Telomere dysfunction causes alveolar stem cell failure
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What was the main question of this paper
How does telomere dysfunction affects the regenerative capacity and function of alveolar stem cells, particularly type 2 alveolar epithelial cells (AEC2s), and contributes to lung diseases like idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema.
Main methods: Organoid Assay
Alveolar cells from telomerase-null mice with short telomeres were cultured to form alveolosphere colonies, assessing the regenerative ability of AEC2s.
Main methods: Conditional Trf2 Deletion
A model was developed to induce telomere dysfunction in AEC2s by deleting the Trf2 gene, which allowed examination of cell senescence and immune response activation in vivo.
Main methods: Injury Model
The response of Trf2-deficient AEC2s to injury was tested using bleomycin, a pulmonary-toxic drug, to analyze the effects of telomere dysfunction under stress.
Key Results: Reduced Regeneration
AEC2s with dysfunctional telomeres exhibited impaired self-renewal and differentiation, resulting in fewer alveolosphere colonies.
Key Results: Senescence and Inflammation
Telomere dysfunction induced cellular senescence in AEC2s, along with an immune response marked by cytokine signaling and inflammation.
Key Results: Injury Susceptibility
Mice with telomere dysfunction in AEC2s showed increased mortality and severe lung damage following bleomycin challenge, highlighting the role of telomere maintenance in lung repair.
Key Results: Findings
The findings suggest that telomere dysfunction in alveolar stem cells drives lung disease progression by limiting regeneration and promoting inflammation, and indicate that restoring telomere function may be beneficial for treating telomere-mediated lung diseases.
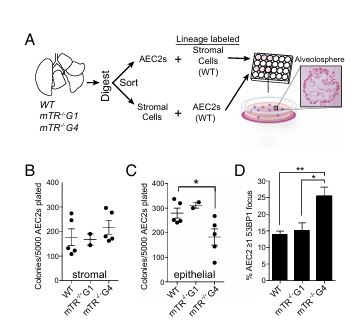
Figure 1
Questions, Methods, Results
Question: How do short telomeres affect AEC2 regenerative capacity?
Methods: The researchers cultured AEC2s with stromal cells to form "alveolospheres" and compared colony formation between telomerase-null mice (mTR−/−) and wild-type mice.
Results: AEC2s from mice with short telomeres (mTR−/−, fourth generation) produced fewer colonies than wild-type cells, indicating reduced regenerative capacity due to telomere shortening.
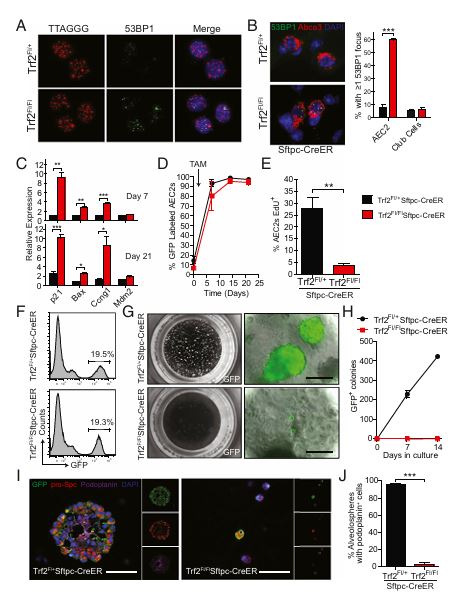
Figure 2
Questions, Methods, Results
Question: Does telomere dysfunction in AEC2s induce senescence?
Methods: The researchers used a conditional model with Trf2 deletion in AEC2s to induce telomere dysfunction and analyzed markers of senescence.
Results: AEC2s with Trf2 deletion showed increased DNA damage response markers and reduced proliferation, signifying cellular senescence as a result of telomere dysfunction.
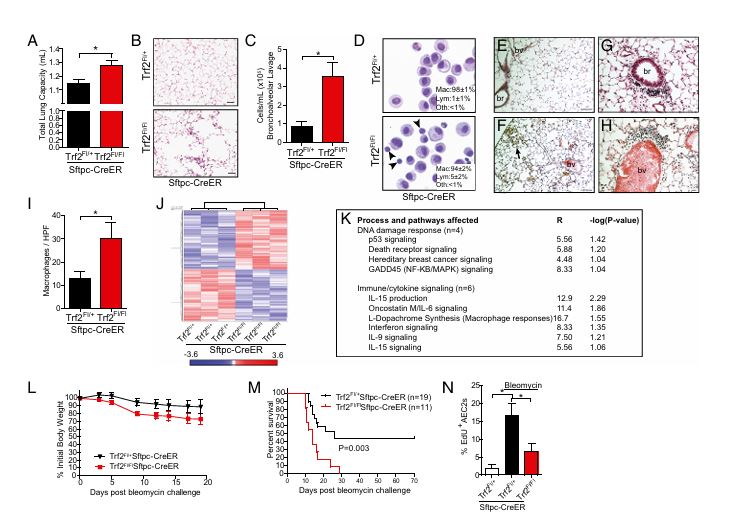
Figure 3
Questions, Methods, Results
Question: How does telomere dysfunction in AEC2s impact lung function and inflammation?
Methods: Trf2-deleted mice were observed for lung function changes and immune cell infiltration after tamoxifen administration and bleomycin challenge.
Results: Mice with Trf2 deletion in AEC2s showed increased lung inflammation, compromised lung function, and a high mortality rate after bleomycin exposure, suggesting vulnerability to injury due to telomere dysfunction.
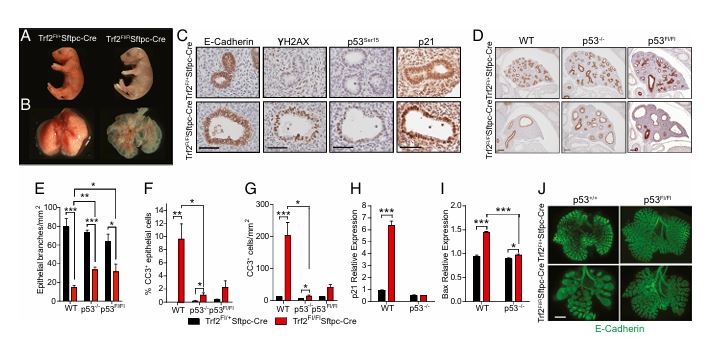
Figure 4
Questions, Methods, Results
Question: Is there a paracrine effect of telomere dysfunction in epithelial cells on mesenchymal cells, and is it p53-dependent?
Methods: Using a model with Trf2 and p53 deletion in epithelial cells, the researchers examined lung morphogenesis and mesenchymal apoptosis.
Results: Telomere dysfunction in epithelial cells triggered mesenchymal abnormalities, including apoptosis, and this effect was p53-dependent. Disabling p53 ameliorated some of the developmental defects