Blood Vessels Introduction
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
When it comes to Blood Vessels, there are 3 types. Can you name them?
Arteries, Capillaries, and Veins
What is the function of the Arteries?
Convey blood from the heart to the capillaries.
What is the function of the Capillaries?
Microscopic porous blood vessels exchange substances between the blood and the tissue.
What is the function of the Veins?
Transport blood from capillaries
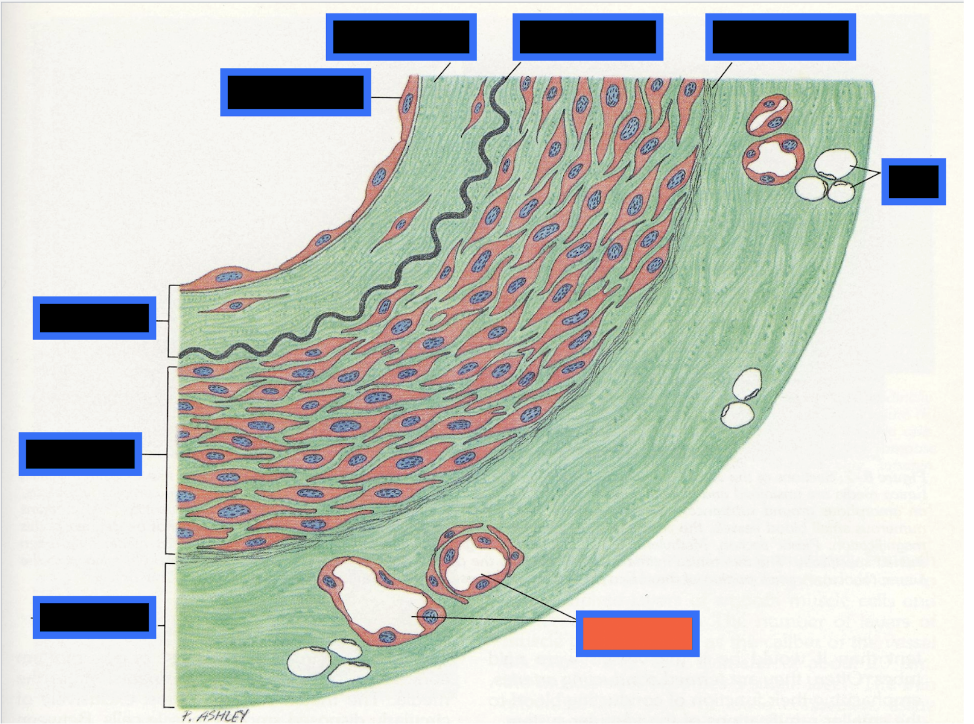
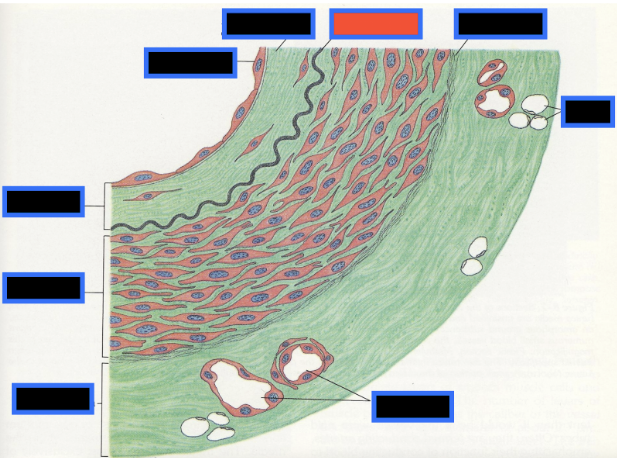
What part of the Blood Vessel (in the red box) is this
Vaso Vasorum
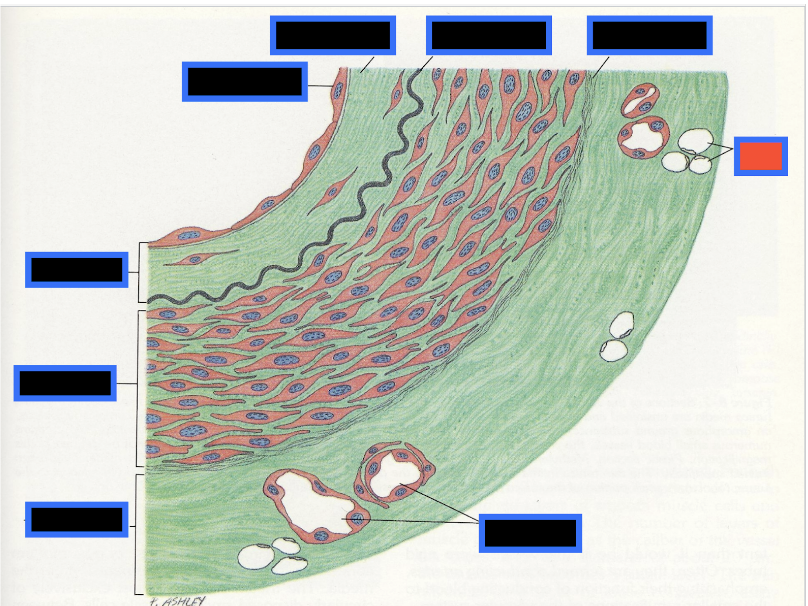
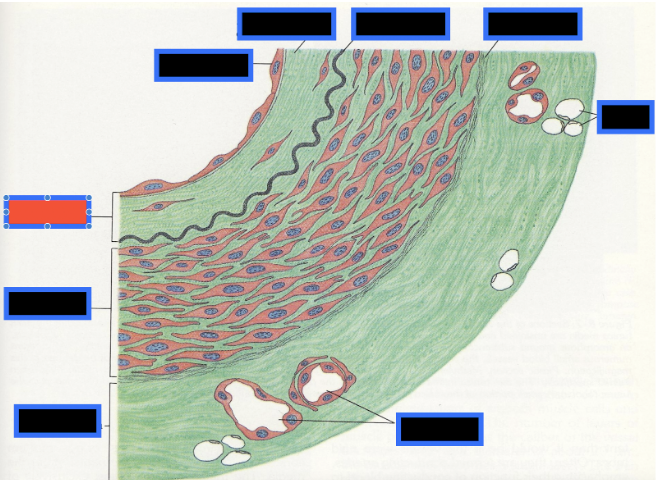
What part of the Blood Vessel (in the red box) is this
Fat Cells
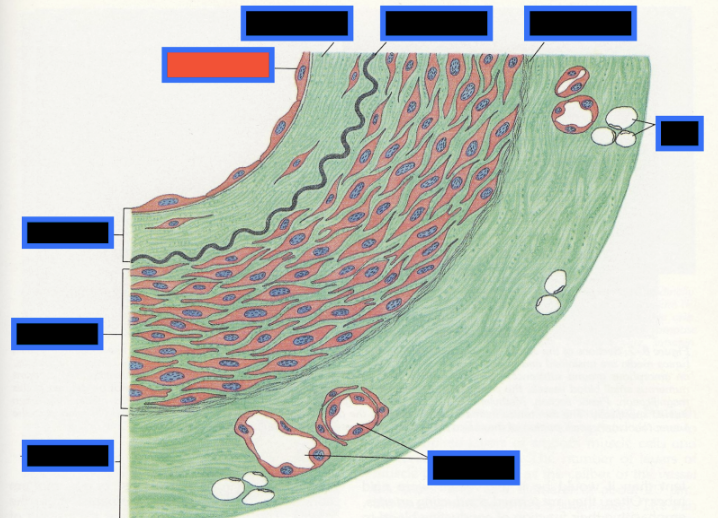
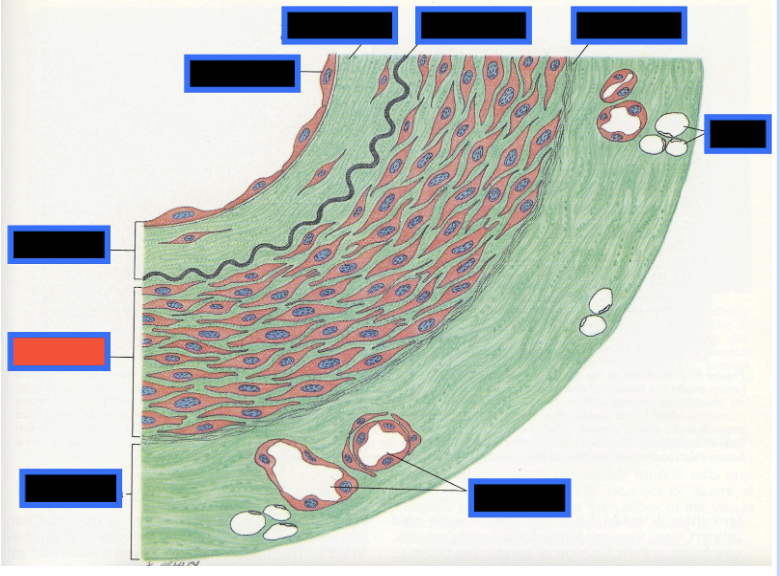
What part of the Blood Vessel (in the red box) is this
Endothelium
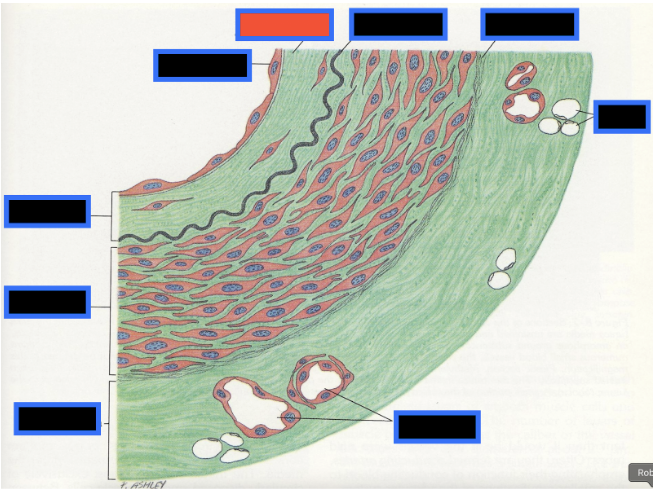
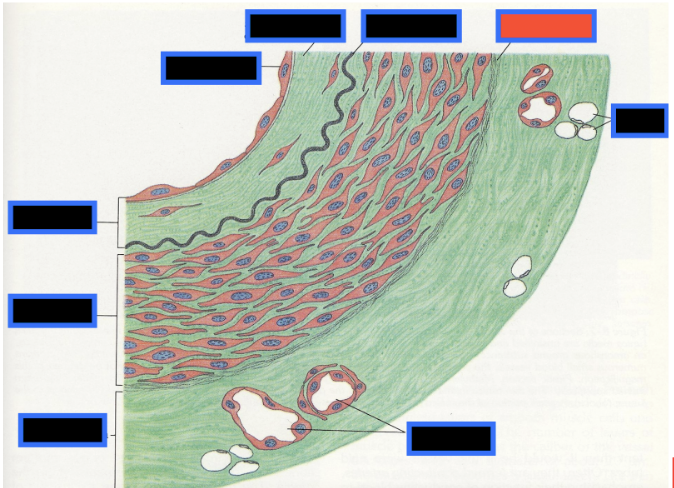
What part of the Blood Vessel (in the red box) is this
Subendothelial Connective Tissue
What part of the Blood Vessel (in the red box) is this
Internal Elastic Membrane
What part of the Blood Vessel (in the red box) is this
Tunica Intima
What part of the Blood Vessel (in the red box) is this
Tunica Media
What part of the Blood Vessel (in the red box) is this
External Elastic
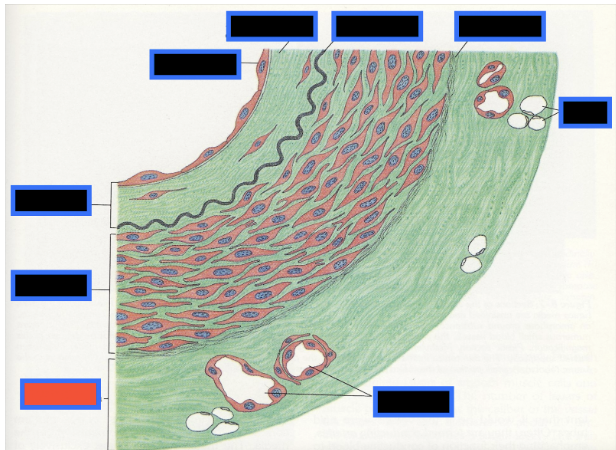
What part of the Blood Vessel (in the red box) is this
Tunica Adventitia (or Externa)
What is the space inside a blood vessel called?
The Lumen
How many layers make up the walls of blood vessels, and what are they called?
Three layers called tunics, the tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa
What is the innermost layer of the Blood vessel wall called?
The Tunica intima
What type of epithelium makes up the endothelium of the tunica intima
Simple Squamous Epithelium
What type of connective tissue is found in the subendothelial layer of tunica intima?
Areolar connective tissue
What is the middle layer of a blood vessel wall called?
Tunica media
What is the middle layer of a blood vessel wall called?
Tunica media
What type of tissue makes up the tunica media
Circularly arranged layers of smooth muscle and elastic fibers
What happens to the lumen when the smooth muscle in the tunica media contracts
It causes vasoconstriction, which narrows the lumen.
What happens to the lumen when the smooth muscle in the tunica media relaxes?
It causes vasodilation, which widens the lumen.
What is the outermost layer of a blood vessel wall called?
The tunica externa
What type of tissue is the tunica externa made of ?
Areolar connective tissue with elastic collagen fibers
What is the main function of the tunica externa?
It helps anchor the vessel to other structures.
What are the small arteries in the tunica externa that supply very large blood vessels called?
Vasa Vasorum
What are companion vessels
Arteries and veins that lie next to each other and serve the same body region
Which type of vessel has a thicker tunica media and a narrower lumen (Arteries or Vein)?)
Arteries
Which type of vessel has more elastic and collagen fibers?
Elastic Arteries
Why are arteries more resilient and resistant to change in blood pressure?
Because they have thicker walls with more elastic and collagen fibers
Which type of vessel has a thicker tunica externa and a larger lumen (Arteries or Veins)?
Veins
Why do veins collapse more easily than arteries when empty?
They have thinner walls and fewer elastic and collagen fibers.
What layers make up the wall of a capillary
Only the tunica intima is composed of endothelium and the basement membrane
Why do capillaries have thin walls?
Their thin walls allow for rapid gas and nutrient exchange between the blood and tissues
As arteries branch farther from the heart, what happens to the lumen diameter?
The lumen diameter decreases
What happens to the amount of elastic fibers as arteries branch into smaller vessels?
The amount of elastic fibers decreases
What happens to the relative amount of smooth muscle as arteries branch into smaller vessels?
The relative amount of smooth muscle increases
What are the three basic types of arteries?
Their thin walls allow for rapid gas and nutrient exchange between the blood and tissues
In general, arteries branch into smaller vessels that extend from which organ?
The heart
In which direction do arteries carry blood?
Away from the heart to the tissues.
Why are the walls of arteries elastic?
Their elasticity allows them to absorb the pressure created by the ventricles as they pump blood into the arteries
What allows arteries to regulate their diameter?
The smooth muscle in the tunica media
What are elastic arteries also known as
Conducting arteries
What is the diameter range of elastic
From 2.5 cm to 1cm
What is the main function of elastic arteries
To conduct blood from the heart to the muscular arteries
Why do elastic arteries have a large portion of elastic fibers?
The elastic fibers allow them to stretch and recoil, helping to propel blood through the arteries during diastole
What are some examples of elastic arteries?
The aorta, pulmonary trunk, common carotid arteries, and common iliac arteries.
What role do elastic arteries (like the aorta) play in blood flow
They act as pressure reservoirs that help maintain continuous blood flow during the cardiac cycle
What happens to the elastic arteries during ventricular contraction (systole)
They stretch as the left ventricle contracts and ejects blood into them.
What happens to the elastic arteries during ventricular relaxation (diastole)?
They recoil, pushing blood forward toward the capillaries even while the ventricle refills.
Why is the stretch and recoil of elastic arteries important?
It smooths out the pressure fluctuations from the heartbeat and ensures continuous blood flow to tissues.
What are muscular arteries also known as
Distributing arteries
What is the diameter range of muscular arteries?
From 1cm to 3mm
What is the primary function of muscular arteries?
To distribute blood to specific body regions
What allows muscular arteries to perform vasoconstriction and vasodilation?
The smooth muscle in their walls
Where is the internal elastic lamina located in a muscular artery?
Between the tunica intima and the tunica media
Where is the external elastic lamina located in a muscular artery?
Between the tunica media and the tunica externa
What type of arteries are usually named arteries of the body?
Muscular arteries
Give examples of muscular arteries.
The brachial artery and the coronary arteries
What are arterioles?
The smallest arteries with diameters ranging from 3mm to 10 micrometers.
How do larger and smaller arterioles differ in structure?
Larger arterioles have three tunics; smaller arterioles have only a thin endothelium and a single layer of smooth muscle.
What is a vasometer tone?
The state in which the smooth muscle of arterioles is somewhat constricted
What is the primary function of arterioles?
To regulate systemic blood pressure and blood flow.
What is atherosclerosis?
A progressive disease of elastic and muscular arteries characterized by the presence of atheromatous plaques (Atheromas)
What is an atheroma?
A thickening of the tunica intima that narrows the arterial lumen.
What can cause atherosclerosis?
Injury to the endothelium caused by infection, trauma, or hypertension.
How does endothelial injury lead to atherosclerosis?
Injury triggers an inflammatory reaction, leading to the formation and enlargement of atheromas, which narrow the lumen.
Why might someone be unaware they have atherosclerosis
Plaques often do not cause symptoms until they restrict blood flow to a region
What condition makes a person more prone to atherosclerosis?
Increased cholesterol in the blood, known as hypercholesterolemia
Which sex is more commonly affected by atherosclerosis?
Males are more affected than females
How do smoking and hypertension influence atherosclerosis risk
They increase vascular injury and the overall risk of developing the disease
What is angioplasty
A treatment that expands a narrowed reigon of an artery
What is the purpose of coronary bypass surgery
To create a new route for blood to flow around a blocked or narrowed artery
What is an aneurysm?
A condition where part of an atrial wall thins and balloons out.
Why is an aneurysm dangerous?
The weekend wall is more prone to rupture, which can cause massive bleeding and death
Which type of arteries are most affected by aneurysms?
Elastic and muscular arteries
Why do arteries become more prone to aneurysms with age?
They become less able to withstand the forces from pulsating blood
Where are aneurysms most commonly found?
in the aorta or arteries at the base of the brain.
How does age affect aneurysm risk?
The risk of developing an aneurysm increases with age
What do capillaries connect?
They connect arterioles to venules
What is the average length and diameter of a capillary?
Average length is about 1 mm, and diameter is 8 to 10 micrometers
How do erythrocytes travel through capillaries?
in a single file, a formation called a rouleau
What is the structure of a capillary wall?
It consists of an endothelial layer resting on a basement membrane
Why are capillary walls thin and their diameters small
to optimize exchange between Blood and Tissue fluid
What are the three types of capillaries?
Continuous, fenestrated, and sinuosoid capillaries
What type of lining do continuous capillaries have?
endothelial cells form a continuous lining
How are endothelial cells in continuous capillaries connected?
by tight junctions that do not form a complete seal
What are intercellular clefs?
gaps between endothelial cells of the capillary wall that allow small molecules to pass
Which substances can and cannot pass through continuous capillary walls?
Larger particles like cells and proteins cannot pass, but smaller molecules such as glucose can pass.
Where are continuous capillaries commonly found?
in muscle, skin, lungs, and the central nervous system
What structural feature distinguishes fenestrated capillaries from continuous capillaries
endothelial cells form a continuous lining, but contain small pores called fenestrations.
What is the function of fenestrations in capillaries?
They allow movement of smaller plasma proteins through the capillary wall.
Where are fenestrated capillaries commonly found?
In areas with extensive fluid transport
Give two examples of locations with fenestrated capillaries
Intestinal capillaries ( for nutrient absorption) and kidney capillaries ( for blood filtration to form urine).
What kind of lining do sinusoid capillaries have?
An incomplete endothelial lining with large gaps.
What is special about the basement membrane of sinusoids?
It is incomplete or absent.
what can pass through the opening in sinusoids capillaries?
large substances such as formed elements and large proteins.
Where are sinusoids commonly found?
In the bone marrow, spleen, and some endocrine glands.
What are capillary beds?
Groups of capillaries that function together to exchange substances between blood and tissues.