Limits [INCOMPLETE]
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
In Progress
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the definition of continuity in terms of limits?
A function is continuous if the limits exist everywhere on the graph.
What are the two methods that you can solve limits of \Big(\dfrac00\Big) form?
factorisation
L’ Hospital
What sort of limits is L’ Hospital’s rule used to solve?
limits of the form \lim_{x \to a}\dfrac{f(x)}{g(x)}=\dfrac00\ \ \text{or}\ \ \dfrac{\infty}{\infty}
What is L’ Hospital’s rule?
if
\lim_{x \to a}\dfrac{f(x)}{g(x)}=\dfrac00\ \ \text{or}\ \ \dfrac{\infty}{\infty}
then
\lim_{x \to a}\dfrac{f(x)}{g(x)}=\lim_{x \to a}\dfrac{f’(x)}{g’(x)}
What is \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}?
1
What is \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\tan x}{x}?
1
What is \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{x}{\sin x}?
1
What is \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\sin^{-1} x}{x}?
1
What is \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{\tan^{-1} x}{x}?
1
What is \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{x}{\tan x}?
1
What is \lim_{x \to \infty}\dfrac{\sin x}{x}?
0
What is \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{1 - \cos x}{x²}?
\dfrac12
What is \lim_{x \to 0}\dfrac{a^x-1}{x}?
\ln a
What is the differentiation of y=x^x?
\dfrac{dy}{dx}=x^x(\ln x +1)
\lim_{x \to \infty}\dfrac{x²+5x+1}{2x²-x-5}
How would you solve this without using L’ Hospital’s rule?
Divide the numerator and denominator with the highest power of x (in this case, x²)
Separate out the terms, all lower powers of x will get cancelled (turn 0) due to infinity being in the denominator.
In this case, since the numerator and denominator both have that power of x, we get a finite limit
\lim_{x \to \infty}\dfrac{5x+1}{2x²-x-5}
How would you solve this without using L’ Hospital’s rule?
Divide the numerator and denominator with the highest power of x (in this case, x²)
Separate out the terms, all lower powers of x will get cancelled (turn 0) due to infinity being in the denominator.
In this case, since the numerator’s power is less than the denominator’s power, we get 0 as our limit
\lim_{x \to \infty}\dfrac{x³+5x+1}{2x²-x-5}
How would you solve this without using L’ Hospital’s rule?
Divide the numerator and denominator with the highest power of x (in this case, x²)
Separate out the terms, all lower powers of x will get cancelled (turn 0) due to infinity being in the denominator.
In this case, since the numerator’s power is more than the denominator’s power, we get \infty as our limit
\lim_{x \to \infty}\dfrac{\sqrt{3x²-1}-\sqrt{2x²-1}}{4x+3}
How would you solve this without using L’ Hospital’s rule?
Eliminate all the terms with lower powers of x, as they will be cancelled anyway and it makes solving easier.
Then cancel the x remaining in numerator and denominator to get a finite (but irrational) limit.
\lim_{x \to \infty}\dfrac{6(2)^x-20(5)^x}{5(2)^x+7(5)^x}
How would you solve this without using L’ Hospital’s rule?
Identify the largest base to the power (in this case 5)
Divide the numerator and denominator by 5^x.
All terms with smaller bases will cancel out.
Simplify.
What is the expansion of \Sigma n?
\dfrac{n(n+1)}{2}
What is the expansion of \Sigma n²?
\dfrac{n(n+1)(2n+1)}{6}
What is the expansion of \Sigma n³?
\Big( \dfrac{n(n+1)}{2}\Big)²
What is the sum of n odd terms?
n²
How would you simplify limits that tend to infinity, where the numerator or denominator is a series?
convert the series into like a different form, a concise form if you will
How would you solve \lim_{n \to \infty}\dfrac{\Sigma n^5}{n^6}?
convert it to \dfrac{\int n^5}{n^6} and solve the integral then cancel the constant term since it does not matter ✨
How would you solve limits which have terms under a square root?
always rationalize, even if there’s no denominator or no square root in the denominator or whatever i guess
What is the series expansion of e^x?

What is the series expanion of e^{-x}?

What is the series expansion of \ln (1+x)?
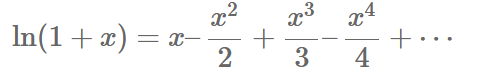
What is the series expansion of \sin x?

What is the series expansion of \cos x?
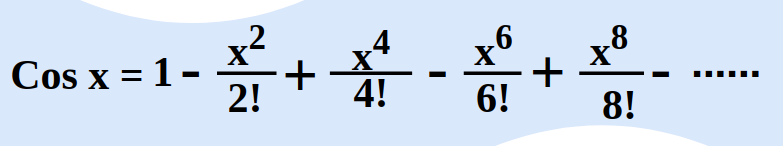
What is the series expansion of \tan x?

What is the series expansion of a^x?
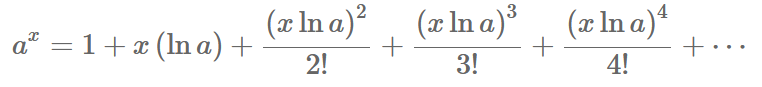
What is the series expansion of \tan^{-1}x?
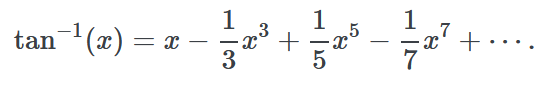
What is the series expansion of \sin^{-1}x?

What is the series expansion of \cos^{-1}x?
\dfrac{\pi}{2}-\sin^{-1}x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}-\Big( x+ \dfrac{x³}{3!}+\dfrac{9x^5}{5!}+…\Big)
What is the series expansion of (1+x)^n?
=1+nx+\dfrac{n(n-1)}{2!}x²+…\infty
What is the series expansion of (1+x)^{\frac1x}?
e\Big( 1- \dfrac{x}{2}+\dfrac{11x²}{24}-…\infty\Big)
How would you solve \lim_{x\to0}\dfrac{\sin2x}{\sin3x}?
multiply by \dfrac{2x}{2x}\times\dfrac{3x}{3x} then cancel stuff
How would you approach \lim_{x\to0}\dfrac{\tan x-\sin x}{x³}? there are 2 ways
manipulate the trigonometric ratios till you get onef the standard forms and then cancel
use series expansions
How would you use series expansoins to solve \lim_{x\to0}\dfrac{\tan x-\sin x}{x³}?
use the series expansions of both \tan x and \sin x
expand till the same power of x as in the denominator
lower powers will get canceled (take my word on this)
higher powers will become insignificant due to the limit tending towards 0
so whatever is remaining, lowkey cancel it and get your answer
\lim_{x\to1}\dfrac{x²-ax+b}{x-1}=5
You need to find a and b, how would you do this?
Well when you substitute x=1, you get \dfrac{1-a+b}{0} and since we need it to be finite and not infinite, we need to get the numerator to also be 0. Then we can apply L’Hospital because it’s of \dfrac00 form
\lim_{x\to0}\dfrac{\sin2x-2\sin x}{x^n}=P
You’re supposed to find n and P. How do you go about that?
use series expansion for the numerator.
The powers of x that are lower than x^n will get cancelled out, so all you have to do is find the first non-cancellable power of x
All higher powers of x will get cancelled because of the limit, so go ahead and vanish them
you then have n, then you substitute, cancel, and find the value of P.
Check page 135 of notes (for other people using my flashcards i’m so sorry idk how to make flashcards for this question)
issok if book is not available but yeah
If you have \lim_{x\to a}\big(f(x)\big)^{g(x)}, and f(x)\to 1 and g(x)\to\infty, then
What is the formula for solving this?
\lim_{x\to a}\big(f(x)\big)^{g(x)}=e^{\lim_{x\to a}(f(x)-1)\times(g(x))}
How do you solve limits with operators like mod, step, and brace?
You have to solve both sides separately (like you have to take the negative limit and positive limit i forgor what they’re called)
use a smol positive value called h, and yea
\lim_{x\to5^-}[6-x]
You can use a small positive value h. What do you do with it?
let x\to5-h
so then replace [6-x] with [6-(5-h)]
and replace x\to5^- with h\to0
and then solve normally
What is the value of \lim_{h\to0}[-kh]?
-1
What is the value of \lim_{h\to0}[kh]?
0