CHEM 103 - UNIT 1
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Element
The simplest type of matter that has unique properties and consists of only one type of atom
ex) H, O, Na, Cl
Molecule
An independent structure made of at least two atoms bonded together by covalent bonds.
ex) H2, O2, CH4, H2O
Compound
A substance formed when atoms of different element are chemically bonded together
ex) NaCl, H2O, NH4Cl
Mixtures
Two or more substances physically combined but not chemically bonded
ex) Air: 78% nitrogen (N₂) and 21% oxygen (O₂), 1% other gases
Proton (p+)
A positive charged subatomic particle with a mass of about 1 amu
the atomic number
Neutron (n0)
A subatomic particle with no charge and a mass of about 1 amu
ex) Carbon-12 has 6 neutrons, 6 protons
Electron
A negatively charged subatomic particle with very small mass
Atomic Number (Z)
The number of protons in an atom; defines the element.
ex) Carbon Z = 6, carbon no matter what
Mass Number (A)
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom
Protons + Neutrons
ex) Carbon-12 → 6 p+ + 6 n0 = 12
Atomic Symbol
The letters used to represent an element
ex) Na = sodium, Cl = chlorine
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
ex)
35Cl → (17 p+ + 18 n0)
37Cl → (17 p+ + 20 n0)
Ion
An atom that has gained or lost electrons and has a net charge
ex) Na+, Cl-
Cation
A positively charged ion formed by losing electrons
ex) Na → Na+ + e-
(A POSITIVE)
Anion
A negatively charged ion formed by gaining electrons
ex) Cl + e- → Cl-
(A NEGATIVE)
Laws of Conservation of Mass
Mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction
Total mass of reactants = Total mass of products
Cathode Ray Experiment
Observation:
Cathode rays bend toward positives plates and away from negative plates
Conclusion:
Cathode rays are made of negative charged particles (electrons)
Result / Why it matters:
Electrons EXIST! and are components of all atoms
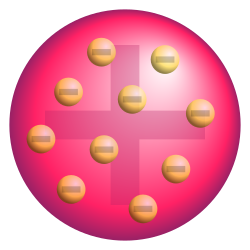
Plum Pudding Model
Observation:
Electrons were known to exist, but atomic mass was spread out
Conclusion:
Atoms were thought to be area of positive charge with electrons embedded in them
Result / Why it matters:
This model was later proven incorrect
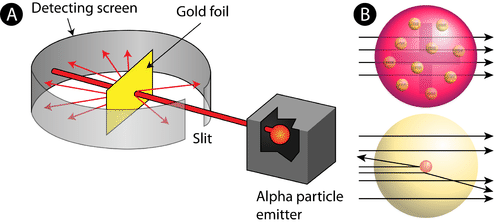
Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment
Observation:
Most alpha particles passed straight through the gold foil; some deflected/bounced back
Conclusion:
Atoms are mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively charged nucleus
Result / Why it matters:
This model was disproved by the nuclear atom model
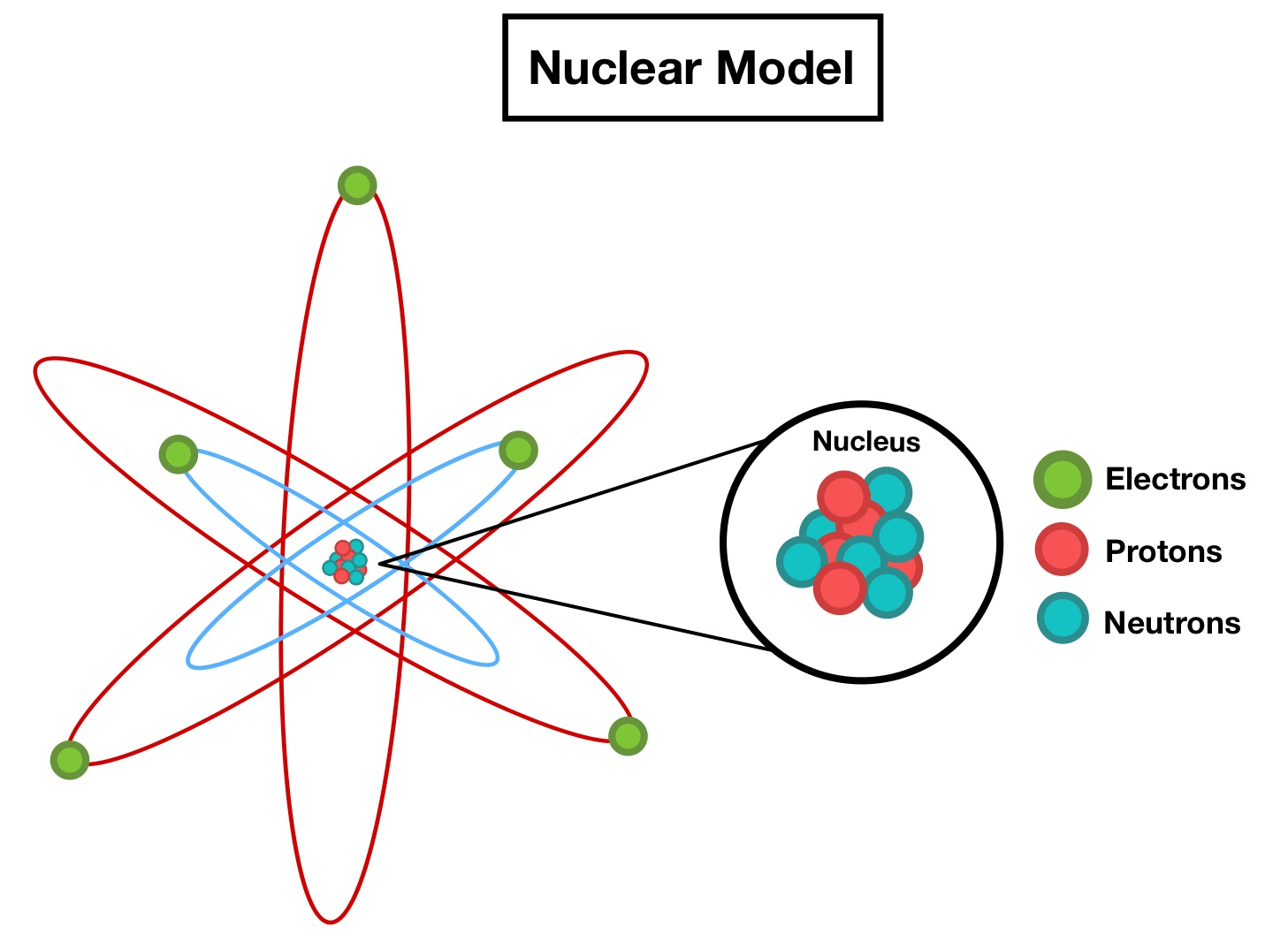
Nuclear Atom Model
Observation:
Alpha particle backscattering occurs only rarely.
Conclusion:
Positive charge and most mass are concentrated in a tiny nucleus.
Result / Why it matters:
Atoms consist of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.
Classical Mechanics
Motion of large, everyday objects
Works for big things, not atoms
Quantum Mechanics
Electrons show wave-like behavior
Successfully explains atoms and electrons