HDLC
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is the primary purpose of flow control in data link control?
To restrict the amount of data the sender can send before waiting for acknowledgment, preventing the receiver from being overwhelmed and avoiding buffer overflow.
What are the two main time components considered in flow control?
Transmission time: Time taken to emit all bits into the medium.
Propagation time: Time for a bit to traverse the link.
What are the three types of ARQ (Automatic Repeat Request) mechanisms mentioned?
Stop-and-Wait ARQ
Go-Back-N ARQ
Selective-Repeat ARQ
How does Stop-and-Wait ARQ operate?
The sender sends one frame at a time.
It waits for an acknowledgment (ACK) before sending the next frame.
If the frame or ACK is lost, the sender retransmits after a timeout.
What is the main problem with Stop-and-Wait ARQ in terms of efficiency?
It wastes bandwidth because the sender must wait for an ACK before transmitting the next frame, leading to low link utilization, especially in high-bandwidth or high-delay networks.
How does Go-Back-N ARQ improve efficiency compared to Stop-and-Wait ARQ?
It allows multiple frames to be in transit before receiving an ACK.
The sender uses a sliding window to track outstanding frames.
If a frame is lost, all subsequent frames are retransmitted.
What is the window size limitation for the sender in Go-Back-N ARQ?
The sender window size must be less than 2m2m, where mm is the number of bits used for the sequence number.
How does Selective-Repeat ARQ differ from Go-Back-N ARQ?
Only the damaged or lost frame is retransmitted, not all subsequent frames.
The receiver buffers out-of-order frames and sends negative acknowledgments (NAKs) for missing frames.
More efficient for noisy links but requires more complex processing.
What is the window size limitation for both sender and receiver in Selective-Repeat ARQ?
The window size must be at most one-half of 2m2m (i.e., 2m−12m−1).
What is the bandwidth-delay product, and why is it important?
It is the product of bandwidth (bps) and round-trip delay (seconds).
It represents the maximum number of bits that can be in transit during the round-trip time.
Helps determine the efficiency of protocols like Stop-and-Wait ARQ.
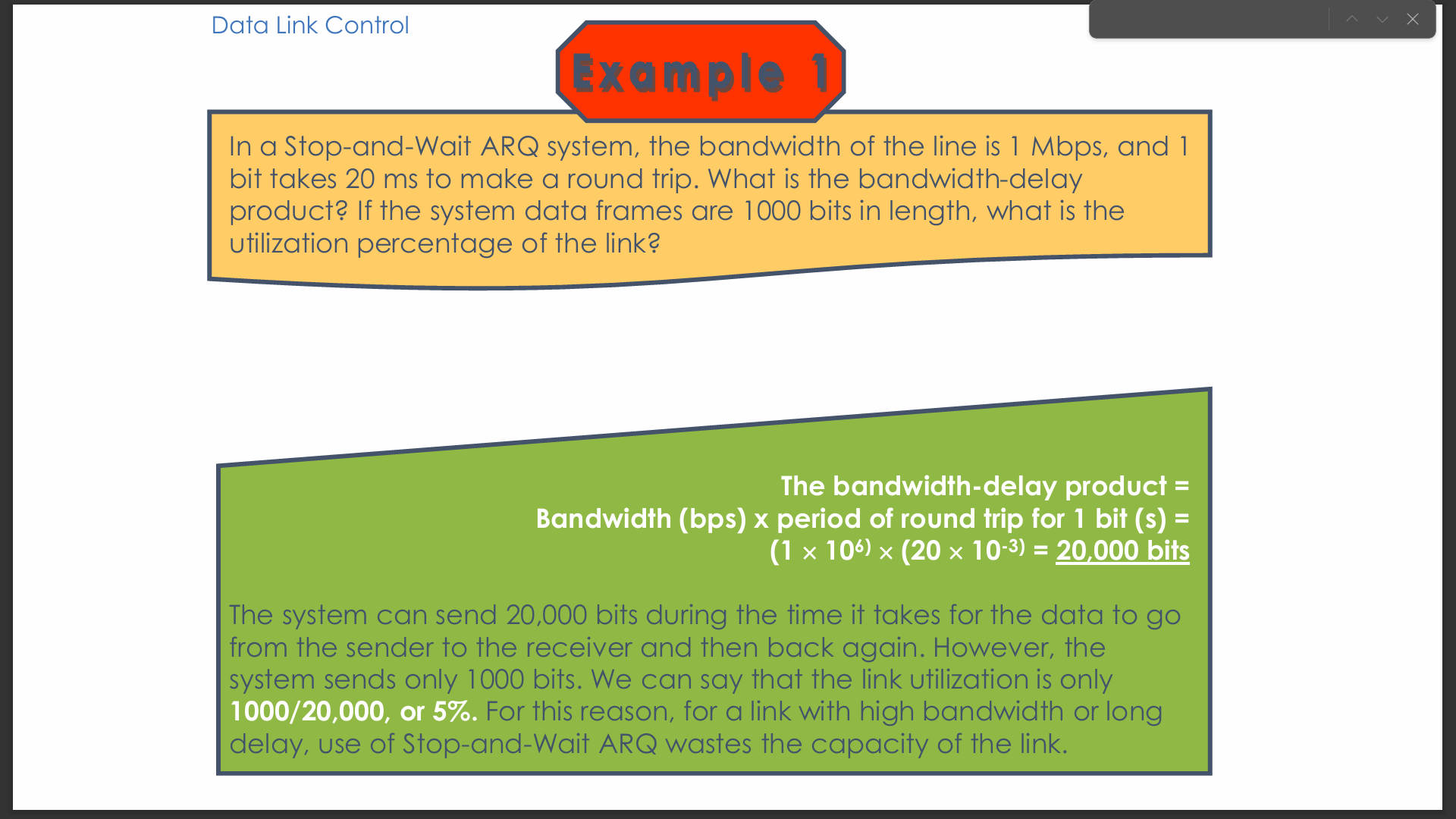
In Example 1 (Stop-and-Wait ARQ), why is the link utilization only 5%?
The system sends 1000 bits during a round-trip time where 20,000 bits could be transmitted (bandwidth-delay product). Thus, utilization is 1000/20000=5%1000/20000=5%.
What is piggybacking in data link control?
A method to combine a data frame with an acknowledgment (ACK) to save bandwidth by reducing the number of separate frames sent.
What is pipelining, and which ARQ protocols use it?
Pipelining allows a task (e.g., sending frames) to begin before the previous task is fully completed.
Used in Go-Back-N ARQ and Selective-Repeat ARQ but not in Stop-and-Wait ARQ.
How does the receiver in Go-Back-N ARQ handle damaged frames?
The receiver discards the damaged frame and all subsequent frames.
It remains silent (no ACK), causing the sender's timer to expire and trigger retransmission of all unacknowledged frames.
What is the role of sequence numbers in ARQ protocols?
They identify frames to detect duplicates (e.g., due to lost ACKs).
Enable the receiver to reorder out-of-sequence frames in Selective-Repeat ARQ.