Halogenoalakanes
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Properties:
Let X = halogen, C-X bond where C is partially (+) and X is partially (-), so has dipole-dipole and van der waals forces
Boiling point: increases with increased chain length, and increases with halogen down the group (increased van der waals)
The C-X bond (where X = halogen)
If the C-X bond is higher in polarity (C-F > C-I) then higher rate of reaction. So, can be attacked by reagents that are electron rich known as nucleophiles (an electron pair donor)
If the C-X bond has lower enthalpy then higher rate of reaction. Iodo-compounds have C-I bond with lowest enthalpy less energy to break bond, so more reactive.
Define Nucleophile
Nucleophiles are negatively charged particles that have attracted towards slightly positive charge. For example, -:OH (hydroxide ion), :NH3 (Ammonia), -:CN (Cyanide)
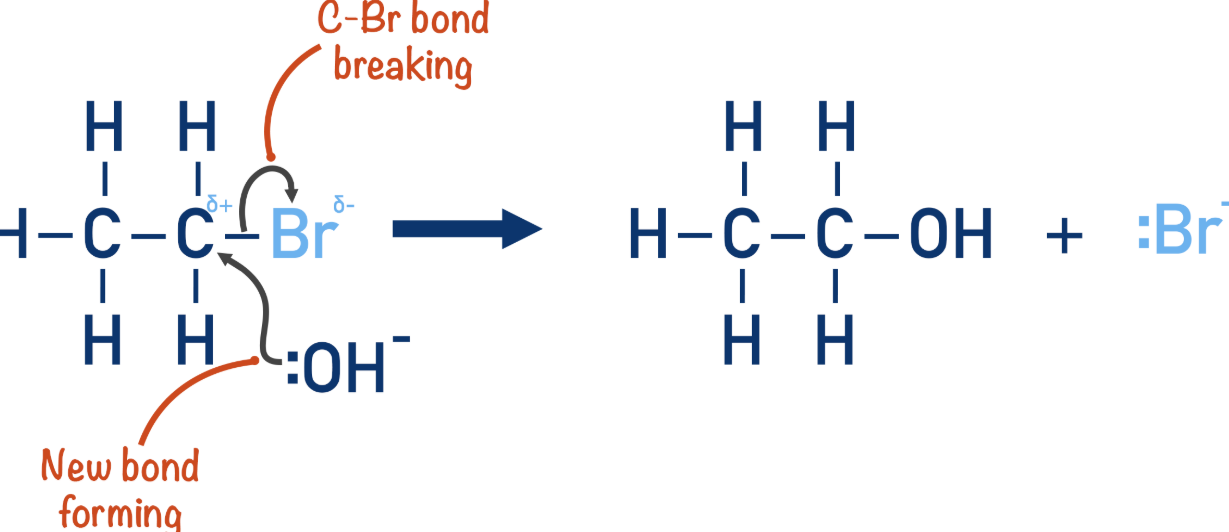
Formation of Alcohol from Halogenoalkane
Conditions: Warm and aqueous
Reaction mechanism: Nucleophillic substitution
Form: Alcohol
Reagent: KOH or NaOH
Nucleophile: -:OH
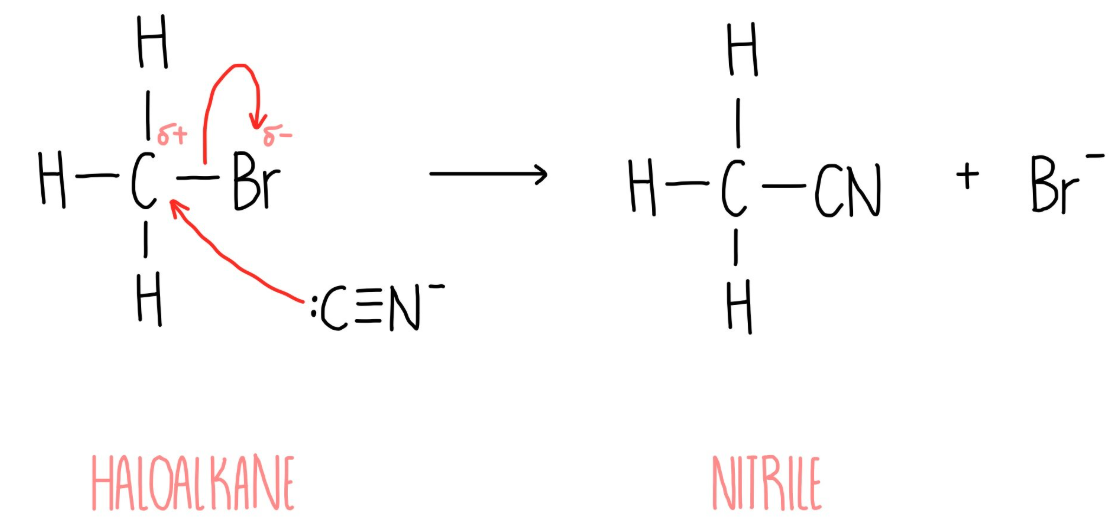
The formation of a nitrile from Halogenoalkane
Conditions: warm and alcoholic
Reaction mechanism: Nucleophillic substitution
Form: Nitrile
Reagent: KCN (potassium cyanide)
Nucleophile: -:CN
KEY: There is an extra C when adding -:CN to carbon chain.
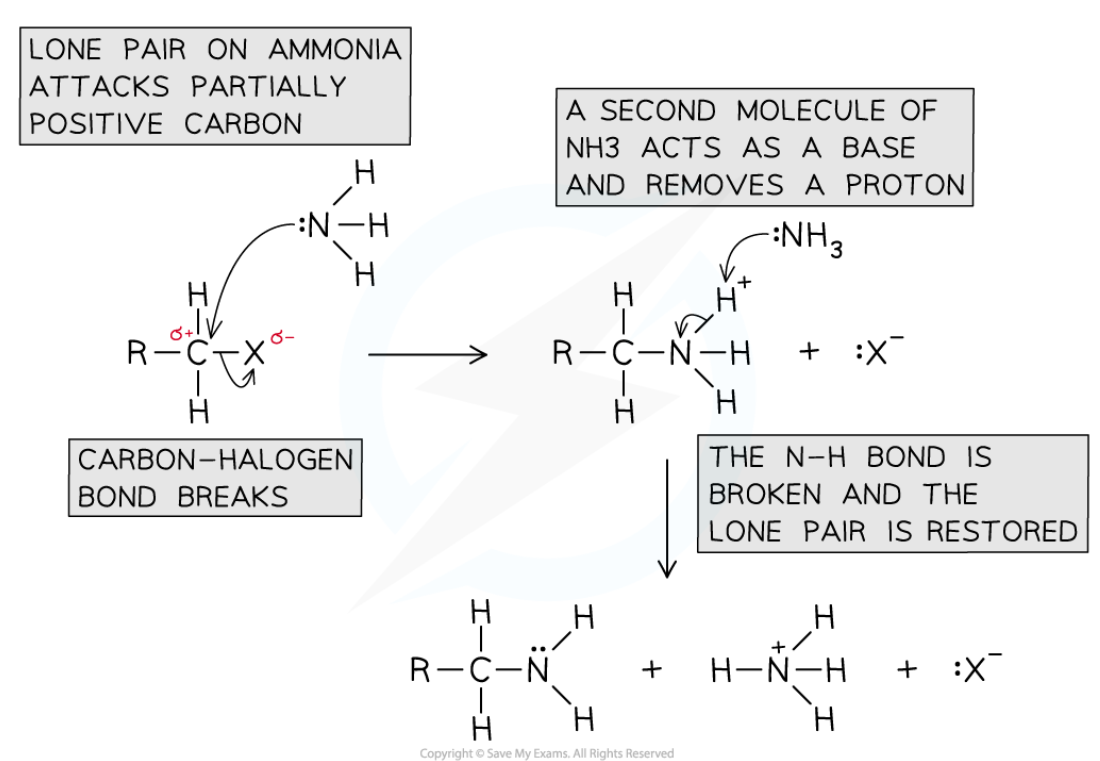
The formation of amine from Halogenoalkane
Conditions: warm, Ethanolic and excess
Reaction mechanisms: Nucleophillic substitution
Form: Amine
Reagent: Ammonia
Nucleophile: :NH3
KEY: N is unstable when having 4 bonds so needs to react again
THE POSITIVE CHARGE ON THE INTERMEDIATE IS ON THE NITROGEN
Define Base
A proton acceptor
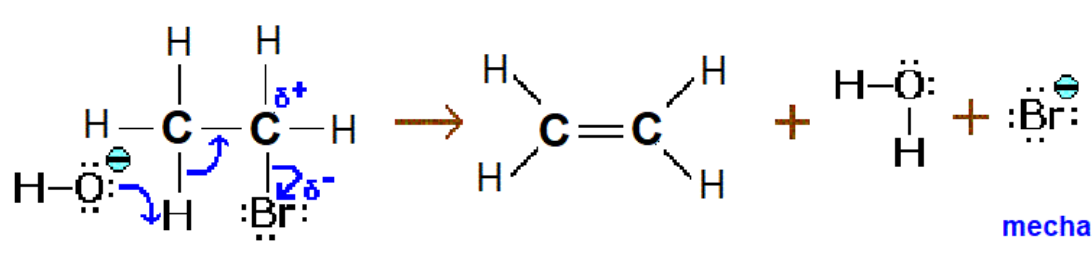
Formation of Alkene from Halogenoalkane
Conditions: Hot and ethanollic
Reaction mechanism: Elimination
Form: Alkene
Reagent: NaOH or KOH
Base: -:OH
KEY: The arrow travels from the base to the hydrogen adjacent to the halogen