BIology IGCSE Edexcel Specification in questions (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/359
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Triple and Double specifications are specified. When triple it says TRIPLE before it. Please make a copy
Last updated 3:11 PM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
360 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
3
New cards
The nature and variety of living organisms
a. Characteristics of living organisms
b. Variety of living organisms
b. Variety of living organisms
4
New cards
what characteristics do all living organisms share
MRSCGREN
Movement
Respiration
sensitivity
control their internal conditions
grow and develop
Reproduction
Excrete waste
require nutrition
\
Movement
Respiration
sensitivity
control their internal conditions
grow and develop
Reproduction
Excrete waste
require nutrition
\
5
New cards
Common features shown by plants
Eukaryotic Organisms
multicellular organism
cells contain chloroplasts so can photosynthesis
cellulose cell walls
store carbohydrates as starch/sucrose
examples: Maize, peas
multicellular organism
cells contain chloroplasts so can photosynthesis
cellulose cell walls
store carbohydrates as starch/sucrose
examples: Maize, peas
6
New cards
Common features shown by animals
Eukaryotic Organisms
Multicellular organism
have nervous co-ordination
can move from one place to another
**carbohydrates are stored as glycogen**
Examples: humans, housefly
Multicellular organism
have nervous co-ordination
can move from one place to another
**carbohydrates are stored as glycogen**
Examples: humans, housefly
7
New cards
Common features shown by fungi
Eukaryotic Organisms
most are multicellular Some are Single-celled Organism
and some have their body organised into a mycelium made from thread-like structures called hyphae (which contain many nuclei)
cell walls are made from chitin
**feed by extracellular secretion of digestive enzymes (saprotrophic nutrition)**
store carbohydrates as glycogen
examples: Mucor (hyphal structure), yeast (single celled)
most are multicellular Some are Single-celled Organism
and some have their body organised into a mycelium made from thread-like structures called hyphae (which contain many nuclei)
cell walls are made from chitin
**feed by extracellular secretion of digestive enzymes (saprotrophic nutrition)**
store carbohydrates as glycogen
examples: Mucor (hyphal structure), yeast (single celled)
8
New cards
Common features of a Protoctists
* Eukaryotic Organism
* Microscopic single-celled organisms
* **some aggregate** (group together) into **larger forms**, such as colonies or chains of cells that form filaments
* Their cells contain a **nucleus** with a **distinct membrane**
* some have an animal-like structure whereas
* some have chloroplasts + a cell wall and is much more like a plant cell
* plant eg. chlorella
* animal eg plasmodium
* Microscopic single-celled organisms
* **some aggregate** (group together) into **larger forms**, such as colonies or chains of cells that form filaments
* Their cells contain a **nucleus** with a **distinct membrane**
* some have an animal-like structure whereas
* some have chloroplasts + a cell wall and is much more like a plant cell
* plant eg. chlorella
* animal eg plasmodium
9
New cards
Common features shown by bacteria
Prokaryotic Organisms
microscopic single-celled organisms
they have a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, circular chromosome of dna
don’t have a nucleus
Examples: Lactobacillus bulgaricus , Pneumococcus
microscopic single-celled organisms
they have a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, circular chromosome of dna
don’t have a nucleus
Examples: Lactobacillus bulgaricus , Pneumococcus
10
New cards
what is a pathogen
an organism causing disease to its host
11
New cards
What do pathogens include
fungi, bacteria, protoctists, viruses
12
New cards
what is a Virus
not living organisms
small particles, smaller than bacteria
parasitic can reproduce inside living cells, can infect every type of living organism.
Variety of shapes and sizes
no cellular structure
Examples: Tobacco mosaic virus , HIV
small particles, smaller than bacteria
parasitic can reproduce inside living cells, can infect every type of living organism.
Variety of shapes and sizes
no cellular structure
Examples: Tobacco mosaic virus , HIV
13
New cards
Structure and Function in living organisms
a. Level of organisation
b.Cell structure
c.Biological molecules
d.Movement of substance into and out of cells
e.Nutrition
f.Respiration
g.Gas exchange
h.Transport
I.Excretion
j.Co-ordination and response
b.Cell structure
c.Biological molecules
d.Movement of substance into and out of cells
e.Nutrition
f.Respiration
g.Gas exchange
h.Transport
I.Excretion
j.Co-ordination and response
14
New cards
Levels of Organisation in organisms
Organelles
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ Systems
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ Systems
15
New cards
What is an organelle
A small structure in a cell that is surrounded by a membrane and has a specific function
\
\
16
New cards
What is a cell
Basic functional and structural units in a living organism
17
New cards
What is a tissue
Groups of cells of similar structures working together to perform the same function
18
New cards
What is an organ
Made from different tissues working together to perform specific function
19
New cards
What is an organ system
Groups of organs with related functions, working together to perform body functions
20
New cards
Describe cell structures including the ; nucleus
a large organelle surrounded by a nuclear envelope (double membrane) which contains many pores. The nucleus contains chromosomes (which are made from protein-bound linear DNA.
the nucleolus is in the nucleus
the nucleolus is in the nucleus
21
New cards
Describe cell structures including the ; Cytoplasm
gel-like structure containing all the cell organisms
22
New cards
Describe cell structures including the ; Cell membrane
the membrane found on the surface of animal cells and just inside the cell wall of other cells. It is mainly made of lipids and protein.
23
New cards
Describe cell structures including the ; Cell wall
A rigid structure that surrounds cells in plants, algae and fungi. Plants and algae, its made mainly of the carbohydrate cellulose. In fungi, it’s made of chitin.
24
New cards
Describe cell structures including the ; Mitochondria
They are usually oval-shaped. They have a double membrane - the inner one is folded to form structures calls cristae. Inside is the matrix, which contains enzymes involved in respiration.
25
New cards
Describe cell structures including the ; Chloroplasts
A small, flattened structure found in plant and algal cells. It is surrounded by a double membrane, and also has membranes inside called thylakoid membranes.
These membranes are stacked up in some parts of the Chloroplasts to form grana.
Grana are linked together by lamellae - thin, flat pieces of the thylakoid membrane.
These membranes are stacked up in some parts of the Chloroplasts to form grana.
Grana are linked together by lamellae - thin, flat pieces of the thylakoid membrane.
26
New cards
Describe cell structures including the ; Ribosomes
A very small organelle that either floats free in the cytoplasm or is attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. It’s made up of proteins and RNA. Its not surrounded by a membrane
27
New cards
Describe cell structures including the ; Vacuole
**A membrane-bound organell**e found in the cytoplasm or plant cells.
It contains **cell sap.**
The surrounding membrane is called the tonoplast.
It contains **cell sap.**
The surrounding membrane is called the tonoplast.
28
New cards
Describe the functions of the ; Nucleus
The nucleus controls the cell's activities (by controlling the transcription of DNA). DNA contains instructions to make proteins. The pores allow substances (e.g. RNA) to move between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleolus makes ribosomes.
29
New cards
Describe the functions of the ; Cytoplasm
medium for chemical reaction
30
New cards
Describe the functions of the ; Cell Membrane
Regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
31
New cards
Describe the functions of the ; cell wall
Supports cells and prevents them from changing shape
32
New cards
Describe the functions of the ; mitochondria
The site of aerobic respiration where ATP is produced.
33
New cards
Describe the functions of the ; chloroplasts
The site where photosynthesis takes place. Some parts of photosynthesis happen in the grana, and other parts happen in the stroma. ( a thick fluid found in chloroplasts)
34
New cards
Describe the functions of the ; Ribosomes
The site where proteins are made
35
New cards
Describe the functions of the ; vacuole
Helps maintain pressure inside the cell and keep the cell rigid. This stops plants from wilting.
Also involved in the isolation of unwanted chemicals inside the cell.
Also involved in the isolation of unwanted chemicals inside the cell.
36
New cards
Similarities and differences in the structure of plant and animals cells
Similarities (found in both):
cell membrane
nucleus
cytoplasm
ribosomes
mitochondria
\
Differences (found in only plant cells):
Cell wall
permanent vacuole
chloroplasts
cell membrane
nucleus
cytoplasm
ribosomes
mitochondria
\
Differences (found in only plant cells):
Cell wall
permanent vacuole
chloroplasts
37
New cards
TRIPLE ONLY: Explain the importance of cell differentiation in the development of specialised cells
cell differentiation is the process by which cell changes to become specialised for its job. So it can turn into any cells.
38
New cards
TRIPLE ONLY : Advantages of using stem cells in medicine
Great potential to treat a wide - variety of diseases from diabetes and paralysis
\
Organs developed from a patients own stem cells reduces the risk of organ rejection and the need to wait for an organ donation
\
Adult stem cells are already used successfully in a variety pf treatments acting as proof of benefits
\
Organs developed from a patients own stem cells reduces the risk of organ rejection and the need to wait for an organ donation
\
Adult stem cells are already used successfully in a variety pf treatments acting as proof of benefits
39
New cards
TRIPLE ONLY : Disadvantages of using stem cells in medicine
Risks/issues
Stem cells cultured in the lab could become infected with a virus which could be transmitted to the patient
There is a risk of cultured stem cells accumulating mutations that can lead to them developing into cancer cells
Low numbers of stem cell donors
\
Social issues
It is possible for embryonic stem cells to be collected before birth (from amniotic fluid) or after birth (umbilical cord blood) and stored by a clinic - but this can be expensive and isn’t an option for everyone
A lack of peer - reviewed clinical evidence of the success of stem cell treatments
Educating the public sufficiently about what stem cells can and cannot be used for
\
Ethical issues
Stem cells may be sourced from unused embryos produced in IVF treatment
It is unethical to create embryos through therapeutic cloning and then destroy them
\
Stem cells cultured in the lab could become infected with a virus which could be transmitted to the patient
There is a risk of cultured stem cells accumulating mutations that can lead to them developing into cancer cells
Low numbers of stem cell donors
\
Social issues
It is possible for embryonic stem cells to be collected before birth (from amniotic fluid) or after birth (umbilical cord blood) and stored by a clinic - but this can be expensive and isn’t an option for everyone
A lack of peer - reviewed clinical evidence of the success of stem cell treatments
Educating the public sufficiently about what stem cells can and cannot be used for
\
Ethical issues
Stem cells may be sourced from unused embryos produced in IVF treatment
It is unethical to create embryos through therapeutic cloning and then destroy them
\
40
New cards
identify the chemical elements present in : carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are made up of **simple sugars**
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
41
New cards
identify the chemical elements present in : Proteins
They all contain Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Oxygen
42
New cards
identify the chemical elements present in : Lipids
Lipids contain Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen atoms
43
New cards
Describe the structure of : Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are made up of Starch and Glycogen
Starch and Glycogen are made up of Simple sugars
\
Starch and Glycogen are made up of Simple sugars
\
44
New cards
Describe the structure of : Proteins
Amino acid chains
45
New cards
Describe the structure of : Lipids
made up of glycerol and fatty acids
46
New cards
PRACTICAL: How to test for glucose
Preparing a food sample
* Break up the food using a pestle and mortar
* Transfer to a test tube and add distilled water
* Mix the food with the water by stirring with a glass rod
* Filter the mixture using a funnel and filter paper, collecting the solution
* Proceed with the food tests
* Add **Benedict's solution** to the sample solution in a test tube
* **Heat** in a boiling water bath for **5 minutes**
* Take the test tube out of the water bath and observe the colour
* A positive test will show a colour change from **blue to orange / brick red**
* Break up the food using a pestle and mortar
* Transfer to a test tube and add distilled water
* Mix the food with the water by stirring with a glass rod
* Filter the mixture using a funnel and filter paper, collecting the solution
* Proceed with the food tests
* Add **Benedict's solution** to the sample solution in a test tube
* **Heat** in a boiling water bath for **5 minutes**
* Take the test tube out of the water bath and observe the colour
* A positive test will show a colour change from **blue to orange / brick red**
47
New cards
PRACTICAL:How to test for starch
* Break up the food using a pestle and mortar
* Transfer to a test tube and add distilled water
* Mix the food with the water by stirring with a glass rod
* Filter the mixture using a funnel and filter paper, collecting the solution
* Proceed with the food tests
* We can use iodine to test for the presence or absence of starch in a food sample
* Add drops of **iodine solution** to the food sample
* A positive test will show a colour change from **orange-brown to blue-black**
* Transfer to a test tube and add distilled water
* Mix the food with the water by stirring with a glass rod
* Filter the mixture using a funnel and filter paper, collecting the solution
* Proceed with the food tests
* We can use iodine to test for the presence or absence of starch in a food sample
* Add drops of **iodine solution** to the food sample
* A positive test will show a colour change from **orange-brown to blue-black**
48
New cards
PRACTICAL:How to test for Protein
* Break up the food using a pestle and mortar
* Transfer to a test tube and add distilled water
* Mix the food with the water by stirring with a glass rod
* Filter the mixture using a funnel and filter paper, collecting the solution
* Proceed with the food tests
* Add drops of **Biuret solution** to the food sample
* A positive test will show a colour change from **blue to violet/purple**
* Transfer to a test tube and add distilled water
* Mix the food with the water by stirring with a glass rod
* Filter the mixture using a funnel and filter paper, collecting the solution
* Proceed with the food tests
* Add drops of **Biuret solution** to the food sample
* A positive test will show a colour change from **blue to violet/purple**
49
New cards
PRACTICAL:How to test for Lipids
* Break up the food using a pestle and mortar
* Transfer to a test tube and add distilled water
* Mix the food with the water by stirring with a glass rod
* Filter the mixture using a funnel and filter paper, collecting the solution
* Proceed with the food tests
* Mix the food sample with **4cm3 of ethanol** and shake
* Allow time for the sample to dissolve in the ethanol
* Strain the ethanol solution into another test tube
* Add the ethanol solution to an equal volume of **cold distilled water (4cm3)**
\
* A positive test will show a **cloudy emulsion** forming
* Transfer to a test tube and add distilled water
* Mix the food with the water by stirring with a glass rod
* Filter the mixture using a funnel and filter paper, collecting the solution
* Proceed with the food tests
* Mix the food sample with **4cm3 of ethanol** and shake
* Allow time for the sample to dissolve in the ethanol
* Strain the ethanol solution into another test tube
* Add the ethanol solution to an equal volume of **cold distilled water (4cm3)**
\
* A positive test will show a **cloudy emulsion** forming
50
New cards
What are Enzymes
* Enzymes are proteins that act as **biological catalysts** to **speed up** the rate of a chemical reaction **without being changed** or used up in the reaction
51
New cards
What are enzymes reactions in a metabolic reaction
* **Step One:** Enzymes and substrates randomly move about in solution
* **Step Two:** When an enzyme and its complementary substrate randomly collide an enzyme-substrate complex forms, and the reaction occurs
* **Step Three:** A product (or products) forms from the substrate(s) which are then released from the active site. The enzyme is unchanged and will go on to catalyse further reactions
\
* **Step Two:** When an enzyme and its complementary substrate randomly collide an enzyme-substrate complex forms, and the reaction occurs
* **Step Three:** A product (or products) forms from the substrate(s) which are then released from the active site. The enzyme is unchanged and will go on to catalyse further reactions
\
52
New cards
What is a metabolic Reaction ?
metabolic reactions are the biochemical reactions that transform food into energy in our body and its cells
53
New cards
How can temperature affect enzyme functions
* Enzymes work fastest at their ‘**optimum temperature**’
* In the human body, the optimum temperature is 37⁰C
\
* Heating to high temperatures (beyond the optimum) will **break the bonds** that hold the enzyme together and it will lose its shape
* This is known as **denaturation**
* Denaturation is **irreversible** - once enzymes are denatured they cannot regain their proper shape and activity will stop
* In the human body, the optimum temperature is 37⁰C
\
* Heating to high temperatures (beyond the optimum) will **break the bonds** that hold the enzyme together and it will lose its shape
* This is known as **denaturation**
* Denaturation is **irreversible** - once enzymes are denatured they cannot regain their proper shape and activity will stop
54
New cards
PRACTICAL:Investigate how enzyme activity can be affected by changes in temperature
* Add 5cm3 starch solution to a test tube and heat to a set temperature using beaker of water with a Bunsen burner
* Add a drop of **Iodine** to each of the wells of a spotting tile
* Use a syringe to add 2cm3 **amylase** to the starch solution and mix well
* Every minute, transfer a droplet of solution to a new well of iodine solution (which should turn blue-black)
* Repeat this transfer process until the iodine solution **stops turning blue-black** (this means the amylase has broken down all the starch)
* Record the time taken for the reaction to be completed
* Repeat the investigation for a range of temperatures (from 20°C to 60°C)
\
\
* Add a drop of **Iodine** to each of the wells of a spotting tile
* Use a syringe to add 2cm3 **amylase** to the starch solution and mix well
* Every minute, transfer a droplet of solution to a new well of iodine solution (which should turn blue-black)
* Repeat this transfer process until the iodine solution **stops turning blue-black** (this means the amylase has broken down all the starch)
* Record the time taken for the reaction to be completed
* Repeat the investigation for a range of temperatures (from 20°C to 60°C)
\
\
55
New cards
how can enzyme function can be affected by changes in Ph altering the active site
* If the **pH is too high or too low**, the **bonds** that hold the amino acid chain together to make up the protein can be **disrupted/destroyed**
* This will **change the shape of the active site**, so the **substrate can no longer fit** into it, reducing the rate of activity
* This will **change the shape of the active site**, so the **substrate can no longer fit** into it, reducing the rate of activity
56
New cards
TRIPLE ONLY/PRACTICAL: test enzyme reaction with dif ph
* Add a drop of **iodine** to each of the wells of a spotting tile
* Use a syringe to place 2 cm3 of **amylase** into a test tube
* Add 1cm3 of **buffer solution** (at pH 2) to the test tube using a syringe
* Use another test tube to add 2 cm3 of **starch solution** to the amylase and buffer solution, start the stopwatch whilst mixing using a pipette
* Every 10 seconds, transfer a droplet of the solution to a new well of iodine solution (which should turn blue-black)
* Repeat this transfer process every 10 seconds until the iodine solution **stops turning blue-black** (this means the amylase has broken down all the starch)
* **Record the time** taken for the reaction to be completed
* Repeat the investigation with buffers at different pH values (ranging from pH 3.0 to pH 7.0)
\
* Use a syringe to place 2 cm3 of **amylase** into a test tube
* Add 1cm3 of **buffer solution** (at pH 2) to the test tube using a syringe
* Use another test tube to add 2 cm3 of **starch solution** to the amylase and buffer solution, start the stopwatch whilst mixing using a pipette
* Every 10 seconds, transfer a droplet of the solution to a new well of iodine solution (which should turn blue-black)
* Repeat this transfer process every 10 seconds until the iodine solution **stops turning blue-black** (this means the amylase has broken down all the starch)
* **Record the time** taken for the reaction to be completed
* Repeat the investigation with buffers at different pH values (ranging from pH 3.0 to pH 7.0)
\
57
New cards
what is The process of diffusion by which substances move in and out of cells
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
particles flow through the cell membrane, they move about randomly so travel both ways but if there is more particles on one side an overall net movement takes place
particles flow through the cell membrane, they move about randomly so travel both ways but if there is more particles on one side an overall net movement takes place
58
New cards
The process of Osmosis by which substances move in and out of cells
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration
59
New cards
The process of Active Transport by which substances move in and out of cells
Active Transport is the movement or particles against a concentration gradient from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration using energy which is released during respiration
60
New cards
How does the surface area to volume ratio affect movement in and out of cells
* The **bigger** a cell or structure is, the **smaller its surface area to volume ratio** is, slowing down the rate at which substances can move across its surface
61
New cards
How does the distance affect movement in and out of cells
* The **smaller the distance** molecules have to travel the **faster** transport will occur
extra info
* This is why blood capillaries and alveoli have walls which are only one cell thick, ensure the rate of diffusion across them is as fast as possible
\
\
extra info
* This is why blood capillaries and alveoli have walls which are only one cell thick, ensure the rate of diffusion across them is as fast as possible
\
\
62
New cards
How does the temperature affect movement in and out of cells
* The **higher** the temperature, the **faster** molecules move as they have more energy
why
* This results in more collisions against the cell membrane and therefore a faster rate of movement across them
why
* This results in more collisions against the cell membrane and therefore a faster rate of movement across them
63
New cards
How does the concentration gradient affect movement in and out of cells
* The **greater the difference** in concentration on either side of the membrane, the **faster** movement across it will occur
why
* This is because on the side with the higher concentration, more random collisions against the membrane will occur
why
* This is because on the side with the higher concentration, more random collisions against the membrane will occur
64
New cards
PRACTICAL: investigate diffusion and osmosis using living and non living systems
* Using a knife, cut 2 **equally-sized** cubes of beetroot
* The pieces must have the same dimensions so that they all have **equal surface areas and volumes**, as these factors could affect the rate at which the pigment leaks out
\
\
* **Rinse** the beetroot pieces
* To **remove** any pigment released during cutting
\
* Put 5 cm3 of water into 2 test tubes labelled A and B
* Keep test tube A at **room temperature** and transfer test tube B to a **hot water bath at 90℃**
* Leave the test tubes for 2 minutes, then add a piece of beetroot into each test tube
* After 10 minutes, **observe the colour of the liquid** in both test tubes
* You should notice that at the **higher temperature**, **more of the pigment has leaked out** of the beetroot
* The pieces must have the same dimensions so that they all have **equal surface areas and volumes**, as these factors could affect the rate at which the pigment leaks out
\
\
* **Rinse** the beetroot pieces
* To **remove** any pigment released during cutting
\
* Put 5 cm3 of water into 2 test tubes labelled A and B
* Keep test tube A at **room temperature** and transfer test tube B to a **hot water bath at 90℃**
* Leave the test tubes for 2 minutes, then add a piece of beetroot into each test tube
* After 10 minutes, **observe the colour of the liquid** in both test tubes
* You should notice that at the **higher temperature**, **more of the pigment has leaked out** of the beetroot
65
New cards
What is the process of photosynthesis
* Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction in which energy from sunlight is transferred to the chloroplasts in green plants
* Energy from sunlight is **absorbed by chlorophyll**, a green pigment found inside chloroplasts
* Green plants use this energy to make the carbohydrate **glucose** from the raw materials **carbon dioxide** and **water**
* At the same time, **oxygen** is made and released as a waste product
* Energy from sunlight is **absorbed by chlorophyll**, a green pigment found inside chloroplasts
* Green plants use this energy to make the carbohydrate **glucose** from the raw materials **carbon dioxide** and **water**
* At the same time, **oxygen** is made and released as a waste product
66
New cards
photosynthesis word equation
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
67
New cards
photosynthesis balanced symbol equation
6CO2 + 6H2O →light → C6H12O6 + 6O2
68
New cards
how does carbon dioxide concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis
* This means the **more carbon dioxide** that is present, the **faster the reaction** can occur
69
New cards
how does light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis
* The **intensity** of the light available to the plant will affect the amount of energy that it has to carry out photosynthesis
* The **more** **light** a plant receives, the **faster** the rate of photosynthesis
* The **more** **light** a plant receives, the **faster** the rate of photosynthesis
70
New cards
how does temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis
* As temperature increases the number of collisions increases, therefore the rate of photosynthesis increases
* However At higher temperatures, enzymes that control the processes of photosynthesis can be **denatured**
– this reduces the overall rate of photosynthesis
\
\
* However At higher temperatures, enzymes that control the processes of photosynthesis can be **denatured**
– this reduces the overall rate of photosynthesis
\
\
71
New cards
Describe the structure of the leaf and explain how it is adapted for photosynthesis
the top layer is the upper epidermis
the palisade mesophyll tissue
spongy mesophyll tissue
lower epidermis
guard cells
vascular bundle (xylem and phloem)
chloroplasts
\
air space
the palisade mesophyll tissue
spongy mesophyll tissue
lower epidermis
guard cells
vascular bundle (xylem and phloem)
chloroplasts
\
air space
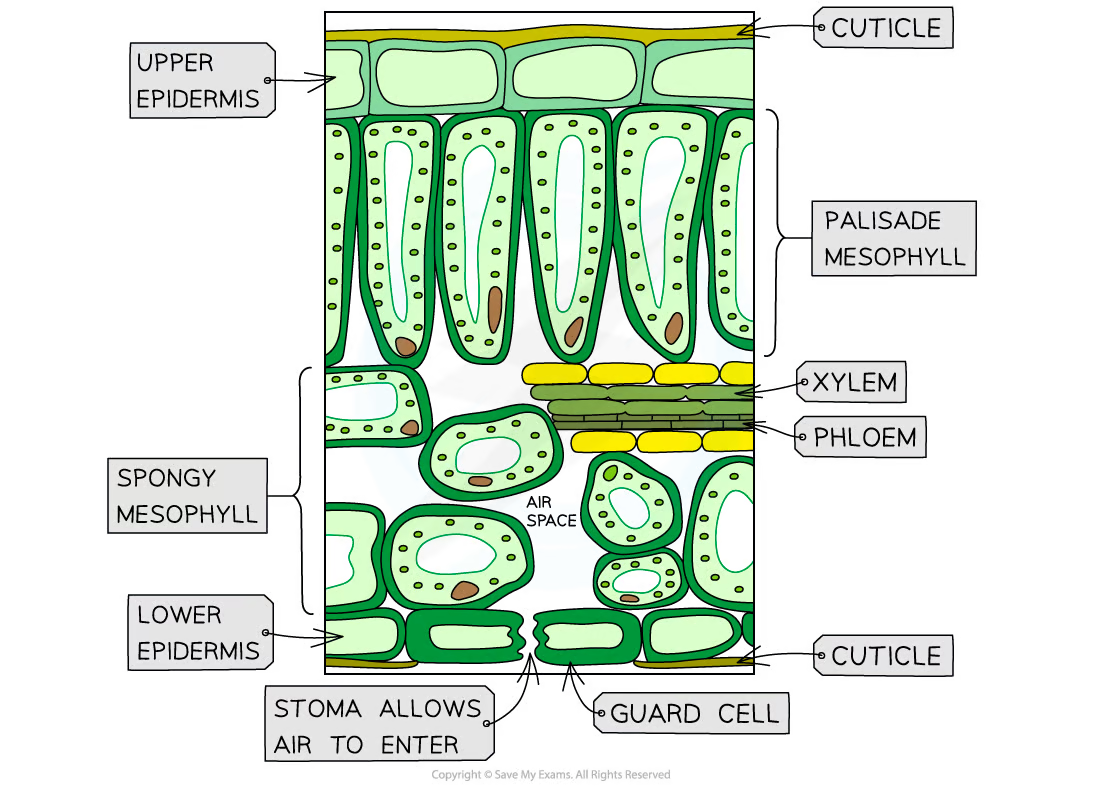
72
New cards
describe the upper epidermis
thin and transparent to allow light to enter palisade mesophyll layer underneath it
73
New cards
describe the waxy cuticle
the protective layer on top of the leaf, prevents water from evaporating
74
New cards
Describe the palisade mesophyll
column-shaped cells tightly packed with chloroplasts to absorb more light, maximising photosynthesis
75
New cards
describe the spongy mesophyll
contains internal air spaces that increase the surface the surface area to volume ratio for the diffusion of the gases mainly carbon dioxide
76
New cards
describe the lower epidermis
contains guard cells and stomata
77
New cards
describe the guard cells
absorbs and loses water to open and close the stomata to allow carbon dioxide to diffuse in oxygen to difuse out
78
New cards
describe the stomata
where the gas exchange takes place; opens during the day, and closes during the night. Evaporation of water also takes place from here. In most plants, found in much greater concentration on the underside of the leaf to reduce water loss.
79
New cards
Describe the vascular bundle
contains xylem and phloem to transport substances to and from the leaf
80
New cards
describe the xylem
transports water into the leaf for mesophyll cells to use in photosynthesis and for transpiration from stomata
81
New cards
describe to phloem
transports sucrose and amino acids around the plant
82
New cards
why do plants require mineral ions for growth
* Photosynthesis provides a source of carbohydrates, but plants contain and require many other types of biological molecule; such as proteins, lipids and nucleic acid (DNA)
83
New cards
What’s the function of magnesium in plants
magnesium is needed to make chlorophyll, a deficiency of magnesium causes yellowing between the veins of the leaves
84
New cards
What’s the function of nitrates in plants
nitrates are a source of nitrogen needed to make amino acids **to build proteins,** a deficiency causes stunted growth and yellowing of leaves
85
New cards
PRACTICAL: Investigate photosynthesis, showing the evolution of oxygen from a water plant, the production of starch and the requirements of light, carbon dioxide and chlorophyll
* **Destarch** the plant by placing it in a dark cupboard for 24 hours
* This ensures that **any starch already present in the leaves will be used up** and will not affect the results of the experiment
* Following de-starching, **partially cover a leaf of the plant with aluminium foil** and place the plant in sunlight for a day
* Remove the covered leaf and test for starch using iodine using the method below
\
* Drop the leaf in **boiling water**
* This **kills the tissue and breaks down the cell walls**
* Transfer the leaf into hot **ethano**l in a boiling tube for 5-10 minutes
* This **removes the chlorophyll** so colour changes from iodine can be seen more clearly
* Dip the leaf in boiling water
* This is done to soften the leaf tissue after being in ethanol
* Spread the leaf out on a white tile and cover it with **iodine solution**
\
* This ensures that **any starch already present in the leaves will be used up** and will not affect the results of the experiment
* Following de-starching, **partially cover a leaf of the plant with aluminium foil** and place the plant in sunlight for a day
* Remove the covered leaf and test for starch using iodine using the method below
\
* Drop the leaf in **boiling water**
* This **kills the tissue and breaks down the cell walls**
* Transfer the leaf into hot **ethano**l in a boiling tube for 5-10 minutes
* This **removes the chlorophyll** so colour changes from iodine can be seen more clearly
* Dip the leaf in boiling water
* This is done to soften the leaf tissue after being in ethanol
* Spread the leaf out on a white tile and cover it with **iodine solution**
\
86
New cards
what are the sections in a diet (7)
1. **Carbohydrates**
2. **Proteins**
3. **Lipids**
4. **Dietary Fibre**
5. **Vitamins**
6. **Minerals (mineral ions)**
7. **Water**
87
New cards
what is the function and source of carbohydrates
source of energy, bread, cereals, pasta, rice, potatoes
88
New cards
what is the function and source of protein
growth and repair of muscles, meat, fish, eggs, pulses, nuts
89
New cards
what is the function and source of lipids
insulation and energy storage, butter, oil, nuts
90
New cards
what is the function and source of dietary fibre
provides bulk (roughage) for the intestine to push food through it, vegetables, whole grains
91
New cards
what is the function and source of vitamins
needed in small quantities to maintain health, fruits and vegetables
92
New cards
what is the function and source of minerals
needed in small quantaties to maintain health, fruits and vegetables, meats, dairy products
93
New cards
what is the function and source of water
needed for chemical reactions to take place in cells, water, juice, milk, fruits and vegetables
94
New cards
what is the function and source of Calcium
Needed for strong teeth and bones and is involved in the clotting of blood. Deficiency can lead to osteoporosis later in life.
Milk, cheese, eggs
Milk, cheese, eggs
95
New cards
what is the function and source of Vitamin D
Helps the body to absorb calcium and so required for strong bones and teeth.
Oily fish, dairy products, also made naturally by the body in sulight
Oily fish, dairy products, also made naturally by the body in sulight
96
New cards
what is the function and source of Vitamin C
Forms an essential part of collagen protein, which makes up skin, hair, gums and bones.
Deficiency causes scurvy
Citrus fruit, strawberries, green , vegetables
Deficiency causes scurvy
Citrus fruit, strawberries, green , vegetables
97
New cards
what is the function and source of Vitamin A
Needed to make the pigment in the retina for vision
Meat, liver, dairy, leafy green vegetables like spinach, eggs
Meat, liver, dairy, leafy green vegetables like spinach, eggs
98
New cards
what is the function and source of Iron
Needed to make haemoglobin, the pigment in red blood cells that transports oxygen
red mat
red mat
99
New cards
why are the Dietary needs dependent on age
The amount of energy that young people need increases towards adulthood as this energy is needed for growth. Children need a higher proportion of protein in their diet than adults as this is required for growth. Energy needs of adults decreases as they age.
100
New cards
Dietary requirements depending on activity levels
The more active, the more energy is required for movement as muscles are contracting more