2.3.3 properties of transition metals
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what is the definition of transition metal
an element with an incomplete d subshell or an element that can form at least one stable cation with an incomplete d subshell
what 2 element are not transition metals and why
scandium because can only forms Sc3+ with configuration of (Ar) 3d0
zinc because forms Zn2+ with configuration 3d10
draw a periodic table. indicate the s p and d blocks
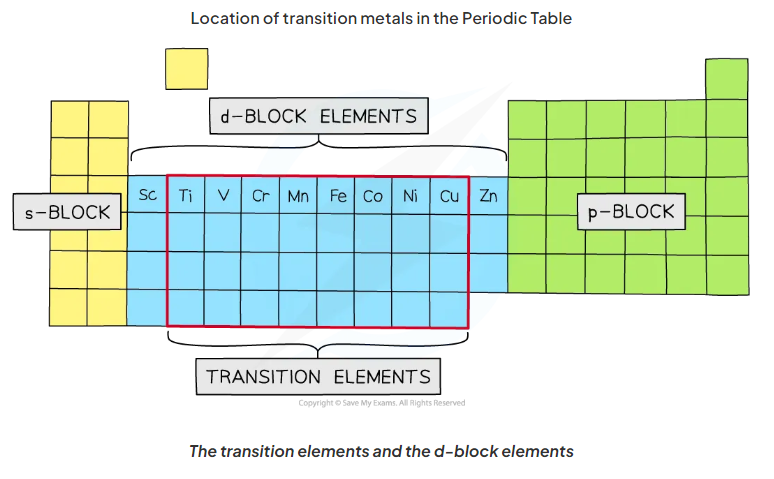
decribe the structure of a transisiton metal
a lattice of positive metal ions surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons
why can transition metals delocalise d electrons
because 3d and 4s subshells so close
why do transition metals have high melting points
can delocalise d block eletrons so have greater electron density. means the electrostatic forces of attraction between large positive charge of ions and delocalised electrons strenghtened and higher melting point as more energy to overcome
high or lower than group 1 and 2 elements
higher melting points than g1 and g2
why do transition metals have a high electrical conductivity
lots of delocalised electrons which are free to flow and carry a charge when a potential difference applied