Chapter 7: Geologic Time and Dating Techniques
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
PreCambrian Eon
The oldest eon in the geologic time scale.
Phanerozoic Eon
The eon following the Precambrian, characterized by abundant fossil evidence.
Paleozoic Era
The first era of the Phanerozoic Eon, known for the development of early life forms.
Mesozoic Era
The second era of the Phanerozoic Eon, known as the age of dinosaurs.
Cenozoic Era
The most recent era of the Phanerozoic Eon, known as the age of mammals.
Relative Dating
Determines sequences of events based on relative positions/relationships of features.
Absolute Dating
Calculates timing of events and rates of geologic processes, assigning a numeric age.
Principle of Superposition
States that in an undisturbed succession of strata, the oldest layers are at the bottom.
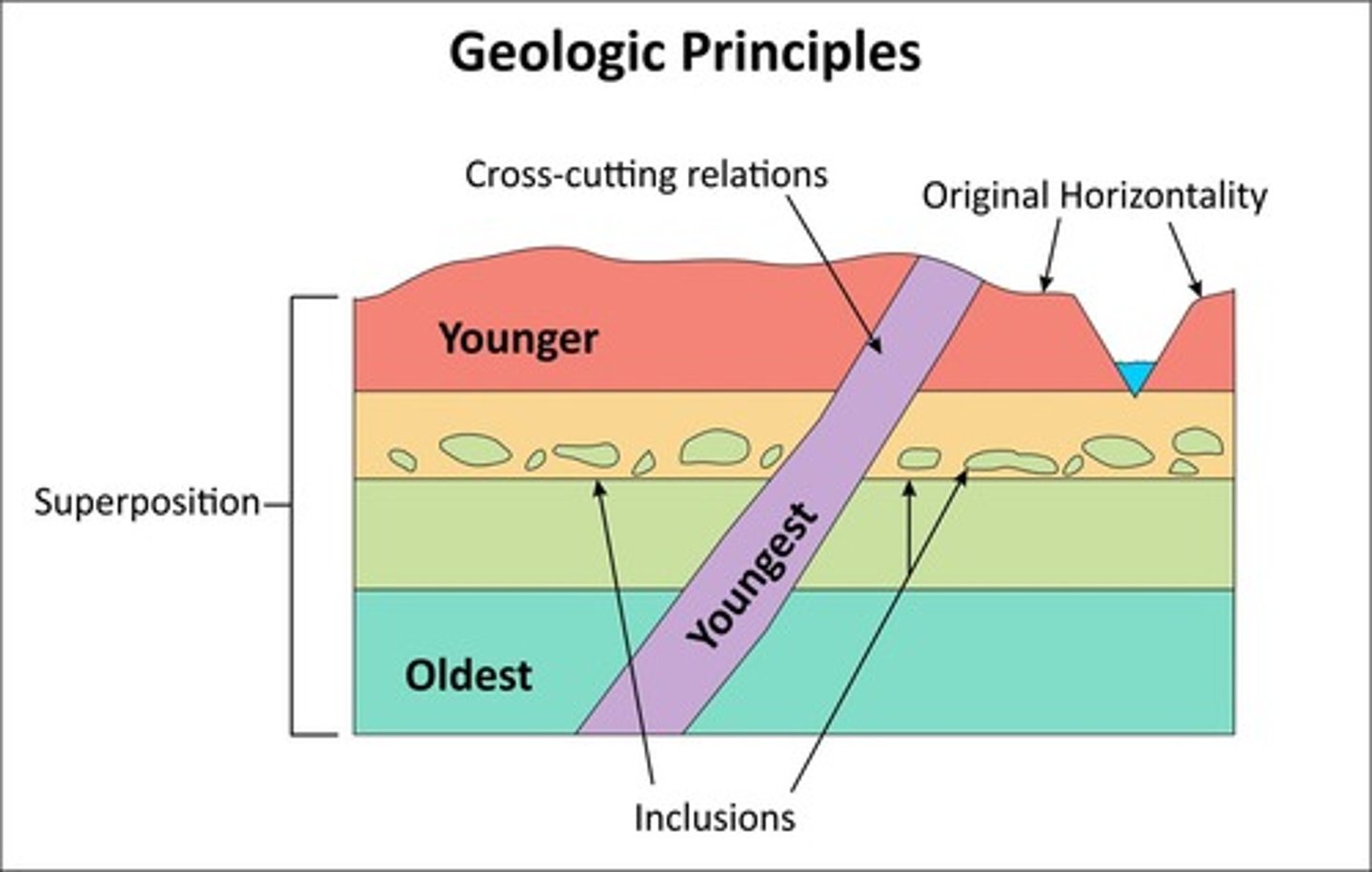
Principle of Original Horizontality
States that sedimentary layers were deposited nearly horizontally and parallel to the Earth's surface.
Principle of Lateral Continuity
Strata layers are continuous in all directions until they thin out at the edge of that basin.
Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships
A rock unit or fault that cuts another geologic unit is younger than the unit that was cut.
Principle of Inclusions
Fragments of rock within a larger rock unit are older than the rock it's enclosed within.
Principle of Fossil Succession
Fossils occur in a definite determinable order due to evolution.
Radioactive Isotopes
Atoms that decay over time, releasing radiation, used to determine absolute age.
Common Isotopes in Dating
Uranium-238 decays to Lead-206 and Carbon-14 decays to Nitrogen-14.
Half-life of a Radioisotope
The time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay into a more stable form.
Applications of Radioactive Isotopes
Used in medical imaging, cancer treatment, and nuclear power generation.
Law of Uniformitarianism
The principle that the same geological processes that operate today also operated in the past.
Quantitative Method
A method that involves assigning numeric ages to geologic events or materials.
Cyclical Features
Features such as tree rings, varves, and layers of ice that can be used in absolute dating.
Environmental Research
Radioactive isotopes aid in climate and environmental research.
Medical Imaging Isotopes
Iodine and Technetium are used in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
Radioisotope
An isotope that has a fixed half-life, meaning the decay rate is constant.
Half-life
The time required for half of the original isotope to decay; after one half-life, 50% remains, after two half-lives, 25% remains.
Radiocarbon dating
A method used to date organic materials such as wood, bones, shells, and charcoal, which can only date things up to 50,000 years.
U-Pb dating
A method used to date rocks and minerals that can date millions to billions of years.
Body Fossils
Remains of the actual organisms that have been altered, providing direct evidence of past life.
Trace Fossils
Evidence of ancient organisms' behaviors, representing activities of the organism while it was alive.
Indirect evidence
Evidence that does not include actual body parts but shows signs of past biological activity, such as trace fossils.
Direct evidence
Physical remains of organisms, providing clear proof of past life, such as body fossils.
Fossilization
The process by which fossils are preserved.
Cats & Molds
A fossilization process where original material dissolves, leaving a cavity.
Carbonization
A fossilization process where organisms get compressed and only carbon is perceived, resulting in a carbon silhouette.
Fossil preservation factors
Factors that increase the chance of fossil preservation: hard parts, low oxygen environment, and rapid burial.
Stratigraphic correlation
Matching or linking strata of rock layers of the same age from different locations.
Lithostratigraphic correlation
A correlation technique based on the physical and chemical characteristics of rock layers.
Chronostratigraphic correlation
A correlation technique that relates rock layers to specific time intervals.
Biostratigraphic correlation
A correlation technique that uses fossil content to correlate rock layers.
Magnetostratigraphy
A correlation technique that uses the magnetic properties of rock layers.
Chemostratigraphy
A correlation technique that uses the chemical composition of rock layers.
Unconformities
Surfaces between rock layers of greatly differing ages, representing 'missing time' in the rock record.
Angular Unconformity
An erosional surface with flat/horizontal rock layers above and tilted rock layers below.
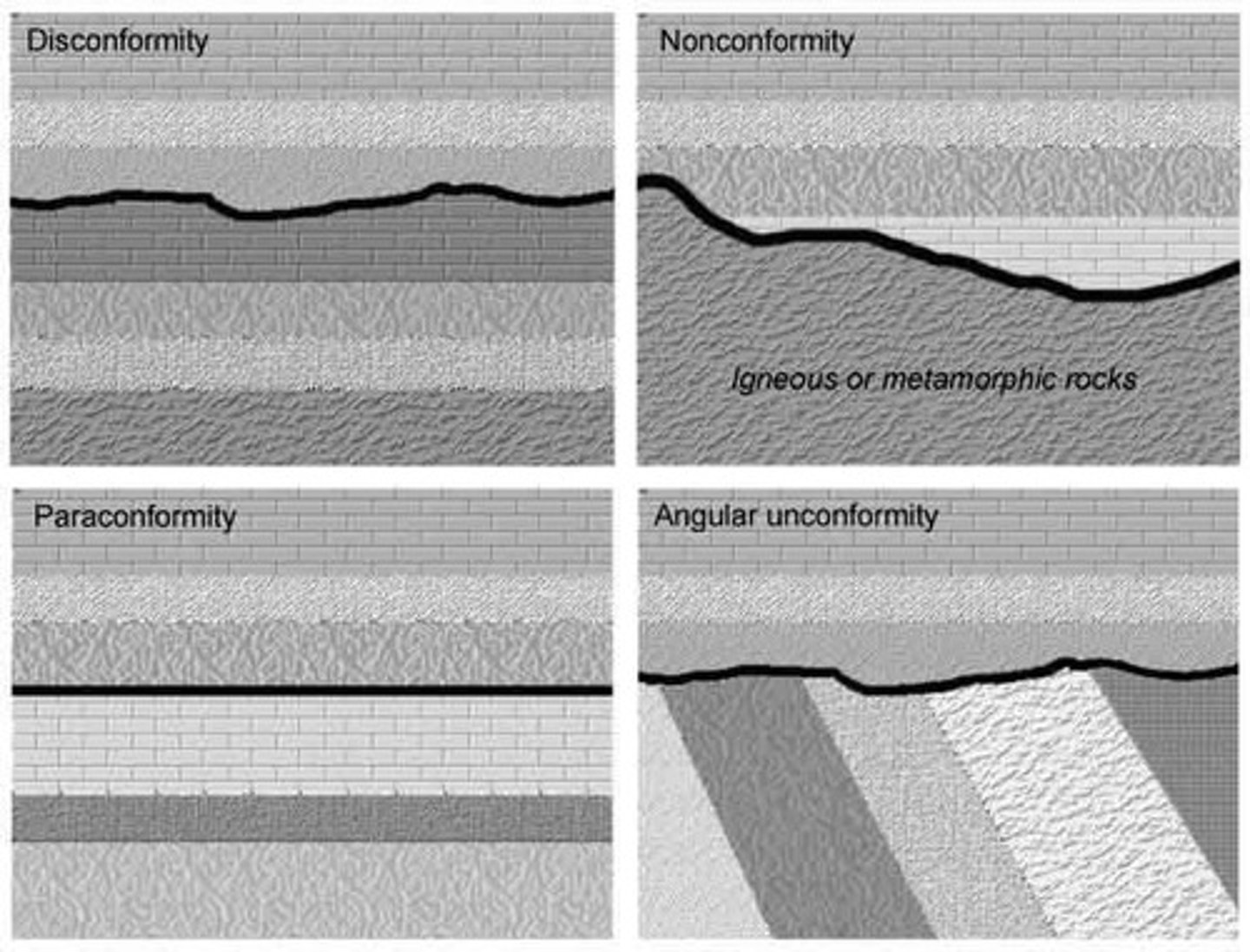
Nonconformity
An erosional surface between sedimentary rocks and crystalline rocks.
Disconformity
A visible, uneven or irregular erosional surface between parallel sedimentary rock layers of different ages.