Chapter 6 - Matrices
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
matrices with n rows and m columns is a what matrix
n x m matrix
what is n
rows
what is m
columns
square matrix
number of rows = number of columns
zero matrix
all the elements are zero
identity matrix
square matrix in which the elements on the leading diagonals starting top left are all 1 and remaining elements are 0
what are identity matrices denoted by
where k describes size
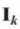
what is the condition for adding and subtracting matrices
they must be same size
conditions for matrix multiplication
you can only multiply if the number of columns in first matrix = number of rows in second
does the order you multiply matrices matter
yes as AB ≠ BA
how to multiply matrices
multiply elements in each row in first matric by corresponding eleements in each column in the 2nd matrix and add together
what is the size of multiplied matrix
number of rows in first and columns in second
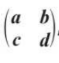
determinant in 2 × 2 matric
ad - bc
type of matric if determinant is equal to 0
singular matrix
what type of matrix if determinant ≠ 0
non singular
which type of matrix has no inverse
non singular
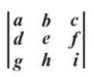
how to find determinant of 3 × 3 matrix
times a b c by its minor
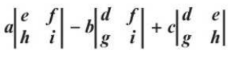
minor of element in 3 x e matric
determinant of the 2 × 2 matrix that remains after the row and column containing the element have been crossed out
imverse of matrix
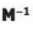
what is the matrix multiplied by its inverse equal to
identity
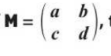
how to find inverse of 2 × 2 matric
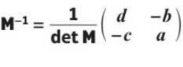
transpose of matric
rows become columns and columns become rowas
how to find inverse of 3 × 3 matric
find determinant
matrix of minors
alternating signs change
transpose
multiply by 1/det
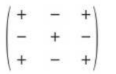
what is (AB)^-1 equal to
B^-1 A^-1
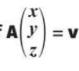
how to work out x y z
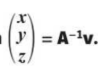
when is a linear equation consitent
if there is at least one se of values that satisfies all the equations simultaneously
matrix meet at one point
consistent
one solution
matrix is non singular so inverse exists
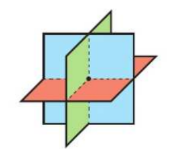
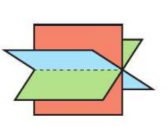
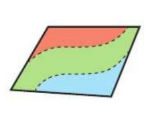
matrix sheaf
consistent
infinetly many solutions
singular matrix
equations all need to be consistent but original equations not multiples of each other
matrix prism
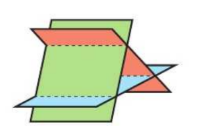
inconsistent equations
no solutions
singular
originals and not any type of multiples
matrix parallel planes
inconsistent
no solutions
singular
at least 2 of the lhs of equations are multiples of eachother
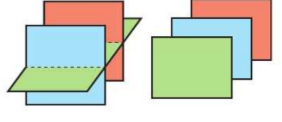
matric same plane
conssitent
infinitely many solutions
singular
if all 3 equatrions of planes are multiples of eachother
self inverse matrix
matrix multiples by itself is identity matrix