Endoplasmic reticulum
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is the central role of the endoplasmic reticulum (rough and smooth) ?
Lipid and protein biosynthesis
What ER consists of (structure) ?
ER membrane : continuous with the nuclear envelope
ER lumen : 10% of the total volume
What are the two types of ER ?
Smooth ER : no ribosome
Rough ER : ribosomes on the outer surface
What are the functions of rough ER ?
protein folding and assembly
post-translational protein modification
protein transport
membrane protein production
What are ribosomes made of ?
RNA (rRNA) and protein
Are ribosomes membrane organelles ?
NO, they lack a surrounding membrane
Where do ribosomes bind ?
Nuclear envelope
Rough ER
Where are located ribosomes ?
Cytoplasm : free ribosomes
RER (cytosolic side) and Nuclear envelope : membrane-bound ribosomes
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts
Where are initially located all ribosomes ?
There is a common pool of free ribosomes in the cytoplasm, then they are orienting themselves thanks to signal sequence
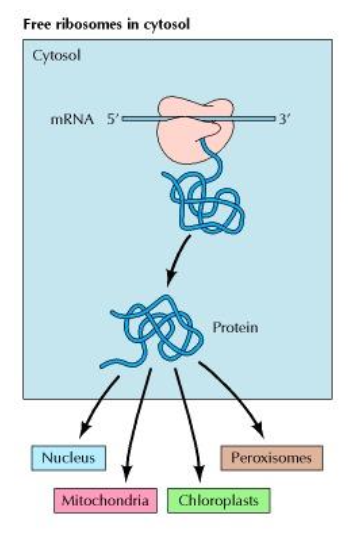
What is the future location of a protein synthesised in free ribosomes ?
Remain in the cytosol
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts
Peroxisome
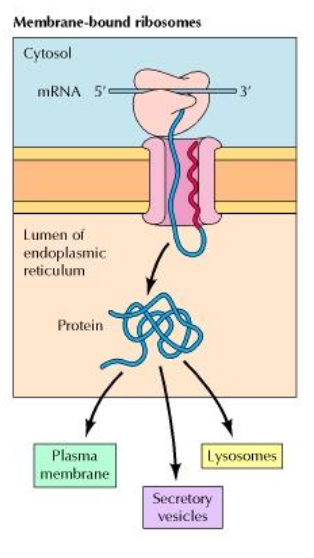
What is the future location of a protein synthesised in membrane-bound ribosomes ?
lumen of ER —> Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Secretory vesicles (cell exterior)
Plasma membrane
Where are assembled ribosomal subunits ?
Directly into the nucleolus by the association of newly transcribed and modified rRNAs with ribosomal proteins
Between eukaryotic and prokaryotic ribosomes, which one is the biggest ?
Eukaryotic ribosome (80S) > Prokaryotic ribosome (70S)
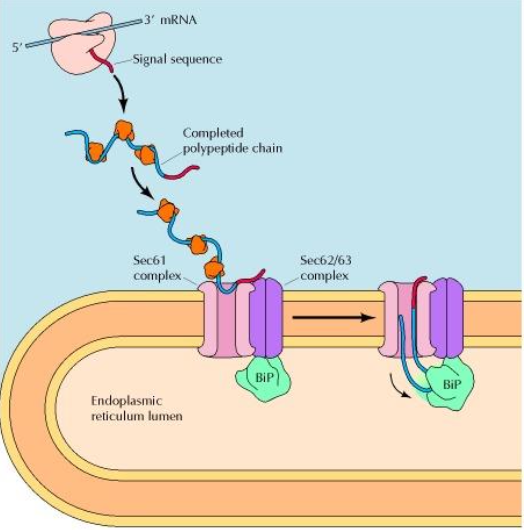
When does ER protein translocation occur ?
Before the polypeptide chain is completely synthesised = co-translational translocation
How does ER signal sequence is guided to the ER membrane ?
With the help of two components :
Signal-Recognition Particle (SRP) : binds to the signal sequence
SRP receptor : in the RER membrane
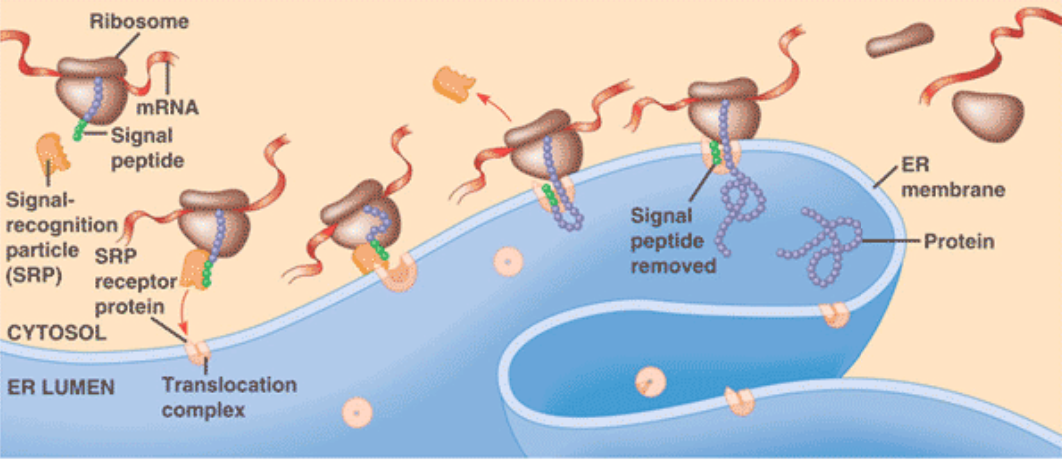
What causes signal recognition particle (SRP) binding on ER signal sequence ?
Because of a ‘pause’ in the protein synthesis
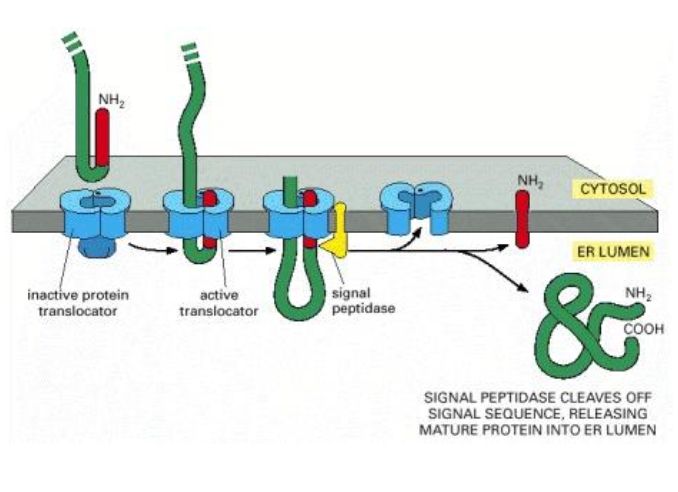
What is the structure that cleaves the signal sequence from the final translocated protein ?
Signal peptidase, which allows the hydrophobic signal sequence to diffuses through the bilayer, where it is degraded into AA by proteases in the ER
What is the difference between single and multiples transmembrane proteins ?
Single pass transmembrane protein : contains either a stop-transfer sequence or an internal signal sequence that is not cleaved off
Multipass transmembrane protein : contains both stop-transfer sequence and internal signal sequence and have several of these
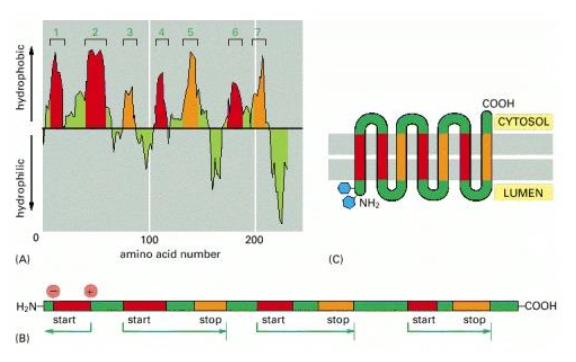
Describe this situation
This is an EXCEPTION where a protein is fully translocated through a free ribosome and is being transported through the help of chaperones that help the protein not folding, and reach the ER membrane where their signal sequence will be recognised by a complex protein associated with the translocation channel in the ER membrane, named a BiP (type of chaperone)
What is the purpose of BiP chaperones ?
they mediate protein folding and the assembly of multi subunit proteins
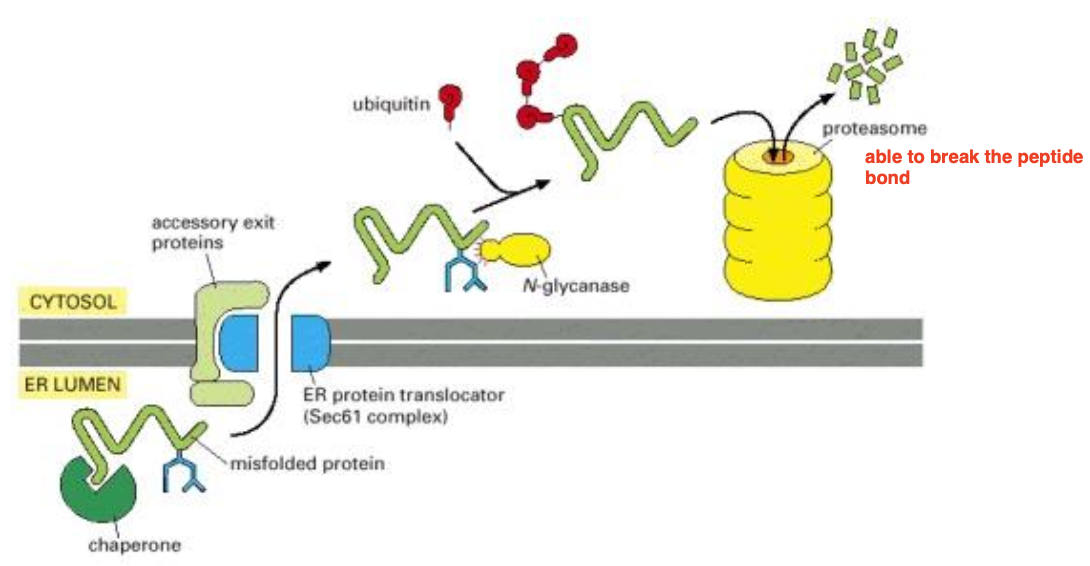
What happens to protein that fail to achieve their properly fold in the ER ?
They leave the ER lumen through the same translocator where they came from, and goes into the cytosol to be degraded into the proteasome
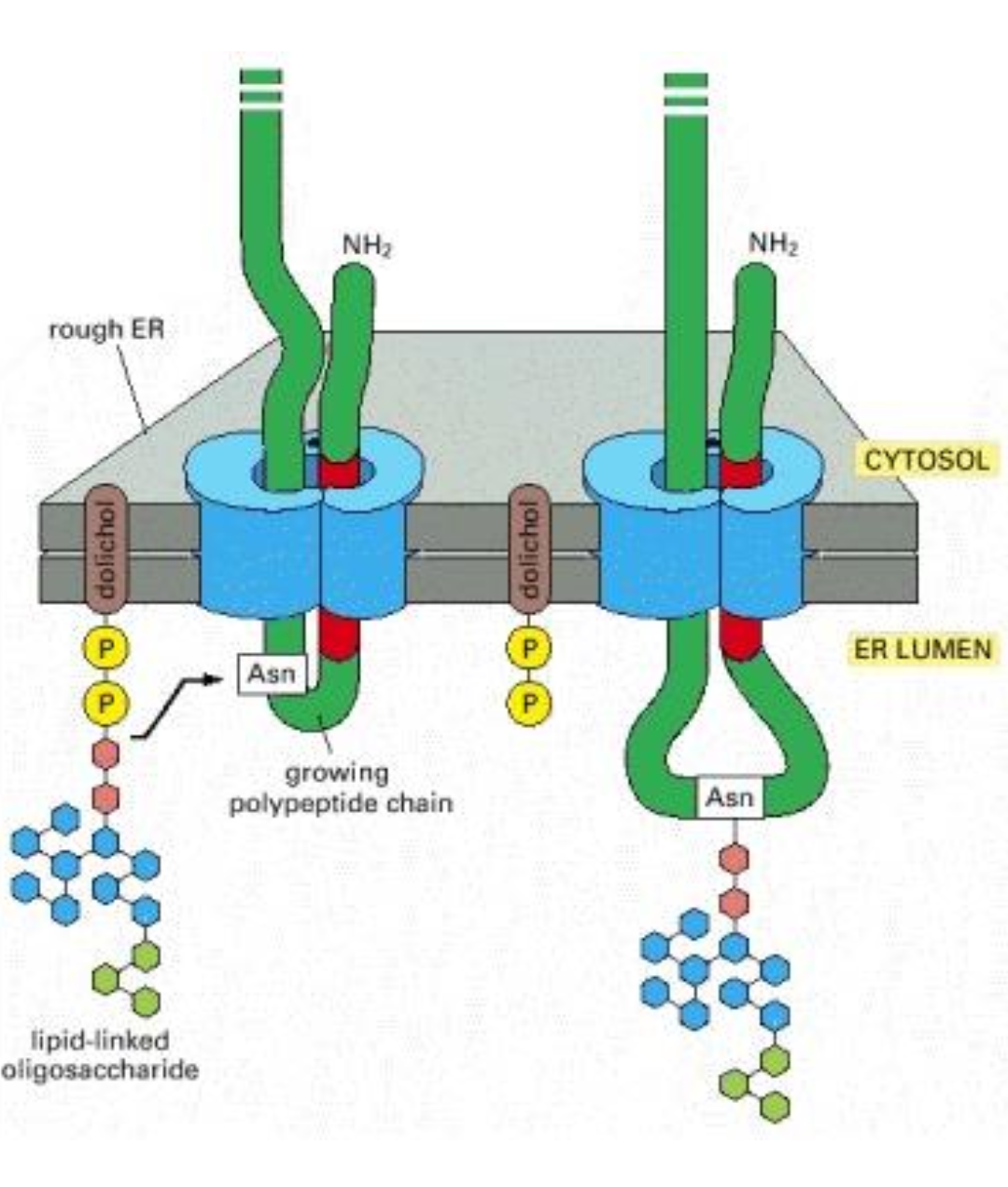
On what type of AA, polypeptide chain, is being glycosylated ?
Asparagine
What are the functions of the smooth ER ?
Lipid metabolism : lipids and lipoprotein synthesis
Detoxification process : drugs & harmful compounds produced by metabolism
Calcium storage : sequester Ca2+ from the cytosol
In what kind of cells smooth ER is abundant ?
In cells specialised in synthesis of steroid hormones form cholesterol (liver cells, adrenal cells, gonadal cells)
What kind of cell is the principal site of production of lipoproteins ?
Hepatocytes in the liver
In the hepatocytes, where are synthesised lipoproteins ?
in the SER
What type of ER is sarcoplasmic reticulum ?
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum