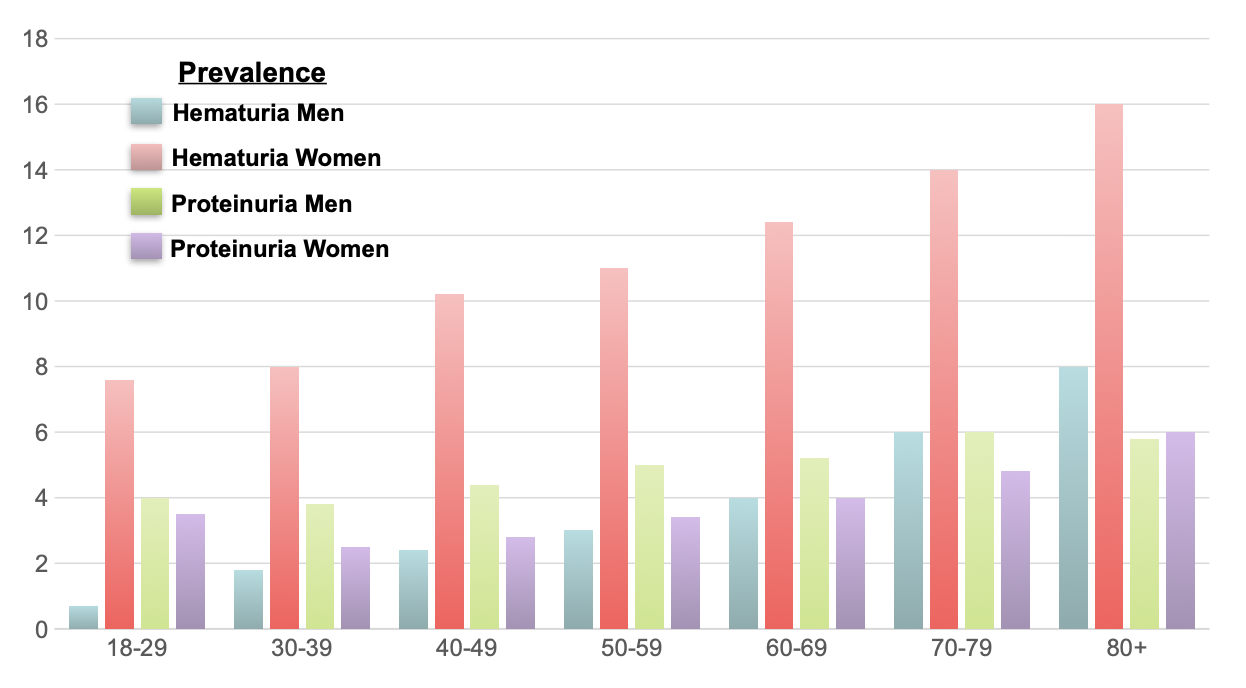
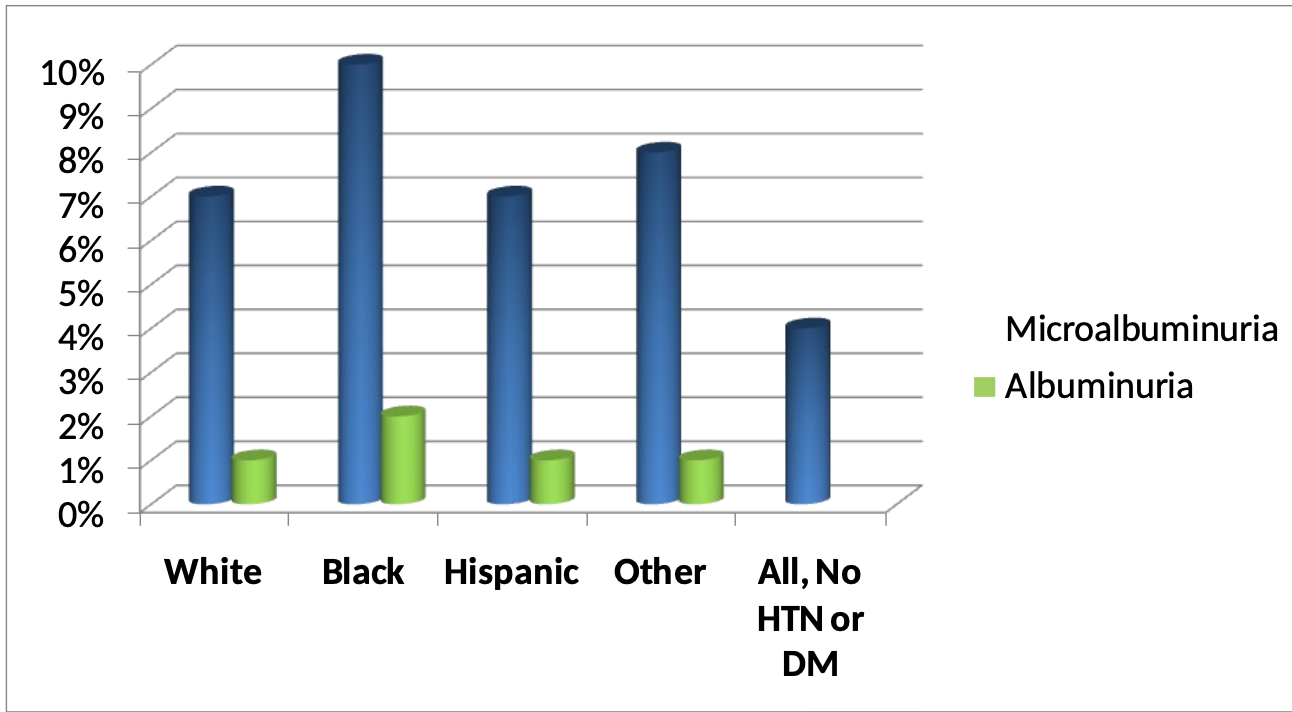
What is the prevalence of albuminuria in the united states?
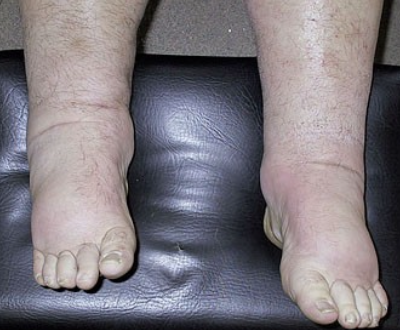
59y/o woman presents with two month history of swollen ankles. She had previously been well. No past history of heart disease, liver disease or diabetes
Examination
BP 142/94
P 72
3+ edema
Chest clear
No JVD
Investigations
renal impairment: Screat 2.2mg/dl (creat clearance 34mls/min)
urine protein 14.7g/24h (normal <0.1g/24h)
Salb 1.8 g/dl
What does she have?
Nephrotic Syndrome
What are the clinical features of Nephrotic Syndrome?
Proteinuria (>3.5g/24 hours)
Hypoalbuminemia
Edema
Hyperlipidemia
Lipidura
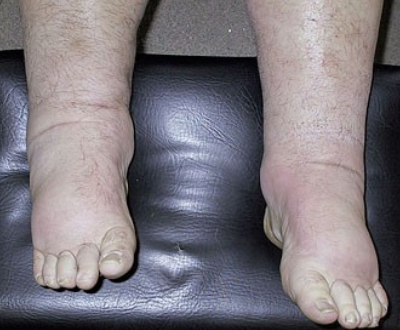
What are the complications of Nephrotic Syndrome?
Clotting/Thrombosis- Liver is losing coagulating proteins
Infection- You lose immunoglobulin in urine
Cardiovascular disease- hyperlipidemia
Why do patients with nephrotic syndrome develop edema?
The kidneys are primarily holding onto kidneys itself because of low oncotic pressure this leads to interstitial shift. Primary sodium retention
Nephrotic syndrome is a disorder of
GLomerular Filtratration Barrier
What are some differential diagnoses of Nephrotic syndrome?
Primary glomerular disease
Minimal change disease
FSGS
Membranous nephropathy
Membranoproliferative GN
Systemic disease
Diabetes
Amyloid
Lupus
To make a differential diagnosis, you’d take a
Kidney biopsy
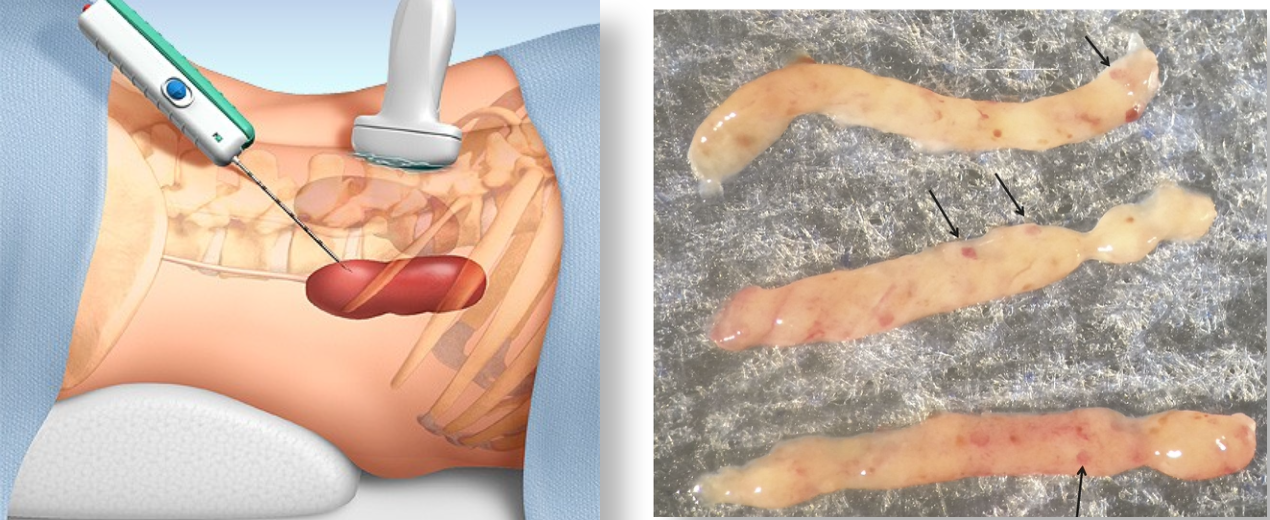
How does the kidney biopsy (pathology) assist in diagnosis?
Kidney biopsies are generally studies by
light microscopy (LM)
Immunofluorescence (IF)
Electron microscopy (EM)
What type of microscopy evaluates which parts of the kidneys are affected?
Light microscopy
What type of microscopy evaluates Immune complexes?
Immunofluoresnece
What type of microscopy evaluates location of immune deposits?
Electron microscopy also looks at podocyte foot process integrity
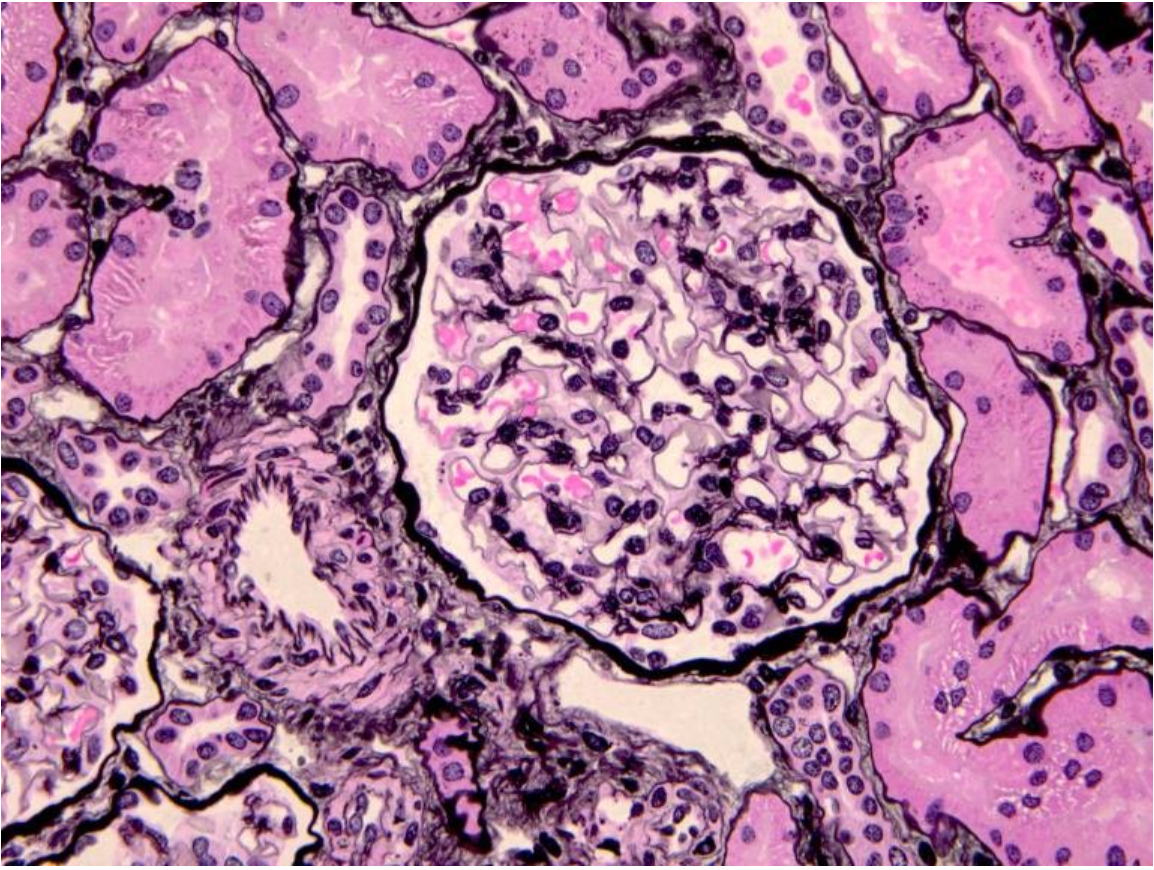
Histological image of normal glomerulus
This slide is stained with Jones Methenamine Silver (JMS) which stains basement membranes and matrix in black- also note the normal tubules and small artery (at 8 o’clock to glomerulus)
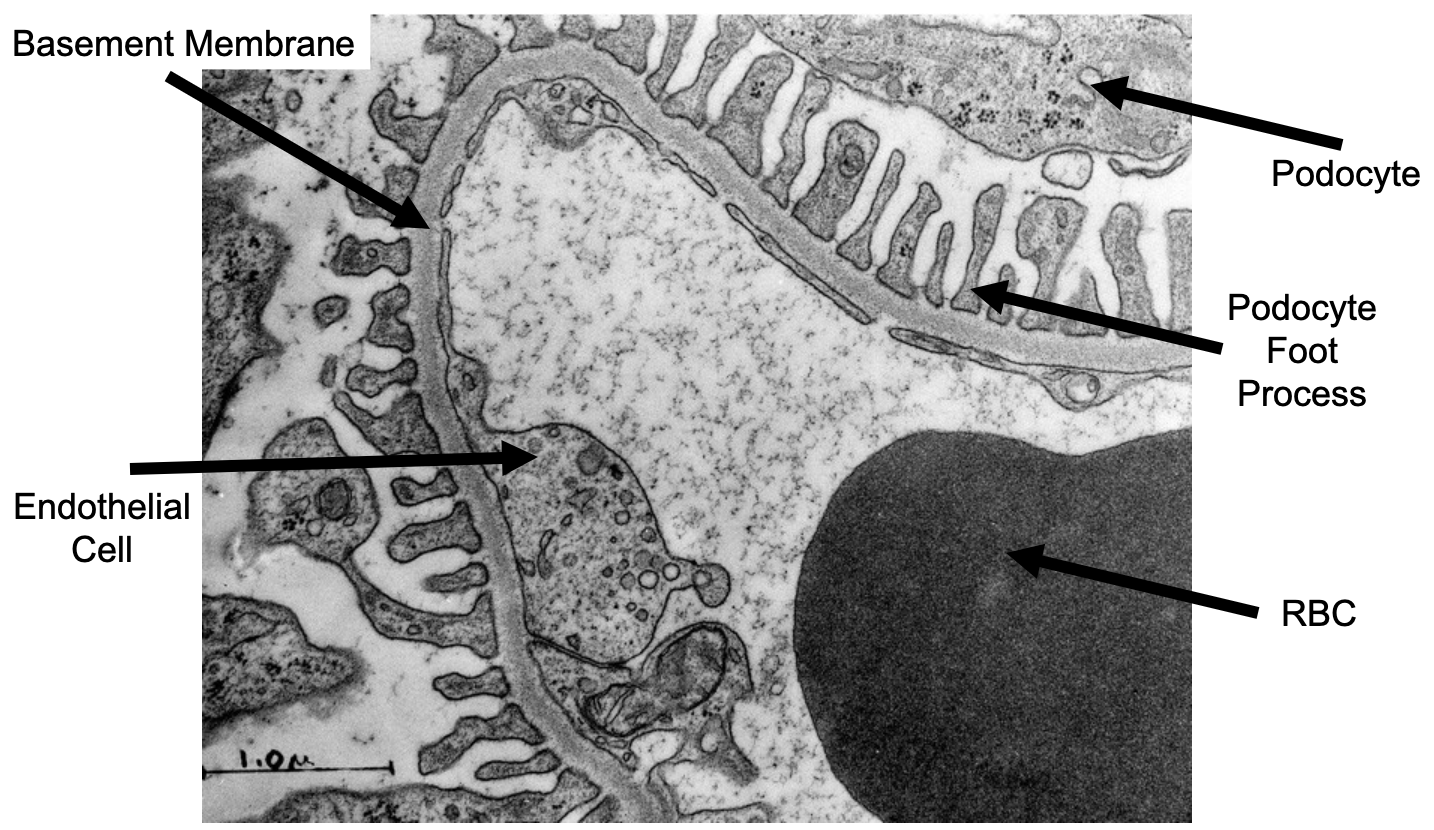
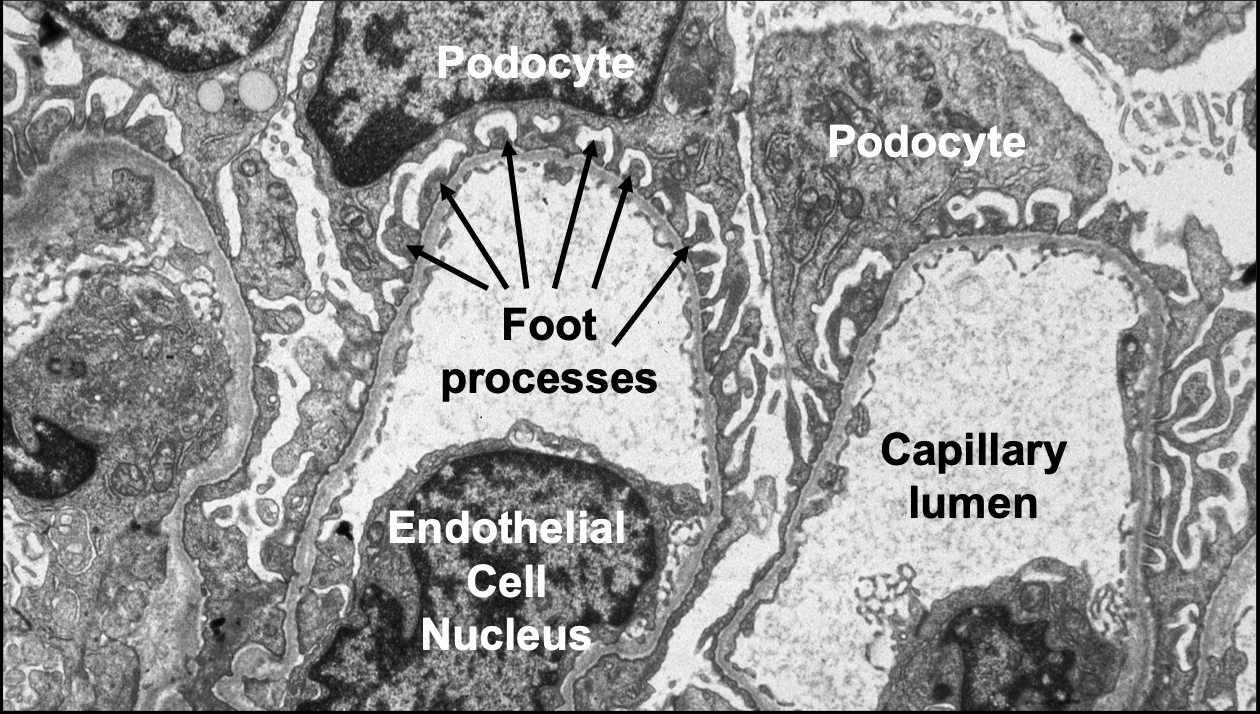
What does a normal glomerulus look like in transmission electron microscopy?
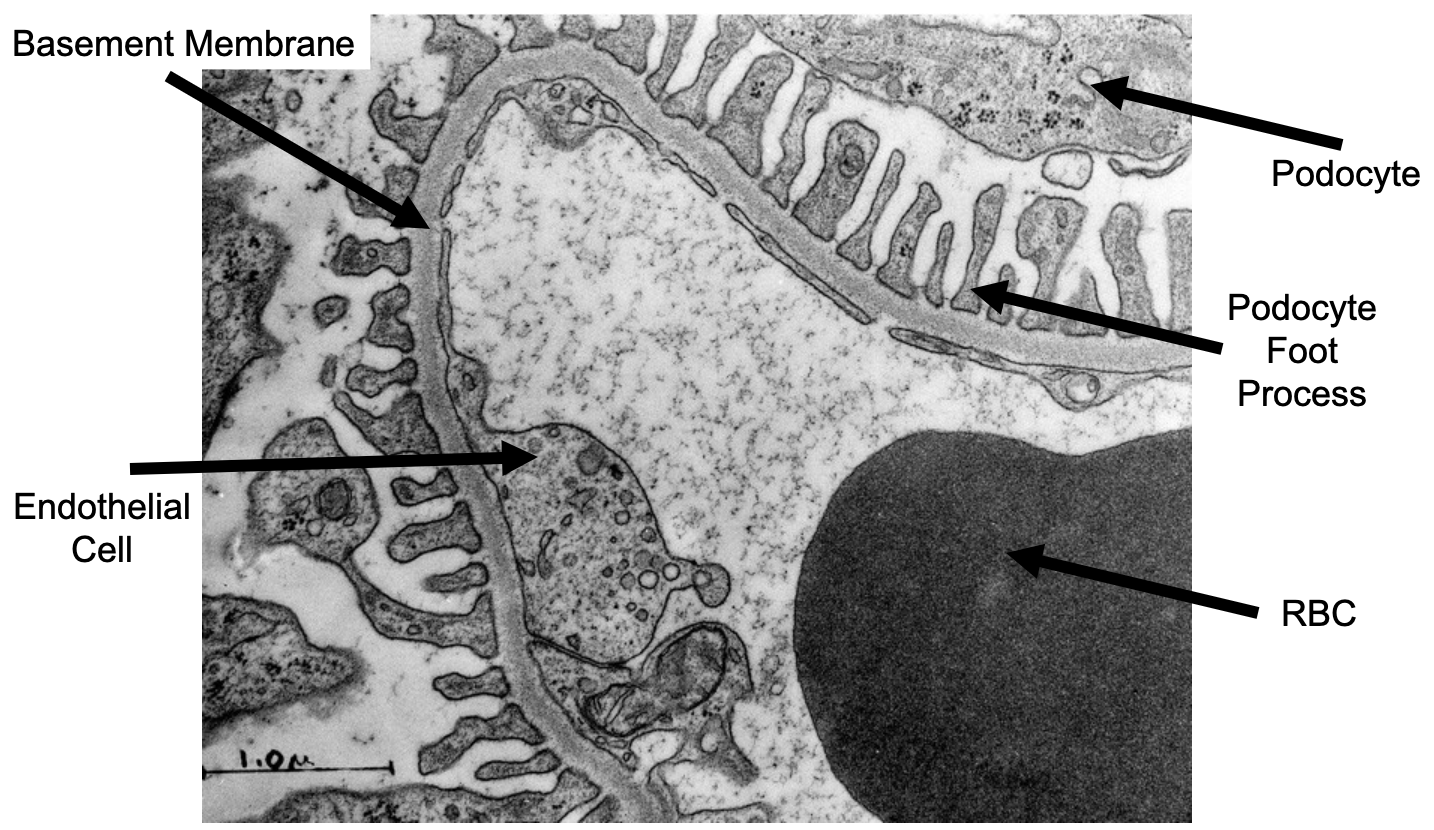
What are podocyte foot process
Fine projections that come from neighboring cells
What is minimal change disease?
Characterized by little if any alterations by light or immunofluorescence microscopy
Instead of seeing a nice smooth pattern, you see
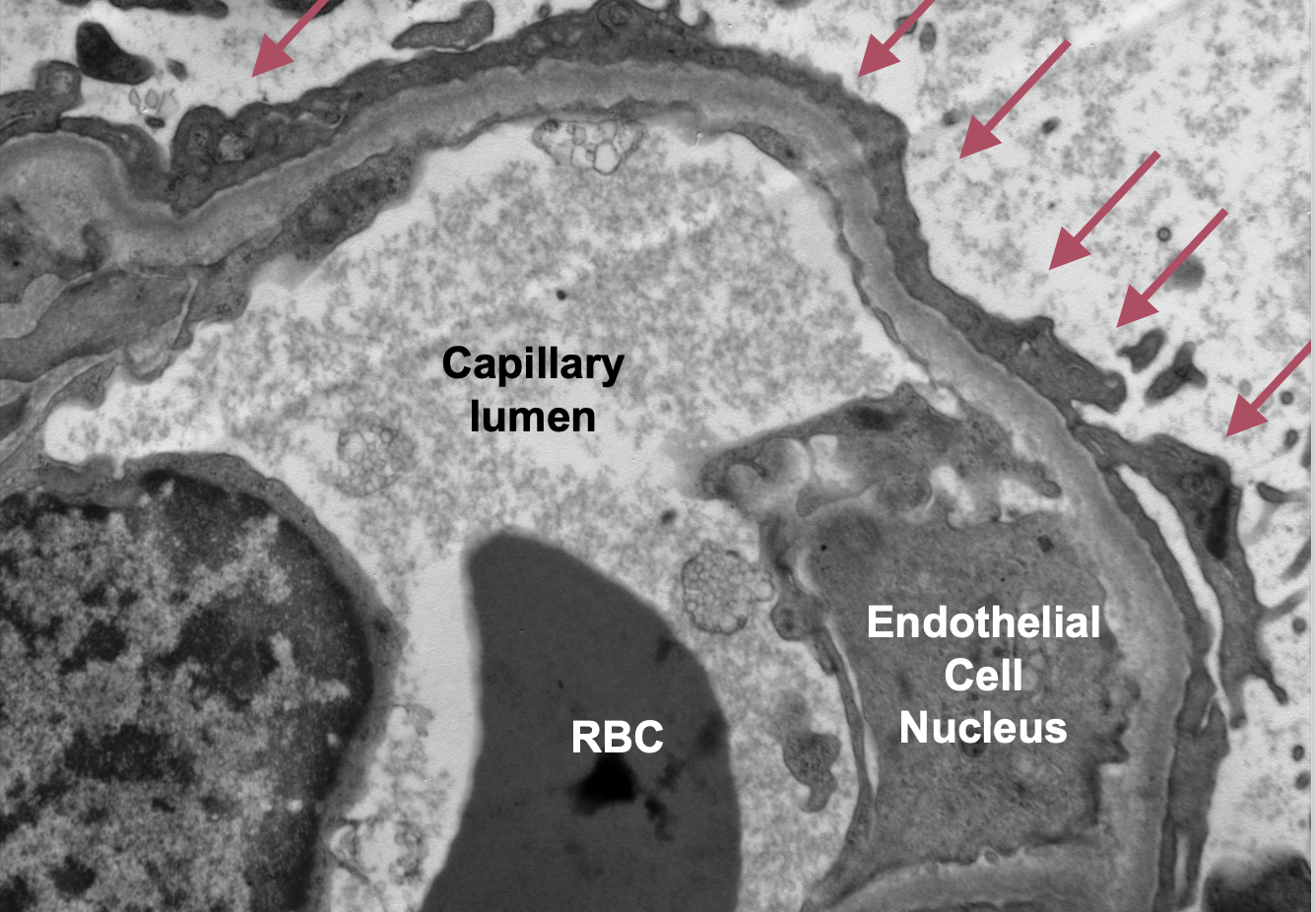
Diffuse effacement of podocyte foot processes by electron microscopy
Electron Micrograph showing normal podocyte foot processes
Minimal change disease histological image
Podocyte foot process effacement
What is Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)?
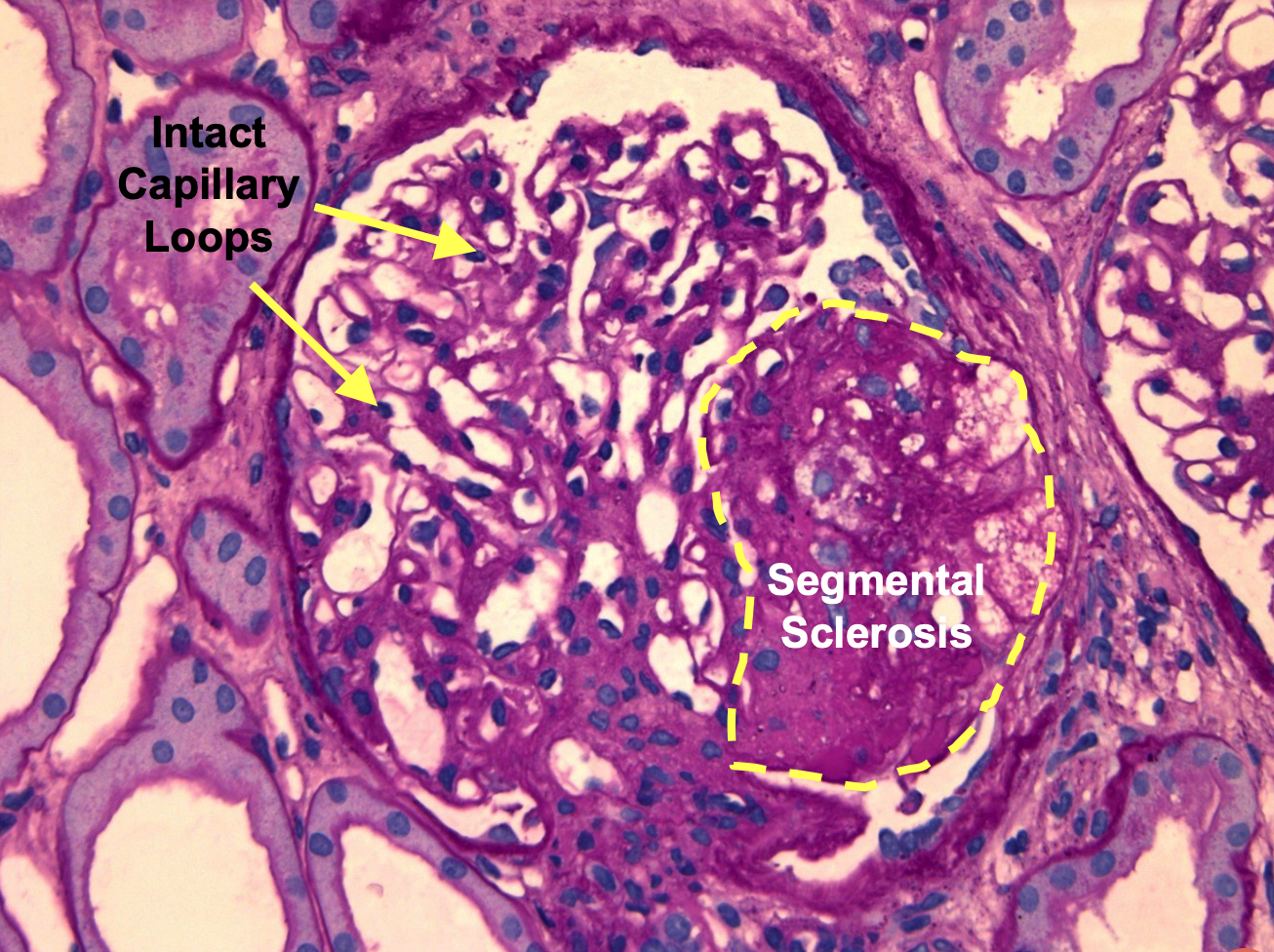
Segmental scarring of capillary loops with attachments to Bowman’s capsule
What does a confident diagnosis of Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) require?
The right clinical context and sufficient sampling (even one glomerulus with the right pattern of injury is enough to make the diagnosis!)
What is the mechanism of Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
Irreversible injury to podocyte —> destabilization of capillary segments scarring
What is the etiology of Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
Circulating factor (anti-nephin antibiotics)
Hyperfiltration injury
Genetics
Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) histological image
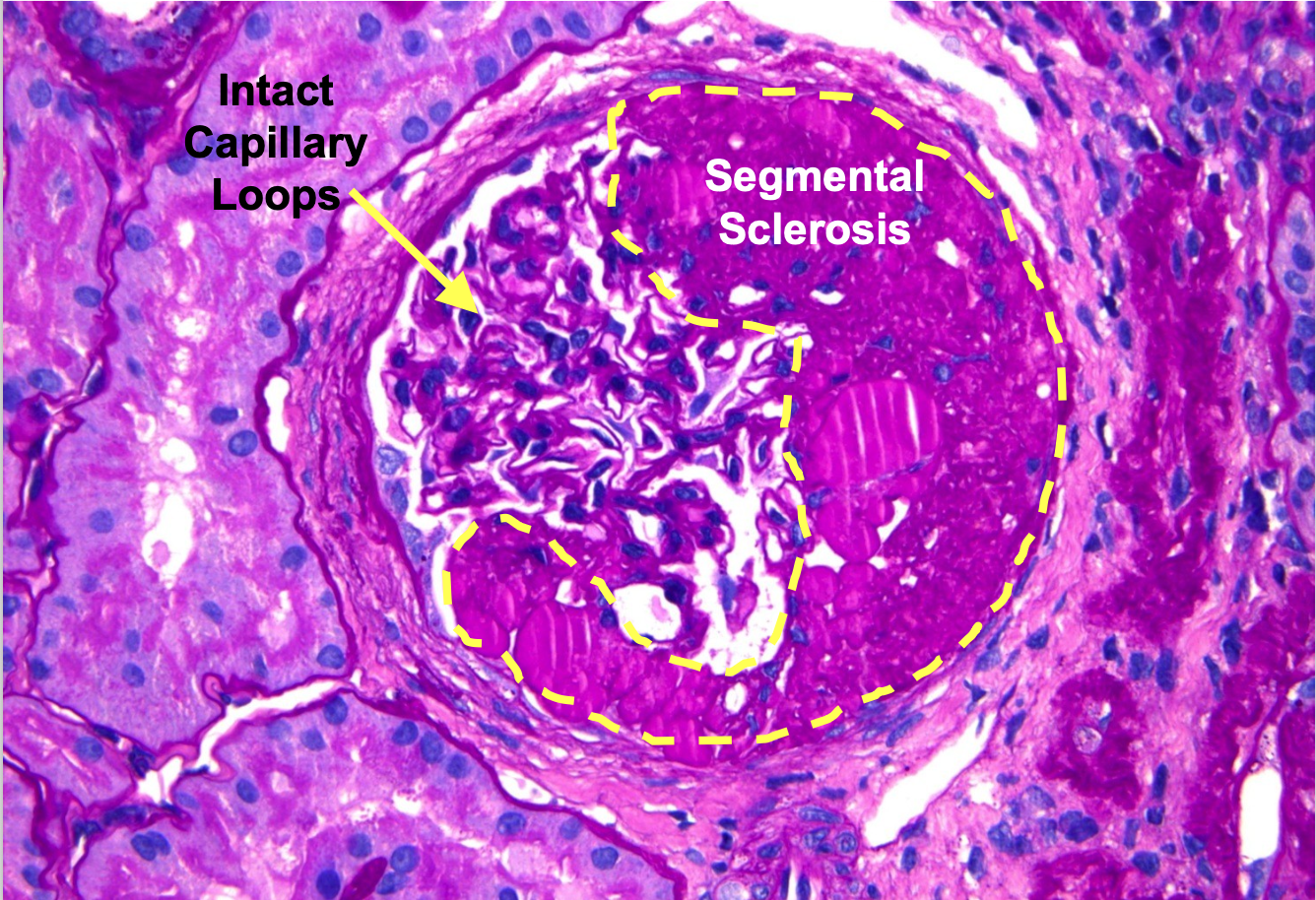
Another Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) Histological image
Podocyte Foot Process Effacement seen in Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
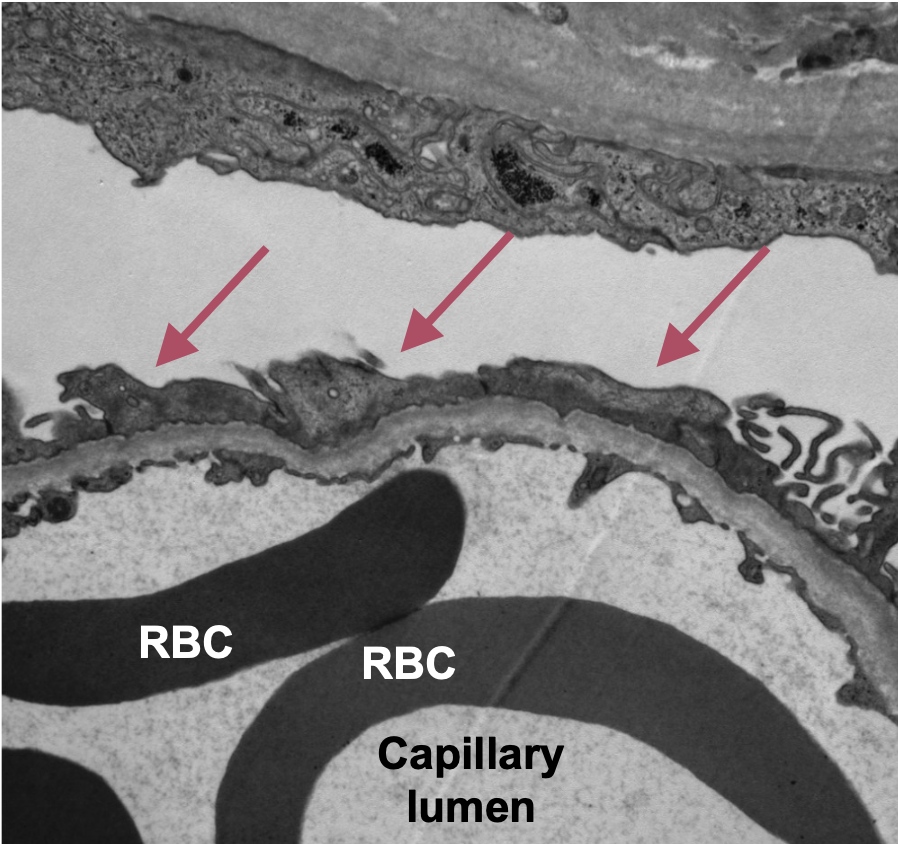
What is membranous nephropathy?
Accumulation of immune deposits in the subepithelial space (below podocytes) that results in podocyte injury and proteinuria. It has a characteristic thickening of glomerular capillary loops with “spike” formation on silver stained sections