GEO CSEC STUDY
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
MAP WORK
MAP WORK
6 fig grid refrence
vertical lines first (bottom numbers)
use a ruler to measure then dived by then use ruler to then mark off at every interval (the ans)
Note: if it falls between 2 numbers use smaller number
Gradient
G= Hight difference/distance
note: always simplify and cancel zeros
note: the first number in the ration should always be 1 (so simplify further )
ex: 4/10 = 1:2.5
note: if given a statement scale to find the distance you must use a ruler to measure the map distance (point A to point B) then use the scale to calculate the ground distance
ENLARGE AND REDUCE
note: the smaller the scale (the bigger the number)
note: if original grid square 2cm x 2cm when reduced by half the new size will become 1cm x 1cm. If we enlarge it by 2x then the grid square will measure 4cm x 4cm.
enlarge
reduce
scale x ½
scale x 2/1
note:
for map sketch remember to add north line, key, title and scale
DIRECTION
DIRECTION
note:
nne & nnw is directly beside the N
sse & ssw is directly beside the S
after filling this out the rest of the 16 point compass is easy
note:
do not use nne, ssw etc unless it is absolutely obvious.
angular bearing of the points
n= 0, 360
e= 90
s= 180
w= 270
ne=45
nw= 315
se= 135
sw=225
protractor tips
always draw a long north line
when the protractor has to turn left draw a south line. then read using outer number still. then add 180
CROSS SECTION
remember to draw vertical line to cut the section if only part of it is shown then shade inside.
INTERVISIBILITY
mutual visibility between 2 point without obstruction
DESCRIBING VEGETATION
1.type:
natural
- forest & woodland: hilly areas, people avoid living
-trees and shrubs: low and drier areas
-swamps: areas of impeded drainage
-mangrove: close to the coast
cultivated
2.distribution
-elevation
-closeness to settlement
-closeness to coast
-extent: pockets or extensive areas
DESCRIBING LANDSCAPE
1.relief
-distribution, height and size of landforms
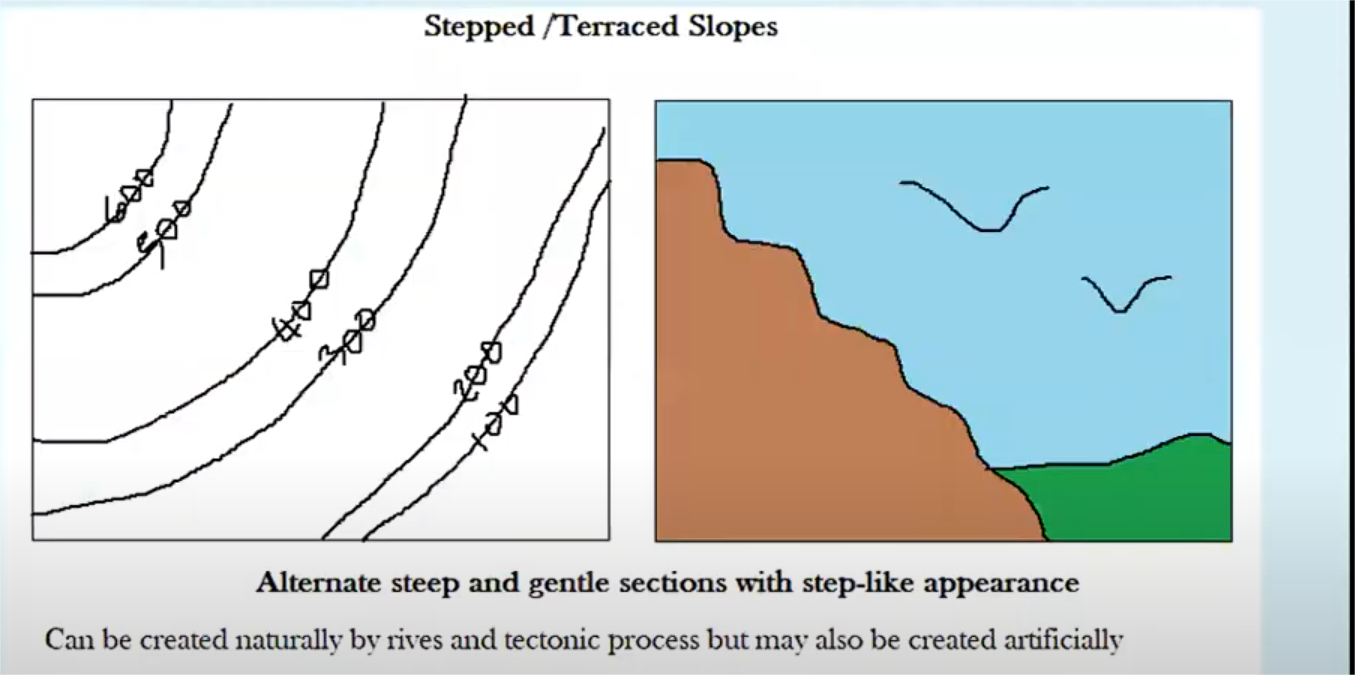
TYPES OF SLOPES
TYPES OF SLOPES
stepped slopes
alternating high and low
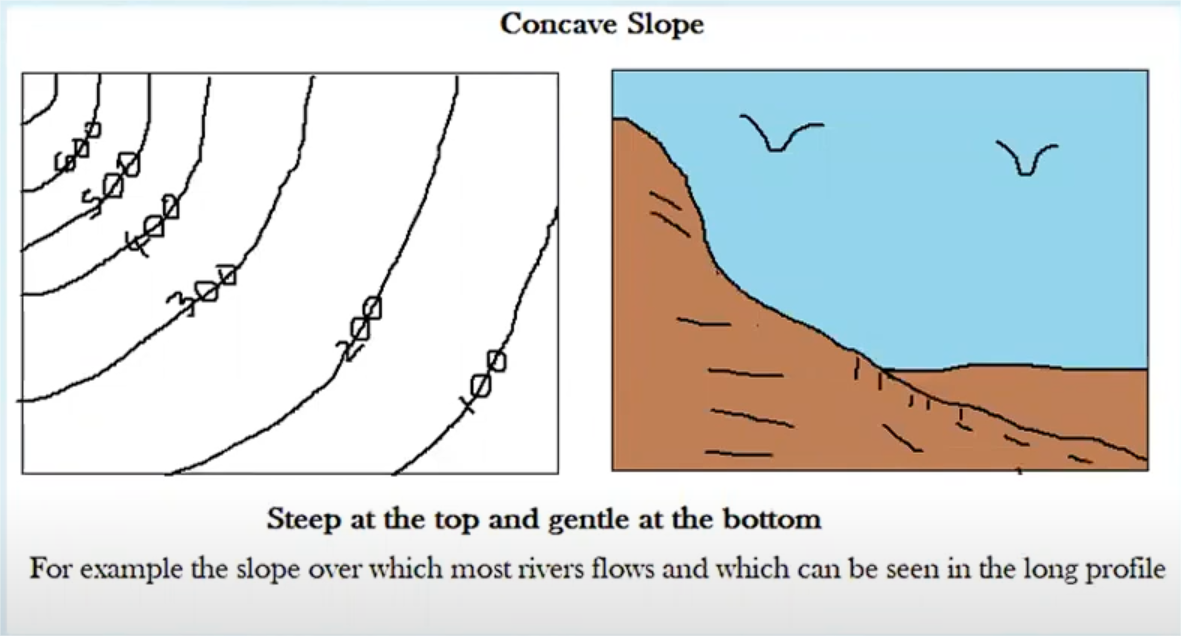
concave
steeper at the top than at the bottom
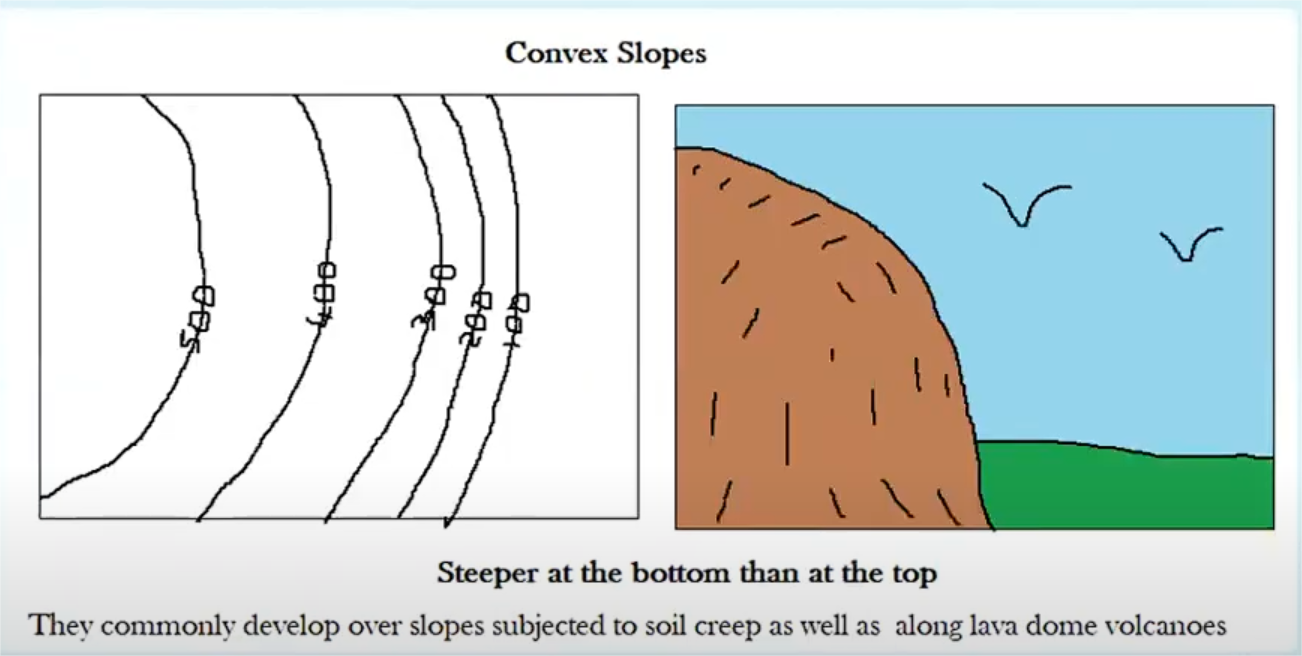
convex
steeper at the bottom and gentle at the top
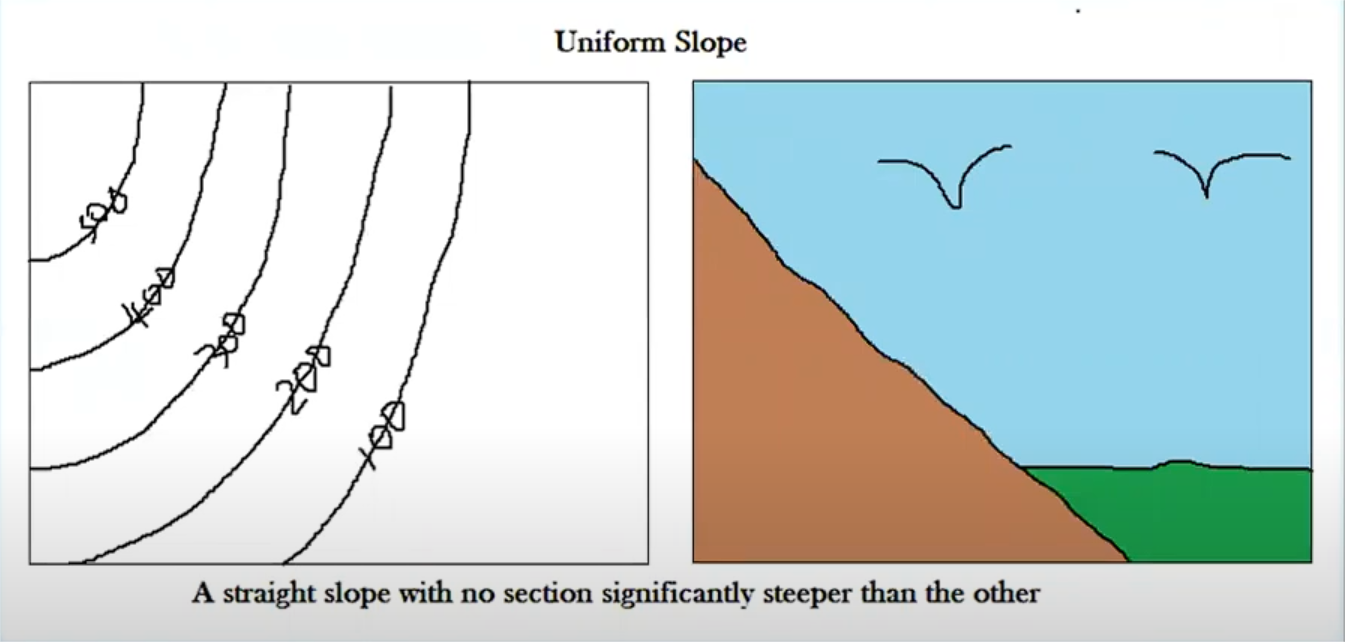
uniform slope
straight slope with no significant interval variation
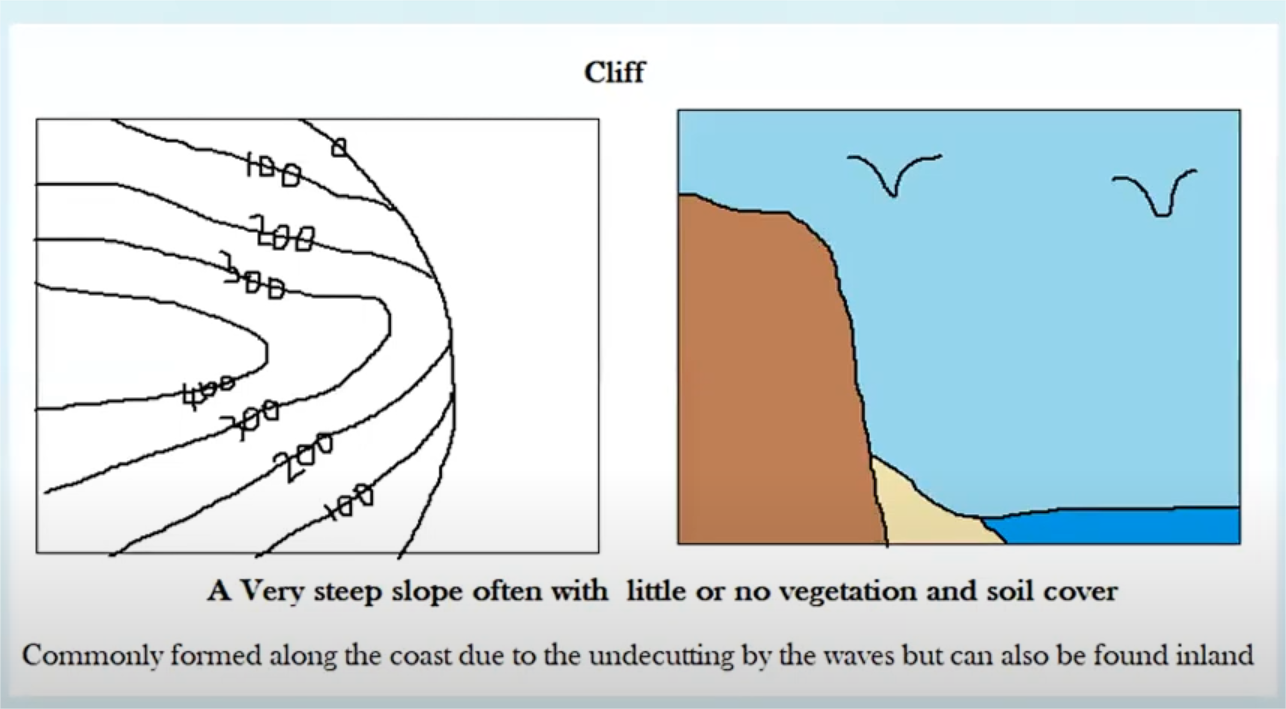
cliff
very steep slope (little or no vegetation)
LANDFORMS ON A MAP
-valley: low land with highland on both sides or v shaped contours
- depression: land rises around the area on all sides.
SECTION 2
SECTION 2
wave action
Wave action is the movement and force of ocean waves as they hit the shore.
It plays a big role in shaping coastlines through erosion, transportation, and deposition.
What is the coast?
where land meet the sea
COASTAL ERSOIONAL PROVCESSES
COASTAL ERSOIONAL PROVCESSES
hydraulic action
a physical process waves force air into joints and cracks causing the rocks to wedge, overtime the rocks become lose and fall into the water.
Abrasion
a physical process where waves caring bits of rock and sand grind against the coastline (in a Scouring motion) wearing it away over time
Attrition
a physical processes where destructive waves causse rocks and pebbles on the shore to smash together, getting smaller and smoother.
solution
a chemical process where acids in sea water dissolves rocks.
ex: limestone
WEATHERING PROCESSES
WEATHERING PROCESSES
physical
physical
Freeze-thaw
Frost action is a physical weathering process where water enters cracks in rocks, freezes, and expands, causing the rock to break apart over time.
This process occurs in regions where temperatures fluctuate above and below 0°C, especially in high altitudes and mountainous areas. These temperature changes allow water to freeze at night and melt during the day, repeating the cycle and widening the cracks. (add more on the exam)
Exfoliation:
a physical weathering process where Rock peels off in layers from repeated heating and cooling.
occurs in areas with drastic temperature change between day and night. (add more on the exam)
Abrasion
Rocks scrape or rub against each other.(add more on the exam)
chemical weathering
chemical weathering
Oxidation
Oxygen reacts with minerals (like iron) and causes rust.
Hydration
Water reacts with minerals, making them soft or crumbly.
feldspar > clay
anhydrite (AN-hy-drite) > gypsum
Carbonation
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) in the air mixes with rainwater
The rain becomes slightly acidic (called carbonic acid).
When this acid rain falls on rocks like limestone (made of calcium carbonate), it causes a reaction turning the calcium carbonate (limestone) into calcium bicarbonate
Calcium bicarbonate is soluble so it gets washed away.
biological weathering
biological weathering
Root action / root tension
Plant roots grow in cracks and split the rock.
(add more on the exam)
Animal activity
Burrowing animals break up rocks.
Organic Acid Weathering
Acids from plants, animals, or bacteria break down rock (chemical).
MASS MOVEMENT (MASS WASTING)
the downslope movement of soil and other materials due to gravity
SOIL
SOIL
what is soil?
how is it formed?
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, water, and air that together supports the life of plants and some organisms
soil is formed from rocks broken down into small pieces by weathering, which is then mixed with animal and plant decay (humus)
soil content
rock particles (minerals) - 45%
organic matter (humus) - 5%
water- 25%
air- 25%
types of soil
sand
clay
silt
Loam soil – A type of rich, fertile soil made of a good mix of sand, silt, and clay.
Ideal for farming and gardening.
Holds water but also drains well.
Latosol – soils found in humid tropical and equatorial regions
- they are rich in iron and aluminum oxides, giving them a reddish or yellowish color
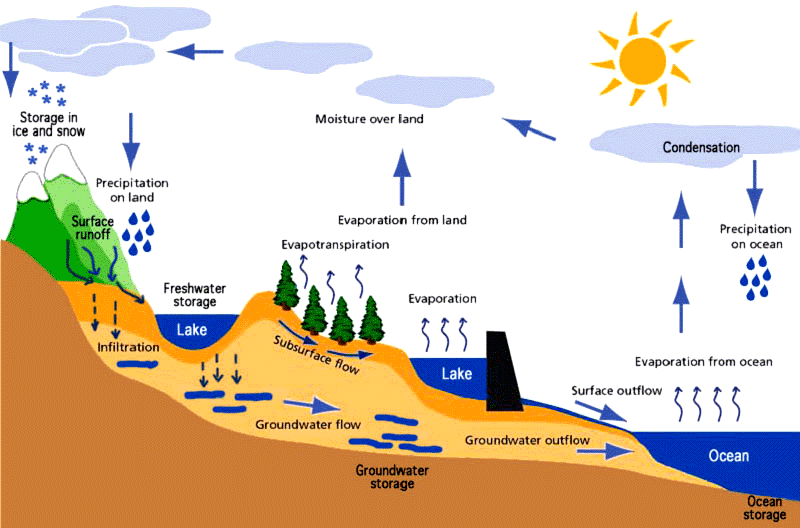
HYDROLOGICAL CYCLE
note: percolation and infiltration the same thing
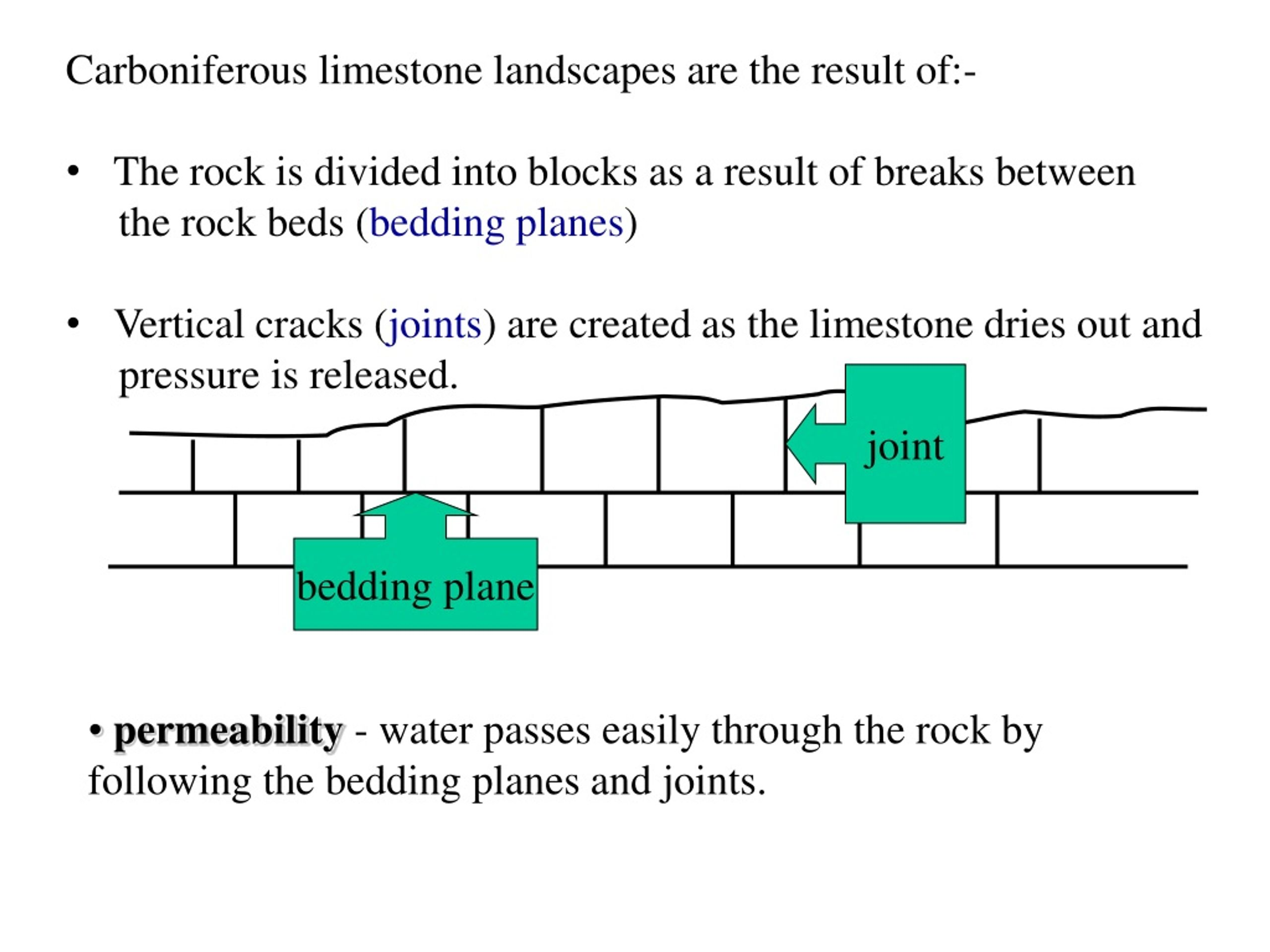
limestone
has 50% or more calcium carbonate
how is it formed?
limestone is a sedementary rock formed when sea water is heated which results in calcium carbonate chemically being precipitated out as very fine prains called oolites
CORAL REEF
CORAL REEF
what is coral
are hard rocky ridges built up from the sea bed by many tiny coral animals (coral polyps)
ideal conditions
temp: 23°C to 25°C
Depth: shallower than 70 meters
types
types
fringing
Grows close to the shore
a type of coral reef that grows directly adjacent to a coastline, island, or mainland. Unlike barrier reefs or atolls they are not separated from the shore by a deep lagoon.
barrier
Grows far from shore
Has a wide, deep lagoon between reef and land
roughly parallel to a shore and separated from it by a lagoon or other body of water.
atoll reefs
a ring-shaped coral reef, island that surrounds a body of water called a lagoon.
atoll reefs grow outward from a fringing-reef stage, as they seek better conditions
RIVER
RIVER
upper course
V-shaped valley – A steep, narrow valley shaped like a “V”
Interlocking spurs – Hills that stick out and the river winds around them
Rapids – Fast-flowing, shallow water over rocks
Waterfalls – Where the river drops suddenly over a rock edge
middle course
Meanders-when water in the stream channel erodes the outer bank of a stream and deposits sediments on the inner bank.
speed causes this (in both lower and mid course)
oxbow lake (in both lower and mid course)
river cliff
lower course
Levees – Raised river banks formed by flooding
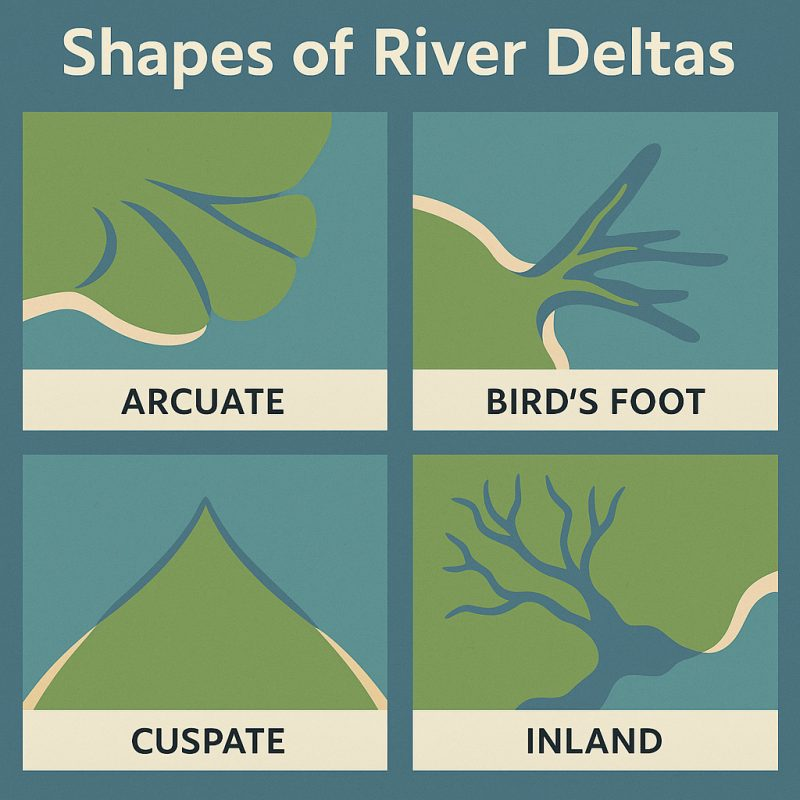
Delta – Land built up where the river meets the sea
types:
arcuate (fan shaped)
bird's foot
estuarine
cuspate
River mouth – Where the river flows into the sea or ocean
PROCESSES OF TRANSPORTATION
PROCESSES OF TRANSPORTATION
Traction
➤ Big rocks roll along the riverbed.
(Think: dragged or rolled)
Saltation
➤ Small stones or pebbles bounce along the bottom.
(Like hopping)
Suspension
➤ Fine particles like silt and clay are carried in the water.
(They float along)
Solution
➤ Minerals dissolve in the water and are carried along.
(Invisible, like sugar in tea)
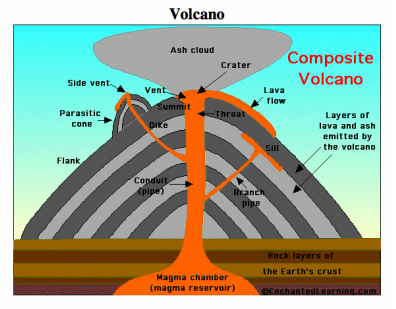
VOLCANO
volcano
how is a volcano formed
what is a volcano
an opening in the Earth's crust where molten rock, ash, and gases erupt from below the surface
types of lava
basic
Low silica content
Low viscosity
Forms gentle sloping volcanoes
– Like shield volcanoes
Erupts gently
– Less explosive than acidic lava
Dark in colour
– Usually black or dark grey
sill-A flat sheet of magma that pushes between rock layers
dyke- A wall-like sheet of magma that cuts across rock layers
types of rocks
igneous:
Granite
Basalt
Obsidian
metamorphic
Marble
Slate
Schist
sedimentary
Sandstone
Limestone
Shale
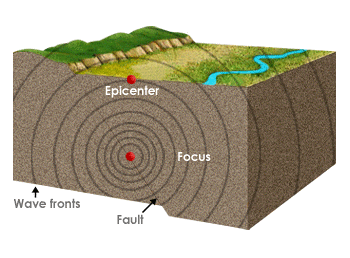
earthquake
WEATER SYSTEMS
Clockwise direction
high pressure
everything is low pressure except anticyclone
relief rainfall
Warm, moist air blows in from the sea.
It hits a mountain and is forced to rise.
As it rises, it cools and condenses.
Clouds form and it rains on the mountain side (windward side).
The other side (leeward side) is drier – this is called a rain shadow.