APHG REVIEW UNIT 1-7
1/292
Earn XP
Description and Tags
review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
293 Terms
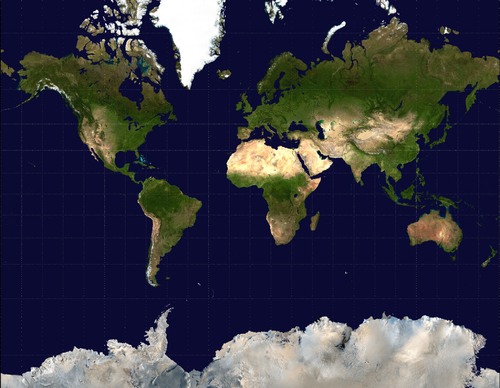
Mercator
looks normal,
used for naval (Sea) expedition,
size and shape distortion
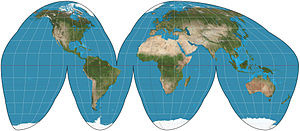
Goode Homolosine
ACCURATE land mass SHAPE and SIZE (continents)
distorts distance and direction
an interrupted map
‘M’
Interrupted map
a map that tries to remove distortion by removing parts globe
(uninterrupted shows the whole globe)
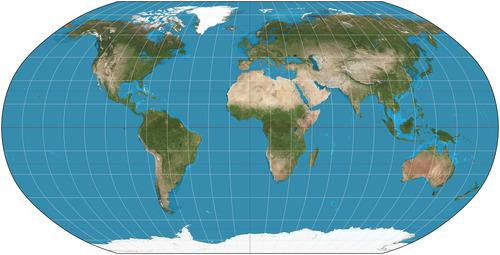
Robinson
they distorted near the poles to minimize distortion, which only made it worse
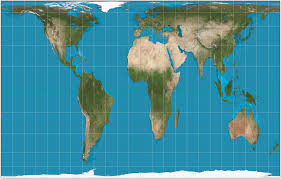
Gall Peters
Shape of countries (especially near the equator) are distorted
shows TRUE SIZE of earth’s land mass
skinny gyal (gall)
Topographic map
uses contour lines to display terrain and elevation changes
Absolute direction
exact direction a person is heading
relative direction
direction given in relation to another object’s current location
ex. the yellow circle is north of the blue circle
absolute distance
the exact distance between two things
ex. 2 miles
relative distance
approximate distance between two things
ex. about 23 hours (not measures in mi/km)
Chloropleth map
different colors or different shades of a color
each shade/color shows a different quantity of data
Dot density
placed dots on a map where the data is occuring
usually for population
good to show distribution bad for density
Graduated/Proportional symbol
distorts shapes/symbols to show the location and amount of data
Isoline
uses lines to connect areas that have similar/equal amounts of data
usually seen representing weather with sgwiggly lines (temp and elevation)
Cartograph
distorts shapes and sizes to show data
ex. in a pop. map china and India would be the biggest
Flow line
shows movement between different areas with arrows
GIS (geographic information system)
computer system for collecting, analysing, and displaying geographic data
it creates layered maps which gives geographers insight on spatial association
GPS ( global positioning System)
uses a network of satellites to determine the location of something on the earth’s surface
Remote sensing
taking pics of the earth using satellites to get info about the eart’s surface
Qualitative data
data in word form
is up for debate
consists of opinions
collected through interviews/surveys
Quatitative data
number form
objective
Census
official count of all the people who live in the area
(US census happens every ten years)
involves info like age, gender, and race
Small scale map
Only SMALL regarding details in data
LARGE portion of earth’s surface
Place
Specific location with unique/distinguishable characteristics
Absolute location
exact spot on earth’s surface
uses latitude and longitude
Relative location
A description of a location based on the surrounding area
Sense of place
strong feeling people have about a place
Placelessness
A place that does not invoke strong response from people due to a lack of unique characteristics
TIme space compression
*counters/goes against distance decay
increasing connectivity between two places even though distance is the same
shorter time it takes to get from one place to another even though distance is the same
*caused by tech and globalization
Distance decay
the effect distance has on cultural or spatial interaction
(the larger the distance, the less interaction)
Environmental determinism
the environment DETERMINES cultural factors
(there is no other option that determines these factors)
the environment tests the possibilities for humans and society
Environmental possibilism
the environment may LIMIT society, but people have the ability to modify the environment to overcome these limits
Scale of analysis
observation of data at (global, regional, national, scale)
HOW zoomed in you are when looking at Geo. data
Formal region AKA Uniform region
based on quantitative data
has common attributes
like climate, land, political boundaries
*all government areas are this because they share a government
ex. Wisconsin
Functional region AKA Nodal region
areas organized around a node - focal point
ex. radio station broadcast area
Perceptual region AKA Vernacular region
areas linked together by people’s feelings/beliefs on a regio
ex. the south
only a region bc people believe it is
Arithmetic density
TOTAL POP/TOTAL AMOUNT OF LAND
shows how densely populated an area is
assumes everything is evenly spread
Physiological desnsity
TOTAL POP/TOTAL AMOUNT OF ARABLE LAND
shows the pressure a population exerts on the environment
Egypt- 97% population on 3% land
Agricultural density
FARMERS/TOTAL AMOUNT OF ARABLE LAND
shows efficiency of agricultural production and reliance on human labor vs tech
high ag density = more manual labor
Urban sprawl
unrestricted growth and expansion of an urban area into the surrounding country side
Carrying capacity
the amount of people that can be supported by the environment w/o damaging it
Malthusian theory
in England during industrial rev
stage 2 dtm
population exponential, food arithmetically
result in famine, war, disease
proven wrong because GMOs can make food grow ep
Neo malthusians
believe earth’s resources can only support a limited population, and pressure on these resources leads to famine and war
they advocate for family planning and contraceptives
Ravensteins’ laws of migration
-people who live in urban areas are less likely to migrate
-males migrate more internationally
-major causes of migration are economic
Intervening obstacles
negeative situations that hinder migration, prevent migrants from reaching final destination
Intervening opportunities
ex. ran out of money, denied entrance
positive situations that hinder migration, prevent migrants from reaching their destination
ex. job offer
Forced migration
when a migrant has no choice but to migrate
ex. Slavery, child soldiers, human trafficking
Refugee
forced to leave home country because of war, persecution, natural disaster ( threatens safety)
crosses international border
Internaly displaced person
refugee within state borders
Transnational migration
migrates form home country to another country but remains connected to original country
Chain migration
begins with one person, and with their contact with a group, pulls people to migrate to the same area
done through kinship links, creates ethnic enclaves
Step migration
happens in stages
ex. make stops on the way to final destination
Material culture
Physical objects that hold significance to individuals
Non material culture
intangible elements of culture
*ideas, beliefs, values, language
Modern/Pop culture
originates in economically developed regions and spreads through hierarchical diffusion
large, heterogeneous, rapid change, material culture, expansive diffusion, ubiquitous
ex. Pokemon
Folk culture
Small, homogenous, resists change, non-material culture, relocation diffusion, isolated
ex. Amish
Indigenous culture
emphasis on community/traditional values, have unique languages and spiritual beliefs, passed down through generations
ethnocentrism
analyzing or judging a culture by the standards of one’s own culture
cultural relativism
the practice of analyzing or judging a culture by its own standards
Sequent occupancy
how different cultures/organizations have left their mark on a geographic location over time
cultural/built landscape
human-made physical surroundings in an area
Placemaking
a community coming together and transforming a public space for different activities
Centripetal forces
aspects that bring people together
homogenity, common language
Education
Nation state
Nationalism
Centrifugal forces
aspects that divide people
significant cultural differences, different languages
Diversity
Balkanization
Devolutionary force
relocation diffusion
the physical movement of a culture or group of people from one place to another
hearth
the location in which an idea/culture/belief/item originated
Expansion diffusion
the spread from one place to another beyond their host cultures while remaining strong among the host culture.
Hierarchiccal diffusion
a type of cultural diffusion where an idea or innovation spreads from a high-status place or person to lower-status places or people
Stimulus diffusion
Veggie burger in Mcdonalds india
culture spreads to another place and it is adopted to better fit the local cultuture
lingua franca
a language used for communication between people who speak different native languages, with English = global lingua franca.
creolization
the process of two culture/lang’s coming together to create a new third on (traditionally due to colonization)
Acculturation
A culture adopts different culture traits from another culture (OG cult. is modified not lost)
Assimilation
a minority culture adopts a a new culture (typically the dominant) resulting on loss in OG cult.
Syncretism
When two or more cultures change over time in a similar manner but remains culturally distinct
diaspora
dispersion of people from their OG homeland (often due to forced migration)
Ecumene
habitable, settled by humans
transhumance
moving herds of animals to the highlands in the summer and the lowlands in the winter
EXTENSIVE SUBSISTENCE
Globalization in politics
democracies being expose dto places around the world drives places to pursue political equity
Arab spring
(series of pro democracy protests that swept across the Arab world)
cultural convergence
different cultures get common ideas/traits and become more similar
cultural divergence
different parts of one culture are exposed to different ideas and become different
Multicuturalism
When a society has a large diversity of cultures which coexist with eachother
State
geographic area w/
-permanent population
-defined borders
-sovereign government
-recognized by other states
Sovereignty
the authority of a state to govern itself
-including domestic and international affairs
Nation
group of PEOPLE w/ shared culture, language, etc.
-typically have a sense of self determination
(the right/desire for a nation to govern themselves)
Nation-State
Sovereign state with a homogenous population
-Japan, Denmark, Poland, France
-Centripetal force
Mono-lingual
DTM 2
-Nigeria, Sudan
-Exponential
-Periphery
-High Agricultural Density
-High youth dependency ratio
-Children are an economic asset
-TFR above 2.1
DTM 3
-Mexico, China, India, Brazil, South Africa
-Moderate
-Urbanizing
-Industrializing
-Semi-periphery
DTM 5
-Western Europe, Japan
-Negative Growth
-High elderly dependency ratio
-Guestworkers
-Children are an economic liability
-TFR below 2.1
-core
Restrictive population policy/ Anti natalist
China= One child policy
India= guns/sterilization
India= federal= less effective policy
Expansive population policy/ Pronatalist
-Stage 5
-Sweden, France, Germany
-Tax incentive
-Free daycare
Guestworkers
France has workers from Algeria
Germany has workers from Turkey
-Typically have guestworkers pay remittance back home
-guest workers create ethnic neighborhoods in their working countries
Universalizing Religion
Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Sikhism
Contagious diffusion, Relocation
Ethnic Religion
Judaism, Hinduism
Relocation diffusion
Judaism = Zionism+ oldest monotheistic
Hinduism = oldest organized religion
Interfaith boundary
Nigeria- Muslim North/Christian South
CAUSES Ethnic conflict
Intrafaith boundary
Northern Ireland (Protestant/Catholic)
Centrifugal force
Multinational State
-Nigeria
-Canada, French canadian-British canadian
-Belgium, French speaking South (Wallonia)- Flemish speaking north
-USA
-Centrifugal force/devolutionary
-Federal
-Multi-lingual
Multistate nation
kurds- spread over 6 states (Iraq, iran..)
basques- in Spain n france
Stateless nation
A nation that has a history of self determination but does not have a recognized state
Kurds, Palestinians
Autonomous regions
A geographic area that is located within a state and has a high degree of autonomy (self governance) from the state
ex. Hong Kong , controlled by China
Semi autonomous region
A geographic area that is controlled by another state but only has a moderate degree of self governance
ex. Native American reservation in the US