Polygenic traits, heritability
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
continuous phenotypic variation vs categorical medelian variation
categorical: white or red populations
continuous: number, quantitative, describes populations, follows bell cuve
degree of pigmentiation in skin, mating calls, diseases
polygentic trait
multiple genes that contribute to single quantitative trait
can mendelian inheritance produce a continuous phenotype
yes, with two or more gene
what smooths out the curve
effects of environmental variation
when can u infer polygenic inheritance
when a trait exhibits continuous variation and its distribution in a population forms a bell-shaped curve
variance
phenotype variance in population
additive allelic inheritance
the more domiance (AABb), the more gene dosage, get a range of values (skin color, hair color)
incomplete dominance is a case of ___ where only _ gene locus is invovled
additive inheritance, one RR (red) + rr (white) → Rr (pink)
Vx= Vg+ Ve describe
vx= phenotype variance
vg= genes (0 if inbred)
ve= environment (0 if controlling temp, diet)
what is the equation for heritability, describe relationship between Vg and Ve
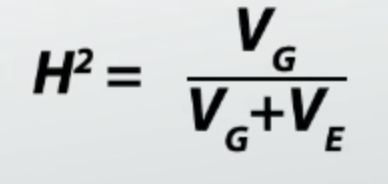
if high Ve= low heritability
concordance- mono and dizygotic
what extent do siblings share particular phenotype?
mono: 100, share, dizygotic: 50
heritability
proportion of population variation that is due to genetics
why are twins useeful in studying heritability
monozygontic (identical twins) share 100% of genes + same environment
dizygotic (fraternal) share 50% of genes, share same environment
If MZ twins are more similar than DZ twins, this suggests that genes play a strong role.
If MZ and DZ twins are equally similar, this suggests that environmental factors are more important.
if heritability = 1 (all variations due to genetics) then monozygotic is
if heritability = 0 then mono and dizygotic
100% concordance
low concordance
make argument for a trait with low heritability, “genes don’t matter” for that trait or that “the phenotype is determined by the environment”. having fingers
Having fingers is entirely determined by genes, but because nearly everyone has 10 fingers, there’s almost no variation in that trait — so heritability is low, even though genes clearly matter.
high concordance _ high heritability
DOES NOT EQUAL
but concordance + shared and unshared environment = heritability
how often two individuals, typically a pair of twins or relatives, will share a particular trait or condition
limitations to heritability estimates, common ways they are misinterpreted
.88 means 88% of phenotypic variation is caused by genetic variation
“If H² low, genes aren’t important” heritability DOES NOT EQUAL inheritance because H^2 refers to POPULATION
environmental variance is high (milk development in cows, genes play role in milk development, but also very dependent on environment)
family studies over-estimate heritability because environment similar
low heritability
few alleles in population
low proportion of phenotypic variance is due to genetics
largely due to environment
high heritability
many alleles in population, minimal environmental effect
heritability does NOT
\equal fate
stays same if environmental changes
mean that group differences are genetic
heritability determines if
determine whether nature/ nurture is more important
inform doctors how much family history will predict patient outcome
determine whether drug treatment/ behavior modification are more successful in treating disease
haplotype
specific combination of SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphism) across loci (specific gene location) on same chromosome
haplotype block
group fo SNPs that are inherited tgt- if on same block linkage disequilibrium,
will find together more,
no recombination- preserved and frequently inherited
a non-random association of alleles at different loci on a chromosome,
Pa= 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5
Pab 0.5, 0, 0, 0.5
if on different block- linkage equilibrium (inheritance of one gene does not influence the inheritance of another)
Pa= 0.5, 0.5
Pab= 0.25, 0.25
evolutionary creation of set of haplocytes
Mutations: Novel haplotypes often originate from polymorphism mutations.
Recombination: during meiosis breaks down ancestral haplotypes and shuffles genetic material, leading to new combinations of alleles.
Gene Flow: The movement of genes between populations through migration and interbreeding can introduce new haplotypes and alter existing haplotype frequencies.
Natural Selection: A haplotype with a genetic advantage that increases an organism's survival and reproduction (fitness) will become more common in the population.
what are the main uses for haplotype blocks
make scanning genome easier
different SNPs in those affected, helps pinpoint disease causing mutations
certain SNPs are associated with population
what does mahattan plot tell
The higher the dot on the plot, the stronger the association of that genetic variant with the trait or disease.
how to show that gene identified in GWAS study is gene causing disease, becase it only tells coorelation
sequence gene w unaffected vs affected individuals can narrow down mutation
determine gene is expressed in unaffected and affected using rna gel
determine function of gene thru LOF knock out
limitations of GWAS
small sample size, small population stratification, shared evironmental factors (socioeconomic), rare variants go undetected