HA 9-11
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
need to know angles for movements (flexion etc) + scoliosis markers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
CN 1
olfactory
symmetrical recognition of smells
CN 2
optic
visual acuity, vision. snellen and rosenbaum charts.
CN 3
oculomotor. paired 3, 4, and 6
extraocular movements. open eyelids. pupil constriction, lens shape. 6 cardinal positions of gaze/ Diagnostic Positions Test. PERRLA
CN 4
trochlear
down and inward eye movement. 6 cardinal positions of gaze / Diagnostic Positions Test
CN 5
trigeminal
sensation of face, scalp, comea, nose, and mouth mucous membranes. mastication muscles. 3 nerve spots (above eyes, cheeks, and chin). teeth clench test
CN 6
abducens
lateral eye movement. 6 cardinal positions of gaze / Diagnostic Positions Test
CN 7
facial
taste (anterior 2/3 of tongue). facial muscles, close eyes, labial speech (with lips), close mouth, saliva and tear secretion. smile, frown, close eyes, lift brows, show teeth, puff cheeks, check for symmetry.
CN 8
vestibulocochlear or acoustic
hearing and equilibrium/balance. whispered voice test
CN 9
glossopharyngeal. 9 and 10 paired.
posterior 1/3 of tongue. gag reflex. pharynx (phonation and swallowing), parotid gland, carotid reflex. use tongue depressor and see uvula rise on “aah”
CN 10
vagus
sensation of carotid body, sinus, pharynx, and viscera. larynx (talking). carotid reflex. trigger gag reflex, test for smooth voice.
CN 11
spinal accessory
trapezius and sternomastoid muscle movement. rotate head against resistance applied to side of chin. shrug shoulders against resistance
CN 12
hypoglossal
tongue movement. move tongue forward, wiggle side to side. “light, tight, and dynamite” for proper tongue movement
ear anatomy
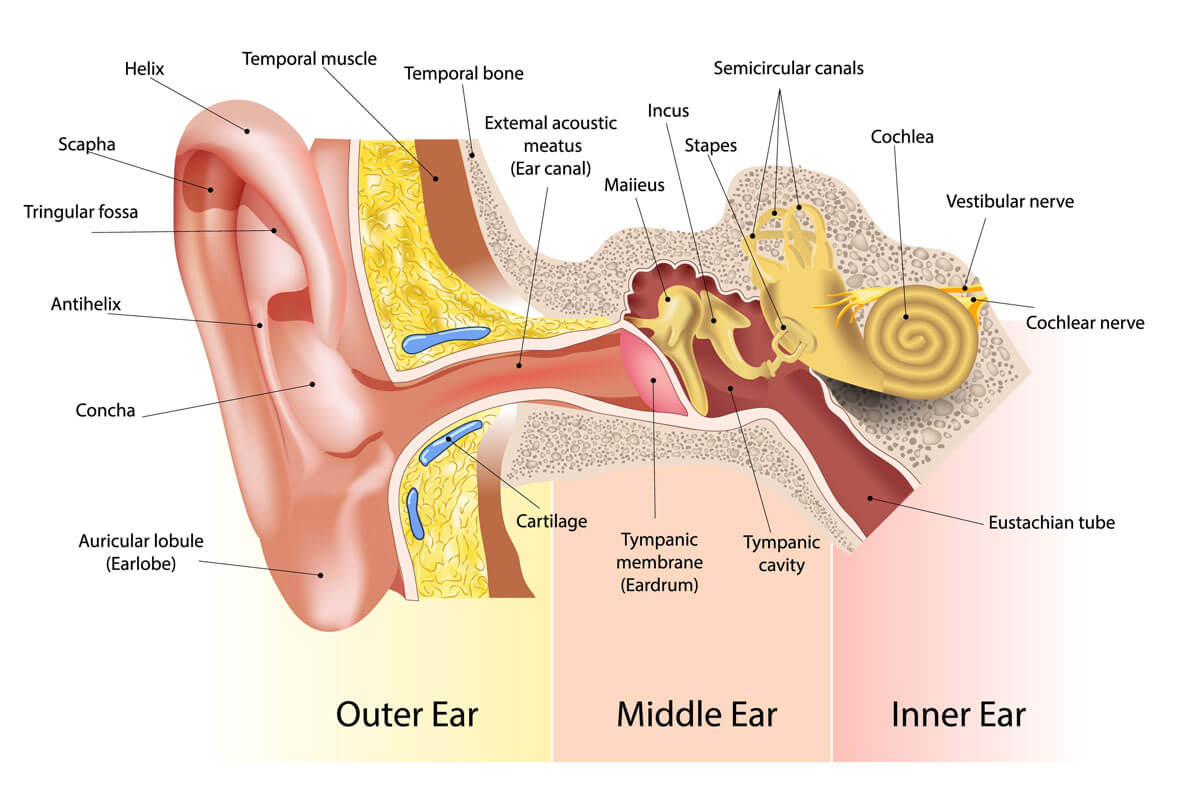
inspection of ears
size and shape, skin condition, tenderness, external auditory meatus. use otoscope to few inside
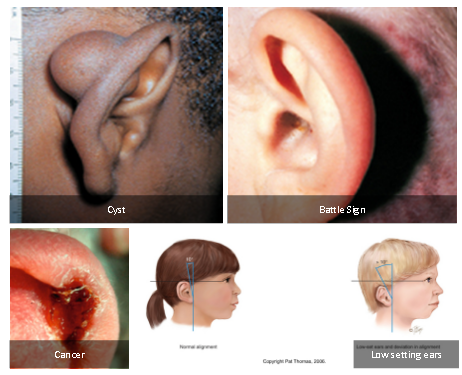
abnormal signs of ears
abnormal is cysts, battle signs, low set ears, and cancer. ear angle is >10 degrees.
subjective data with ears in adults
ear pain, infections, discharge, hearing loss, environmental noise, tinnitus, medications, vertigo, cleansing habits
subjective data with ears in children
ear pains, infections, surgeries (tubes, tonsils), discharge, childcare outside of home (bottlefeeding), environmental noises, school health, speech, contact sports
otoscope for adults
pull pinna up and back
otoscope for children
pull pinna down and back
air conduction
most efficient pathway of hearing. sound waves go thru external ear canal, tympanic membrane vibrates (inner ear and cochlea), CN8 interpretation
test using conversation, whispered voice, and audiometry
bone conduction
less efficient pathway of hearing. sounds travel thru bones of skull, causing skull vibration directly on cochlea
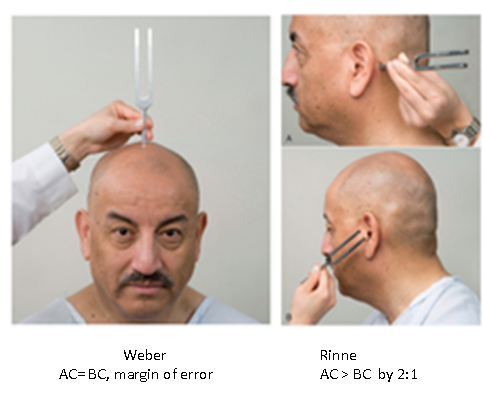
test using tuning fork, weber and rinne
presbycusis
gradual sensorineural hearing loss with age. affects 50% of people over 60 and 80% of people over 85.
hearing loss in inner ear
consider social isolation, diminished quality of life, cognitive impairment, and depression. consider hearing aids.
also caused by trauma, bone fracture, tumor, noise, medication ototoxicity, and age
hearing leaves through cochlea hair loss, change of blood vessels, high tone frequency loss, consonant (s, z, cg, sh, f) loss. require shouting. sound localization difficulty.
conductive hearing loss
hearing loss in the outer ear. caused by foreign body, cerumen (wax), otitis externa, perforated tympanic membrane.
hearing loss in outer and middle ear
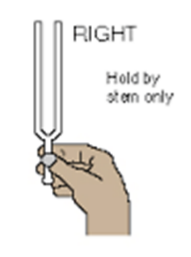
tuning fork test
for bone conduction test. do not hold vibrating prongs. distinguishes if patient prefers to hear via air conduction or bone conduction. AC should be 2x as long as BC for how long the patient can hear it before they can no longer.
test using weber and rinne
weber - put fork on patient’s head and ask if they hear it equally biliterally
rinne - ask patient when they stop hearing sound behind their ear, then place in front of their ear
audiometry test
for air conduction test. headphones that play different frequencies
whispered voice test
for air conduction. stand 1-2 feet behind patient, cover other ear, whisper words and have patient repeat
sensorineural hearing loss
presbycusis
ROS
range of sight
subjective data for eyes
ask patient difficulty with vision (acuity, blurring, blind spots), eye pain, diplopia (double vision), redness, swelling, watering, discharge, glaucoma, cataracts, strabismus (lazy eye).
ask about current and past eye problems. ask about contacts or glasses and when last eye test was.
cranial nerves for eyes
CN 2 - peripheral vision screening, far and near central vision screening
CN 3 - external ocular, PERRLA
CN 3, 4, 6 - extra-ocular muscle
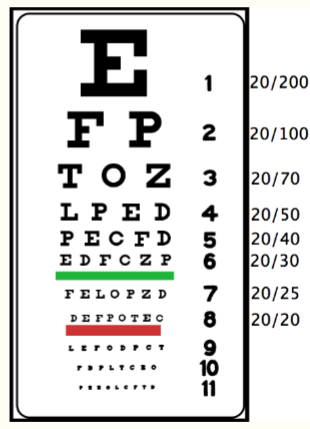
snellen test
far vision. on the wall
opaque card or occluder. expectation: 20/20
eye anatomy
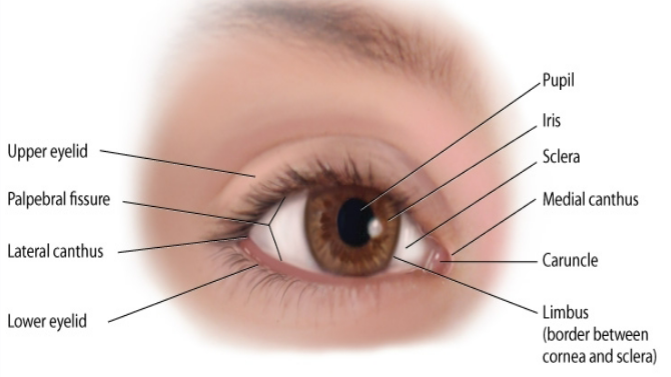
limbus
border between cornea and sclera
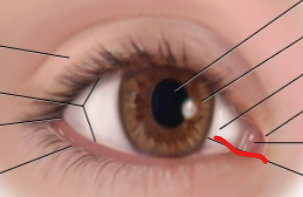
lateral canthus
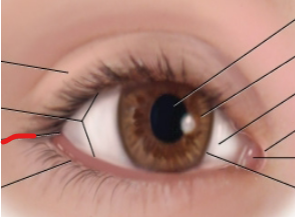
palpebral fissure
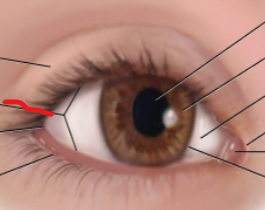
caruncle
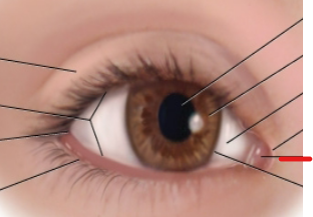
medial canthus
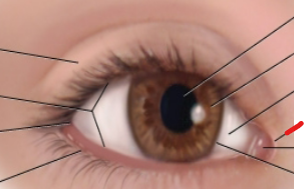
sclera
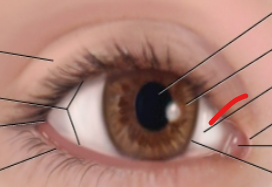
iris
infant hearing test
test within 24 hrs of birth. expected is normal biliteral heaering. lack of hearing can impact speech abilities
ptosis
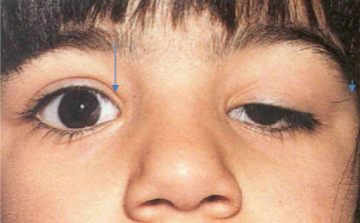
CN 3 deficit.
ectropian
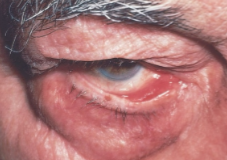
outward turning of the eyelids. exposes the inner eyelid to air. causes burning, blurry vision, red eyes, red eyelids, and tearing
entropian
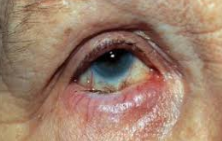
inward turning of eyelids. eyelashes may rub against the eyeball.
PERRLA
pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation
accommodation - put finger in the middle of eyes to see if eyes move inward
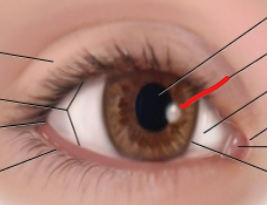
superior rectus
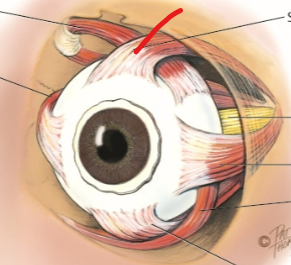
superior oblique
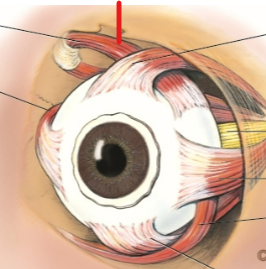
medial rectus
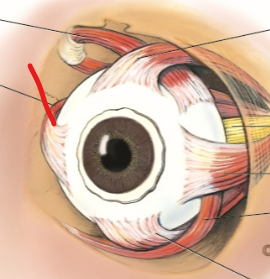
lateral rectus
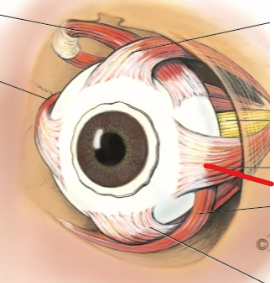
inferior oblique
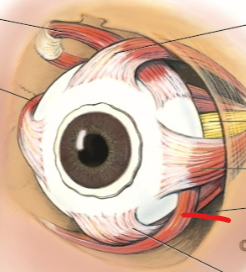
inferior rectus
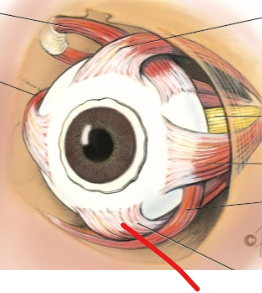
optic nerve
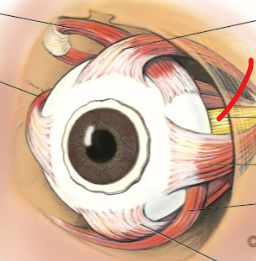
corneal light reflex
AKA hirschberg test. NOT PUPIL REFLEX. used to test that the light reflects off of the corneas equally. different positions indicate unequal eye sizes and shapes. use this to test for strabismus (lazy eye)


6 cardinal fields of gaze

AKA diagnostic positions test. check that all eye muscles work
50 superior, 90 temporal, 70 inferior, then 60 nasal on covered eye side
strabismus
lazy eye
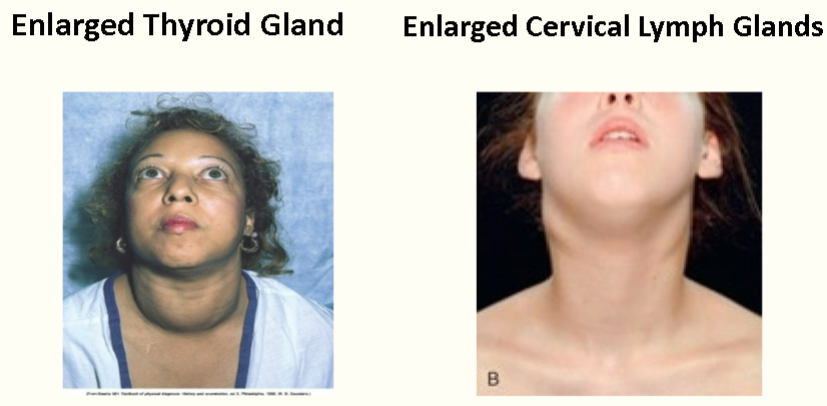
lymph nodes
remove foreign substances from body. immune system. lymph system brings fluid to the heart, preventing edema.
large or warm lymph nodes are sign of infection
removing lymph nodes from breasts can cause lymphedema
palpable in kids, especially when sick. not palpable in adults
60-70
number of lymph nodes in neck
lymph node documentation
document location, size, mobility, tenderness, and firmness of lymph nodes
sternomastoid
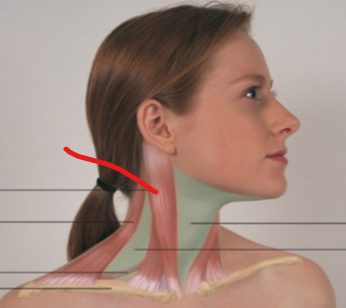
trapezius
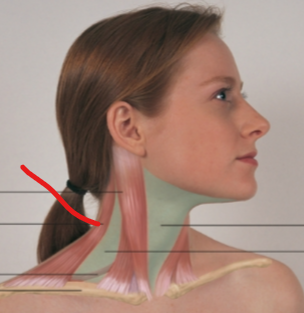
omohyoid
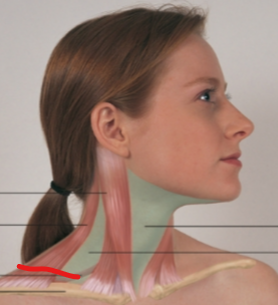
anterior triangle
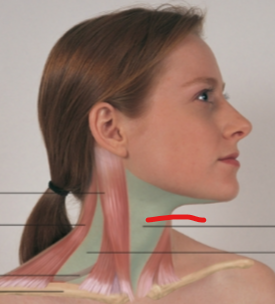
posterior triangle
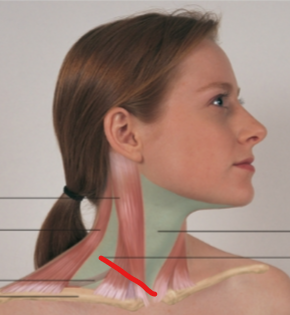
cricoid cartilage
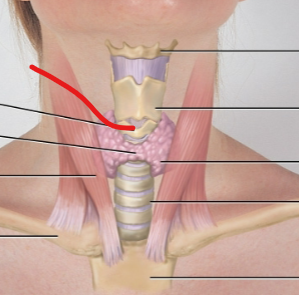
thyroid cartilage
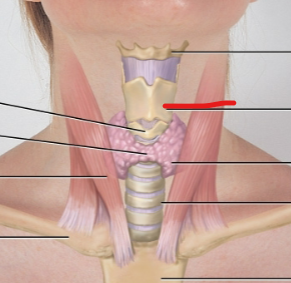
thyroid gland
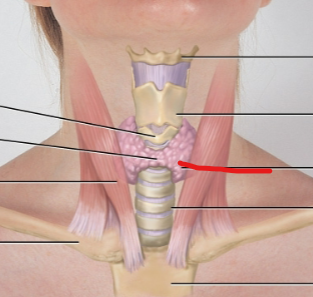
subject data for lymph nodes
neck pain, limitation of motion, lumps, swelling, enlarged or tender LNs, energy level, fatigue, goiter, history of neck surgery, history of throat or neck cancer
lymph node inspection
ROM, symmetry, trachea midline, no swelling or enlargement
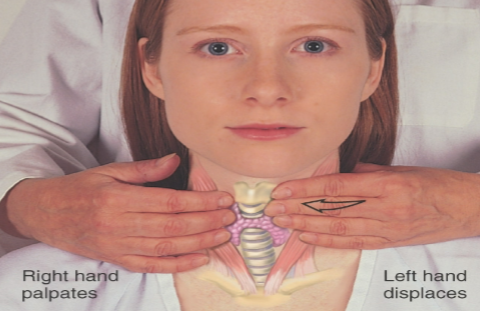
lymph node palpation
feel lymph nodes and thyroid on neck for swelling
thyroid palpation
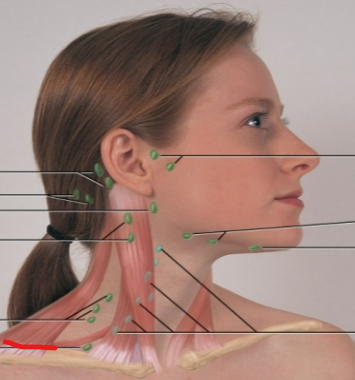
periauricular LN
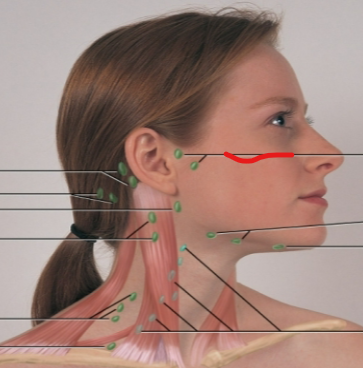
submandibular LN
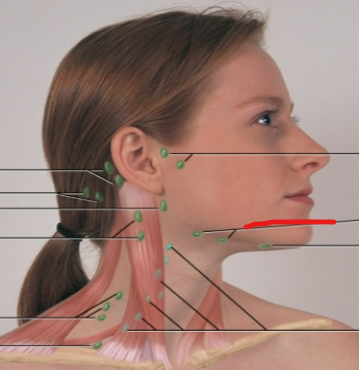
submental LN
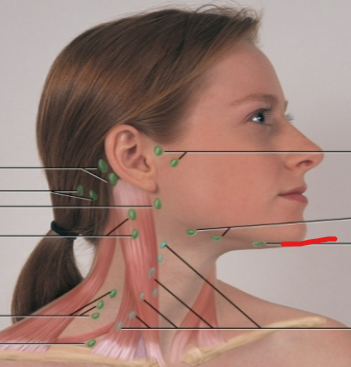
deep cervical chain LN
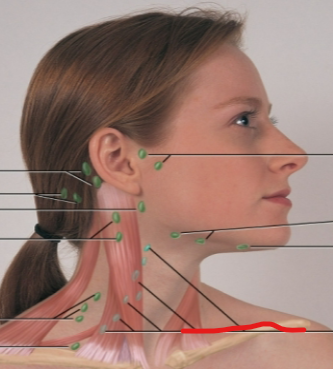
posterior auricular LN
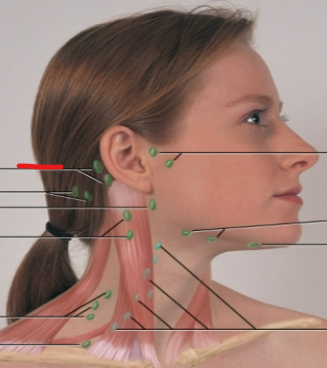
occipital LN
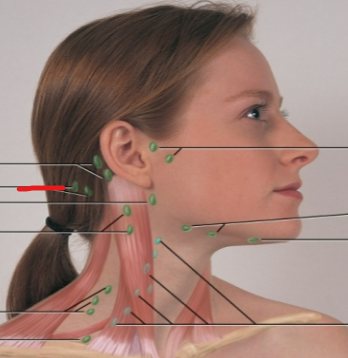
tonsillar, retropharyngeal, jugulodigastric LN
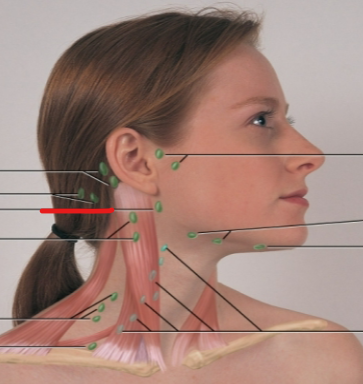
posterior cervical LN
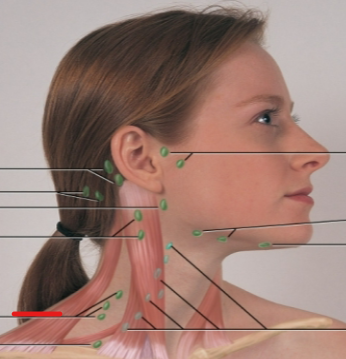
supraclavicular LN
visual fields
left visual field is left side of each eye
right visual field is right side of each eye
rosenbaum test
near vision test. handheld, 14 inches from eye. expectation: 20/20.
tests for presbyopia, loss of eyes’ ability to focus on nearby objects

visual acuity test
sharpness of vision

cataracts
progressive loss of vision
glaucoma
peripheral loss of vision
macular degeneration
central loss of vision
diabetic retinopathy
general poor vision
types of muscles
skeletal (voluntary), smooth, cardiac
skeletal muscle movements
flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, pronation, supination, eversion, inversion, protraction, retraction, elevation, depression, rotation, circumduction
subjective data collection for musculoskeletal
joints, muscles, bones, functional assessment (ADL), patient-centered care
musculoskeletal inspection
size and contour of joints. skin and tissues above joint. movement, gait, body alignment, involuntary movements
SEE (skin color, edema, equal)
musculoskeletal palpation
skin temperature, muscles, strength and tone, joints
PEET (pain, edema, equal, temperature)
hypertonia
excess muscle tone
hypotonia
minimal muscle tone
active range of motion
AROM
passive range of motion
PROM
support above and below the joint to be moved
muscle strength
the muscle’s ability to contract and create force in response to resistance
upper body: shoulder flexion, elbow flexion and extension, hand grip strength
lower body: hip extension, knee extension, ankle dorsiflexion and plantarflexion
muscle tone
tension in a muscle at rest
shoulder flexion
180 flexion, 50 extension
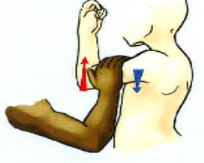
elbow flexion and extension
0 extension. 160 flexion
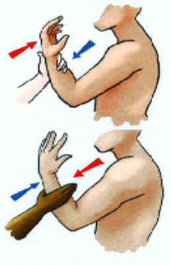
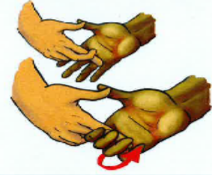
elbow supination and pronation
supination: 90 thumb moves outwards.
pronation: 90 thumb moves inwards
grip strength