CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIA | 4.1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Equilibrium
state in which there are no observable changes as time goes by

Chemical Equilibrium is achieved when
macroscopically, molecular level
in the characteristic of chemical equilbrium
*****, reaction may appear to have stopped
**** ****, the forward and reverse reactions are constantly occuring
Law of Mass Action
expresses the relative concentrations of reactants and products at
equilibrium in any reaction
Equilibrium Constant (Keq)
- temperature dependent
has no units (dimensionless)
product predominates
Keq»»»1
Reactant Predominates
Keq«««1

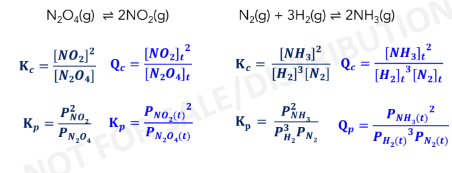
Kp Expression
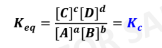
Kc Expression
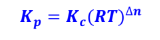
kp and kc law
universal gas constant (0.082056 L-atm/mol-K)
R = ****
= no. of moles of gaseous products – no. of moles of
gaseous reactants
∆n
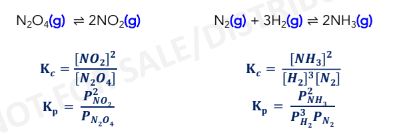
Homogenous Equilibria
refers to reactions where all the species are in the same phase
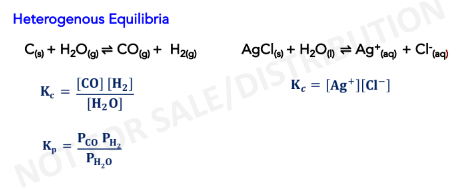
Heterogenous Equilibria
refers to reactions where reactants and
products are of different phases
- The concentrations of pure solids, pure
liquids and solvents do not appear in
the equilibrium constant expressions.
Reaction Quotient (Q)
used to determine if the given reaction is at equilibrium, and if it
is not, the direction in which the reaction will proceed to attain
equilibrium
- same expression with the Keq
In equilibrium
Q=Keq
Reaction to Product (Shift to Right)
Q<Keq
Product to Reactant (Shift To Left)
Q>Keq
partially offset, equilibrium position
If an external stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the
system adjusts in the direction that the stress is *****
the stress as the system reaches a new ***** *****.

consume
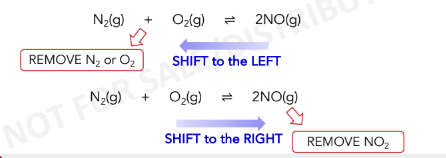
If a reactant or product is added, the equilibrium will shift in the
direction that will *** the added substance
replace the removed
If a reactant or product is removed, the equilibrium will shift in
the direction that will **** **** *** substance
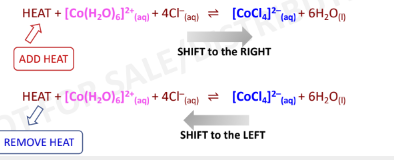
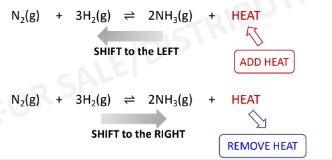
Change in Temperature
the only factor that can change the value of the equilibrium
constant
endothermic (+)
HEAT = Reactant (in an ***** reaction)
exothermic (-)
HEAT = Product (in an ****** reaction)
Endothermic reaction: Heat = Reactant
Exothermic reaction: Heat = Product

reduces
if pressure is increased (will decrease in volume), the system will shift towards the direction which **** the total number of gaseous molecules.

increases
if pressure is decrease (will increase in volume), the system will shift towards the direction which the **** total number of gaseous molecules.
does not change K
• does not shift the position of an equilibrium system
• system will reach equilibrium sooner
Effect of Catalyst