Speech Pathology HI Child Exam 2
1/248
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
249 Terms
Visual inspection regarding otoscopy
information regarding basic anatomical normality
happens before performing otoscopy
during the case history gathering process
structure of pinna and parts of ear canal
what is the importance of the visual inspection before otoscopy?
to monitor the external health of the outer ear, report changes to the managing physician, audiologist
what do you look for during a visual inspection?
examine the shape and size of the pinna
pits
tags
atresia/microtia
keloids
What is an example of a skin tag?
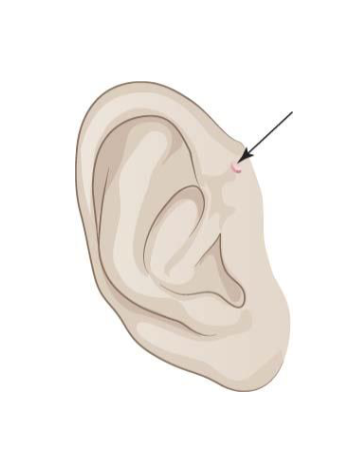
What is an example of a preauricular pit?
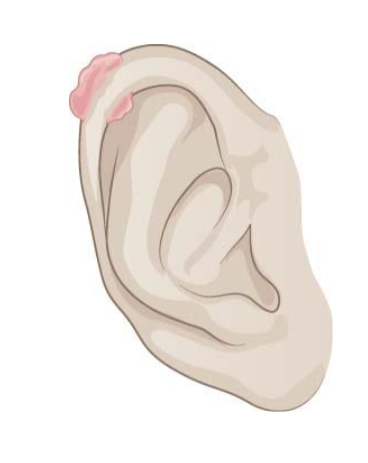
What is an example of a keloid on the pinna?
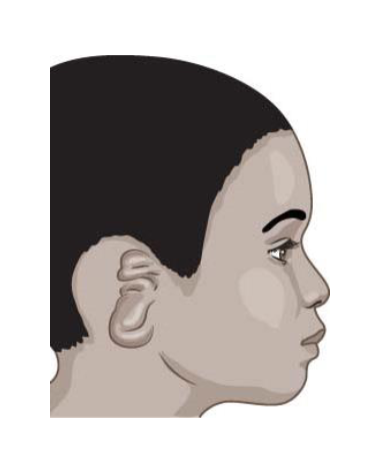
What is an example of microtia of the pinna with atresia of the external auditory canal?
Questions to consider for visual inspections
facial features symmetrical?
head proportional to body?
forehead protruding?
eyes appropriately apart?
eyes sunken?
Otoscopy includes:
the otoscope
choosing a speculum
positioning the otoscope
positioning the pinna
What is an example of an otoscope?

What are the otoscopy Dos
Do
earn patients’ trust
exercise precautions when coming in contact with the patient
explain the process (I’m going to take a look in your ear)
What are the otoscopy Don’ts
Don’t
perform otoscopy on ear with drainage
push the process if there is ear pain
perform otoscopy on a child first if child is hesitant about testing process
Although you might speculate or have a good idea of otitis media, it is NOT within the scope of practice to diagnose those medical conditions audiology or slp
true
What are some common physical findings of otoscopy?
bug in ear
perforated ear drum
excessive wax
drainage
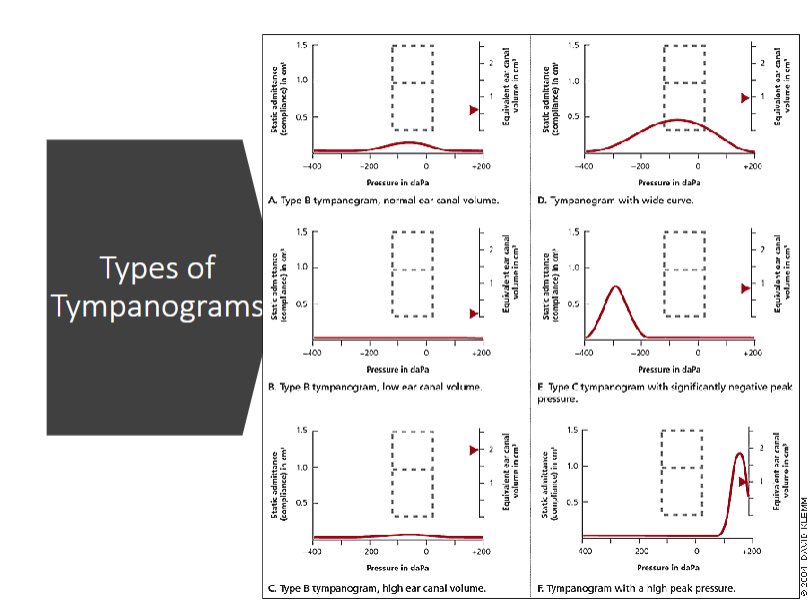
Tympanometry
Nonbehavioral direct measurement of the function of the middle ear system
evaluates functional properties such as ear canal volume and mobility of the tympanic membrane and ossicles
provides information regarding health of middle ear structures
Tympanometry regarding pressure
decapascals
referenced to atmospheric pressure
provides info regarding the function of the eustachian tube
tympanometry regarding compliance
units: cc or mL
measurement of mobility
provides information regarding ossicular chain, TM health, and ME pathology
tympanometry regarding ear canal volume
units: mL
measurement of physical volume of ear canal
provides information regarding outer ear pathology, TM perforation, pressure equalization tube patency
When not to perform tympanometry
surgery
drainage
visual obstructions
The audiogram
interpreting is a skill every SLP should have
help understand degree and type of hearing loss
allow you to educate that specific loss may impact child’s education/ comm.
sometimes you are the hearing expert
Audiogram in a nutshell
scaled graphic description of a person’s hearing perceptibility
dB SPL to dB HL for clarity of understanding intensity by function of frequency
What is the lowest level at which normal hearing people begin to detect sound?
audiometric zero (does not mean no sound)
It is inappropriate to describe hearing loss as percentage as it is a scale of hearing.
true
How are audiograms described?
degrees
normal
slight
mild
moderate
moderately-severe
severe
profound
Components of the audiogram
frequency
number of cycles of vibration per one second of time
Hz
intensity
measure of pressure per unit area
dB HL
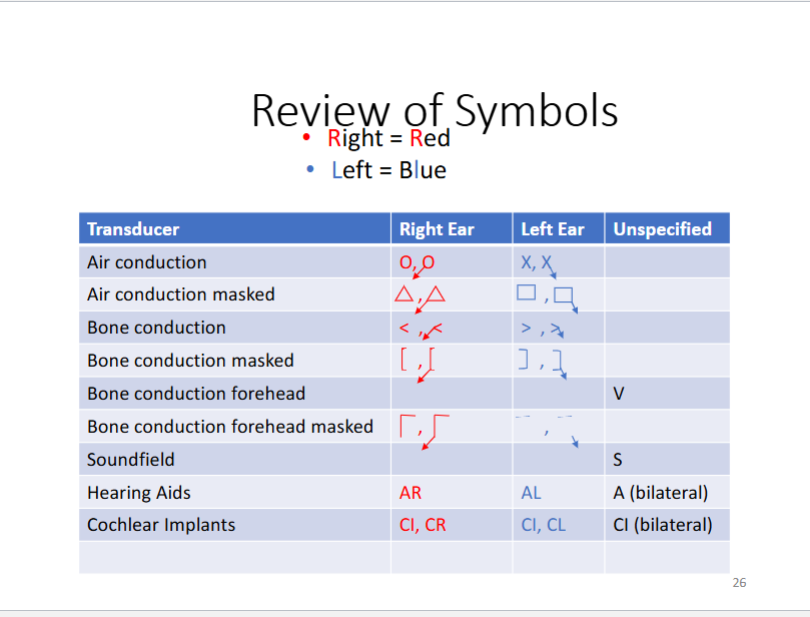
What transducers are used to test sound field, ear specific, bone?
headphones
insert earphones
speakers
oscillator
Plotted thresholds softer than (below) 20 dB HL are normal thresholds
true
Plotted thresholds louder than (higher) 20 dB HL are deemed part of hearing loss and described by degree.
true
review of symbols
(no response: recorded as downward arrows in the direction of the ear that is being test)
Pitch is the perception of
frequency
Loudness is the perception of
intensity
What does air conduction test?
the entire system
outer, middle, inner, neural
What does bone conduction test?
the inner ear and neural
What transducers does masked bone conduction use?
both insert and headphones
What is the anticipated speech ability between around a mild hearing loss at 20 dB HL?
the sound S at about 21 dB HL
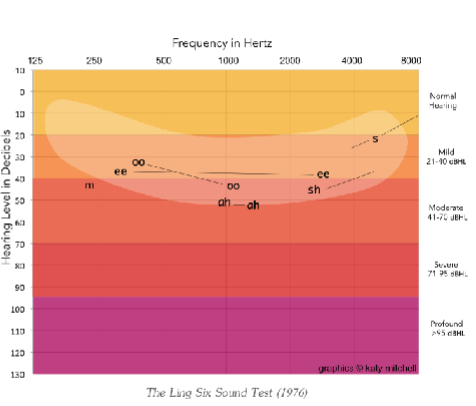
What is the anticipated speech ability around a mild hearing loss between 21 and 40 dB HL?
oo at about 30 dB HL
ee at about 40 dB HL
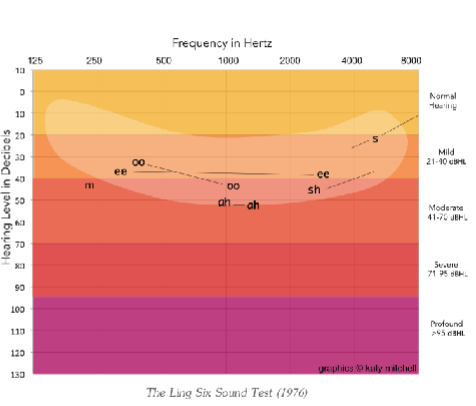
What is the anticipated speech ability around a moderate hearing loss between 41 and 70 dB HL?
m at about 41 dB HL (oo again)
sh at about 45 dB HL
ah at about 50 dB HL
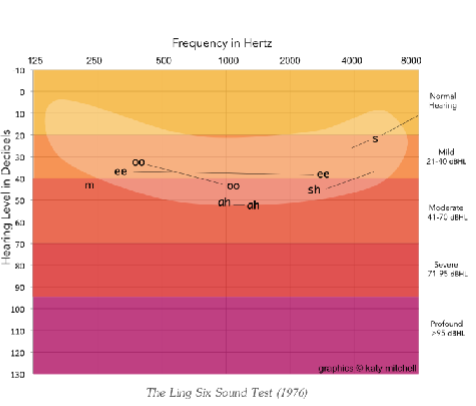
For a normal hearing sensitivity, hearing losses should be symmetric meaning
the same in both ears
What does air and bone conduction look like for normal hearing sensitivity?
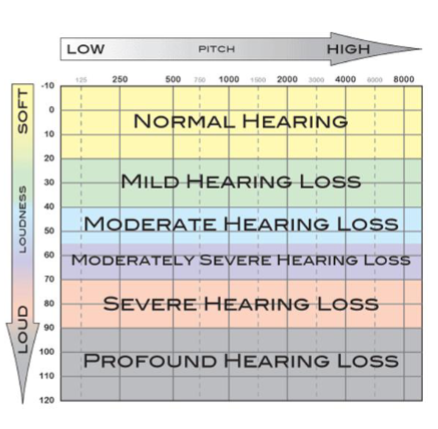
What is the range for a normal hearing loss?
-10 to 20 dB HL
What is the range for a mild hearing loss?
20-40 dB HL?
What is the range for a moderate hearing loss?
40-50 dB HL
What is the range for a moderately severe hearing loss?
55 ish to 70 dB HL
What is the range for severe hearing loss?
70-90 dB HL
What is the range for a profound hearing loss?
90-120 dB HL
Degrees on hearing loss on the audiogram
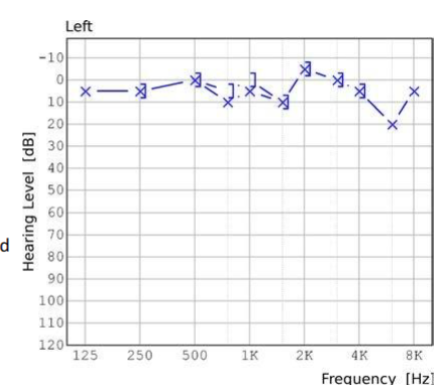
What is asymmetric hearing sensitivity?
it is not the same hearing sensitivity in both ears
what is sloping on the audiogram?
when the hearing loss continuously goes down creating a slope on the graph
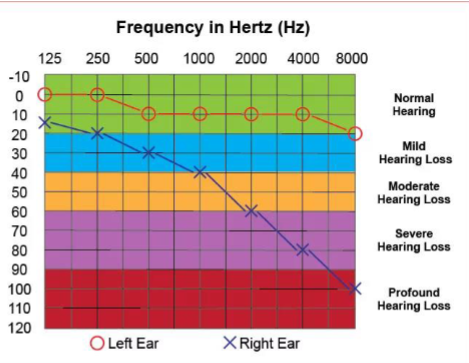
Explain the results of this audiogram?
the right ear has normal hearing
the left ear has mild sloping to profound hearing loss
What is a conductive hearing loss?
a hearing loss in the outer or middle ear
abnormal air conduction
normal bone conduction
presence of air-bone gap
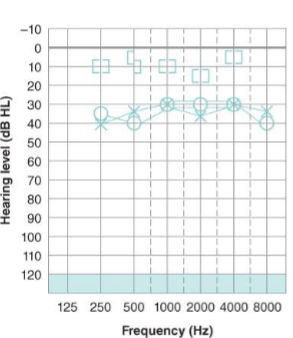
What type of hearing loss is this ad describe the results?
bilateral mild conductive hearing loss
What is a sensorineural hearing loss?
hearing loss in the inner ear or neural pathways
air and bone gap aligned exceeding 20 dB HL
no air-bone gap
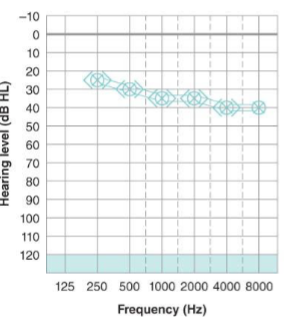
What type of hearing loss is this and what are the results?
bilateral mild sensorineural hearing loss
What is a mixed hearing loss?
hearing loss in the outer or middle ear along with the inner or neural pathways
combination of abnormal air and bone conduction
air conduction is significantly worse than bone
are bone gap present
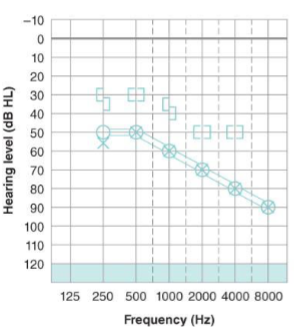
What type of hearing loss is this and describe the results?
bilateral mild to severe mixed hearing loss
What is normal hearing sensitivity for a child?
-10-15 dB HL
When should you screen for hearing loss?
25 dB HL
What is the conversation level for 35-45 dB HL?
soft
What is the conversation level for 55-65 dB HL?
normal
what is the conversation level for 75 dB HL and greater?
loud
conversation level for speech in dB HL
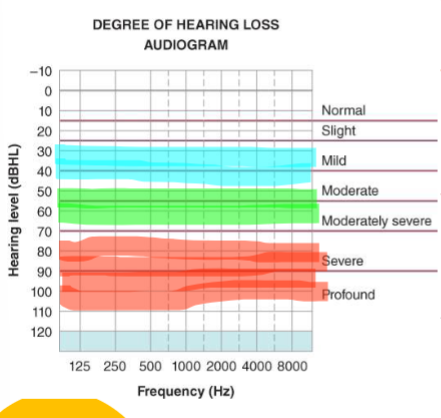
speech sounds in relation to audiogram and hearing loss
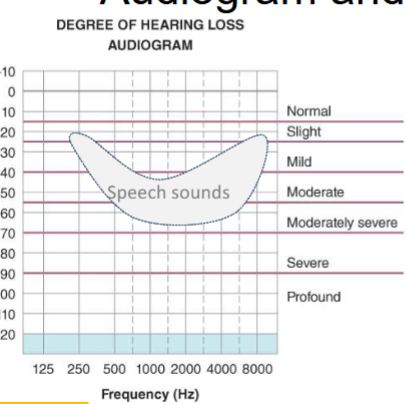
slight hearing loss regarding speech understanding abilities
not hear the endings of words
mild degree of hearing loss regarding speech understanding abilities
significant delays in development
difficulty in early reading skills
can mis 24- 40 %of speech signal
moderate degree of hearing loss regarding speech understanding skills
can miss up to 80% of average level conversational speech
flat voice quality, atypical speech production, bad syntax, limited vocabulary
moderately severe hearing loss regarding speech understanding skills
miss 100% of average conversational speech
severe and profound hearing loss regarding speech understanding abilities
can miss 100% of ALL speech
What is high frequency hearing loss?
greater loss in higher frequencies than in lower
What is the word recognition score?
it determines how well a person can recognize and repeat words when presented in an ideal listening environment.
What is speech audiometry?
the assessment of awareness and identification of a speech signal
speech audiometry is used as a cross check to confirm hearing sensitivity by pure tone thresholds.
true
What is the purpose of speech audiometry as it relates to hearing sensitivity?
a sound is presented to the patient at descending levels until the patient can indicate repetition or awareness of the word or sound 50% of the time
What are other methods of obtaining speech thresholds if the patient does not want to speak?
picture boards
toys
pointing to body parts
What are the stimulus types for speech audiometry?
words
speech sounds
warble tones
What is the Speech Recognition/Reception Threshold (SRT) ?
repeat words at barely audible level
What is Speech Awareness Threshold (SAT)?
indicates awareness of words at barely audible level
What is Word Discrimination Testing (WDT)?
determines clarity of word understanding given the hearing sensitivity level
Word discrimination testing/ word recognition testing
different btw detection and discrimination/recognition ability
relationship btw pure tone thresholds and discrimination/recognition ability
hearing and understanding
What is the purpose of pure tone audiometry?
it determines loudness or intensity threshold in dB HL where a sound is barely audible
Air conduction testing represents entire auditory system including
outer, middle, inner ear
Air conduction audiometry represents
how we are hearing day to day
During pure tone audiometry, instructions for the patient are important in obtaining accurate information
true
For pure tone audiometry, what are the air conduction testing instructions?
indicate the purpose of the test
emphasize that it is necessary to sit quietly
indicate that the participant is to respond whenever tone is heard
What are patient responses that are appropriate in air conduction testing?
hand raising
response button
play audiometry
visual reinforcement
What does bone conduction testing represent?
how sound is transduced through the cochlea and neural pathways
In bone conduction audiometry, regardless of the oscillator placement, the better cochlea will always respond first.
true
Auditory disorder
abnormality of the anatomical structures of the auditory system
Auditory impairment
loss of function of the auditory system
Disability
any restriction of lack of ability to perform an activity in the manner or within the range considered normal for a human being
Hearing Handicapped
difficulty an individual experiences as a result of an impairment
What is the purpose of audiologic screening?
to identify those who need further treatment
When should you refer for audiologic screening?
failure for any part of the screening
concerns from professional
concerns from family
How do you test otoacoustic emissions function?
sound is presented to the ear via a probe, in response the ear produces a sound and sends it back. The probe records the sound sent back
Are otoacoustic emissions function tests sensitive enough to determine mild ear loss?
no
It is within the scope of an SLP to conduct OAE and ABR screening.
yes
What do electrophysiological measures do? (like ABR)
determines transduction of sound beyond the cochlea via electrodes
recorded in dB nHL (neural hearing level)
predominant waveforms correspond with specific points along neural pathways
Electrophysiological measures are used in conjunction with other tests to identify hearing loss.
true
What is the best tool for newborn hearing screening regarding electrophysiological measure?
automated auditory brainstem response
Hearing aids made into earrings

body style hearing aid
