Study for FTCE Engineering and Technology Education 6-12 Test
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
221 Terms
architectual drafting
the creation of drawings and models used to build structure
electrical drafting
formulate charts, plans and drawings that consist of electric wiring designs, which are used to set up and restore electrical equipment
mechanical drafting
based on technical drafting and computer-aided drafting (CAD) that concentrates on blueprints of machines and machine components used by engineers. Deals with 2d and 3d drafting and robotics
line conventions
Standardization of lines used on technical drawings by line weight and style.
dimensioning
The process of placing measurements and notes on a drawing to completely communicate its meaning.
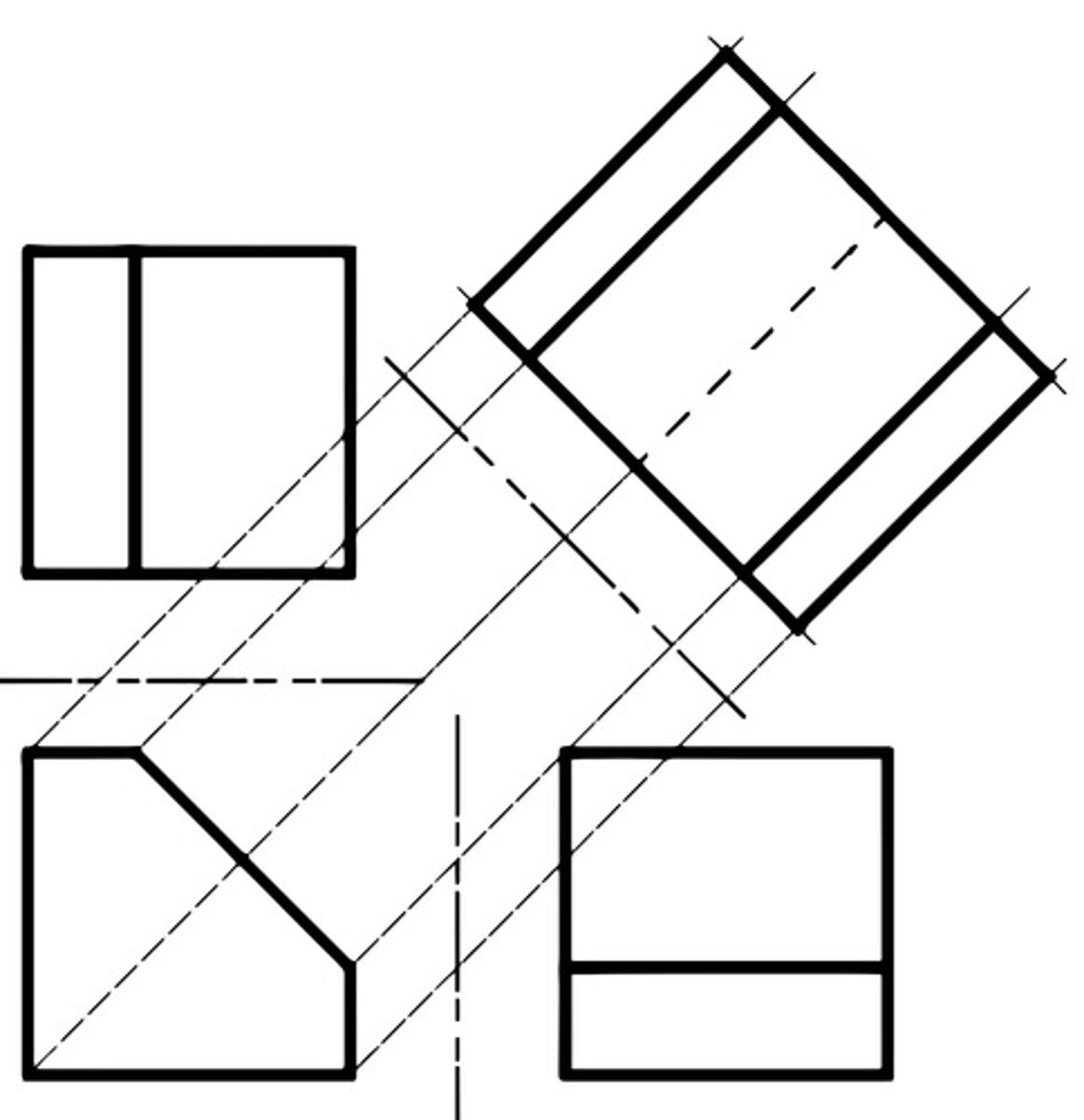
orthographic
2D flat reprsentation of a 3D object (ortho means straight, rectangular, upright) view of an object when you look at the top, front, back, left, right.
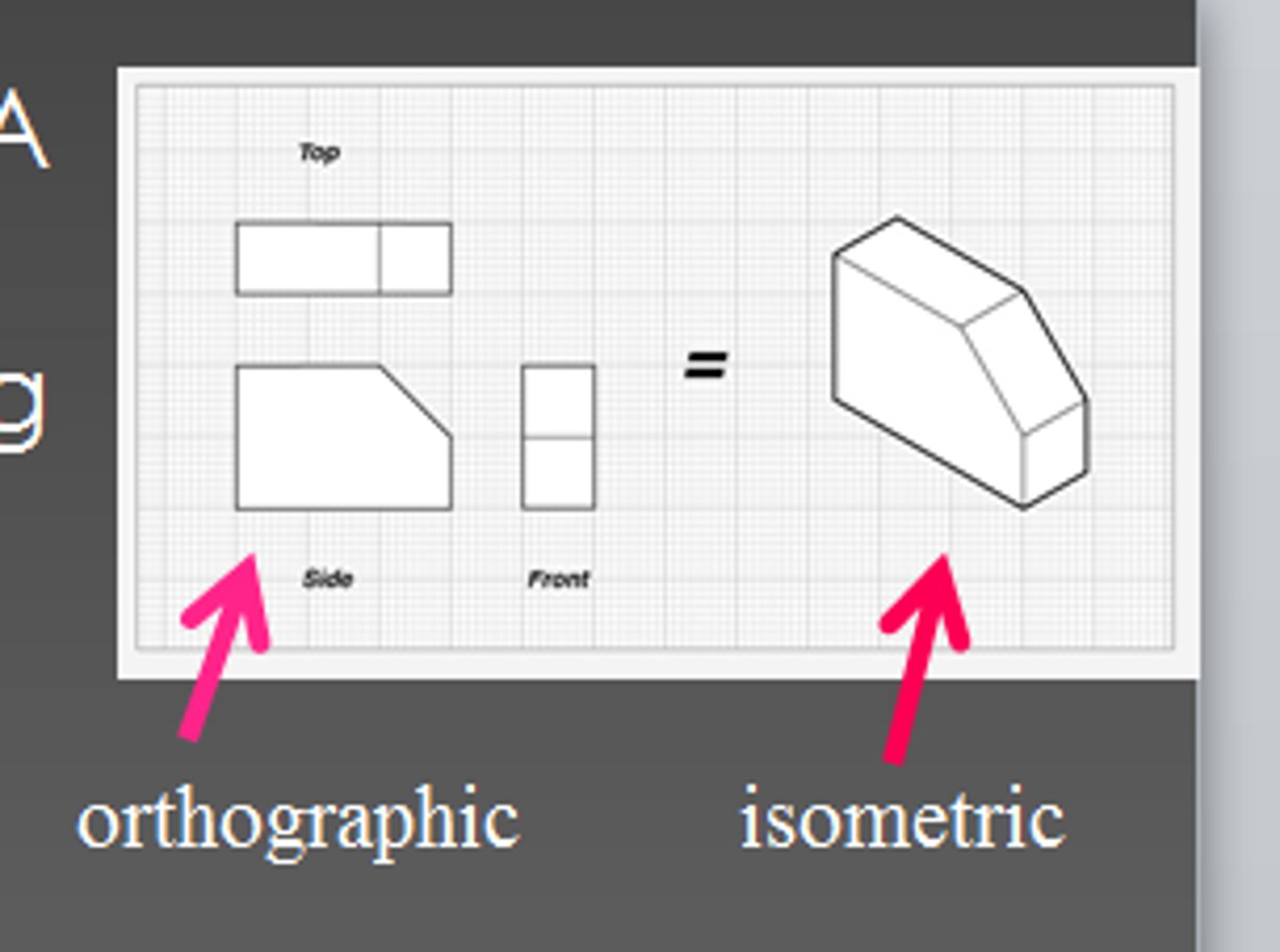
auxiliary view
planes through the object which are not common planes, surfaces that dont line up with the 3 major axes. view that is used to show features that are located on an inclined surface in true size and shape. is an orthographic view which is projected onto any plane other than the frontal, horizontal, or profile plane. (aux means to help)
resolution
number of lines per inch that a device can create
touch screen
Arrays of infrared light sources and array of
detectors are used to generate invisible light
grids. A finger interrupts two light beams and
provides x and y coordinates.
AC
alternating current. the flow of charge that changes direction periodically. As a result, the voltage level also reverses along with the current. AC is used to deliver power to houses, office buildings, etc.
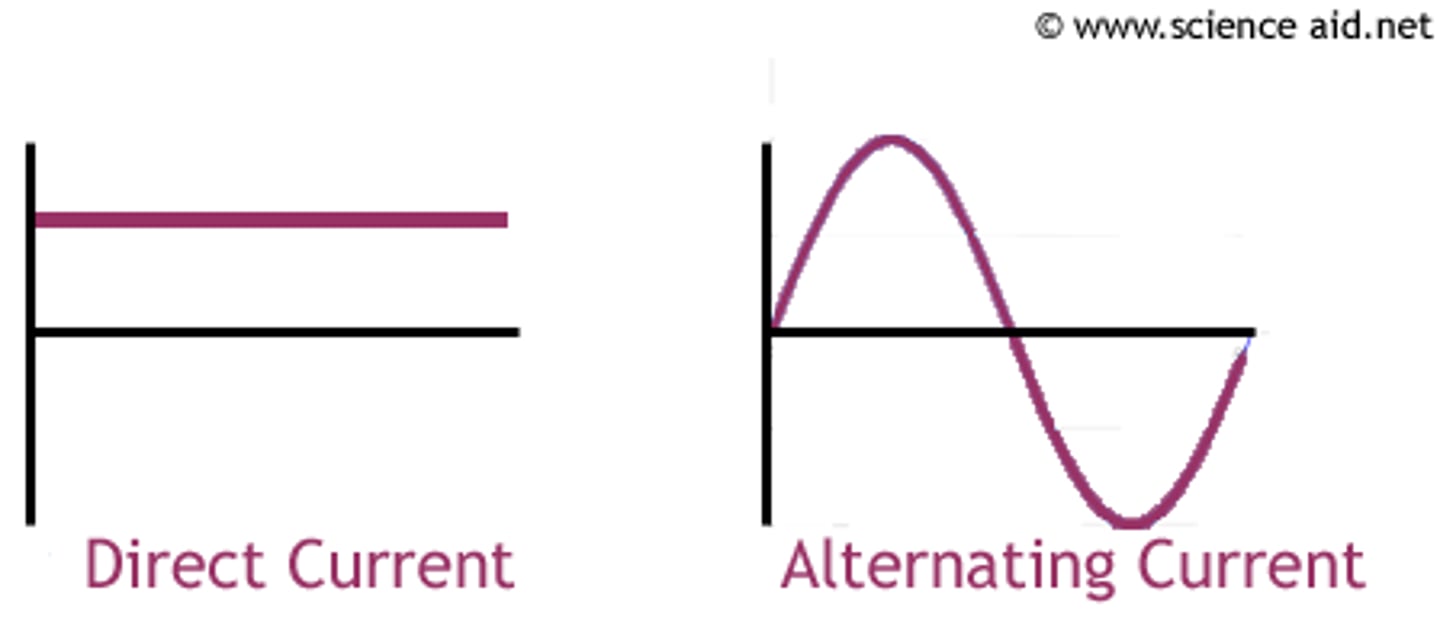
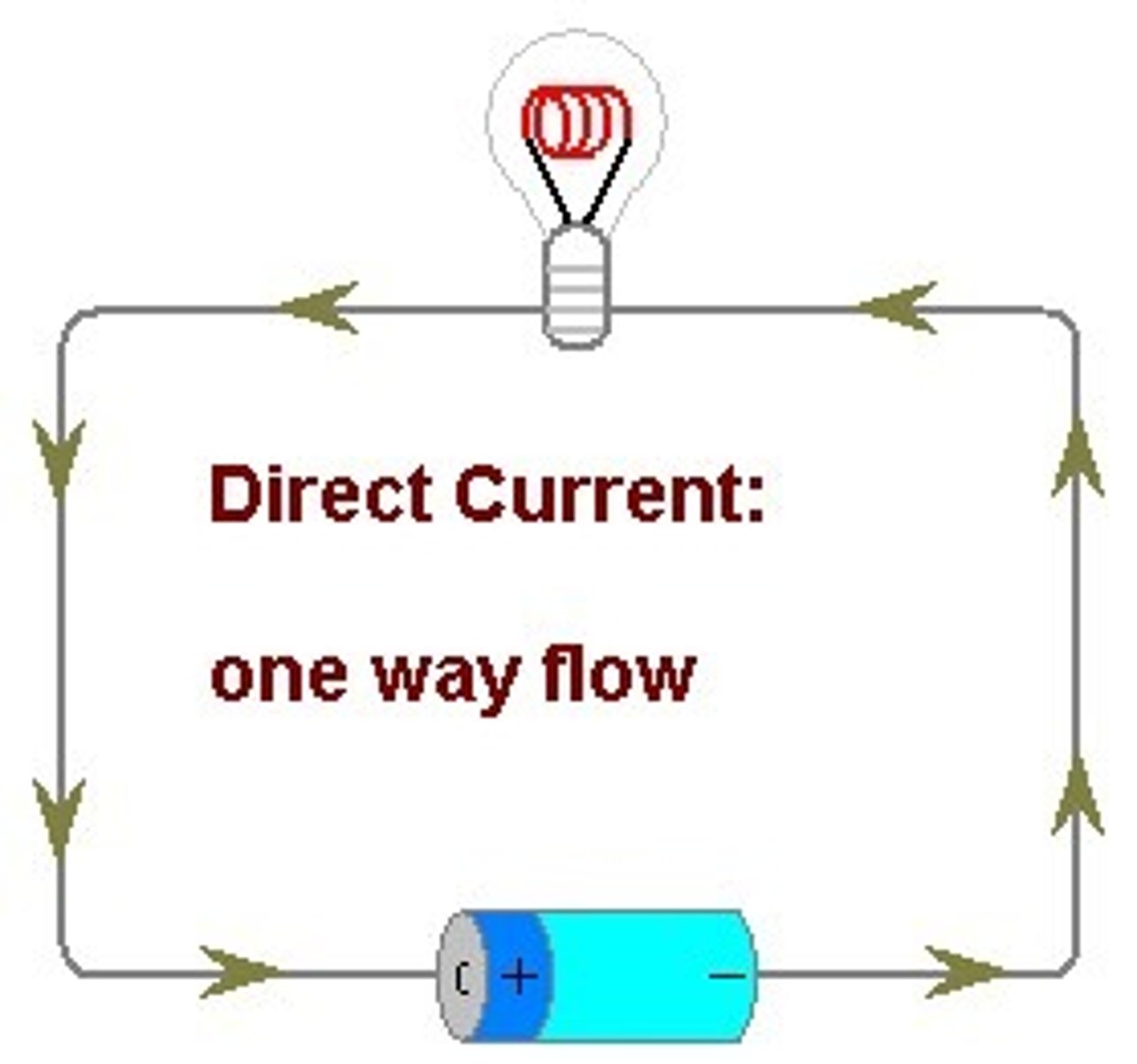
DC
direct current. an electric current that flows in one direction steadily. provides a constant current or voltage. Batteries provide DC, which is generated from a chemical reaction inside of the battery. Everything that runs off of a battery, plugs in to the wall with an AC adapter, or uses a USB cable for power relies on DC.
Kirchoff's law
law that deals with the conservation of energy around a closed circuit path. His voltage law states that for a closed loop series path the algebraic sum of all the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is equal to zero.
Ohm's law
how electrical resistance is measured; current = voltage/resistance or I = V × R which means current will rise when voltage rises but resistance is cut in half
analog circuit
information is translated into electric pulses of varying amplitude. denoted by sine waves. example: human voice

digital circuit
translation of information is into binary format (zero or one) where each bit is representative of two distinct amplitudes. denoted by square waves. example: computer, CD

electrical current
the flow of electrons. it only exists when there is a flow of electrons in one direction. it's measured in amperes (A).
1 ampere (A)
how we measure the strength of electrical currents and says how many electrons pass a fixed point in one second. the flow of one coulomb of charge per second.
coulomb's law
describes the relationship between 2 charged particles. F=k(q:q q2/d2) where f is force and q are 2 different particles and d2 is distance. like charges repel and opposite charges attract.
1 amp of current in 1 second. describes the magnitude of a charge but amps are the moving charge, the current, so they are more important :p
electrical resistance
the property of a material that resists electric current, measured in ohms. some metals, like copper, have no resistance while rubber has a high resistance.
voltage
this is pressure in an electrical system that pushes the electrons in a direction. there must be a difference in pressure on opposing ends of the circuit. example: battery which has high pressure on one end and low pressure on the other.
nuclear energy
the potential energy stored in the nucleus of an atom that is separated with nuclear fission. a chain reaction then happens which makes energy in the form of heat. this heat goes into water in nuclear reactors, steam rises up, goes into turbines which power electric generators.
fuel cell
A device that converts hydrogen or another fuel into electricity. It powers space shuttles and buildings. Cant use it on cars because the amount of hydrogen gas needed to power a car has too much volume to work

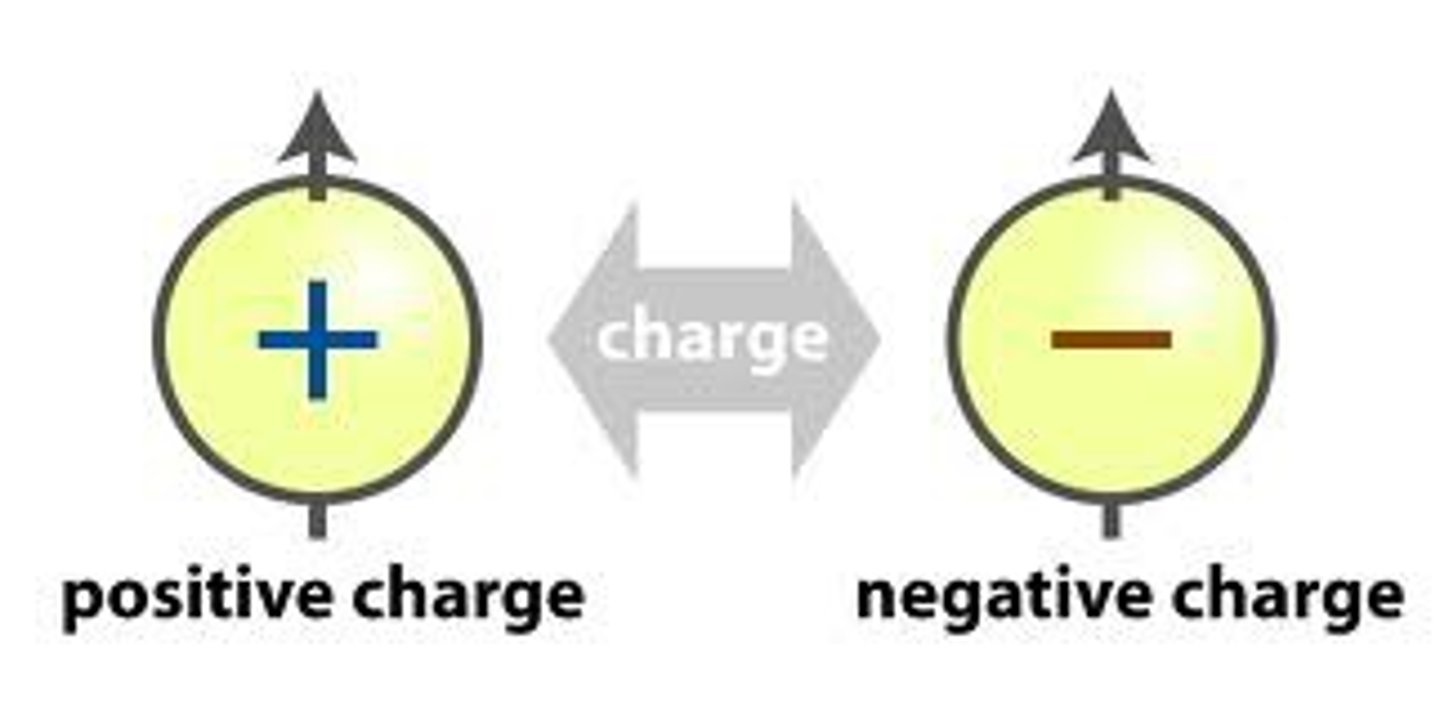
electrical charge
an excess or deficit of electrons on an object. like charges repel, opposite charges attract
fossil fuel
made of dead fossils that are hydrogen and carbon. coal is carbon. gas is in porous rocks (main ingredient in it is methane). oil in porous rocks or in pools and then is purified to be gas, kerosene, diesel
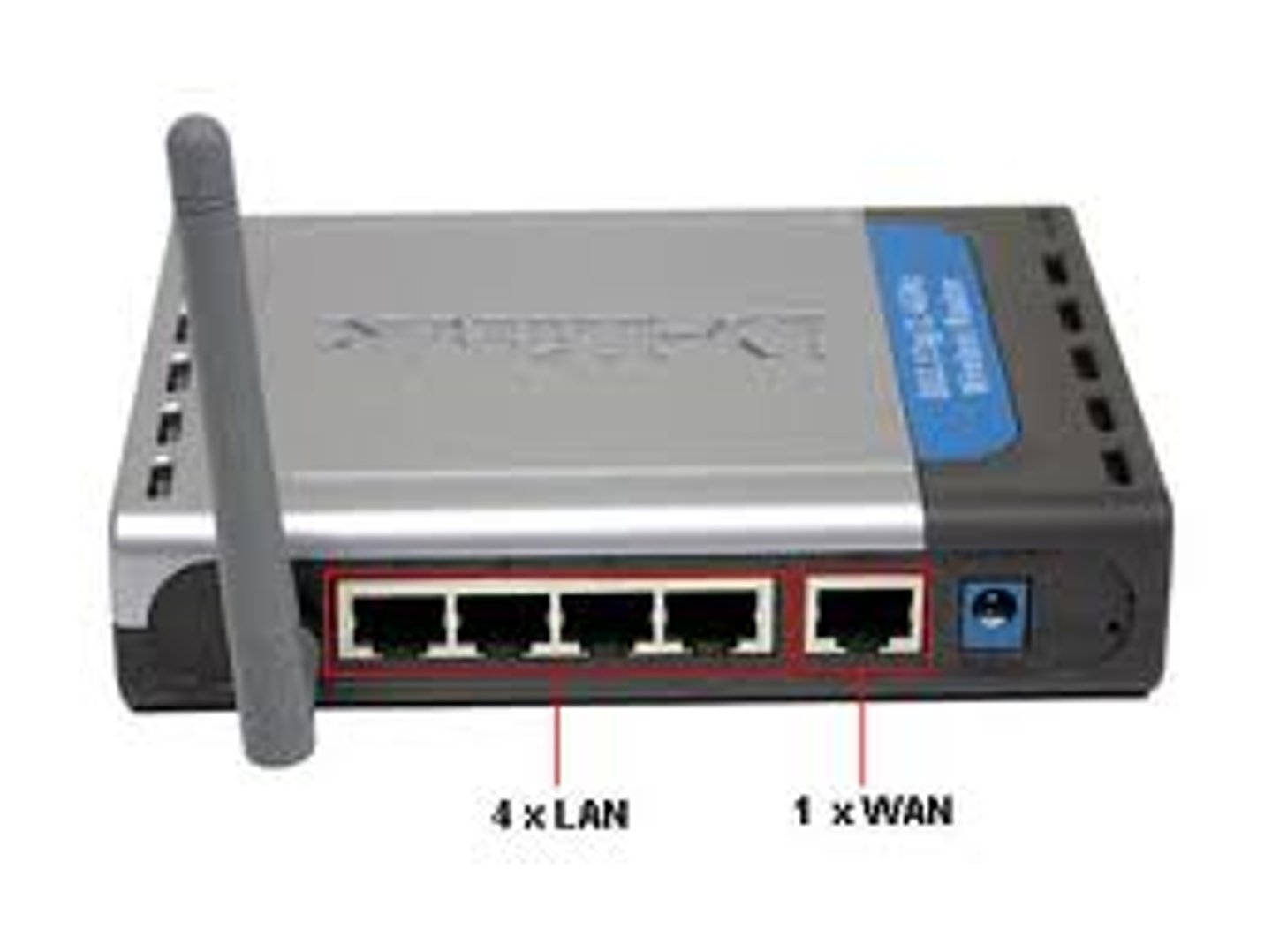
router
device that routes packets of data between two or more networks, the internet

cache memory
in the CPU, its a type of high-speed memory used to hold frequently used data immediately
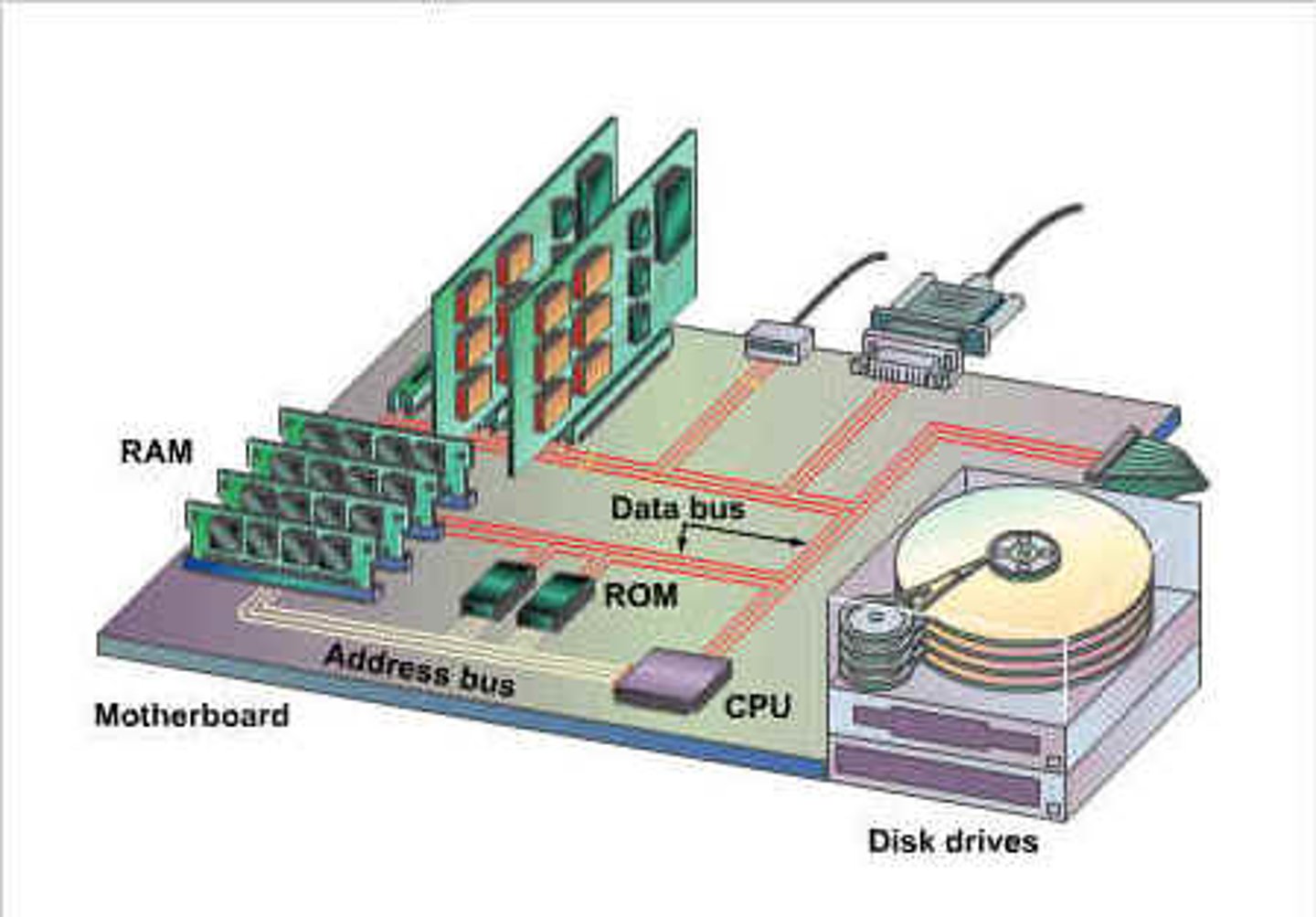
main memory in CPU
area in which a computer stores info, has RAM and read-only memory, ROM, which enables BIOS operation
bus
The electronic pathways between hardware components used to transfer data back and forth.
CAD
computer aided design; created 2D vector based drawing and 3D solid and surface modeling
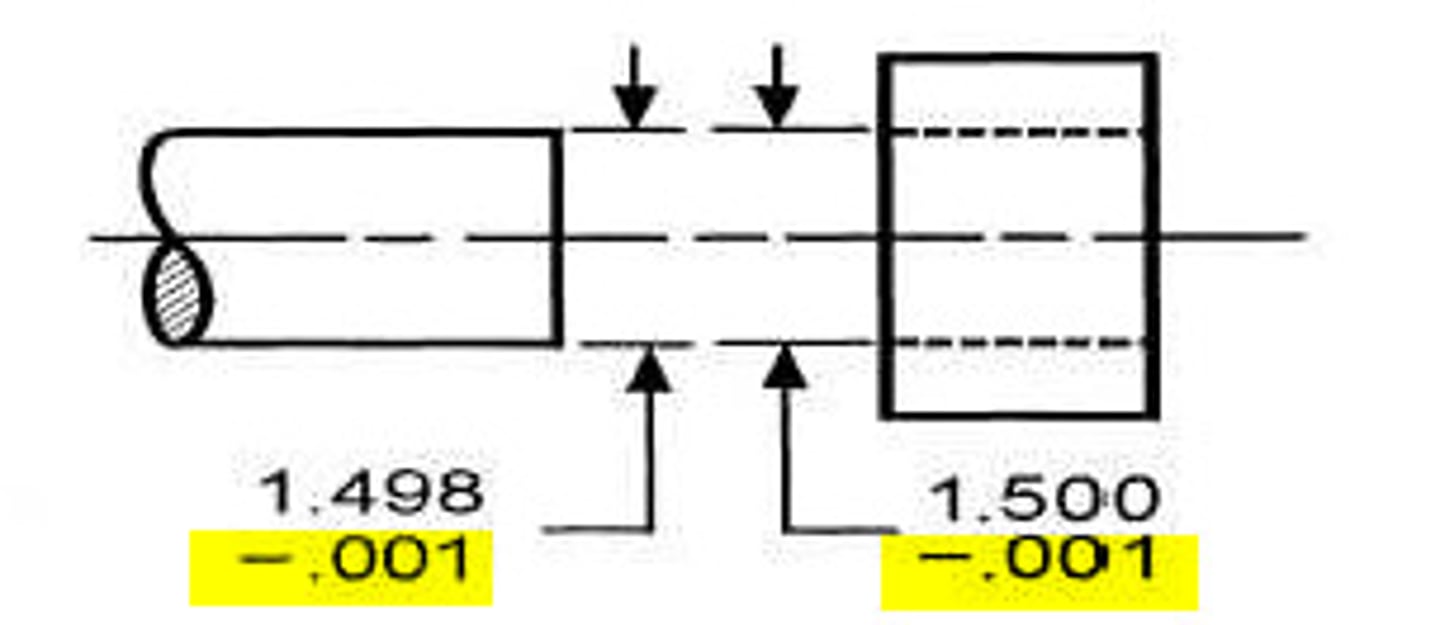
tolerances
the limits from identified criteria that will be allowed during production, such as height or width
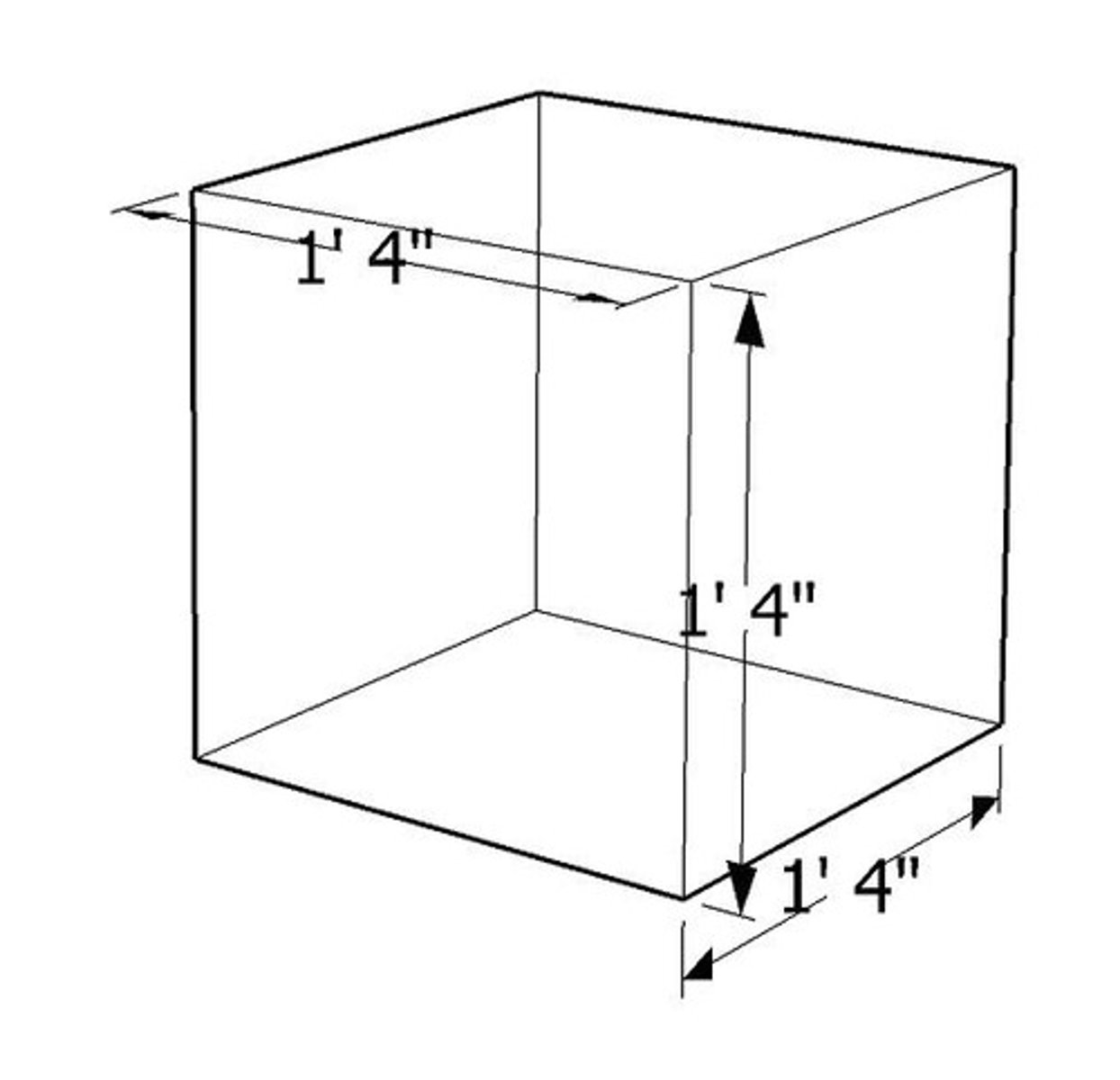
dimensions
Measurements in width, length, and sometimes depth
section lines, or cross-hatching
Thin lines used in a section view to indicate where the cutting plane line has cut through material.
phantom line
Lines that are made visible as dots or dashes. they stand for an object not included in the assembly or part specs
soler and peters 1993
protects confidentially of students
transmission
part of a machine that directs the energy created to the intended task.
Power is transmitted to the ENGINE, then the crankshaft which creates torque, or rotational force, and then sends it to the axles which sends it to the WHEELS
SPC
Statistical Process Control. control tools such as control charts are used by quality engineers to identify statistical variations within a process. help decide the specific metrics that should be monitored and the method by which they should be sampled
Six Sigma
A business process for improving quality, reducing costs, and increasing customer satisfaction
lean manufacturing
manufacturing whose goal is to eliminate waste in all aspects of the process
excel formula to add cells
=SUM(A1:A2) entered into cell A3
patent
inventor can exclude others from using, selling or importing the technology for the duration of the patent
GD&T
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing, engineer drawings follow standard conventions that mandate the use of certain layouts, typefaces, etc
how to treat deep cuts
apply CONSTANT pressure until bleeding has stopped. once it has stopped, wrap the wound with cloth and leave it alone.
when not to move people
if head or back injury
parallel projection
uses perspective to represent a 3D object in 2D on a flat piece of paper. the projection lines that run parallel on the paper run parallel in real life.
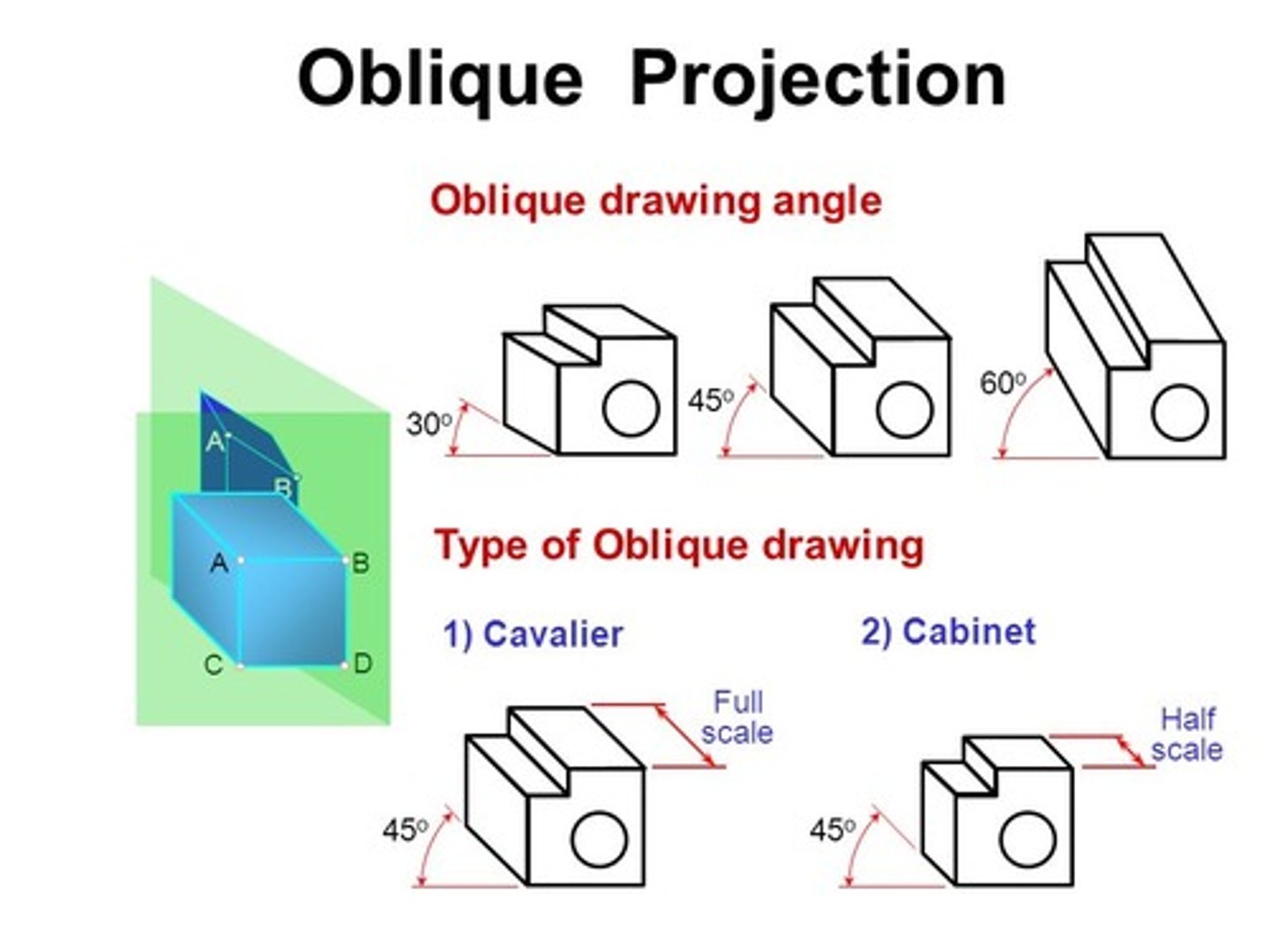
oblique projection
take parallel projection lines and have them intersect the viewing plane at an angle OTHER THAN 90 degrees.
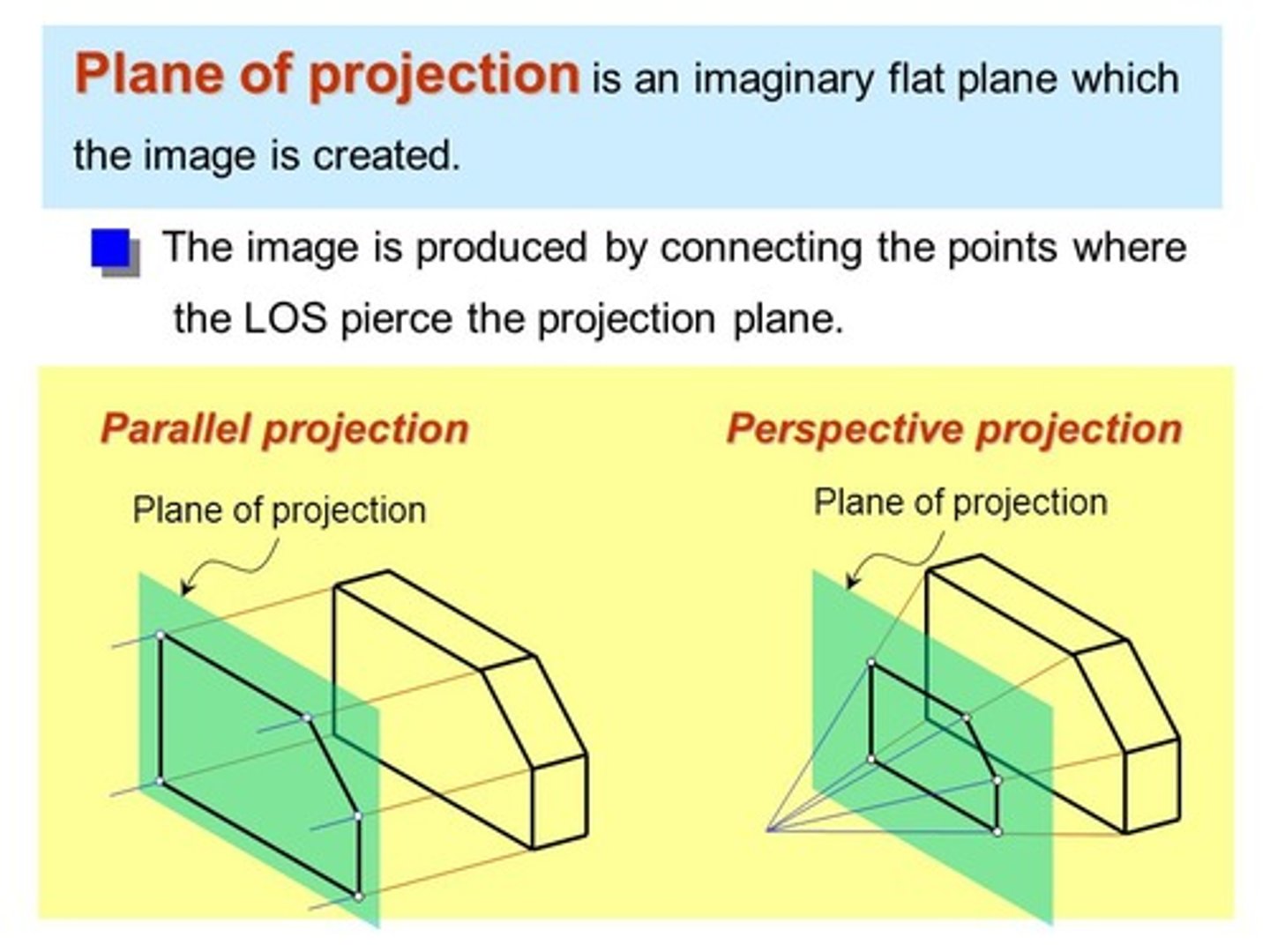
plane projection
imaginary flat plane in which an image is created
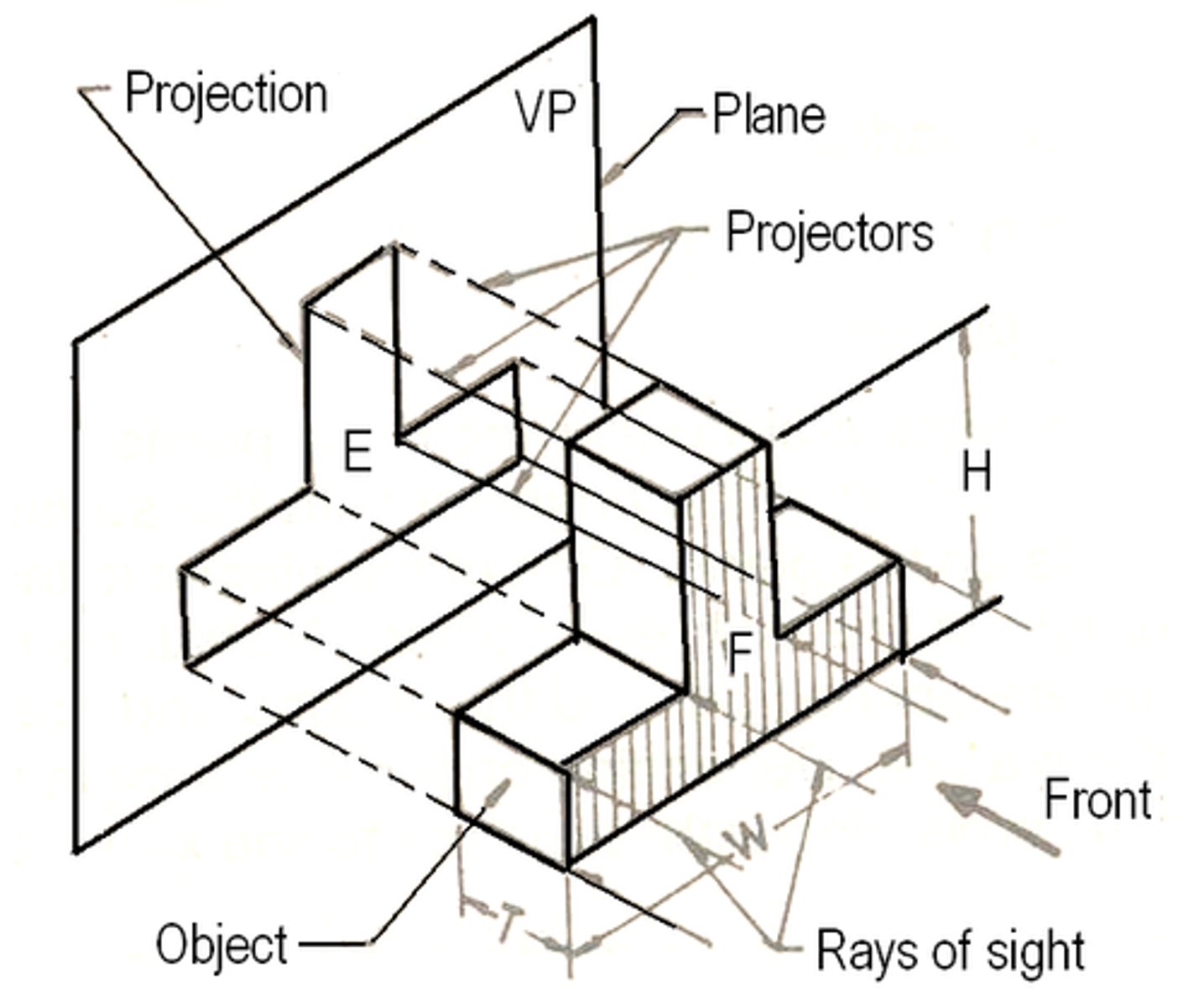
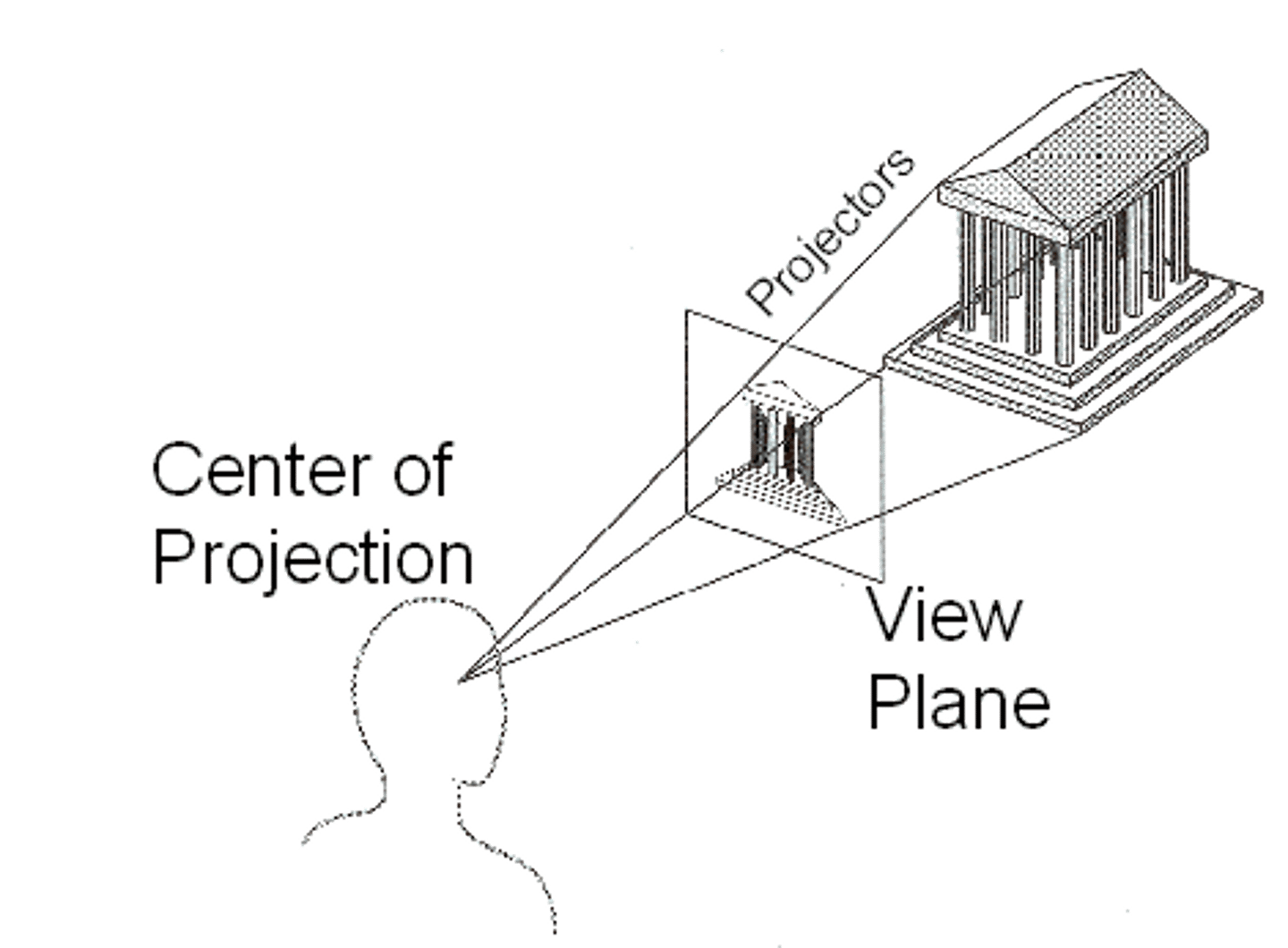
perspective projection
a 3D object can be represented by projecting points upon a picture plane using straight lines converging at a fixed point, representing the eye of the viewer.
ISO 9000
International Orgz for Standardization, quality standards for products

auto engine blocks are made of
iron
ship hulls are made of
steel
airplanes are made of
aluminum alloys & composite materials
pistons in the engine are made of
aluminum
software developer
aka analyst developer, programmer. examines requirements for applications and translates them into program specs, design, write, test and use programs to solve problems.
business systems analyst
aka business systems planner and solutions architect. identify the business and info needs and then enhance productivity by developing new IT solutions
database programmer
aka database coordinator and database admin. design, implement and maintain database. develop strategies to improve database
information systems analyst
aka information systems designer. decides whether or not the computer system is fulfilling the orgz's need in the most efficient manner. need to know telecom technology, software apps and business operations
piston
movable part in the cylinder forced into motion by explosion of fuel
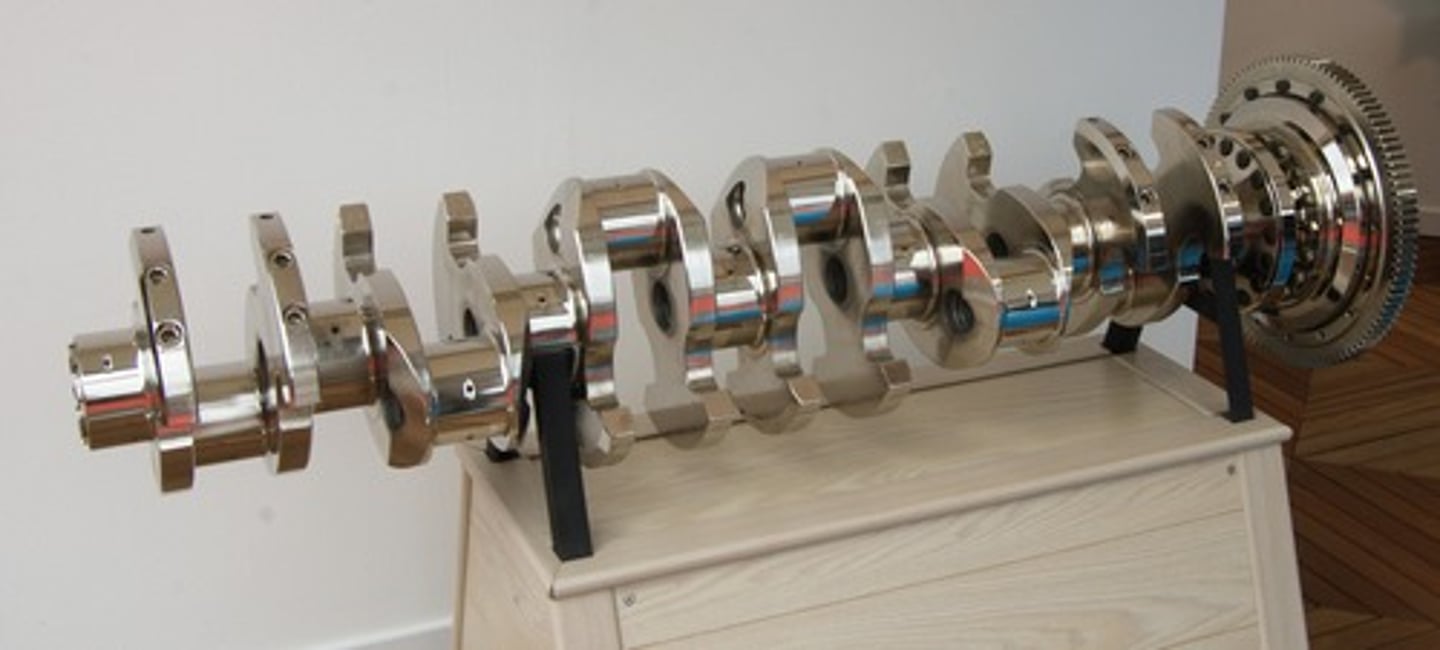
crankshaft
The power from the engine is too fast for the wheels so it goes here. The cylinders with pistons in them make an up and down motion which turns into circular motion which creates torque, or rotational force, and that is sent to the transmission which sends it to the wheels.

1st phase of the engineering design process
RESEARCH
2nd phase of the engineering design process
CONCEPTUALIZE potential solutions
trigger word
say a word associated with a problem until this leads to words that create solutions
morphological chart
design characteristics of the problem and then propose solutions for each characteristic
phases of the engineering design process
research, conceptualize (brainstorm), feasibility, design, preliminary design, detailed design, production planning and tool design, production (RCF DPD PP)
3rd phase of the engineering design process
FEASIBILITY assessment. its to determine whether or not the solution is possible by asking: is it based on an achievable idea AND is the project within the cost constraints?
4th phase of the engineering design process
DESIGN requirements. its to establish the software and hardware parameters and testability, maintainability and other key requirements. it's carried out with the feasibility phase
physics: Bernoulli's principle
when the speed of an inviscid (not sticky) flow increases, the pressure (or potential energy) of the flow will decrease AKA fast flow: lower pressure, faster air, slower static pressure & higher dynamic pressure. EXAMPLES: carburetors & pitot tubes
carburetor
Provides fuel and air to the engine in appropriate proportions and volume.
vaporizes gas before it enters the cylinders.

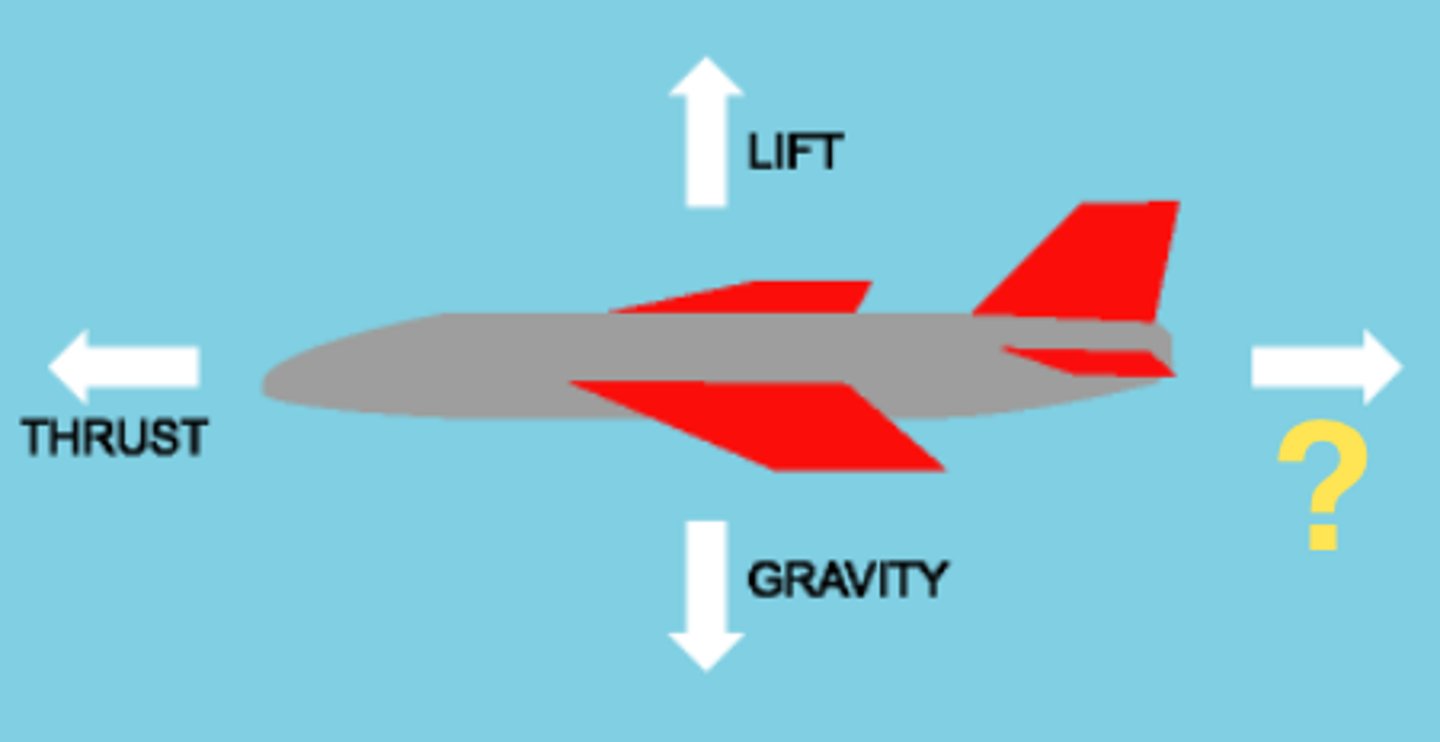
physics: Aerodynamics
4 forces relevant to flight: thrust, lift, drag, weight. to achieve flight, all forces must be balanced.
thrust
reaction force explained by Newton's 2nd and 3rd laws. When mass is accelerated in one direction, it will generate an equal force in the opposite direction. Jet engines, propeller blades and rockets generate thrust by pushing air in the direction opposite to flight.
lift
a force that is generated perpendicular to the oncoming air flow (using Bernoulli's Principle). Airplane wings are designed to take advantage of lift (climbing, descending, banking)
drag
a force that's generated parallel to the oncoming airflow and OPPOSES the motion of an object.
5th phase of the engineering design process
aka embodiment design. defines the overall system design: layouts, diagrams, schematics. early diagrams.
6th phase of the engineering design process
detailed design phase
7th phase of the engineering design process
production planning and tool design. a plan is made for mass producing the product and identifies the tools needed. working prototype is made and tested.
8th phase of the engineering design process
production!
resource leveling
balance the uses of resources by eliminating inventory shortage & excess. a technique for resolving resource conflicts by delaying tasks
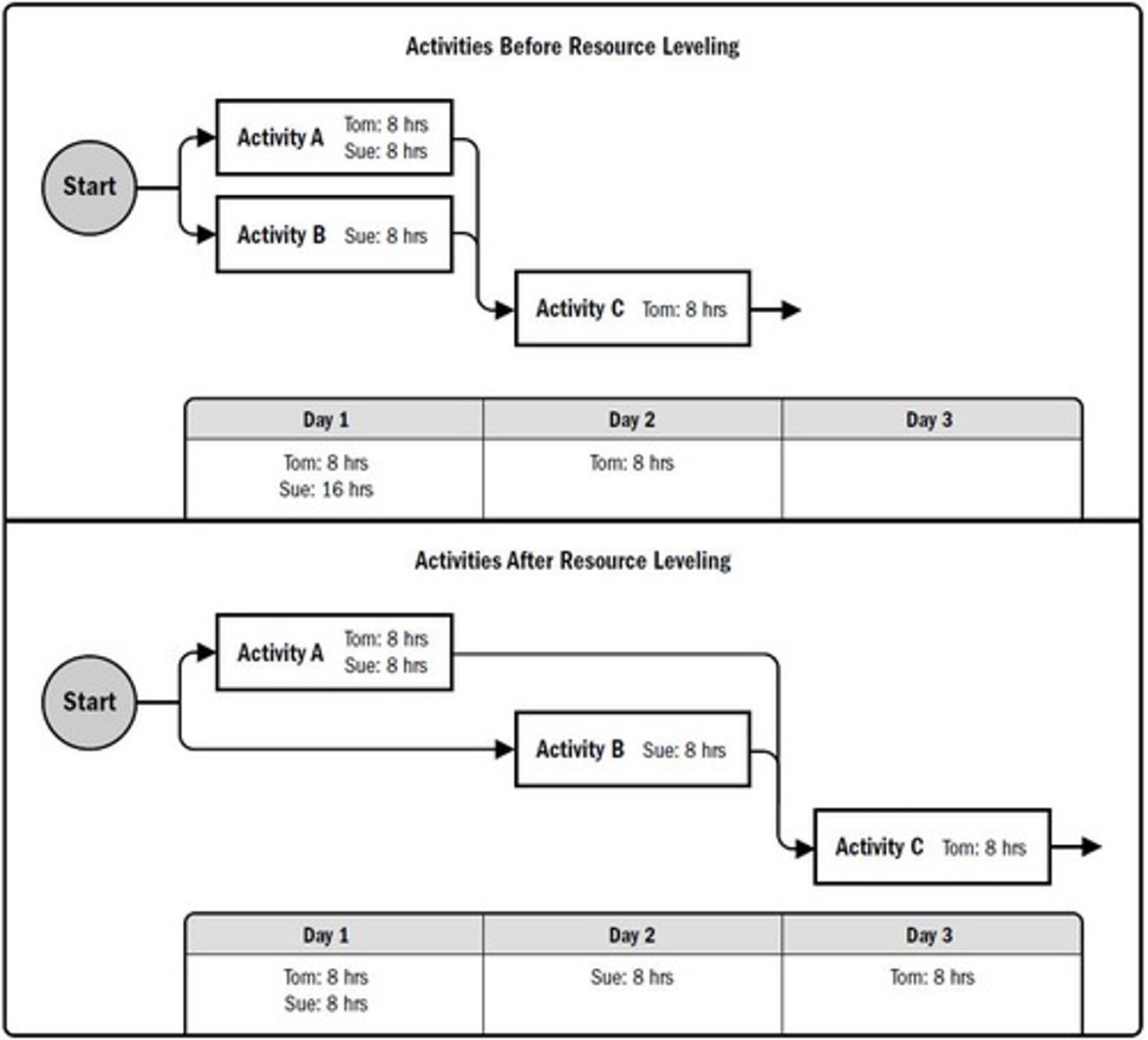
terminal elements
basic work activities that can be divided into smaller tasks
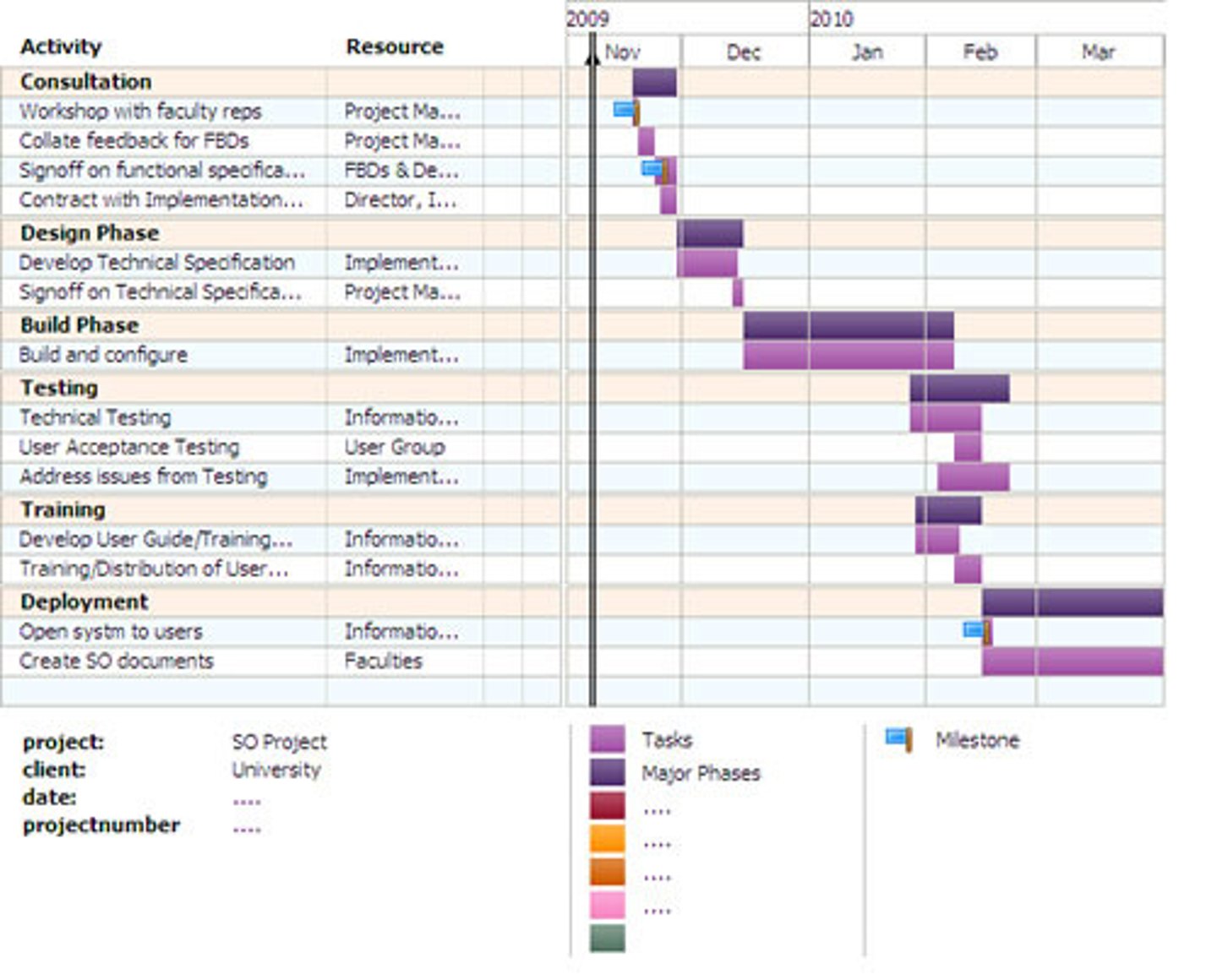
work schedule
breaks a project down into its most basic terminal elements, or work activities. has estimates for resources, duration of work activities, arrange them by order of completion
Gantt chart
A horizontal bar chart that graphically displays project tasks and durations. It shows terminal elements, or work activities
safety or risk assessments involve 3 steps
1) identify the hazard 2) perform a dose response analysis to see dosage necessary to produce a response 3) perform exposure quantification to determine the dosage the population is to receive
historical context of the car
granted a patent to Benz in 1885.
historical context of the plane
1903. Wilbur and Orville Wright. they used aerodynamic principles, drag and lift, to develop the first power and controlled flight.
historical context of the integrated circuit
1958 by Kilby of TI and Noyce of Fairchild. led to the development of the microchip by enabling semiconductor devices to perform the same functions as vacuum tubes. revolutionized electronic equipment, leading to PC, cell phones, etc
historical context of the internet
1983 by Kahn and Cerf who came about with the first TCP/IP protocol.
integrated circuit
A group of tiny TRANSISTORS and electric wires built ON a SILICON wafer, or chip.

vacuum tube
A tube that resembles a light bulb, was used in first generation computers. controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. electricity passes through it.

semiconductor
a material that conducts current under certain conditions

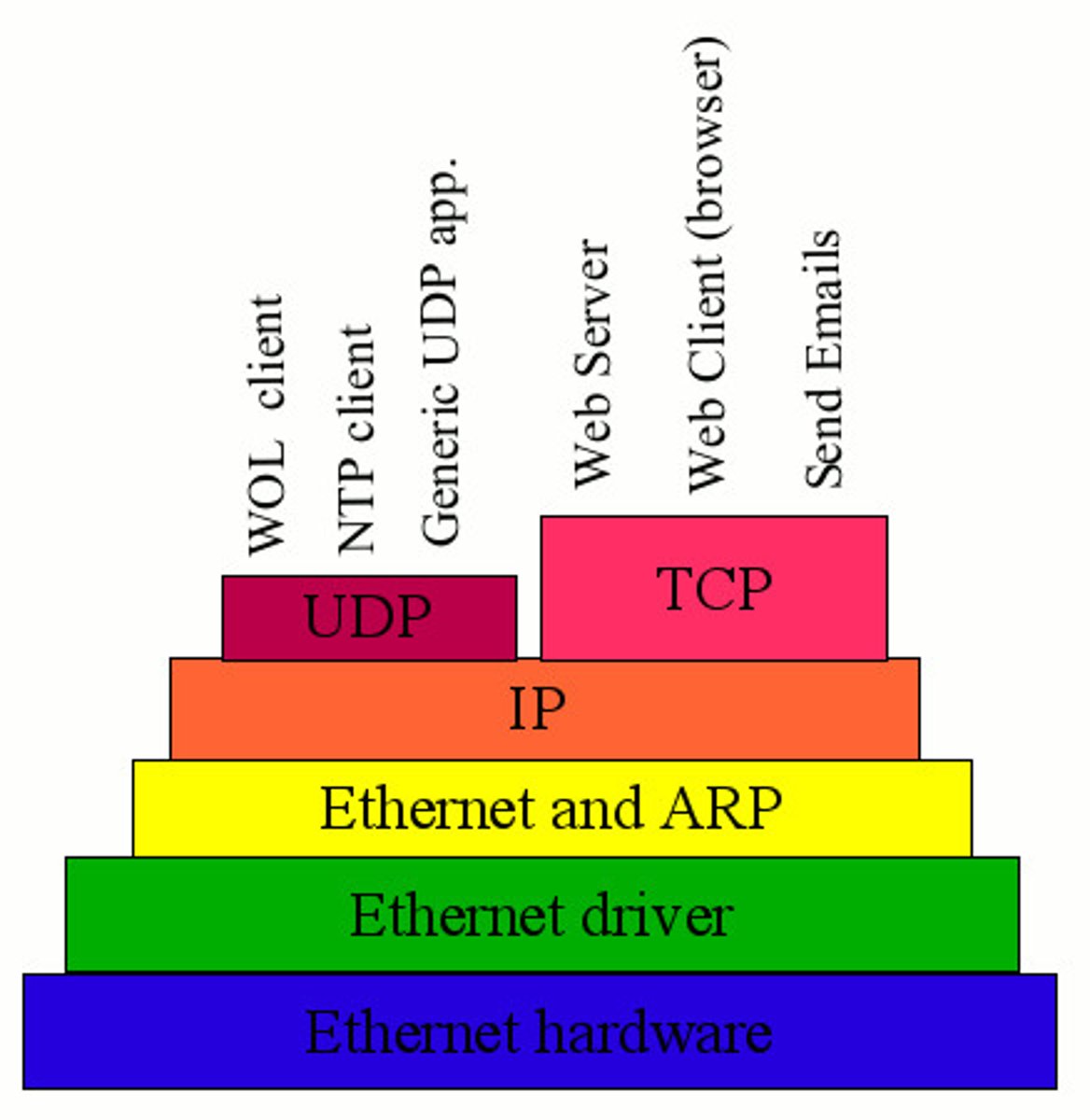
TCP/IP protocol
a scheme of 5 protocol types arranged in layers. protocls are rules determining transmission of data.
rules governing the transfer of information between computers = the rules.
how to help electrocuted person
don't touch them! if power cant be turned off, use a piece of nonconducting material (lumber) to separate them from energized conductor. damaged equipment can be hazardous!
s curve
Nearly all technology cycles follow this pattern of innovation with upwards, stabilized and then downward growth. also called diffusion
synergistic
works together
role of the career and technical education curriculum advisory committee aka CTE
to establish criteria and tools that the state and district will use to evaluate courses. also, to determine if CTE courses fulfill their requirements
anecdotal record
informal measurement based on observation of student work or performance

steel
metal alloy that is made by alloying iron with carbon
alloy hardness
increased levels of carbon increase this
ductility
the ability of a substance to be pulled into a wire, twisted and warped. the levels of this go down when carbon levels go up and the alloy hardens

flat carbon steel
used in major appliances, like cars and boats.
stainless steel
an alloy of iron, carbon, and nickel or chromium.
steel containing chromium that makes it resistant to corrosion. used in medical and surgical equipment and cutting tools.
aluminum alloys
aerospace, shipbuilding, cycling and automotive industries.
long steel
high strength wires, bridges, building structures.