Prokaryotic Cell Structures and Microbiology Foundations
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is the significance of Pasteur's fermentation experiment?
It demonstrated that bacteria and yeast cells are responsible for fermentation and led to the development of pasteurization to prevent spoilage.
Who proposed the idea of spontaneous generation and what does it entail?
Aristotle proposed spontaneous generation (abiogenesis), the idea that living things arise from non-living matter.
What were the findings of John T. Needham regarding spontaneous generation?
Needham suggested that spontaneous generation was possible after observing microbial growth in boiled beef gravy.
How did Spallanzani's experiments challenge Needham's findings?
Spallanzani boiled beef gravy and found no microbial growth, contradicting Needham's results and suggesting that Needham's experiments were flawed.
What experiment did Louis Pasteur conduct to disprove spontaneous generation?
Pasteur used a swan-necked flask to show that microbes in the liquid originated from dust particles in the air, not spontaneous generation.
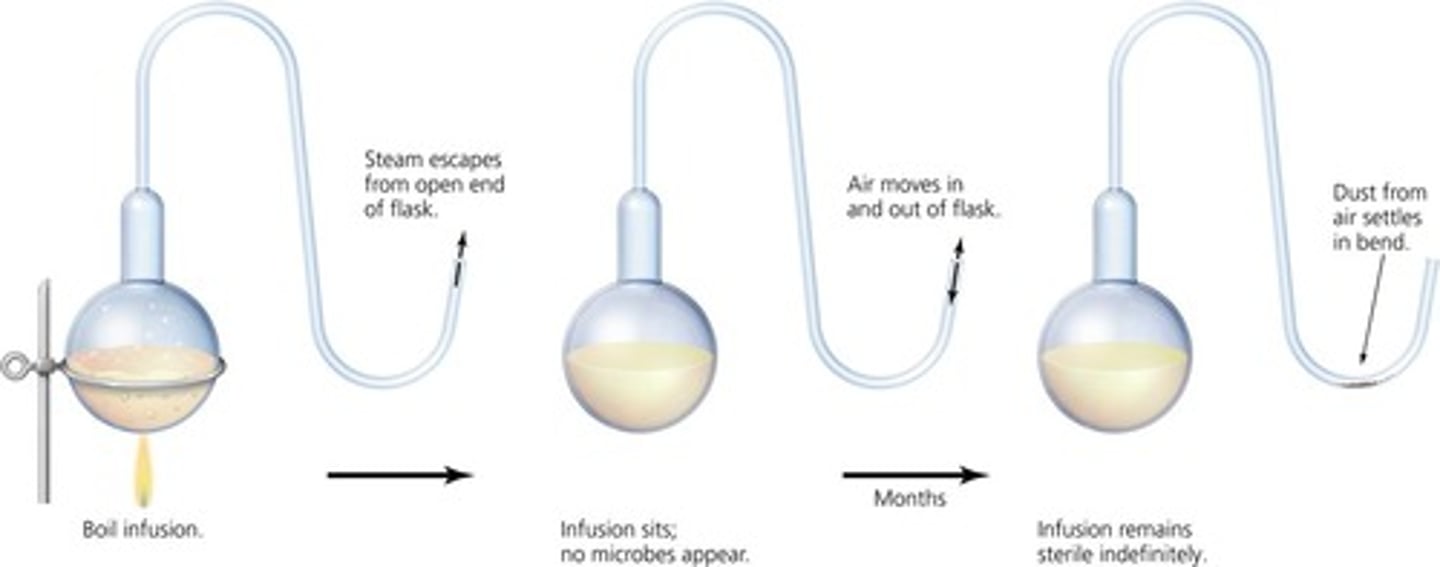
What is pasteurization and why is it important?
Pasteurization is the process of heating liquids to kill most contaminating bacteria without altering the liquid's basic qualities, crucial for eliminating pathogens in food and beverages.
What did Pasteur discover about anaerobic bacteria and fermentation?
He discovered that anaerobic bacteria fermented sugars into acids, leading to the understanding of fermentation processes.
What was Fracastoro's contribution to the understanding of disease?
Fracastoro proposed the idea of 'germs of contagion' causing disease, a significant advancement over the belief in evil spirits and foul vapors.
How did Pasteur's work influence the germ theory of disease?
Pasteur's discovery that microorganisms spoil wine supported the idea that microorganisms are responsible for diseases.
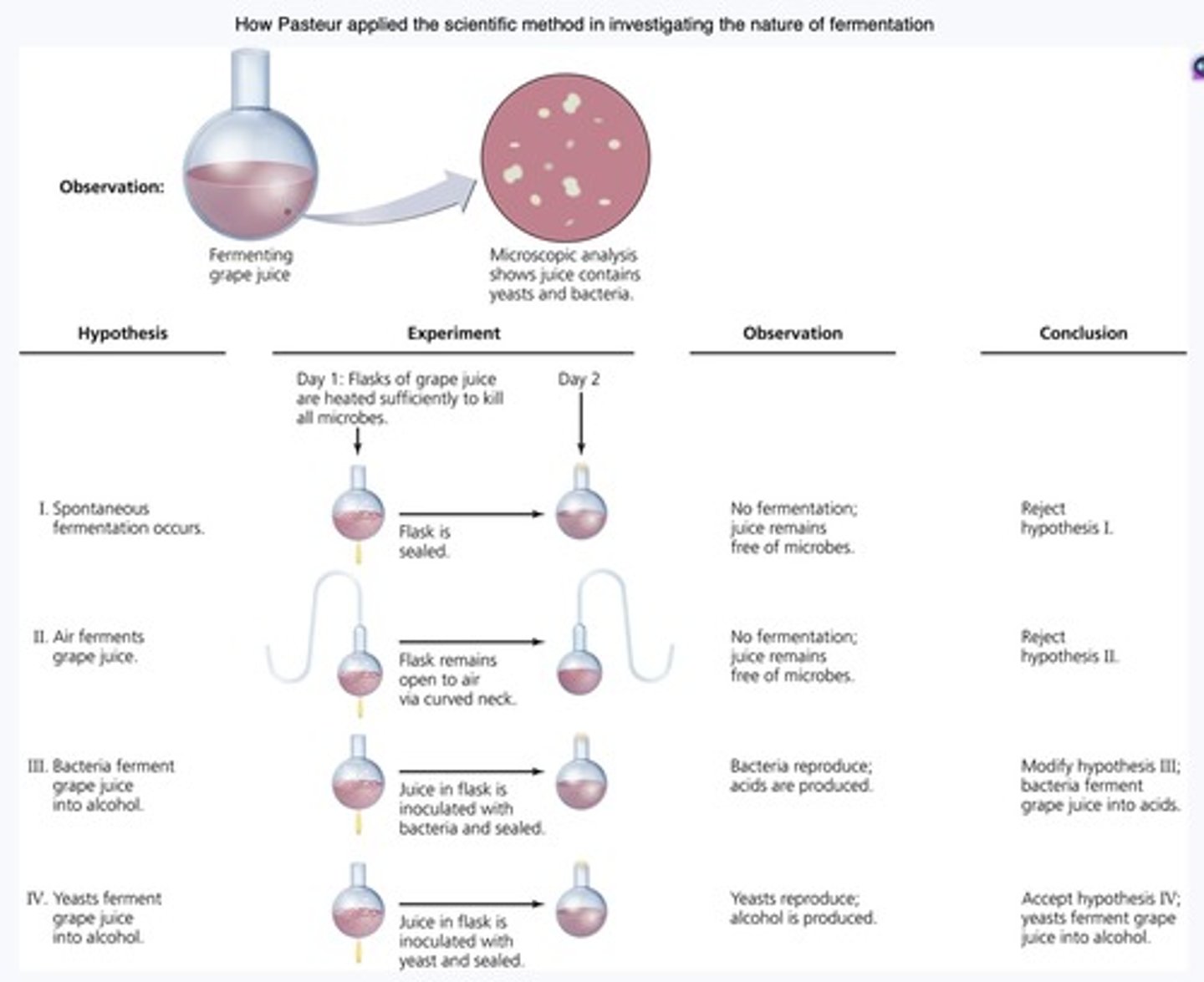
What was Robert Koch's major contribution to microbiology?
Koch discovered that rod-shaped bacteria with endospores caused anthrax, proving for the first time that a specific bacterium can cause a specific disease.
What key questions drove research during the Golden Age of Microbiology?
1. Is spontaneous generation of microbial life possible? 2. What causes fermentation? 3. What causes disease?
What impact did the Golden Age of Microbiology have on scientific research?
It sparked intense competition among scientists and led to major discoveries that shaped the field of microbiology.
What are the distinguishing characteristics of prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are unicellular organisms without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, characterized by their simple structure.
What are common cell morphologies of prokaryotic cells?
Common morphologies include cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), and spirilla (spiral-shaped) cells.
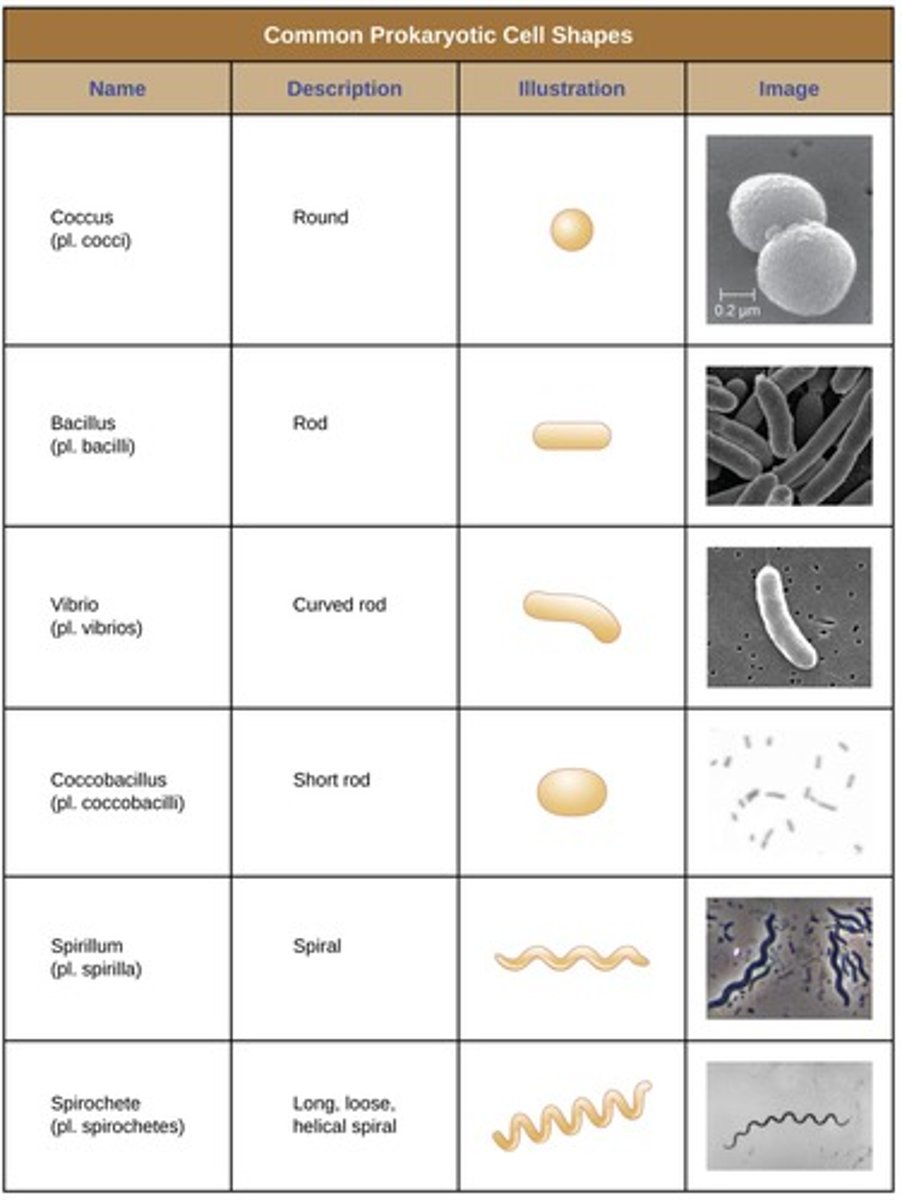
How do prokaryotic cells maintain their morphology?
Prokaryotic cells maintain their morphology through their rigid cell wall structure and cytoskeletal elements.
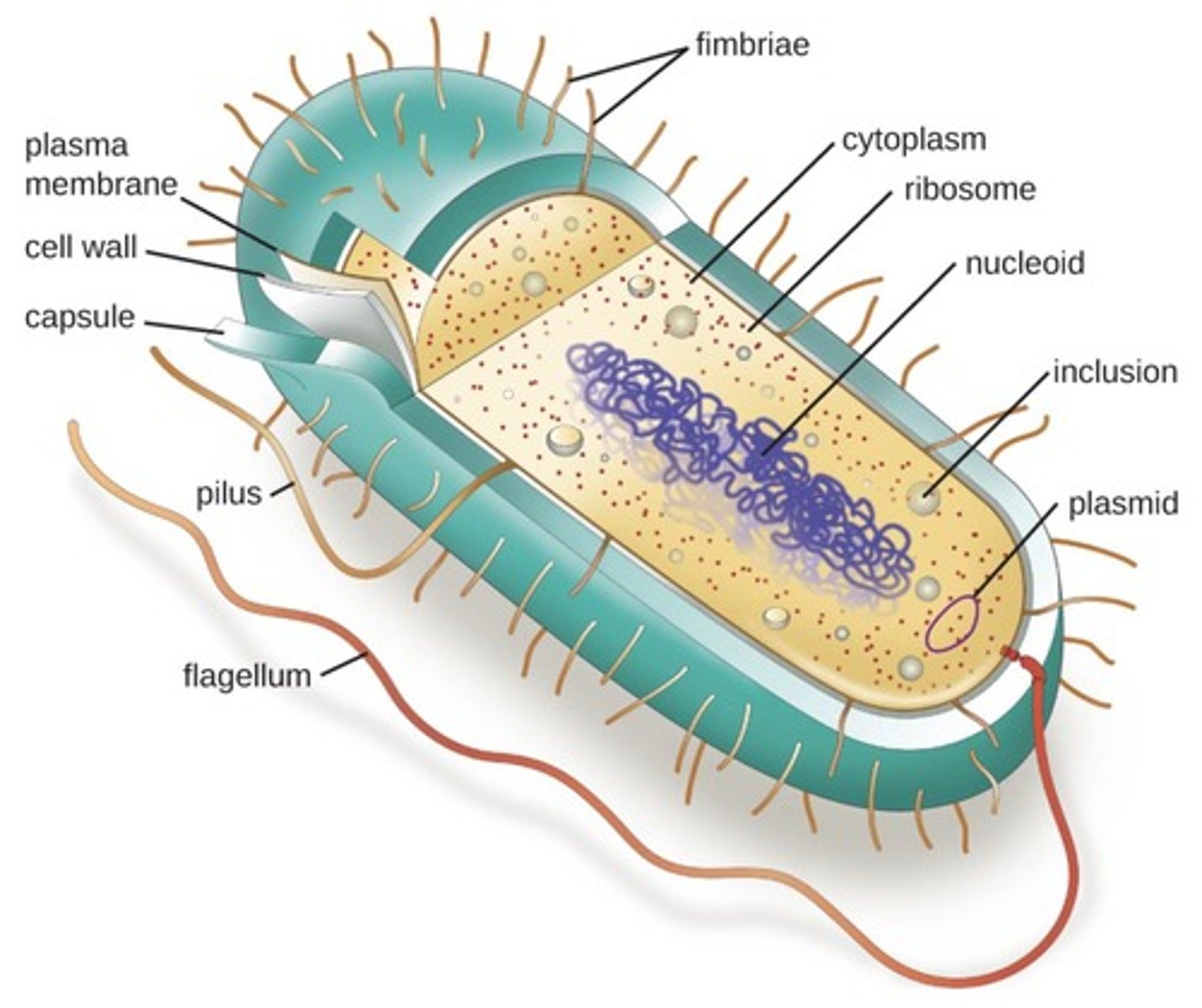
What are the internal structures of prokaryotic cells?
Internal structures include the nucleoid (containing DNA), ribosomes (for protein synthesis), and various inclusions for storage.
What are the external structures of prokaryotic cells?
External structures include the cell wall, plasma membrane, pili, and flagella, each serving specific functions.
What role did competition between Pasteur and Koch play in microbiology?
The competition drove both scientists to make significant discoveries regarding the causes of fermentation and disease.
What is the historical context of the Golden Age of Microbiology?
The Golden Age of Microbiology spanned from 1857 to 1914, marked by significant discoveries and advancements in understanding microorganisms.
How did the understanding of disease evolve from ancient beliefs to the germ theory?
Initially attributed to evil spirits and foul vapors, the understanding of disease evolved to recognize microorganisms as causative agents through the work of scientists like Pasteur and Koch.
What is the importance of Koch's postulates?
Koch's postulates provide a framework for linking specific microorganisms to specific diseases, establishing a foundation for microbiological research.
What problem did Fanny Hesse solve in microbiology?
She worked with agar, a gel derived from red algae, to grow bacteria instead of using potatoes.
What is the significance of Koch's postulates in microbiology?
They outline the criteria for establishing a causative relationship between a microbe and a disease.
What are the four main postulates proposed by Koch?
1. The suspected causative agent must be found in every case of the disease and absent in healthy hosts. 2. The agent must be isolated and grown outside the host. 3. When introduced to a healthy host, the agent should cause the disease. 4. The same agent must be found in the diseased experimental host.
What did Koch discover about Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
He identified it as the causative agent of tuberculosis, which earned him the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1905.
What are the key characteristics shared by all living cells?
Cytoplasm, plasma membrane, one or more chromosomes, and ribosomes.
What is a key characteristic of prokaryotic cells?
They lack a nucleus; their nucleic acid is condensed in a nucleoid but not enclosed by a membrane.
What is the cell envelope in prokaryotes?
It includes the plasma membrane and all its external surroundings, such as the cell wall, capsule, and slime layer.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
It allows selective permeability to acquire nutrients and remove waste, and it interacts with the external environment.
What is the structure of the plasma membrane?
It is a phospholipid bilayer known as a 'fluid mosaic' that is 7-8 nm thick.
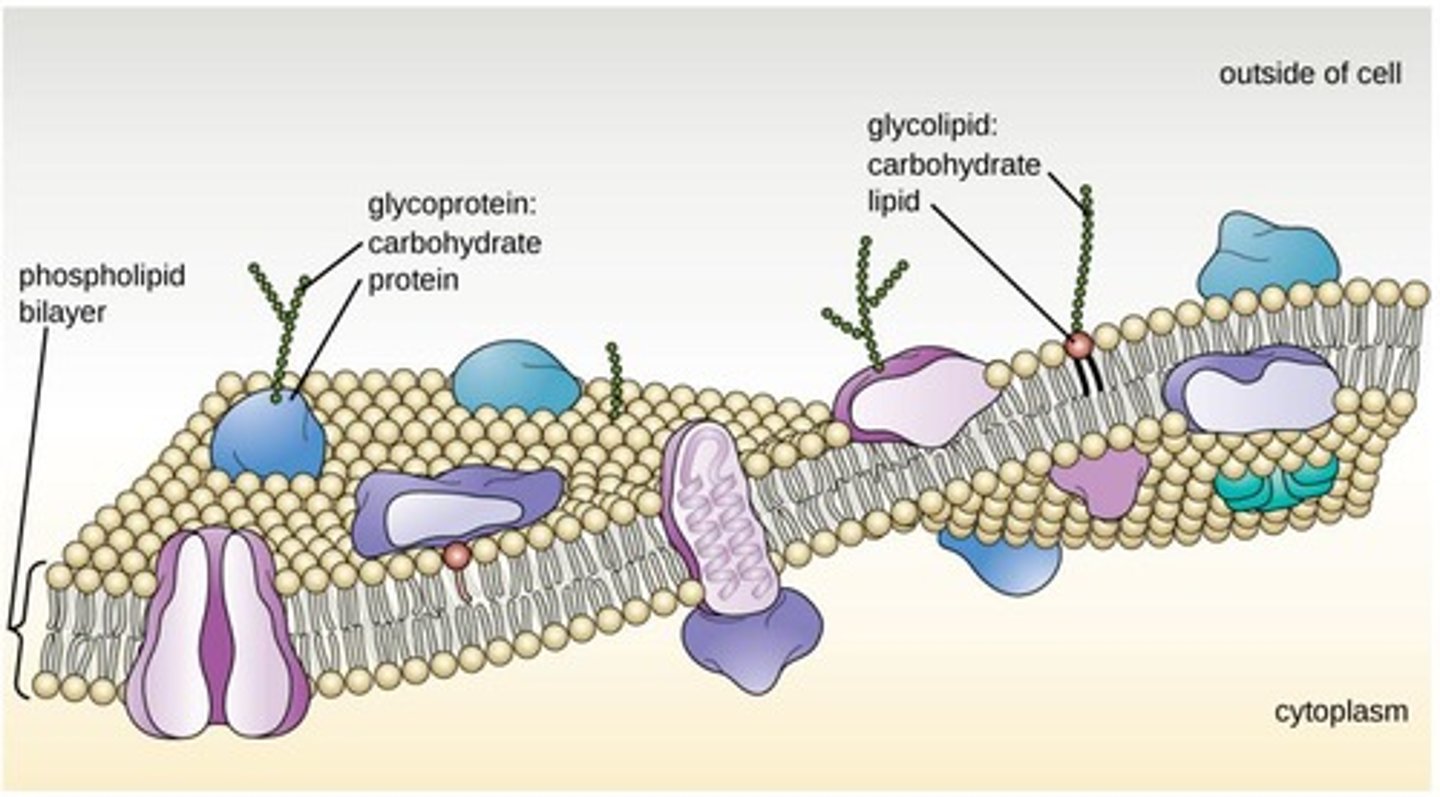
What are the two types of transport mechanisms across the plasma membrane?
Passive transport (simple diffusion) for small molecules and active transport for ions or large molecules.
What is passive transport in the context of membrane transport?
It is the movement of small molecules following a concentration gradient without the use of energy.
What is active transport in membrane transport?
It requires energy (ATP) to move ions, sugars, or amino acids against their concentration gradient using transporter proteins.
What is the function of the bacterial cell wall?
It maintains the shape of the bacterium, protects from osmotic pressure and toxic materials, and may contribute to pathogenicity.
What is peptidoglycan?
A rigid structure lying outside the plasma membrane that is a key component of the bacterial cell wall.
What is the significance of colony size and morphology in bacteria?
Each colony is the progeny of a single cell, which helps in identifying bacterial species.
What techniques did Koch develop for studying bacteria?
Simple staining techniques, the first photomicrograph of bacteria, and methods for estimating bacterial numbers based on colony formation.
What role did steam play in Koch's laboratory techniques?
He used steam to sterilize growth media.
What is the role of ribosomes in prokaryotic cells?
They are responsible for protein production.
How do bacterial shapes vary?
Bacterial shapes can differ widely, affecting their classification and identification.
What is the function of glycocalyces in bacteria?
They provide protection and help in adherence to surfaces.
What is the significance of inoculating colonies into animals?
It helps determine which bacterial species cause disease.
What are the two groups of bacteria based on cell wall characteristics?
Gram positive and Gram negative.
What is the primary component of bacterial cell walls?
Peptidoglycan.
What are the two main components of peptidoglycan?
N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM).
What is the role of amino acids attached to NAM in peptidoglycan?
They are cross-linked to provide additional strength and stability.
What distinguishes Gram positive bacteria from Gram negative bacteria in terms of peptidoglycan layers?
Gram positive bacteria have many layers of peptidoglycan (30-100nm), while Gram negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan.
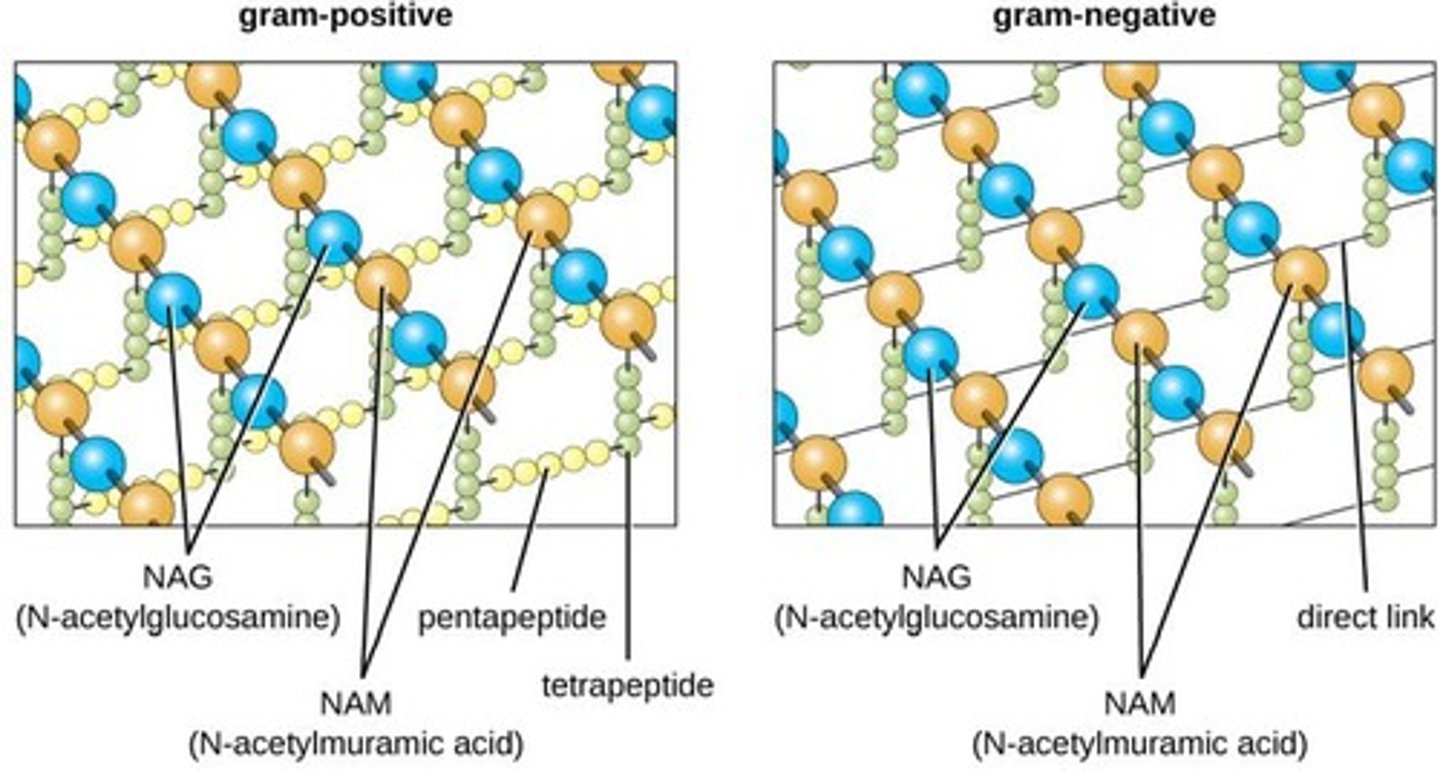
What is teichoic acid and its role in Gram positive bacteria?
Teichoic acid provides rigidity and may help maintain the cell envelope and protect from environmental substances.
What is the structure of the Gram negative cell wall?
It consists of a thin layer of peptidoglycan sandwiched between an inner and outer membrane, with a large periplasmic space.
What is lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and its significance in Gram negative bacteria?
LPS is an endotoxin that contributes to pathogenicity in infections.
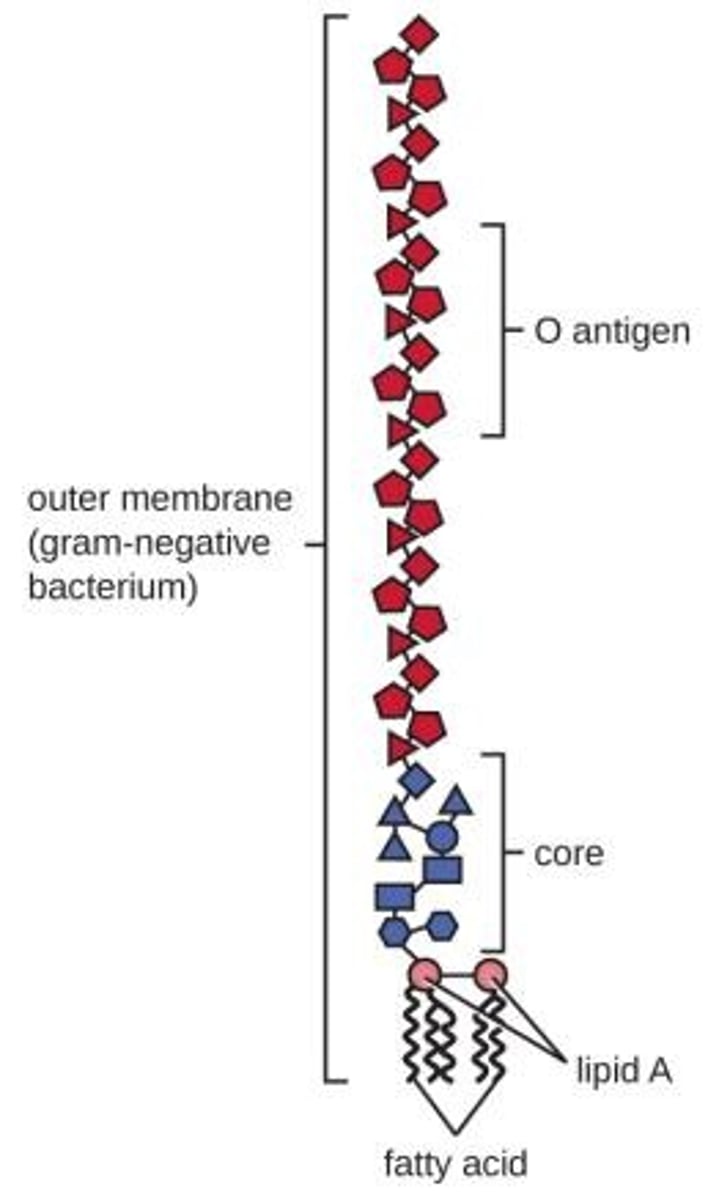
What are glycocalyces and their components?
Glycocalyces are external to the cell wall and made of polysaccharides and/or proteins, including capsules and slime layers.
What is the difference between a capsule and a slime layer in glycocalyces?
A capsule is a tightly organized layer firmly attached to the cell wall, while a slime layer is less organized and loosely attached.
What are filamentous appendages in bacteria?
Structures like flagella, fimbriae, and pili that are important for DNA transfer, movement, and surface attachment.
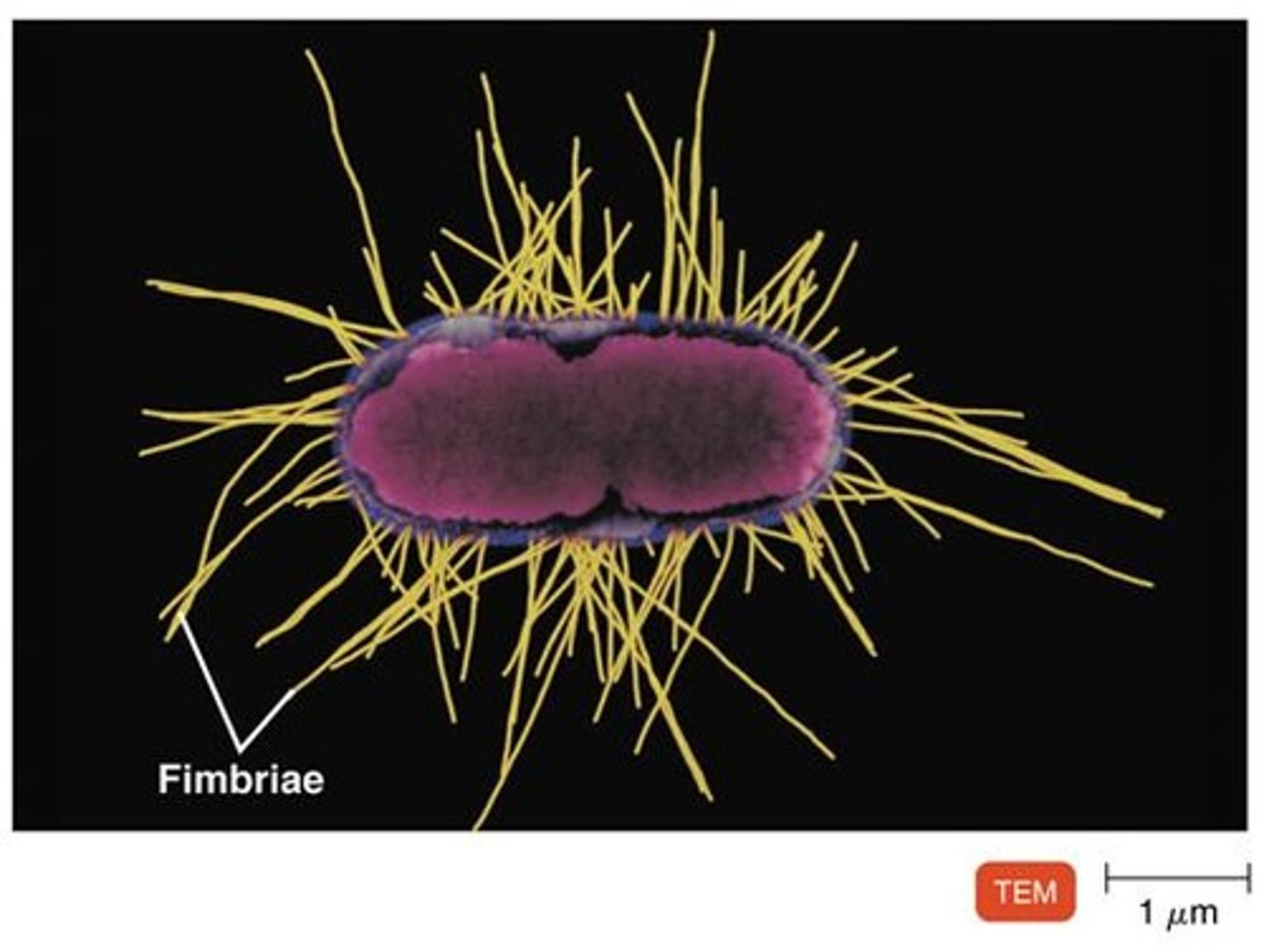
What is the function of fimbriae in bacteria?
Fimbriae are short hair-like structures important for adhesion, especially in pathogens.
What is the role of pili in bacteria?
Pili are longer than fimbriae, important for motility and DNA transfer (F pilus or sex pilus).
What is the function of flagella in bacteria?
Flagella are structures used by bacteria to move in liquid media.
What factors dictate the movement of flagella?
External factors such as light (phototaxis), magnetic fields (magnetotaxis), and chemical gradients (chemotaxis).
What is the structure of the prokaryotic chromosome?
It is circular, haploid, and not surrounded by a membrane.
What are plasmids and their significance in bacteria?
Plasmids are small, circular, extrachromosomal DNA that can contain genes important for bacterial survival, such as antibiotic resistance.
What are ribosomes and their composition in bacteria?
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, composed of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and consist of two subunits (30S and 50S), known as 70S ribosomes.
What is the function of inclusions in bacteria?
Inclusions are used for storage of excess nutrients and help avoid osmotic pressure.
What are endospores and their purpose?
Endospores protect the genome under harsh environmental conditions such as lack of nutrients, extreme temperatures, radiation, and chemical damage.
What is the process of forming endospores called?
Sporulation.
What happens to endospores when conditions become favorable?
They undergo a germination process.