Incomplete dominance ( 画到F1) (copy)
1/17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
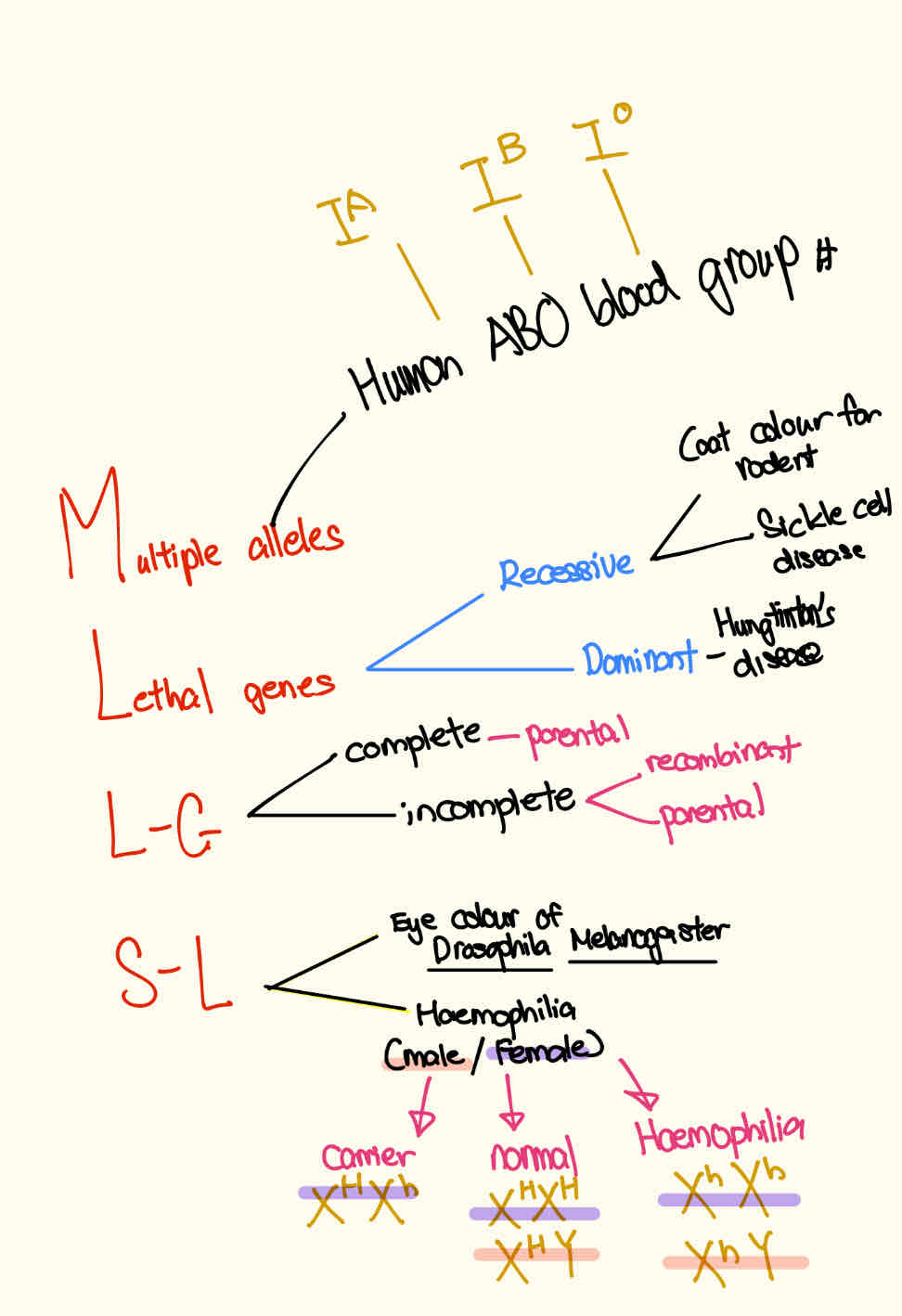
Multiple alleles
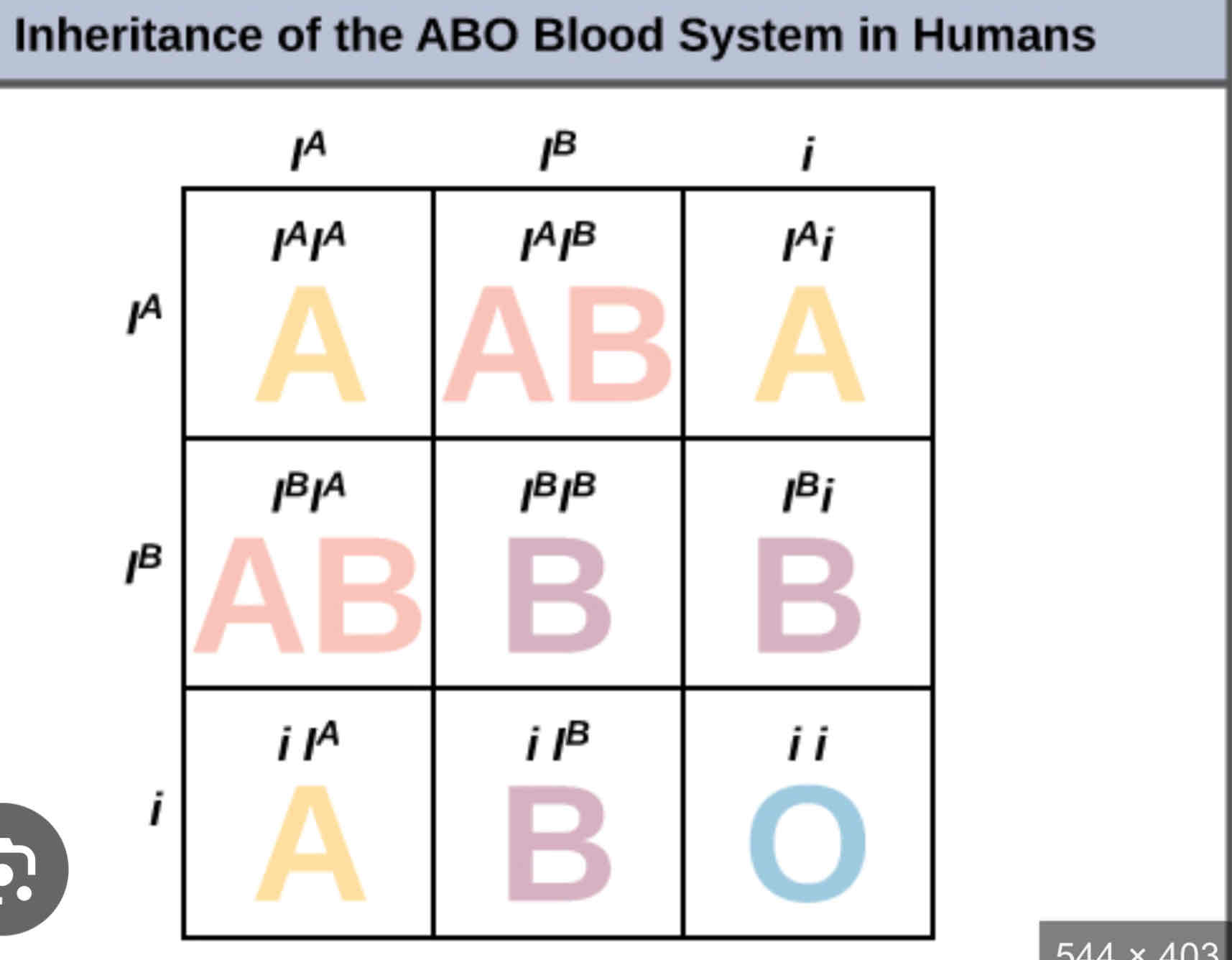
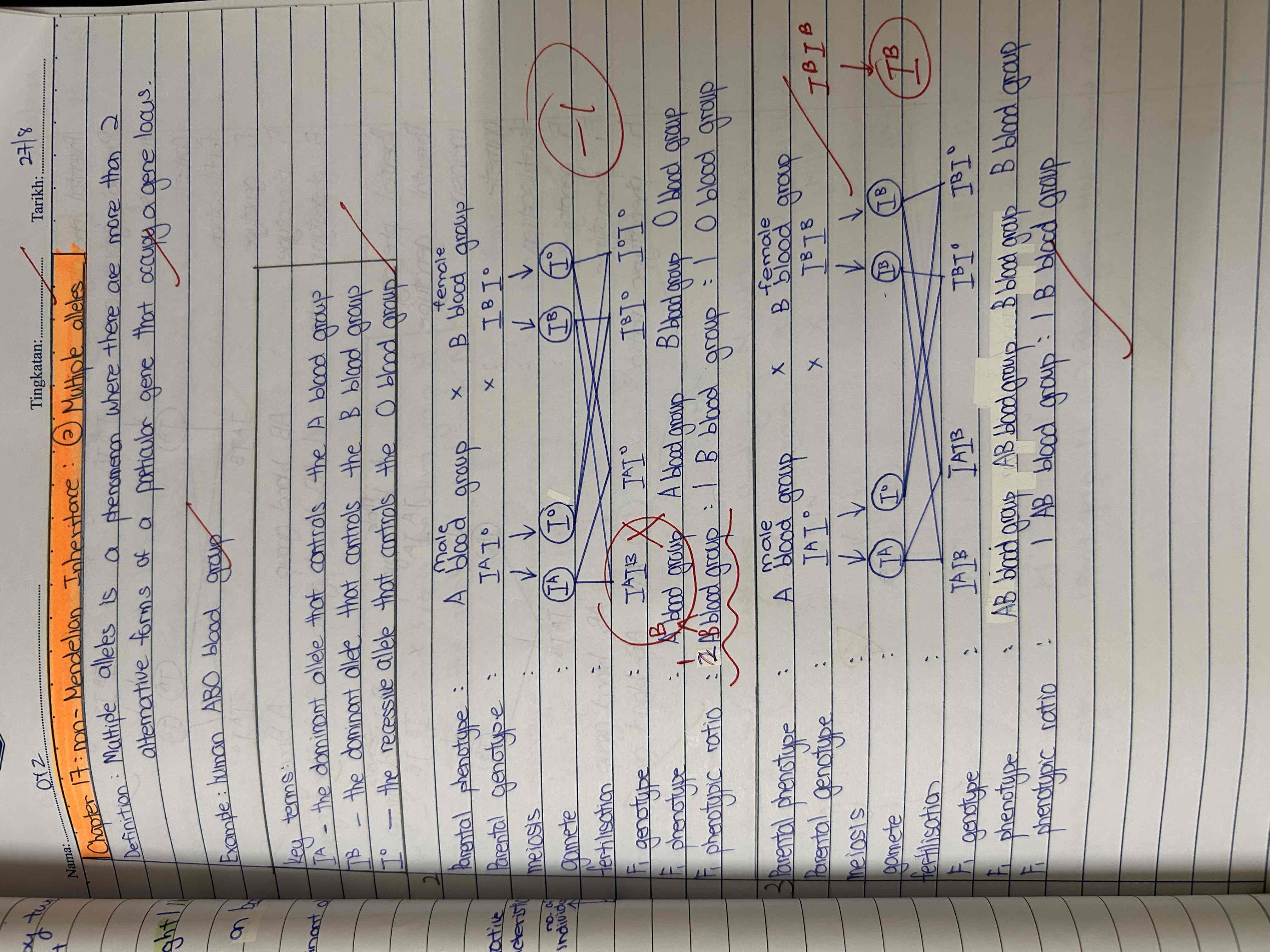
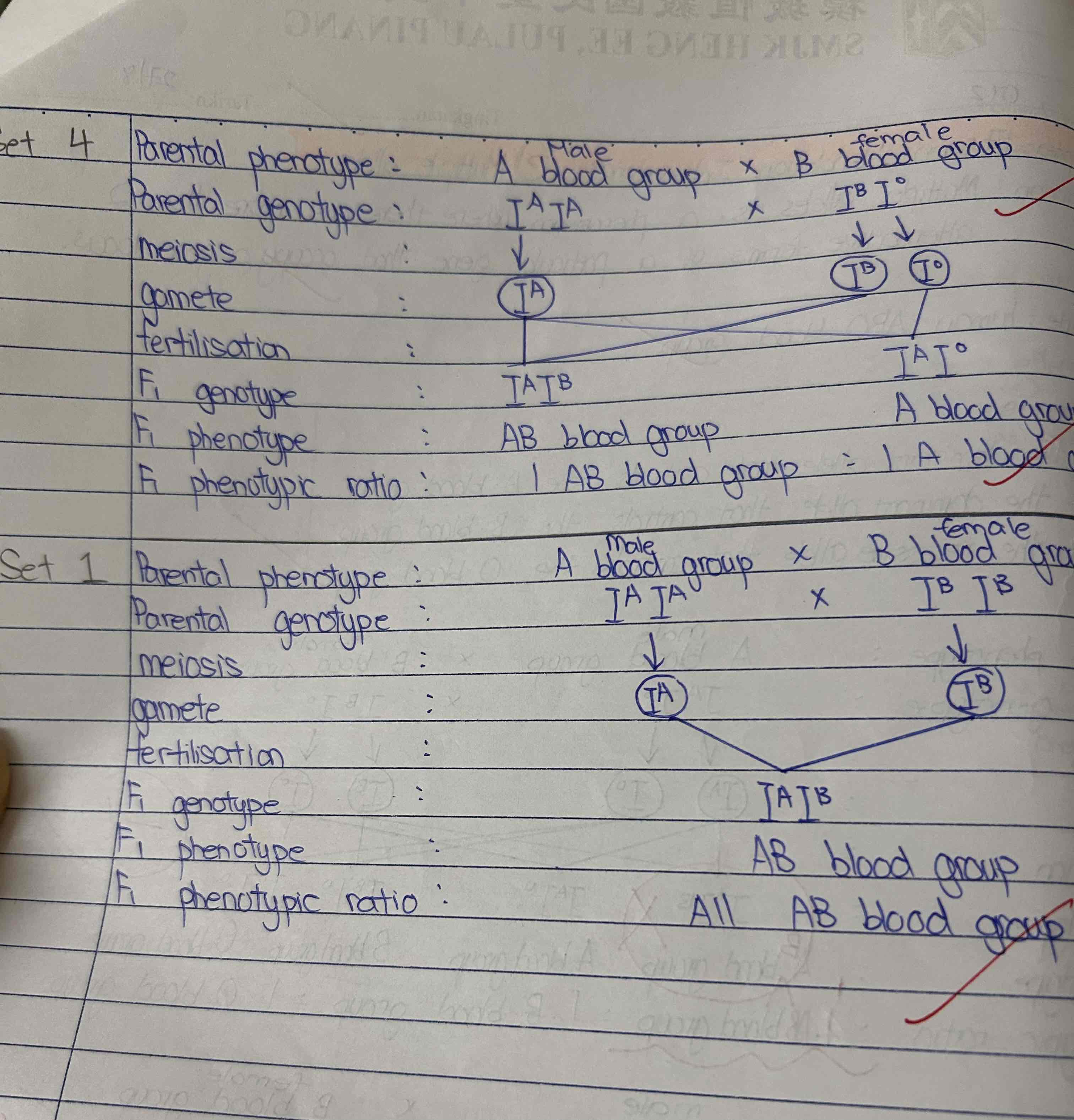
Phenomenon where there are more than 2 alternative forms of particular gene that occupy same gene locus on chromosome that influence the same characteristic
Types of multiple alleles
Human ABO blood group
Lethal genes
Single genes may affect more than one characteristic, including death. (Textbook)
Any gene that has an effect on the organism’s death at any stage of life. (Reference)
Teacher : Results in the death of organism during postnatal stage/ premature stage
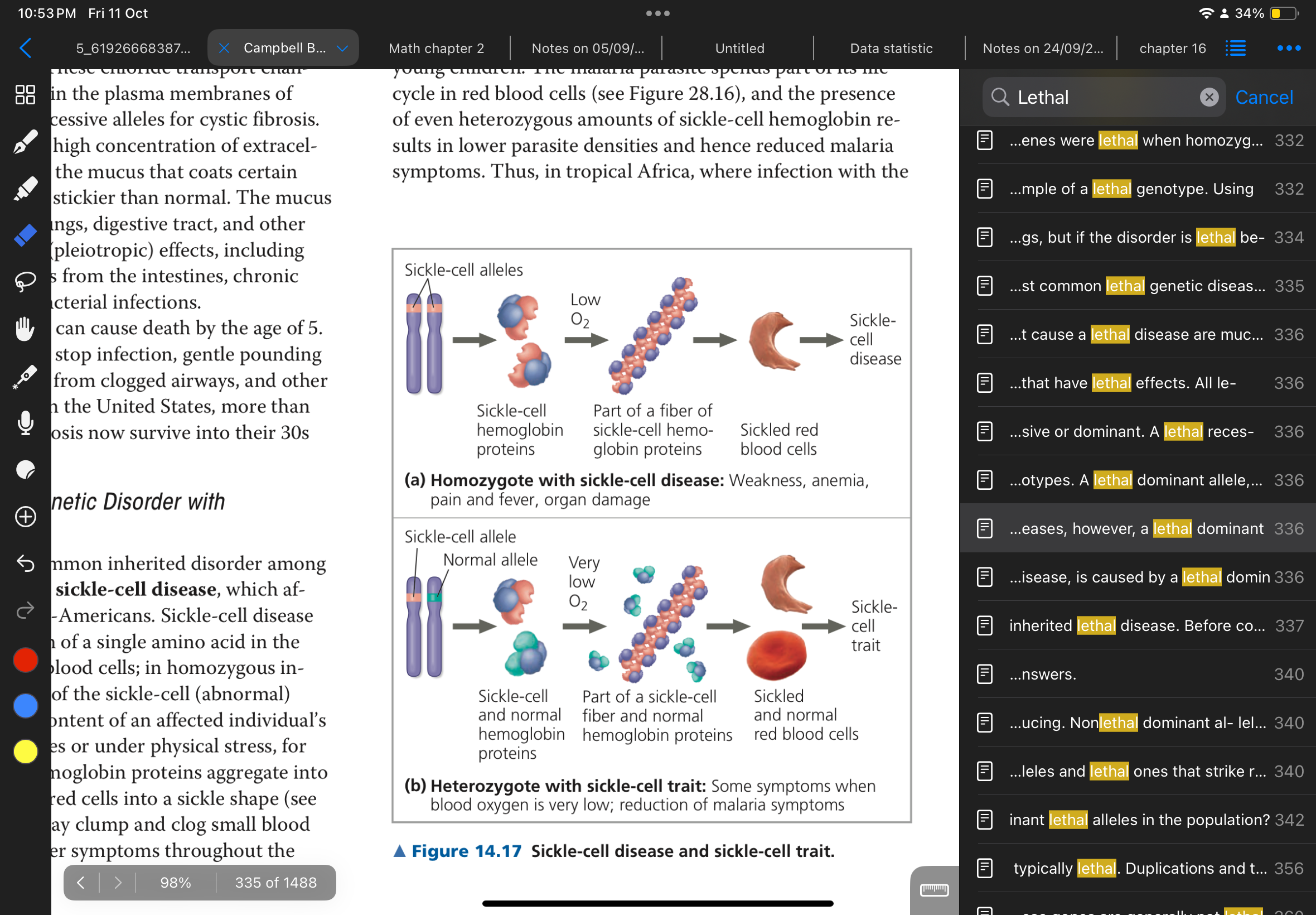
Recessive Lethal genes
KILLING POWER WEAK : Hb^(A) dominant: normal
Hb^(S) recessive : sickle
: only homozygous recessive will get sickle-cell disease.
Sickle-cell disease ( by Campbell) : sickle red blood cell
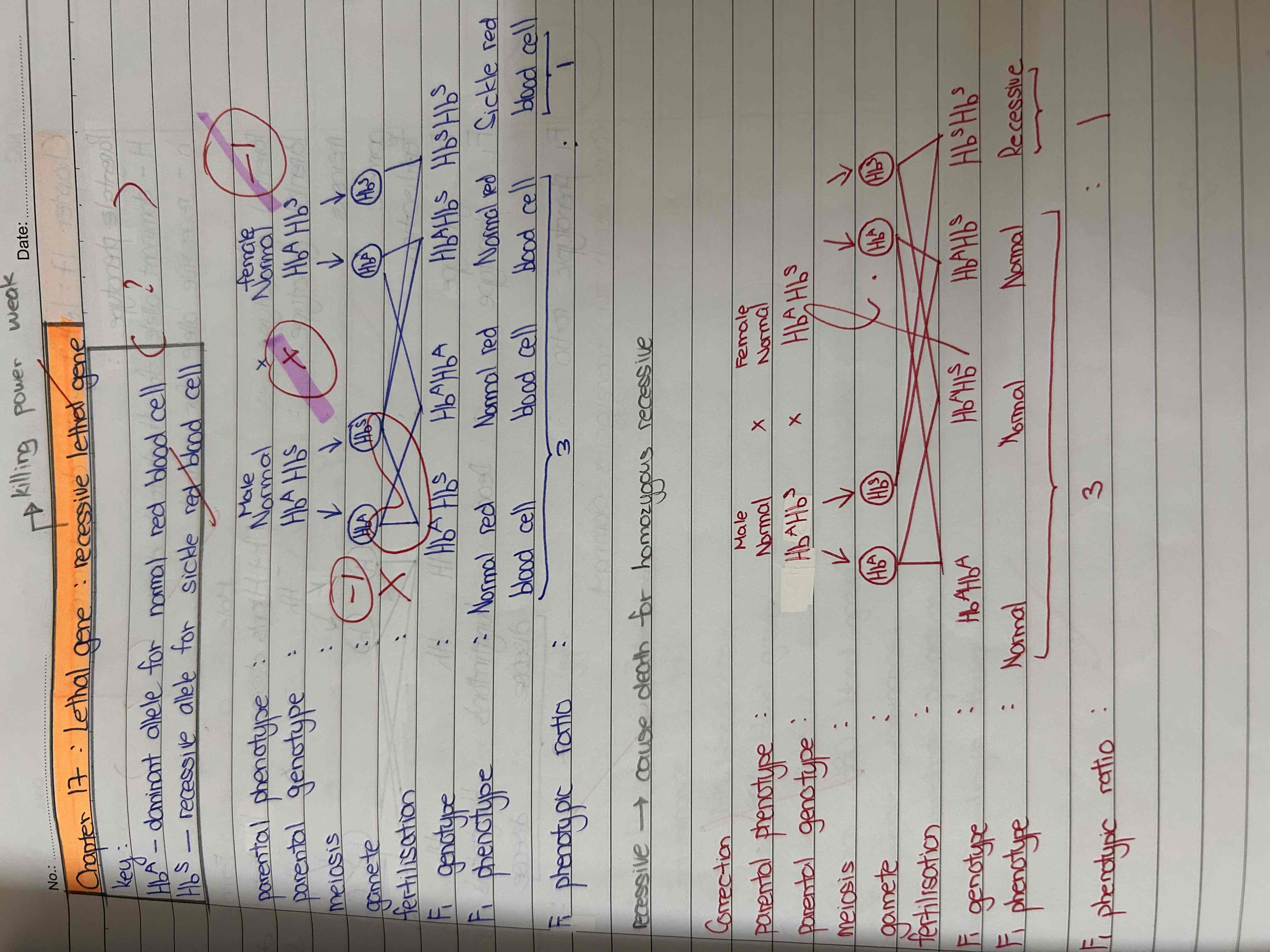
Extra knowledge !!!!!!!!
大胆猜测why sickle-cell disease ( carrier ) cannot donate blood

What condition does a sickle cell disease cause ?
Anaemia (not disease)
= condition in which the number of red blood cells or the haemoglobin concentration within them is lower than normal. It mainly affects women and children.
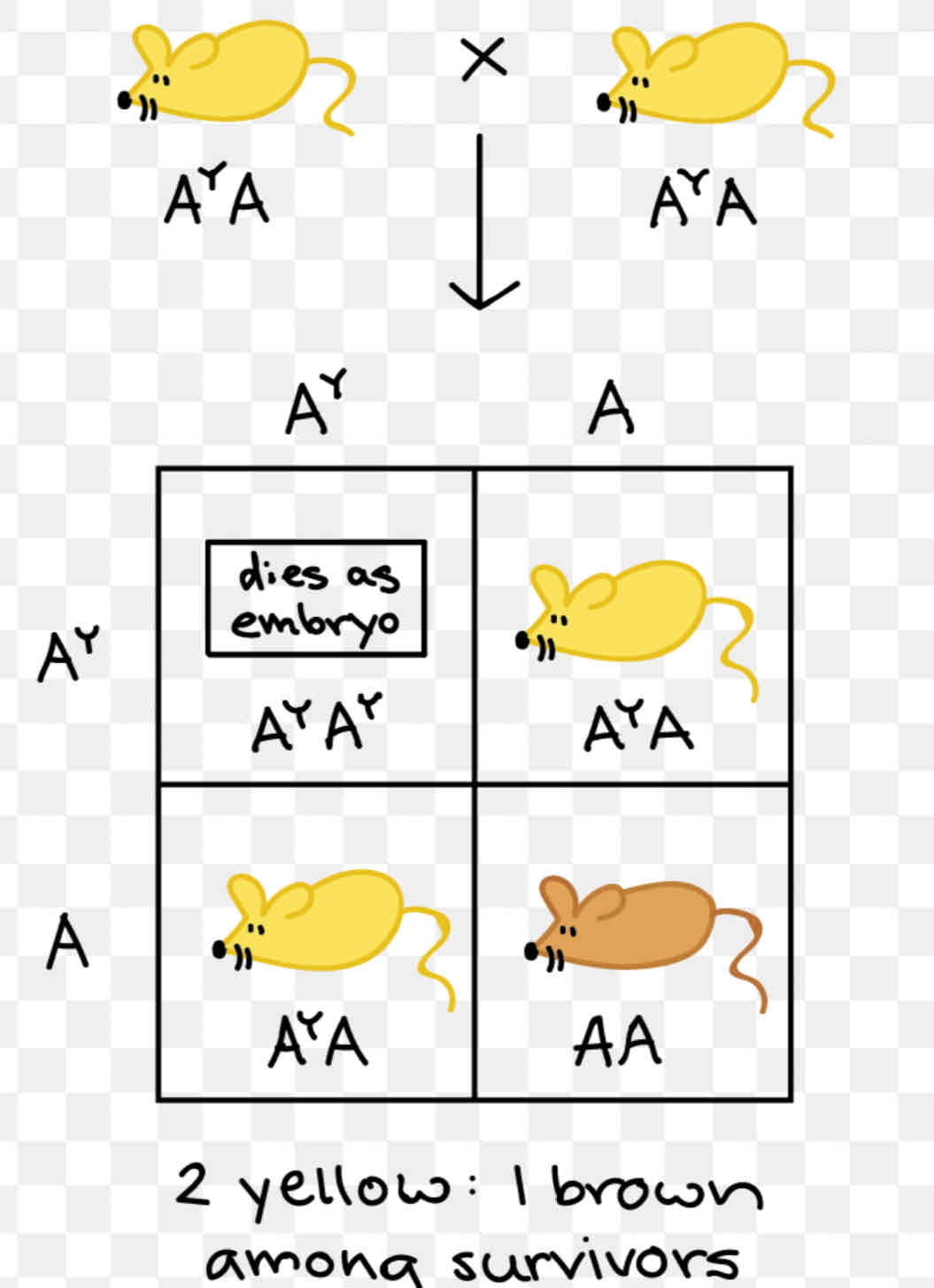
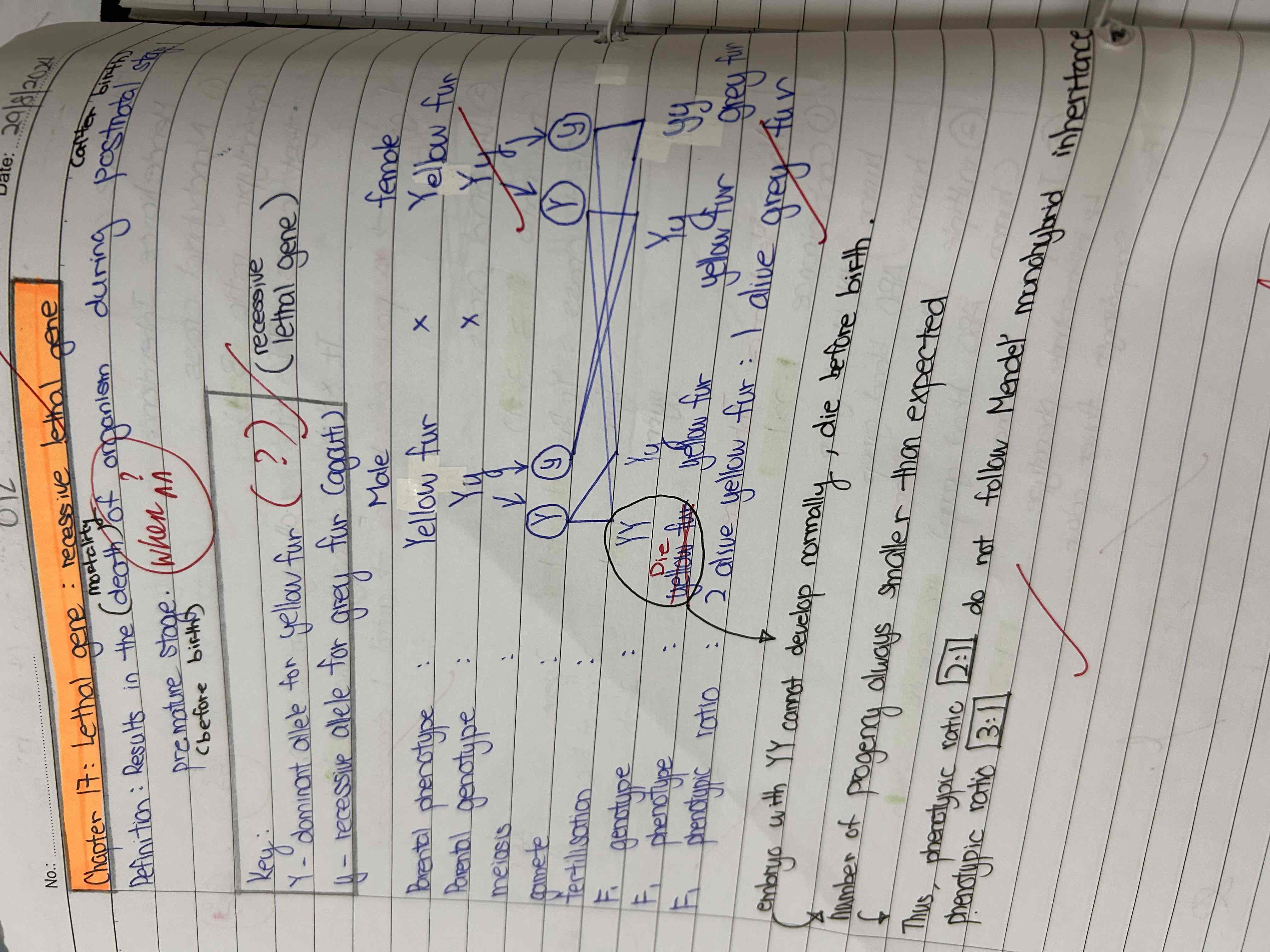
Recessive lethal genes in rodent
Why do not follow typical Mendeliance monohybrid ratio?
Key: Y -dominant lethal genes code for yellow fur
y- recessive allele code for grey fur (agouti )
Embryo with YY cannot develop normally ,die before birth.
Number of progeny always smaller than expected.
Thus phenotypic ratio (??? Active recall) do not follow MMI phenotypic ratio (???)
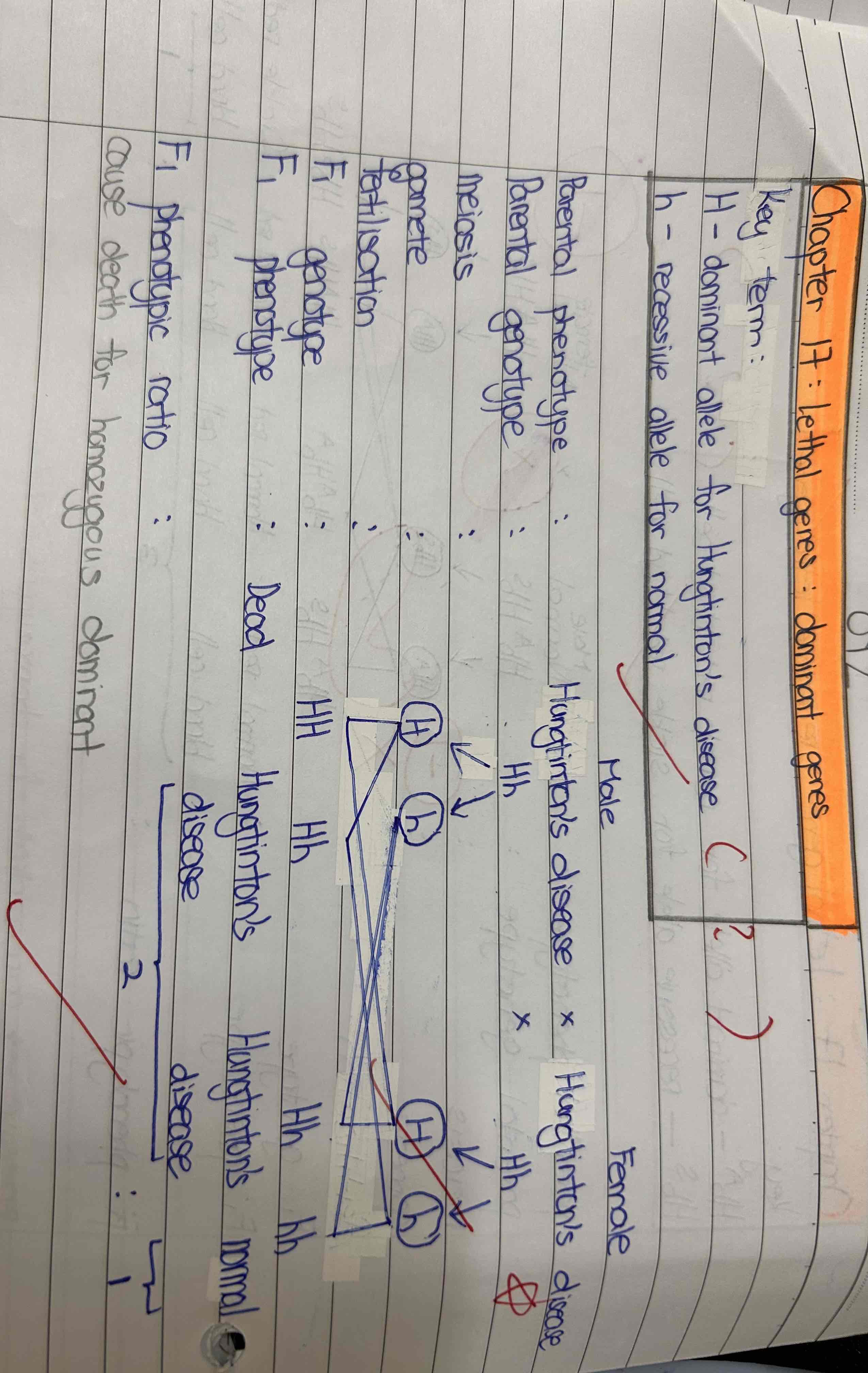
Example of Dominant lethal genes
Key : H- dominant lethal genes code for Hungtinton’s disease
h- normal
- Dead for F1 homozygous dominant individual (??????)
-Heterozygous individual (Hh) : Hungtinton’s disease
Before sex-linked genes, 要知道 reciprocal graph ???
A cross reversing the roles of males and females to confirm the result obtained from an earlier cross to determine wether the gene is an autosome or sex chromosome ( sex-linked gene)
Sex-linked genes
The gene that control a characteristic is link onto sex chromosome, normally X chromosome.
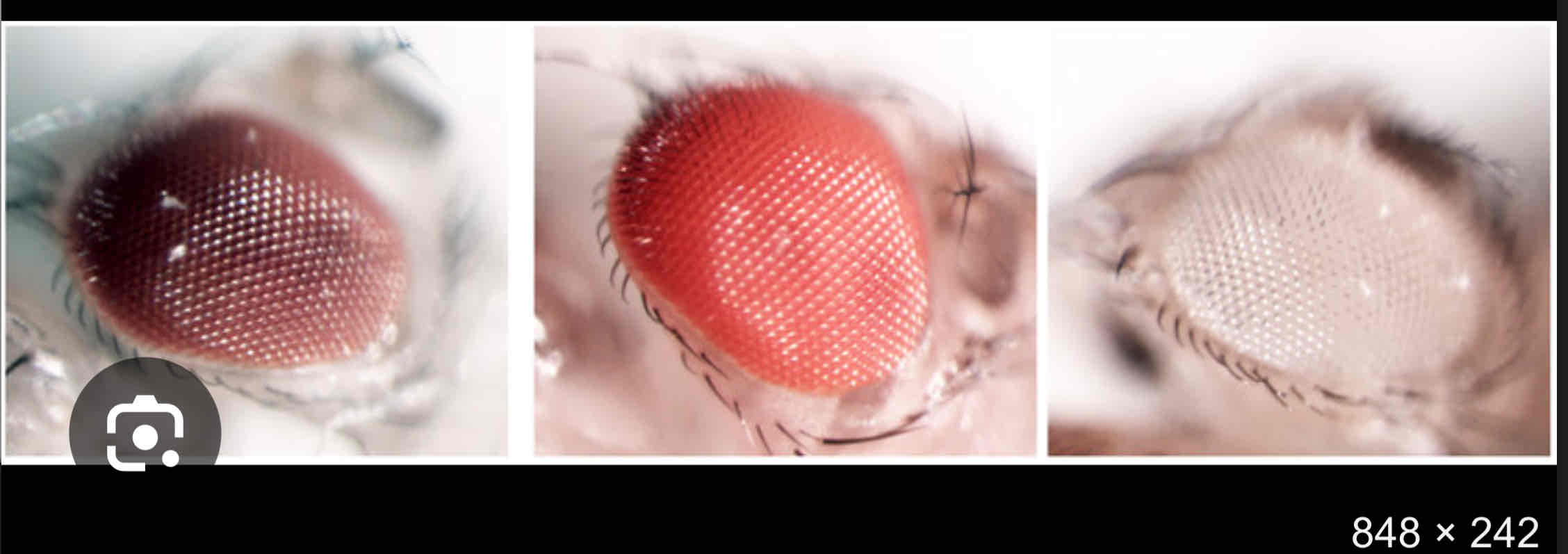
Example
-eye colour of Drosophila melanogaster ( scientific name )
-可能要画reciprocal graph to show that it is a sex linked gene
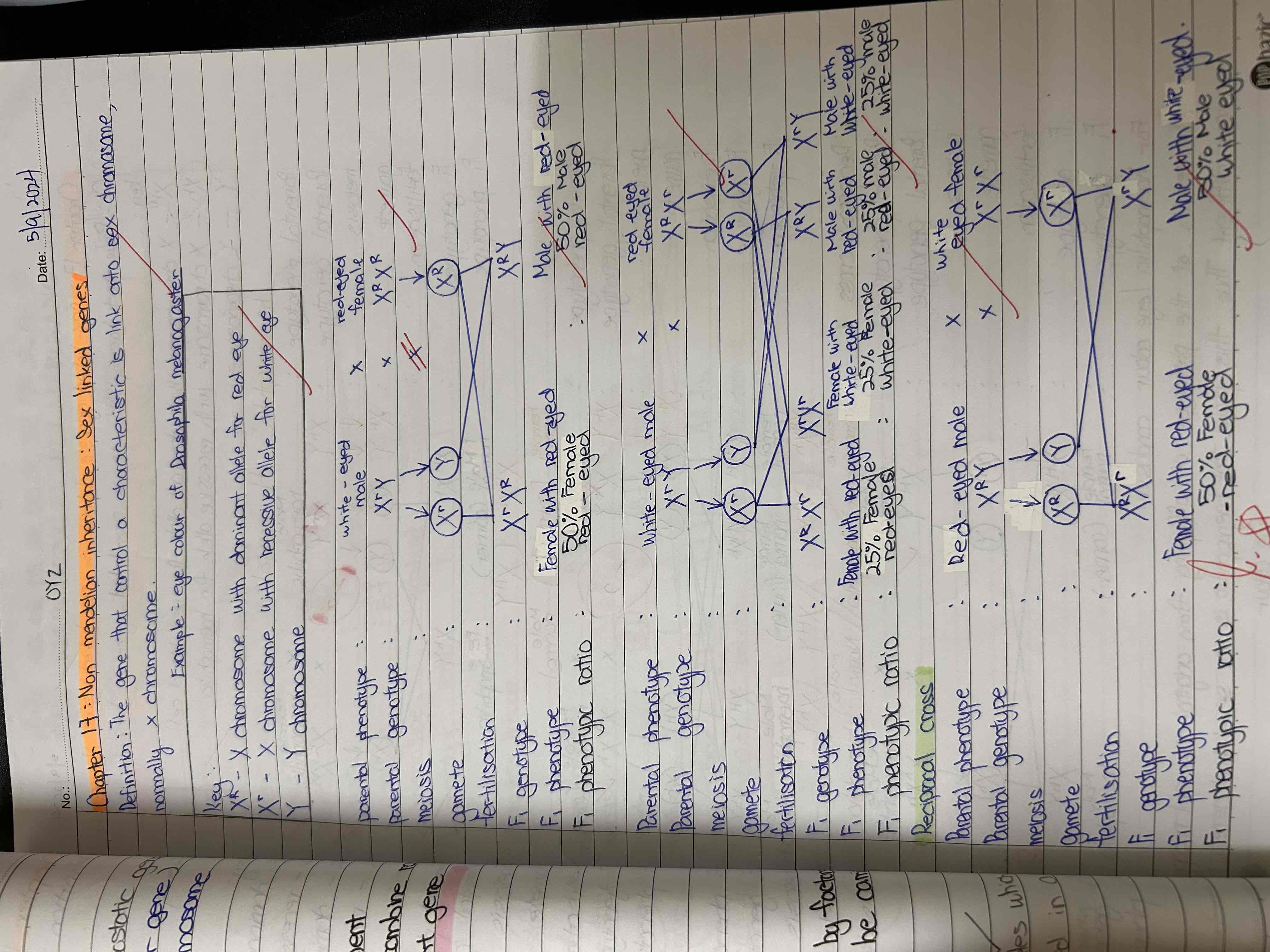
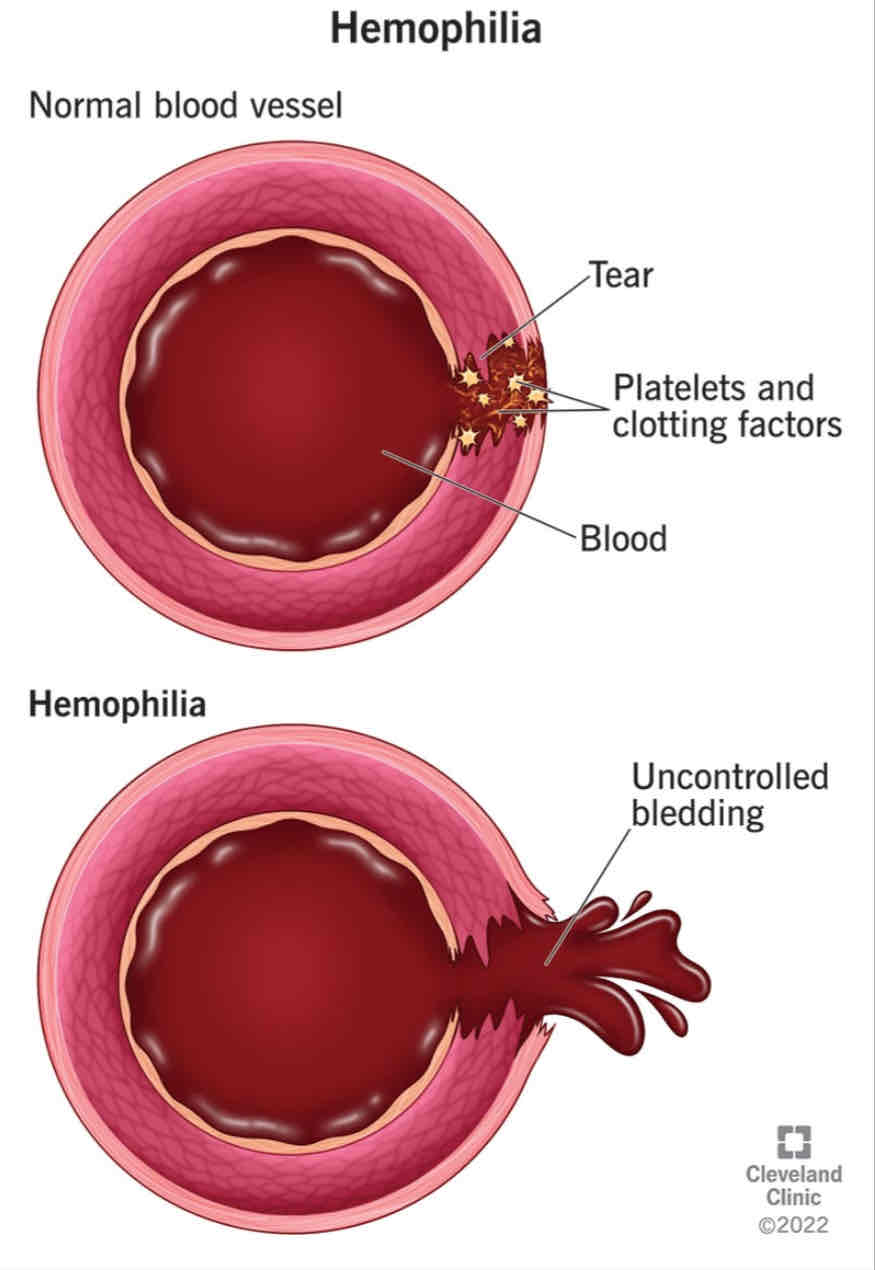
Example of sex-linked gene in human ?
X^(H)- dominant alleles for red blood cell
X^(h)- recessive alleles for haemophilia
Haemophilia ( 不能止🩸)
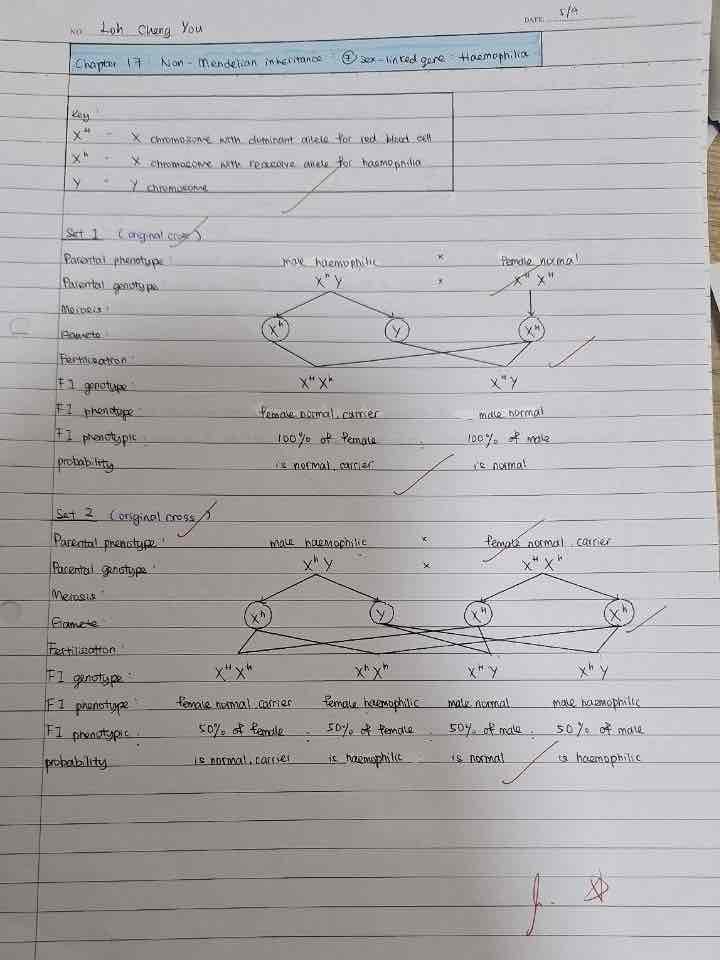
Justify your answer why Drosophila Melanogaster and Haemophilia is sex-linked genes ?
Draw genetic diagram with reciprocal cross and original
Conclusion : (Template)
The results of the phenotype of offspring from original cross and reciprocal cross are different.
Thus, this prove that XXXX is a sex-linked gene which linked on X chromosome .

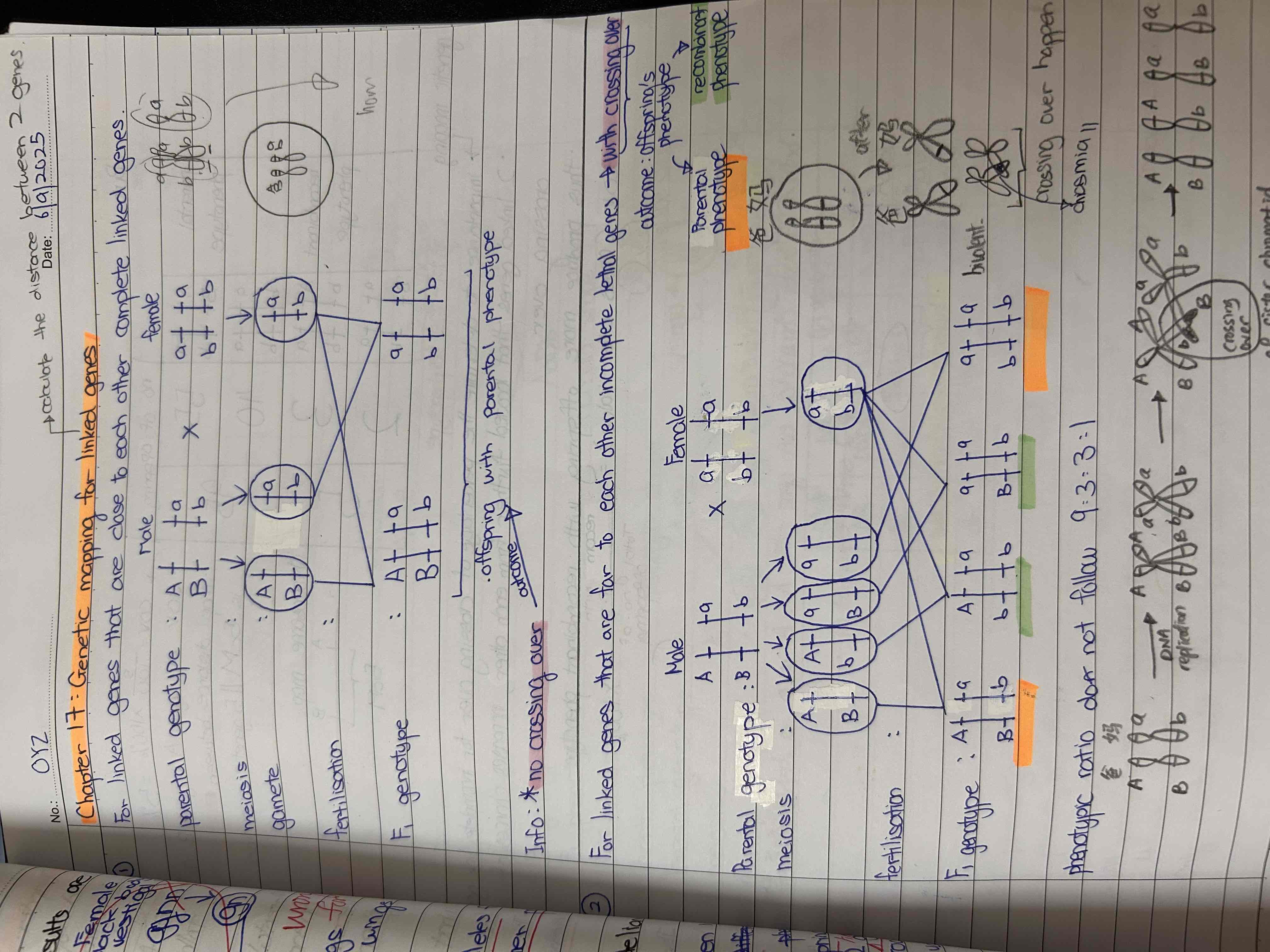
Linked-genes / gene linkage
Genes that are located at different gene loci of the same chromosome and will be inherited together.

recombinant phenotype / crossover
Meiotic products produced by crossing over have recombined the original linkage relationships of the parent into two new forms.
Types of linked genes
-complete linked genes
-incomplete linked genes ( crossing over happen )
Crossing over
Exchange of genetic material between non sister chromatids during prophase 1 when synapses occur.
( hasn’t been checked by teacher Alice yet )
MPM report shown at the image

What type of cases do we only draw until the F1 generation, results show don’t follow the Mendelian monohybrid ratio ?
bu yao chu xin