Chapter 12 Textbook Qs
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Which are characteristics of an ideal antimicrobial drug?
(a) Microbiostatic rather than microbicidal
(b) Slow or nonexistent development of antimicrobial resistance
(c) Toxic to microbe but nontoxic to the host
(d) Prevents host’s immune response from interfering with its effects
(e) Soluble in body fluids
(f) Quickly inactivated to reduce toxic effects to the host
(a) Microbiostatic rather than microbicidal ❌
Ideally, drugs should be microbicidal (kill the pathogen) rather than just inhibit growth.
Microbiostatic drugs are sometimes used, but they are not the ideal choice.
(b) Slow or nonexistent development of antimicrobial resistance ✅
An ideal drug should not easily promote microbial resistance, so it remains effective long-term.
(c) Toxic to microbe but nontoxic to the host ✅
This is the principle of selective toxicity — one of the most important characteristics.
(d) Prevents host’s immune response from interfering with its effects ❌
Ideally, the drug should work with the immune system, not prevent it from acting.
(e) Soluble in body fluids ✅
To reach the site of infection, a drug must be soluble and stable in body fluids.
(f) Quickly inactivated to reduce toxic effects to the host ❌
The drug should remain active long enough to destroy the microbe, not be inactivated quickly.
Briefly describe the characteristics of an ideal antimicrobial drug.
An ideal antimicrobial drug is:
Selectively toxic (kills microbes, not the host)
Resistant to inactivation and
Soluble in body fluids (in order to reach the site of infection)
Stable and effective over time
Unlikely to cause resistance
The term antimicrobials describes ________________.
The term antimicrobials describes any drug that works against microbes, no matter which microbes are targets.
The use of a drug to prevent imminent infection of a person at risk is called ________________.
The use of a drug to prevent imminent infection of a person at risk is called prophylaxis.
The use of chemotherapeutic drugs to control infection and diseases caused by many types of microorganisms is called __________ chemotherapy.
The use of chemotherapeutic drugs to control infection and diseases caused by many types of microorganisms is called antimicrobial chemotherapy.
T or F: An antibiotic is a substance produced by the natural metabolic processes of some microorganisms.
True
Why do some microbes produce antibiotics?
Some microbes produce antibiotics naturally to inhibit or kill other competing microbes in their environment.
T or F: Antimicrobial drugs are difficult to make because substances that are toxic to the bacteria are likely to be toxic to the host.
True
Provide 2 reasons why it’s difficult to make effective antimicrobial drugs for human pathogens.
(1) Human & pathogen similarity
Many human pathogens are eukaryotic, therefore share similar cellular structures w/ humans
This makes it hard to achieve selective toxicity (i.e. kill/inhibit pathogenic cells w/o harming host cells’)
(2) Complex Life Cycles & Host Dependence:
Eukaryotic pathogens (like protozoa and worms) have complex life cycles with different stages that may each need a different drug.
Viruses use the host’s own cells to reproduce, so there are very few safe targets for drugs.
👉 This makes it hard to kill the pathogen without harming human cells.
Penicillin is _________.
(a) Chemically synthesized in a laboratory
(b) Naturally-derived from the Penicillium fungus
(c) Harvested from genetically-modified bacteria
(d) Naturally-derived from Streptomyces bacteria
The answer is (b)
Penicillin is naturally-derived from the penicillium fungus
An all-inclusive term for any drug used to fight an infection, regardless of what type of microbe it targets, is ____________.
An all-inclusive term for any drug used to fight an infection, regardless of what type of microbe it targets, is antimicrobial.
Prophylaxis is a practice of administering an antimicrobial drug ______.
(a) when symptoms of an infectious illness first appear
(b) before onset of infection
(c) throughout full course of the infection, from start of symptoms until they’re no longer present
(b) before onset of infection
Prophylaxis means preventive treatment — using an antimicrobial drug before an infection occurs to prevent disease.
It’s commonly used:
Before surgery to prevent postoperative infections.
Before dental procedures in patients at risk of endocarditis.
In people exposed to certain pathogens (e.g., malaria prophylaxis).
Antimicrobial chemotherapy is a _________ term used to describe the use of drugs to control infections caused by _________.
Antimicrobial chemotherapy is a general term used to describe the use of drugs to control infections caused by (a variety of) microbes.
The _________ technique is an agar diffusion test to determine antibiotic susceptibility of a particular bacterial strain.
(a) Southern blot
(b) Kirby-Bauer
(c) Sanger method
(d) Therapeutic index
(b) Kirby-Bauer technique is an agar diffusion test to determine antibiotic susceptibility.
A substance produced by the natural metabolic processes of some microorganisms, and that can inhibit or kill other microorganisms, usually targeting bacteria, is a(n) __________.
A substance produced by the natural metabolic processes of some microorganisms, and that can inhibit or kill other microorganisms, usually targeting bacteria, is a(n) antibiotic.
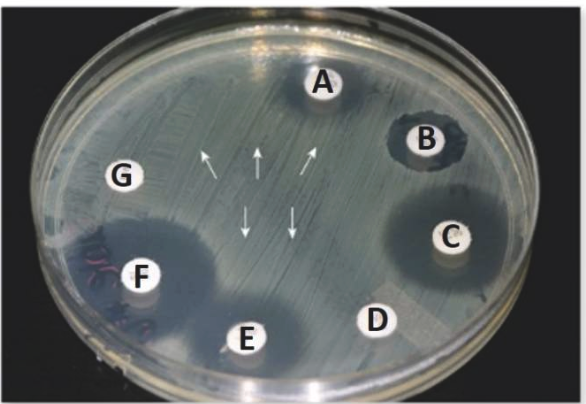
Consider the relative sizes of the zones of inhibition surrounding the antibiotic discs in the image. Provide a brief analysis of the effect of each antibiotic (A-G) on the microbe in the petri dish.
Microbe is likely susceptible to antibiotics C & F
Microbe is resistant to antibiotics D & G
Microbe is somewhat inhibited by antibiotics B & E
Penicillin is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic that is naturally produced by a(n) ________ named Penicillium.
Penicillin is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic that is naturally produced by a(n) fungi named Penicillium.
The ratio of toxic dose to the effect dose of a drug use to assess its safety and reliability, is called the ______________.
The ratio of toxic dose to the effect dose of a drug use to assess its safety and reliability, is called the therapeutic index (TI) .
The property of an antimicrobial agent to be highly toxic against its target microbe while being far less toxic to the cells of the host organism is called _________ toxicity.
The property of an antimicrobial agent to be highly toxic against its target microbe while being far less toxic to the cells of the host organism is called selective toxicity.
The clearing surrounding an antibiotic disk, where there is no growth of the organism, as indicated by arrow B in this image, is called the __________.
The clearing surrounding an antibiotic disk, where there is no growth of the organism, as indicated by arrow B in this image, is called the zone of inhibition.
Which of the following are primary sites for action of antimicrobial drugs in bacteria?
(a) Cell membrane
(b) Cell wall
(c) Nucleic acids
(d) Mitochondria
(e) Ribosomes
(f) Golgi apparatus
(a) Cell membrane (selective permeability barrier)
(b) Cell wall (structural shape & support)
(c) Nucleic acids (DNA/RNA used for protein synthesis)
(d) Ribosomes (site of protein synthesis)
Nucleic acids are ____________ used for protein _________.
Nucleic acids are DNA and RNA used for protein synthesis.
T or F: DNA and RNA are located w/in the ribosome.
False.
Ribosomes = Site of protein synthesis
So ribosomes used RNA & DNA, but don’t contain them
DNA → in nucleus or nucleoid region
RNA → freely in cytoplasm (not inside membrane-bound organelle)
The ______________ is the ration of the toxic dose to the effective dose of a drug.
The therapeutic index is the ration of the toxic dose to the effective dose of a drug.
T or F: Interference of the cell membrane structure and function is one of the general mechanisms of antimicrobial drug action?
True
T or F: Inhibiting cell wall synthesis is one of the general mechanisms of antimicrobial drug action?
True
T or F: Inhibiting nucleic acid structure and function is one of the general mechanisms of antimicrobial drug action?
True
T or F: Inhibiting protein synthesis is one of the general mechanisms of antimicrobial drug action?
True
T or F: Inhibiting the electron transport chain system is one of the general mechanisms of antimicrobial drug action?
False
The use of a ________—spectrum antibiotic can have far-reaching affects on beneficial resident species.
The use of a broad—spectrum antibiotic can have far-reaching affects on beneficial resident species.
T or F: Drugs that are selectively toxic kill the host cells w/o harming the microbial cells.
False. Selectively toxic drugs kill the microbe without harming the host.
Kirby-Bauer is an ____________ to determine the antibiotic ___________ of a particular ___________ strain.
Kirby-Bauer is an agar diffusion test to determine the antibiotic susceptibility of a particular bacterial strain.
Antibiotic susceptibility refers to…
Refers to how sensitive a microorganism is to an antibiotic.
If a bacterium is susceptible, the antibiotic can inhibit or kill it effectively
T or F: An antimicrobial that is effective against a limited array of microbial types is called a limited-spectrum drug.
True —> they are also referred to as “narrow-spectrum” drugs
Current antimicrobial drugs interfere with essential cell processes such as:
(1) Inhibiting the replication of ________,
(2) the production of ________ by transcription, or the production of proteins by the (3) ________
Current antimicrobial drugs interfere with essential cell processes such as:
(1) Inhibiting the replication of DNA,
(2) the production of RNA by transcription, or the production of proteins by the (3) ribosome
T or F: A broad-spectrum drug is only effective for patients with normal immune function.
False —> “Broad-spectrum” refers to the drug’s ability to target a wide range of microorganisms, not the characteristics of the patient. Therefore, its effectiveness is not guaranteed for all patients, including those who are immunocompromised.
T or F: One potential side effect of women using broad-spectrum antibiotics is that they can lead to the overgrowth of the yeast Candida albicans leading to yeast infections.
True
What infection can result from broad-spectrum antibiotic use disrupting vaginal lactobacilli?
Primary infection —> Candida albicans (yeast infection)
Secondary infection —> Superinfection
Superinfection
Secondary infection
Occurs in addition to pre-existing infection (oftentimes bc the og treatment disrupted the person’s normal flora)
____________ is a secondary infection that occurs on top of a pre-existing one.
Superinfection is a secondary infection that occurs on top of a pre-existing one.
T or F: Different types of penicillins differ in the nature of their side chains.
True
Reason:
The variety of side chains is responsible for the differences in biological activity.
Which of the following is a bacterial cell wall inhibitor found in over-the-counter antibacterial ointments?
(a) Bacitracin
(b) Streptomycin
(c) Amoxicillin
(d) Tetracycline
(e) Ciprofloxacin
(a) Bacitracin
Bacitracin is a cell wall synthesis inhibitor commonly found in over-the-counter topical ointments like Neosporin.
It targets Gram-positive bacteria by interfering with peptidoglycan synthesis.
___________ inhibits protein synthesis and belongs to the aminoglycoside group.
Streptomycin inhibits protein synthesis and belongs to the aminoglycoside group.
___________ is a cell wall inhibitor that is typically prescription-only.
Amoxicillin is a cell wall inhibitor that is typically prescription-only.
___________ inhibits protein synthesis and is considered a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
Tetracycline inhibits protein synthesis and is considered a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
___________ inhibits DNA replication and belongs to the fluoroquinolone class.
Ciprofloxacin inhibits DNA replication and belongs to the fluoroquinolone class.
If an antimicrobial drug is only effective against gram-negative bacteria, it has a(n) __________ spectrum.
If an antimicrobial drug is only effective against gram-negative bacteria, it has a(n) narrow spectrum.
Which semisynthetic penicillins are useful in treating infections caused by penicillinase-producing bacteria? Briefly explain why.
✅ Nafcillin
✅ Methicillin
✅ Cloxacillin
These are penicillinase-resistant penicillins, designed to withstand the action of beta-lactamase enzymes that would otherwise inactivate regular penicillins.
Explain why each of the following are not useful in treating infections caused by penicillinase-producing bacteria.
Penicillin G
Erythromycin
Streptomycin
❌ Not effective for penicillinase-producing bacteria:
Penicillin G – susceptible to beta-lactamase
Erythromycin – not a penicillin; it's a macrolide
Streptomycin – not a penicillin; it's an aminoglycoside
Which specific mode of action do -cillin drugs use to target bacterial cells that humans lack? Briefly explain how this works.
Bacterial cell walls
contain peptidoglycan, which is essential for structural integrity.
-cillin antibiotics inhibit enzymes involved in peptidoglycan synthesis, leading to cell lysis.
Human cells don’t have cell walls, so these drugs can selectively target bacteria without harming human cells.
What is a potential consequence of using a broad-spectrum antibiotic on vaginal microbiota?
Destruction of protective lactobacilli, leading to yeast infection.
“Use of a broad-spectrum antibiotic can have far-reaching affects on beneficial resident species.”
Briefly explain what this means.
Using a broad-spectrum antibiotic…
can disrupt the body’s normal, helpful bacteria —> can lead to unwanted side effects or longer-term health issues
The group of antibiotics originally isolated in the late 1940s from the mold Acremonium are the _____________.
The group of antibiotics originally isolated in the late 1940s from the mold Acremonium are the cephalosporins.
Cephalosporins belong to the __________ class of antibiotics, similar to penicillins, and are used to treat a __________ range of bacterial infections.
Cephalosporins belong to the β-lactam (Beta-lactam) class of antibiotics, similar to penicillins, and are used to treat a broad range of bacterial infections.
T or F: Cephalosporins are similar to penicillins.
Justify your answer.
Cephalosporins are structurally and functionally similar to penicillins.
Both belong to the beta-lactam class of antibiotics
work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, leading to cell lysis and death.
Every penicillin is composed of a __________ ring, and a variable _________ chain that determines its microbicidal activity.
Every penicillin is composed of a Beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring, and a variable side chain that determines its microbicidal activity.
(Part A) The enzyme that cleaves the beta-lactam ring of penicillin and cephalosporin is known as ______________ or ______________.
(Part B) What does this lead to?
The enzyme that cleaves the beta-lactam ring of penicillin and cephalosporin is known as beta-lactamase or penicillinase.
Causes the inactivation of antibiotic — meaning the drug can no longer interfere with bacterial cell wall synthesis
Therefore, provides antibiotic resistance (bacteria become resistant to the antibiotic — they survive and continue to grow even in its presence)
What does antibiotic resistance mean?
Bacteria have changed in a way that makes antibiotics no longer effective against them
Therefore, bacteria survive & continue to grow even when exposed to antimicrobial drug that would normally slow their growth or kill them
Methicillin, cloxacillin, and nafcillin are useful in treating infections caused by ________-producing bacteria.
Methicillin, cloxacillin, and nafcillin are useful in treating infections caused by penicillinase-producing bacteria.
(a) What class of antibiotics is designed to resist destruction by beta-lactamase (penicillinase) enzymes that inactivate regular penicillins like Penicillin G?
(b) Name 2 examples.
(a) Penicillinase-resistant penicillins — antibiotics formulated to withstand beta-lactamase activity.
(b) Methicillin, cloxacillin, and nafcillin
Name 1 example of a penicillinase-resistant penicillin that was among the first developed but is rarely used today due to resistance.
Methicillin
Which penicillinase-resistant penicillin is commonly used in clinical settings to treat Staphylococcus aureus infections?
Nafcillin
Which part of bacterial cell is affected by the action of -cillin drugs?
cell wall
Aminoglycosides are composed of one or more amino _______ and a(n) _______-carbon ring.
Aminoglycosides are composed of one or more amino sugars and a(n) six-carbon ring.
Cephalosporins closely resemble which group of antibiotics in terms of structure and function?
Penicillins
Most drugs that inhibit protein synthesis, or translation, block the action of the 30S or 50S subunits of the __________.
Most drugs that inhibit protein synthesis, or translation, block the action of the 30S or 50S subunits of the ribosomes.
Ribosomes in bacterial cells have a _____ and _____ subunit.
Ribosomes in bacterial cells have a 50S and 30S subunit.
Different types of pencillins differ in their biological activity depending on the nature of their _________.
Different types of pencillins differ in their biological activity depending on the nature of their side chains.
Tetracycline has the ability to bind to ribosomes and inhibit _________.
Tetracycline has the ability to bind to ribosomes and inhibit protein synthesis.
A narrow-spectrum antibiotic that affects cell wall synthesis, found in Neosporin ointment and used to treat superficial skin infections, is called ________________.
A narrow-spectrum antibiotic that affects cell wall synthesis, found in Neosporin ointment and used to treat superficial skin infections, is called bacitracin.
T or F: Fluoroquinolones only inhibit gram-negative bacteria.
False. Fluoroquinolones inhibit both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, although they are especially potent against many Gram-negative species.
_______________ are antibiotics that work by interfering with DNA replication enzymes like DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV.
Fluoroquinolones are antibiotics that work by interfering with DNA replication enzymes like DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV.
Polymyxins are narrow-spectrum antibiotics containing a fatty acid component that allows them to interfere with the cell __________ of gram-negative bacteria.
Polymyxins are narrow-spectrum antibiotics containing a fatty acid component that allows them to interfere with the cell membrane of gram-negative bacteria.
Antibiotics composed of one or more amino sugars and a 6-carbon ring are called
______________.
Antibiotics composed of one or more amino sugars and a 6-carbon ring are called
aminoglycosides.
The most significant reason that bacteria in a biofilm are much less susceptible to antibiotics is that….
they express different genes than those expressed by free-living bacteria
The phenomenon by which microbes begin to tolerate an antimicrobial agent at a level which would normally be inhibitory is called ______________.
The phenomenon by which microbes begin to tolerate an antimicrobial agent at a level which would normally be inhibitory is called antibiotic resistance.
Tetracyclines inhibit _____________.
Tetracyclines inhibit protein synthesis.
T or F: Drug resistance only arises from an organism gaining the genetic information for the resistance from another organism.
Justify your answer.
False.
Drug resistance can also arise from spontaneous mutations within the chromosomal genes.
Fluoroquinolones, antibiotics that inhibit DNA synthesis, are _______________ drugs.
Fluoroquinolones, antibiotics that inhibit DNA synthesis, are broad-spectrum drugs.
The group of antibiotics that targets cell membranes is ___________.
The group of antibiotics that targets cell membranes is polymyxins.
Plasmids called R factors confer _____________.
(a) resistance to temperature changes
(b) resistance to damage from ultraviolet light
(c) resistance to pressure changes
(d) antibiotic resistance
Plasmids called R factors confer…
(d) antibiotic resistance.
Which statement regarding antibiotics and biofilms is correct?
(a) Bacteria express different genes and exhibit a different phenotype when they are attached to surfaces in a biofilm.
(b) Antibiotics lacking a chemical charge easily penetrate the extracellular material surrounding biofilm organisms.
(c) Biofilm bacteria are often 1000X more susceptible to the effects of antibiotics compared to free-living bacteria.
Correct Answer is (a) Bacteria express different genes and exhibit a different phenotype when they are attached to surfaces in a biofilm.
Drug resistance is a situation in which microorganisms ________ tolerate an amount of drug that would ordinarily be ________.
no longer; inhibitory
no longer; stimulatory
begin to; inhibitory
begin to; stimulatory
begin to; inhibitory
Select the types of horizontal gene transfer that can allow bacteria to acquire antibiotic resistance genes.
Translation
Transduction
Transposition (movement of transposons)
Replication
Conjugation
Transformation
transduction
transposition
conjugation
transformation
Name the 3
T or F: A mold is a type of fungus.
True
Fungi v.s. Mold
FUNGI
Large kingdom of organisms
Includes yeasts, molds, mushrooms, etc.
MOLD
Type of fungus that grows multicellular filaments called “hyphae”
Forms fuzzy colonies
Name the 3 mechanisms fungi can use to become antibiotic-resistant.
Interfering RNA
Horizontal gene transfer → acquiring resistance genes from other organisms.
Spontaneous mutation → random genetic changes that alter drug targets or pathways.
_____________ is a form of cell-to-cell communication used by bacteria to coordinate group behaviors, such as the activation of virulence factors, by producing and detecting signaling molecules called autoinducers.
Quorum sensing is a form of cell-to-cell communication used by bacteria to coordinate group behaviors, such as the activation of virulence factors, by producing and detecting signaling molecules called autoinducers.
An R factor is a type of ________ that confers (grants/provides) antibiotic resistance.
An R factor is a type of plasmid that confers (grants/provides) antibiotic resistance.
Important Review Material
Define “Plasmid”
A small, circular piece of DNA found in bacteria, separate from the main chromosome.
The “R” in R Factor stands for…
R Factor = Resistance Factor
An epimutation, such as gene silencing that produces drug resistance in fungi, is a ________ change in ________.
(a) temporary; genotype
(b) temporary; phenotype
(c) permanent; phenotype
(d) permanent; genotype
(b) temporary; phenotype
An epimutation, such as gene silencing that produces drug resistance in fungi, is a temporary change in phenotype.
What is the most significant reason that bacteria in a biofilm are much less susceptible to antibiotics than bacteria not w/in a biofilm?
Bc bacteria in biofilms express different genes than free-living bacteria
Transformation, transduction, and conjugation are all types of ___________________), a process by which plasmids called ____________ can be moved from one bacterial cell to another.
Transformation, transduction, and conjugation are all types of horizontal gene transfer (AKA “horizontal transfer”), a process by which plasmids called resistance factors can be moved from one bacterial cell to another.
Which of the following are mechanisms that give bacteria resistance to a drug?
(a) An affected metabolic pathway is shut down or an alternative pathway is used.
(b) Permeability or uptake of the drug is increased.
(c) Drug is immediately eliminated using a transmembrane pump.
(d) Binding sites for the drug are increased in number or affinity.
(d) New enzymes that inactivate the drug are synthesized.
(a) An affected metabolic pathway is shut down or an alternative pathway is used.
(c) Drug is immediately eliminated using a transmembrane pump.
(d) New enzymes that inactivate the drug are synthesized.
T or F: Drug resistance only arises from an organism gaining the genetic information for the resistance from another organism.
False
Only one of the following statements about persisters is correct. Which one is it?
(a) Persisters are commonly found in biofilms.
(b) Persister cells represent spontaneous mutants.
(c) Persisters have a high metabolic rate.
(d) Persister cells are produced only in E. coli and close relatives.
(a) Persisters are commonly found in biofilms.
In fungi, a small regulatory ______ binds to a gene and silences it, preventing the synthesis of the target of an antifungal drug. The fungus is temporarily resistant to that drug.
In fungi, a small regulatory RNA binds to a gene and silences it, preventing the synthesis of the target of an antifungal drug. The fungus is temporarily resistant to that drug.
In fungi, the temporary silencing of genes needed to produce the target of an antibiotic is an epigenetic event referred to as an ___________.
In fungi, the temporary silencing of genes needed to produce the target of an antibiotic is an epigenetic event referred to as an epimutation.