Final Study guide Chapter 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What's Glycolysis?
Rxns where glucose is oxidized into pryuvate. Most microbes use this to get energy
Citric Acid Cycle
-When pyruvate is oxidized into CO2, result is NADH that needs to be balanced (turned into NAD+)
-Strict fermenters don't undergo this process, they just turn pyruvate into acids/alcohols
Fermentation
-anaerobic metabolic process in which cells break down glucose (or other sugars) to produce energy (ATP) without using oxygen.
-Waste as alcohol/acids
- No electron transport chain or external electron acceptor
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Membrane-bound proteins that oxidize NADH/FADH2 into their electron acceptor NAD+/FAD correspondents using a final electron acceptor (usually O2)
ETC fuels the..
Proton motive force (pmf) that fuels ATP synthesis and motility, which is generated by electron flow
The PMF gives energy to..
ATP synthase to make ATP
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
ATP formation by ATP synthase when PMF is generated by ETC
Do fermenters have a PMF?
Yes, but only for motility, they do this by using ATP synthase to actively pump out protons. (ATP synthase used to use ATP instead of make)
Difference between Anaerobic and Aerobic microbes
Aerobic uses O2 as final acceptor, Anaerobic uses other molecules
Key features of Chemolithotrophy
-Uses Inorganic chemicals as electron donors
-Typically use CO2 as carbon source, making them autotrophs
Key features of phototrophy
-Light energy is used instead of chemical rxns to drive electron flow
-Use chlorylphyll to absorb light energy
Calvin Cycle
a biochemical pathway of photosynthesis in which carbon dioxide is converted into glucose using ATP
Growth Cycle phases
Lag, exponential, stationary, death (decline)
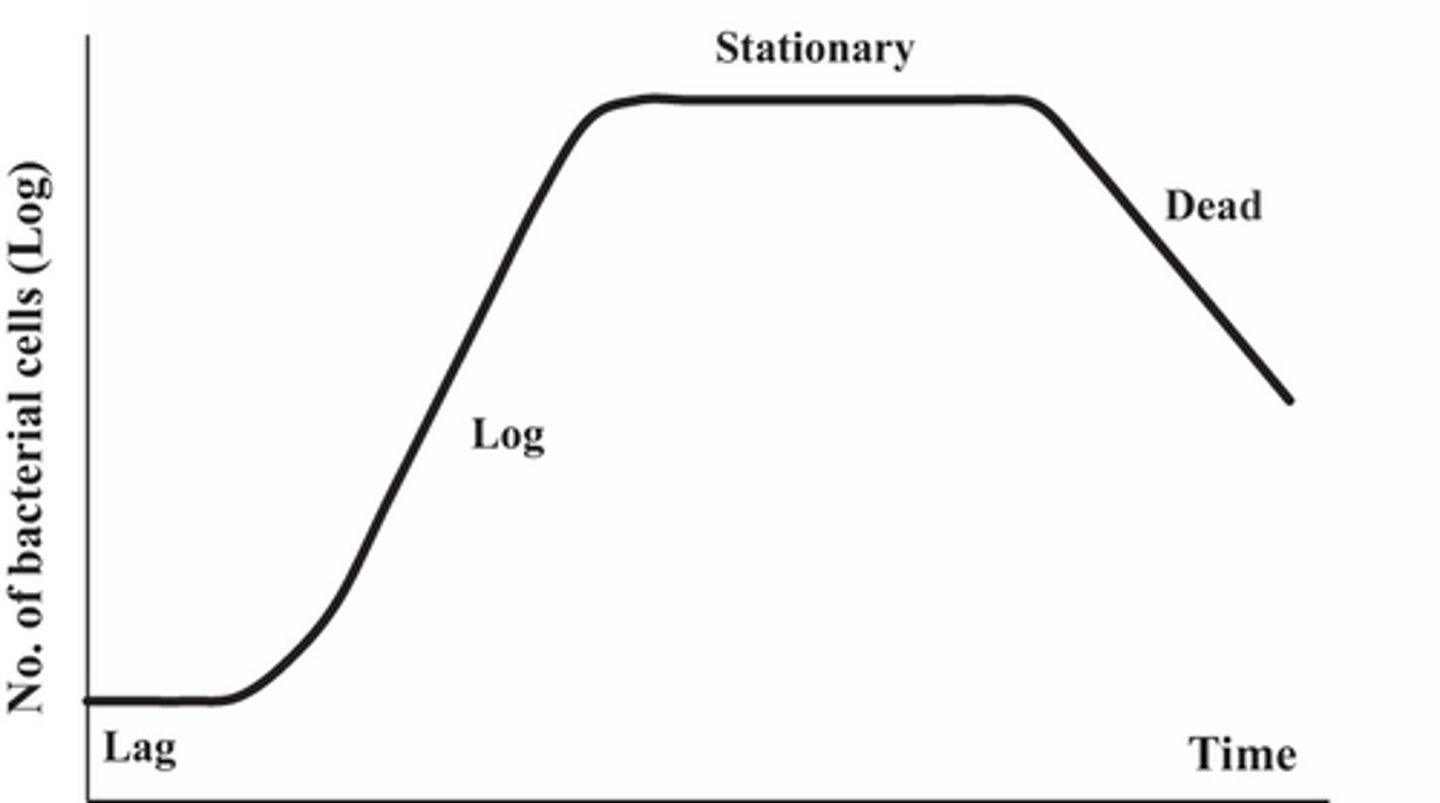
Lag phase `
Cells do not grow, new environment for cells takes time to adjust
Exponential Phase
Period where cell population doubles at regular intervals
Stationary Phase
No net increase or decrease in cell number, cells shift focus to maintenance instead of growth
Decline Phase
Total Cell number decreases due to cell death
What is a chemostat
A system used for the continuous culture of microbial cells, enables control over growth rate thru flow of nutrients
What are Halophiles?
Organisms that live in salty environments
Obligate anaerobes
organisms that cannot live where molecular oxygen is present
Facultative anaerobes
can live with or without oxygen
Oxygenic photosynthesis
-Electron Donor?
-Energy Source?
-Carbon Source?
Electron Donor: H2O
Energy Source: Light
Carbon Source: CO2
Anoxygenic photosynthesis
-Electron Donor?
-Energy Source?
-Carbon Source?
Electron Donor: H2S
Energy Source: Light
Carbon Source: CO2
Chemosynthesis
-Electron Donor
-Energy Source
-Carbon Source
-Electron Donor: H2S
-Energy Source: H2S
-Carbon Source: CO2
Anaerobic Respiration
-Terminal electron Acceptor?
-Product?
-S
-H2S