Cognitive - HL Extension
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(2025 onwards course) The digital world
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Working Memory
The temporary storage and manipulation of information that is needed for cognitive tasks such as language, problem-solving and learning. The information available in our conscious attention at any one time.
Executive Function
A general term that refers to a range of cognitive processes that require careful and conscious processing, including working memory, delaying gratification and system two processing.
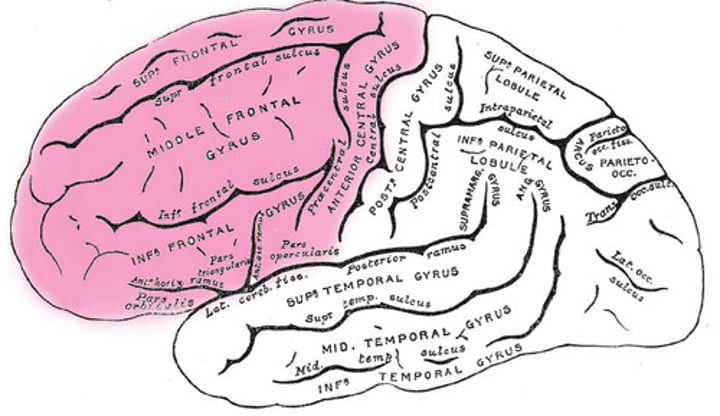
Working memory capacity
The amount of information we are able to hold in our conscious attention at any one time.

Inattentional Blindness
A cognitive phenomenon whereby we are unable to see things immediately in front of us because our attention is focused on something else.

Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy
A type of psychiatric therapy that uses virtual reality to expose patients to the environments or stimuli for which they have a conditioned fear.

Central Executive
The part of the working memory model that controls our focus of attention and the flow of information between the long-term and short-term stores.

Correlational Study
A study that measures how strongly two variables are related to one another. Instead of a directional effect, it shows a relationship between co-variables.
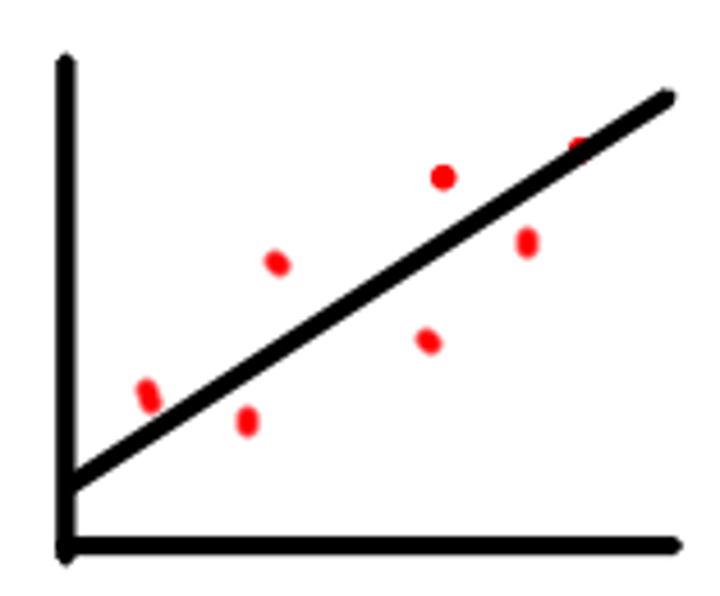
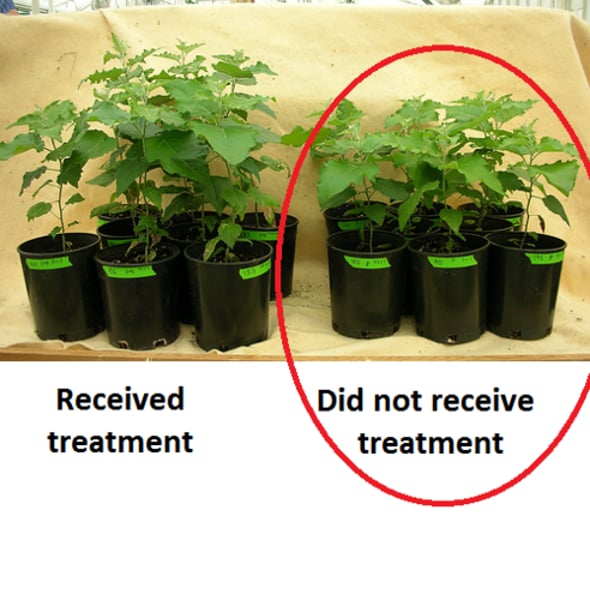
True Experiment
A study that involves manipulating an independent variable to see its effects on a dependent variable in a controlled environment.

transactive memory systems
Information to be remembered is distributed to various members of the group who can then be relied upon to provide that information when it is needed.
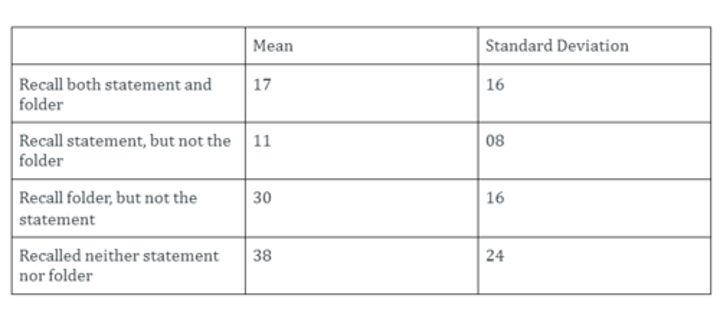
Sparrow et al (2011)
Aim: to investigate how well people recall where information can be found compared to recall of the information itself. Participants were asked to read and type a series of trivia facts.
Procedure:
-participants were asked to read and type a series of trivia facts.
-after typing each fact participants were given the name of a specific folder that this information would be stored in
***not explicitly given this information or asked to recall the folder names.
Participant were then given ten minutes to write down as many of the statements as they could remember and was also asked which folder it was saved in
Results:
The results showed that being asked to remember the information made no significant difference to the participants' ability to recall the trivia facts, but there was a significant difference if the participant believed that the information would be stored in the computer.
Participants were much more likely to remember the name of the folder (i.e. where the information could be found) than the information itself
Google effect
The tendency to forget information that can be found readily online by using Internet search engines.

confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that confirms one's preconceptions

self-concept
individual's belief about oneself, including the person's attributes and who and what the self is

Self-esteem
our emotional response to our self-concept. For example, are we happy about who we are?

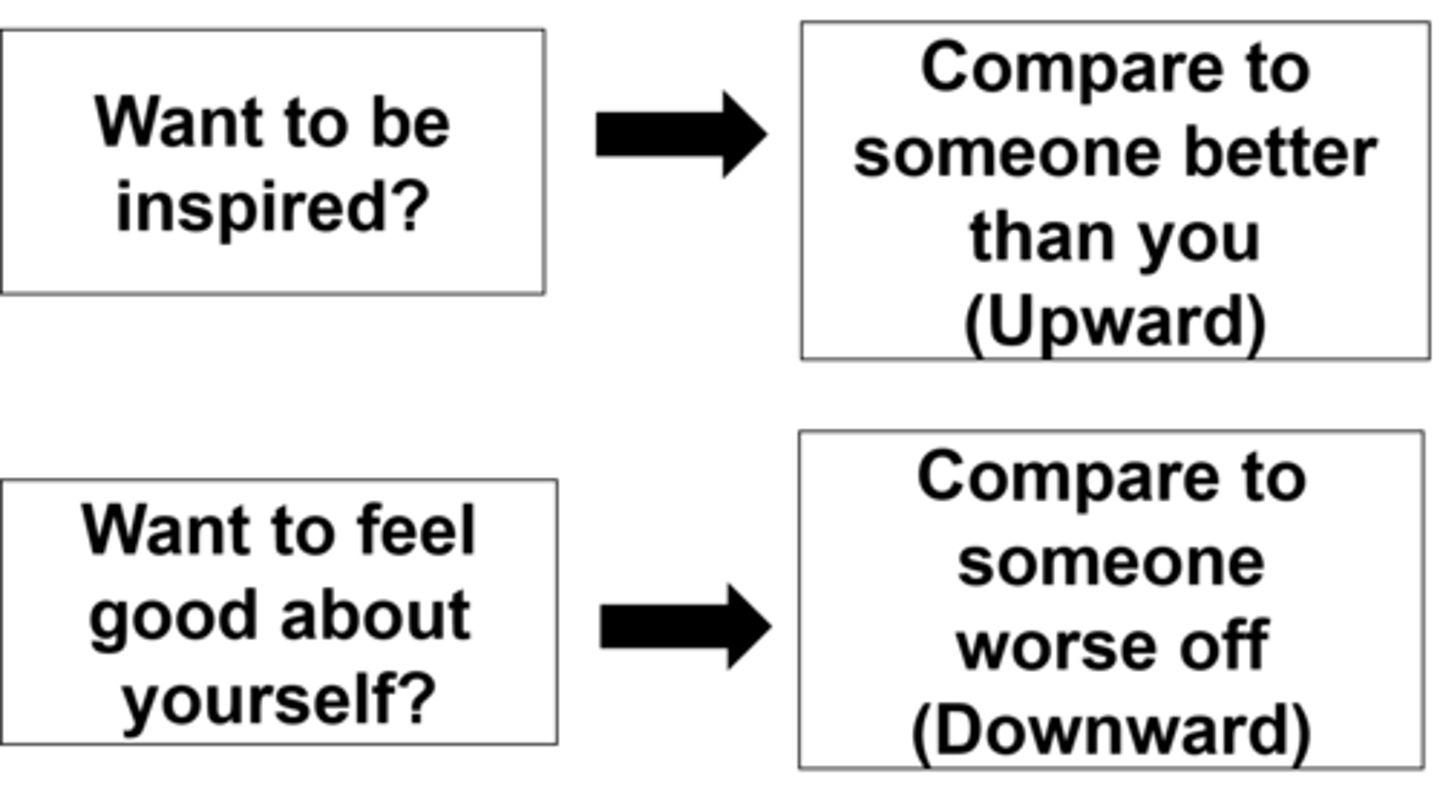
Social Comparison Theory
We determine our own social and personal worth based on how we compare to others. People compare their experiences to that of those around them as a way to work out what kind of person they are (self-concept) and how they should judge themselves (self-esteem)

negative cognitive bias
Consistently distorting experiences in a negative way

upward comparisons
comparing oneself to another person who is more competent or in a better situation, which tends to confirm a person's low self-esteem. This may happen on social media.
availability heuristic
basing the estimated probability of an event on the ease with which relevant instances come to mind

flashbulb memory
A clear and vivid long-term memory of an especially meaningful and emotional event.

Participant variability
the extent to which the participants may share a common set of traits that can bias the outcome of the study
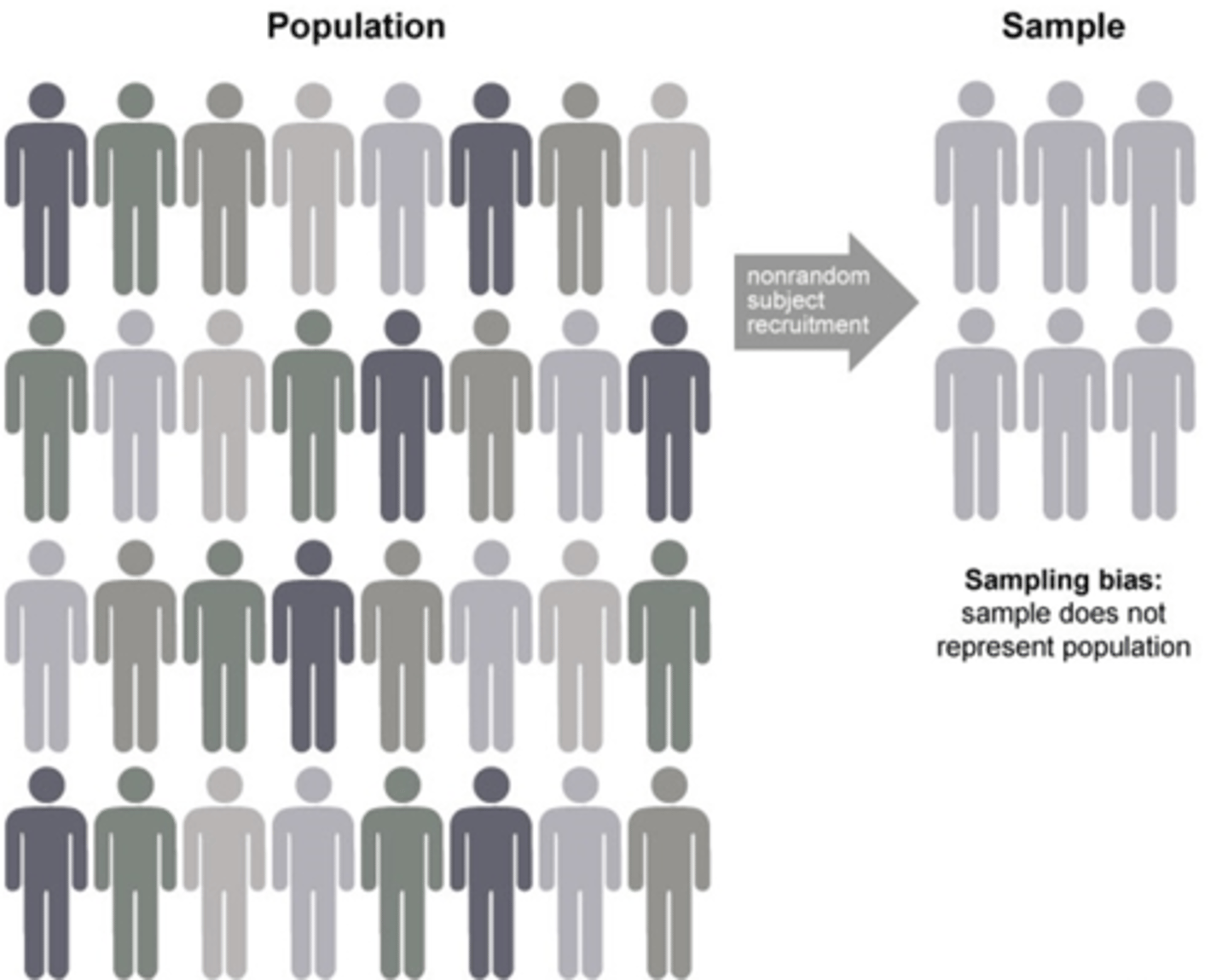
demand characteristics
Any aspects of a study that communicate to the participants how the experimenter wants them to behave.

Internal validity
This is high when the study is well controlled, guaranteeing that the IV is affecting the DV - and not some other variable.
Storm et al (2016)
Aim - To investigate how likely one would rely on Google as opposed to their individual memory store
Procedure-
Condition 1: Internet
Condition 2: Memory
Condition 3: Baseline
PHASE 1: Answer 8 questions - difficult general knowledge
a. INTERNET: Used Google
b. MEMORY: Used memory; no internet access
c. BASELINE: NO QUESTIONS WERE ASKED
PHASE 2: Answer 8 questions - easy and fast
Participants had access to Google; no explicit instruction to use
SAMPLE: 60 undergraduates
Results -
Internet: 83%
Memory: 63%
Baseline: 65%
Evaluation-
Strengths:
- Google research is a realistic task
- Highly controlled environment: lab experiment/ conditions
- Clear relationship between IV and DV
Weaknesses:
- Ecological validity: relied entirely on trivia information which may not be meaningful
- Not enough triangulation to form an effective conclusion