American Government Ch. 4 and 5 and Key Constitutional Clauses
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10/1/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Bill of Attainder Clause
Congress cannot single out a person for punishment without a trial
Commerce Clause
Clause stating that Congress can regulate interstate and international commerce.
Contracts Clause
No state can interfere with the execution of contracts
Due Process Clause
part of the 14th Amendment which guarantees that no state deny basic rights to its people
Elastic Clause
the part of the Constitution that permits Congress to make any laws "necessary and proper" to carrying out its powers
14th Amendment Equal Protection Clause
Constitutional guarantee that everyone be treated equally-14th amendment
Ex Post Facto Clause
Congress cannot pass a law that punishes a person after the fact. A person cannot be punished for something he/she did that was not a crime committed.
Full Faith and Credit Clause
Constitution's requirement that each state accept the public acts, records, and judicial proceedings of every other state
Privileges & Immunities Clause
constitutional clause that prevents states from discriminating against people from out of state
Supremacy Clause
Federal law is supreme over state law
13th Amendment (1865)
Abolition of slavery w/o compensation for slave-owners
19th Amendment (1920)
Women gain the right to vote
Strict Constructionists (Originalists)
Those who believe that the text of the Constitution is important and that interpretation should be kept to a minimum.
Broad Constructionists (Living Constitutionalists)
Those who take a broader approach to constitutional interpretation.
Necessary and Proper Clause
Article I Section 8 Clause 18
Authorizes Congress to make all laws necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers, and all other powers vested by the Constitution in the government of the United States.
Gives Congress authority to do its job completely.

Amendment Process
The formal means of adapting the Constitution to meet changing needs.
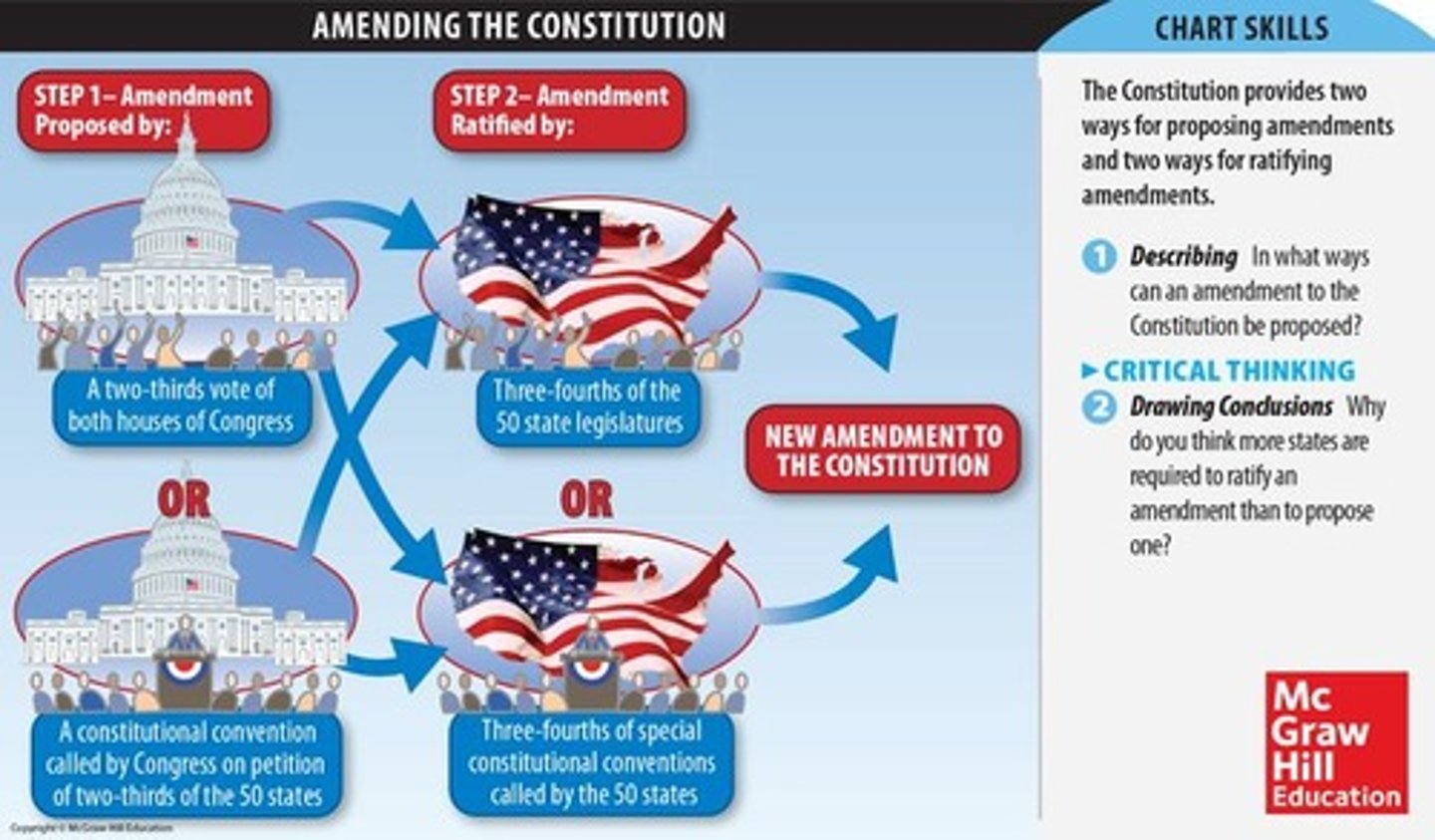
Proposal
The formal introduction of an amendment
Needs 2/3

Ratification
A state level responsibility to formally approve an amendment
Needs 3/4
Bill of Rights
The first 10 amendments that were added in 1791 and were closely tied to the original ratification effort.

Limited Government
Means that government does not have absolute power but rather is limited to those powers that the people have given it through law.

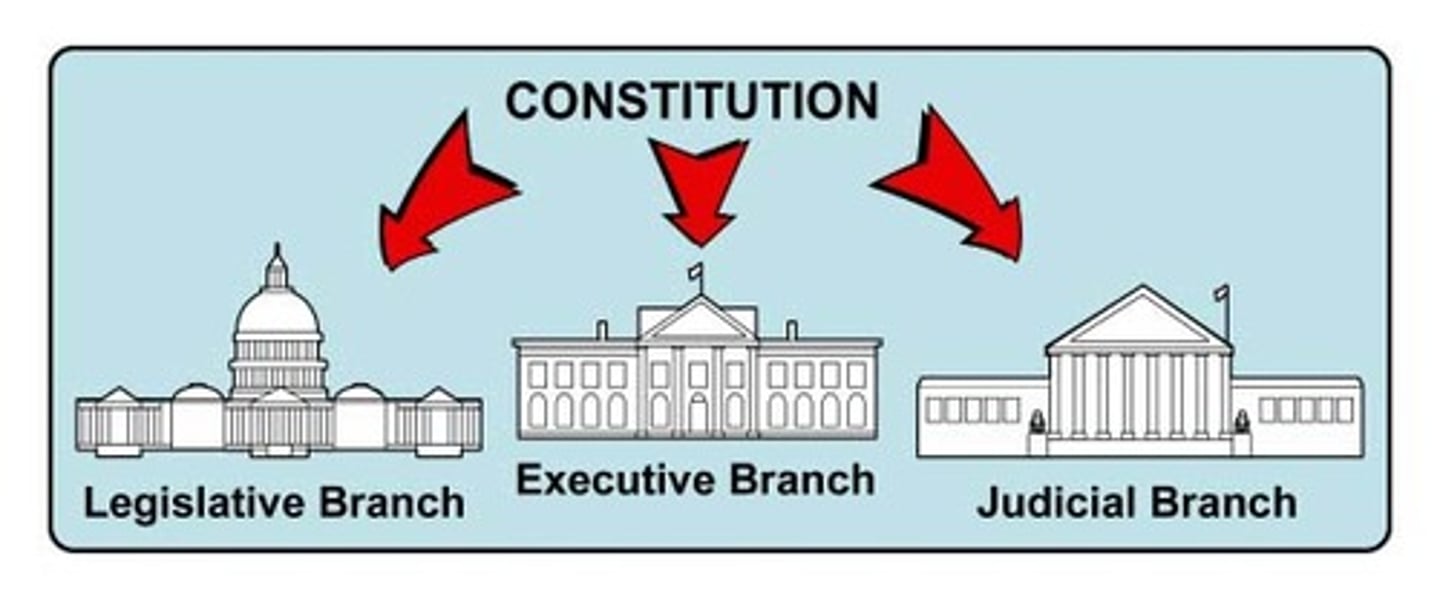
Separation of Powers
All three branches of have been housed in different buildings and vested with different powers.
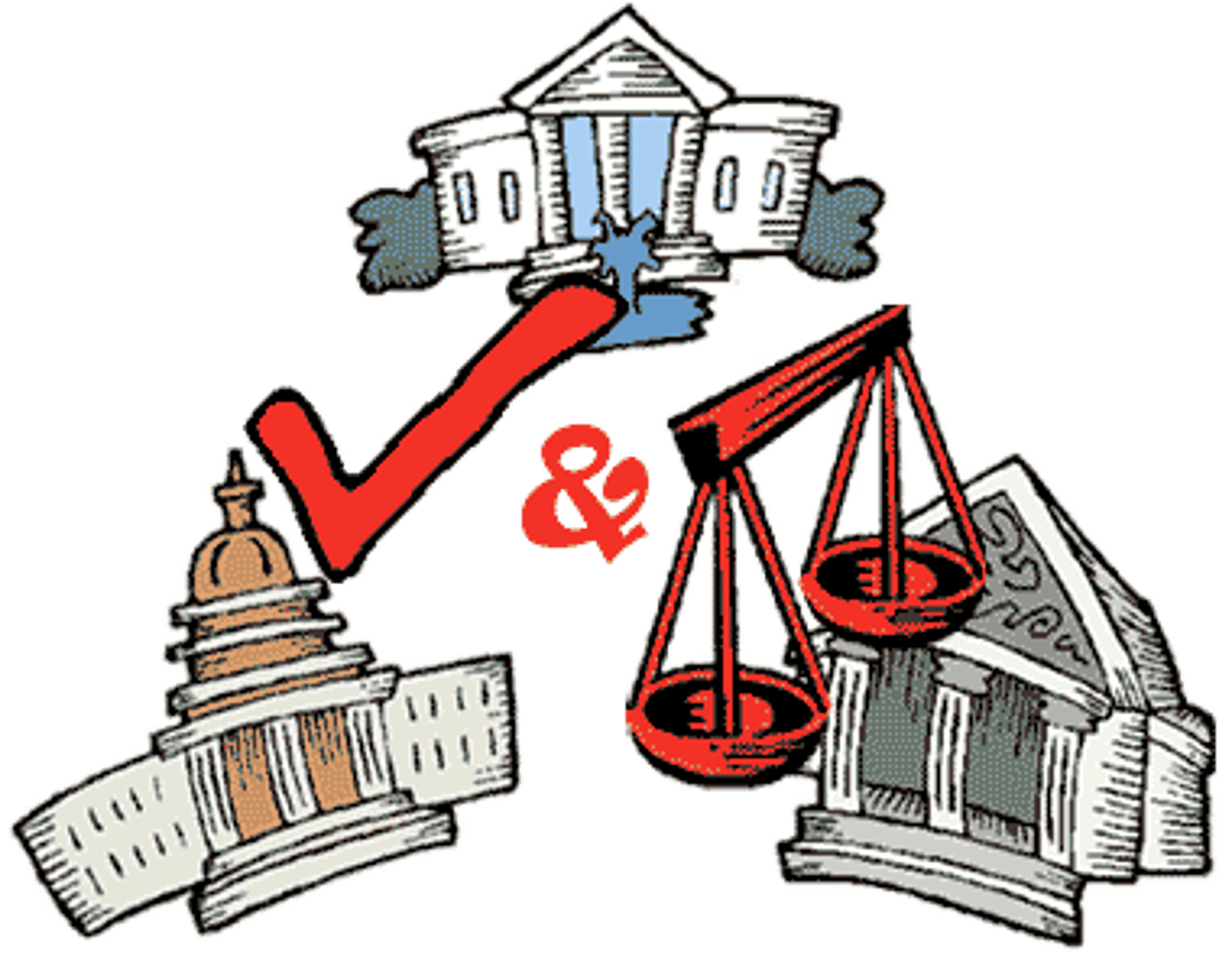
Checks and Balances
Thwarts accumulation of power for any one branch of government.
Veto
Rejection of a bill

Impeachment
The ability to charge the president or federal judges with misconduct in office.
Gridlock
One branch halts the political process.
Judicial Review
The judicial branch's power to review the constitutionality of laws passed by the legislative branch or of actions taken by the executive branch,

Marbury v. Madison
Asserted the principle of judicial review.

Federalism
The division of power between national and state levels of government.
Popular Sovereignty
The idea that the people are the ultimate source of their government's authority.

Preamble
Introduces the Constitution by explaining its nature and purpose.

Legislative Branch
Whose primary function is to make laws.

Bicameral
A legislative system with two houses.
Census
A counting of the population.

President Pro Tempore
Serves as leader of Senate when the vice president is absent.

Quorum
The minimum number needed to transact business.

Sergeant at Arms
Responsible to bring in absent members who are needed to make up a quorum in each house in Congress.
Congressional Record
Each house keeps a record of what it does each day.

Franking Privilege
The right to send official mail free of charge.

Pocket Veto
If the president does not sign a bill and Congress adjourns within ten days, the bill is vetoed automatically.

Naturalization
The process by which a foreignborn person gains citizenship.

National Guard
The modern militia. Under the control of the army and air force.

Writ of Habeas Corpus
Forces authorities to charge an arrested person with a crime before a judge or else release him.

Bill of Attainder
Permits punishment without trial.

Ex Post Facto Law
Makes a law retroactive. Acts that were legal when they were committed cannot be made illegal afterward.
Appropriation
A certain amount of money set apart for a certain purpose.
Executive Branch
Whose primary function is to carry out (enforce) the nation's laws.

Electoral College
Composed of electors from each state. Elects the president.
Reprieves
Temporary postponement of punishment

Pardons
Complete forgiveness of a crime and its consequent punishment
Judicial Branch
The function has been to interpret the law.

Original Jurisdiction
Means that a case can start in the court in question and that the court has first opportunity to hear and decide the case.

Appellate Jurisdiction
Means that the case must first have been tried in a lower before it can be appealed in a higher court.
Extradition
The process of returning a criminal.
Supremacy Clause
This clause upholds the US Constitution as the supreme law of the nation.
Slander
Defaming a person verbally
Libel
Defaming a person in writing
Grand Jury
Composed of a panel of citizens who considers the prosecution's case against the accused in a trial.

Due Process
A fair and proper trial before sentencing.

Eminent Domain
Private property can be taken for the public good but has to be paid for.
Subpoena
A document requiring a person to appear in court as a witness.

Bail
Money held by a court to ensure an accused person's appearance at court.

Prohibition
A ban on the manufacture, sale, or transportation of liquor.
Suffrage (Franchise)
The right to vote.

Lame Duck
An official who is still in office but has not been reelected.
Poll Taxes
Taxes used to keep poor blacks from voting.
Gerrymandering
Process of redrawing legislative boundaries for the purpose of benefiting the party in power.
First Amendment Rights
The rights of the First Amendement can not be taken away by the government. Gives freedom of speech, press, assembly, petition, and religion
Second Amendment Rights
Right to keep and bear arms
Third Amendment
The government may not house soldiers in private homes without consent of the owner
Fourth Amendment Rights
Protection from unreasonable search and seizure
Fifth Amendment Rights
right to a grand jury indictment, double jeopardy, right against self incrimination, due process of law,
Sixth Amendment
A constitutional amendment designed to protect individuals accused of crimes. It includes the right to counsel, the right to confront witnesses, and the right to a speedy and public trial.
Seventh Amendment (1791)
Right to a trial by jury in civil cases
Eighth Amendment Rights
Excessive bail shall not be required, nor excessive fines imposed, nor cruel and unusual punishments inflicted.
Ninth Amendment Rights
People's rights are not limited to those listed in the Constitution
Tenth Amendment Rights
Powers not granted to the Federal Government in the Constitution belong to the states or the people.
Local Government
The definition of local government is the government of a town, city, or county. Towns, cities, and countries exist as divisions within a state. Local governments are the governments that ordinary people have the most direct control over.
Legislative Government
A government in which there is a branch that is charged with such powers as making laws, levying and collecting taxes, and making financial appropriations
Limited Government
The term "limited government" refers to any central government in which that government's powers over the people are limited by a written or otherwise agreed to constitution or overriding rule of law.
House of Burgesses (1619)
The House of Burgesses (1619-1776 CE) was the first English representative government in North America, established in July 1619 CE, for the purpose of passing laws and maintaining order in the Jamestown Colony of Virginia and the other settlements that had grown up around it.

1760
The year in which the French and Indian War ended, and George III ascended the British throne.
Stamp Act (1765)
Parliament passed a series of taxes and trade restrictions on the colonies that produced more resentment than revenue from America.

Petition of Right
A document guaranteeing basic civil liberties to all British subjects.
Boycott
An act of protest in which business is withheld or refused.
First Continental Congress (1774)
Representatives from every colony except Georgia gathered in Philadelphia. The Congress met for two months and issued a declaration of grievances to George III.
Second Continental Congress
On June 14, 1775 they established the Continental Army. They made George Washington General of the Army. On July 8, 1775 they tried again for peace by sending the Olive Branch Petition to the King of Britain.
Declaration of Independence
Its basis was a resolution proposed by Virginia delegate Richard Henry Lee.

Thomas Jefferson
Did the actual writing for the Declaration of Independence.

John Hancock
President of the Continental Congress who signed the Declaration of Independence first.

Age of Enlightenment
Stressed the importance of natural laws.
Deism
A religious outgrowth of the Enlightenment that regards God as maker of natural law and then had little else to do with human affairs.
Social Contract
Holds that rulers and subjects are in their positions because of agreement.
Articles of Confederation
Formalized the status quo by proposing a central government with characteristics very similar to those of the provisional Second Continental Congress.

1777
The year the Articles of Confederation were ratified by 11 states.
1781
The year Maryland finally ratified the Articles of Confederation.
Unicameral
One house legislature.
1785
When negotiations took place for navigation rights on the Potomac between Maryland and Virginia.
Mount Vernon
George Washington's home.

1786
Virginia called states to send representatives to Annapolis to recommend a federal plan for regulating commerce.
Annapolis Convention
Only five states sent representatives.
