Anml Sc 511 - Exam #5: Digestive/Respiratory/Gastrointestinal Systems
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
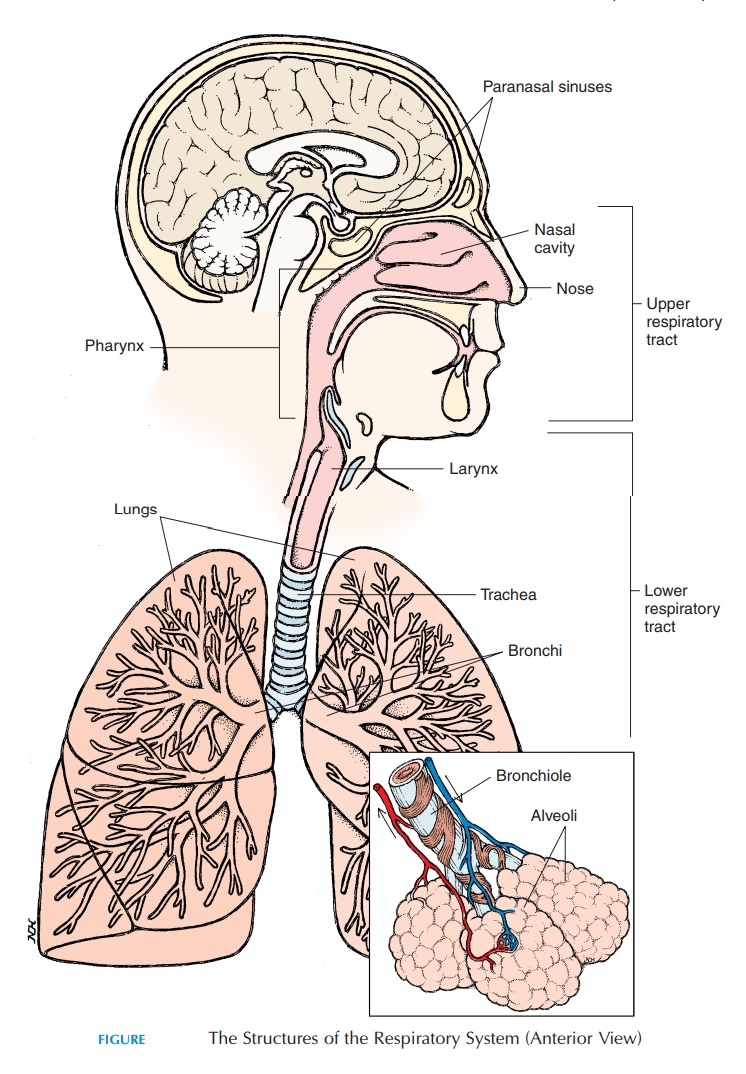
upper
Functions of the Larynx
Part of the __________ airway
voice
Functions of the Larynx
__________ production
inhalation
Functions of the Larynx
Prevent _____________ of foreign matter
vocal box
Reminder: the larynx is our ___________
airflow
Functions of the Larynx
Control of _______ to lungs
conduit
Getting something from point A to point B
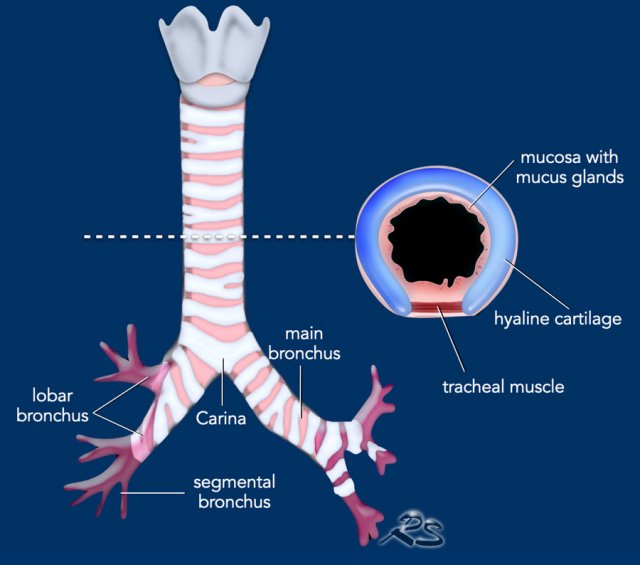
trachea
Windpipe of the body
short, wide
The Trachea = Windpipe
______________ tube
fibrous tissue + smooth muscle + cartilage rings
thorax
The Trachea = Windpipe
extends: larynx into __________ then divides
bifurcation of the trachea
furcate
Meaning to fork/branch off
collapse
The Trachea
C-shaped rings prevent __________ during inhalation
ciliated lining
mucous layer
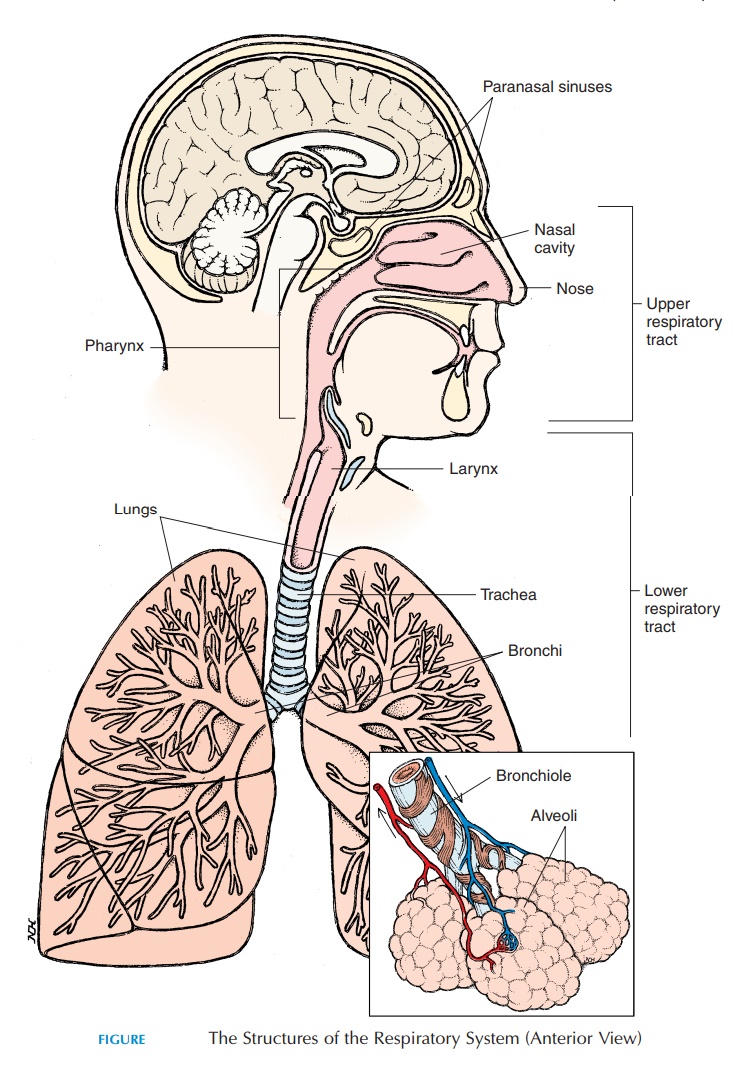
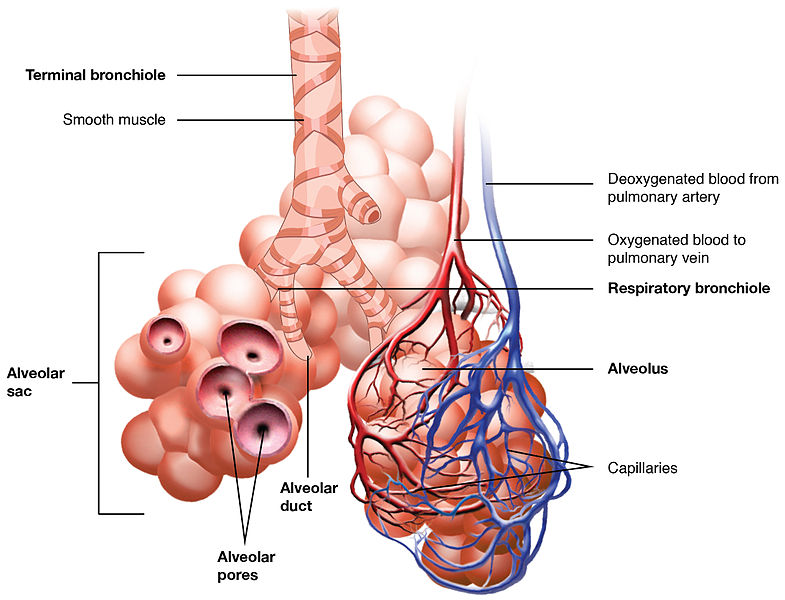
lower respiratory
_________________ tract = the bronchial tree
bronchi
bronchioles
alveolar ducts
alveoli
diameter
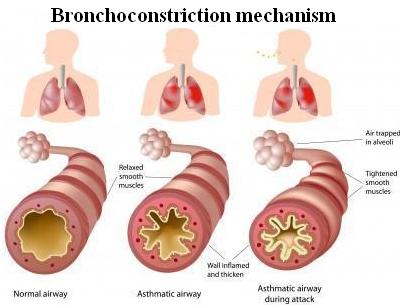
Autonomic nervous system controls ____________ of tubes
bronchodilation
bronchoconstriction
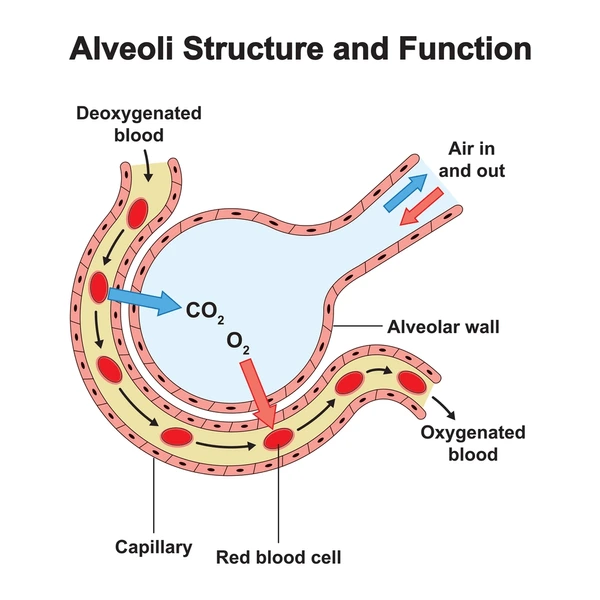
capillaries
Alveoli are surrounded by _________________
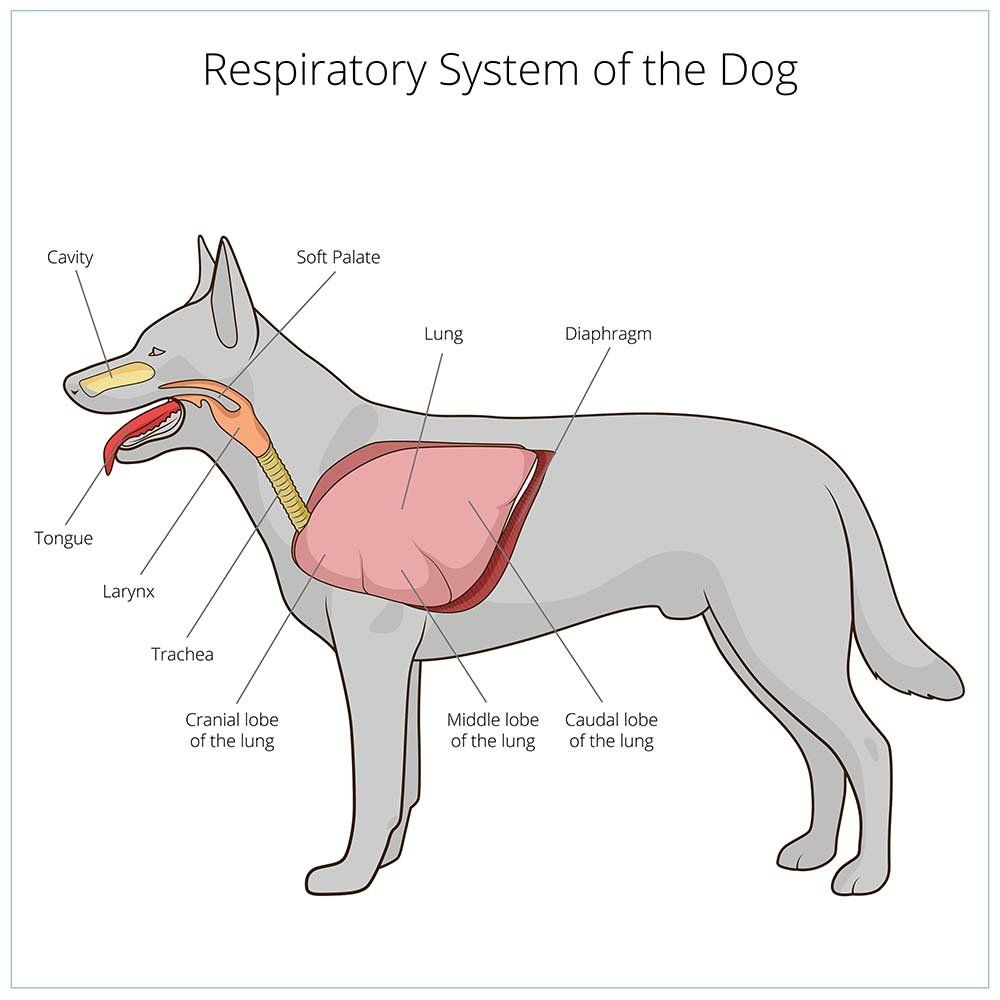
lungs
cone-like shape
light, spongy
base lies directly on diaphragm
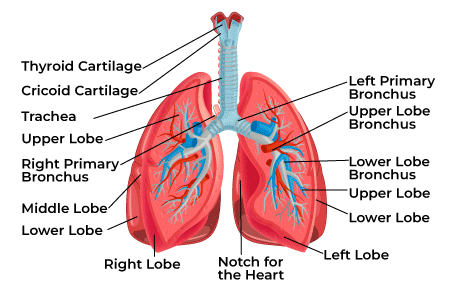
mediastinum
area between lungs
contains the heart, trachea, esophagus, blood vessels
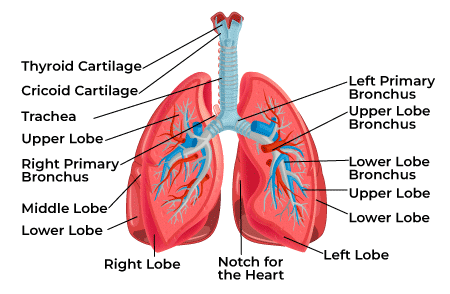
lobes
The lungs are subdivided into __________
external
Part of the Lungs called grooves
internal
Part of the Lungs that have major branches of bronchi
pulmonary
Deoxygenated blood enters lungs through the _________ artery
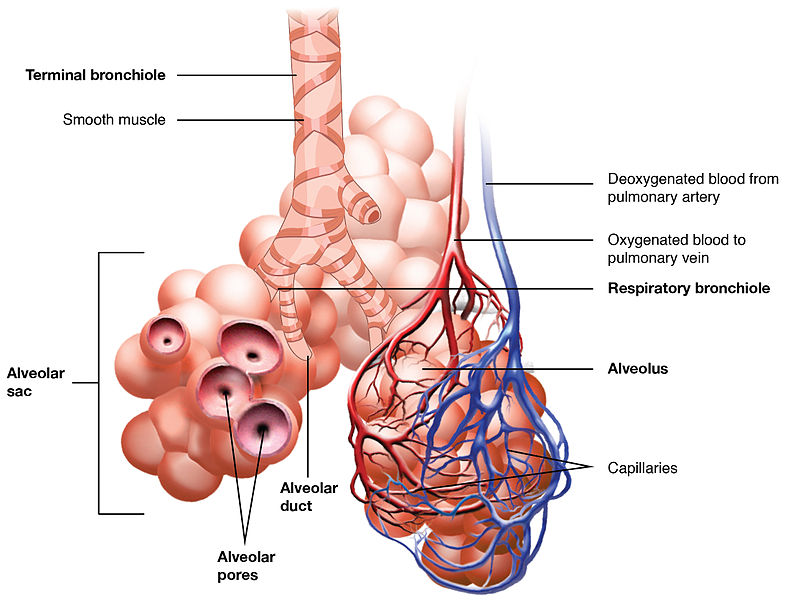
circulation
In Pulmonary _________________
deoxygenated blood enters lungs
vessels divide, follow bronchial tree
capillary networks around alveoli
CO2 and O2 are exchanged
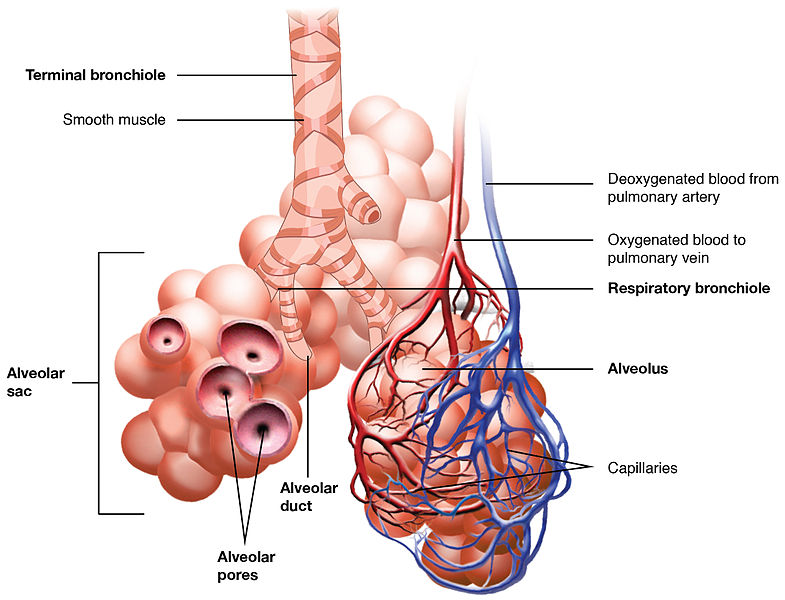
hilus
A groove or cleft in an organ where blood vessels and nerves enter or exit through it.
aveoli
tiny, thin-walled sacs surrounded by capillaries
sacs lined with fluid: contains surfactant
external respiration: in alveoli
oxygen and carbon dioxide exchanged between blood and air
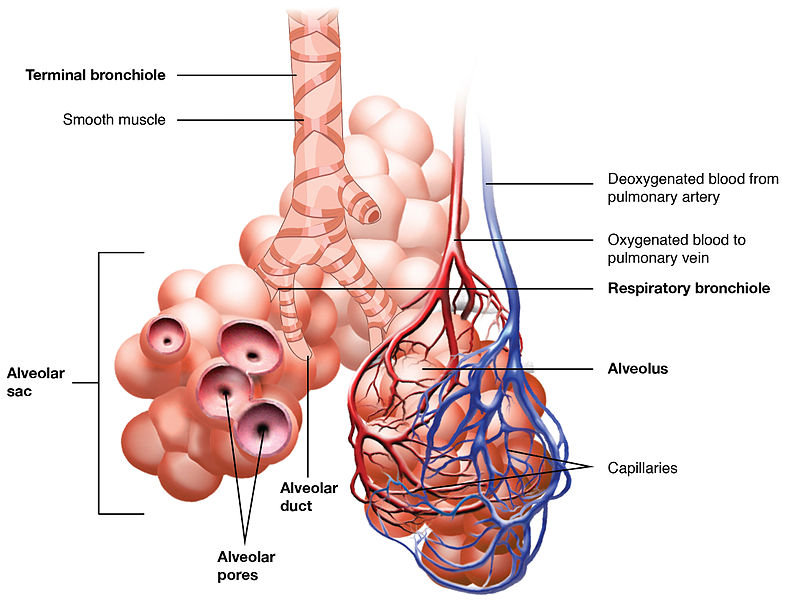
500 million
How many aveoli do humans have?
thorax
Chest cavity
area bounded by
thoracic vertebrae
ribs
sternum
intercostal muscles
surfactant
made in the alveoli
prevent the alveoli from collapsing
reduces surface tension at the air–water interface in the alveoli
trachea, lungs, heart, large blood vessels, esophagus
Main contents of the Thorax
(hint: look at picture)
diaphragm
thin sheet of skeletal muscle
forms caudal boundary of thorax
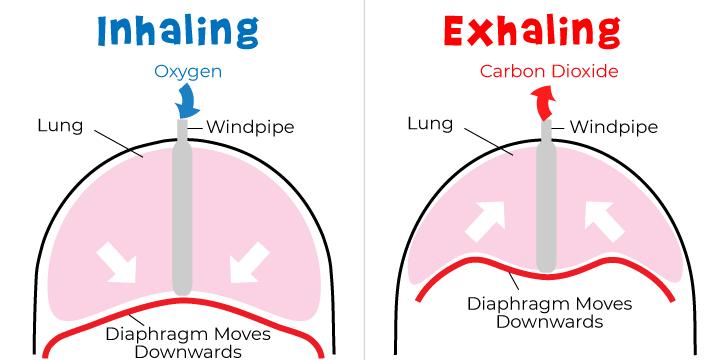
respiratory muscle
The diaphragm acts as a _____________________
bases of lungs lie on cranial surface
dome-shaped: relaxed
flattens: muscle contracts and enlarges volume of thorax
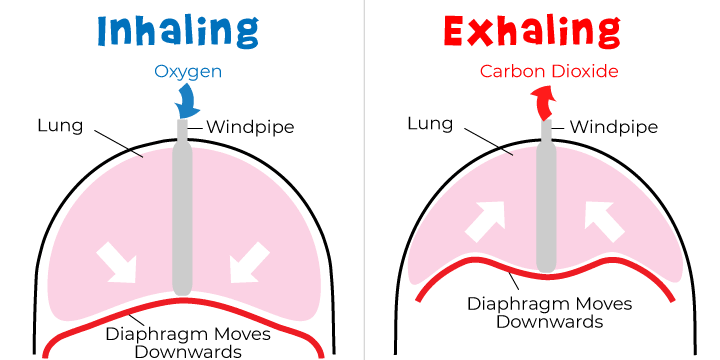
mediastinum
Heart is sitting in the __________________
Intrathoracic
Negative _____________________ Pressure
partial vacuum within thorax
pulls lungs tight against thoracic wall
lungs follow thoracic wall and diaphragm
inspiration and expiration
pneumothorax
Occurs when air leaks into the space between the lung and chest wall, causing the lung to collapse.
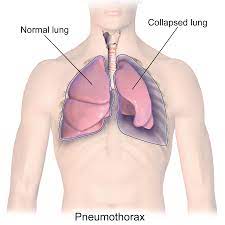
lungs
______________ cannot move on their own
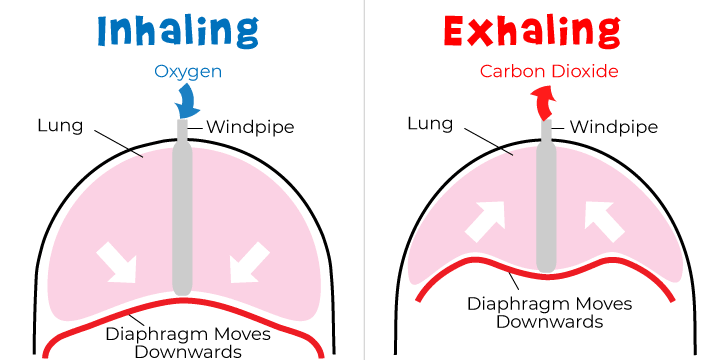
inspiration
____________________ = Inhalation
to draw air into lungs
volume of thorax enlarges
lungs follow passively
air is drawn into lungs
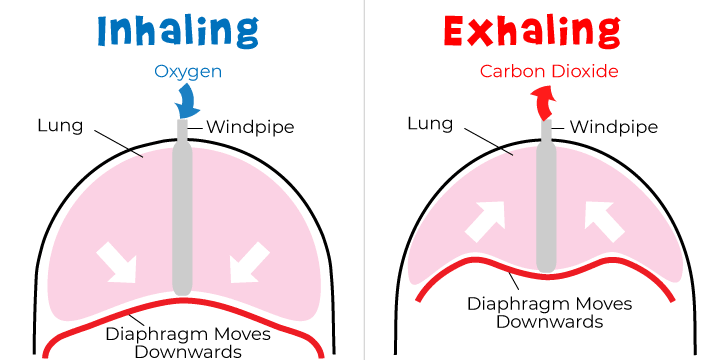
main inspiratory muscles
Diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
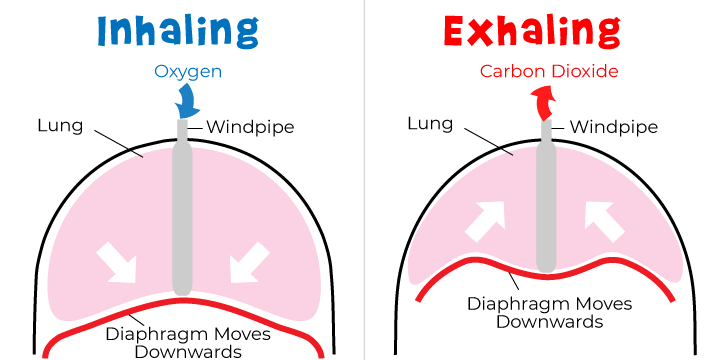
expiration
_____________________ = Exhalation
push air out of lungs
opposite of inspiration
size of thorax decreases
lungs compressed
air is pushed out
Respiratory Volumes
quantity of air respired
tidal volume
vol of air moved in/out during normal breathing
carbon dioxide
Every celll in the body makes ________________
minute volume
vol of air breathed in 1 min
Acid-Base Balance
The more CO2, the lower the blood pH
7.4
normal pH of blood
medulla oblongata
Breathing controlled by brain
directs timing and strength of muscle contraction
Respiratory Center
individual control centers for inspiration, expiration
controlled consciously, mechanically or chemically
automatic system
nerve impulses sent to respiratory center
indicate lungs inflation
lungs full: inspiration stopped, expiration are started
lungs empty: expiration is stopped; inspiration started
Mechanical
________________ Control System for Breathing
stretch receptors in lungs
preset, automatic system
net effect is normal, rhythmic, resting breathing baseline pattern
Chemical
_______________ Control System for Breathing
change breathing only when out of balance
makes adjustments (homeostasis)
chemical receptors monitor blood
in carotid artery, aorta, and brain stem
characteristics monitored
CO2 content
the pH
O2 content
Carbon dioxide
_____________ Variations in the Blood
blood CO2 and blood pH usually linked
increased CO2 in blood
decreases blood pH
triggers respiratory center to increase RR, depth
decreased CO2 in blood
increases blood pH
triggers respiratory center to decrease RR, depth
increased CO2 in blood
decreases blood pH
triggers respiratory center to increase RR, depth
decreased CO2 in blood
increases blood pH
triggers respiratory center to decrease RR, depth
Oxygen
____________________ Variations in the Blood
effects of variations not as clear-cut as with CO2
slight hypoxia
Respiratory center signaled to increase RR, depth
severe hypoxia
Respiratory center so depressed that impulses cannot be sent to respiratory muscles
can cause breathing to decrease or stop completely
ruminants
Herbivores like cattle, sheep and goats
very specialized animals
non-ruminants
Herbivores like horses and rabbits
Do not have a rumen; don’t sufficiently digest plants
cats
Carnivores that eat only meat
humans, pigs, dogs
Omnivores that eat both plants and animals.
digestion
disassemble large molecules
small molecules enter the body
mechanical digestion
GI tract movements during breakdown processes
chemical digestion
chemical reactions during breakdown processes
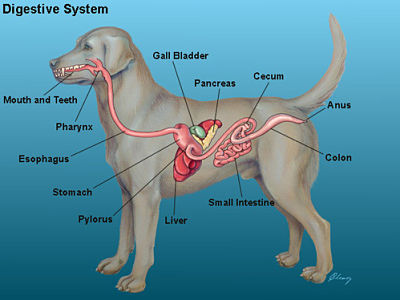
GI
means Gastral Intestinal
tube
oral cavity to anus
includes:
oral cavity
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
mucosa, submucosa, muscular layers, serosa
4 layers of tissue in the GI Tract
Buccal Cavity
The Oral Cavity = Mouth = ___________
entrance to the GI tract
2 parts
vestibule
oral cavity
vestibule
Part of the Mouth: between lips/cheeks, and outside of teeth
rabbits
________________ can’t always eat carrots, they need grass as well
oral cavity
Part of the Mouth: inside of teeth, and hard and soft palates
amino acids
sub-units of proteins
mechanical breakdown
_________________ is not enough for most animals to digest food
enzymes
chemical reactions that break things down into digestible amino acids
the teeth
embedded in upper maxilla and lower mandible
open
The GI Tract is __________ to the outside environment unlike the respiratory and circulatory systems
crown, root, apex, neck
parts of a tooth
cats, snake and teenagers
____________ don’t chew a lot
dentin
bulk of tooth
surrounds pulp cavity w/blood and nerves
dentin
periodontal membrane
Thousands of little fibers that attach the surface of the tooth to the side of the socket (or alveoli)
cementum
thin bone
gingiva
Scientific name for gum
Dental Formula
number of each type on one side of upper and lower jaws
baby teeth
Deciduous Teeth = Milk Teeth = ____________
2
all domestic species: __ sets of teeth
deciduous and permanent
The 2 sets of teeth every animal has
deciduous teeth
__________________ = Milk Teeth = Baby Teeth
smaller, whiter
present at birth
erupt through gums at different times, depending on species
enamel
The crown of a tooth eventually leads to the _________
incisor, canine, premolar, molar
4 types of teeth of different shapes and sizes each has a different function
dog
A cat has fewer teeth than a ________
permanent teeth
adult teeth
brachyodont teeth
found it…
carnivores, humans, pigs
also ruminant incisors
small crowns, well-developed roots
do not grow continually
hypsodont teeth
found in…
horse’s incisors and cheek teeth
boar’s canine teeth
rodents, lagomorphs
large reserve of crown beneath gingiva
“grow” continually
the tongue
muscular: ventral oral cavity
epithelium
stratified squamous
papillae: dorsal surface
mechanical functions…
grooming, moving food to pharynx
specialized functions…
taste, pain, temperature, touch, thermoregulation (panting)
epithelium
stratified squamous of the tongue
papillae
dorsal surface of the tongue
grooming, moving food to pharynx
mechanical functions of the tongue
taste, pain, temperature, touch, thermoregulation (panting)
specialized functions of the tongue
saliva
deposited into oral cavity via ducts
production varies
herbivores the most
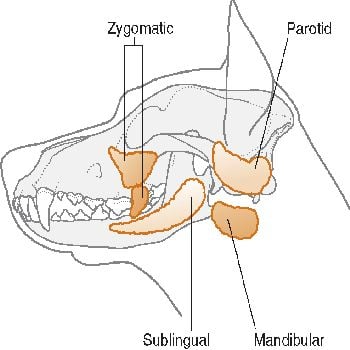
mainly water, salivary bicarbonate, enzymes
saliva composition
Lysozyme
Damage bacteria…
tears (for the eyes)
phagocytes (part of the immune system)
amylase
The pancreases makes ________ which digest starch in the salivary glands.
antibodies on tongue
lubrication, enzymatic digestion, antibacterial action, pH regulation, thermoregulation
saliva functions