Chapter 7.1-2
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
What are the two structural divisions of the skeleton
the axial and appendicular skeletons
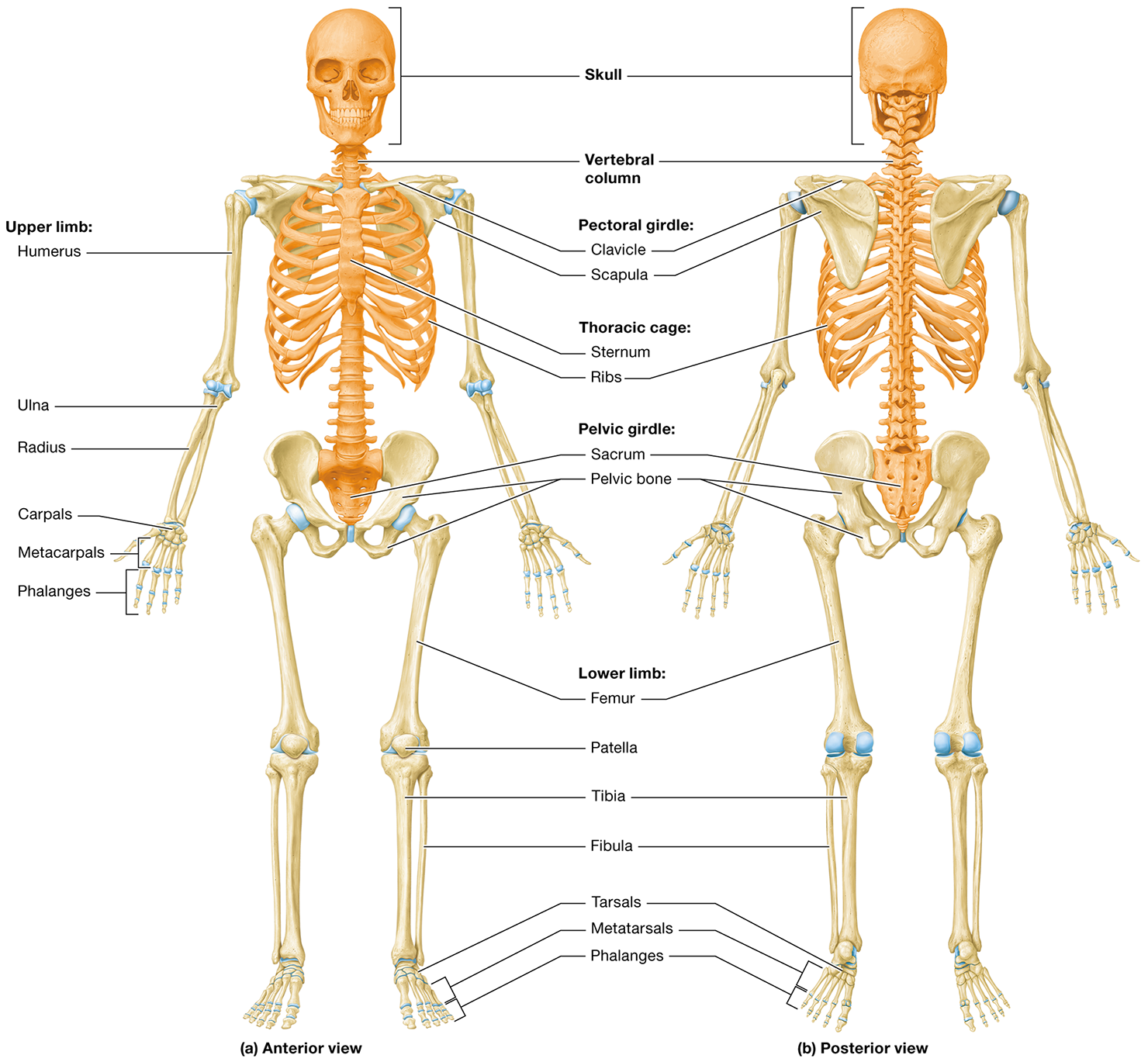
What does the axial skeleton consist of
the bones of the skull, the vertebral column, and the thoracic cage
The main function of the axial skeleton
is protection, as it encases body cavities and protects underlying organs
The appendicular skeleton
consists of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and the pectoral and pelvic girdles
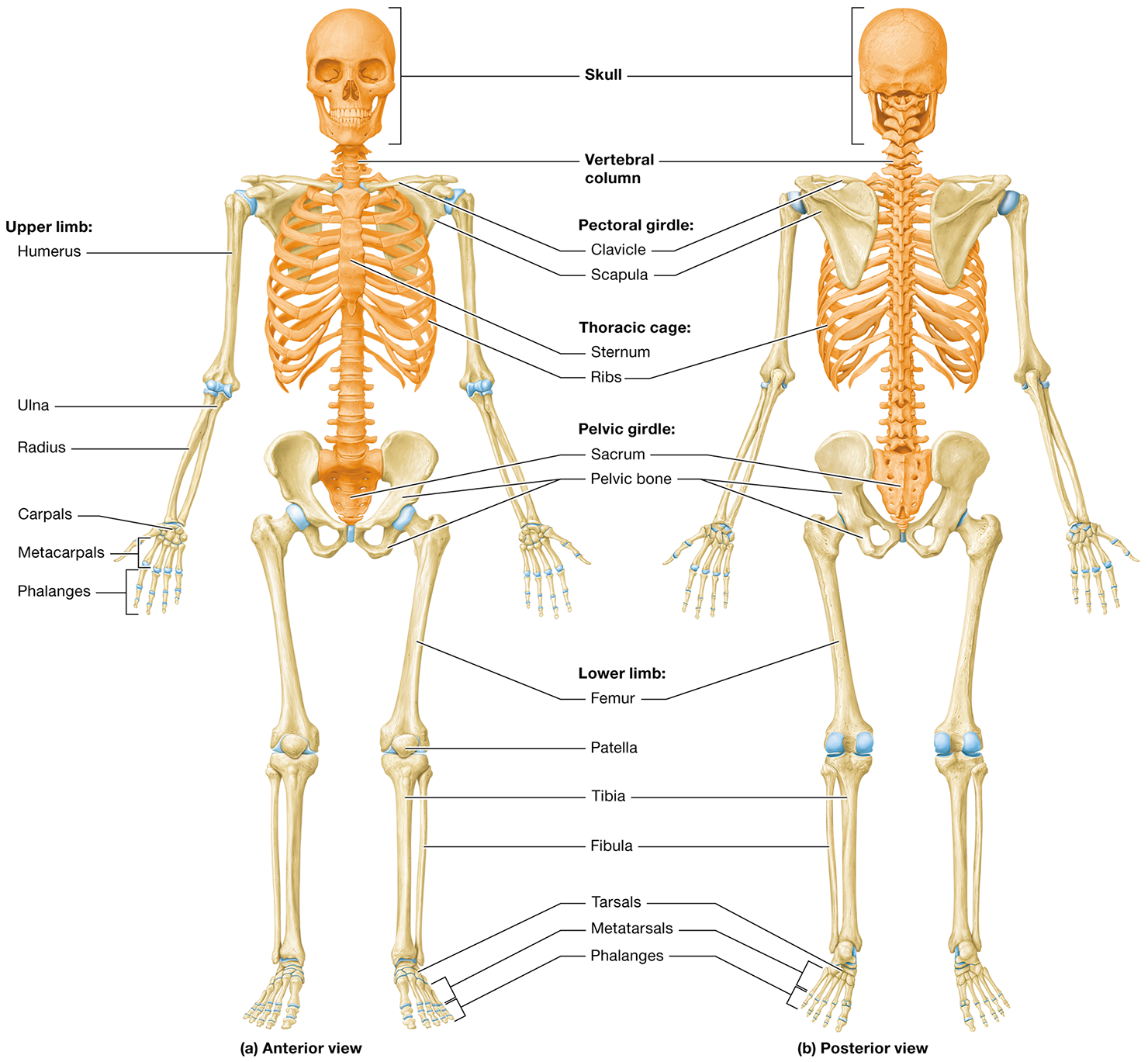
The main function of the appendicular skeleton is
motion, acting primarily as levers and supportive structures for muscle attachment
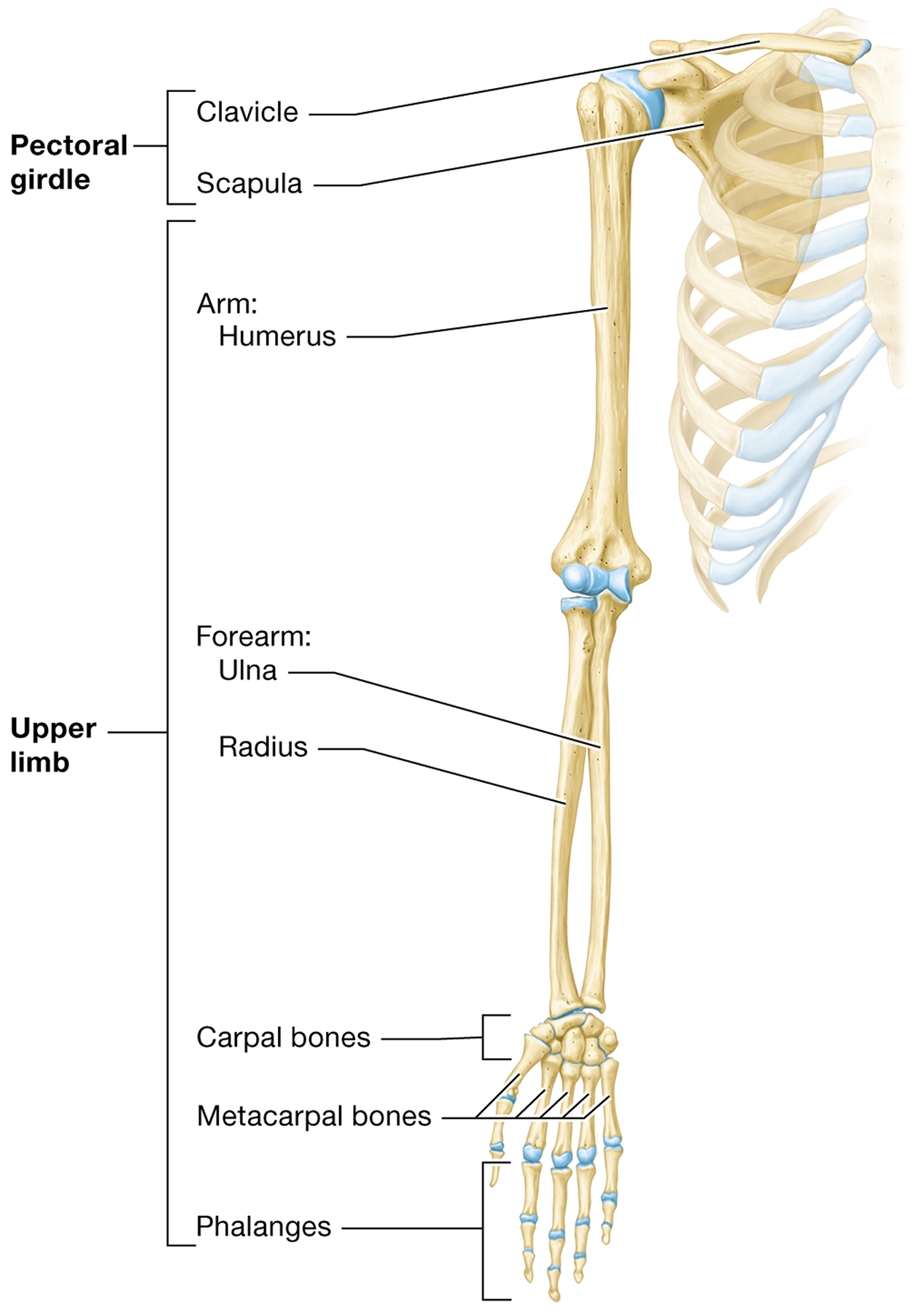
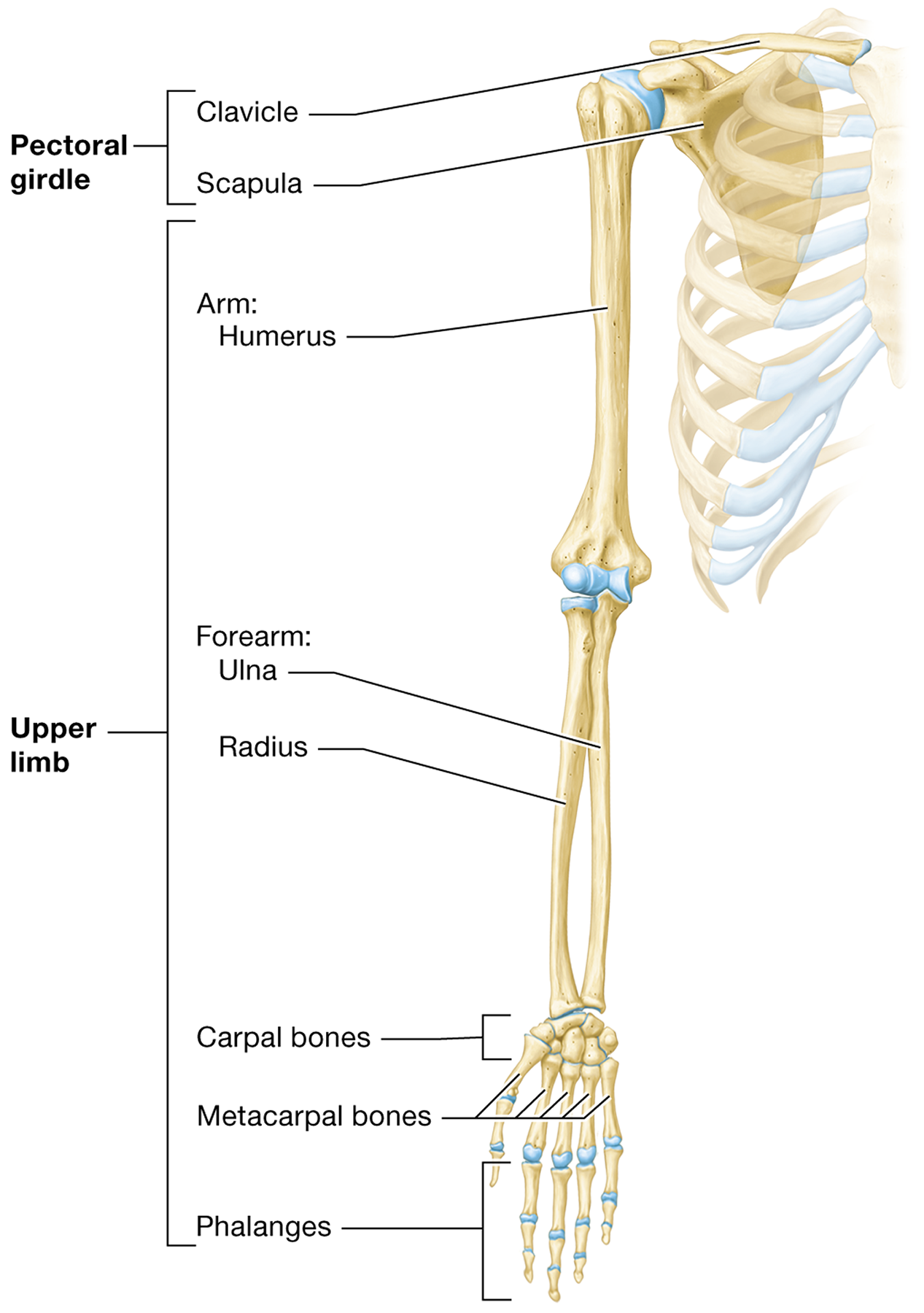
The bones of the upper limb are
the humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges
lower limbs are
the femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges
The pectoral girdle is made up of
The clavicle and the scapula
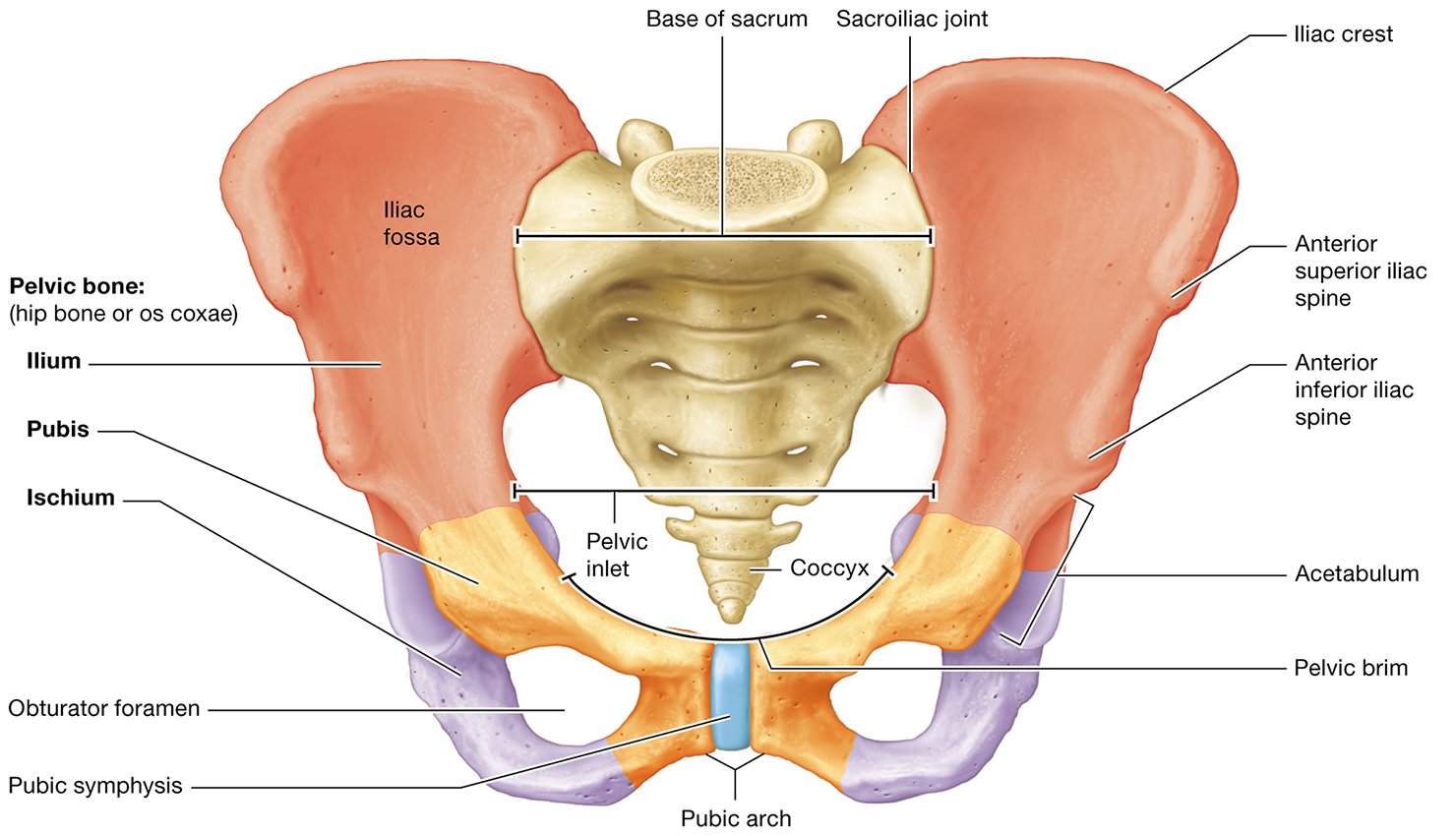
What bones form the pelvic girdle
formed by the two pelvic bones and the sacrum. Each pelvic bone is composed of three fused bones: the ilium, ischium, and pubis
What are bone markings?
surface features of bones, including depressions, openings, and projections
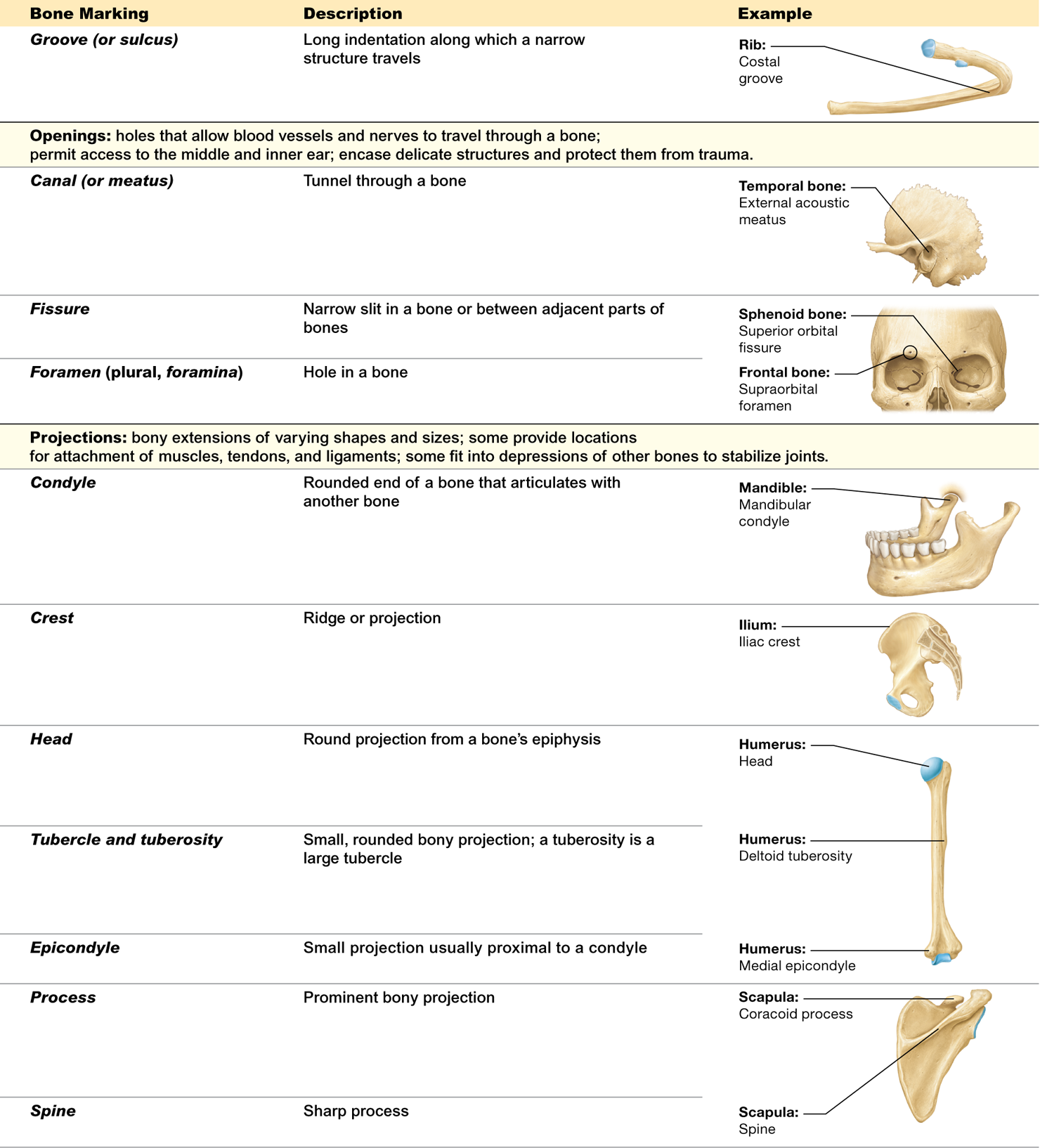
Describe depressions and give examples
clefts of varying depths in a bone and are located where a bone meets another structure, such as another bone or a blood vessel Examples include
Facets
Fossae
Foveae

What is a facet? Give an example
a shallow convex or concave surface where two bones articulate. For example, a rib has an articular ____ for articulation with a transverse process
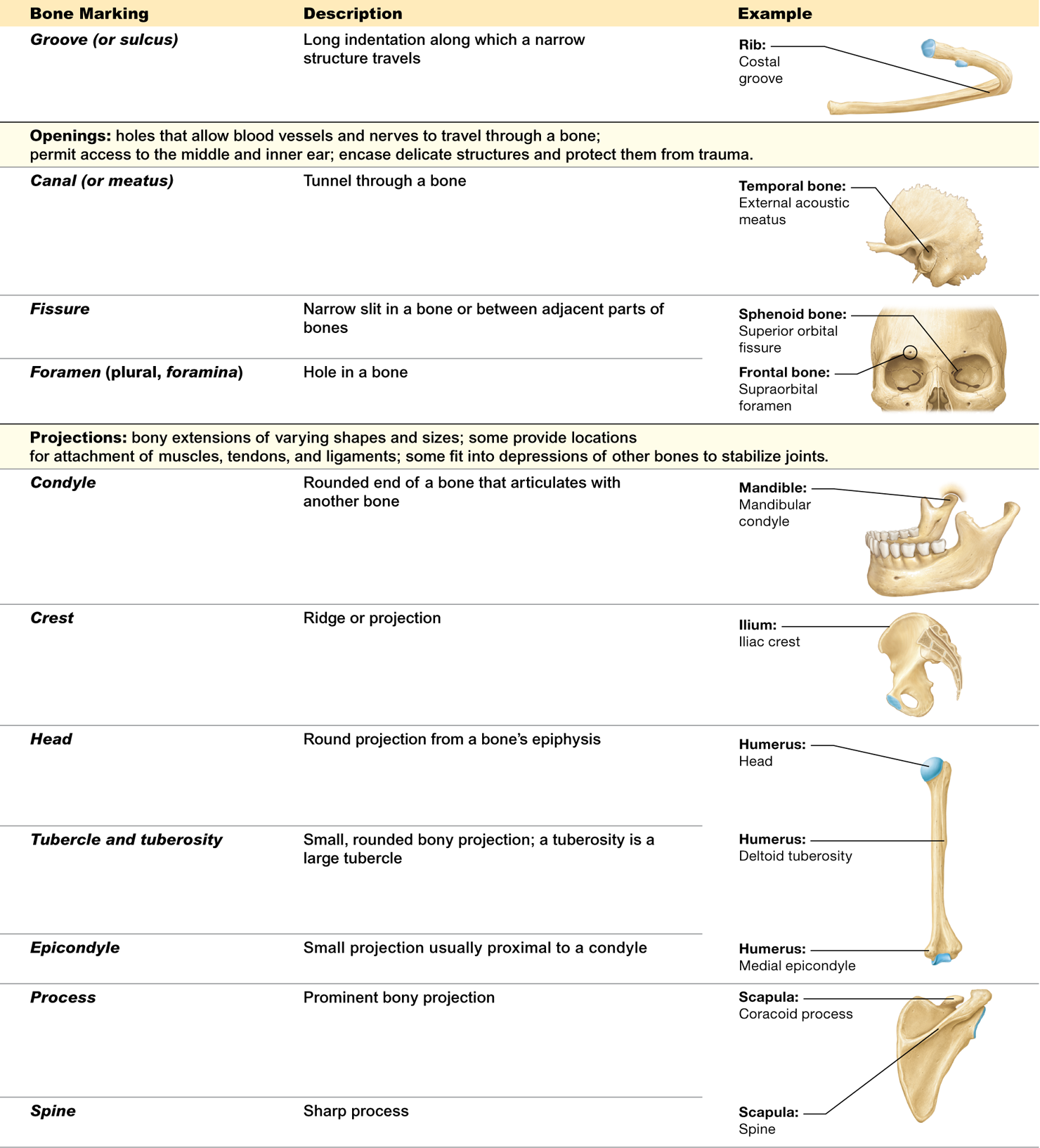
What is a fovea? Give an example
a shallow pit. For example, the femur has a ____ capitis
What is the function of openings in bones?
enclose delicate structures and allow them to travel through bones
What is the function of projections on bones?
provide sites to which ligaments and tendons attach or where bones articulate
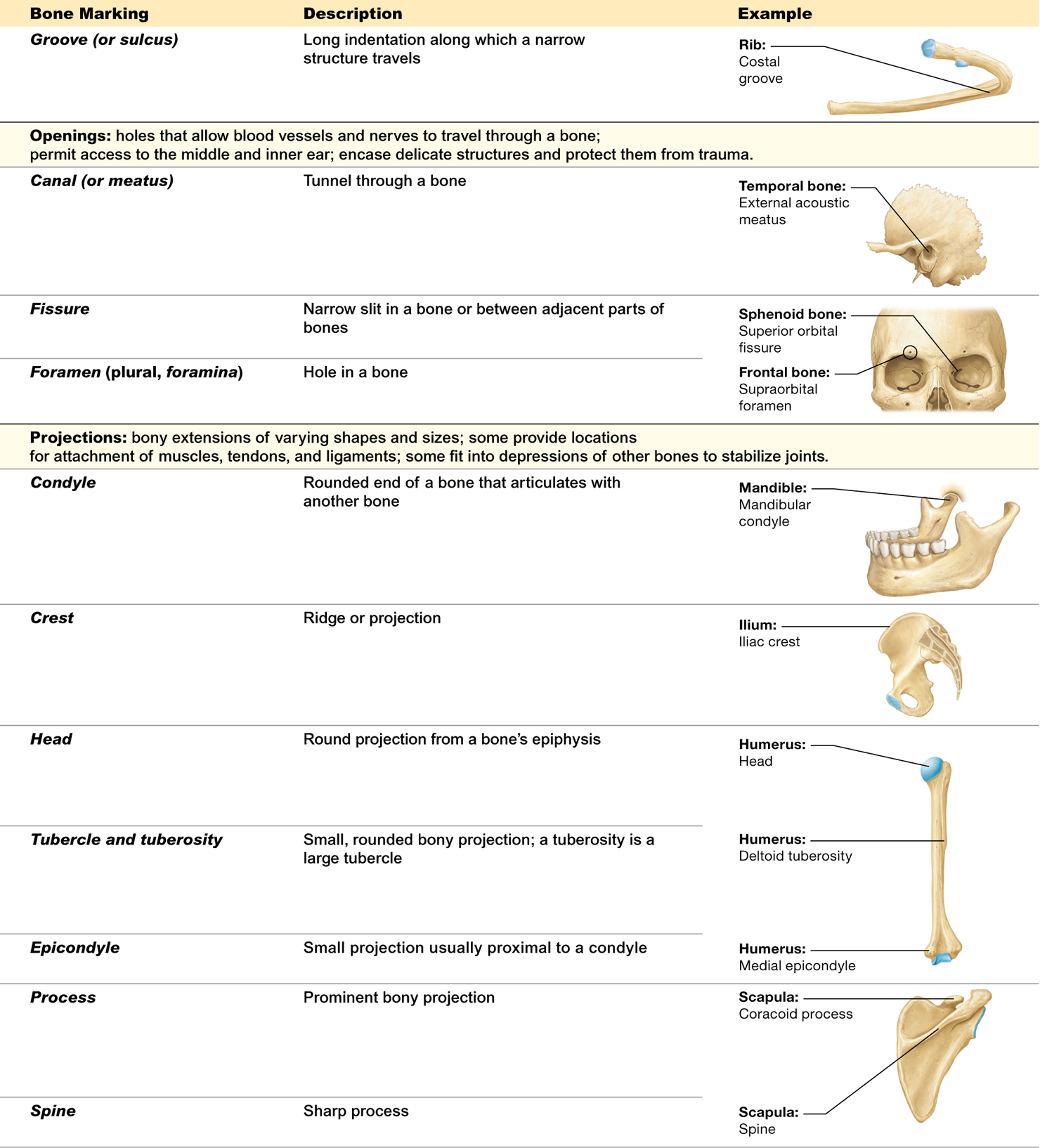
What does the skeleton consist of?
bones and skeletal cartilages
What types of cartilage tissues are found in the skeleton?
hyaline cartilage and fibrocartilage
Where can hyaline cartilage be found in the skeleton?
Hyaline cartilage can be found at articulations between bones of the upper and lower limbs, between the ribs and sternum, and in epiphyseal plates
Where can fibrocartilage be found in the skeleton?
at articulations between the vertebrae and the two pelvic bones
What are the functions of hyaline cartilage in the skeleton?
provide flexibility during movement and breathing in the rib cage and allows for long bone growth at the epiphyseal plates
What are the functions of fibrocartilage in the skeleton?
Fibrocartilage functions to provide articulations between the vertebrae and the two pelvic bones
.
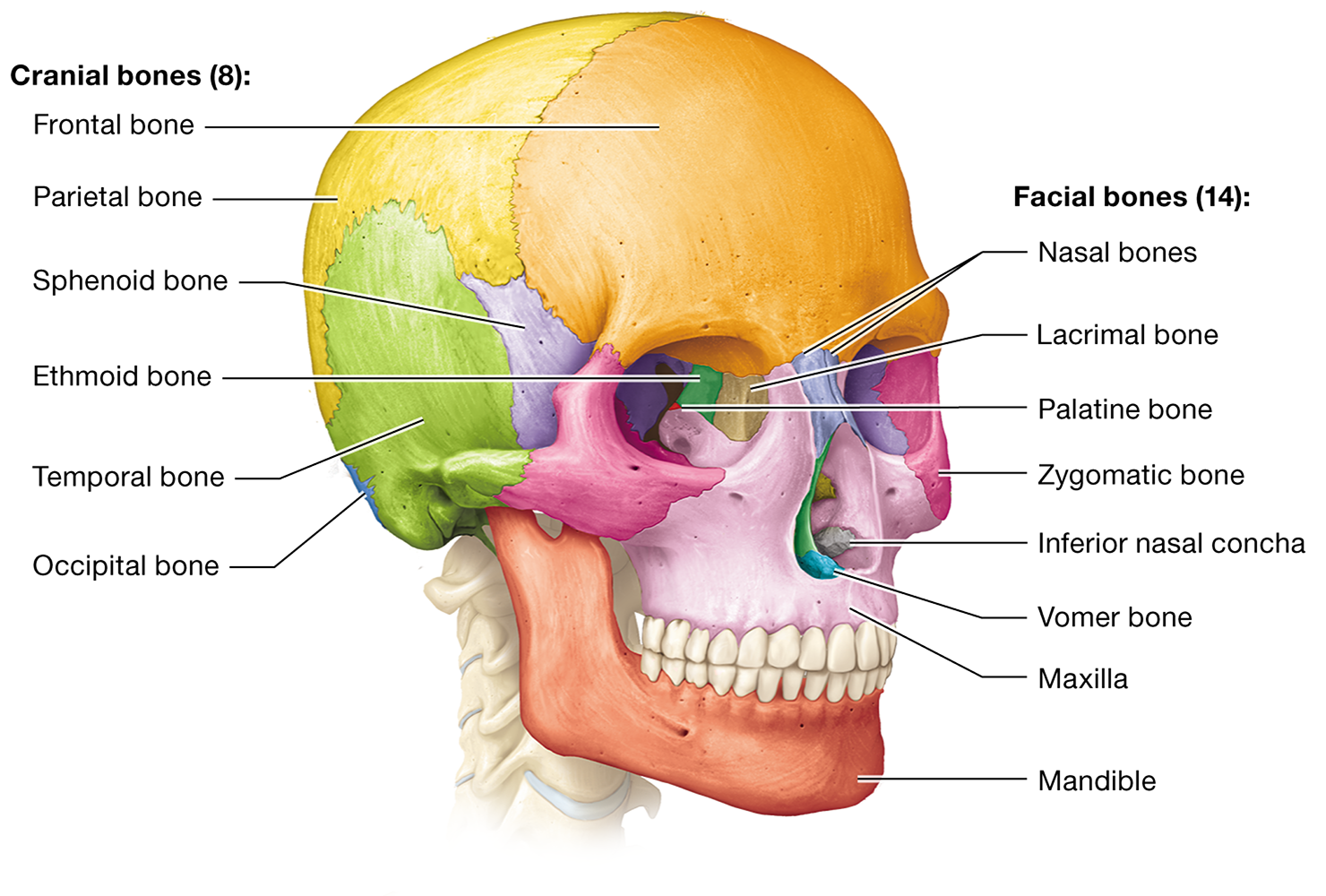
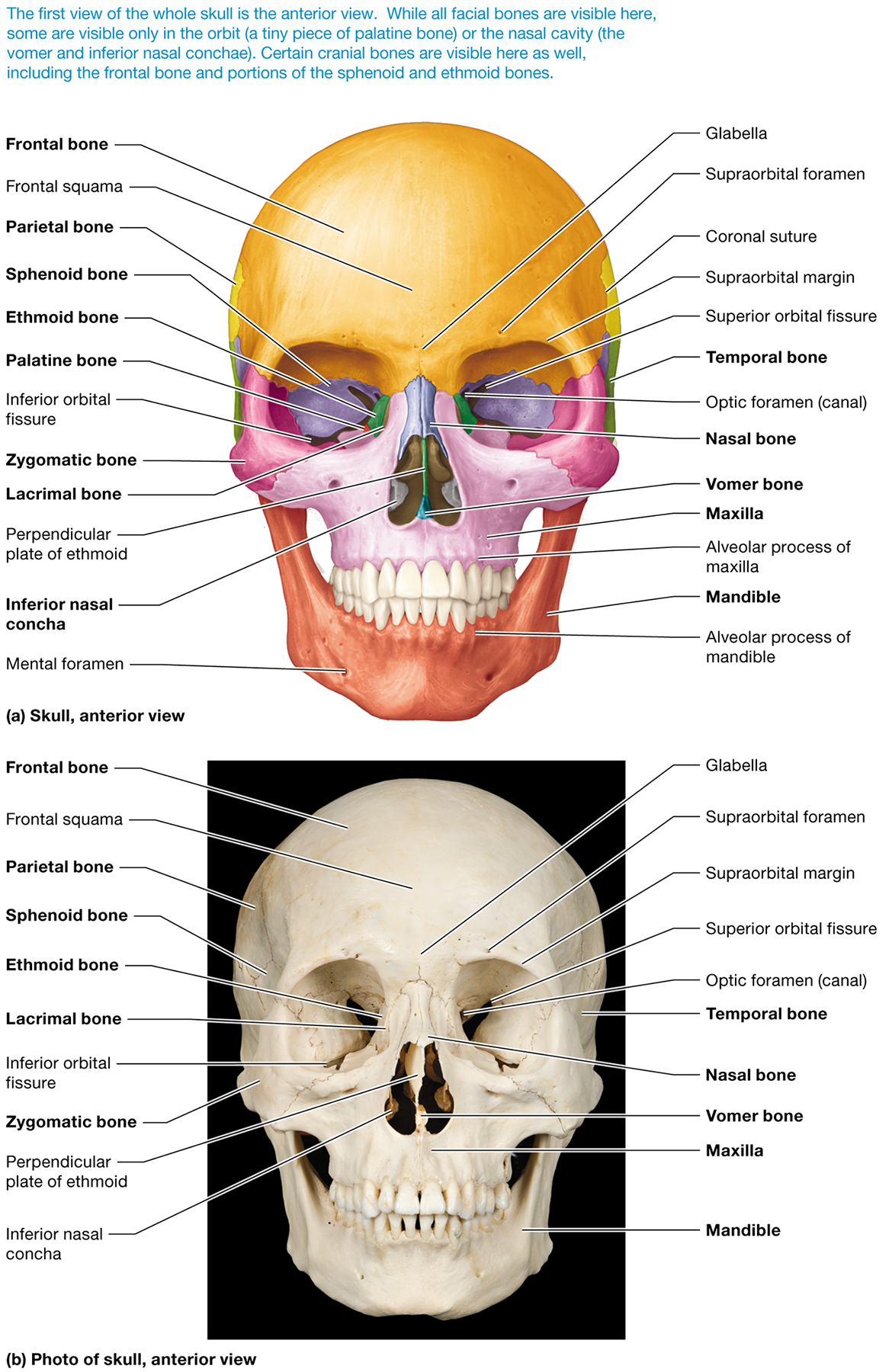
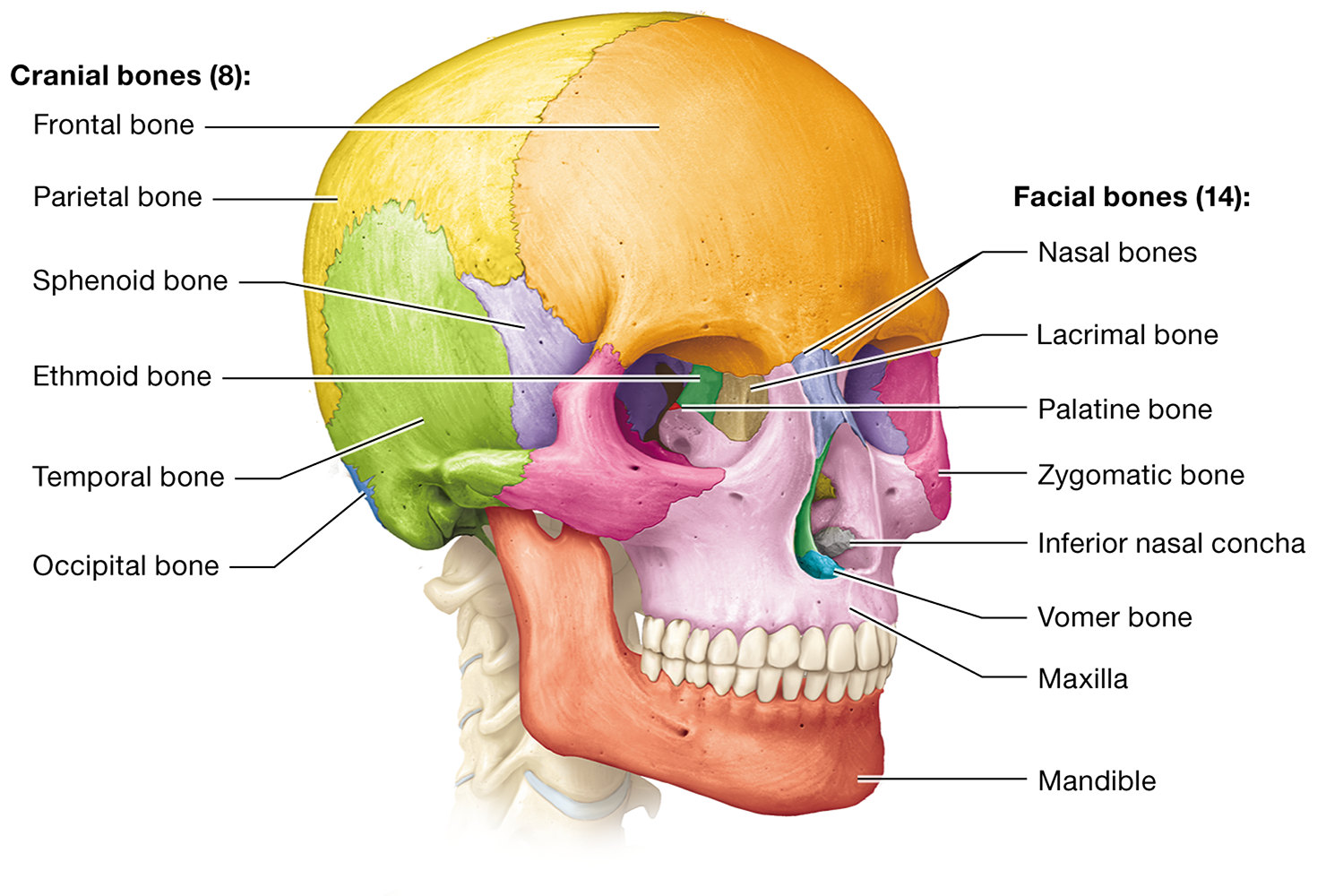
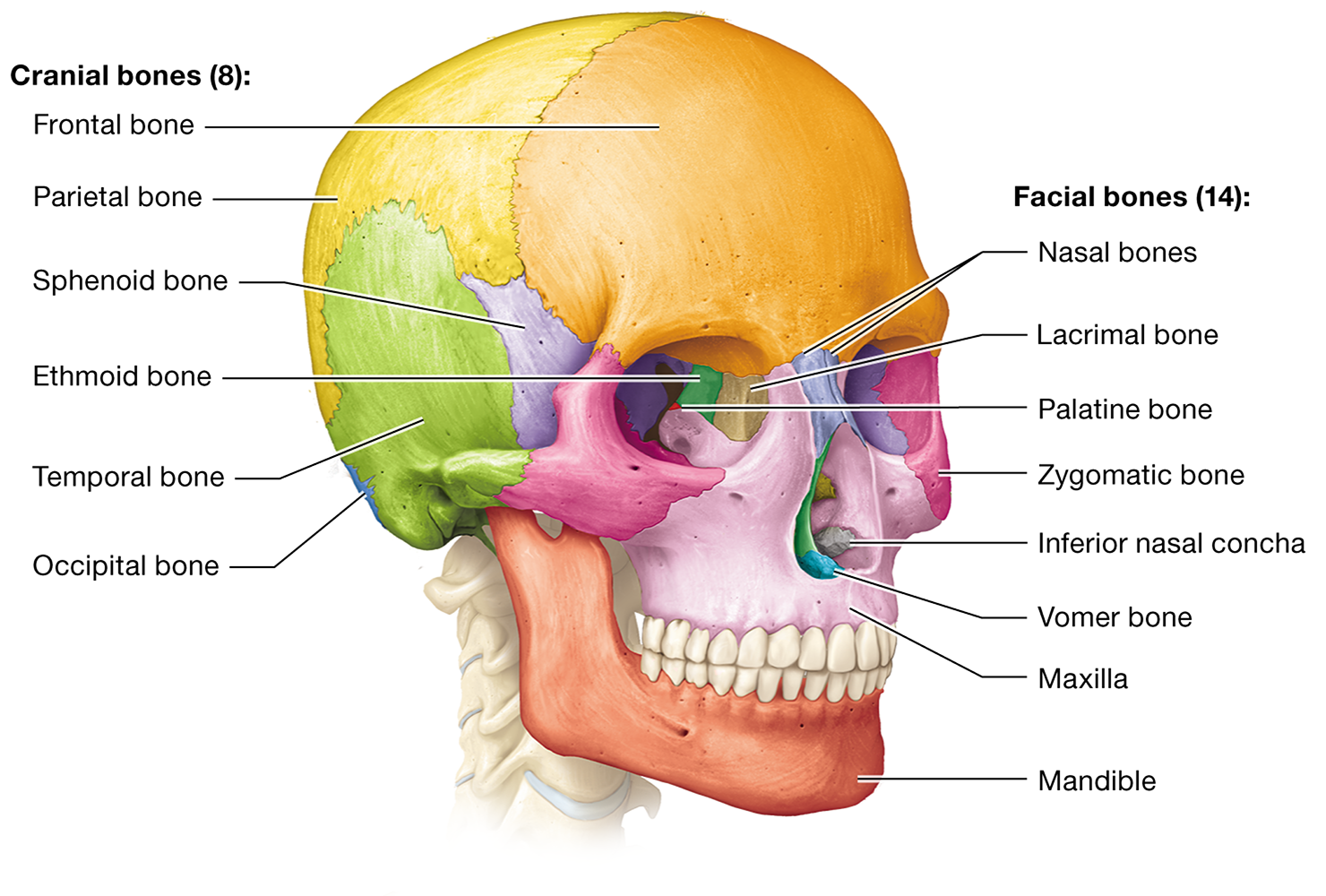
What are the eight cranial bones?
frontal, occipital, ethmoid, sphenoid, temporal (2), and parietal (2)
Which cranial bones are single, and which are paired?◦
Frontal, occipital, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones are single. Temporal and parietal bones are paired
What is the function of the cranial bones?
encase and protect the brain
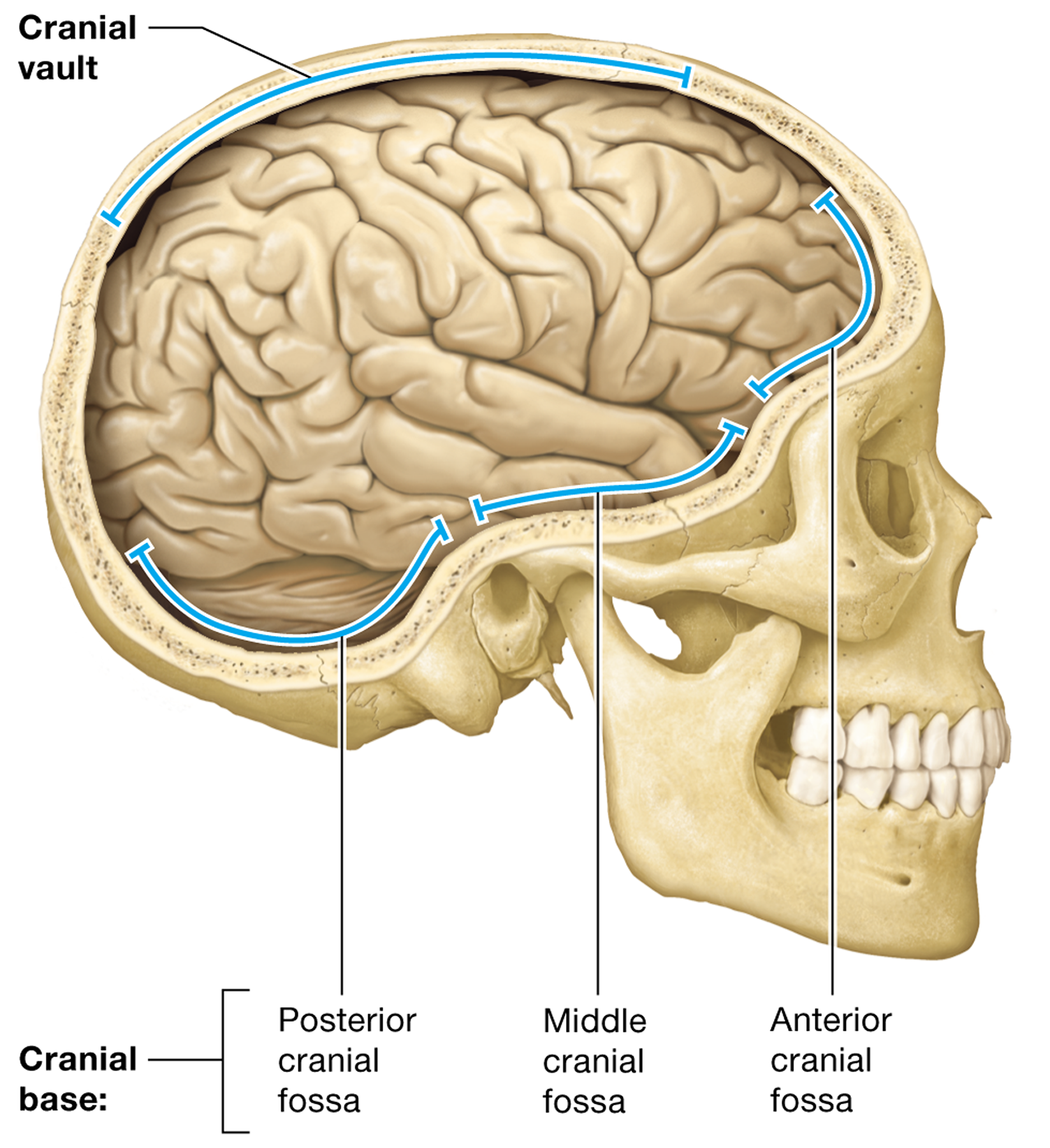
Which cranial bones form the cranial vault?
the frontal, parietal, and occipital bones
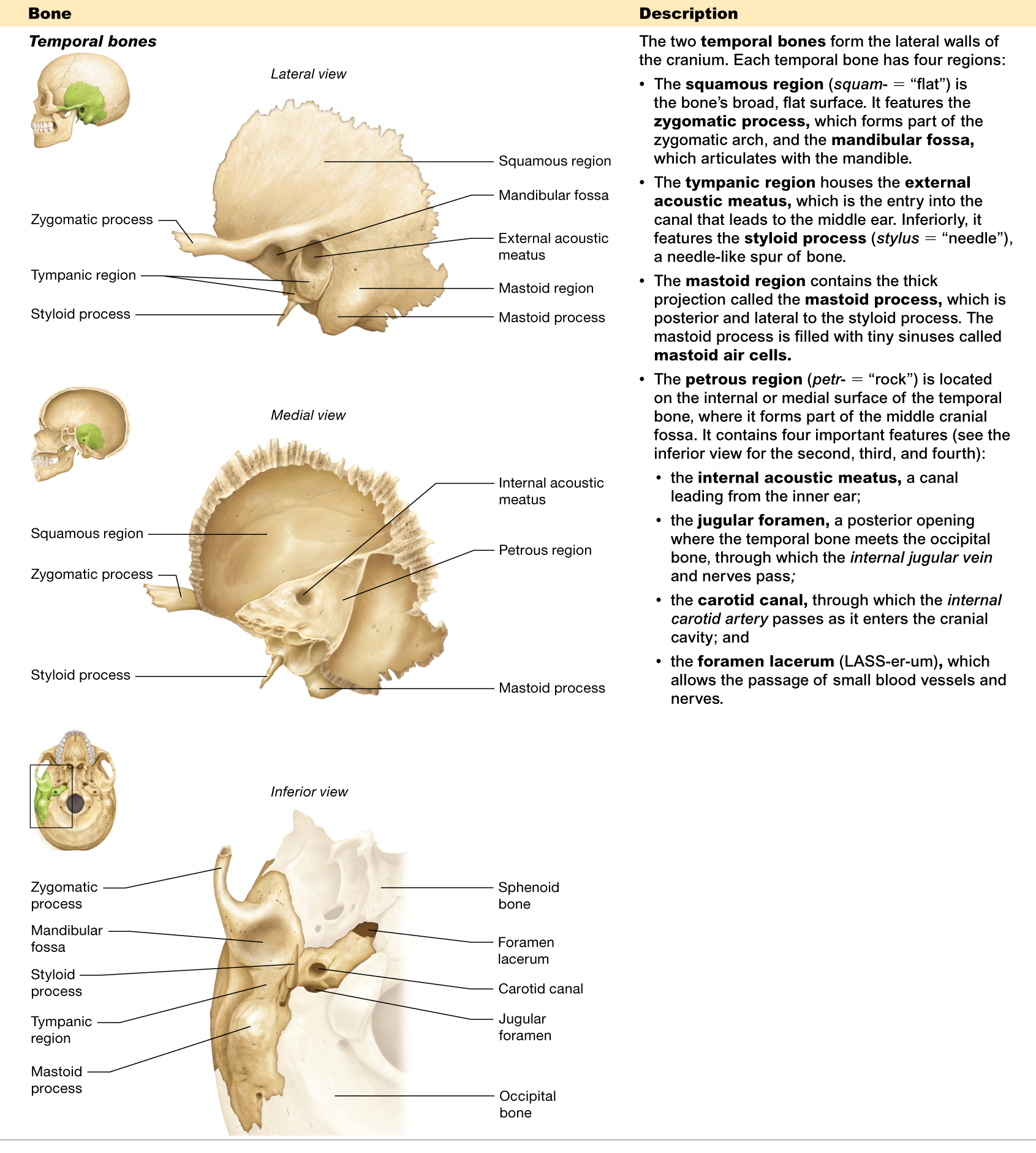
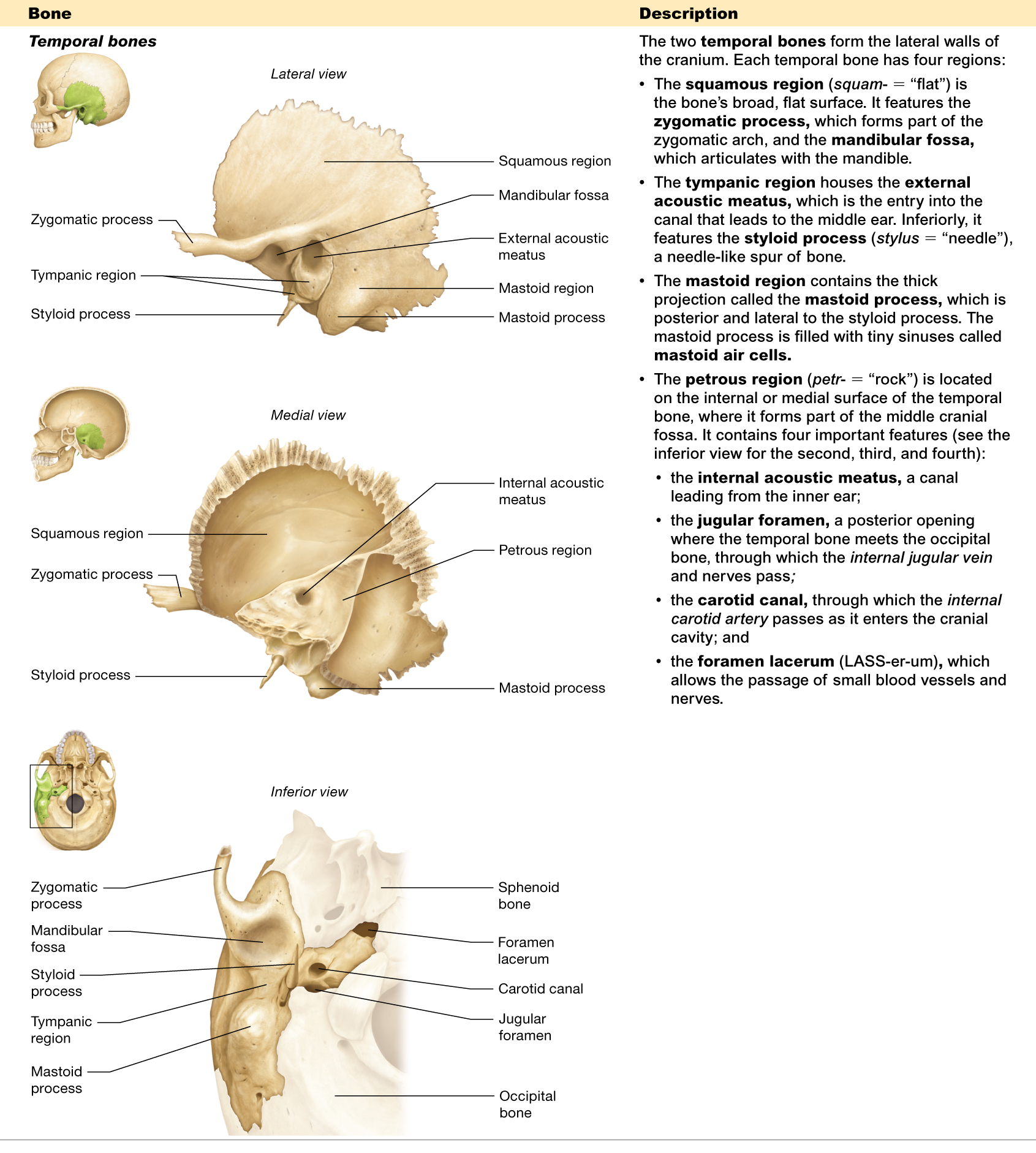
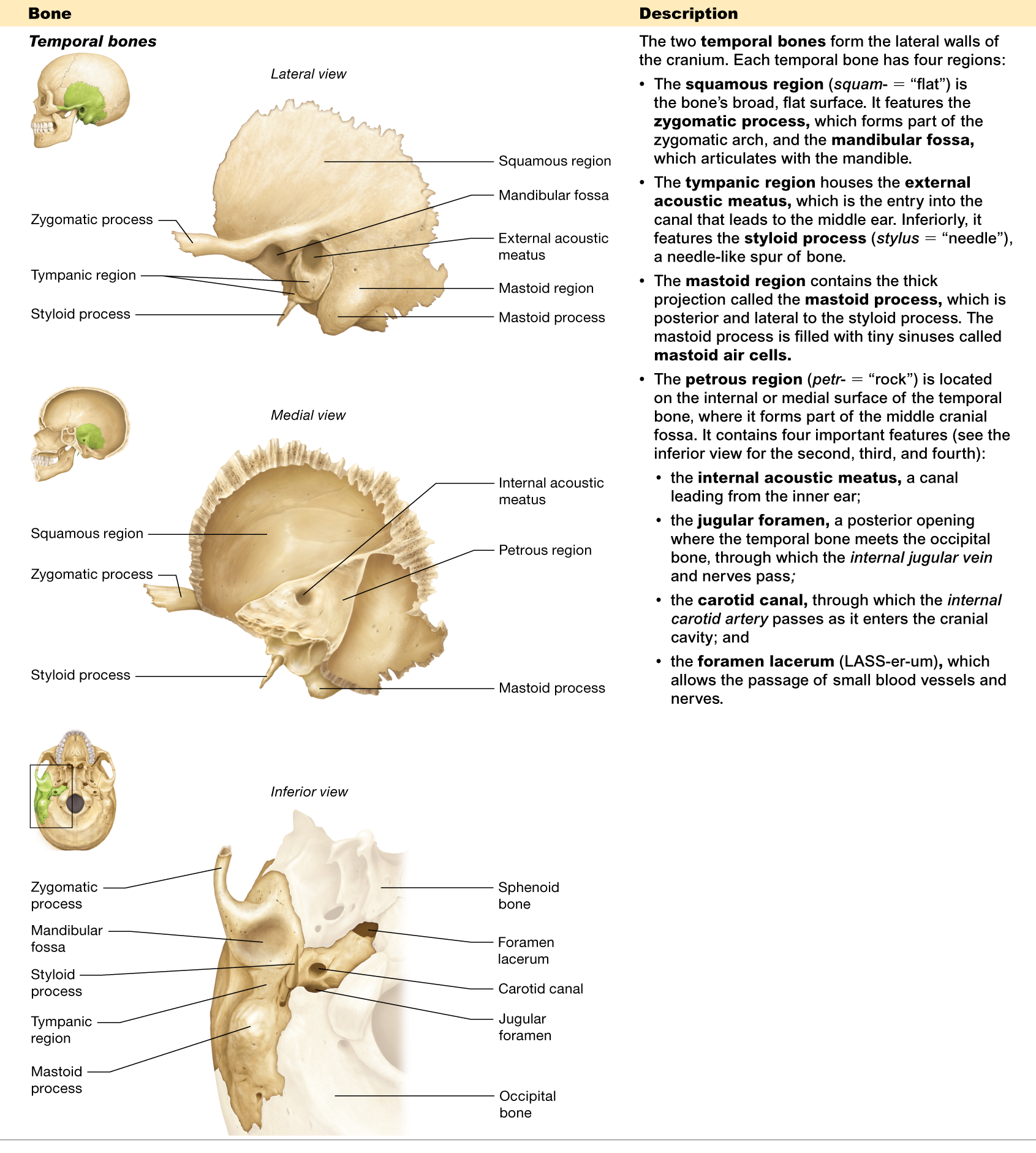
Name the four regions of the temporal bone.
squamous, tympanic, mastoid, and petrous
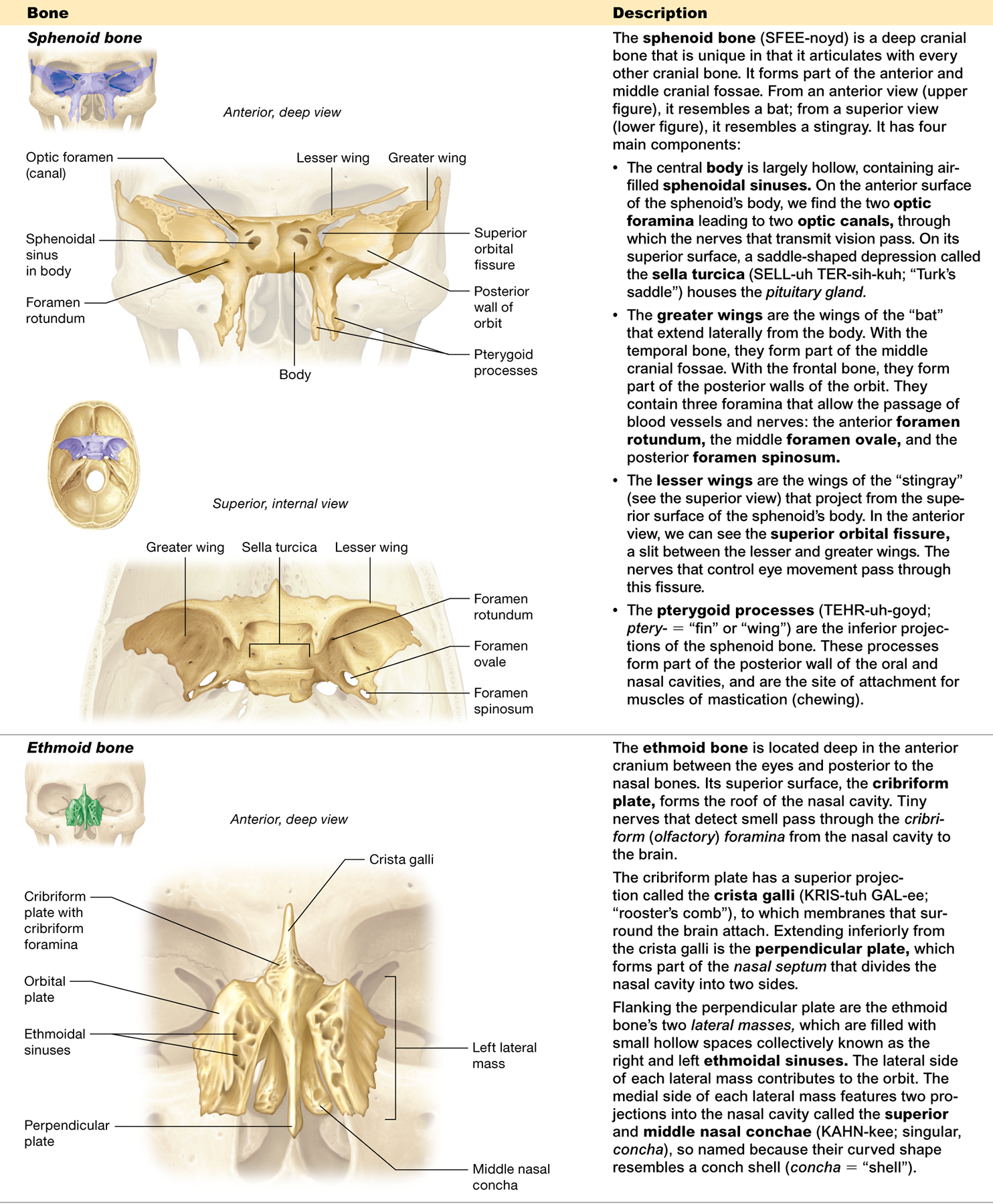
Which bones does the sphenoid bone articulate with?
every other cranial bone
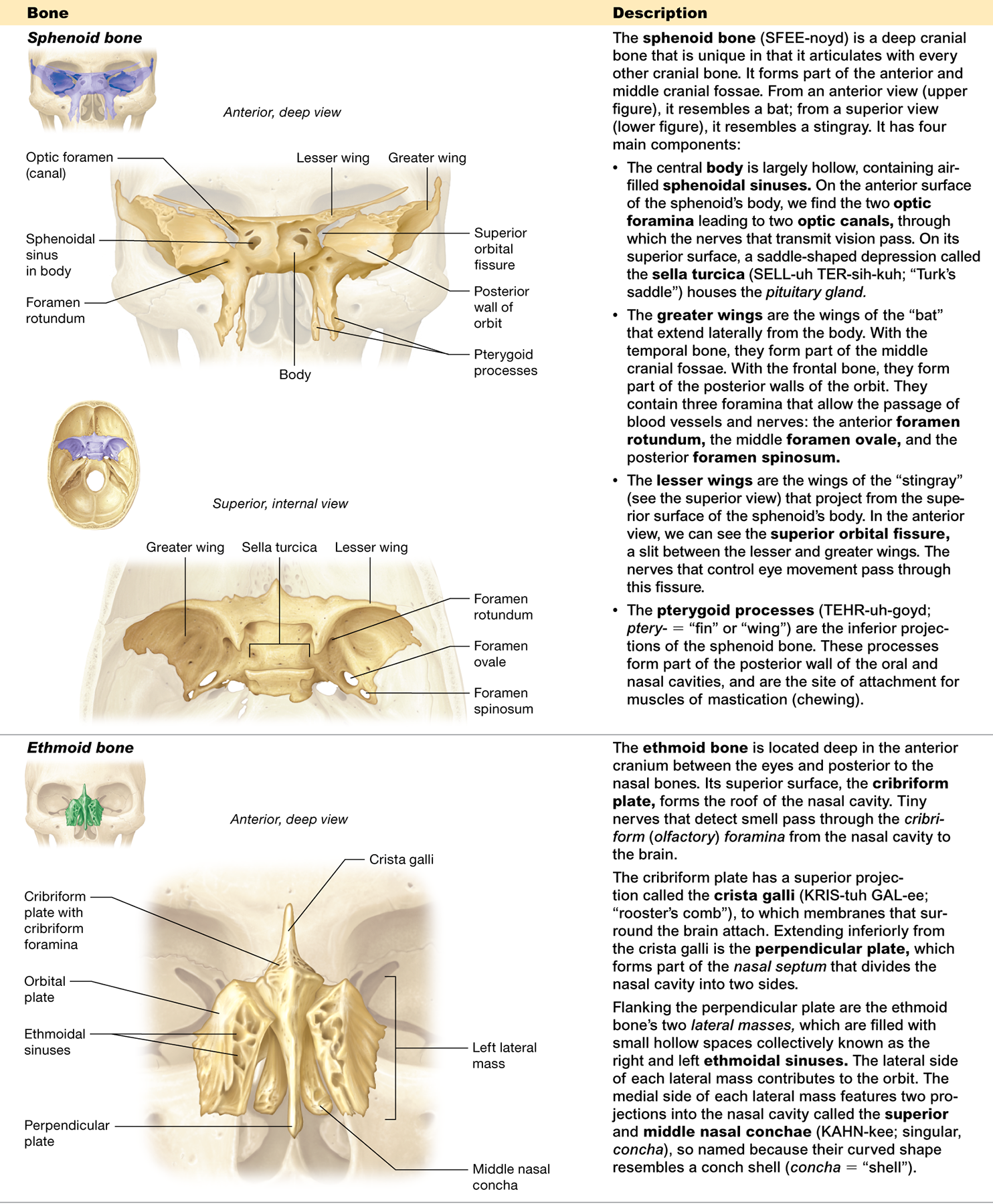
What are the main components of the sphenoid bone?
the body, greater wings, lesser wings, and pterygoid processes
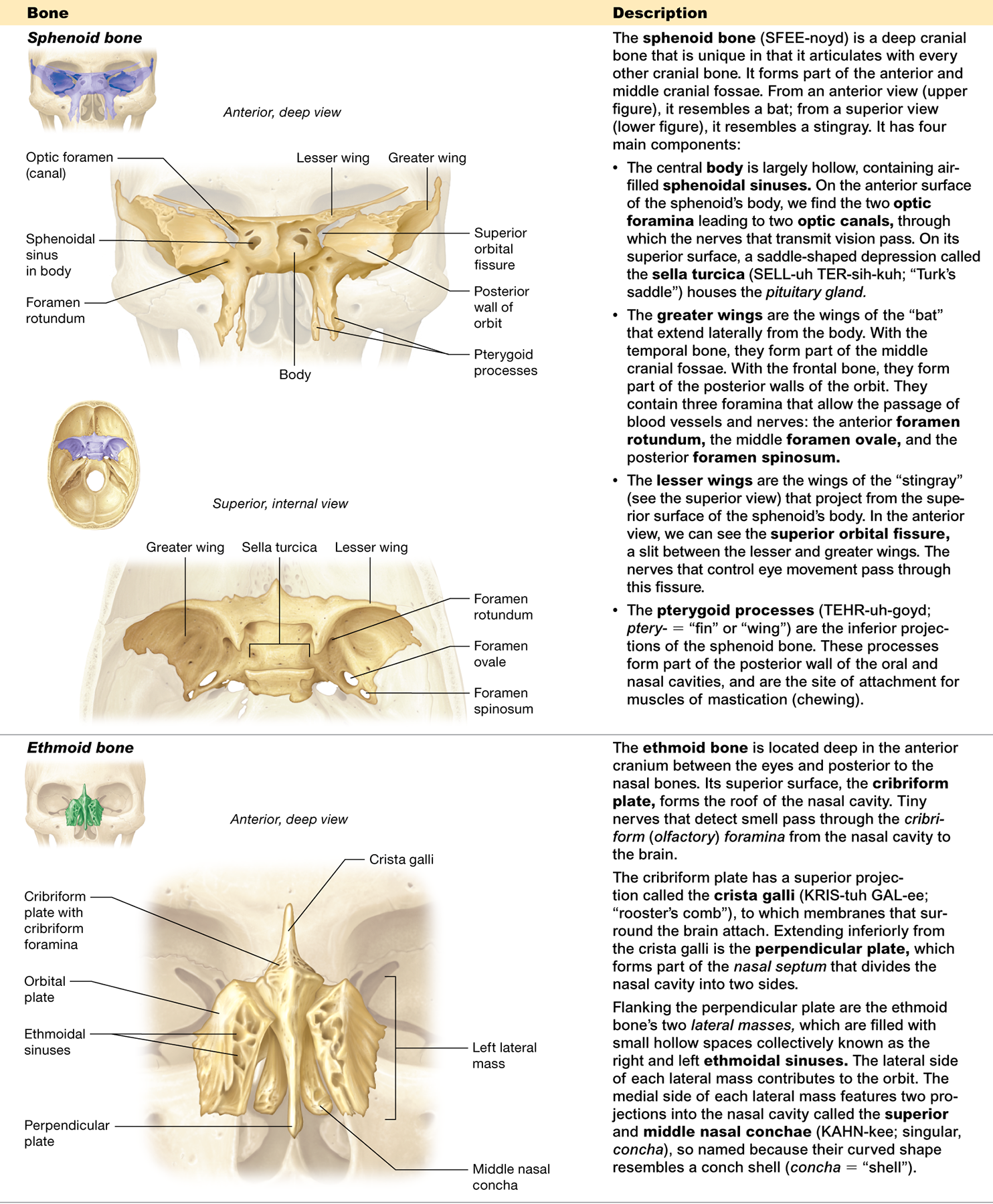
Which cranial bones contain sinuses?
frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and maxillary bones
"Four Empty Spaces Make Sinuses"
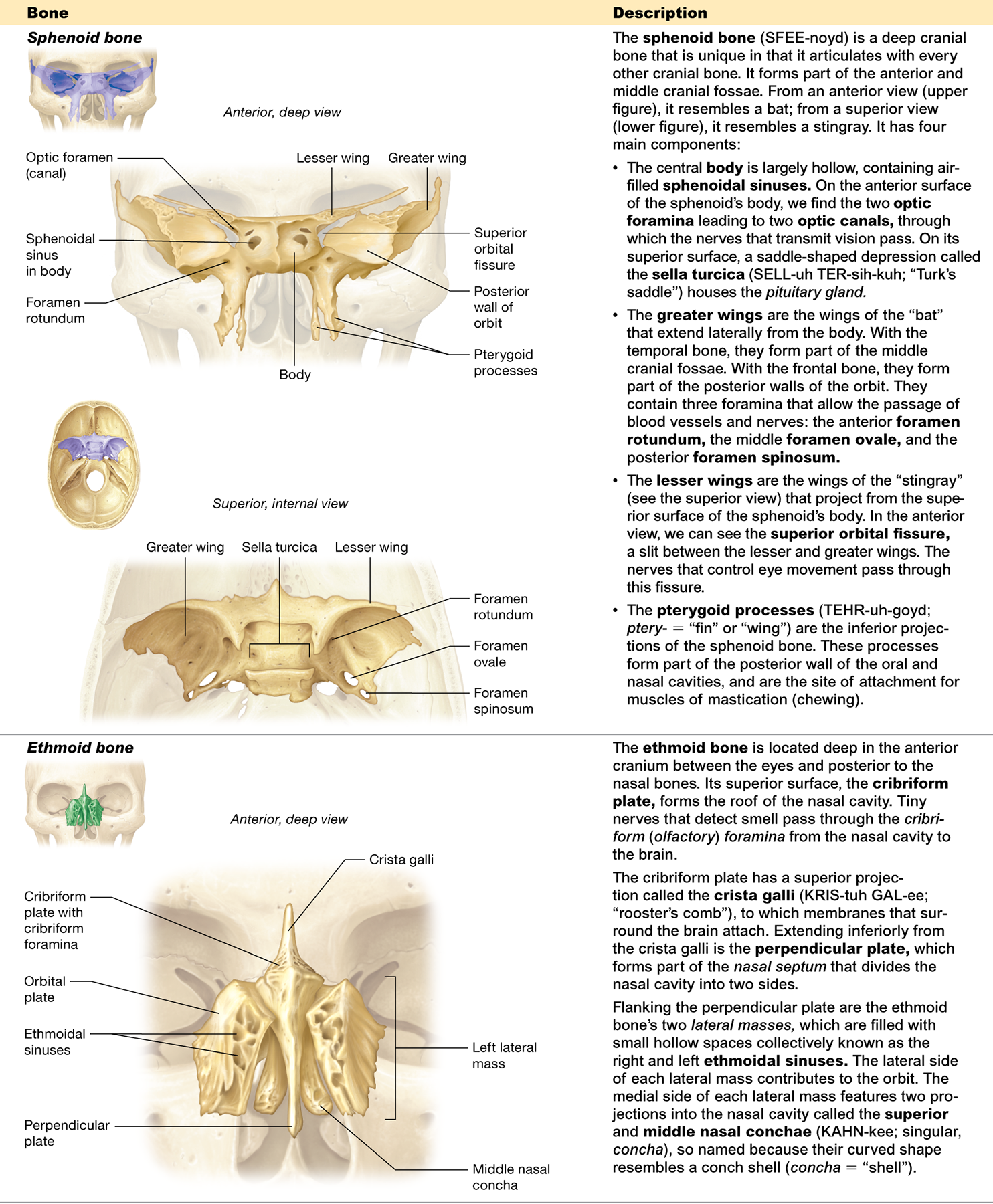
Describe the ethmoid bone.
located between the eyes, has a cribriform plate, crista galli, and contributes to the nasal cavity and orbits
What is the cribriform plate and where is it located?
on the superior surface of the ethmoid bone and forms the roof of the nasal cavity
What are the four main cranial sutures?
coronal, squamous, lambdoid, and sagittal
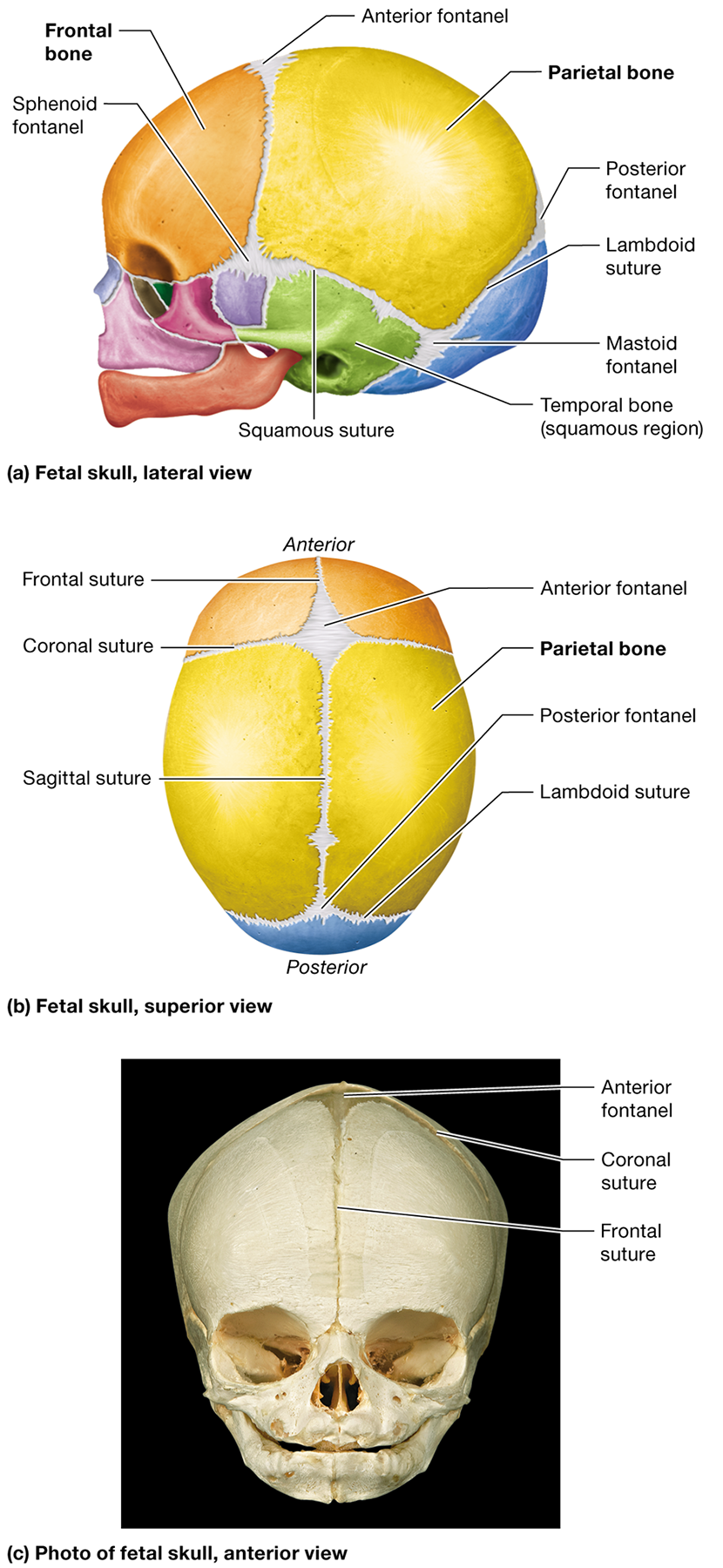
Where is the coronal suture located?
where the parietal bones meet the frontal bone
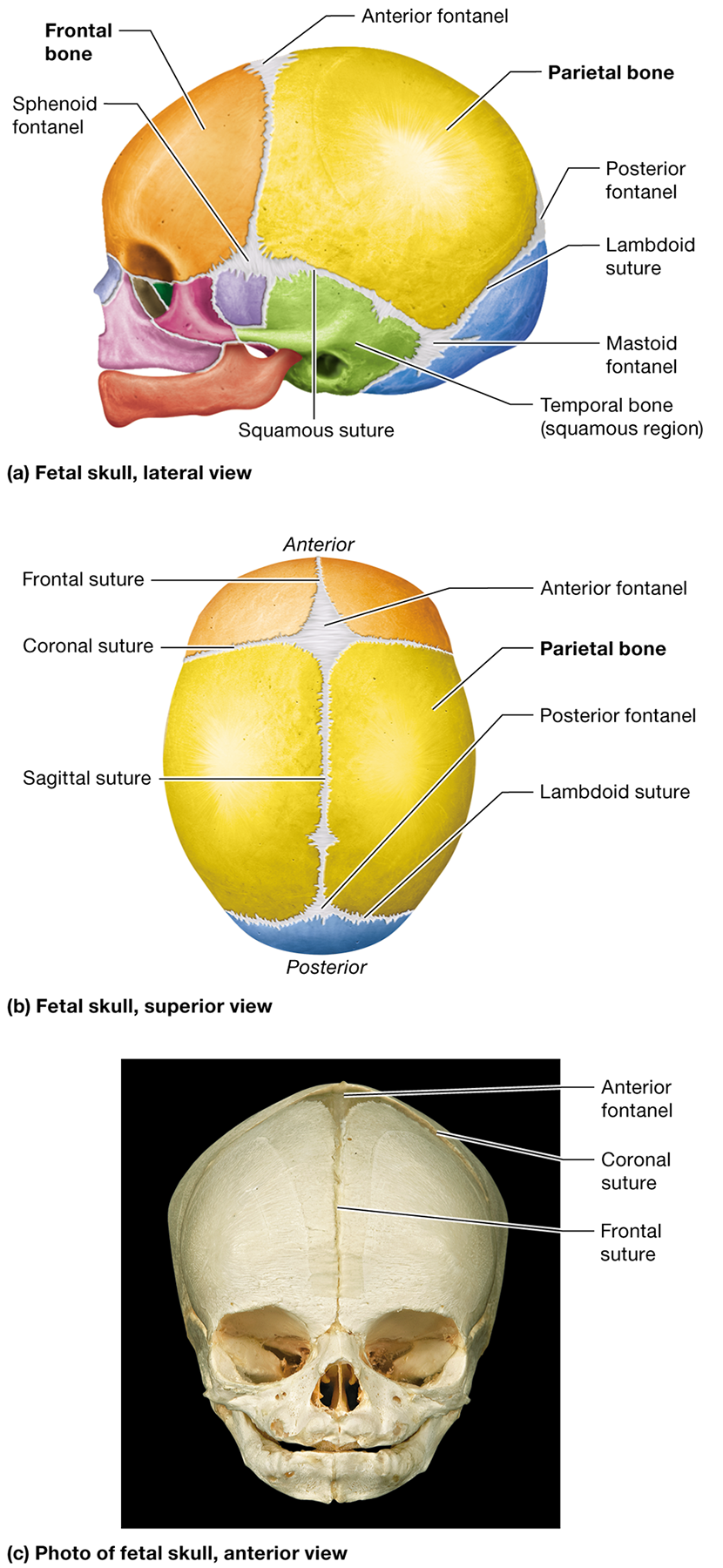
Which bones does the squamous suture unite?
unites the parietal and temporal bones
Where is the lambdoid suture located
between the parietal and occipital bones
What bones does the sagittal suture unite?
the two parietal bones
Describe the mastoid process.
a thick projection on the temporal bone, behind the ear
What is the sella turcica and what is its function?
a depression in the sphenoid bone that houses the pituitary gland
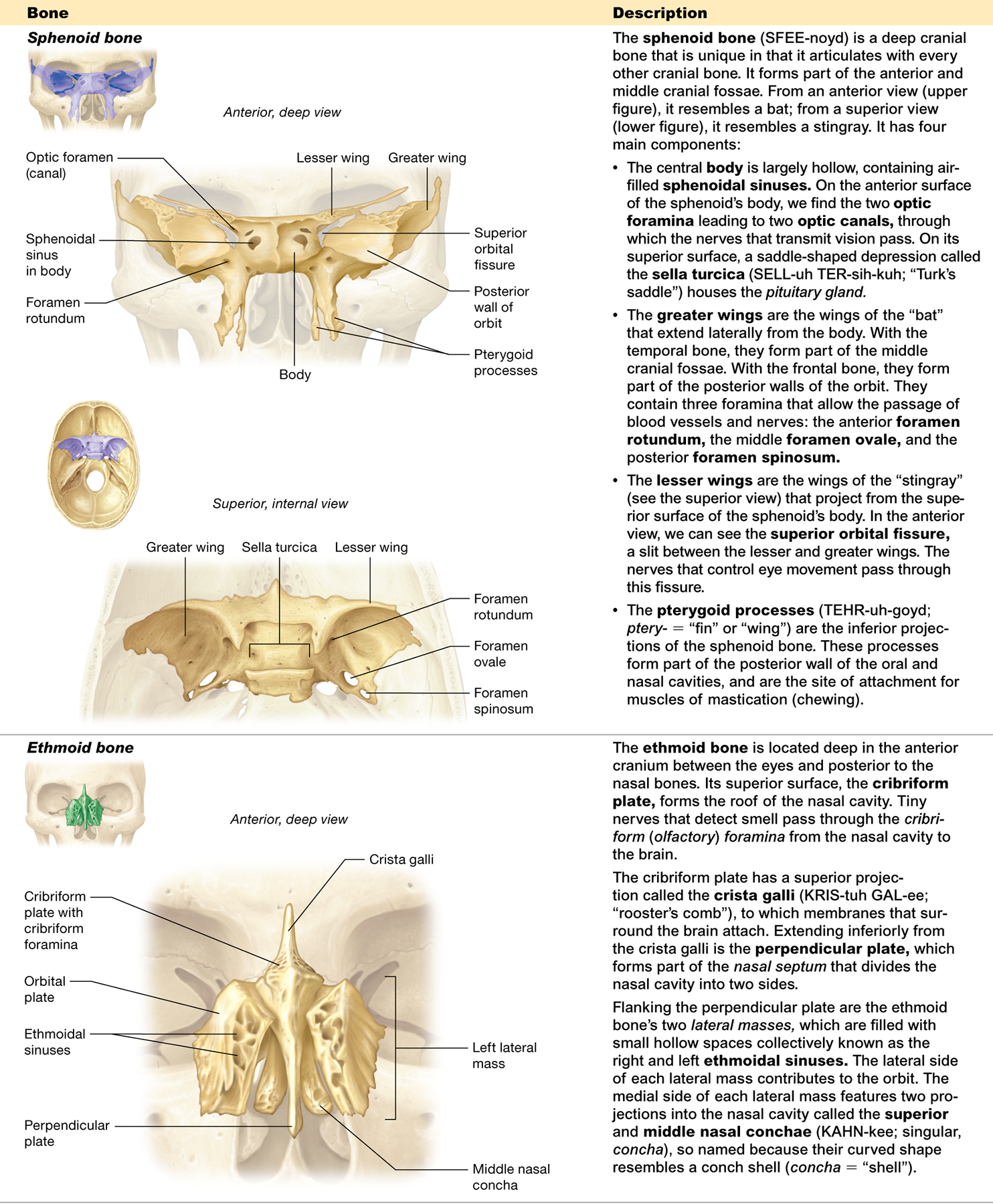
Describe the foramen magnum
a large opening in the occipital bone through which the spinal cord passes
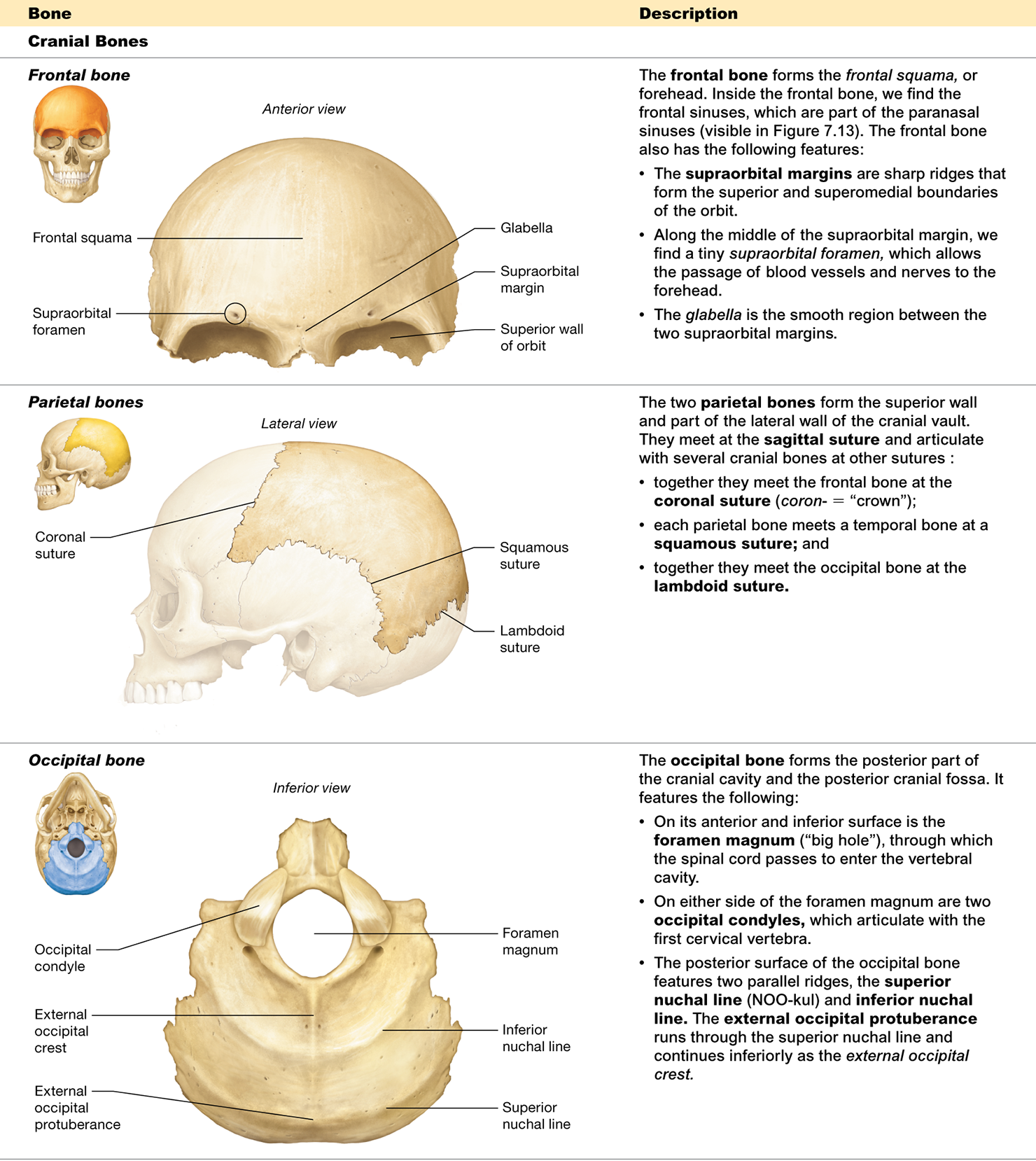
What is the function of the cribriform foramina?
tiny holes in the cribriform plate that allow nerves for smell to pass through
What is the crista galli
a projection on the ethmoid bone where membranes surrounding the brain attach
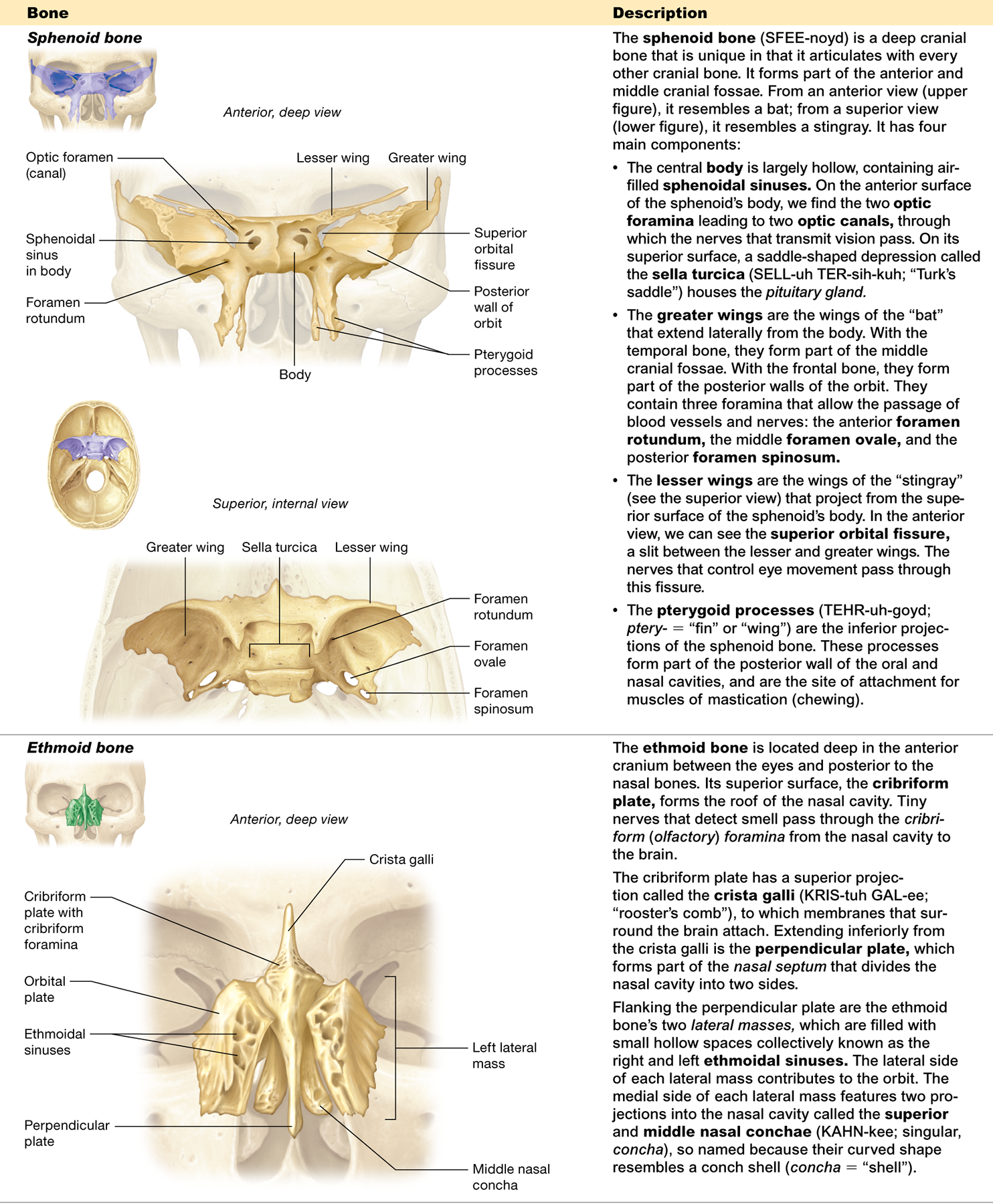
What structures pass through the optic canal?
allows the nerves that transmit vision to pass through
Where is the petrous region located?
is located on the internal/medial surface of the temporal bone
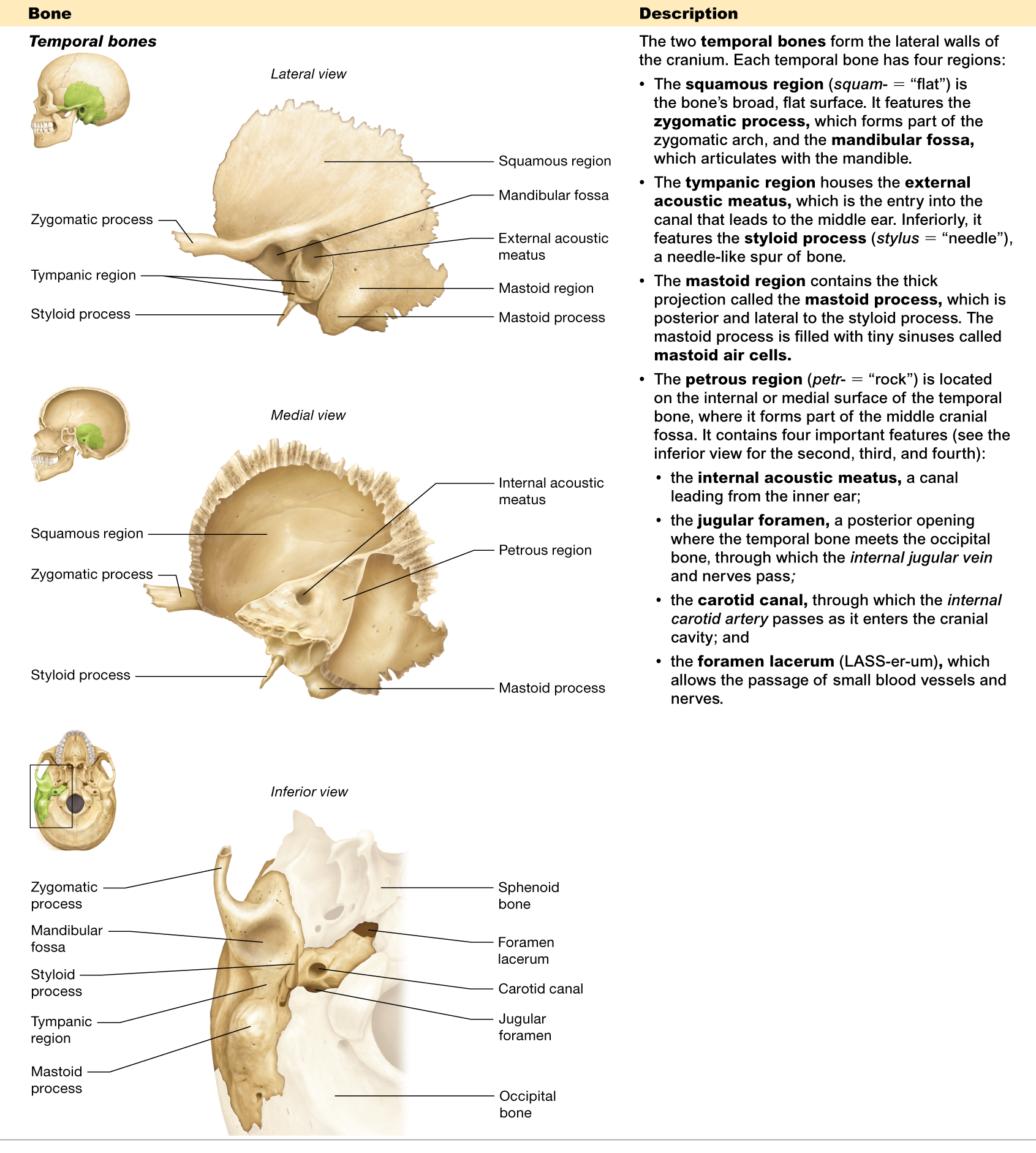
What passes through the jugular foramen?
is where the temporal and occipital bones meet, and the internal jugular vein passes through it
What structure passes through the carotid canal?
allows the internal carotid artery to pass through
What is the function of the external acoustic meatus?
the entry to the canal that leads to the middle ear
What is the function of the mandibular fossa?
articulates with the mandible
What is the function of the styloid process?
is a needle-like spur of bone
What is the pterygoid process?
an inferior projection of the sphenoid bone and is the site of attachment for muscles of mastication (chewing
What is the perpendicular plate?
forms part of the nasal septum
What is the function of the occipital condyles?
articulate with the atlas (C1)
Where is the squamous region located?
is the broad, flat surface of the temporal bone
What is the foramen lacerum?
allows the passage of small blood vessels and nerves
What is the sphenoidal sinus?
an air-filled space within the sphenoid bone
What are the superior and inferior orbital fissures?
slits in the sphenoid bone that allow passage of nerves for eye movement
Where is the anterior cranial fossa located?
in the frontal part of the cranial cavity
Where is the middle cranial fossa located?
in the middle part of the cranial cavity
Where is the posterior cranial fossa located?
in the posterior part of the cranial cavity
What are the 14 facial bones?
the paired maxillary, zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal, palatine, and inferior nasal conchal bones, as well as the unpaired mandible and vomer
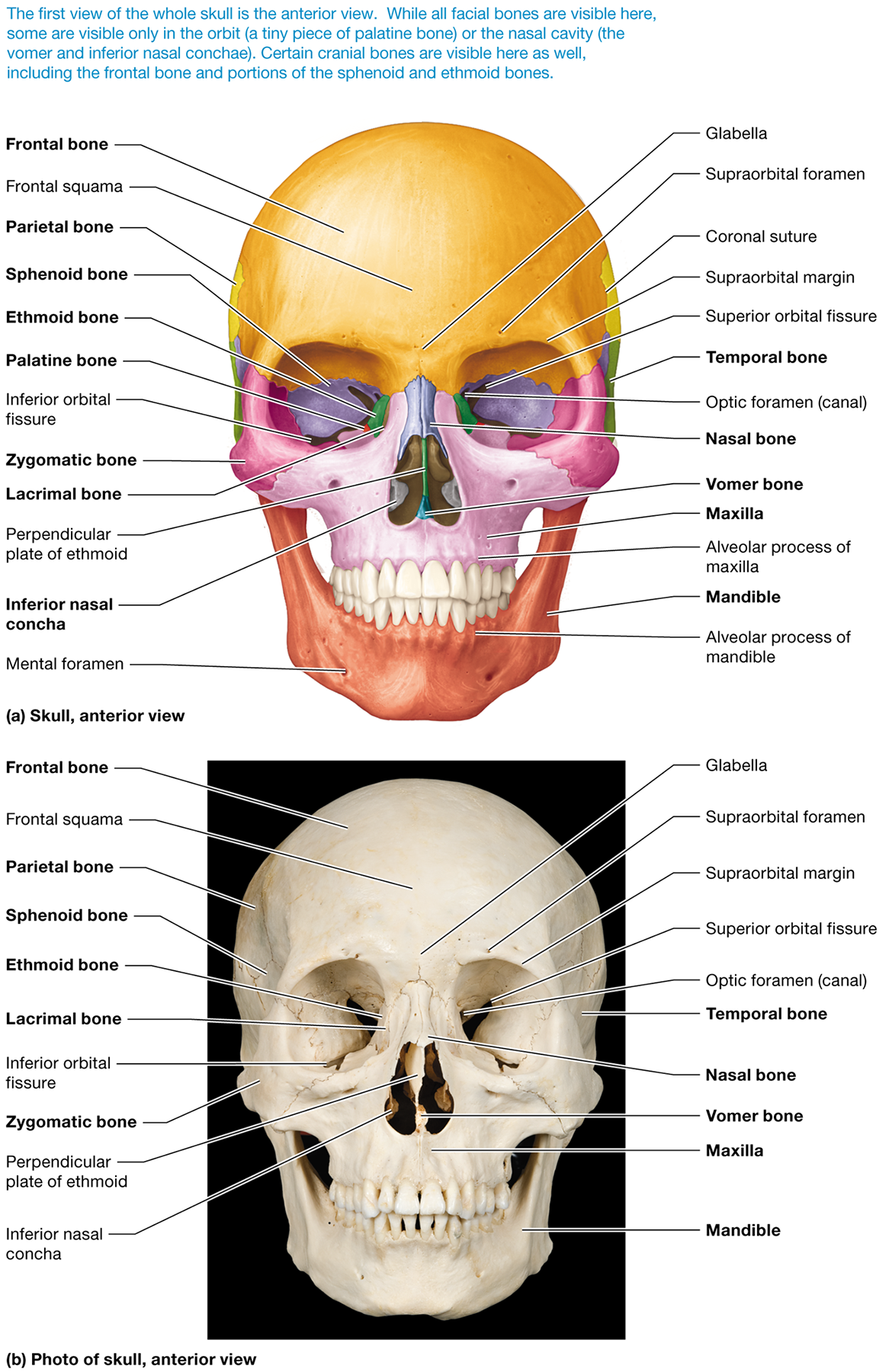
What is the function of the facial bones?
form the framework for the face
Which facial bones are single and which are paired?
The mandible and vomer are unpaired, while the maxillary, zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal, palatine, and inferior nasal conchal bones are paired
Which is the only skull bone that moves?
mandible (the lower jaw bone)
Which facial bones contribute to the orbit “funny Eyes See Many People looking zesty”
The maxilla, zygomatic, lacrimal, and palatine bones
Which facial bone is also known as the lower jaw bone?
The mandible
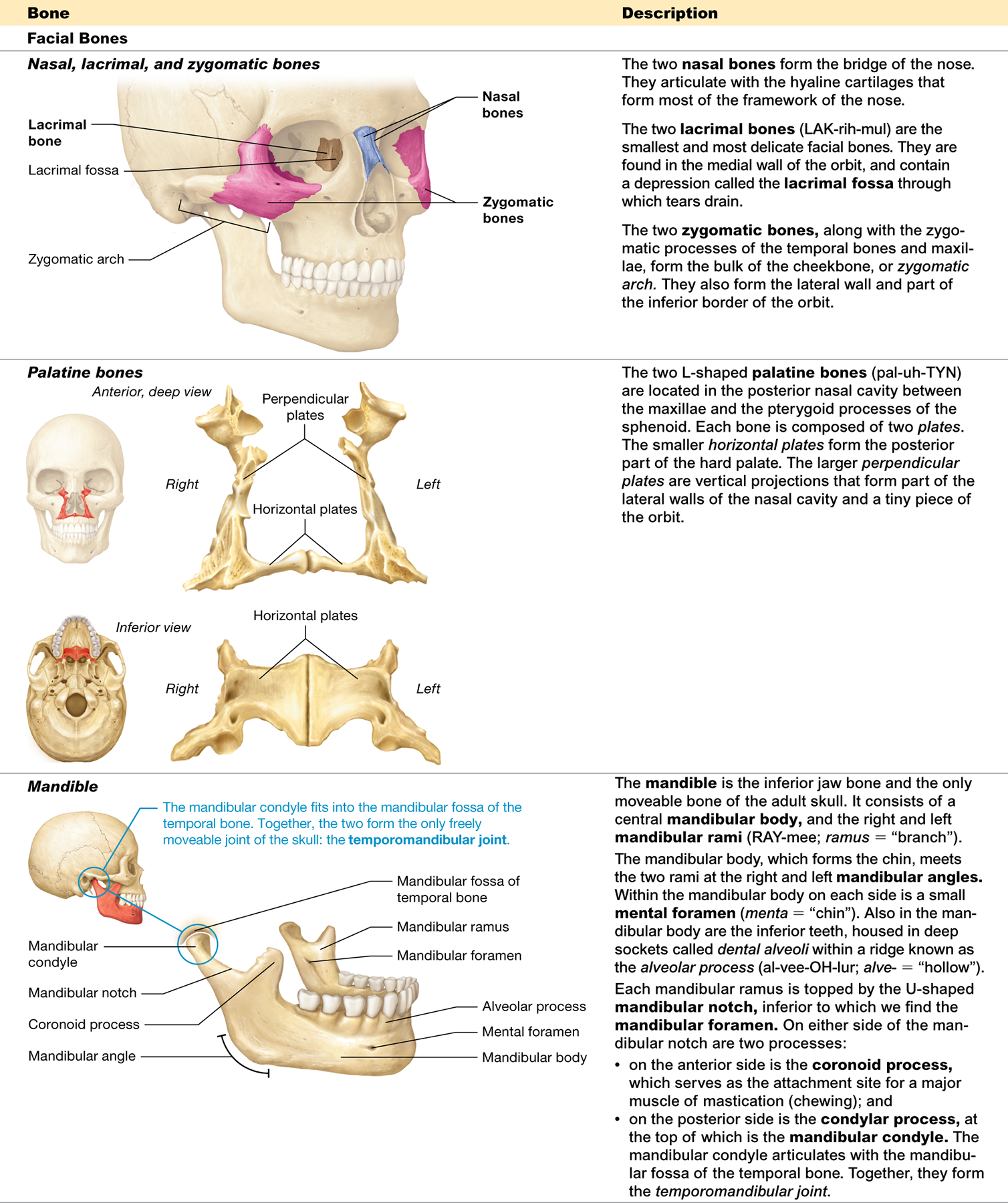
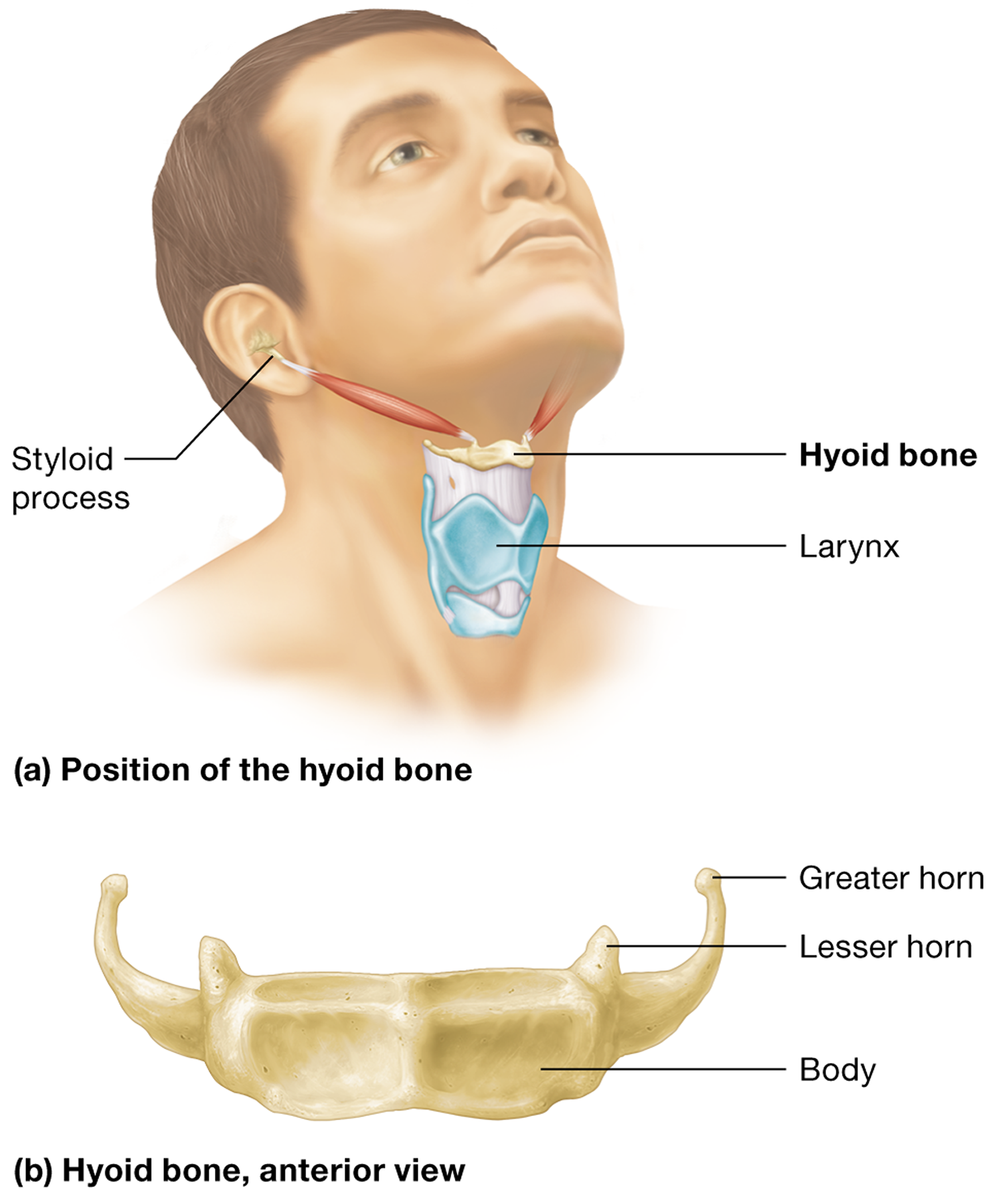
What is the only facial bone that doesn't articulate with any other bone?
The hyoid bone. It is suspended by muscles and ligaments
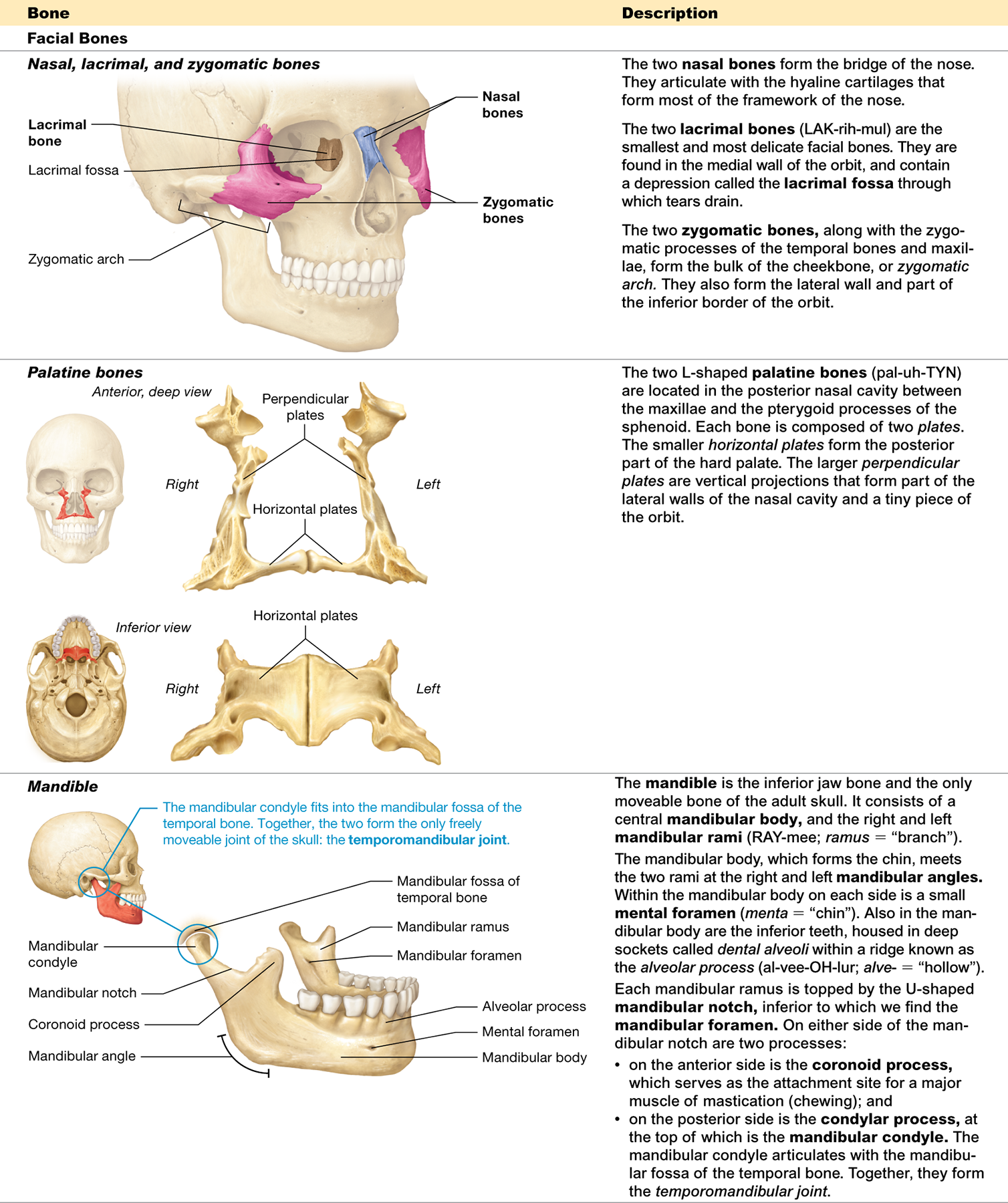
Which bones form the cheekbones?
The zygomatic bones
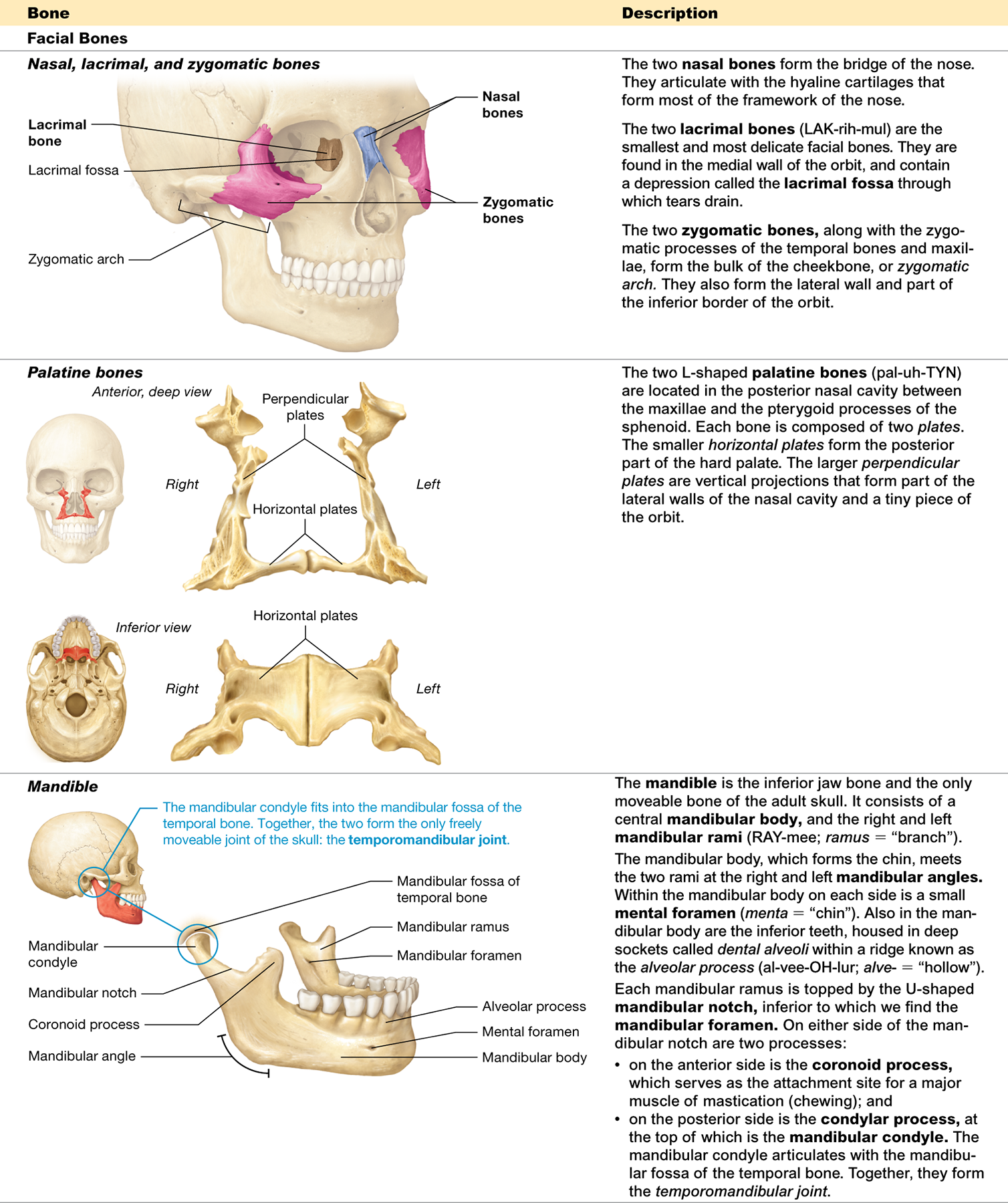
Which facial bones contribute to the inferomedial walls of the orbits?
The maxillae
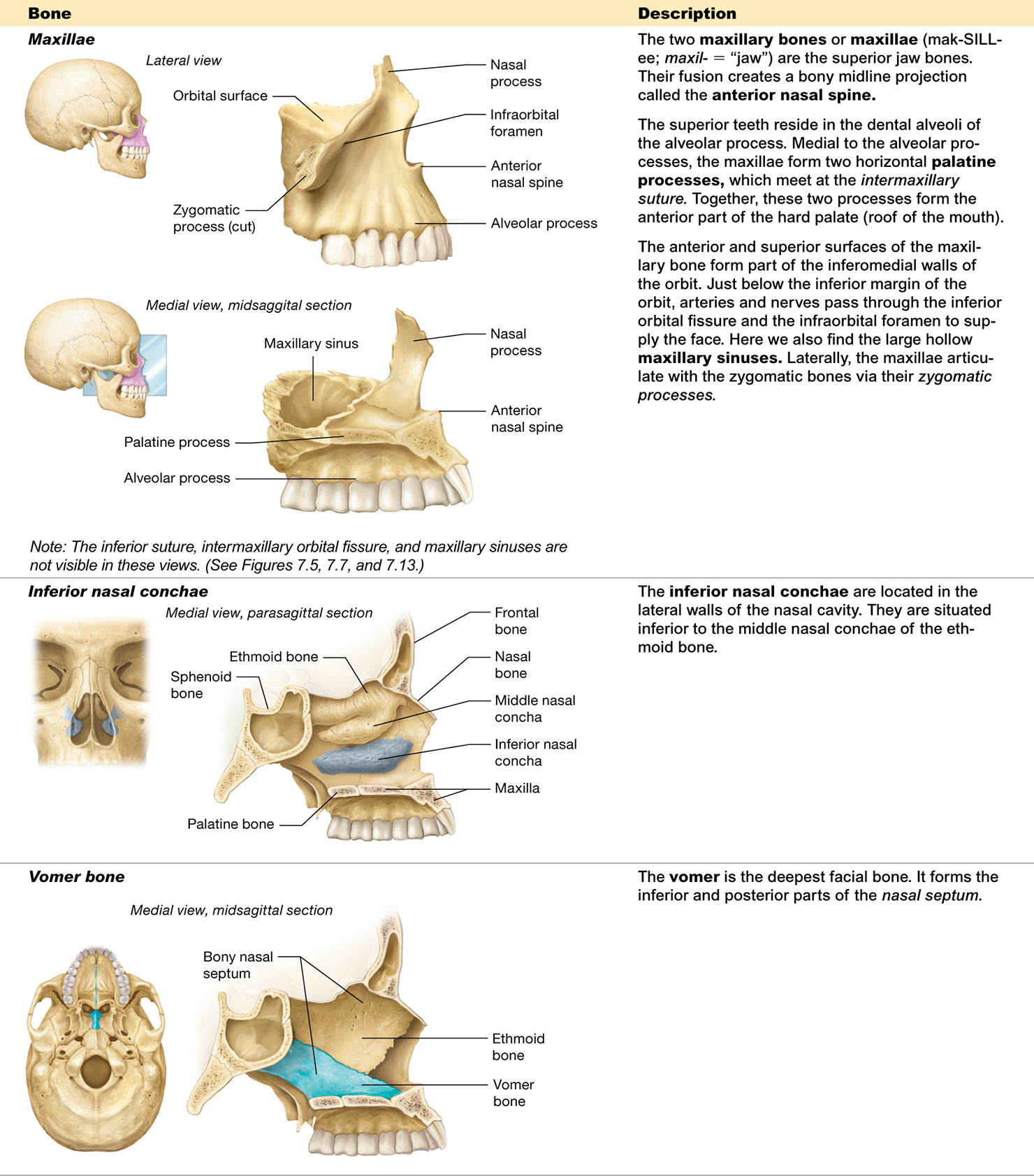
What two bones form the bony nasal septum?
The vomer and the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone
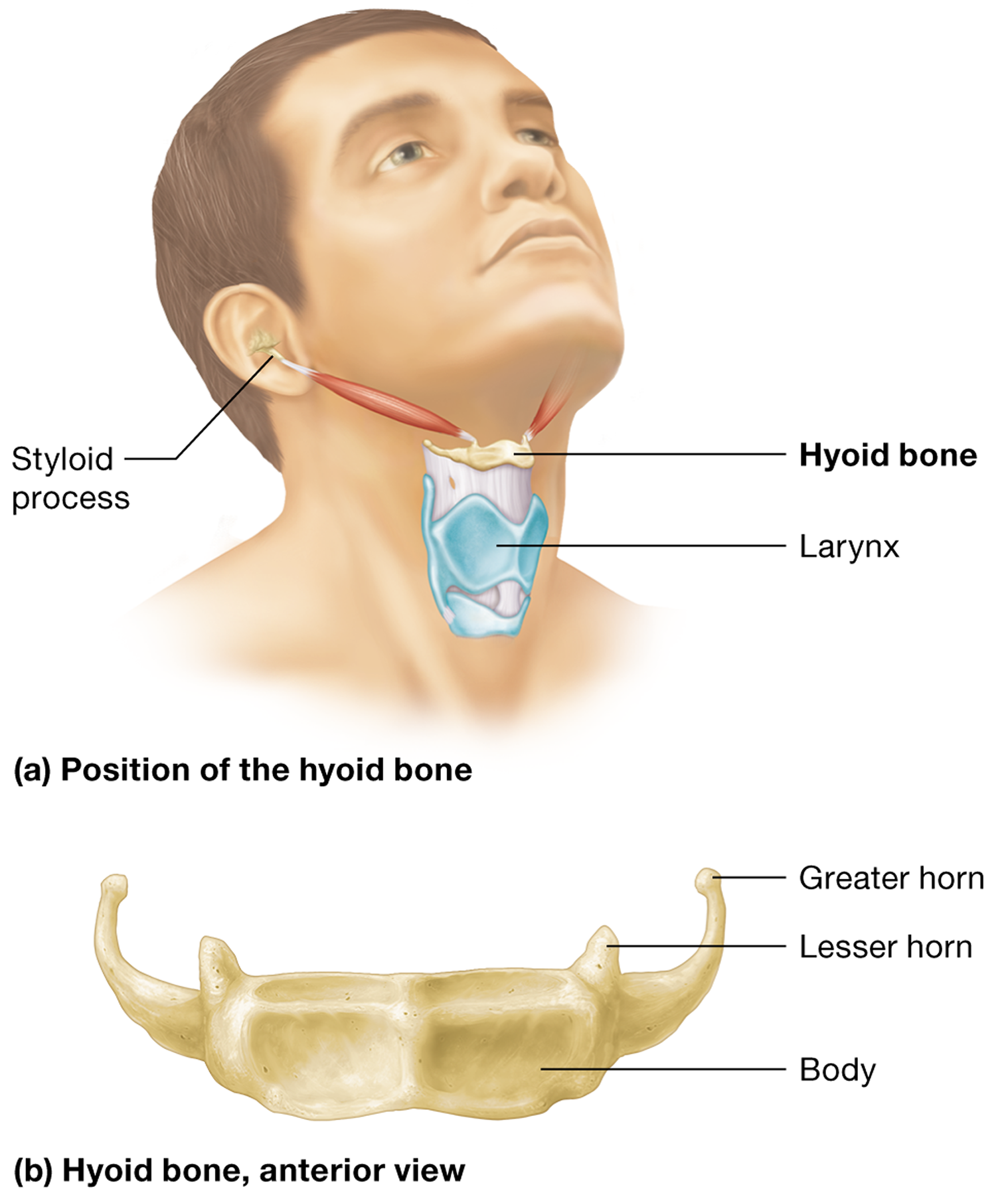
What is the function of the hyoid bone?
serves as an attachment point for numerous muscles, including those involved in swallowing and speech
Which bones form the anterior part of the hard palate (roof of the mouth)?
The palatine processes of the maxillae
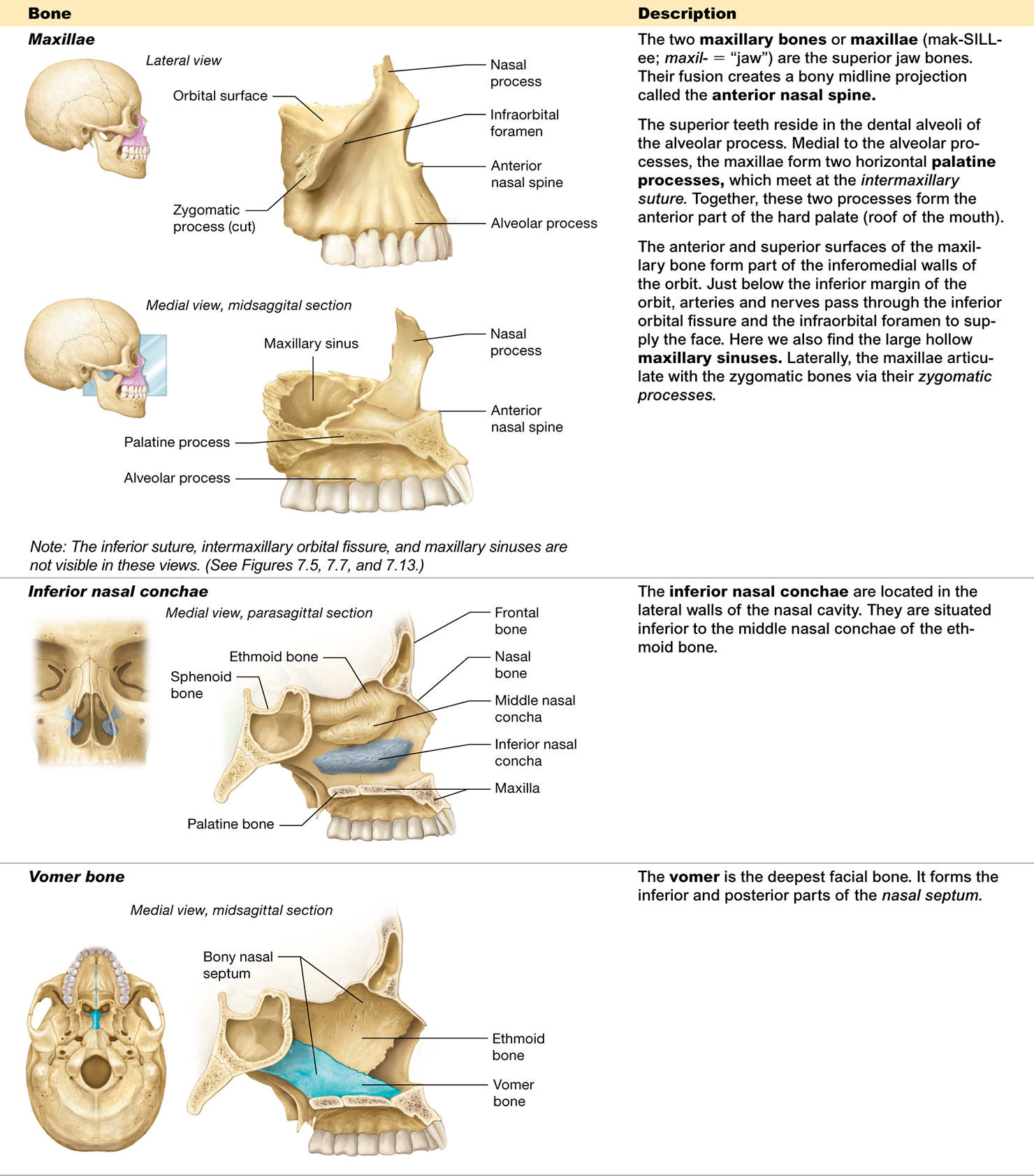
What facial bones are located inside the nasal cavity? "Every Massive Nose Picks Some Interesting Vapors."
The inferior nasal conchae, vomer, palatine bones, parts of ethmoid and maxilla.
What facial bone forms the inferior and posterior part of the nasal septum?
the vomer
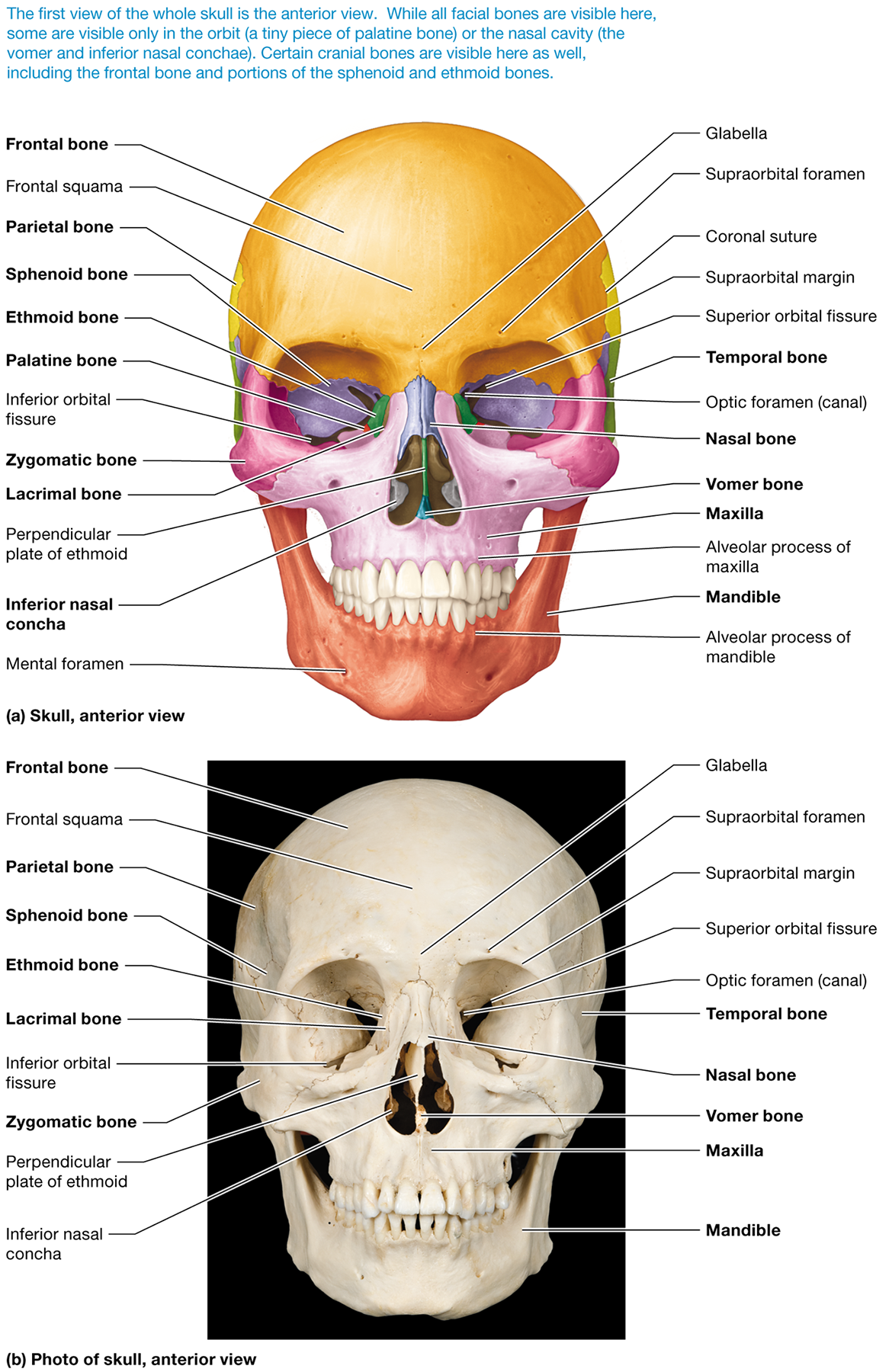
.
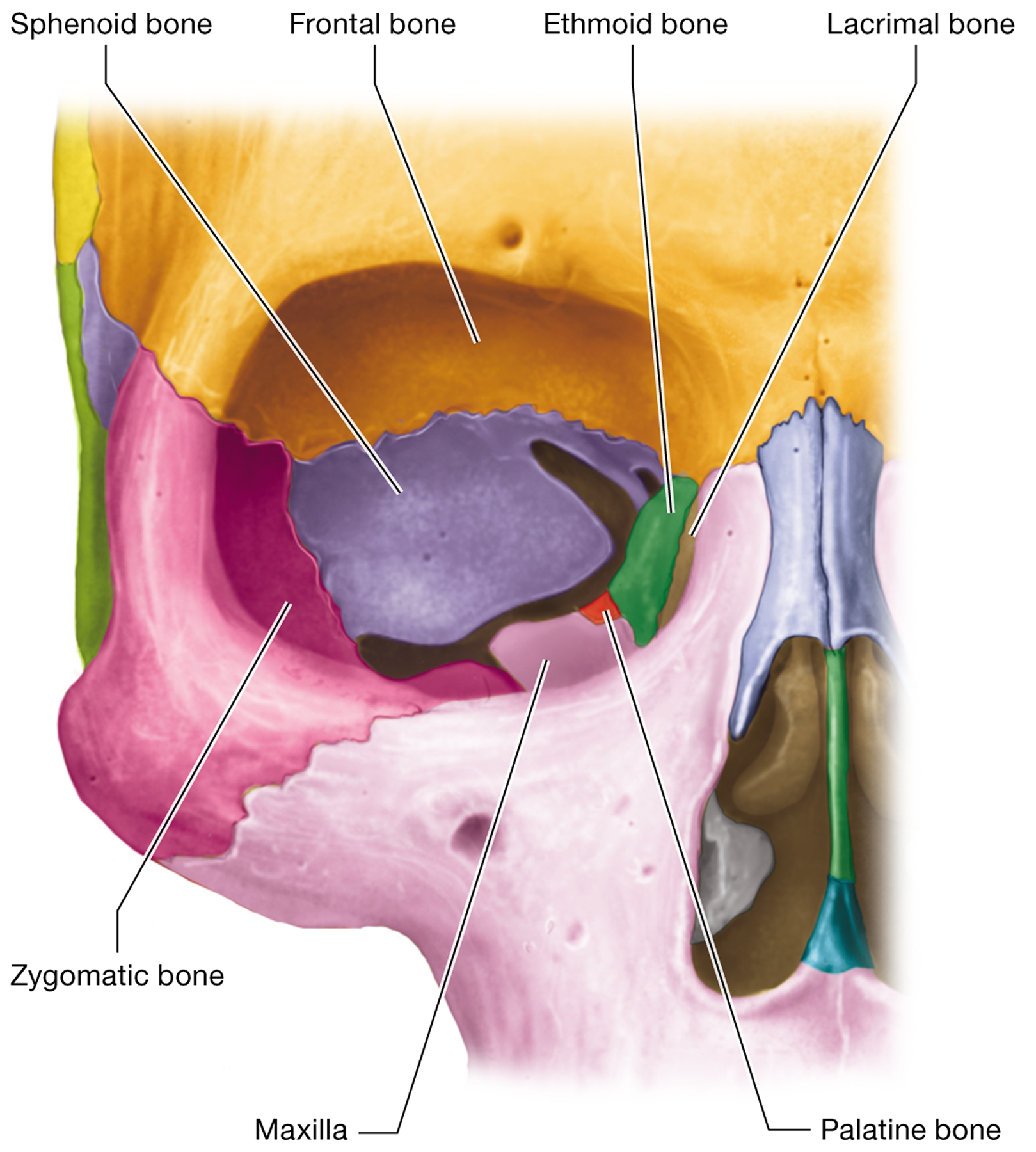
What facial bone is located between the eyes and contains a fossa for the lacrimal sac?
The lacrimal bone
What structure is formed by the fusion of the two maxillary bones?
The anterior nasal spine
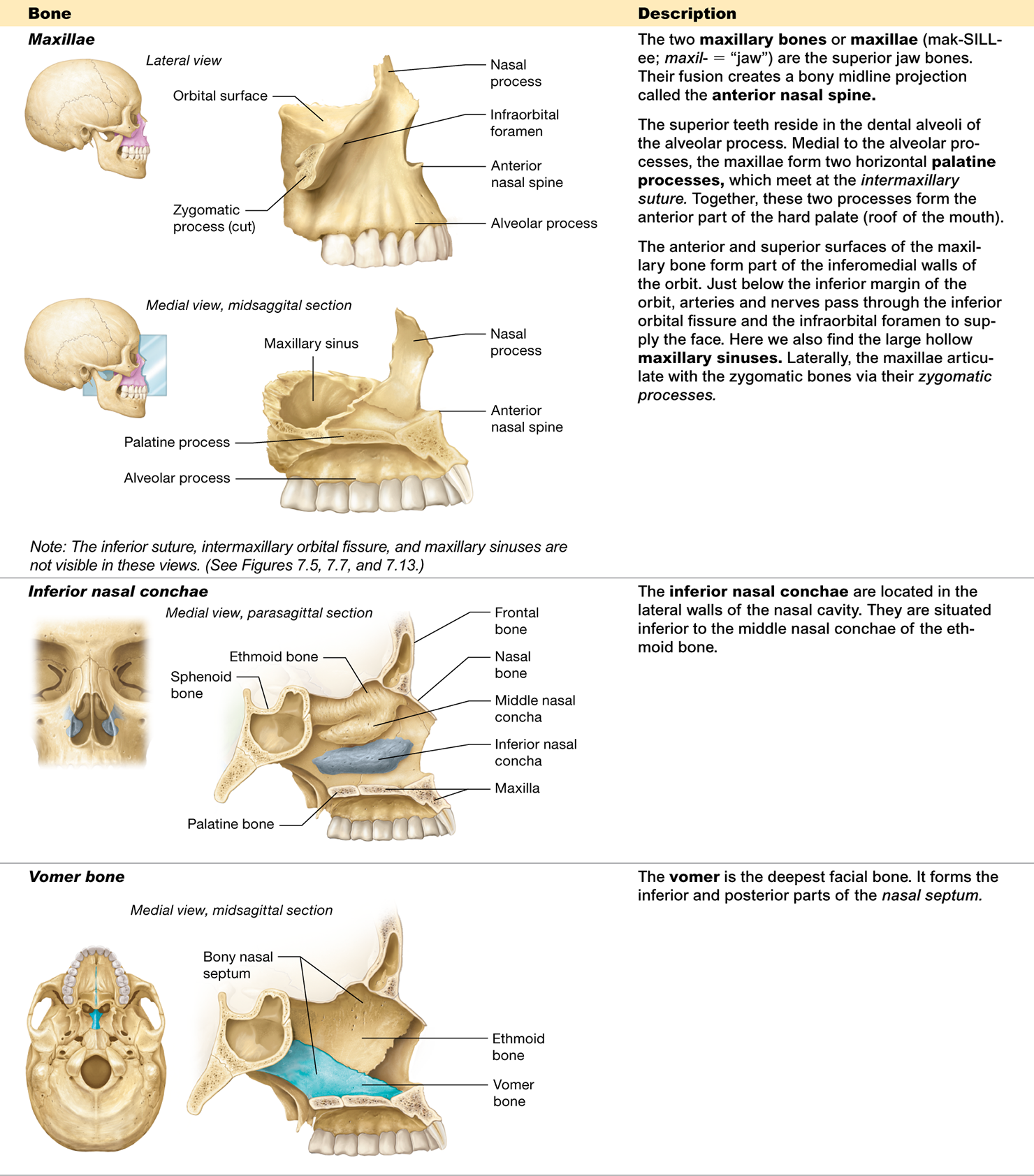
What part of the temporal bone does the hyoid bone attach to via ligaments?
The styloid processes
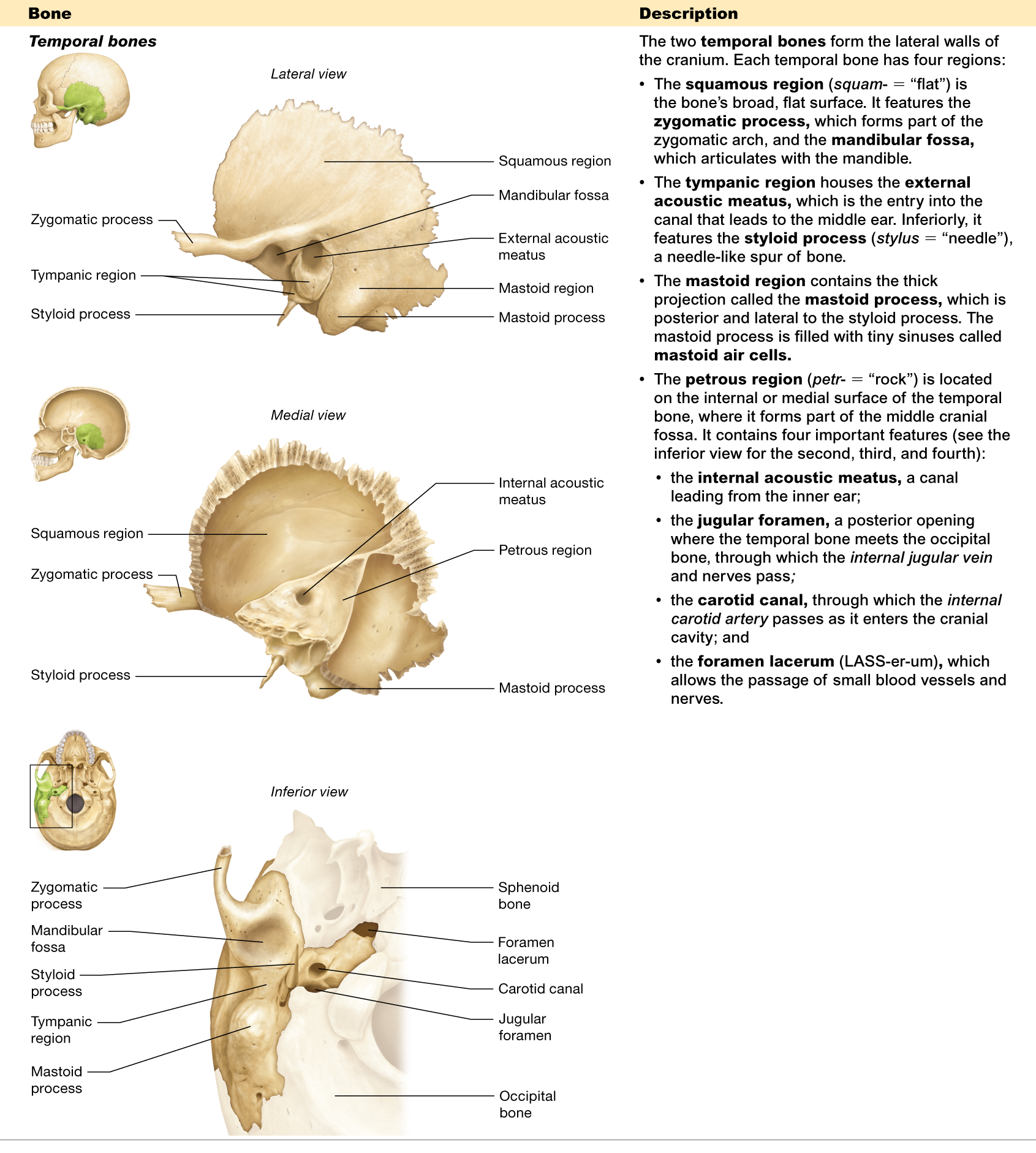
Which bones form the anterior boundary of the nasal cavity?
The nasal bones and maxillae
Which bone is the deepest facial bone?
The vomer
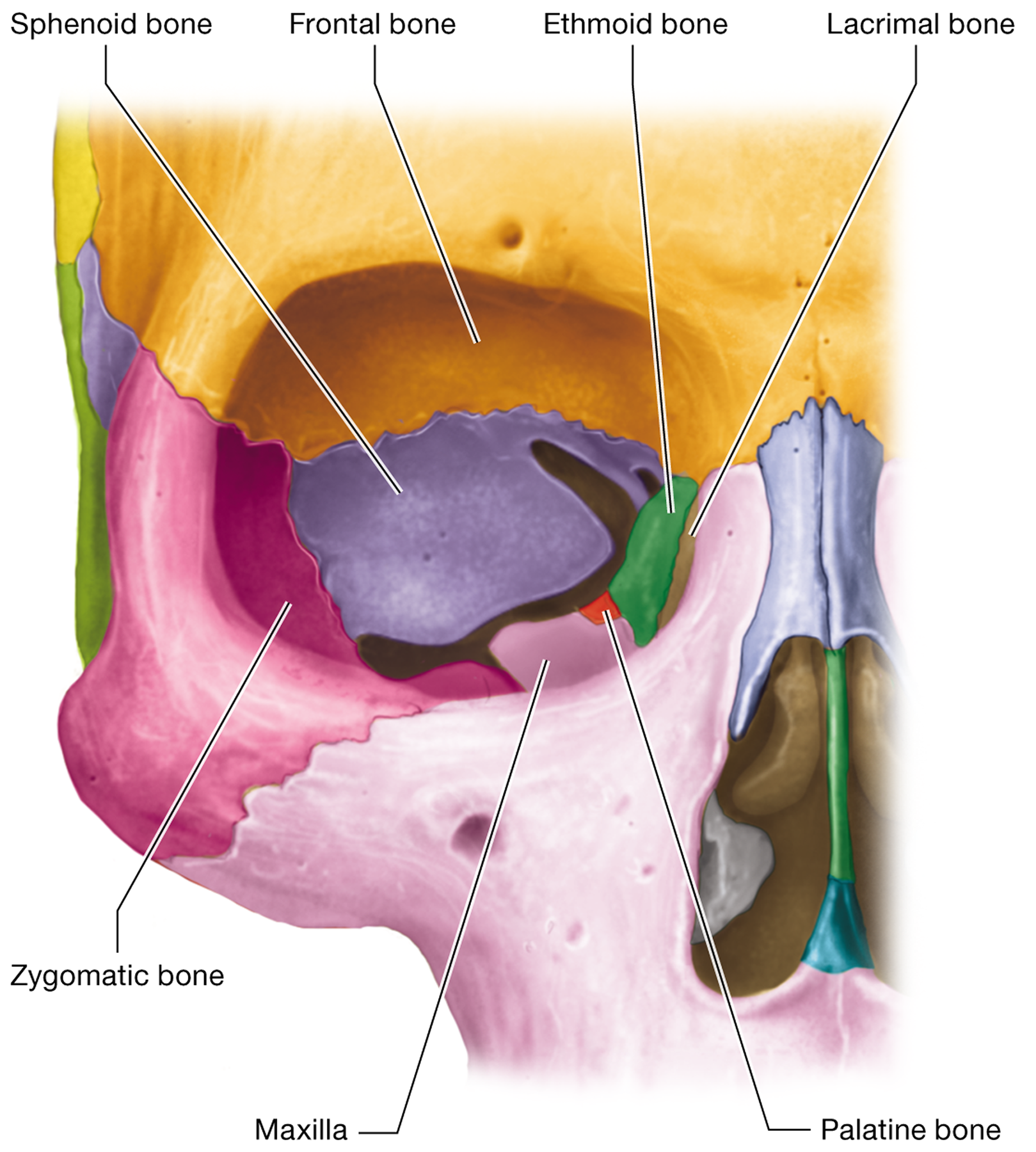
Which seven bones contribute to the formation of the orbit? “Funny eyes see many people looking zesty”
The frontal, maxilla, zygomatic, sphenoid, ethmoid, lacrimal, and palatine bones
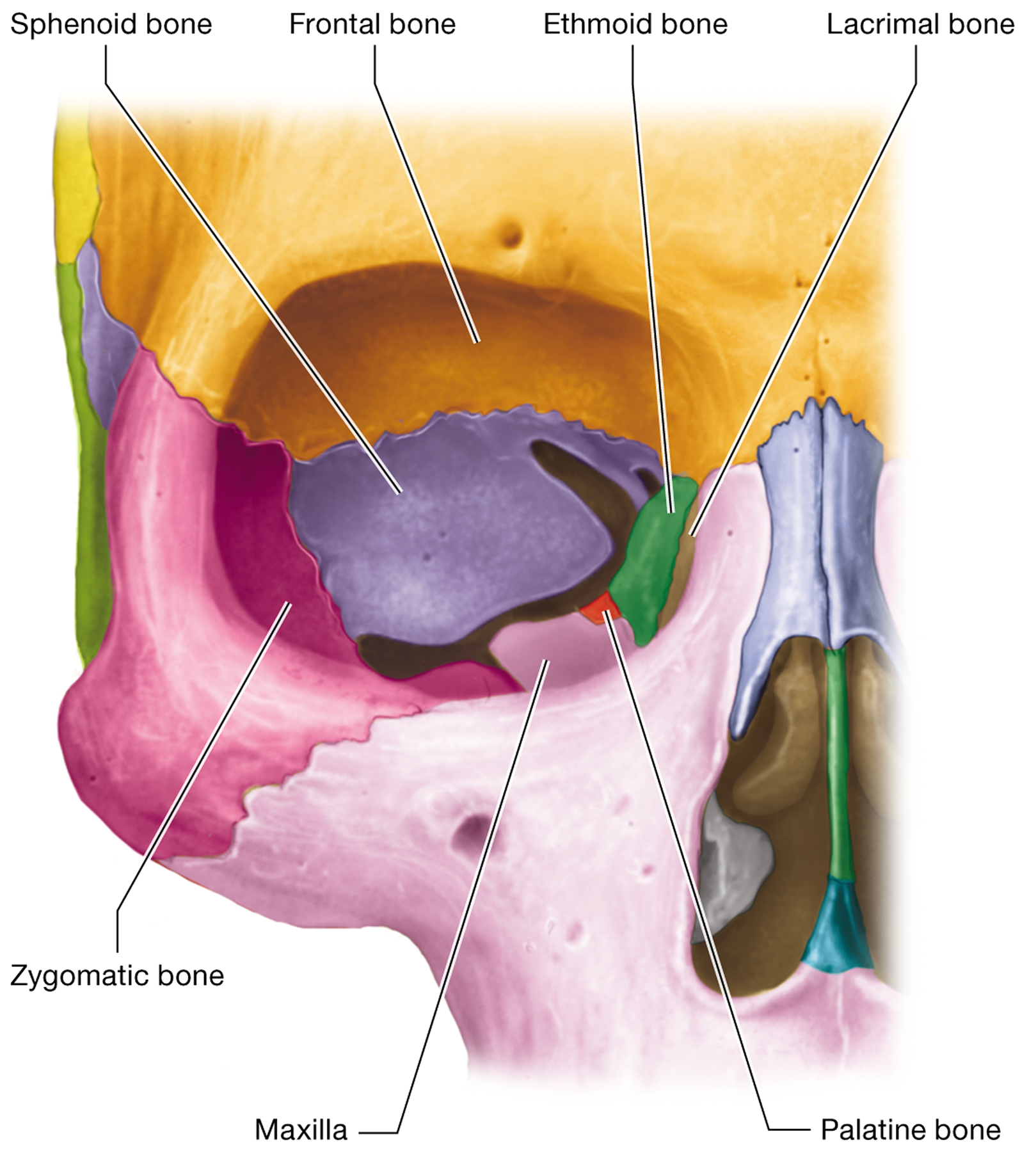
What gland is housed within the orbit?
The lacrimal gland, which produces tears
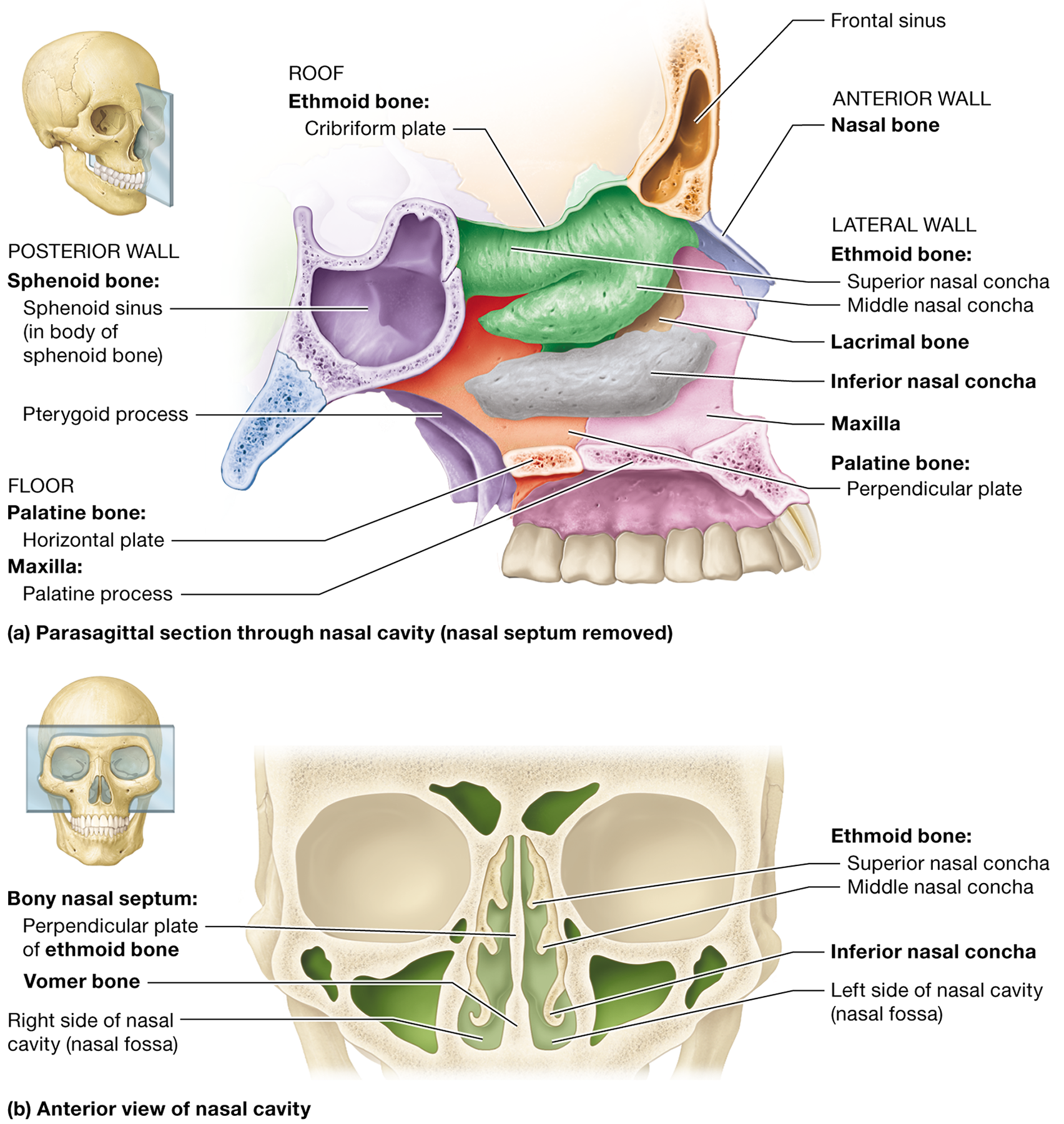
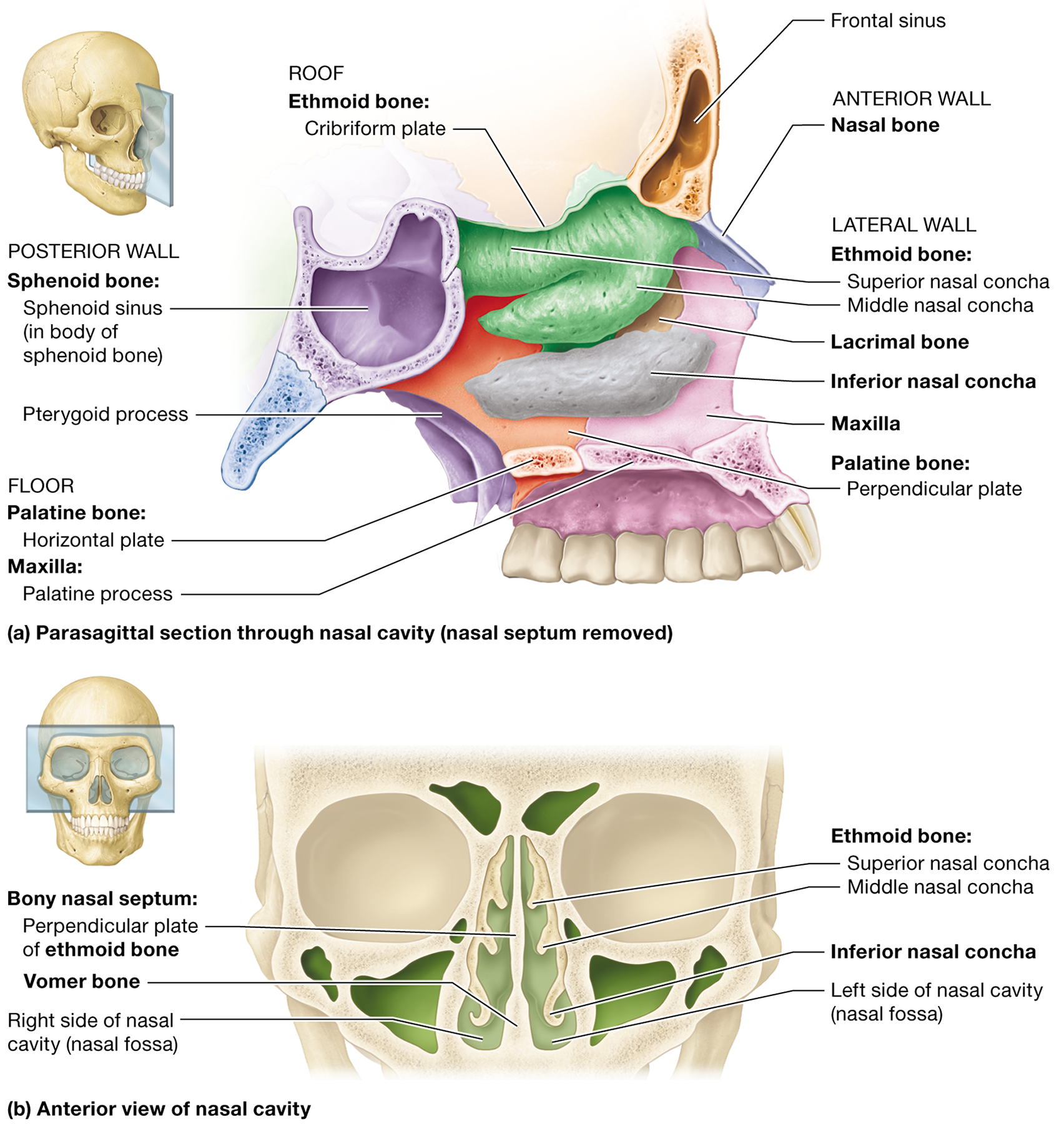
Which bone forms the roof of the nasal cavity?
The cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone "Every Massive Nose Picks Some Interesting Vapors."
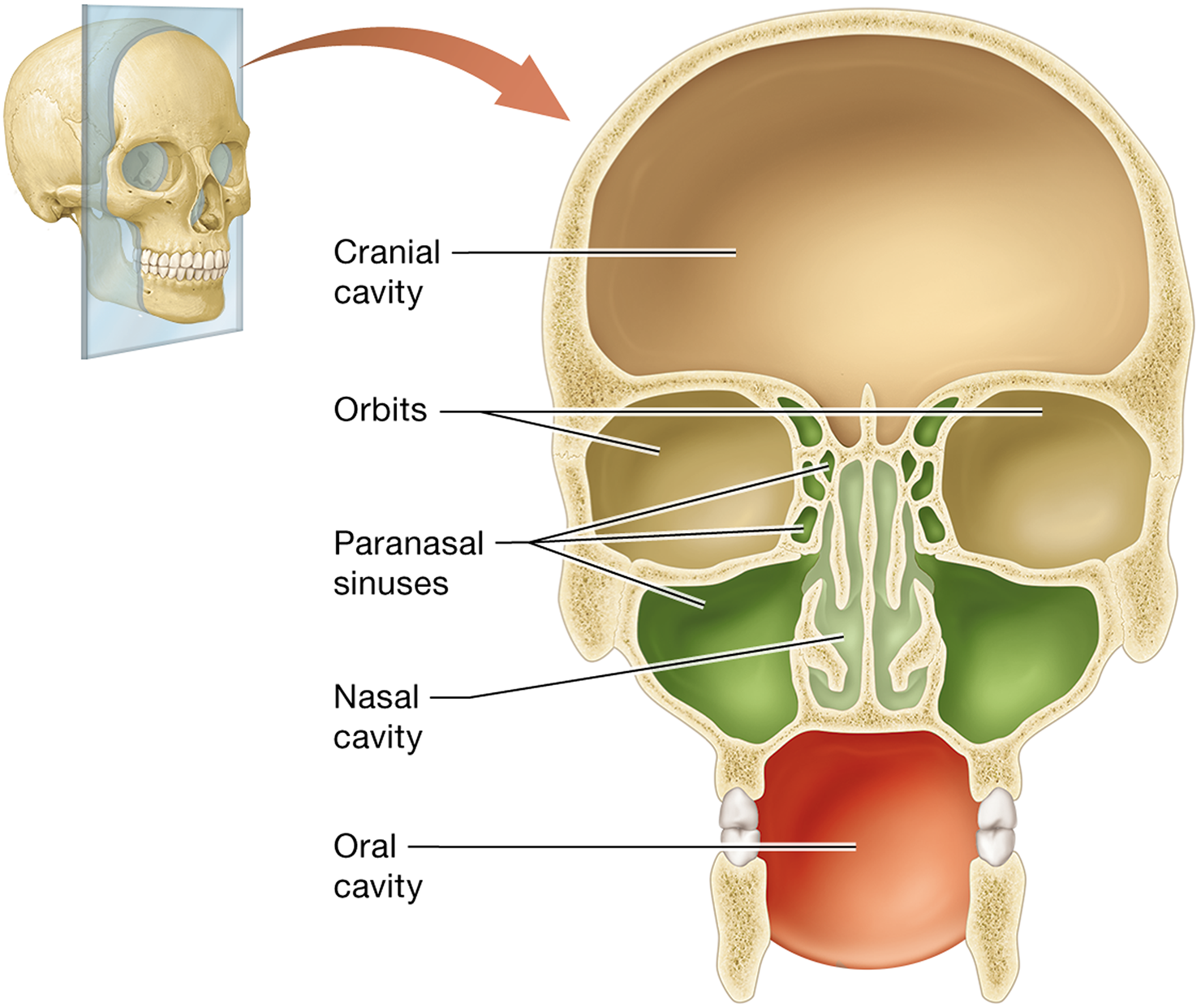
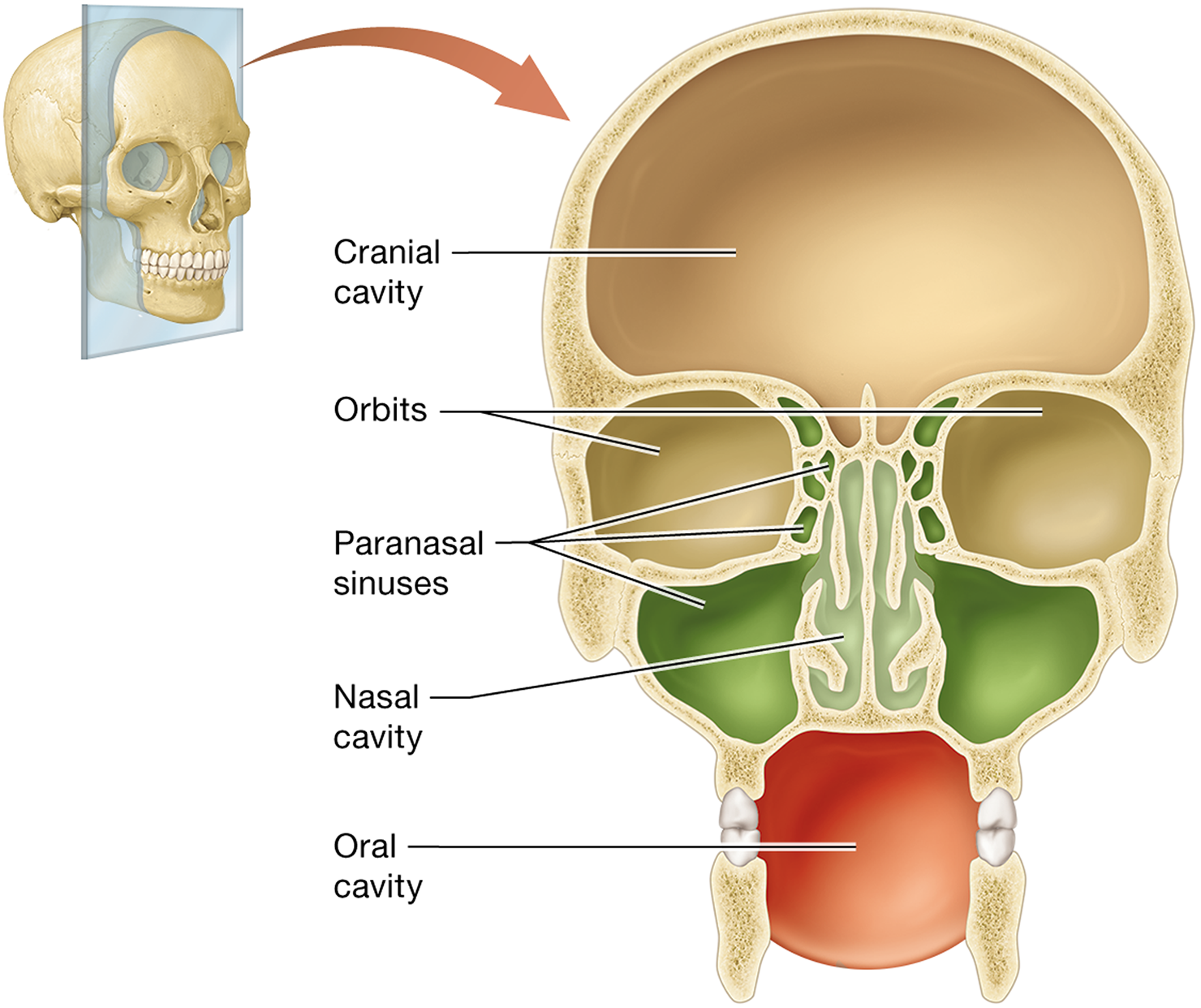
What are the paranasal sinuses?
The sinuses within the frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, and maxillary bones that connect to the nasal cavity
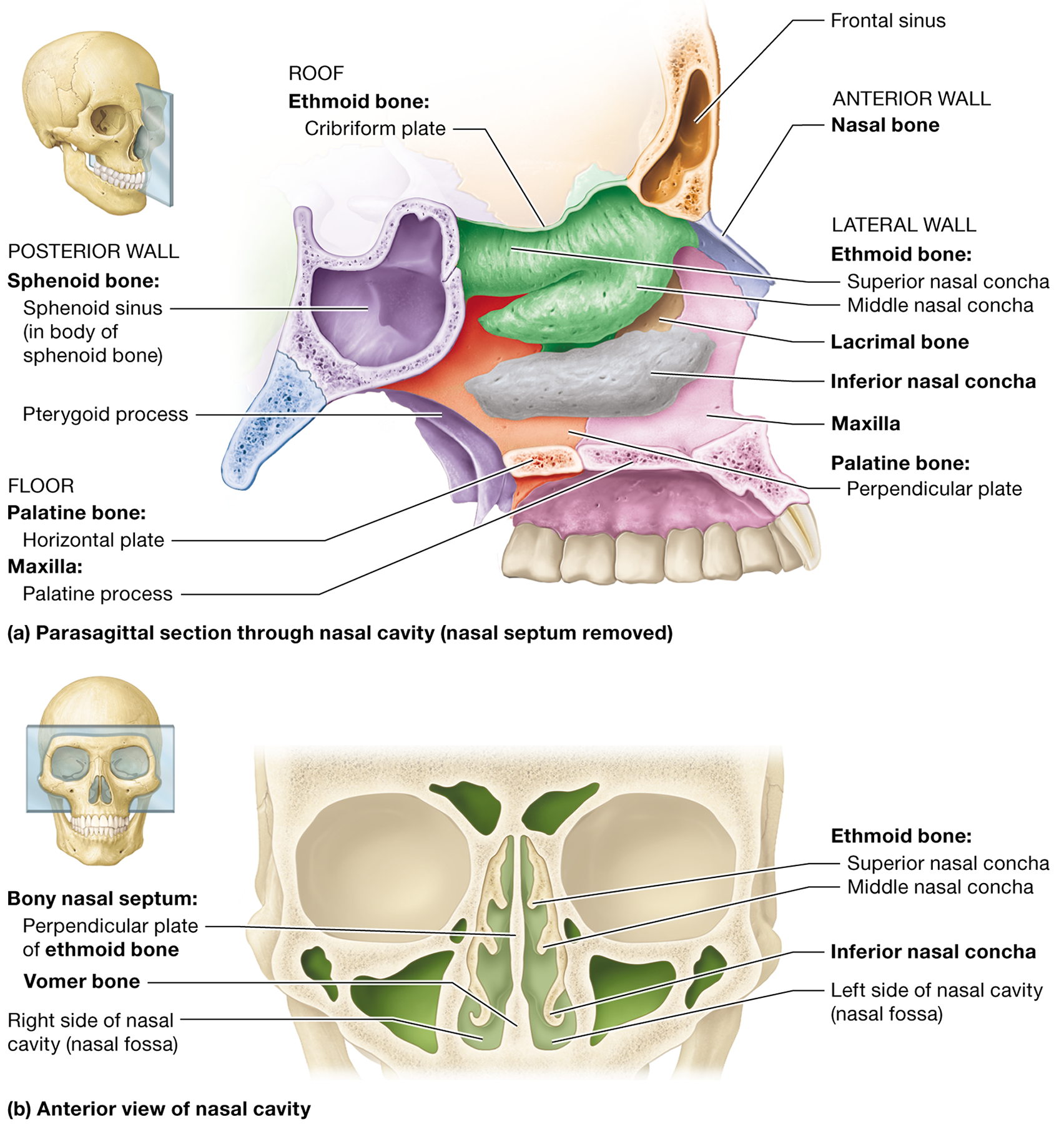
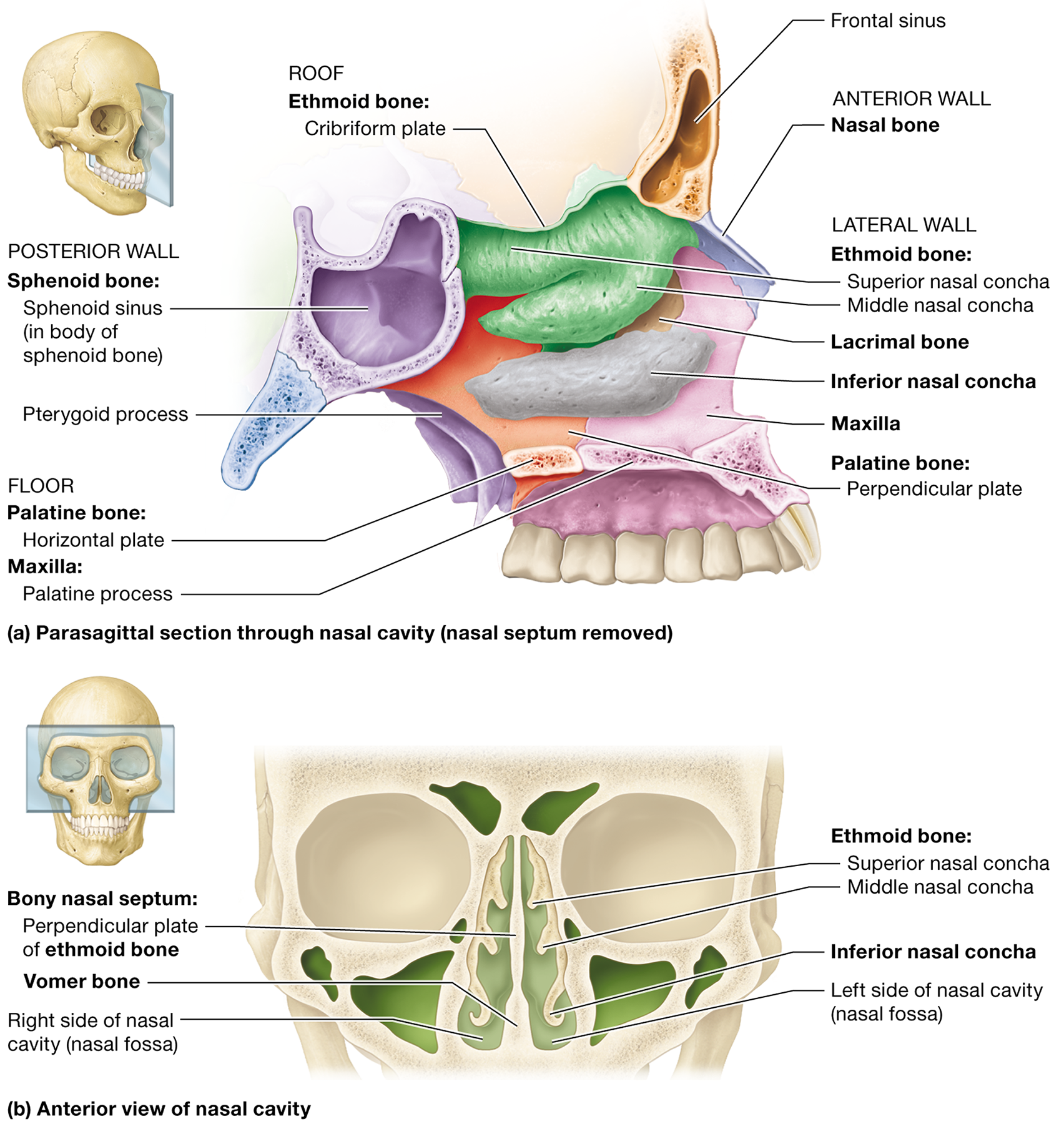
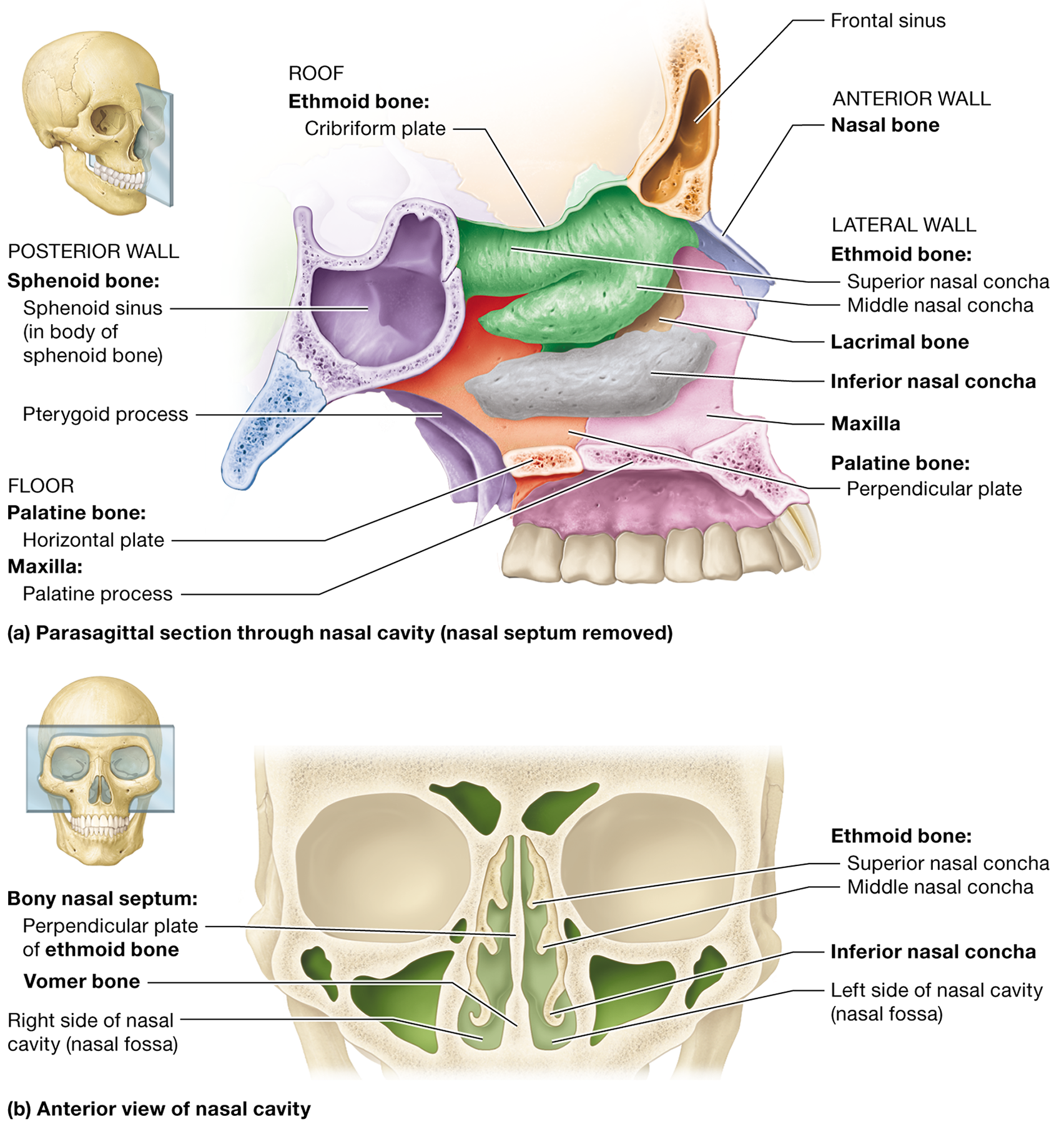
What are the functions of the paranasal sinuses?
They filter, warm, and humidify air, lighten the skull, and enhance voice resonance
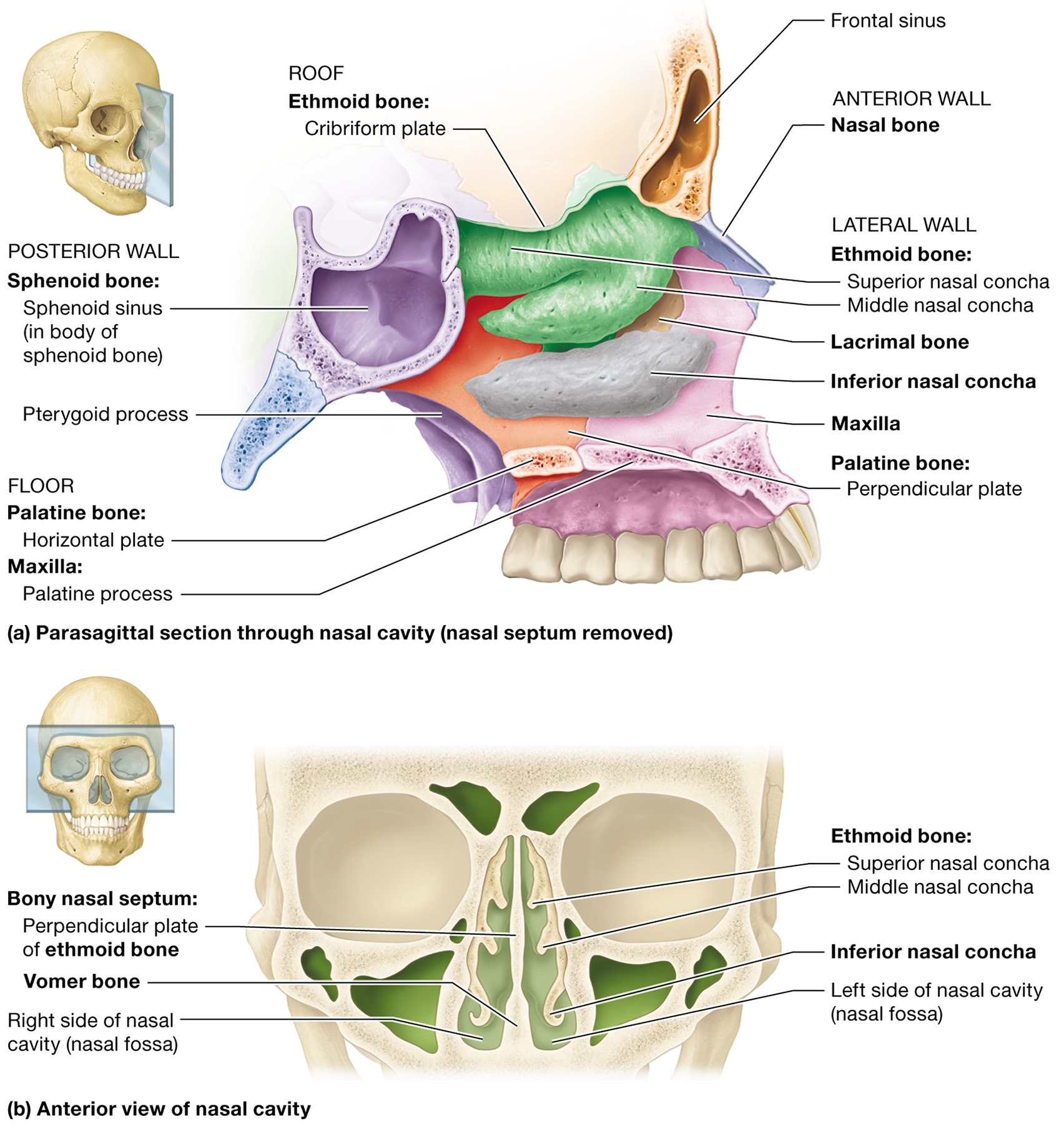
What forms the posterior boundary of the nasal cavity?
The sphenoid body and pterygoid processes
What is the nasal septum made of?
Hyaline cartilage (anteriorly), the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, and the vomer (posteriorly)
What is a deviated septum?
When the nasal septum is shifted to one side, potentially making it difficult to breathe through the nose
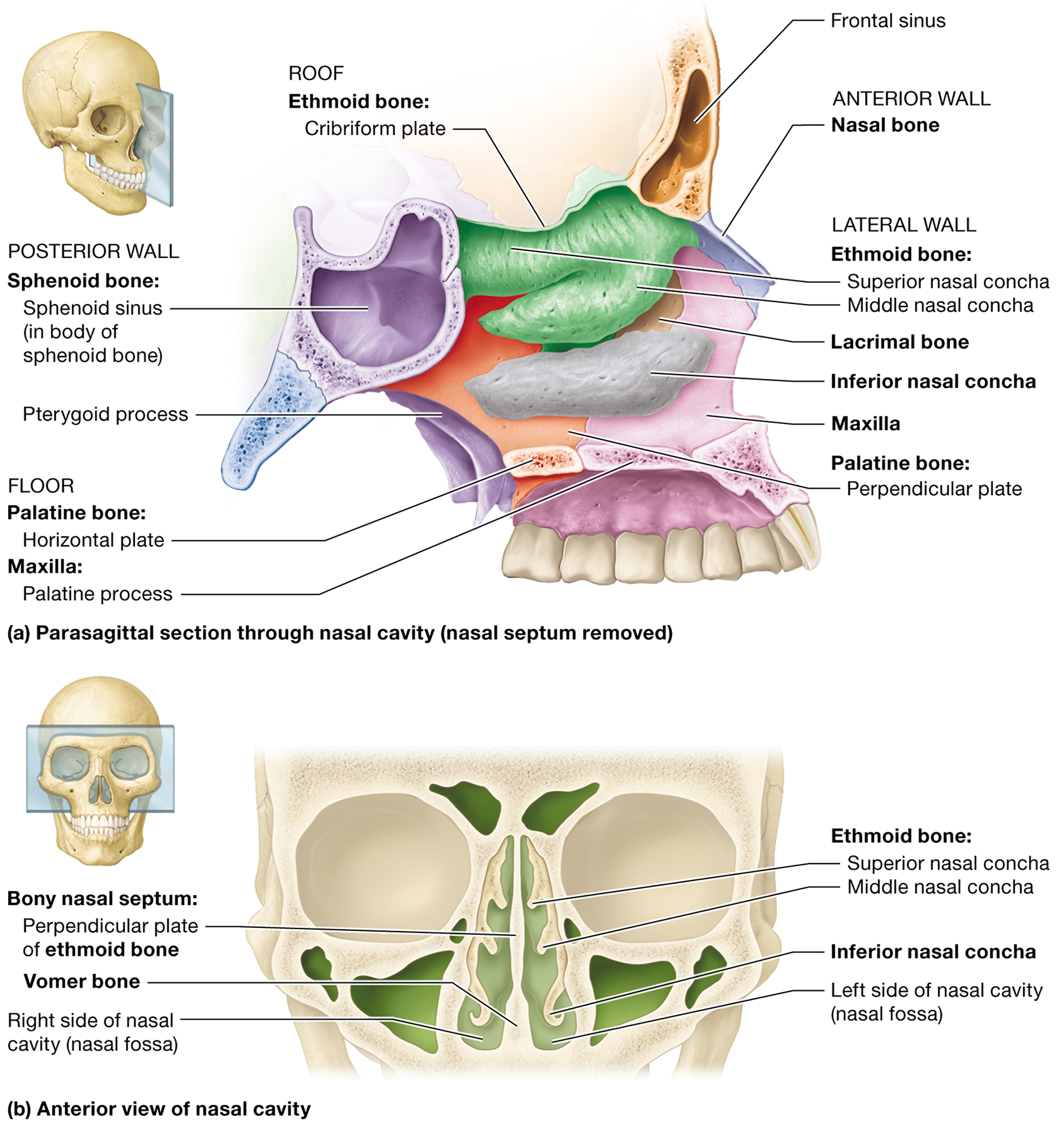
Name the bones that form the lateral walls of the nasal cavity.
The ethmoid bone, the perpendicular plate of the palatine bones, the inferior nasal conchae, and the maxilla
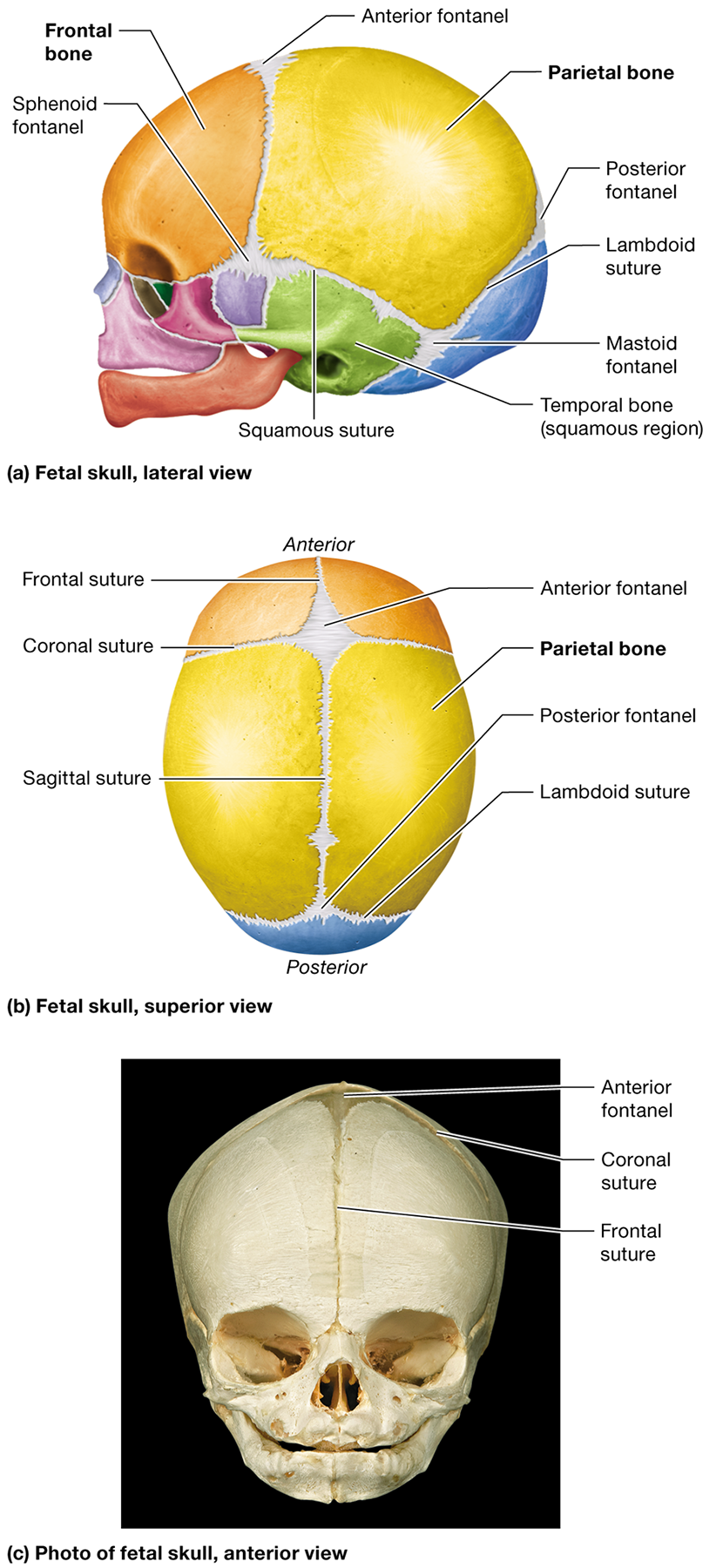
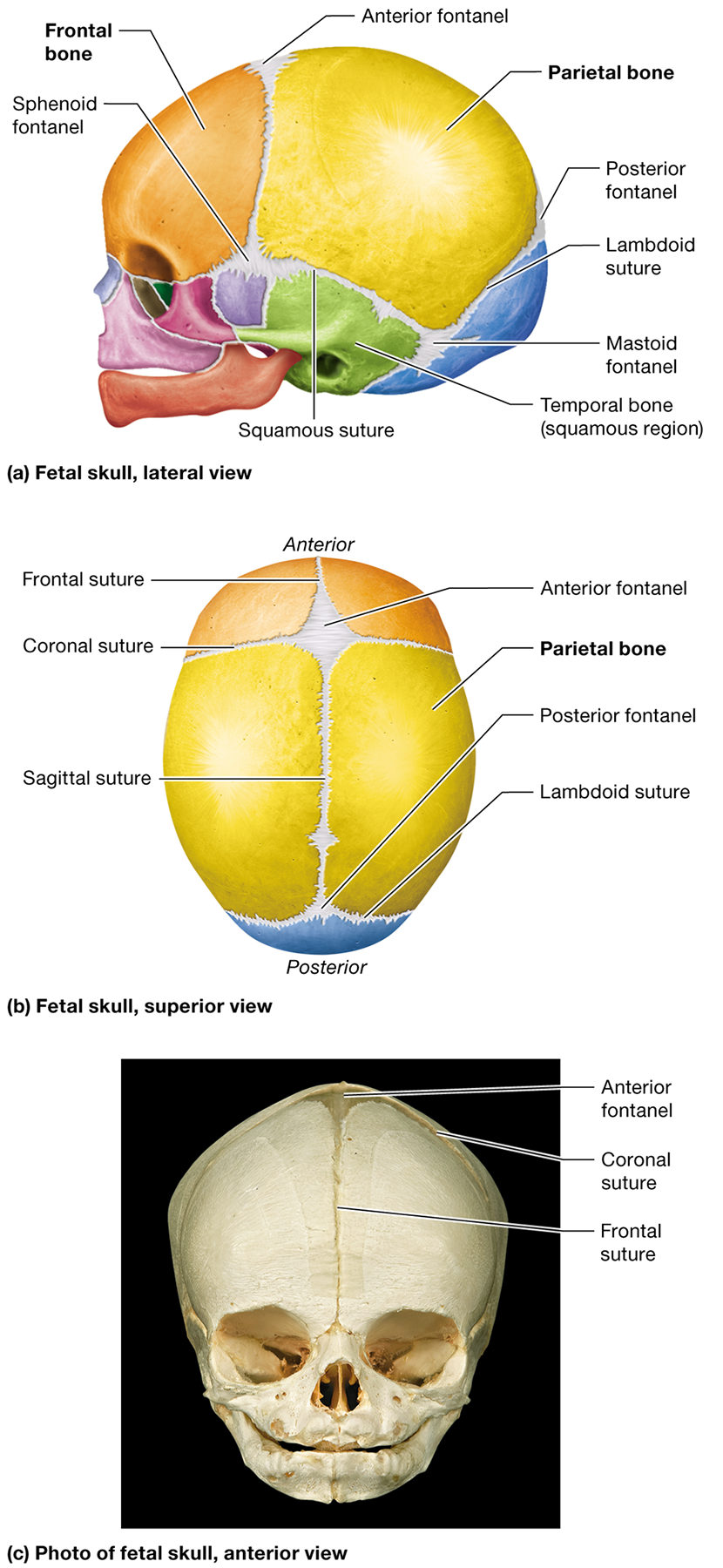
What are fontanels in an infant's skull?
Membranous areas where ossification of the cranial bones has not yet completed. They are often called "soft spots"
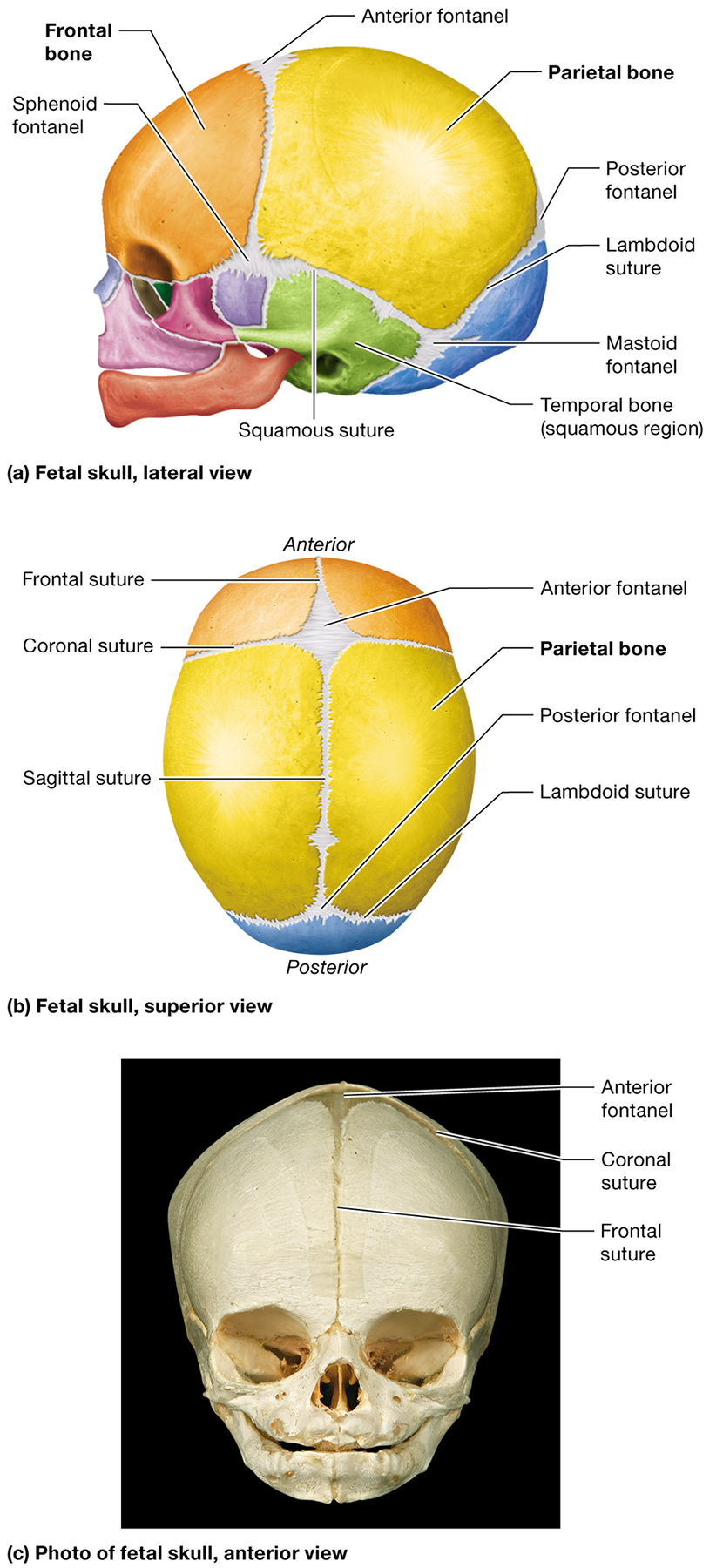
How do fontanels and unfused sutures help during birth?
They give the fetal skull flexibility, allowing it to fit through the mother's vaginal cana
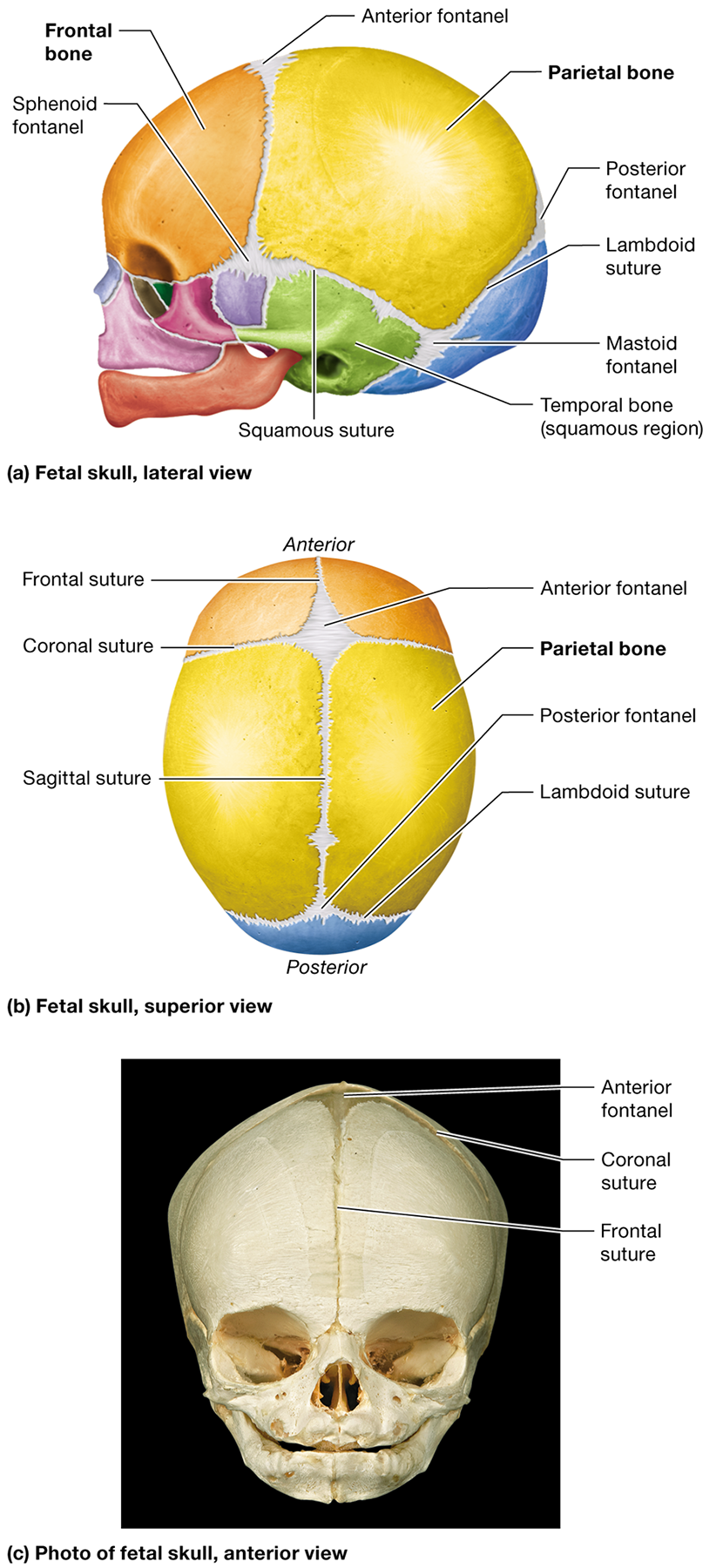
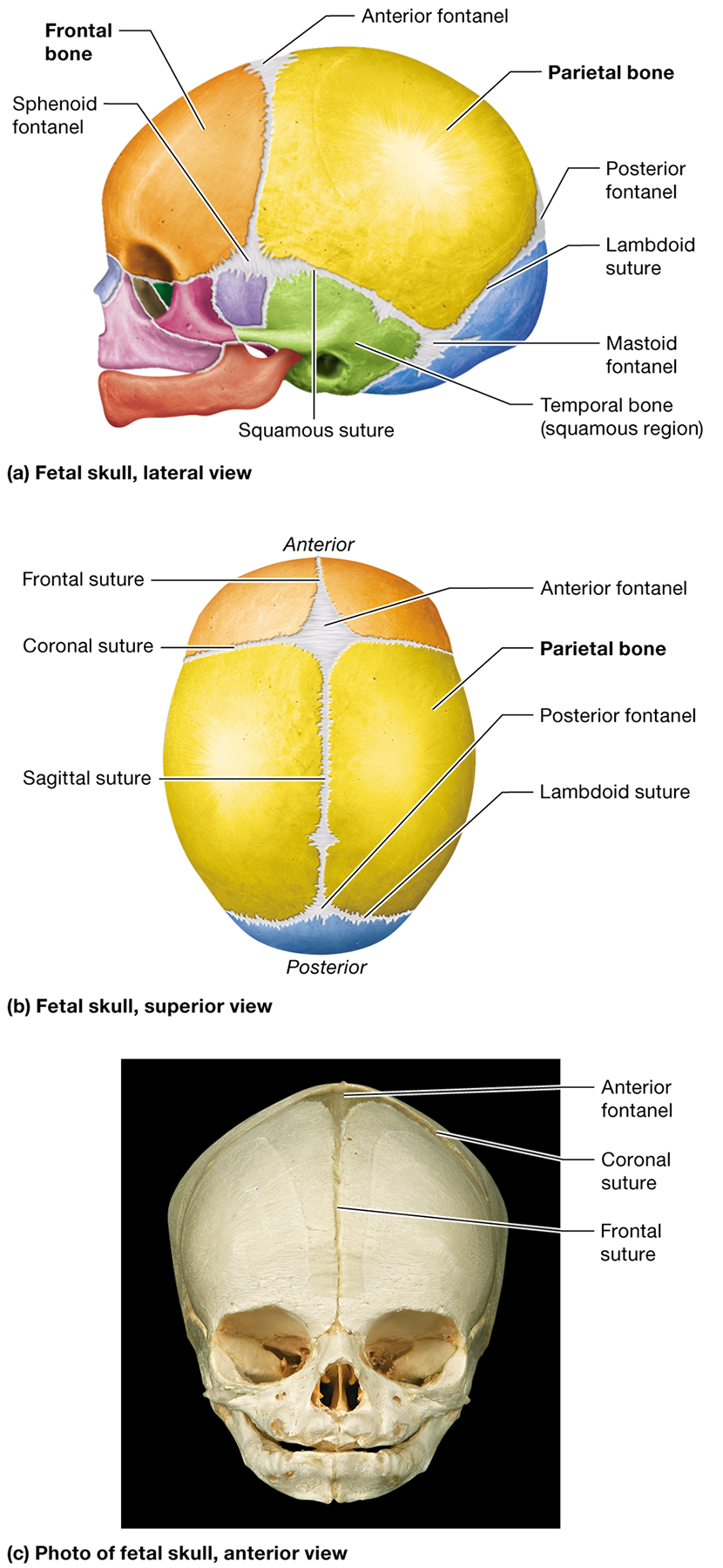
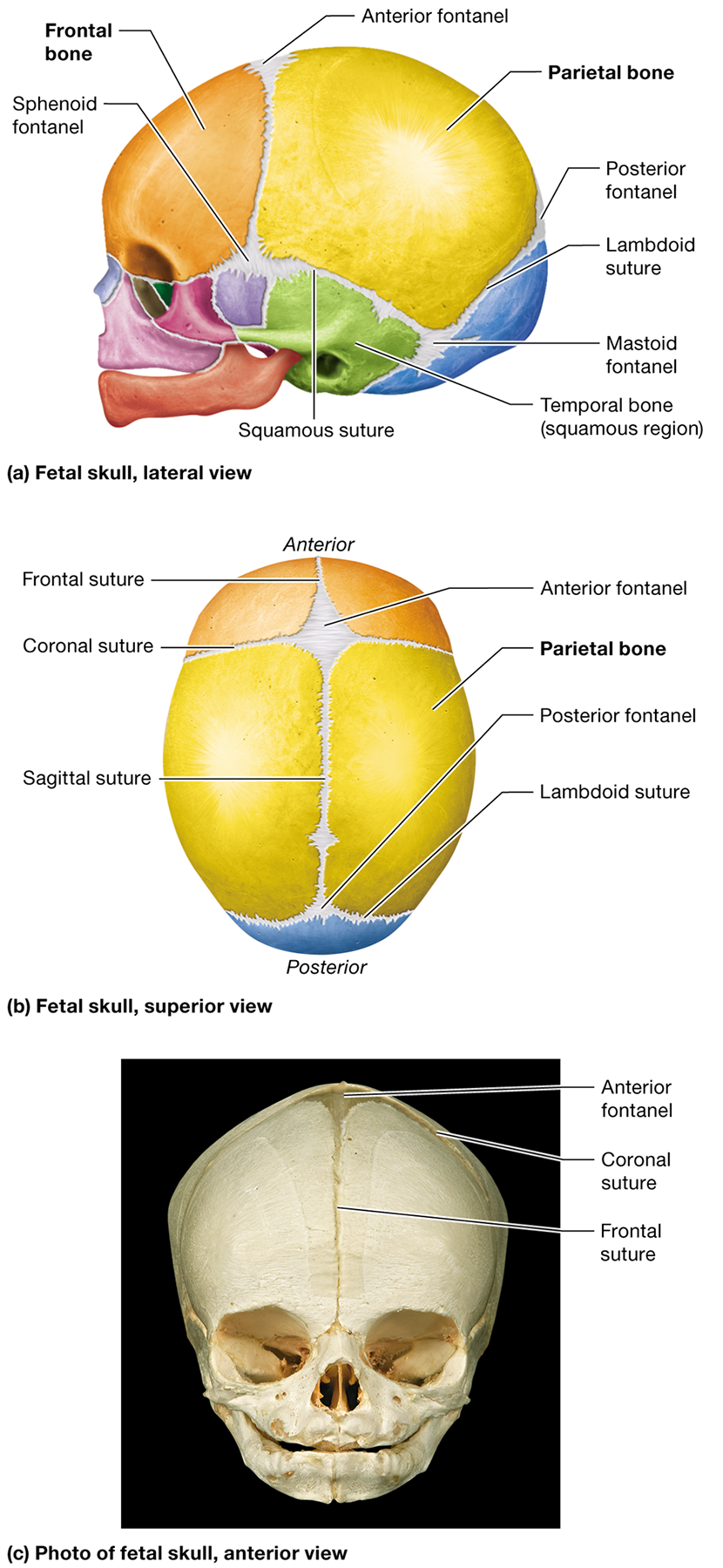
Where is the anterior fontanel located?
Between the developing frontal and parietal bones where the coronal and sagittal sutures meet
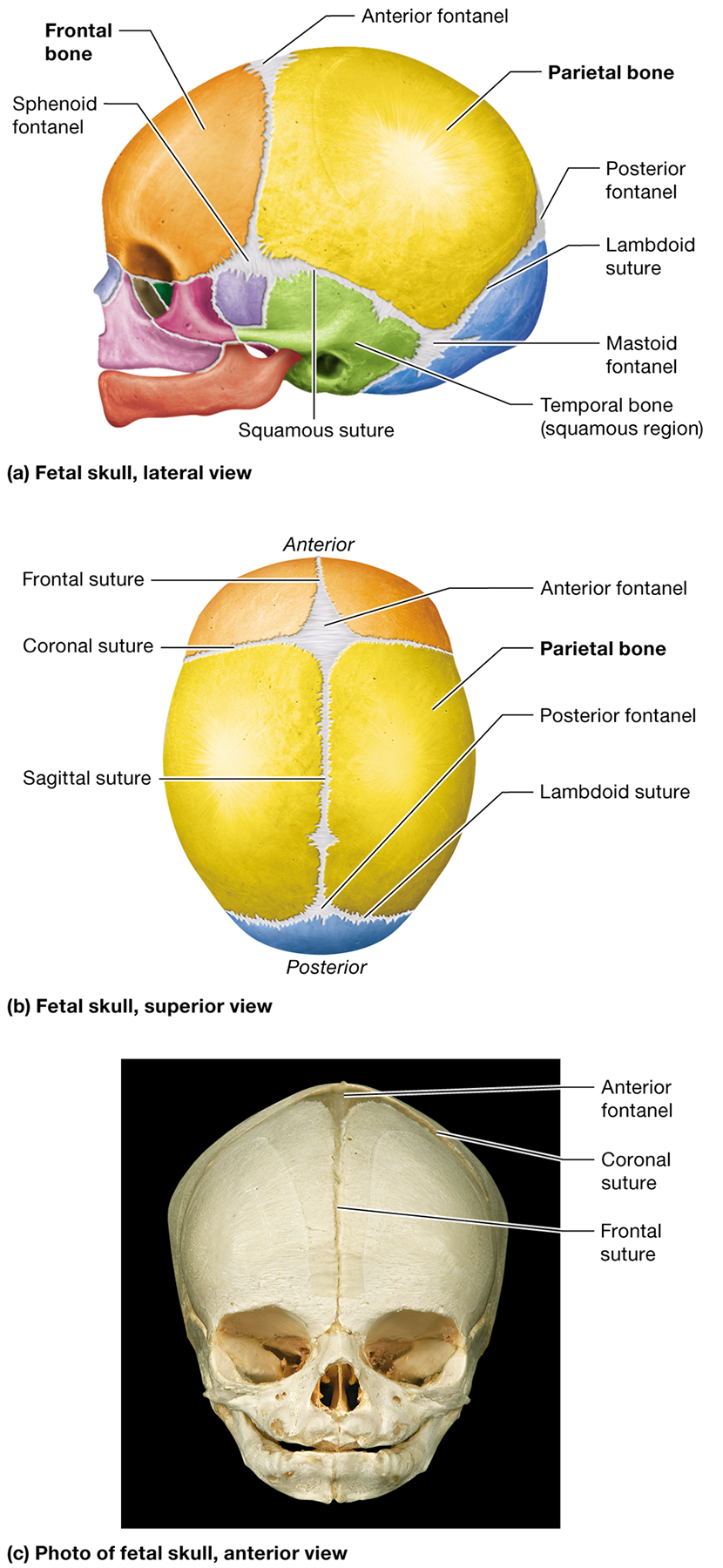
Where is the posterior fontanel located?
Between the developing parietal and occipital bones at the apex of the lambdoid suture
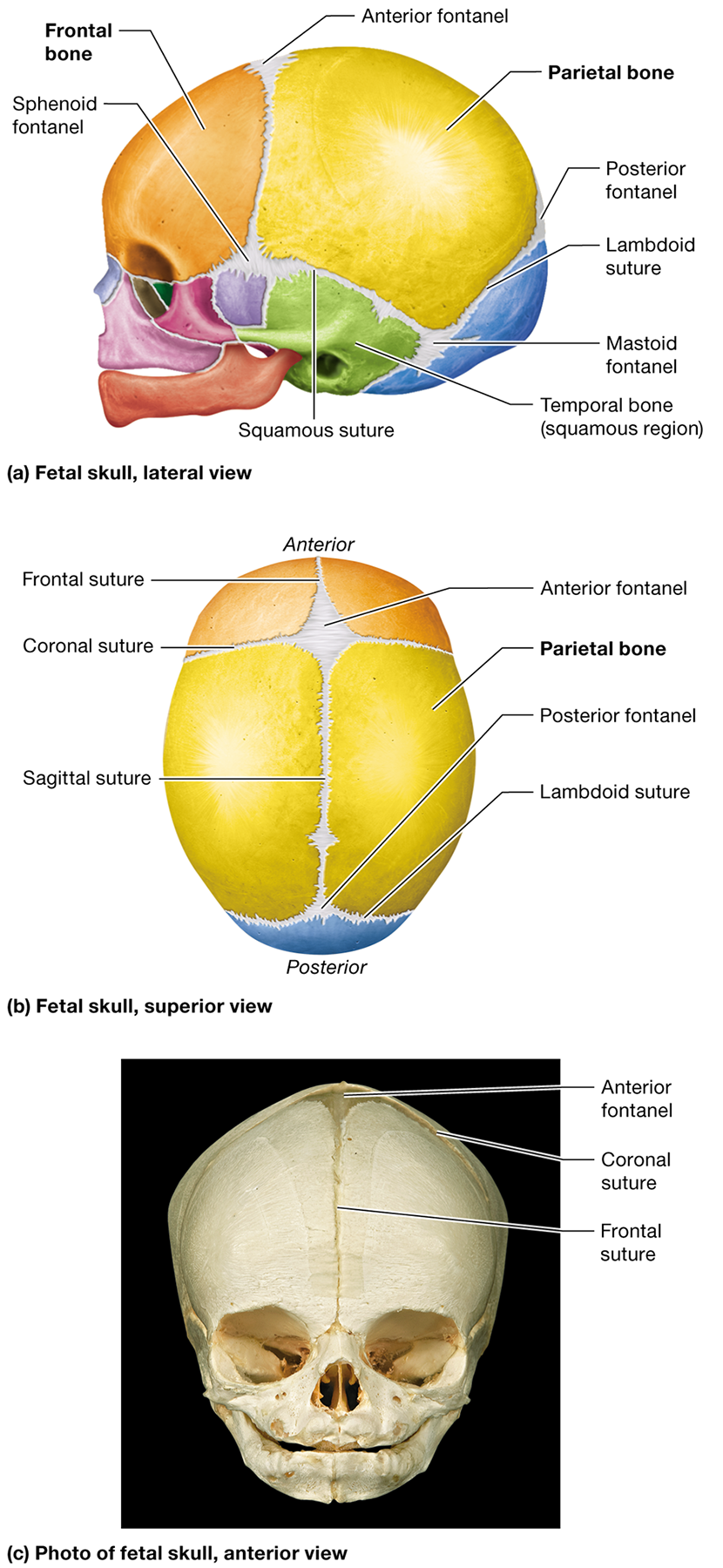
Name two other fontanels in the fetal skull and their locations.
The sphenoid fontanels, located in the temple on the right and left sides, and the mastoid fontanels, located at the junction of the lambdoid and squamous sutures
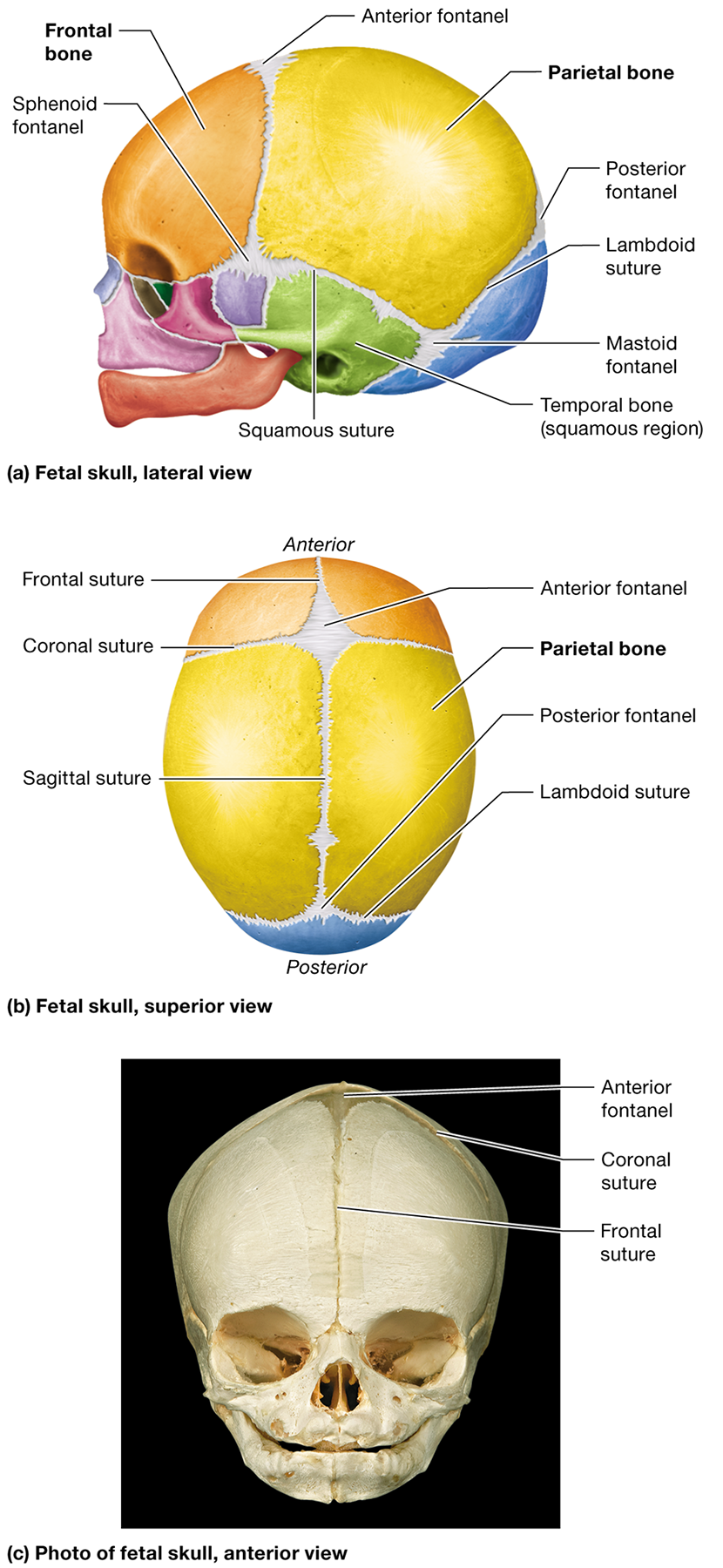
What is the metopic suture, and when does it typically fuse?
A suture within the frontal bone that fuses completely after birth
What is the benefit of fontanels for an infant's brain development?
allow the skull to enlarge as the infant experiences normal brain growth