HOSA - Surgical Instruments
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
have to state name (spelling correctly) and the purpose
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
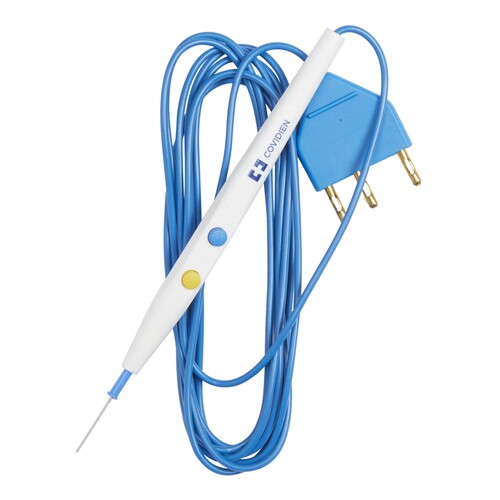
Electrosurgical Pencil
during surgery, the pencil uses electrical currents to coagulate and cut blood vessels and tissues to provide balance
Remember:
Cut with the color of the sun
Coagulate with the color of the sky
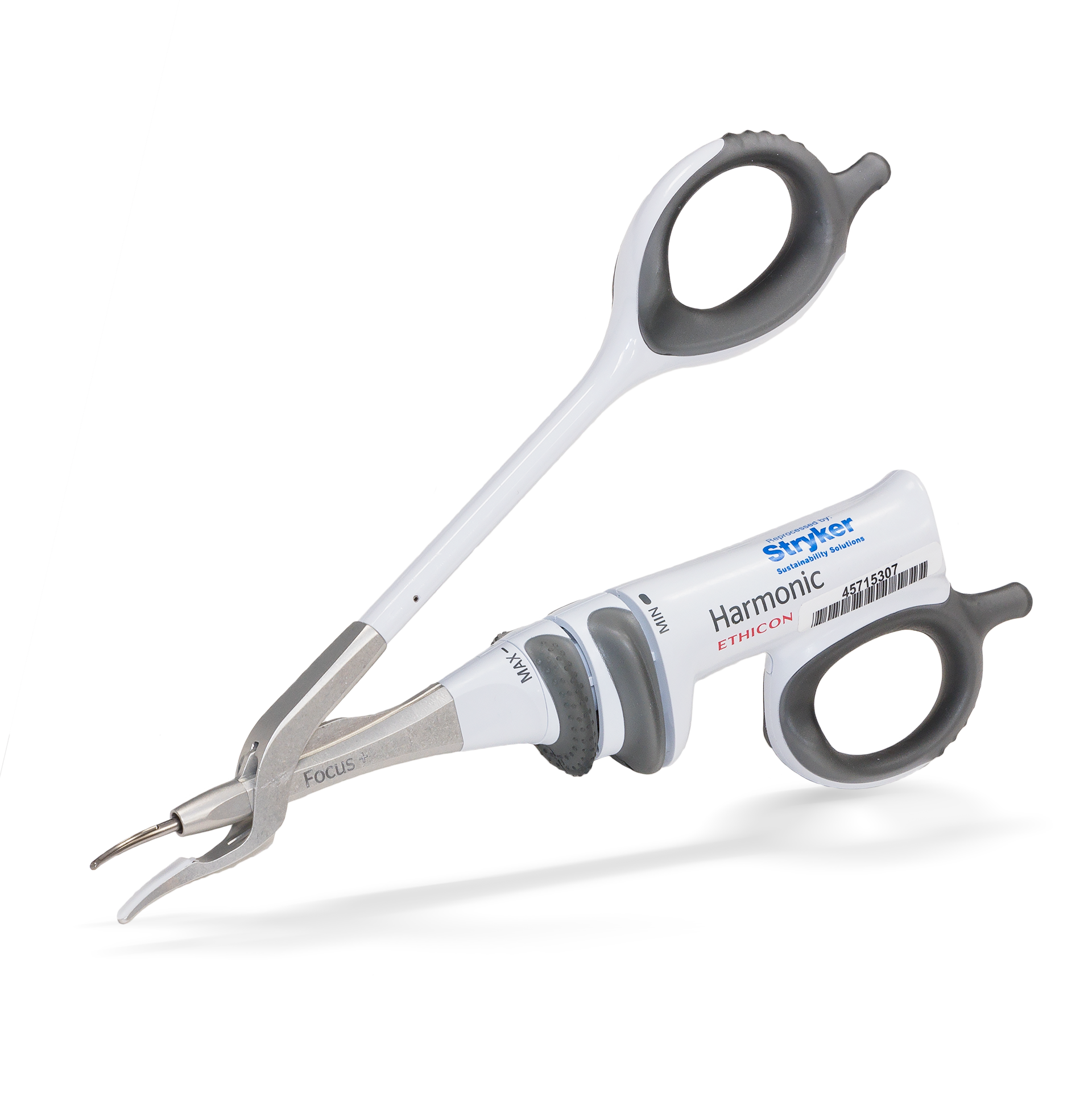
Harmonic Scalpel
a instruments that is used to give ultrasonic energy between jaws to coagulate and divide tissues by low temperature cavitation
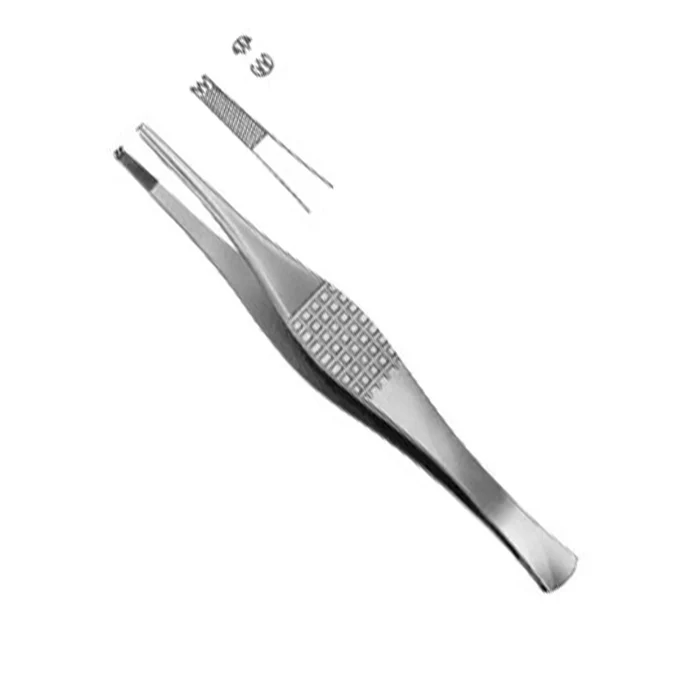
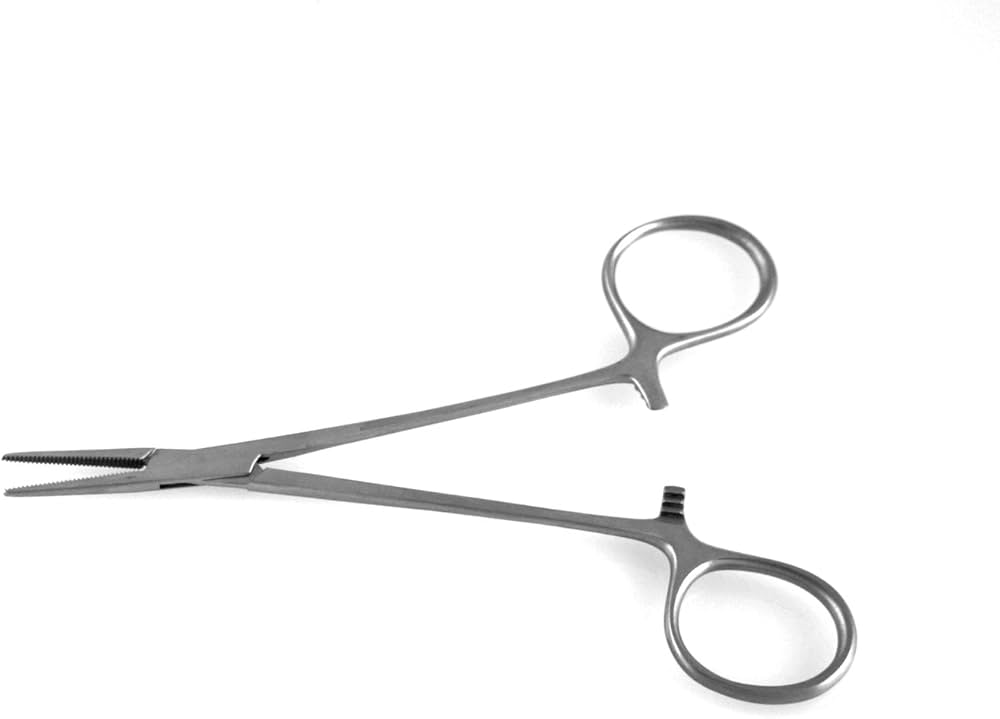
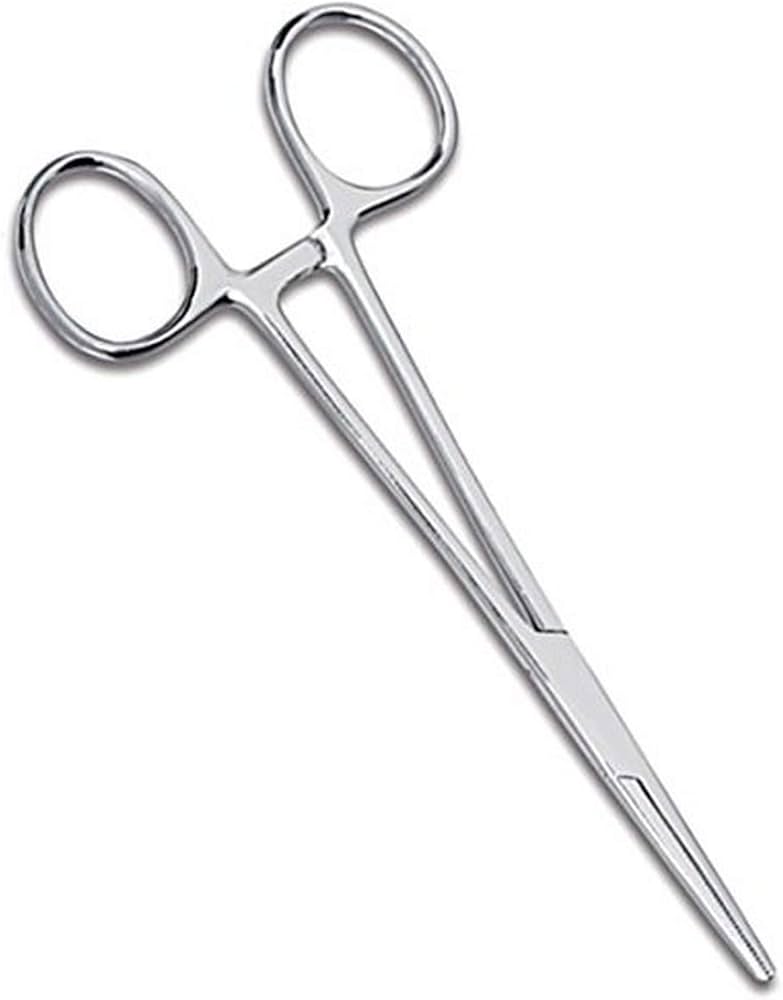
Halstead Forceps
used for occluding bleeders (forceps) in small or superficla wounds beofre ligation or cauterziation, used for small procedure.
Remember:

Crile Forceps
used for occluding bleeders before ligation (forceps), but more specfically blunt dissection when separting planes and tissues
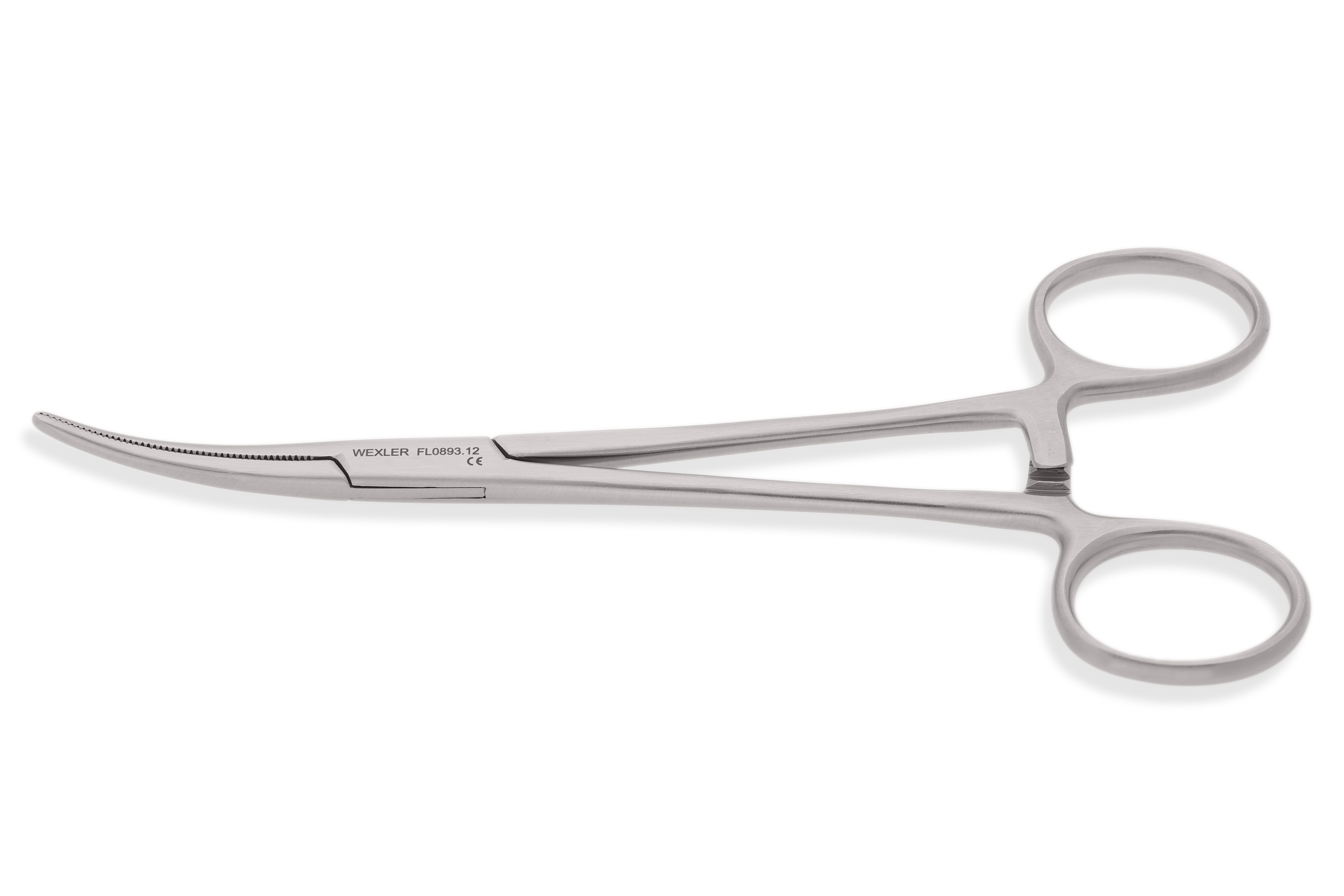
Kelly Forceps
used for occluding bleeders before ligation (forceps) ; running about half down the jaw ; (BIGGER JAW)
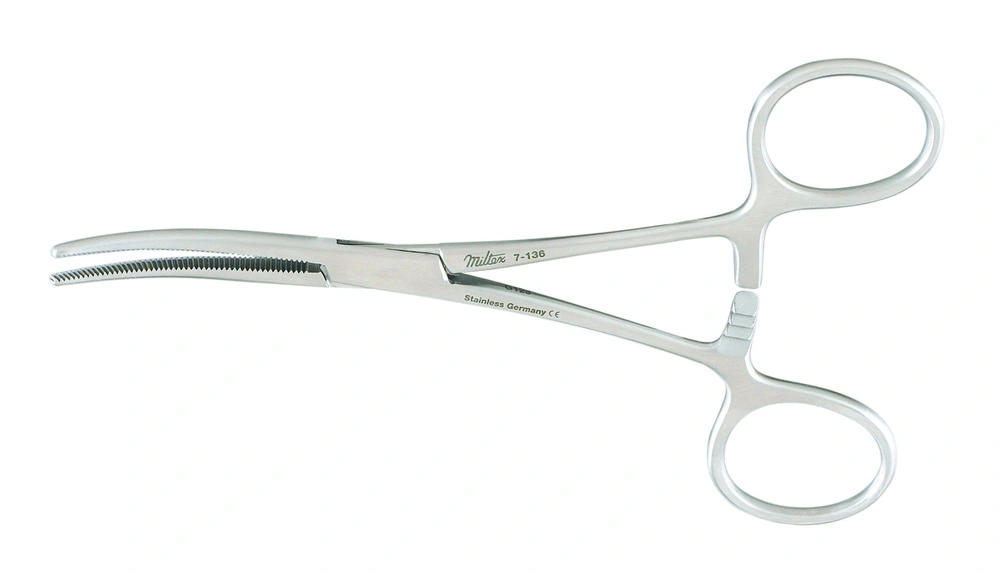
Rochester-Pean Forceps
Used for occluding larger blood vessles and tissues before ligation; usually deeper wood on heavier tissues (heavier, broader jaws and straight clamp)
Carmalt Forceps
Used for occluding larger blood vessels and tissues beofre ligation, and oftern the forceps that the kittner is leaded on. (straight clamp with crosshatch pattern with vertical serrations running to the tip of the jaw)
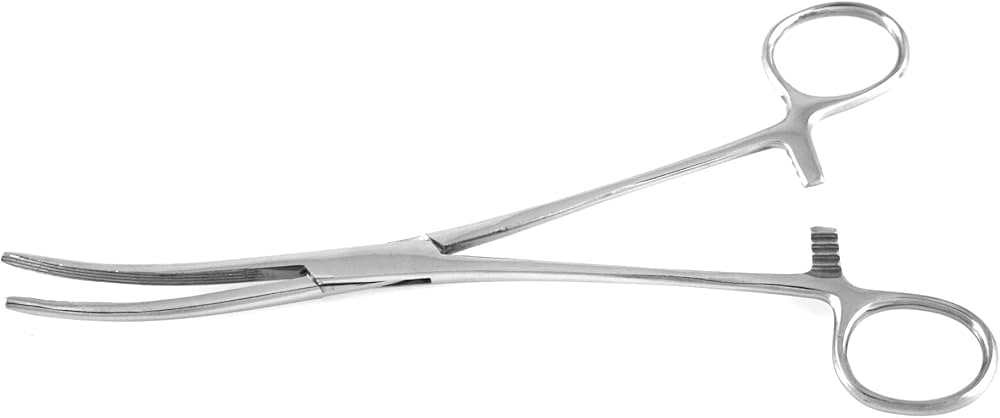

Mixter Forceps
is used to clamp, dissect and occlude tissues, to place a tie or vessel loop under and around a tublar structure such as a vessel for the surgeon to grasp the ligature or loop and pull it up and around the structure (45 degree calmp with horzzainal serrations)

Adson Forceps
clamps small vessels in a deep wound or holds tonsil sponges. may be used to create a tie on a passer (loading a loose suture (the "tie") onto a long, thin instrument (the "passer," like a tonsil/mosquito forceps), making it an extension of the surgeon's hand to tie off blood vessels or secure structures deep in a wound, saving time and conserving material by avoiding passing a needle. (Fine, curved or straight clmap with horizontal serrations running halfway down)
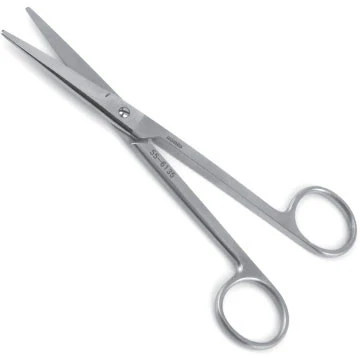
Straight Mayo Scissors
used for cutting sutures (heavy scissors with straight blades)
Curved Mayo Scissors
Used to dissert or undermine heavy fibrous tissues
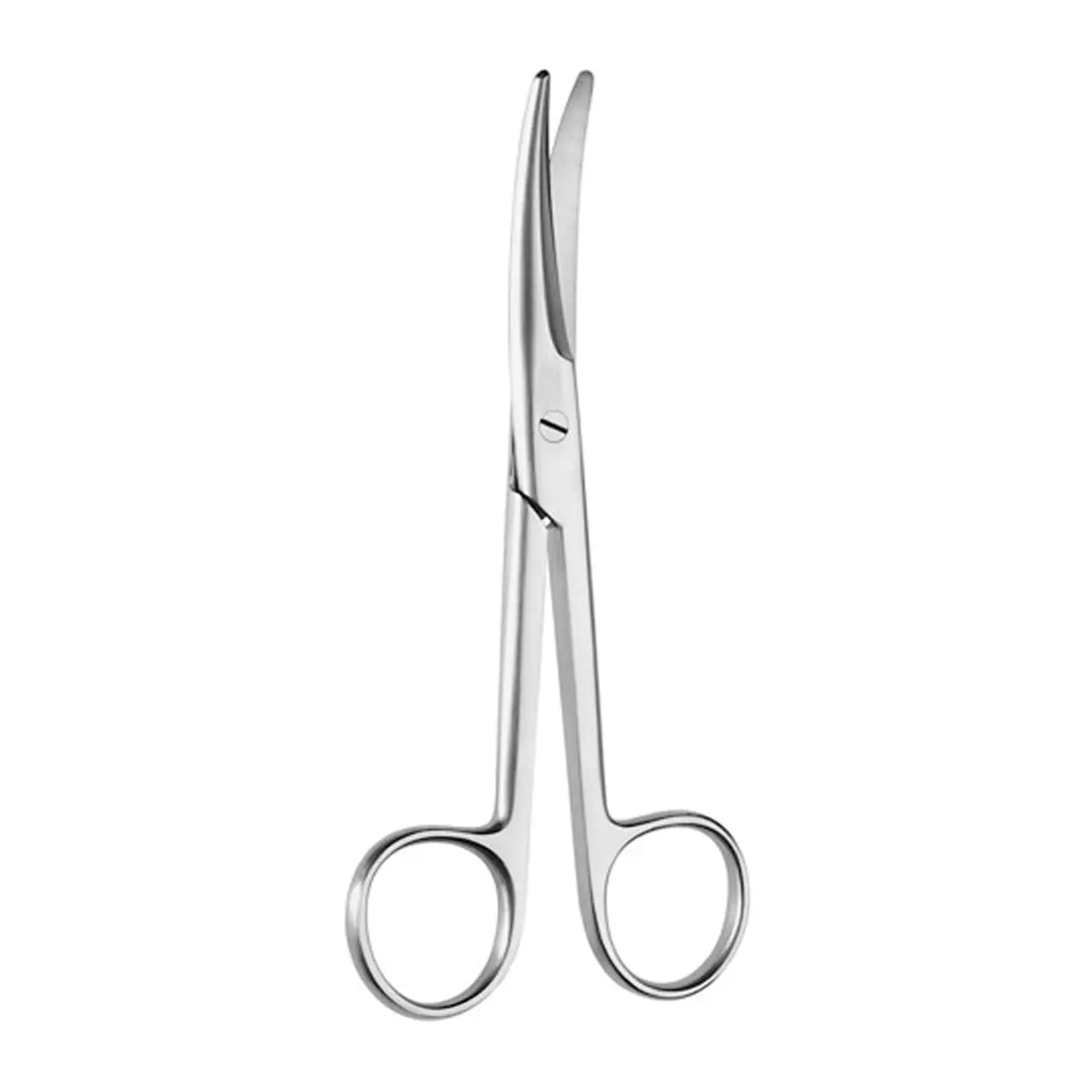
Curved Metzenbaum Scissors
used to dissect and undermine delicate tissues (longer thinner sccissors with curved or straight blades)

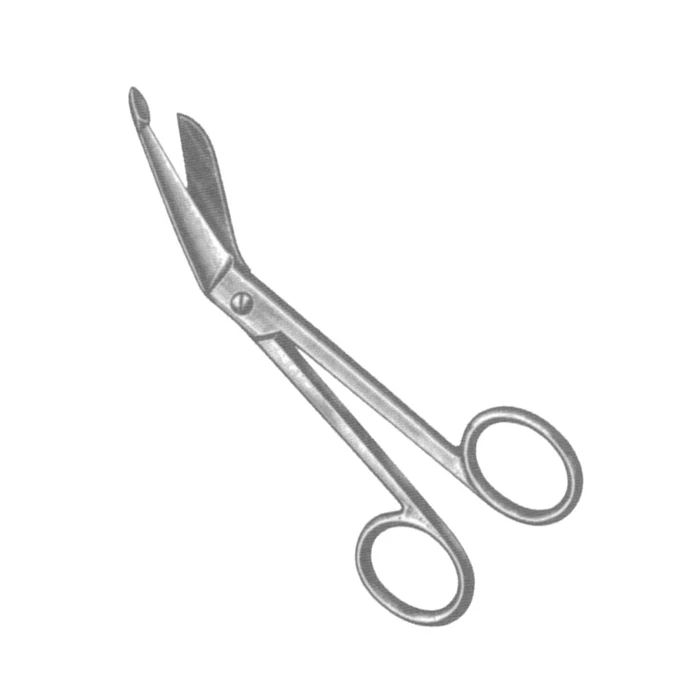
Lister Bandage Scissors
cut dressing drapes and other items and also used in a C-section to open the uterus without harming the baby (angle blunt scisosrs in which lower blade has smooth flattened tip)

Wire Scissors
used to cut small guage wire and sutreus ( angled scissors with fine serrations on the blades and circular notch in the inner jaws

No. 3 Long Knife Handle
used for precision cutting deep within a wound (a no.4 long knife holds blades 10,11,12 and 15)
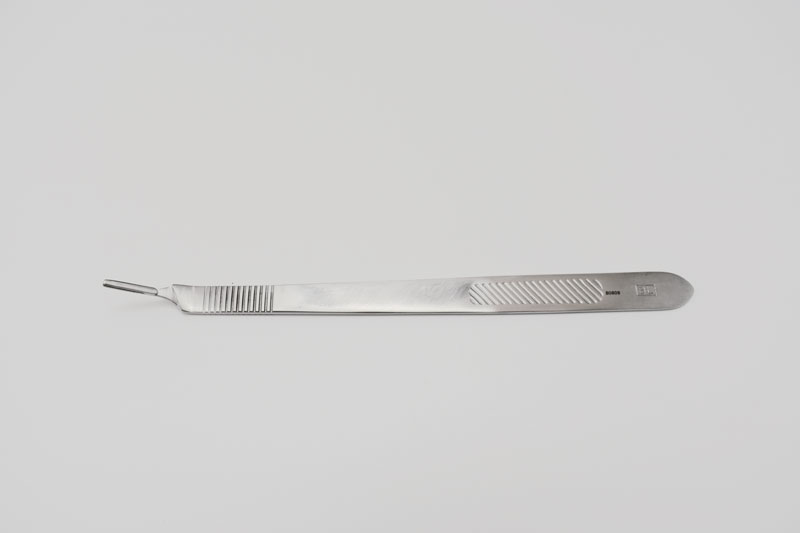

No. 7 Knife Handle
used when precision cutting is needed in a confined space or a deep wound
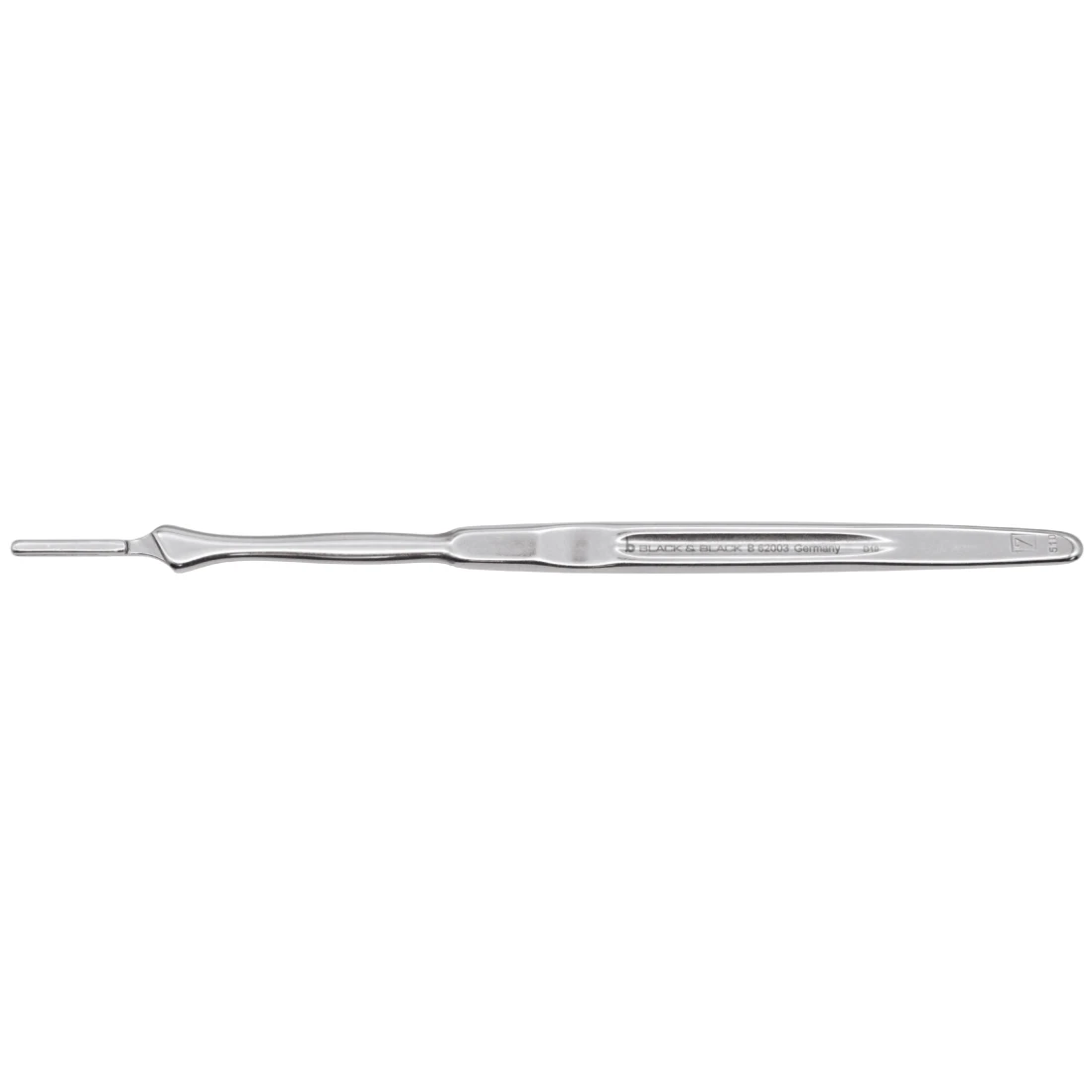
No. 10 Blade
used to make a skin incision (extensive body blade with a curved cutting edge to the tip )

No. 11 Blade
used for puncturing the skin or to initate the opening of an artery

No. 12 Blade
used during tonsillectomies, parotid surgeries, septoplasties, and cleft palate procedures. It can also be utilized for removal of calculi in the ureter and the kidney (a small crescent-shaped blade sharpened along the inside edge of the curve)

No. 15 Blade
used for creating small precise incisions (a narrow blade that has a small, rounded cutting edge)

No. 4 Knife Handle
used with the no. 20 blade to create a larger and/or deeper incision in heavy tissue areas (has a larger tip to accommodate the larger blades)
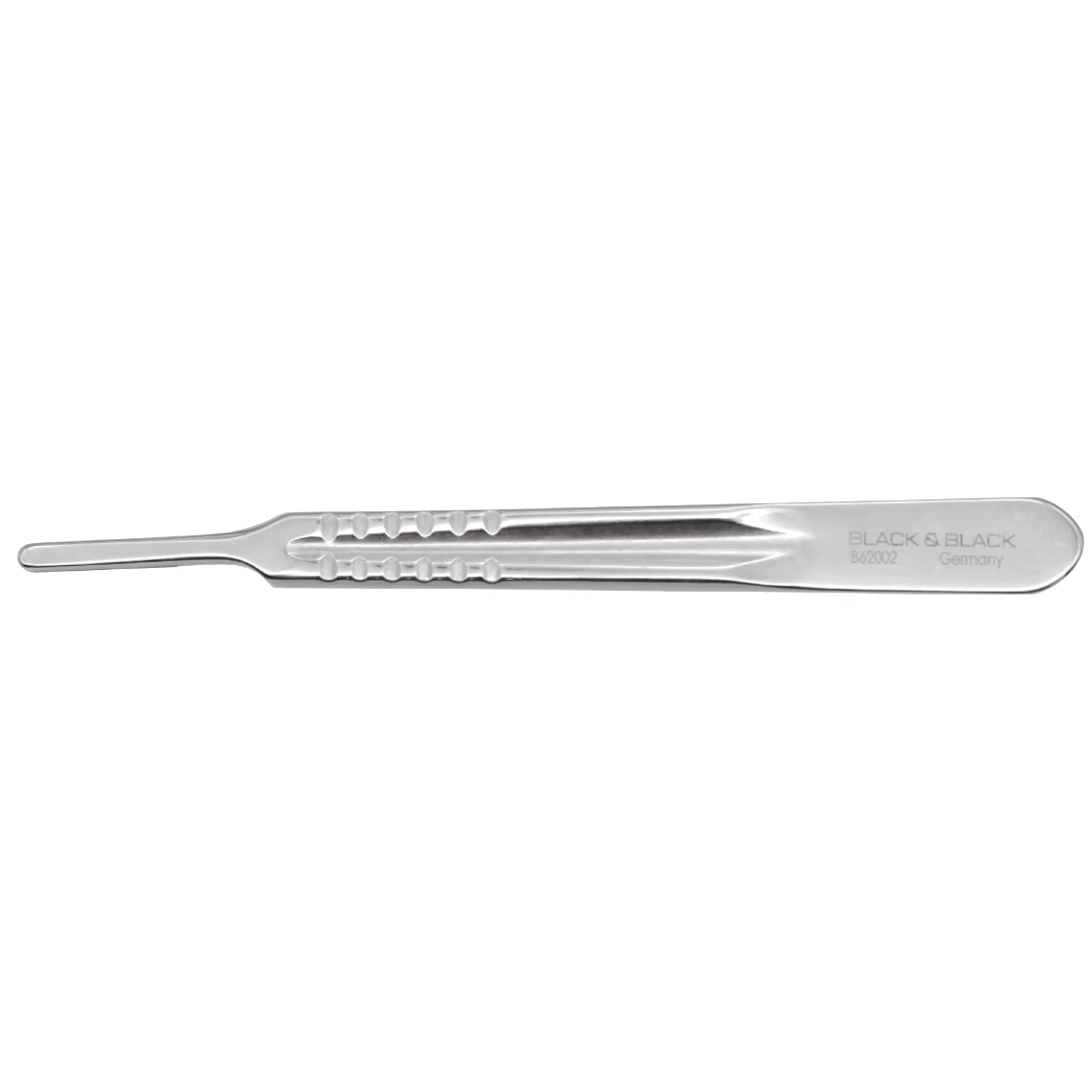

No.20 Blade
Used with the no. 4 handle to create a larger and/or deeper incision and on heavy tissues and bones (a broader body blade with a curved cutting edge to the tip)

Beaver Handle
used when precision cutting is needed in a confined space or when incising a small structure, commonly used in ENT, ophthalmic, neurology, podiatry, and small orthopedic procedures. The rounded tip has a slot that accepts the blade. As the tip is screwed into the handle , it tightens to hold the blade. (round handle with a ball tip that screws into the handle to tighten the blade in place)

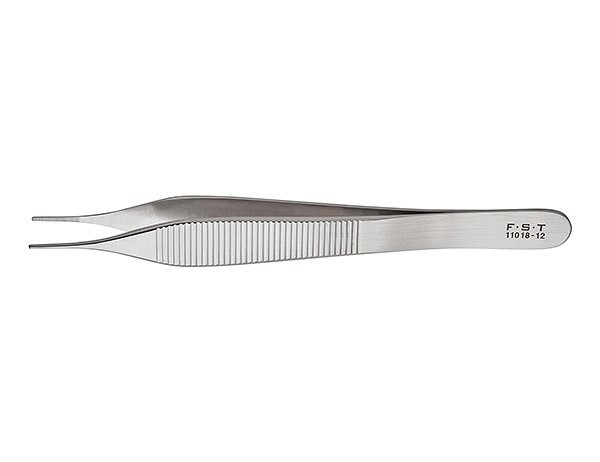
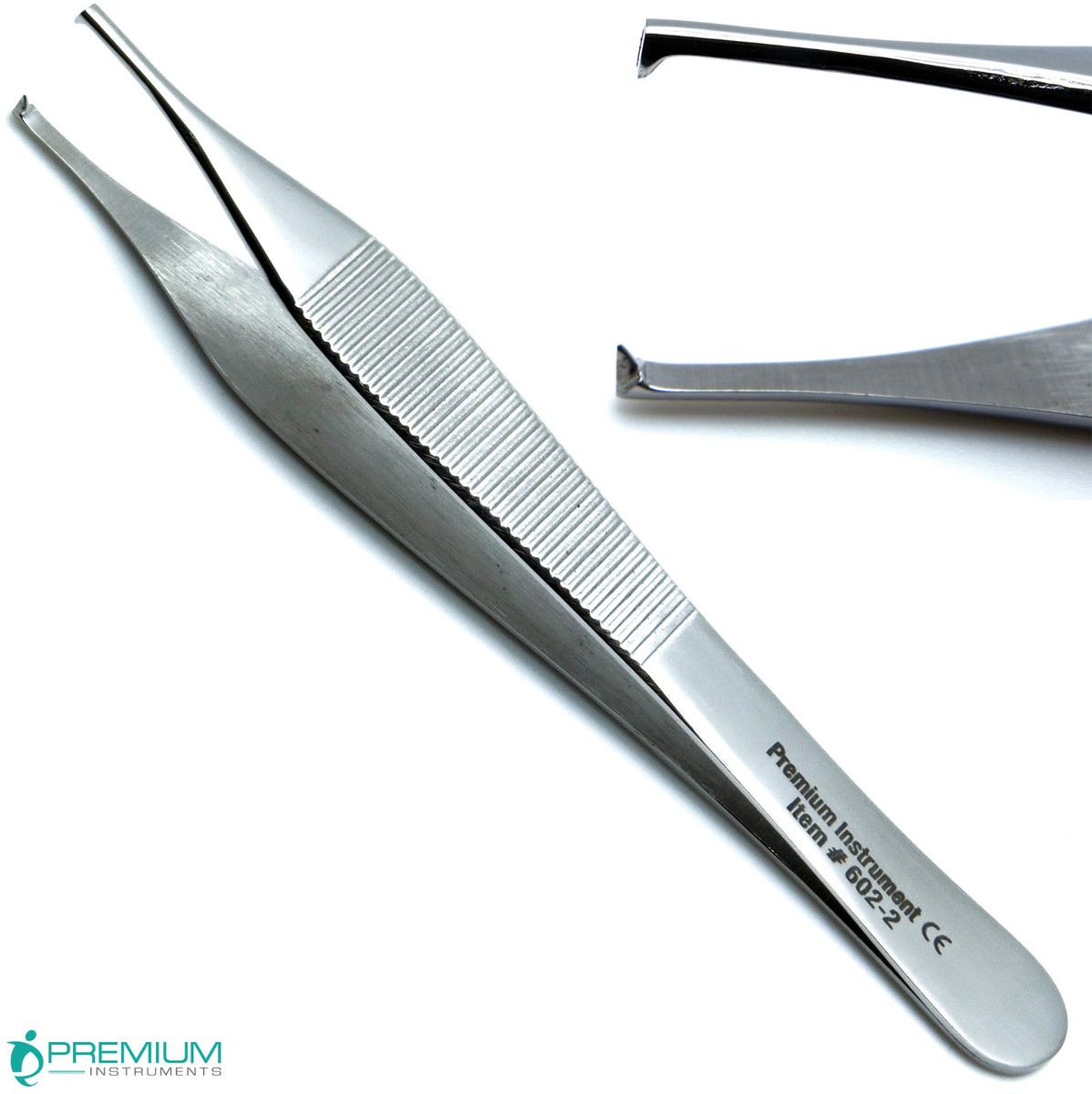
Plain Adson Tissue Forceps
used for grasping delicate tissue (fine tips with horizontal serrations)

Toothed Adson Tissue Forceps
aligns the edges of the wound during stapling of the skin, grasps superficial tissues so the Steri-strips (the fine tips have two small teeth on one side and one small tooth on the other side that fit together when close)

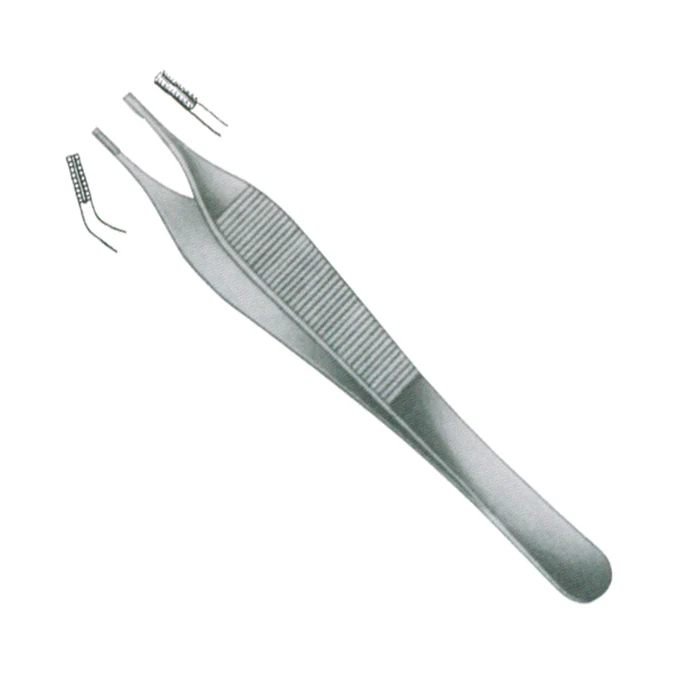
Brown-Adson Tissue Forceps
used for grasping superfiical delicate tissues. Often used in plastic or hand surgery. (on each side of the tip there are two rows of mulitiple teeth that interlock when closed)

Plain Tissue Forceps
used for grasping tissue and dressing application (atraumatic tissue forceps with horizontal serrated tips that vary from fine to heavy)
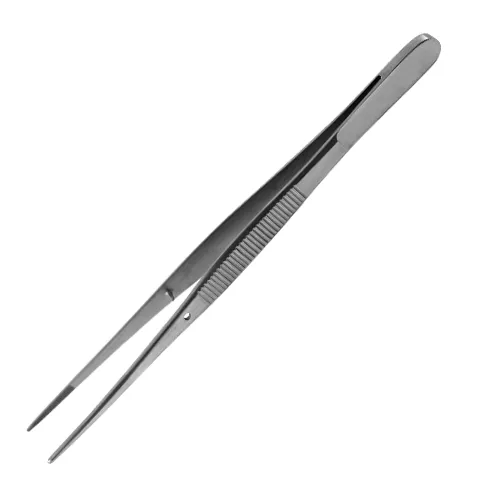

Toothed Tissue Forceps
used for grasping moderate to heavy tissue and used during wound closure (the tips have two teeth on one side and one tooth on the other side that fits between the opposite when closed)
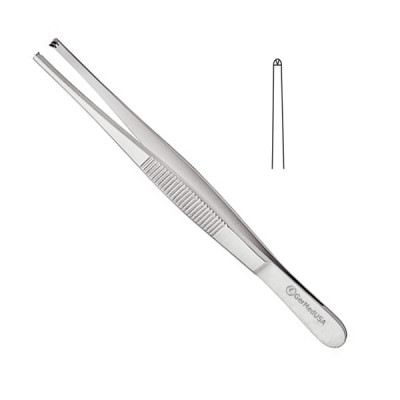

Debakey Tissue Forceps
grasps numerous types of tissue; commonly used in cardiac, vascular surgery, and gastrointestinal procedures (an atraumatic tissue forceps with an elongated, narrowed blunt tip. a set of parallel fine serrations runs the length of one jaw with a center row of serrations on the opposite side that interlocks to grip when closed)
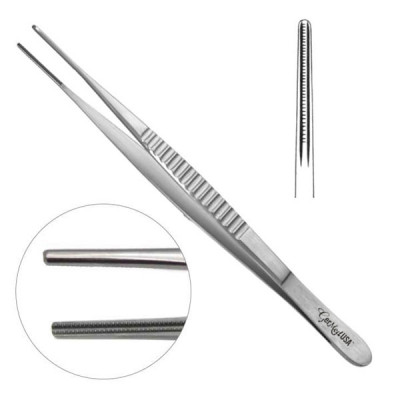

Bonney Tissue Forceps
used to grasp heavy tissue, muscle, or bone; often used in obstetrics and orthopedics (this is always the same size and shape. the tips have 1×2 interlocking teeth)
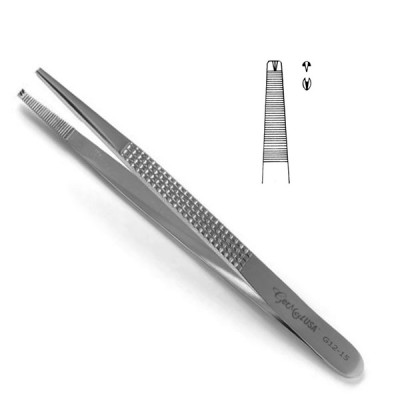

Ferris-Smith Tissue Forceps
used for grasping intestinal tissue, delicate tissues or dressings materials and sponges; often used in general, urology, thoracic, and OB/GYN surgeries. (this is always the same size and shape. the tips have 1×2 interlocking large teeth followed by a crisscrossed pattern serration)